Chapter 6: Integumentary System Layers: Epidermis and Dermis; Lines of Cleavage
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What is the integumentary system?
skin
covers body and accessary tissues (nails, hair, sweat glands, sebaceous glands)
cutaneous membrane, barrier to the outside world (first line of defense)
visual indicator of our physiology and health
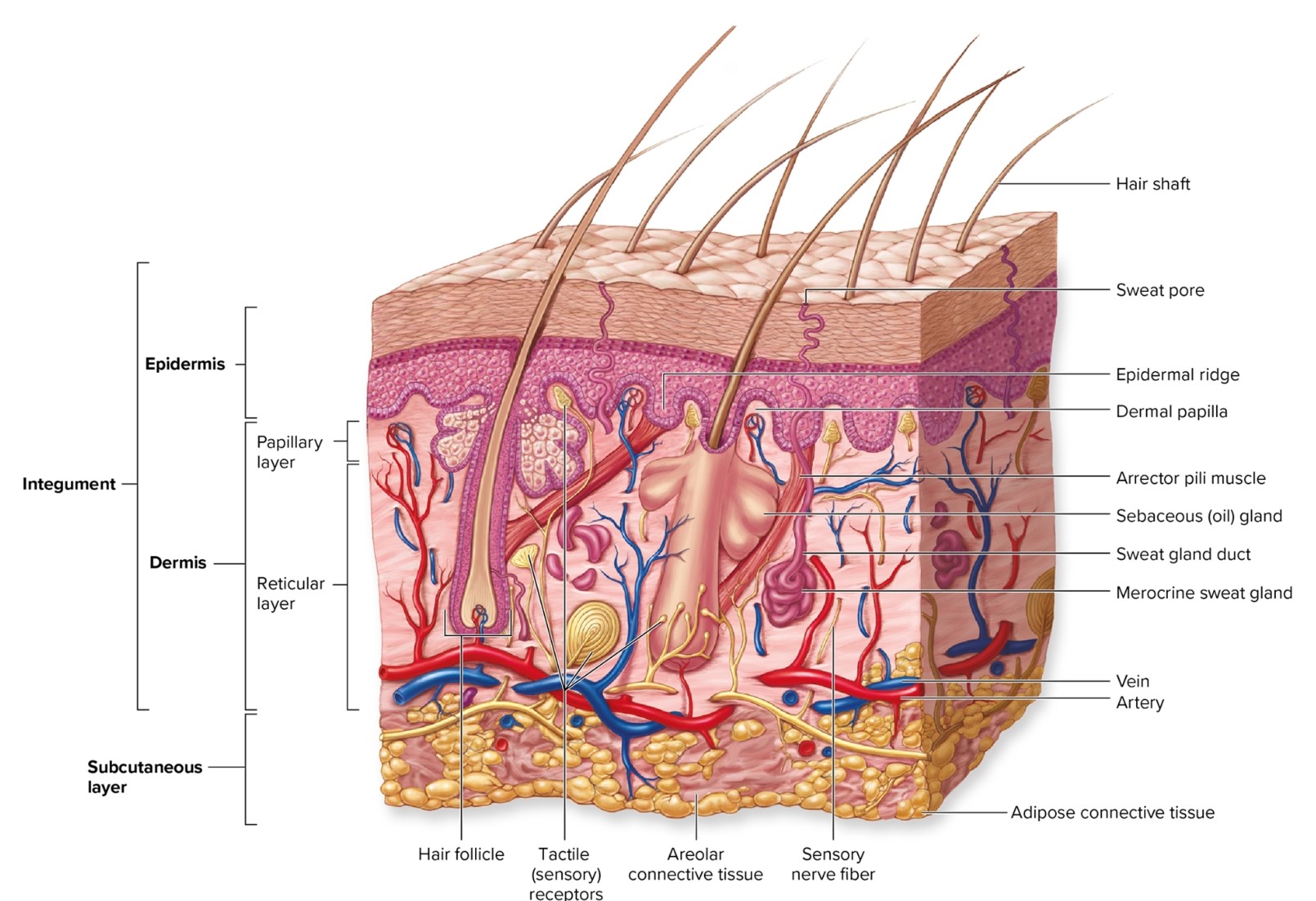
What are the layers of the integument?
epidermis: stratified squamous epithelium
