Physics Forces and Newton's laws Review
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
How much force must be applied to keep a 5-kg object moving at a constant speed if there is no friction?
0.2 N
0 N
5 N
5 kg
If there is no friction and the object is moving at a constant speed, then no net force is needed to keep it moving (Newton’s First Law).
Newton’s 3rd law states that forces always act in ______.
pairs
perpendicular ways
quadruples
a vacuum
Newton’s 3rd Law says that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction — meaning forces always act in pairs.
A 15 N force and a 45 N force are applied to an object in opposite directions. What is the magnitude of the net force?
3 kg
60 N
30 N
15 N
The forces are in opposite directions, so you subtract them: 45 N − 15 N = 30 N
An overconfident bird collides with a skyscraper. Newton's third law states that the force of the bird on the skyscraper is __________ the force of the skyscraper on the bird.
greater than
lesser than
the same as
According to Newton’s Third Law, the bird and the skyscraper exert equal and opposite forces on each other — even though the effects are very different!
Newton’s Third Law says that when object A pushes on object B, object B pushes back on A with an equal and opposite force.
So, when the bird hits the skyscraper, the bird pushes on the building with the same amount of force that the building pushes on the bird.
You must apply a force of 25 N to a 10 kg box on a rough surface to keep it moving at a constant velocity. What is the magnitude of the frictional force opposing the motion of the box?
2.5 N
250 N
0.25 N
25 N
Since the box moves at a constant velocity, the applied force and frictional force are equal in magnitude (they balance each other). So, the frictional force = 25 N
You throw a baseball. The action force is your hand pushing on the ball. What is the reaction force?
the ball pushing on your hand
air resistance
your feet pushing on the floor
gravity
According to Newton’s Third Law, every action has an equal and opposite reaction — so when your hand pushes on the ball, the ball pushes back on your hand with the same amount of force.
With unparalleled ferocity, you bring your foot down on top of a defenseless cardboard box with a force of 100 N, crushing it. What force did the box enact on your foot?
half of 100 N
way more than 100 N
way less than 100 N
exactly 100 N
By Newton’s Third Law, when you push down on the box with 100 N, the box pushes back up on your foot with an equal and opposite force of 100 N — even though the box gets crushed because it can’t withstand that force.
Jimbo has a mass of 200 kg. What is his weight on Earth?
1,960 N
980 N
200 lbs
400 kg
Weight = mass × gravitational acceleration 200kg x 9.8m/s2 = 1,960N
The weight of a 20-kg object on the Sun is _______ its weight on Earth.
less than
the same as
greater than
The Sun’s gravity is much stronger than Earth’s, so a 20-kg object would weigh much more on the Sun than it does on Earth.
Compared to its mass on Sun, the mass of a 99 kg object on the Earth is _______.
greater
lesser
the same
Mass is the amount of matter in an object, and it does not change based on location.
A box is being pulled along a flat surface at a constant velocity. Which of the following are true?
The net force is zero
The normal force plus the weight is zero
The acceleration is zero
All of the above
None of the above are true
When a box is pulled at a constant velocity on a flat surface, the acceleration is zero because its speed isn’t changing. This means the net force is zero: the pulling force exactly balances the frictional force opposing motion.
In the vertical direction, the normal force from the surface balances the box’s weight, keeping it from sinking or lifting, but these vertical forces do not contribute to horizontal motion.
Overall, all forces are balanced, so the box moves steadily without speeding up or slowing down.
When will an object accelerate, according to Newton?
Responses
it has zero net force
all its forces are balanced
there is an applied net force greater than zero
there is no friction
it is experiencing gravity
According to Newton’s Second Law, an object will accelerate only when the net force acting on it is not zero. If all forces are balanced (net force = 0), the object will not accelerate.
How much force should you apply to accelerate a 20 N textbook across a frictionless desk at 325 m/s?
750 N
20 N
650 N
162.5 N
given:
Weight of the book: W=20 N
Acceleration: a=325 m/s²
Frictionless surface
Step 1: Convert weight to mass
Weight = mass × gravity:
W=m⋅g ⟹ m=w/g = 20/10 = 2 kg
Step 2: Use Newton’s 2nd Law
F=m⋅a F= 2 ⋅325 = 650
What causes acceleration?
friction
mass
a net force of zero
a non-zero net force
Acceleration occurs only when the net force on an object is not zero, according to Newton’s Second Law. Friction or mass can affect the motion, but they don’t directly cause acceleration unless they create an unbalanced force.
