14: Transcription regulation (eukaryotes)
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
T or F. general transcription factors are required at every polymerase II promotor
true
The control of gene expression requires _
chromatin remodeling
T or F. Every gene requires activation to be transcribed.
t
Most eukaryotic promoters are (positively / negatively) regulated.
positively
Access to eukaryotic promoters is restricted by the structure of _
chromatin
_ are commonly involved in eukaryotic transcriptional regulation
long noncoding RNA’s
chromatin is in _ form to undergo gene regulation
euchromatin
Most eukaryotic promoters are _ regulated.
positively
In eukaryotes, every gene requires _ to be transcribed
activation
proteins involved in transcription in eukaryotes
1. Transcription activators
2. Architectural regulators
3. Chromatin modification and remodeling proteins
4. Coactivators (Mediator)
5. Basal transcription factor
regulatory sites can be far from the promotor in eukaryotes / prokaryotes
eukaryotes
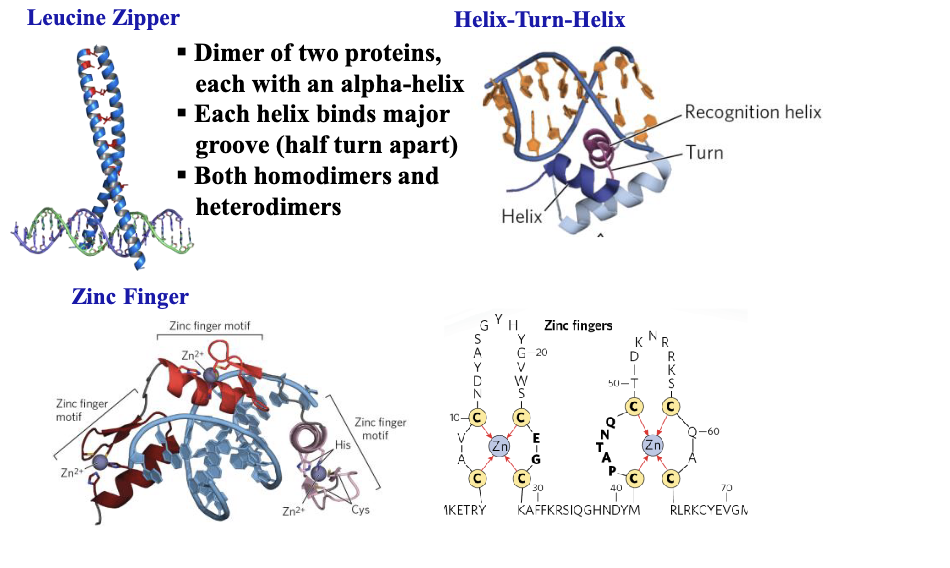