dermis: deeper (reticular) layer; primarily dense irregular connective tissue
subcutaneous layer (hypodermis): deep to dermis, layer of alveolar and CT, not part of integumentary system
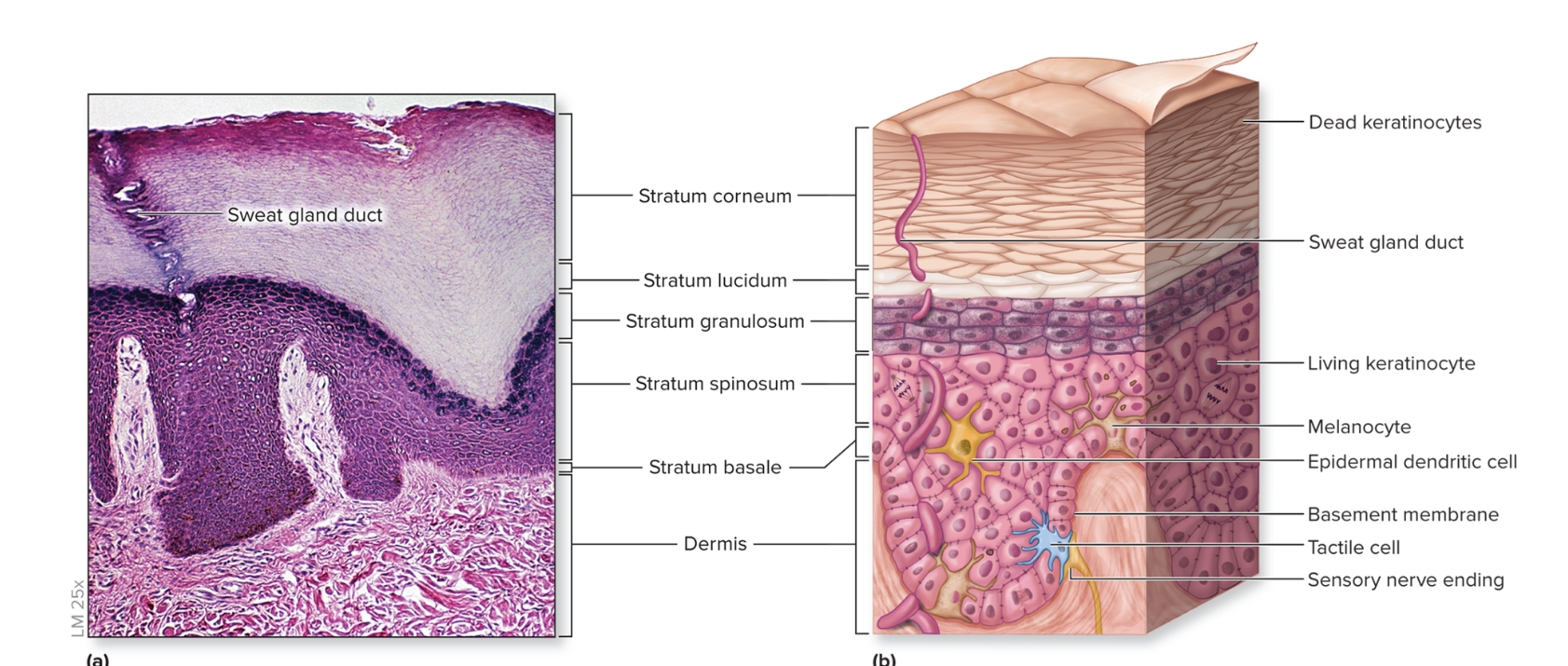