If a non-zero net force is applied to an object, which of the following must be false?
The object remains in motion at the same speed in the same direction
The object's velocity increases
The object's speed decreases
The object moves in a circle
If a non-zero net force is applied, the object cannot continue moving at the same speed in the same direction because a net force always causes acceleration (a change in speed or direction), according to Newton’s Second Law.
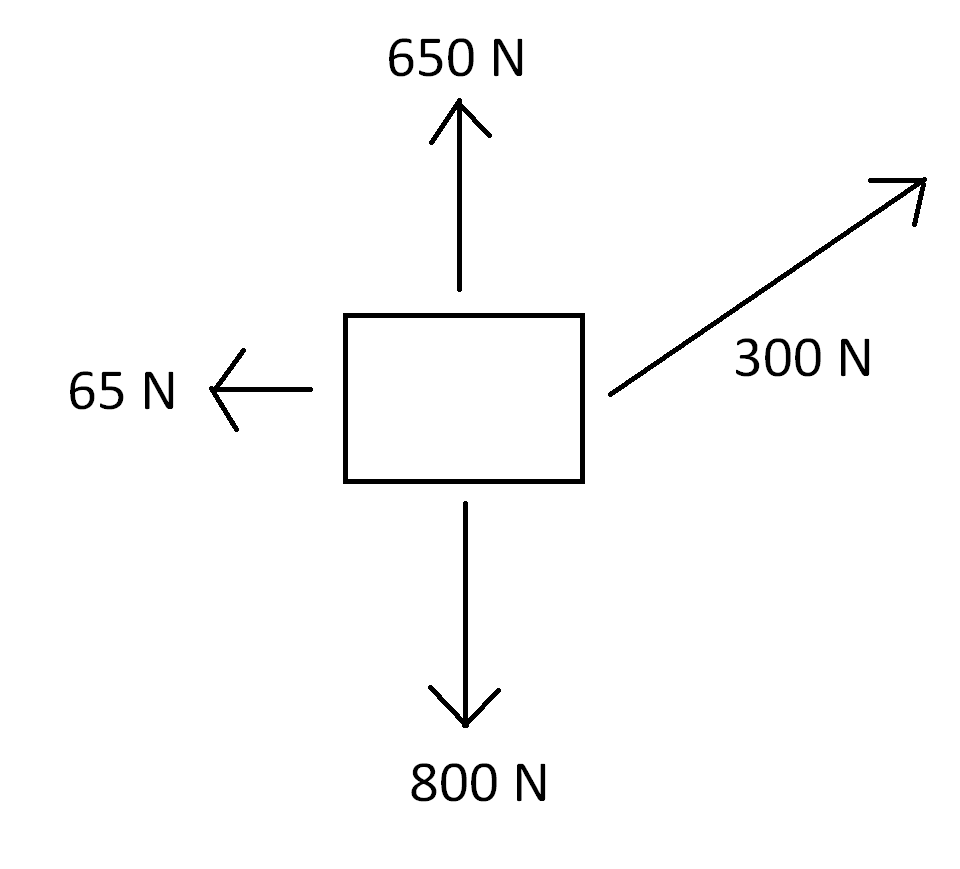
In the free-body diagram shown above, when the box is dragged to the right, the 300 N force represents
force of friction
force of weight
applied force
normal force
In a free-body diagram, the force used to drag or move an object is called the applied force. The force of friction would oppose this motion, the weight points downward, and the normal force points upward.
