pyruvate oxidation
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
where does glycolysis happen
in the cytoplasm, it is anaerobic
mitochondria
oval shaped membrane w/ double-membrane
inner membrane folds = cristae, increases surface area of the membrane
proteins and molecules are embedded into the inner membrane to help with cellulalar respiration
matrix = protein rich fluid inside cristae
intermembrane space is filled w/ fluid
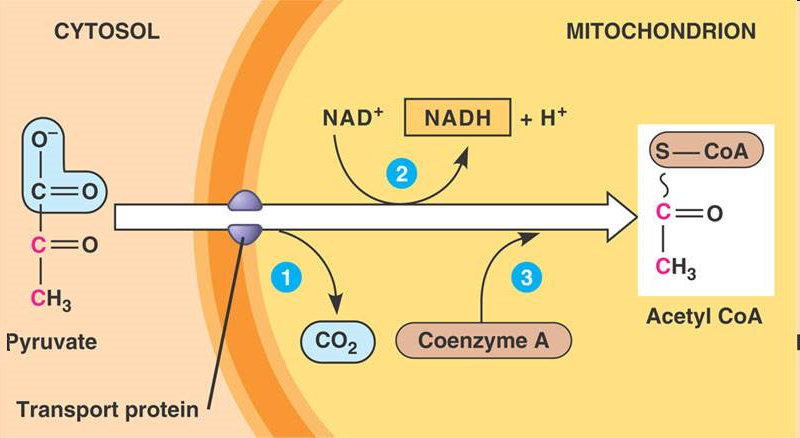
about pyrvuate oxidation
goal of pyruvate oxidation is to convert 3 carbon pyrvuate into acetyl CoA
2 pyruvates formed at the end of glycolysis are transported into the matrix
Acetyl CoA is a 3 carbon molecule containing Coenzyme A, impo for krebs cycle
STEPS to pyruvate oxidation
carboxyl end on pyruvate is removed and released as CO2 waste (decarboxylation) → 2-carbon molecule (acetyl group)
acetyl group is oxidized into acetate (oxidation reaction). NAD+ reduced to NADH & H+
CoA (sulfur-containing compound coming from vitamin B5) is attached to the acetate, making acetyl CoA
enzyme used in all steps of pyruvate oxidation
pyruvate decarboxylase complex
results of pyrvuate oxidation
2 acetyl CoA enter krebs cycle
2 NADH go to ETC to make ATP
CO2 diffuses out of the cell as waste product (2?)
2 H+ protons stay in the matrix (ETC proton gradient??)
after NAD+ is reduced to NADH, where does the extra H+ go
stays in the matrix