ALCOHOL
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
general formula
CnH2n+1OH
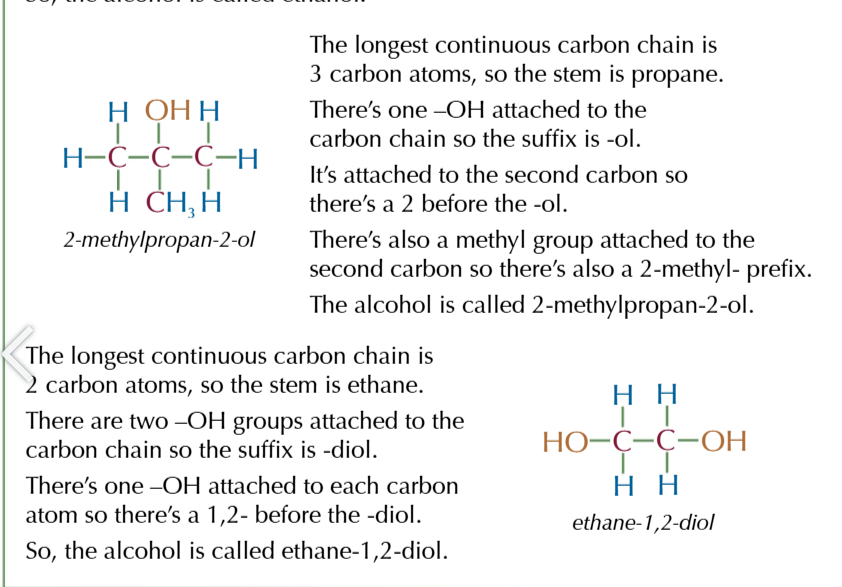
primary
OH group attached to a carbon with 1 AKYL
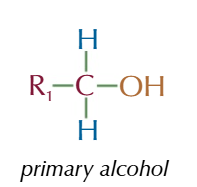
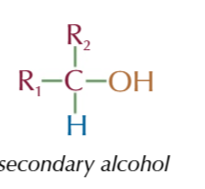
secondary alcohol
OH group attached to a carbon with 2 AKYL
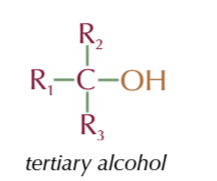
tertiary alcohol
OH group attached to a carbon with 3 AKYL
dehydrating alcohols equation (ELIMINATION REACTION)
CnH2n+1OH → CnH2n + H2O
dehydrating alcohols produces
alkenes from renewable resources
you can produce ethanol by fermenting glucose from plants
so polymers like polyethene can be made without oil
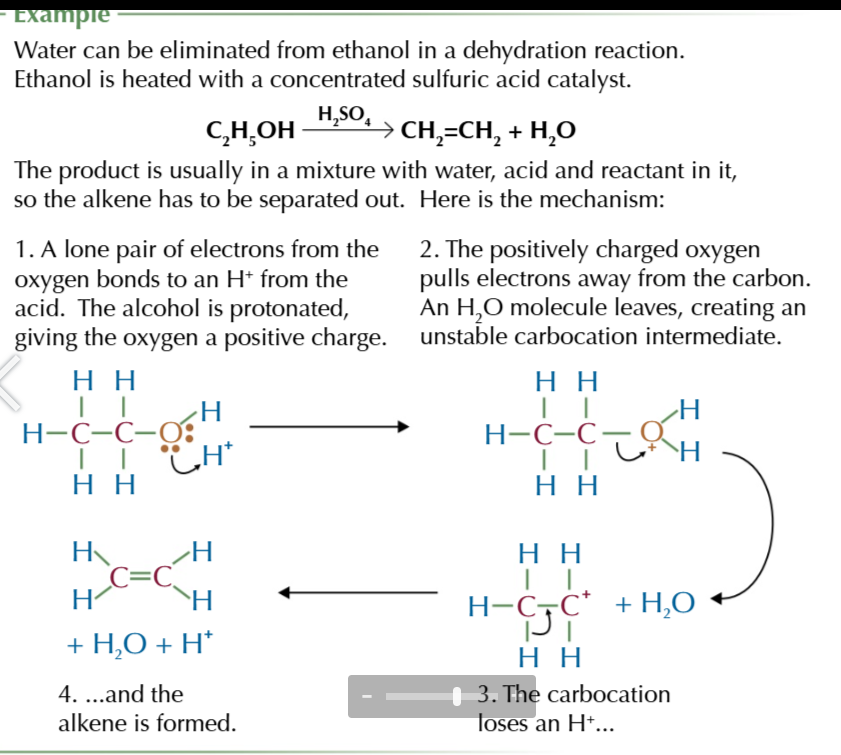
water can be ELIMINATED from alcohols in a dehydration reaction
alcohols are heated with a concentrated sulphuric acid catalyst producing water and alkene
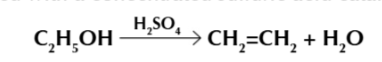
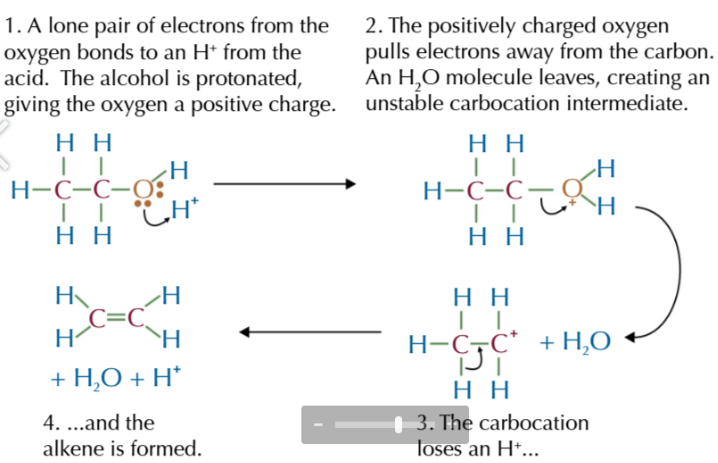
elimination mechanism
Lone pair from oxygen bonds with H+ from acid
this protonates the oxygen, giving it a positive charge
the positively charged oxygen pulls electrons from its bond between C-O, producing a water molecule + carbocation intermediate
carbocation loses a H+
alkene is formed and acid is reformed
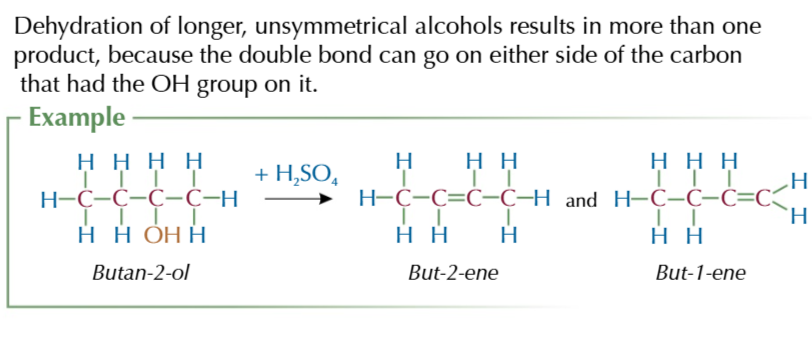
dehydration of longer unsymmetrical alcohols produce multiple products