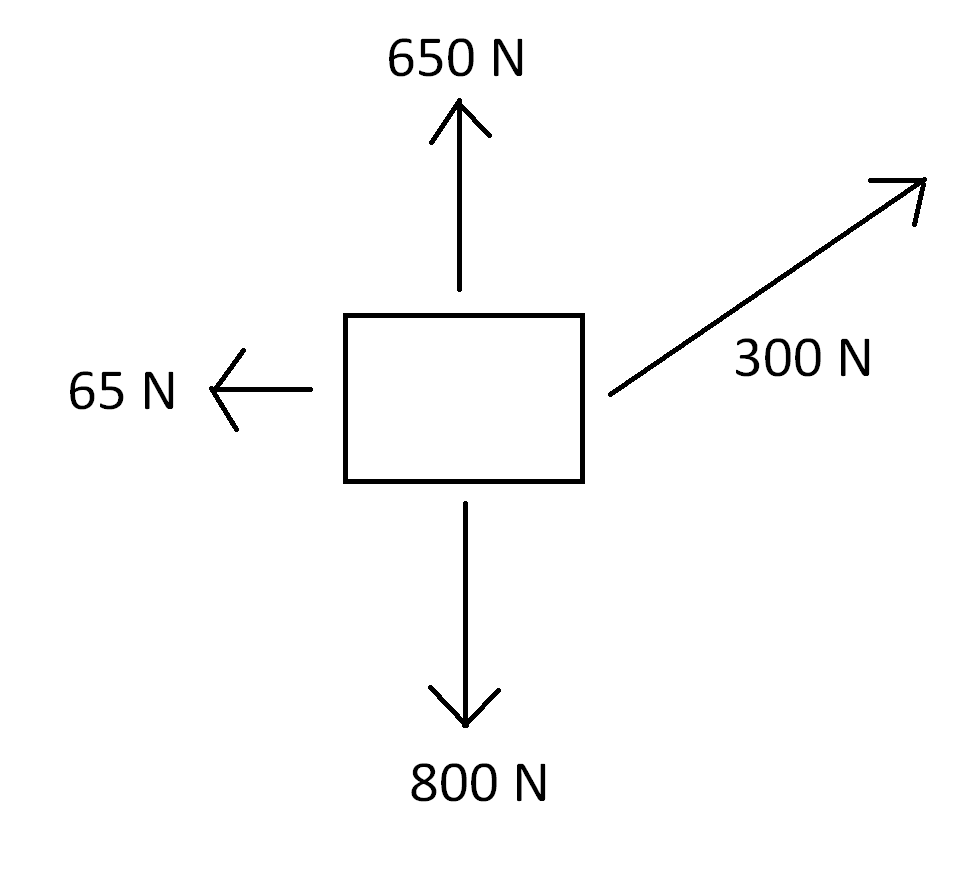
In the free-body diagram shown above, when the box is pulled to the right, what is the magnitude of the frictional force?
650 N
800 N
300 N
65 N
The frictional force is the arrow pointing opposite the direction of motion, so in this diagram, the 65 N arrow to the left represents the friction opposing the box’s movement to the right.
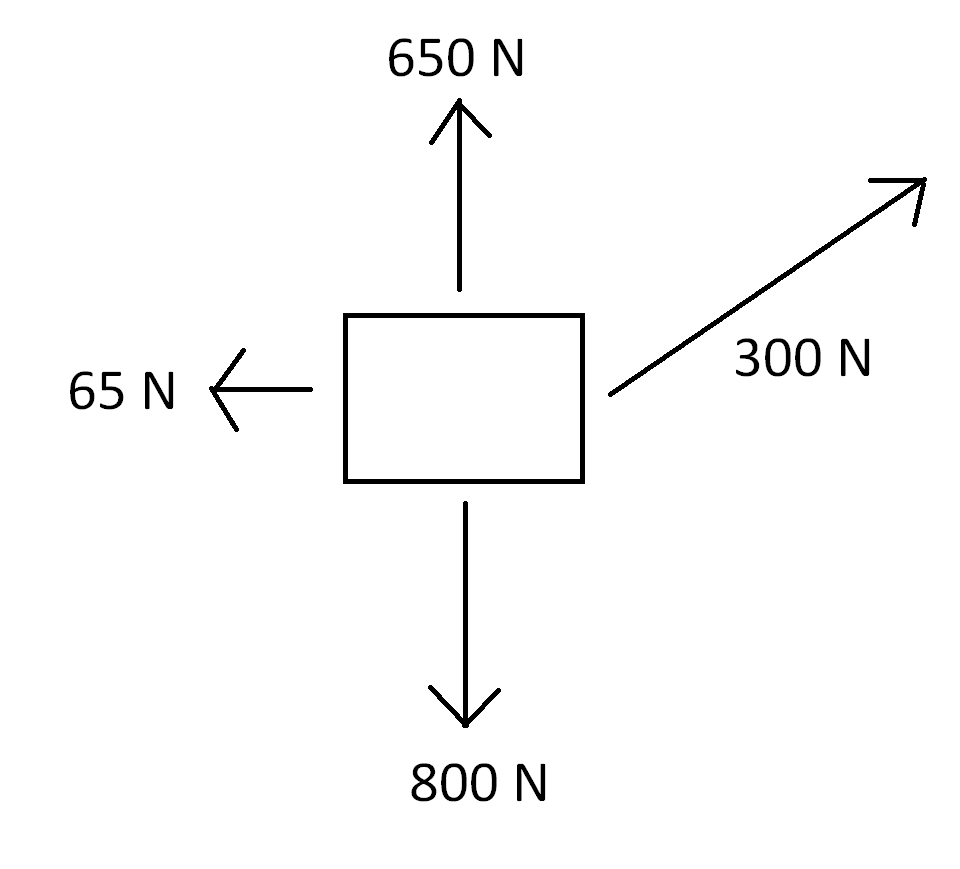
In the free-body diagram shown above, what is the weight of the box being dragged to right?
