Theme 1 - Microeconomics
1/144
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
145 Terms
Model
simplified representation of reality to provide insight into economic decision
Ceteris parabus
All other things being equal
Demand
The quantity of a good or service that consumers are able and willing to buy at a given price
Law of demand
There is an inverse relationship between the quantity demanded of a good and its own price
Demand is downwards sloping because…
Income effect (price of goods falls, purchasing power of income increases)
Substitution effect (price of goods falls, consumers switch away from expensive substitutes)
Law of diminishing marginal utility (each extra unit provides less satisfaction than the prior one)
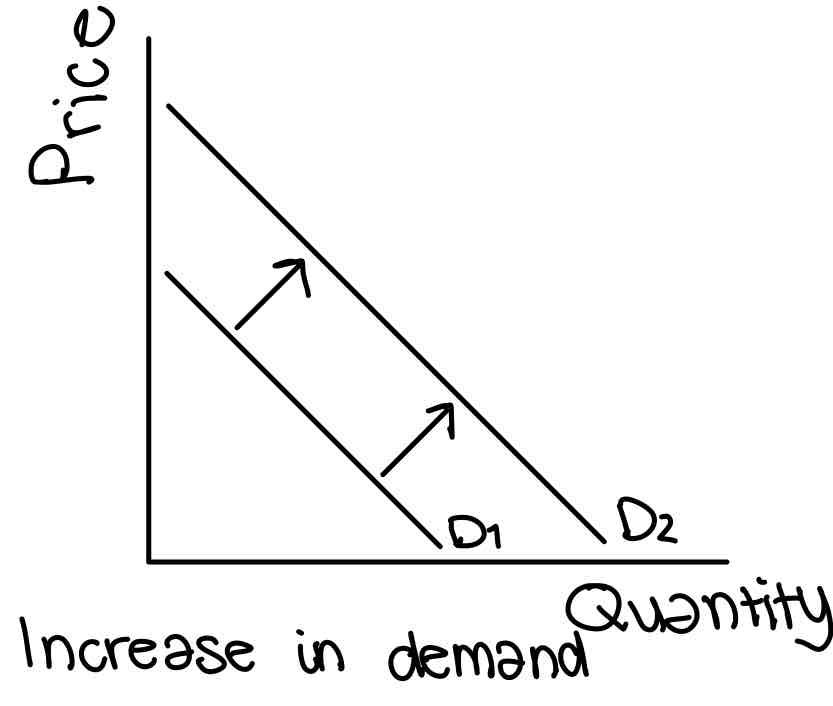
Normal good
As income rises quantity demanded also rises
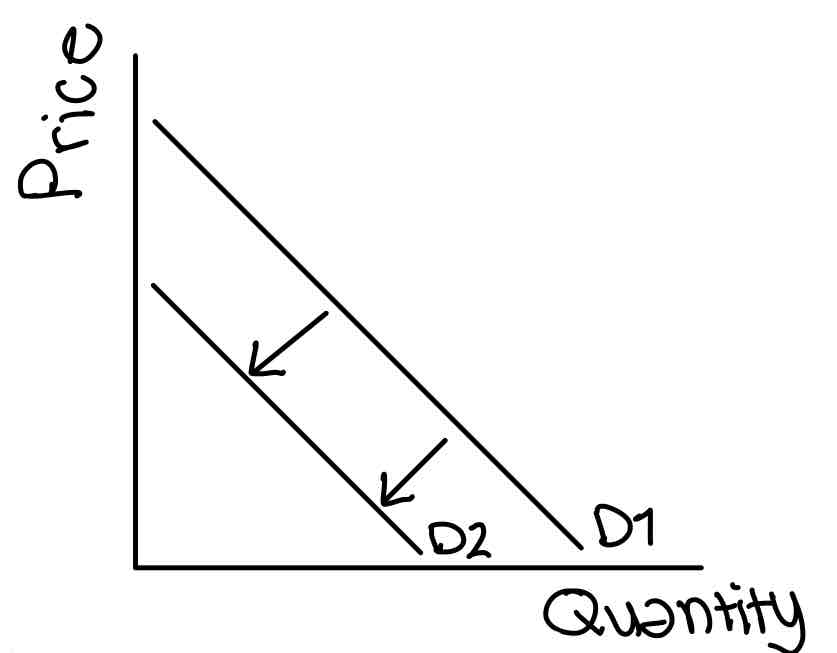
Inferior good
As income rises quantity demanded falls
Complementary goods
Good that is consumed with another good as they’re joint in demand
Substitute good
Good that is consumed instead of another good as they’re competitive in demand
The law of supply
The quantity demanded of a good or service that a producer is willing and able to supply at a given price level
The supply curve is upward sloping because…
Higher prices and supply expansion (rise in the market price brings expansion of supply-producers responding to profit motive)
Lower prices and supply contraction (if market prices fall, we expect a contradiction of supply and less incentive to produce at lower prices)
Joint supply