because the double bond can go on either side of the carbon
products of organic reactions
are often impure
in the dehydration of alcohols to form alkenes
the end mixture contains:
product
reactant
acid
water
impurities
distillation
use the fact different chemicals have different boiling points to separate them
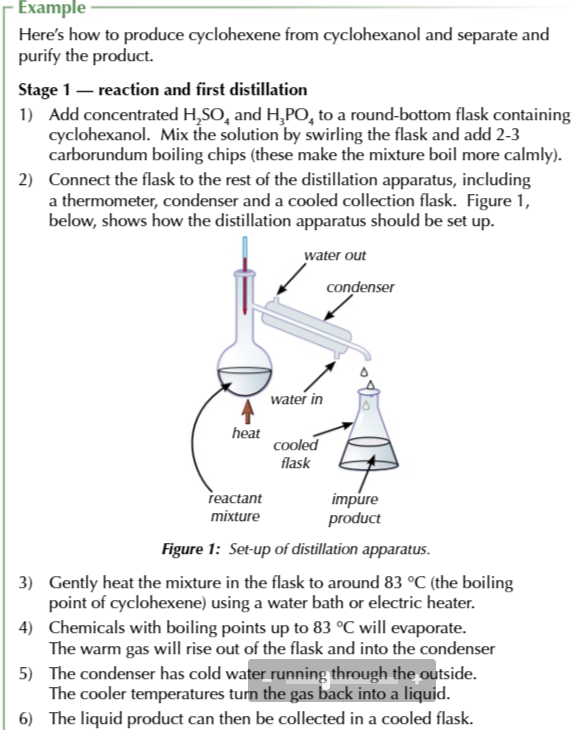
there are 3 steps to produce cyclohexene on its own from cyclohexanol
reaction + first distillation
separation
purification
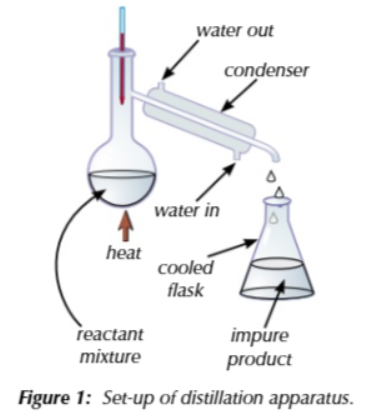
Reaction + first distillation
add conc sulfuric acid and phosphoric acid to a round bottom flask with carborundum boiling chips (so the reaction boils calmly)
connect flask to distillation apparatus (thermometer, condenser, cooled collection flask)
gently heat flask around 83℃ using a water bath
chemicals with a boiling point around 83℃ evaporate, rise out of the flask and into the condenser to be collected
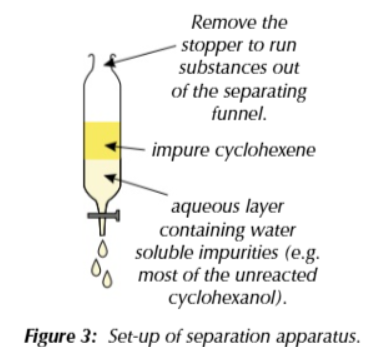
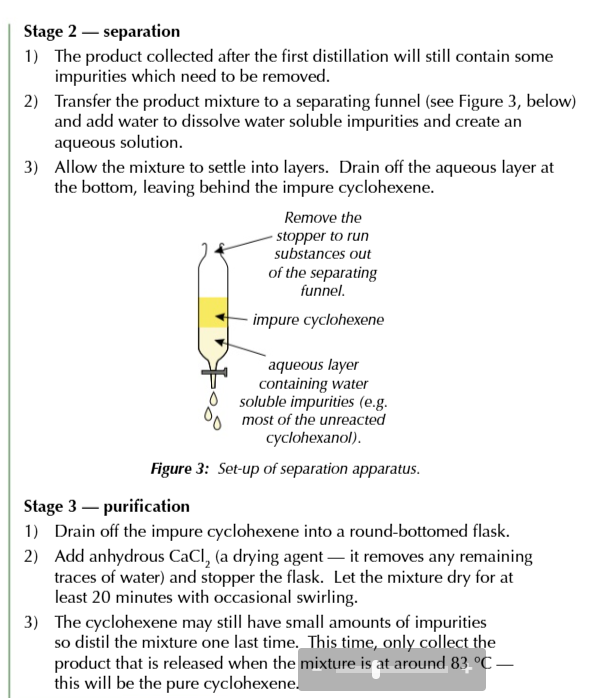
seperation
products of first distillation will contain impurities that must be removed
add water to mixture to dissolve soluble impurities then transfer mixture to separating funnel so an organic and aqueous layer forms
allow the layers to settle then drain off the aqueous layer leaving the impure cyclohexene
purification