800 N
300 kg
65 N
650 N
In a free-body diagram: The downward arrow represents the weight of the object. The downward arrow represents weight because weight is the force of gravity acting on an object, and gravity always pulls objects toward the center of the Earth (or whichever planet the object is on).
Which of Newton's laws states that an object will remain at rest or remain in constant motion in the same direction unless it is acted upon by a non-zero net force?
Thirtieth
Third
First
Second
Zeroeth
Newton’s First Law (also called the law of inertia) states that an object will stay at rest or keep moving in a straight line at constant speed unless acted on by a non-zero net force. This law basically explains why motion doesn’t change on its own — a force is needed to speed up, slow down, or change direction.
If the net force applied to an object triples, what will happen to the magnitude of its acceleration?
it will be reduced by a factor of one third
it will triple
it will not change
it will double
Tripling the net force triples the acceleration because, according to Newton’s Second Law (a=Fnet/m), acceleration is directly proportional to the net force when mass stays the same. Since the mass doesn’t change in this case, the acceleration increases by the same factor as the force.
If the mass of an object quadruples while you apply a constant force to it, what happens to the magnitude of its acceleration?
it is quartered
it doubles
it quadruples
it is halved
Since acceleration is inversely proportional to mass, quadrupling the mass reduces acceleration to one-fourth, not one-half. As mass increases and the force stays constant, acceleration decreases.
You stub your toe on a book carelessly left on the floor. Which of the following is an action-reaction pair?
toe hits book, toe hits floor
toe hits book, book hits toe
toe hits book, book hits floor
toe hits book, book accelerates
According to Newton's third Law for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. An action-reaction pair involves two forces that are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction, acting on two different objects.
A book is at rest on a flat surface. What is the name of the force that counteracts the weight of the object?
paranormal force
friction
normal force
opposing force
applied force
The normal force is the upward force exerted by a surface that balances the downward weight of an object at rest. Weight = downward force due to gravity, Normal force = upward force from the surface. These two forces are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction, keeping the book from sinking through the surface.
If the inertia of a rocket has decreased, which of the following have decreased?
the mass of the rocket
the speed of the rocket
the net force applied to the rocket
the force of air resistance on the rocket
the velocity of the rocket
Inertia is an object’s resistance to changes in motion, and it depends directly on mass. If a rocket’s inertia decreases, it means its mass has decreased, making it easier to accelerate. Speed, velocity, net force, and air resistance are not the same as inertia.
A chonky goldfish has a mass of 20 kg. Jimbo pulls with a force of 325 N to the left, while his cousin Dimbo pulls with a force of 225 N to the right. What is the acceleration of the fat fish?
100 m/s2 to the left
5 m/s2 to the left
5 m/s2 to the right
2.5 m/s2 to the right
Given:
Mass: m=20 kg
Jimbo’s force: FJimbo=325 N (left)
Dimbo’s force: FDimbo=225 N (right)
Step 1: Find the net force
Since the forces are in opposite directions, subtract the smaller from the larger:
Fnet=325−225=100 N to the left
Step 2: Use Newton’s 2nd Law
a= Fnet/m = 100/20 = 5m/s2 to the left
An 112 kg NFL quarterback running at 15 m/s trips and skids to a stop in 5 seconds. What was the magnitude of the force of friction from the turf acting on the disgraced quarterback?
336 kg
3.36 x 10³ N
3.36 x 10² N
1.12 x 10² N
Given:
Mass: m=112 kg
Initial velocity: vi=15 m/s
Final velocity: vf=0 m/s
Time: t=5 s