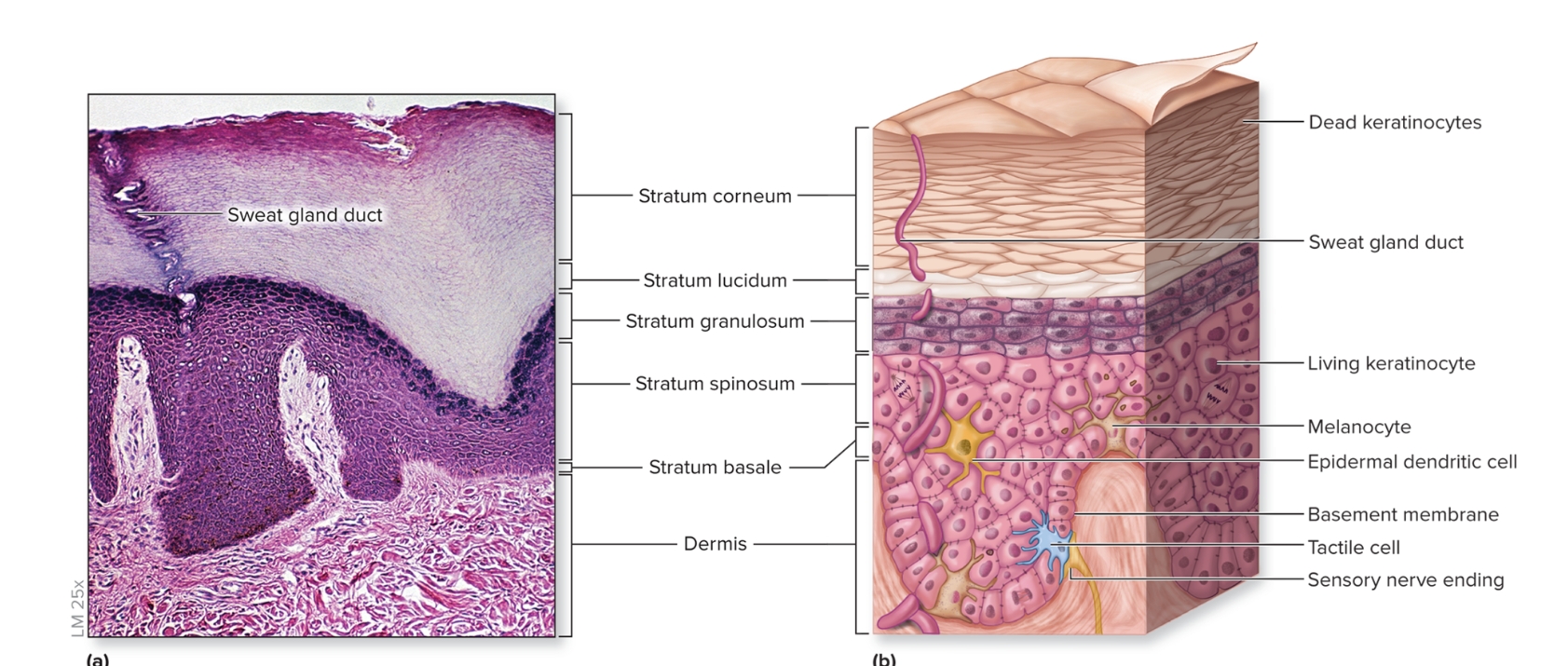
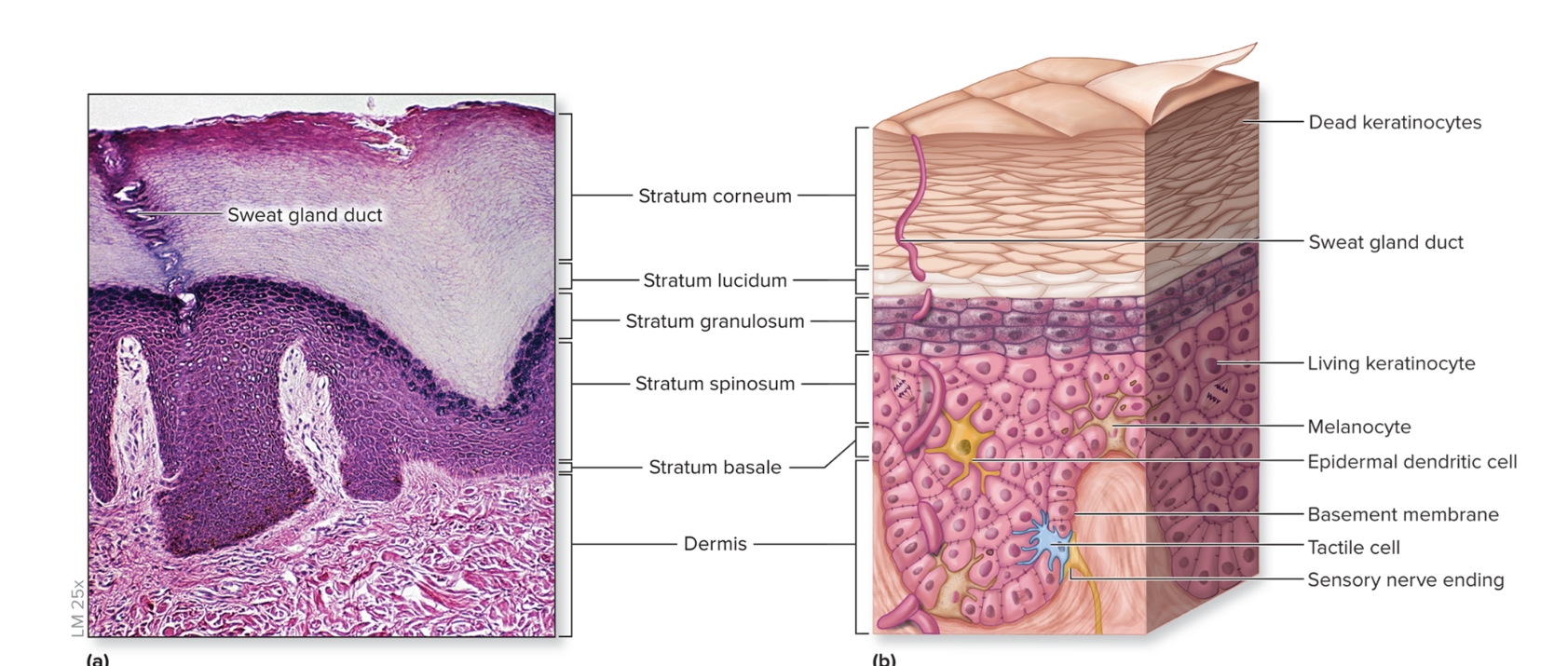
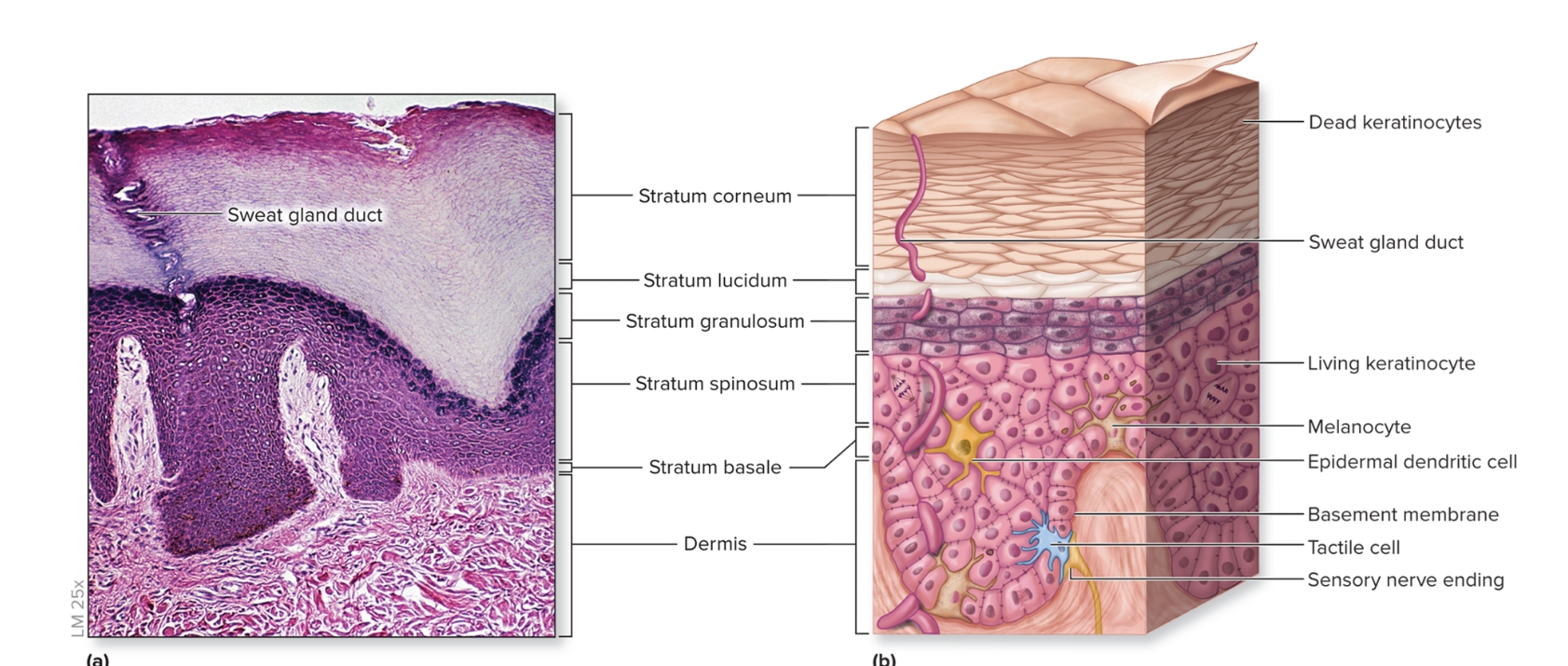
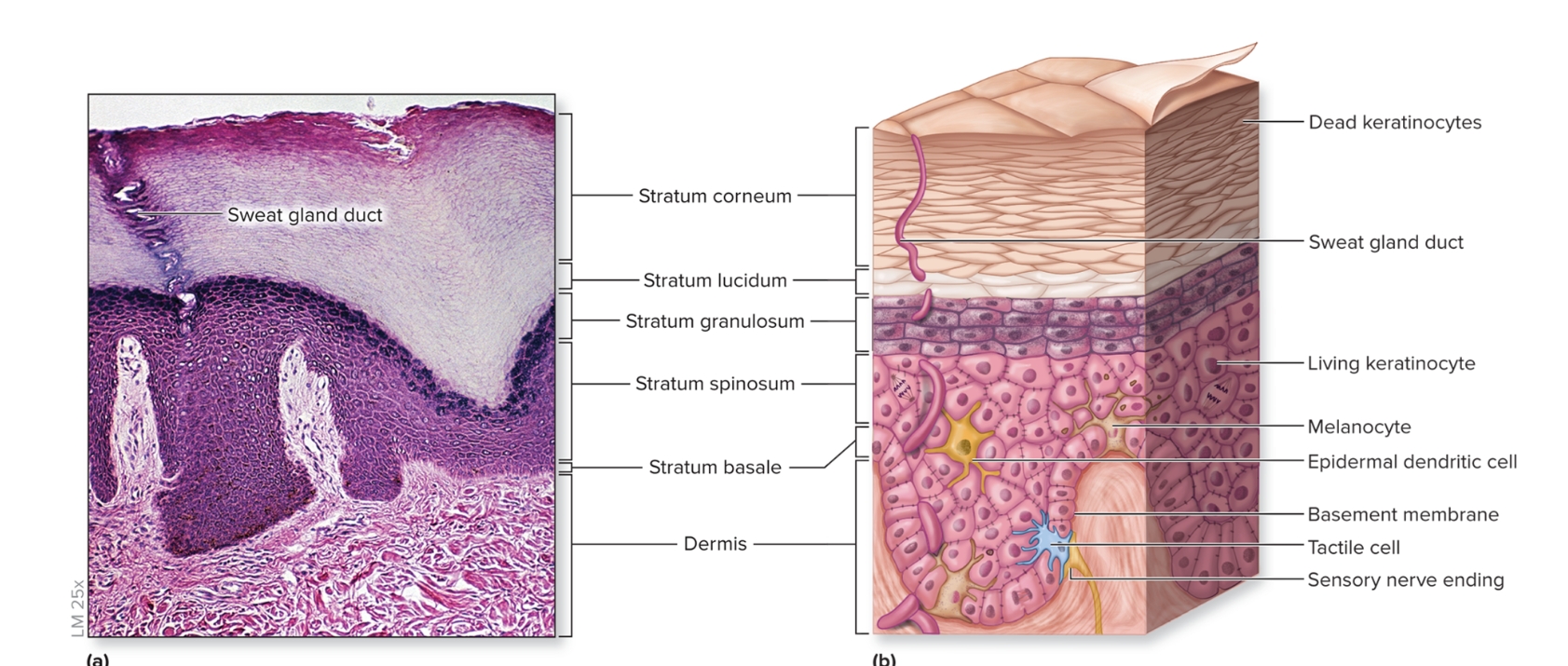
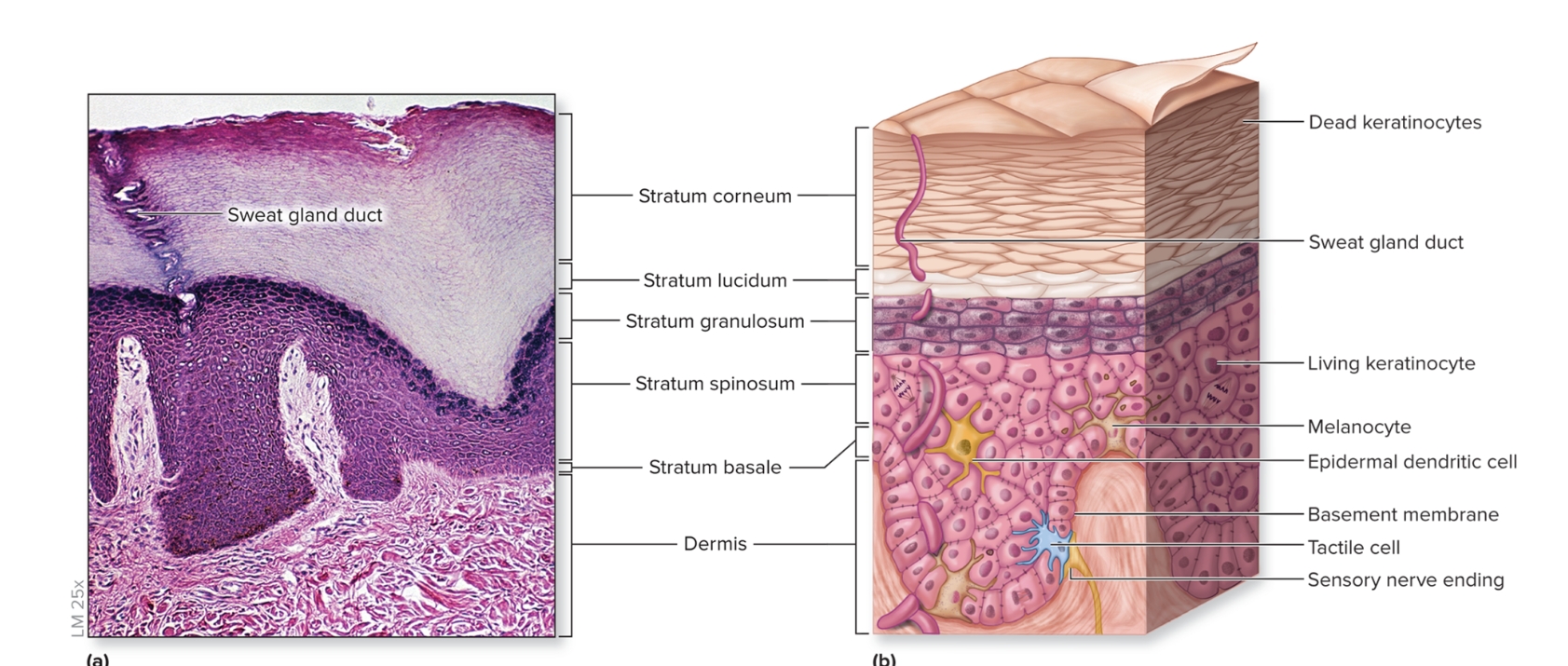
What is the epidermis?