drain off cyclohexene into round bottom flask
add anhydrous CaCl2 (a drying agent that will remove water) and stopper the flask
leave the flask for 20 minutes with regular shakes
distil the solution 1 last time at 83℃ and collect the pure cyclohexene
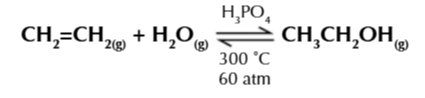
hydrating alkenes in the Prescence of an acid catalyst + steam
CnH2n + H2O ⇄ CnH2n+1OH
steam hydration of ethene is used industrally to produce ethanol, condition:
300℃
60 atm
solid phosphoric acid catalyust
the reaction yeild is low, only 5%, but wiht the recycled unreacted ethene gas the overall yeild is 95%
ethene comes from cracking heavy fractions of crude oil
crude oil is a finite resource
in the future when crude oil supplues start running off making petrochemicals like ethanol very expensive
so producing ethanol by fermentation will be very important
fermentation is an exothermic process carried out by yeast in anaerobic conditions
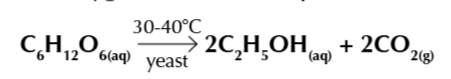
yeast produces enzymes which convert glucose into ethanol and carbon dioxide
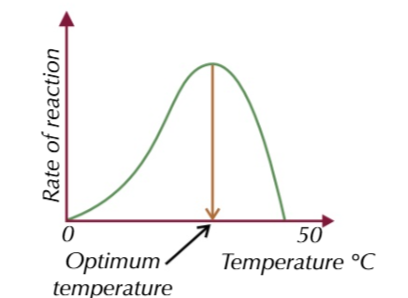
the enzymes work at an optimum temperature of 30-40℃
when the solution reaches around 15% ethanol yeast dies
fractional distillation increases the concentration of ethanol
fermentation is relatively cheap as low cost expirtment and renewable resources