Increase or decrease in the supply of one good leads to an increase or decrease in supply of a by-product
Competitive supply
The same resources could be switched between the production of different goods
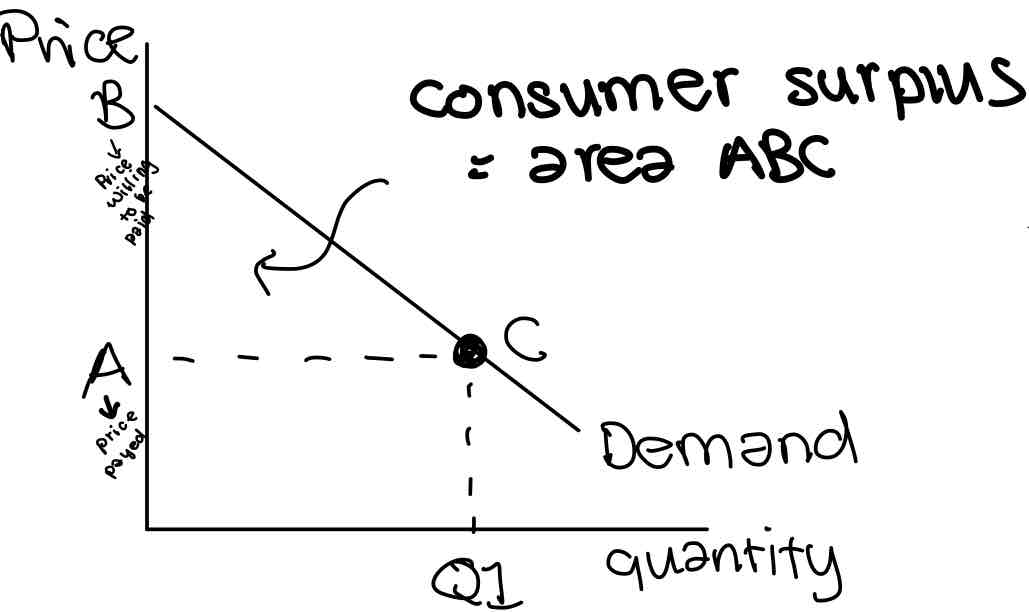
Consumer surplus
Total difference between the total amount that consumers are willing and able to pay for a good or service and the total amount they actually pay
Effective demand
Quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to buy at a given period of time
Effective supply
Quantity of a good or service that producers are able and willing to sell at a given price
Disposable income
Income left over after taxes and benefits are deducted
Discretionary income
Income left over after taxes, benefits and essential bills have been deducted
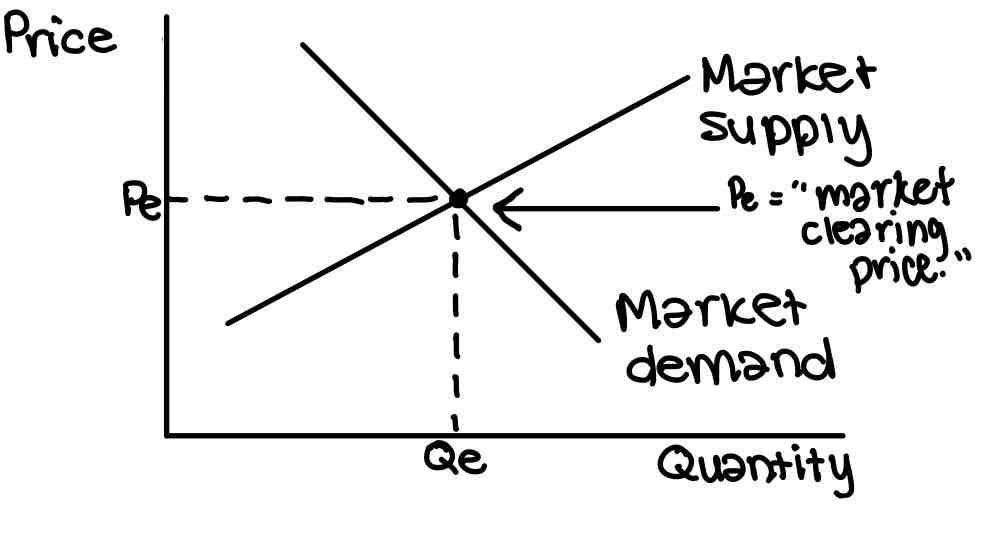
Equilibrium
State of balance met between demand and supply
Total revenue =
Market price x quantity sold
Price mechanism
The way price responds to a change in demand or supply for a product or factor input so that a new equilibrium position is reached in a market
Signalling
Changes in prices provides information to producers and consumers about changes in market conditions
Incentives
Changes in prices act as an incentive to producers to change their output levels and improve their profits
Rationing
Shortage of a product, prices will rise and deter customers from buying the product
Free market economy
Resources are owned by private individuals and resources are allocated by the price mechanism
Command economy