epithelium of the integument
keratinized
stratified squamous epithelium
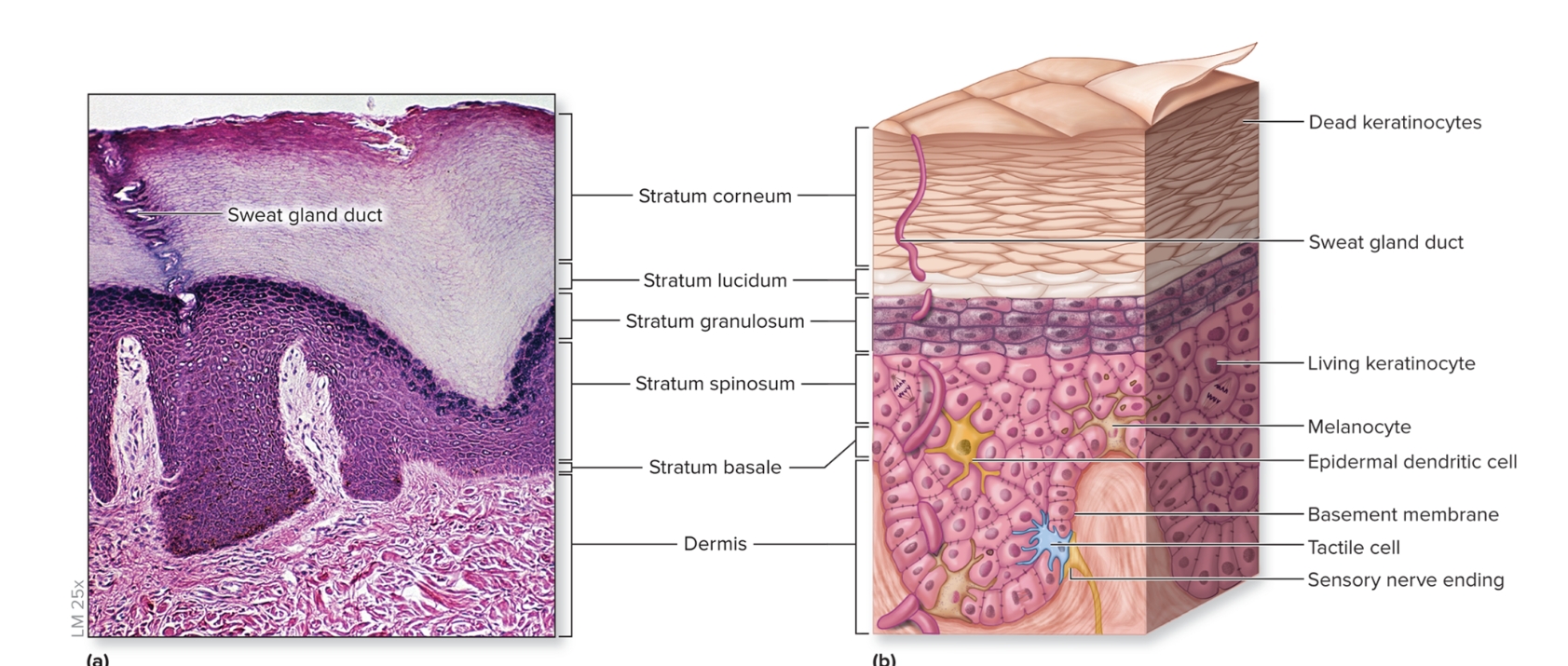
First three layers composed of living keratinocytes
consists of stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, stratum corneum
What are the layers of the epidmeris?
deep to superficial
stratum basale
stratum spinosum
stratum granulosum
stratum lucidum
stratum corneum
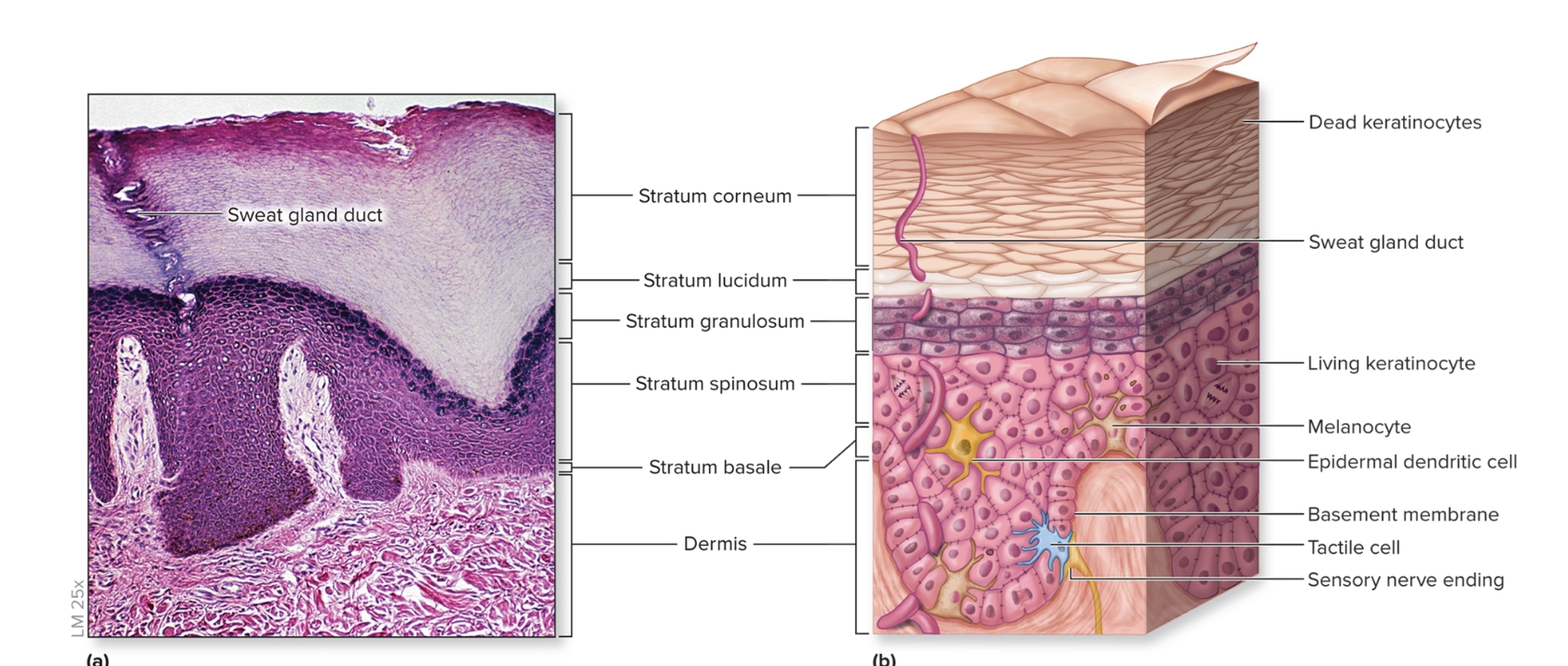
What is the stratum basale of the epidermis?
