Lecture 1: Intro to Microbiology (copy)
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Which is best described below:
Unicellular
a) Bacteria
b) Parasites
c) Fungi
d) Viruses
a)
Which is best described below:
Single or multicellular
a) Bacteria
b) Parasites
c) Fungi
d) Viruses
e) A and B
f) B and C
g) All of the Above
f)
Which is best described below:
Much smaller than bacteria
Acellular
a) Bacteria
b) Parasites
c) Fungi
d) Viruses
d)
What are the Five Kingdoms:
a) Monera
b) Protista
c) Fungi
d) Plantae
e) Animalia
f) All of the Above
f)
Which has Hierarchy in order (From largest to smallest)
a) Species —> Genus —→ Family —→ Kingdom
b) Family —> Kingdom —> Species —> Genus
c) Kingdom —> Family —> Genus —> Species
d) Kingdom —> Genus —> Species —> Family
c)
Which is best described below:
Before there was nucleus
No Nucleus. Only Nucleoid with a bacteria genomic DNA, RNA, and a few proteins
a) Prokaryotic cell
b) Eukaryotic cell
a)
Which is best described below:
No membrane bound organelles
a) Prokaryotic cell
b) Eukaryotic cell
a)
Which is best described below:
70S ribosomes
a) Prokaryotic cell
b) Eukaryotic cell
a)
Which is best described below:
Most lack sterols in cell membrane
a) Prokaryotic cell
b) Eukaryotic cell
a)
Which is best described below:
Cell division- Binary fission
a) Prokaryotic cell
b) Eukaryotic cell
a)
Which is best described below:
Cells that have a true nucleus with chromosomes
a) Prokaryotic cell
b) Eukaryotic cell
b)
Which is best described below:
Membrane bound organelles
a) Prokaryotic cell
b) Eukaryotic cell
b)
Which is best described below:
80S ribosomes
a) Prokaryotic cell
b) Eukaryotic cell
b)
Which is best described below:
Contains sterols in cell membrane
a) Prokaryotic cell
b) Eukaryotic cell
b)
Which is best described below:
Cell division= Mitosis and Meiosis
a) Prokaryotic cell
b) Eukaryotic cell
b)
Which of the following is best described below:
Curved Bacilli
a) Bacilli
b) Streptobacilli
c) Vibrio
d) Actinomyces
e) Spirochetes
c)
Which of the following is best described below:
Branching filamentous bacilli
a) Bacilli
b) Streptobacilli
c) Vibrio
d) Actinomyces
e) Spirochetes
d)
Describe the structure of a bacterial cell
cell wall
cytoplasmic membrane
nucleoid
plasmid ribosomes
storage granules
capsules
flagella and pili
Which of the following terms of bacterial cell structure is best described:
Extra-chromosomal DNA
Role in virulence/toxin formation, drug resistance, etc.
a) Nucleoid
b) Plasmids
c) Ribosomes
d) Storage granules
b)
Which of the following terms of bacterial cell structure is best described:
Double stranded DNA
a) Nucleoid
b) Plasmids
c) Ribosomes
d) Storage granules
a)
Which of the following terms of bacterial cell structure is best described:
Protein synthesis
Target for antibacterial drugs
2 components= 30S and 50S
a) Nucleoid
b) Plasmids
c) Ribosomes
d) Storage granules
c)
Which of the following terms of bacterial cell structure is best described:
Glycogen, Lipids, Phosphates, etc.
a) Nucleoid
b) Plasmids
c) Ribosomes
d) Storage granules
d)
Which of the following is true about: Cytoplasmic membrane
a) Phospholipid bilayer with proteins lacking sterols (exception-Mycoplasmas have sterols in their cell)
b) Outer cover that protects the cytoplasmic membrane
c) Determines staining characteristics (Gram positive vs. Gram negative bacteria)