ffractional distilation is needed to purify the ethanol using processes that take extra time and money
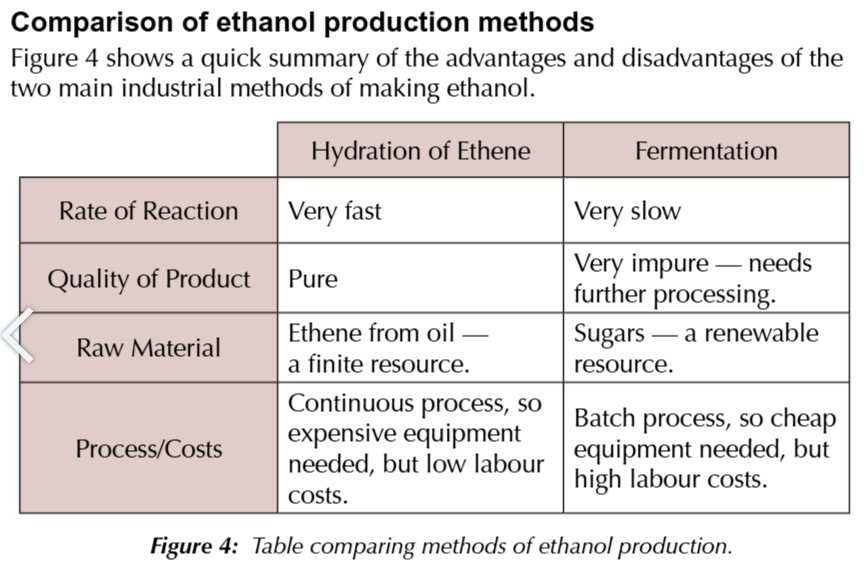
biofuel
a fuel made from biological material thats recently died:
example: sugars from sugar canes can be fermented to produce ethanol
ethanol produced this was is a biofuel
advantages of biofuels
renewable energy source therefroe more sustainable
produce the same amount of CO2 that plants take in as they grow so its considered carbon neutral
disadvantages of biofuels
food Vs fuel- the land used to grow crops for fuel cannot be used to grow food therefroe might not be able to feed everyone in the country
many trees cut down in order to create more land to frow crops for biofuel. deforestation destroys habitats and removes trees that take in CO2. the trees cut down are often burn which releases more CO2
fertilisers are often added to soils in order to increase biofuel crop production, fetrilisers can pollute waterways and some release nitrous oxides which is a greenhouse gas
the most current car engines are unable to run on fuels with high ethanol concentrations without being modified
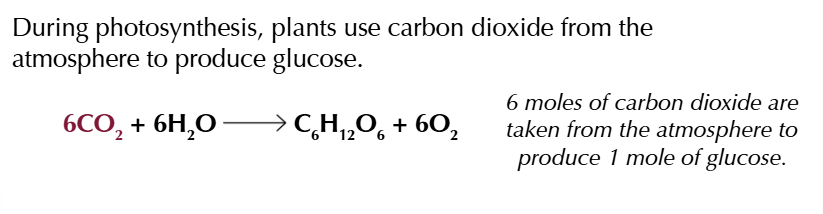
equations to support the theory ethanol is a carbon neutral biofuel
combining the 3 equations youll see exactly 6 moles of CO2 TAKEN IN AND OUT
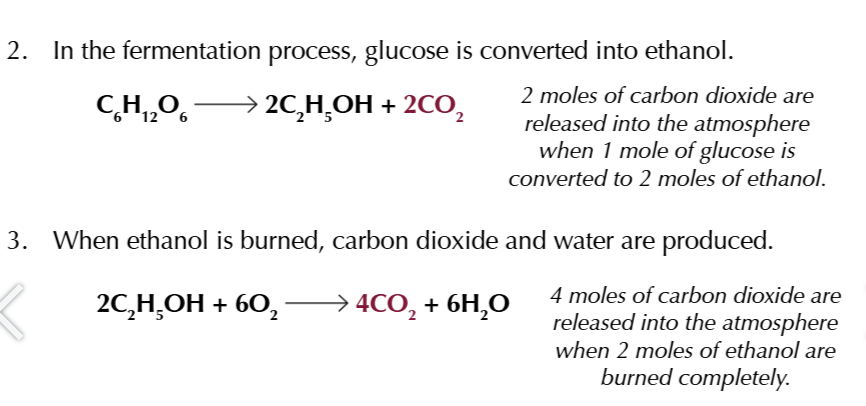