deepest epidermal layer,
single layer of cuboidal to low columnar cells
three types of cells
keratinocytes
melanocytes
tactile
What are the keratinocytes of the stratum basale layer?
Found in all layers
those in stratum basale are large stem cells
divide to regenerate new cells
synthesize keratin
a protein that strengthens epidermis
What are the melanocytes of the stratum basale layer?
produce and store pigment (melanin) in response to ultraviolet light,
transfer pigment granules (melanosomes) into keratinocytes,
shield nuclear DNA from UV radiation
Scattered among keratinocytes in stratum basale
What are the tactile cells of the stratum basale?
Merkel cells, few in number
sensitive to touch, when compressed,
release chemicals, stimulate sensory nerve endings
What is the stratum spinosum?
Several layers of polygonal keratinocytes
new cells from stratum basale pushed into this layer
nondividing keratinocytes attached by desmosomes
epidermal dendritic cells (Langerhans cells)
What is the stratum granulosum?
3 to 5 layers of keratinocytes that begin to fill with keratin
nucleus and organelles to disintegrate
cells are dead
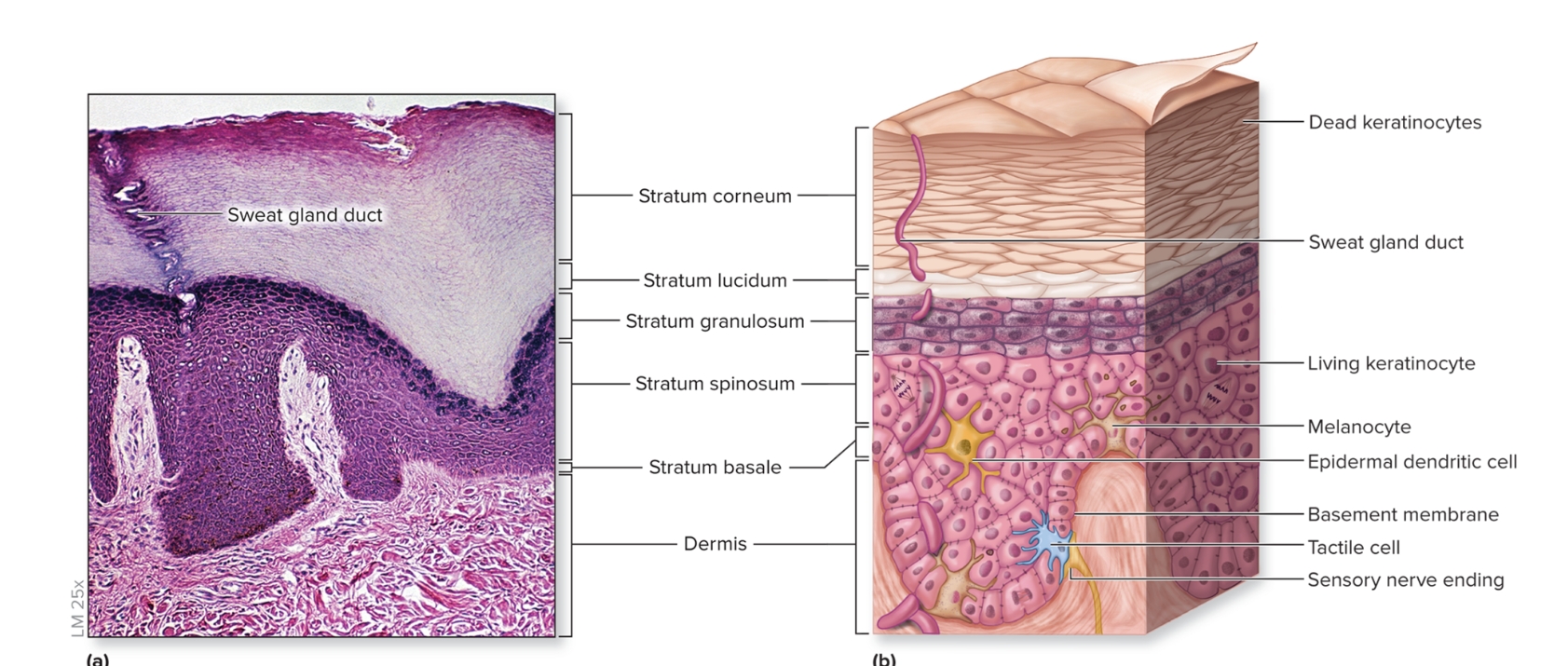
What are epidermal dendritic cells?