Economy where resources are owned and allocated by the government
Mixed economy
Resources are owned by the government and private individuals. Resources are allocated by government orders and the price mechanism.
Free market economy example
Hong Kong
Mixed economy example
France
Command economy example
North Korea
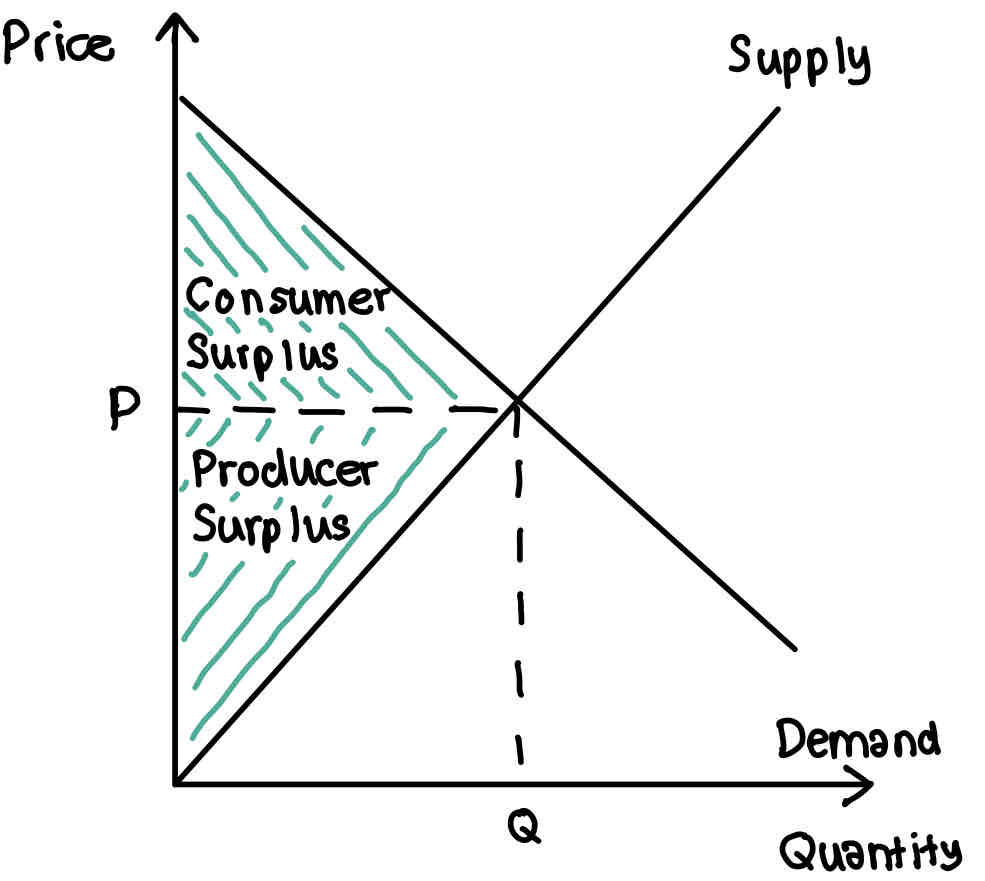
Producer surplus
Total amount that a producer profits from producing and selling a quantity of a good at the market price
Advantages of Free market economy
Efficiency (greater competitiveness resulting in allocative efficiency)
Choice (firms producer whatever consumer are prepared to buy)
Innovations (firms produce new goods and improve products to get ahead of competitors)
Disadvantages of free market economy
Inequality (people who become wealthier ad people who become poor)
Monopoly power (firms may have more as they’re higher in the market so they charge higher prices)
Too high demerit goods (high levels of cigarettes, gambling and alcohol)
Non-rivalry
Persons use of the good will not reduce the amount available for others
Non-excludable
Once good is provided, no one can be excluded from using it
Division of labor
where the production process is broken down into a sequence of stages with specific workers assigned to different tasks
Advantages of division of labour
Workers become specialists at their task
Workers don’t waste time moving between tasks
Firms are more efficient and profitable
Disadvantages of diving of labour
Repetitive work reduces productivity
People move to less boring jobs so theres higher training costs.