d) Main function= Transport and energy production
e) B and C
f) A and D
g) All of the above
f)
Which of the following is true about: Cell Wall
a) Phospholipid bilayer with proteins lacking sterols (exception-Mycoplasmas have sterols in their cell)
b) Outer cover that protects the cytoplasmic membrane
c) Determines staining characteristics (Gram positive vs. Gram negative bacteria)
d) Main function= Transport and energy production
e) B and C
f) A and D
g) All of the above
e)
Which of the following is best described below:
_____ is a target for antibacterial drugs
a) cytoplasmic membrane
b) cell wall
c) All of the above
d) None of the above
b)
Which of the following is best described below:
Has peptidoglycan (murein) which contains subunits of N-acetyl muramic acid (NAM) and n-acetyl glucosamine (NAG)
NAM has peptide side chains that are crosslinked by transpeptidases
Transpeptidases are also called Penicillin Binding Proteins (PBPs) as the antibiotic class of penicillin binds to these while acting on _____
Mutations in the genes coding for PBPs lead to altered PBPs with low affinity to penicillin
Basis for methicillin resistance in S.aureus (MRSA)
a) cytoplasmic membrane
b) cell wall
c) All of the above
d) None of the above
b)
Which of the following is best described below:
Extends from the cell wall up to the cytoplasmic membrane
a) Gram positive cell envelope
b) Gram negative cell envelope
a)
Which of the following is best described below:
Thick peptidoglycan (murein)
Teichoic acid
Lipoteichoic acid
a) Gram positive cell envelope
b) Gram negative cell envelope
a)
Which of the following is best described below:
Outer membrane: functions as a barrier, sieve and for attachment
Has porins, proteins, and Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) in outer leaflet and phospholipids in inner leaflet
a) Gram positive cell envelope
b) Gram negative cell envelope
b)
Which of the following is best described below:
Periplasmic space and thin peptidoglycan layer
a) Gram positive cell envelope
b) Gram negative cell envelope
b)
Which of the following is best described below:
Inner membrane is plasma membrane
a) Gram positive cell envelope
b) Gram negative cell envelope
b)
True or False
Bacterial LPS is specific to Gram negative bacteria and is also called Endotoxin
a) True
b) False
a)
Endotoxin
Stimulator of immune response and consists of:
O antigen
Core polysaccharide
Lipid A
What is best described below:
Polysaccharide chains
Major surface antigen
a) O antigen
b) Core polysaccharide
c) Lipid A
a)
What is best described below:
Unusual carbohydrate residues
a) O antigen
b) Core polysaccharide
c) Lipid A
b)
What is best described below:
Disaccharide with fatty acid tails extending into outer membrane
Toxic moiety
a) O antigen
b) Core polysaccharide
c) Lipid A
c)
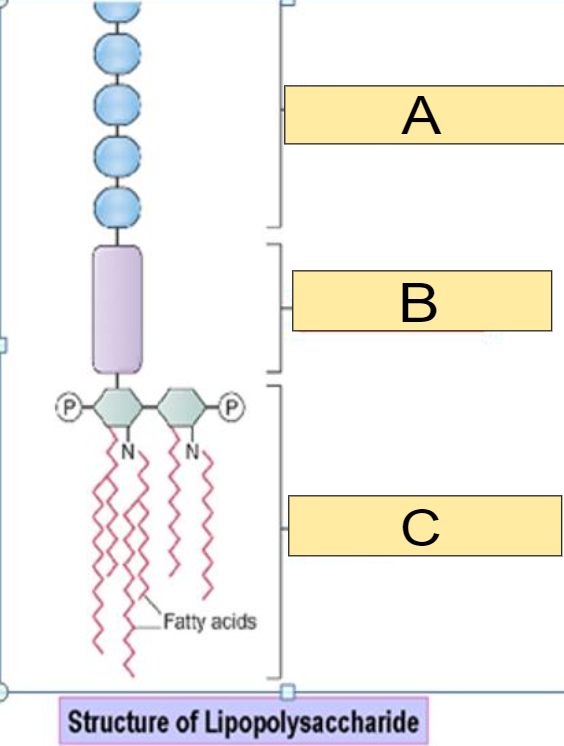
What part of the Lipopolysaccharide is shown in the image for: A
a) O antigen
b) Core polysaccharide
c) Lipid A
a)
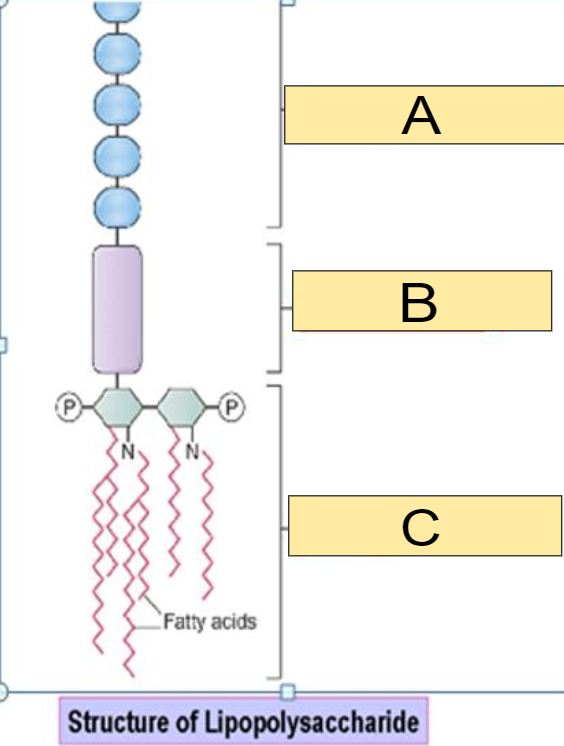
What part of the Lipopolysaccharide is shown in the image for: B
a) O antigen
b) Core polysaccharide
c) Lipid A
b)
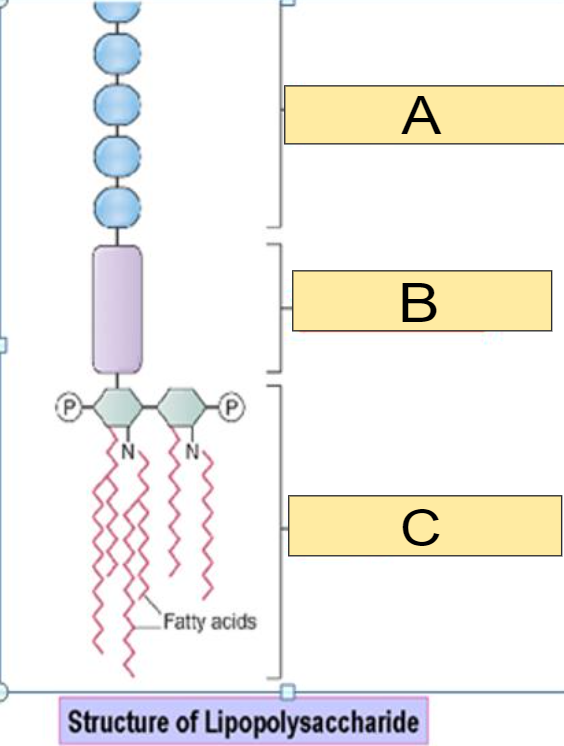
What part of the Lipopolysaccharide is shown in the image for: C
a) O antigen
b) Core polysaccharide
c) Lipid A
c)
Which of the following is best described below:
Firmly adherent, usually made of polysaccharide
Do not stain by the grams stain and appear as haloes around stained bacteria
a) Capsules
b) Biofilm
c) SLIME
d) All of the Above
e) None of the Above
a)
Which of the following is best described below:
Clinical significance
Important virulence factors as they inhibit phagocytosis
Antigenic-used in vaccine preparations
a) Capsules
b) Biofilm
c) SLIME
d) All of the Above
e) None of the Above
a)
Which of the following is best described below:
Loose, sticky polysaccharide matrix due to glycocalyx formation
a) Capsules
b) Biofilm
c) SLIME
d) All of the Above
e) None of the Above
c)
Which of the following is best described below:
SLIME leads to _____ formation
a) Capsules
b) Biofilm
c) SLIME
d) All of the Above
e) None of the Above
b)
Which of the following is best described below:
Communities of microorganisms growing on inert or living surfaces within a protective and adhesive polysaccharide matrix
a) Capsules
b) Biofilm
c) SLIME
d) All of the Above
e) None of the Above
b)
Which of the following is best described below:
Clinical significance:
_____ formation is associated with dental caries, indwelling catheters and prosthetic devices
Bacteria growing within ____ do not allow easy penetration by antibiotics
Important factor leading to nosocomial infections
a) Capsules
b) Biofilm
c) SLIME
d) All of the Above
e) None of the Above
b)
What are the steps of biofilm formation in order:
a) Cell to cell adhesion —→ Attachment to surface —> Maturation —→ Proliferation —> Dispersion
b) Attachment to surface —→ Cell to cell adhesion —> Maturation —→ Proliferation —→ Dispersion
c) Attachment to surface —→ Cell to cell adhesion —> Proliferation —> Maturation —> Dispersion
d) Attachment to surface —→ Cell to cell adhesion —> Proliferation —→ Dispersion —→ Maturation
c)
Which of the following is best described below:
Hair like fibers made of pilin (protein subunits)
a) Pili or Fimbriae
b) Flagella
a)
Which of the following is best described below:
Act as adhesins/ lectins
Important virulence factors for adherence to host cell surfaces
a) Sex pili
b) Common pili
b)
Which of the following is best described below:
Used for conjugation
Help transfer of genetic material like plasmids
a) Sex pili
b) Common pili
a)
Which of the following is best described below:
Rope-like propellers, help bacteria move from one location to another
Made of proteins- Flagellin
a) Pili or Fimbriae
b) Flagella
b)
Which of the following is best described below:
Antigenic. Used for serotyping bacteria (H antigen)
a) Pili or Fimbriae
b) Flagella
b)
What are the different arrangements of flagella?
a) Peritrichous
b) Polar or Monotrichous
c) Lophotrichous
d) Amphitrichous
e) All of the above
e)
Endoflagella or Axial Filament
Flagella like structure wrapped around bacteria
Ex: Seen in Spirochetes
Which of the following is true about Bacterial Spores:
a) Under adverse conditions, sporulation leads to spore formation. When nutrients/water available, germinate to vegetative forms
b) Contain high concentration of Calcium dipicolinate. Resistant to environmental stresses- heat, chemicals, desiccation, UV rays, etc.
c) Destroyed by autoclaving: 121 C, 15 min, 15 pounds pressure
d) Dormant forms of some bacterial cells and are highly resistant structures
e) All of the Above
f) None of the above
e)