initiate immune response
found un spinosum and granulosum
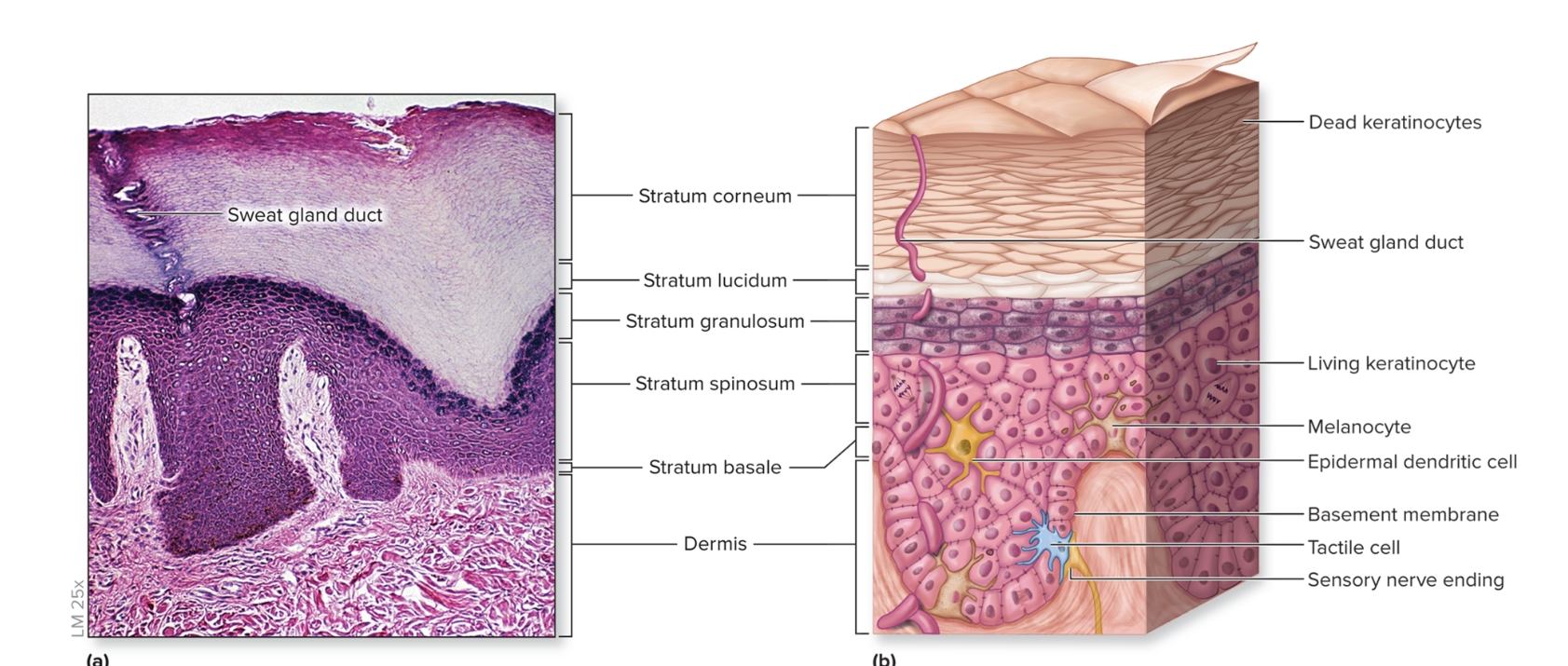
What is the stratum lucidum?
translucent layer
2 to 3 cell layers thick
found only on thick skin on palms and soles
What is the stratum corneum?
superficial stratum composed of 20 to 30 layers of dead interlocking, anucleate (lacking a nucleus), keratinized cells, dry,
thickened surface is protective against abrasion and infection

What is the dermis?
Deep to epidermis
composed of CT proper
other structures present: blood vessels, sweat glands, sebaceous glands, hair follicles, nail roots, sensory nerve endings, arrector pili, motile dendritic cells
What are the layers of the dermis?
papillary
reticular
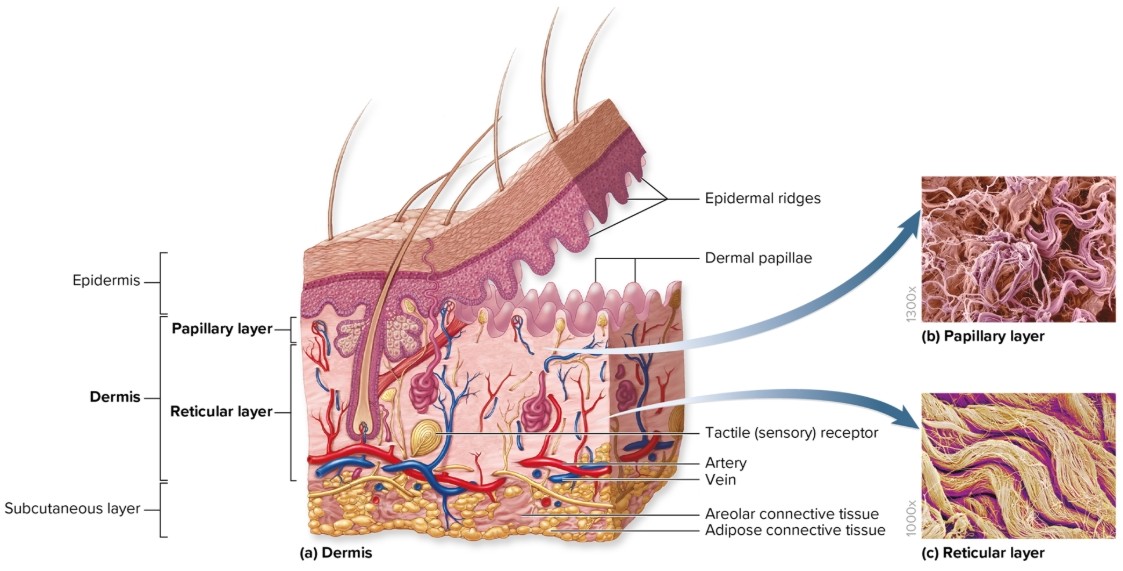
What is the papillary layer of the dermis?