zinc-finger is (DNA-binding / activation) domain
dna binding
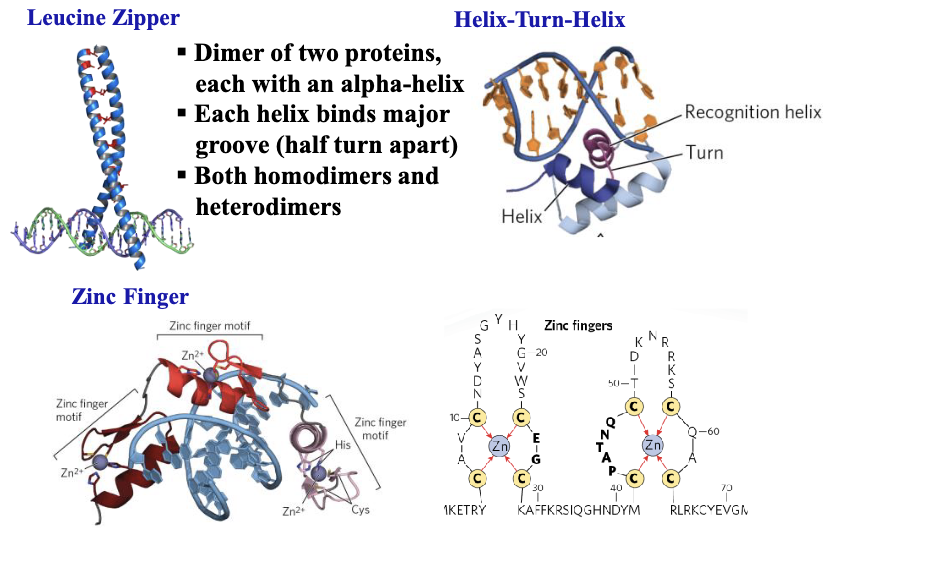
leucine zipper is (DNA-binding / activation) domain
dna binding
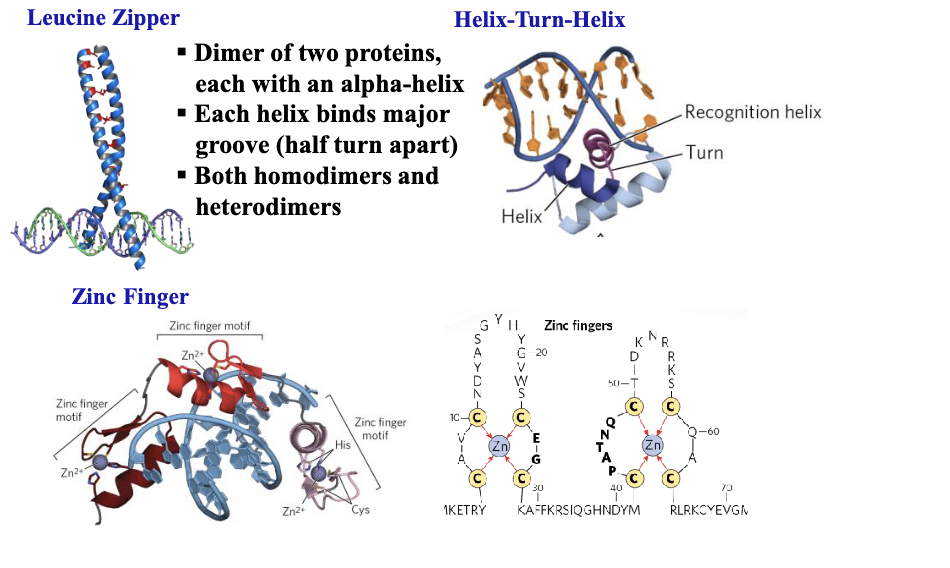
helix loop helix is (DNA-binding / activation) domain
dna binding
glutamine-rich domain is (DNA-binding / activation) domain
activation

proline-rich domain is (DNA-binding / activation) domain
activation

outline transcription activation
binding of activator to enhancers
recruitment of coactivators and histone modification, mediator
recruitment of TBP
recruitment of basal transcription factors and poly II
HMG proteins
3 types of activation domain
(less focused on structure than dna-binding)

leucine are (hydrophilic / hydrophobic)
hydrophobic
true or false. removing activation region can turn the lacz off
true
true or false. adding activation region can turn the lacz on
true
types of alterations in chromatin
covalent modification
structural modification
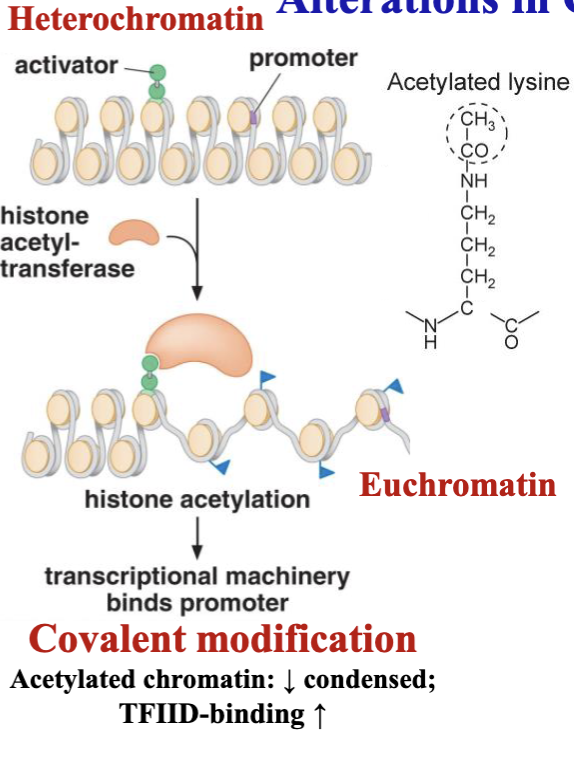
outline covalent modifications
heterochromatin → euchromatin