bioethanol is not completely carbon neutral
fossil fuels will need to be burned to power machinery used to make fertilisers/crops/harvesters
refining and transporting the bioethanol also uses energy
reducing agent: acidified potassium dichromate, K2Cr2O7
oxidises primary and secondary alcohols
acidified potassium dichromate colour change:
orange(Cr2O72-) → green (Cr3+)
primary alcohols oxidise to
aldehydes
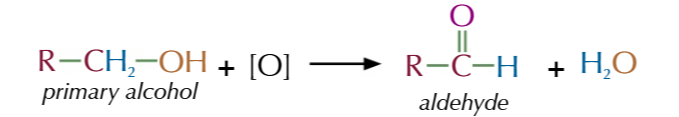
aldehydes oxidise to
carboxylic acids
secondary alcohols oxidise to
ketones only
tertiary alcohols DO NOT…
OXIDISE
aldehyde + ketone general formula
CnH2nO
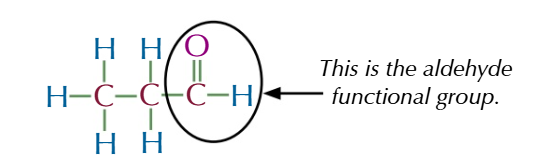
aldehyde functional group
ON THE ENDDDDD
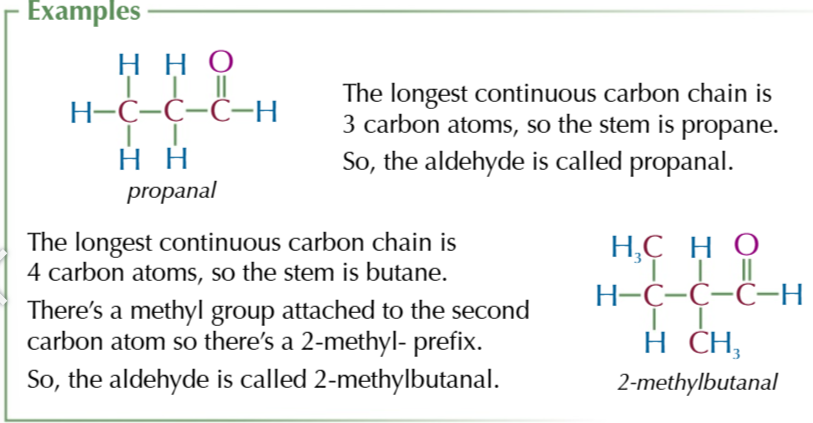
aldehyde suffix
-al
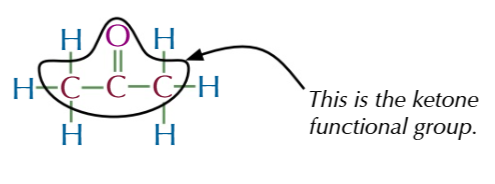
ketone functional group
IN THE MIDDLEEE
KETONE SUFFIX
-ONE

gently heating ethanol with potassium dichromate solution and sulfuric acid in a test tube till it produces an “apple” smell AKA ALDEHYDE
HOWEVER ITS TRICKY TO CONTROL THE HEAT and the aldehyde formed can get a vinager smelling ethanoic acid instead if oxidised too much
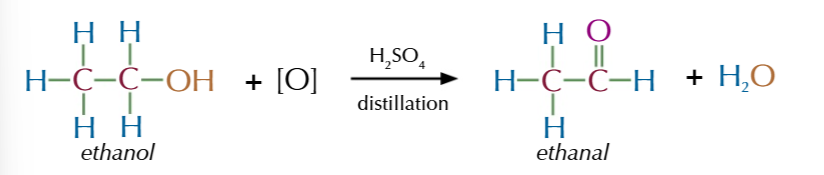
to get JUST the aldehyde you need to seperate it from the solution as soon as it forms
this is done by gently heating excess alcohol with a controlled amount of oxidising agent in distillation apparatus so when the aldehyde boils (at a lower temeprature than alcohol) its immediately distilled off