superficial region of dermis (named for projections of dermis; dermal papillae)
deep to epidermis
areolar connective tissue
interlock with epidermal ridges to increase area of contact between layers
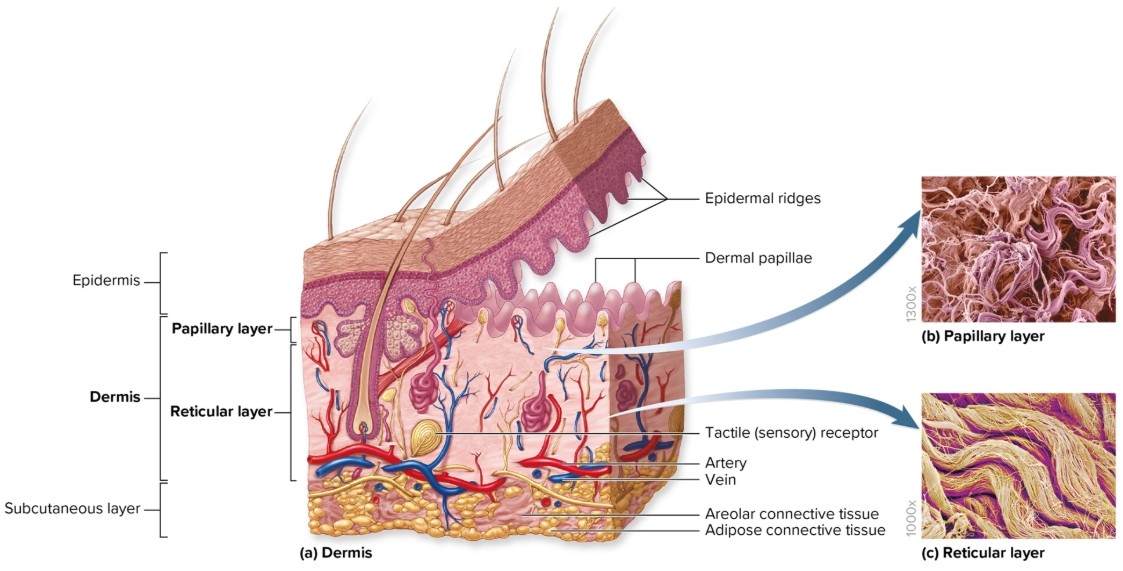
What is the reticular layer of the dermis?
deeper
major portion of dermis
dense irregular connective tissue
What is the subcutaneous layer?
hypodermis, superficial fascia
Not part of integument, areolar and adipose CT
protection, energy storage, and insulation, common drug injection site, extensive vascular network promotes rapid absorption, thickness/distribution influenced by sex hormones

What are lines of cleavage?
collagen and elastic fibers oriented in parallel bundles at specific locations
Bundles function to resist stress during routine movement
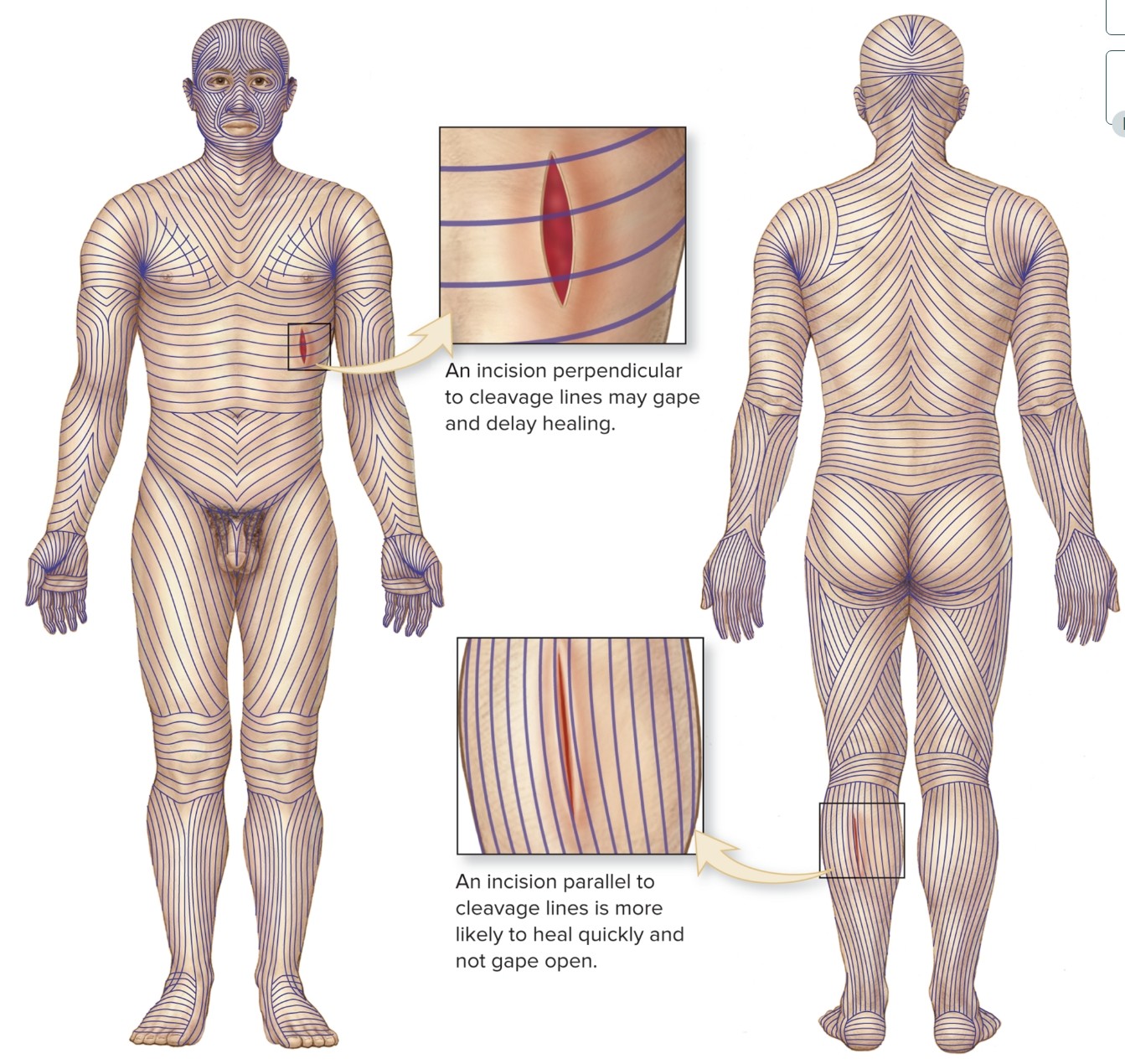
What is the orientation indicated by lines of cleavage?
incisions parallel to cleavage lines more likely to heal quickly
incisions perpendicular to cleavage lines are more likely to open due to cut elastic fibers
What causes stretch marks?
skin is stretched beyond its capabilities, results in striae
some collagen fibers torn