histone acetyltransferase (like lysine)
acetylates chromatin
outline structural modifications
changes accessibility of binding sites in DNA to proteins by remodeling nucleosomes
loosens promoter region
chromatin remodeling complex
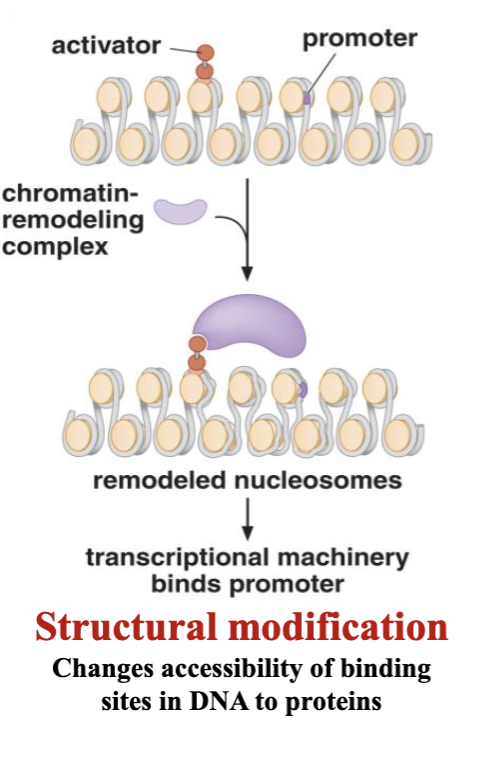
mediator complex is a type of _
coactivator
function of architectural regulators (high mobility group proteins)
high mobility group proteins that help bend DNA to move enhancer closer to promotor
_ mediates the silencing of many genes
microRNAs
receptor can be repressed by binding to _ to turn off transcription
lncRNA (long noncoding rna)
_ is a technique used to silence posttranscriptional genes and turn them off
RNA interference
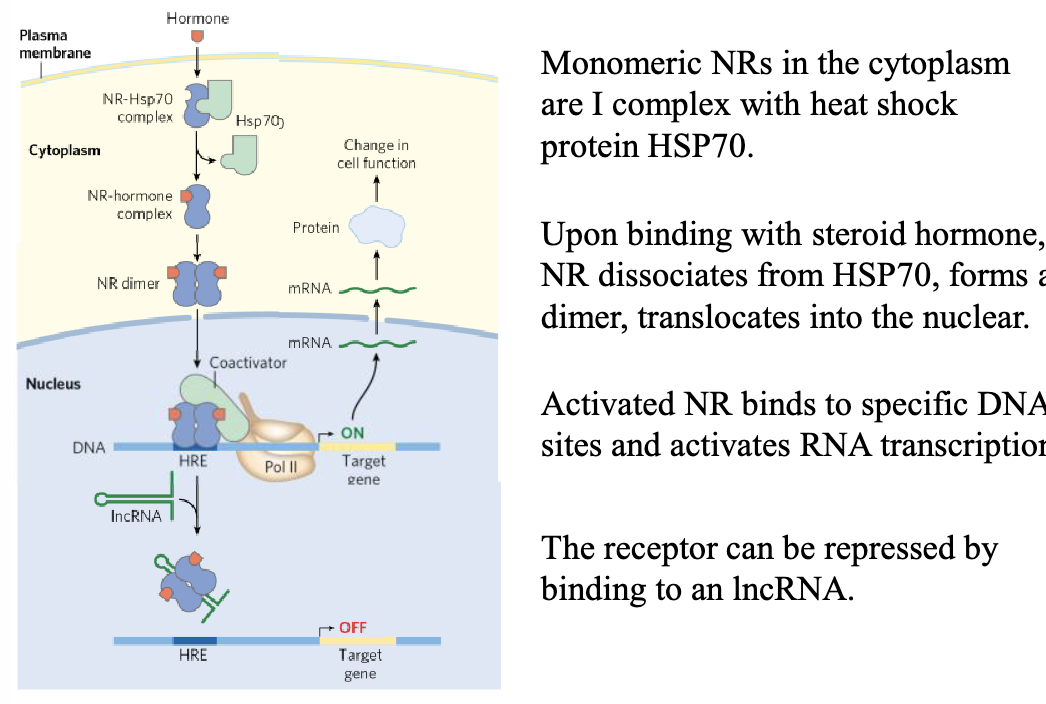
outline gene expression regulated by steroid hormone (nuclear) receptor
nuclear receptors have heat shock protein
when steroid hormone binds to receptor, it dissociates from heat shock protein → dimer
activated receptor binds to DNA site → transcription to turn on gene
binding to long noncoding RNA can repress transcription