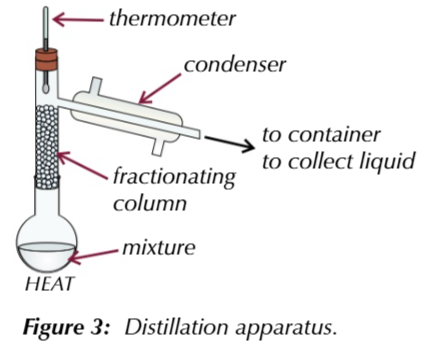
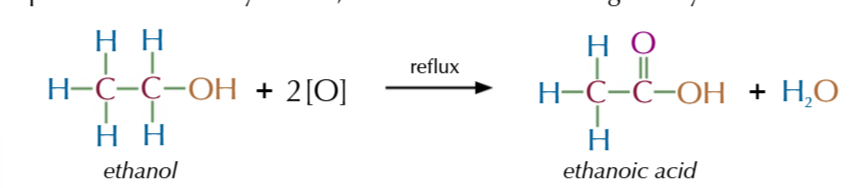
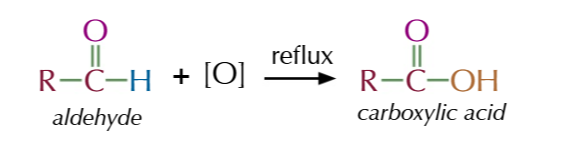
vigorous oxidation of primary alcohols produces carboxylic acid
oxidasing agent in excess and heated under reflux
heating under reflux means
you can increase the temeprature of an organic reaction to boiling without losing volatile solvents, reactants or products and any vapourised compunds are colled condensed and drip back into the reaction mixture
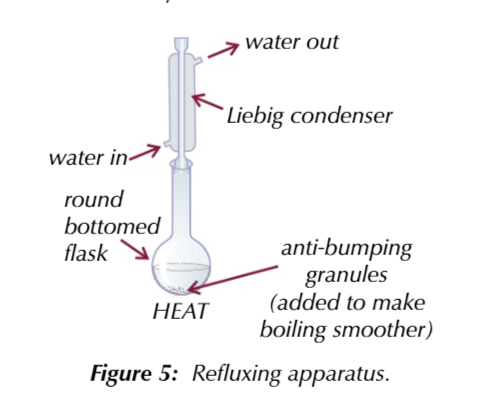
aldehydes stay in the reaction mixture
till they’re oxidised to become carboxylic acid
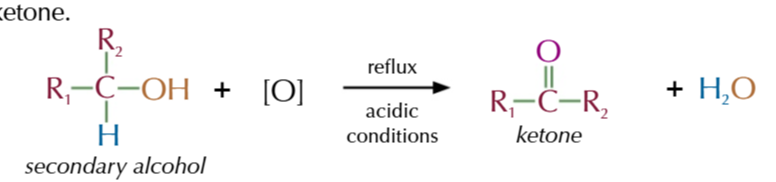
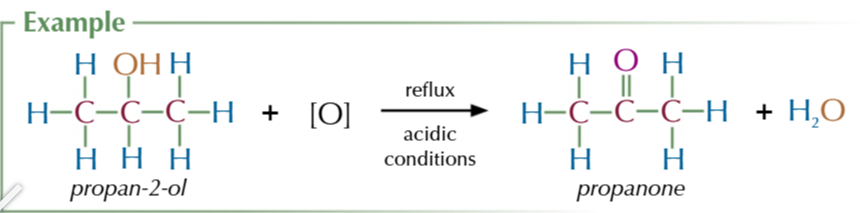
refluxing secodnary alcohols with acidified potassium dichromate produces ketones
the only way to oxidise tertiary alcohols
is to burn them
aldehydes can be easily oxidisedd
ketones cannot be easily oxidised
fehlings solution and benedicts solution are both deep blue Cu2+ complexes (alkaline solutions of copper 2 sulfate)
which reduce to brick red CuO precipitate when warmed with an aldehyde but stay blue with a ketone
tollens reagent is colourless [Ag(NH3)2]+ complex
is reduced to silver by aldehydes but not ketones. this silver will coat the inside of the apparatus to form a silver mirror