Some workers receive little training and are unable to find alternative jobs
Occupational immobility
No skills to move into a new job
Structural unemployment
In a job with a specific skill but it closes down leading to struggles to get a job as they don’t have the skills
Specialisation
Country’s/businesses decide to concentrate on a particular product or task
Advantages of specialisation
High labour productivity and business profits
Specialisation creates surplus output that can be traded internationally
Lower prices give consumer great real purchasing power
Disadvantages of specialisation
World prices for a product might fall leading to declining revenues
Risk of over-specialising and structural unemployment
Might lead to over-extraction of a country’s natural resources
4 functions of money
Unit of account
Store of value
Medium of exchange
Standard of different payment
Unit of account
A nominal unit of measure used to value/cost products, assets, debts, incomes and spending
Store of value
An asset that holds value over time
Medium of exchange
Money is any asset widely acceptable as medium of exchange. It facilitates transactions between buyer and seller
Standard of different payment
Accepted way in each market to settle debt
Digital money
Any means of payment that exists purely in electronic form
Digital money is more popular because…
Convenience
Globalisation
Security
COVID-19
Elasticity
Measures how much one variable responds to changes in another variable
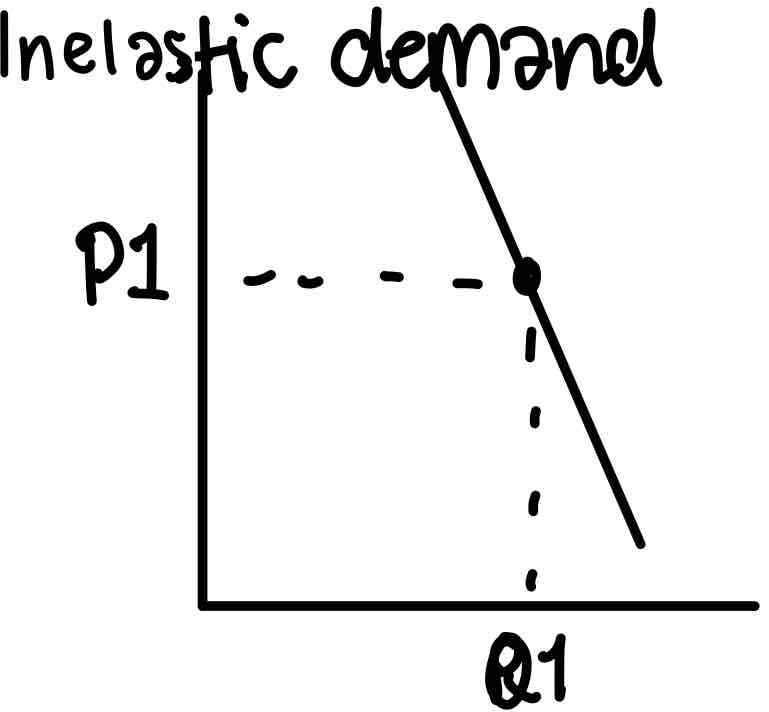
Inelastic demand
Quantity demanded is not very responsive to a change in price
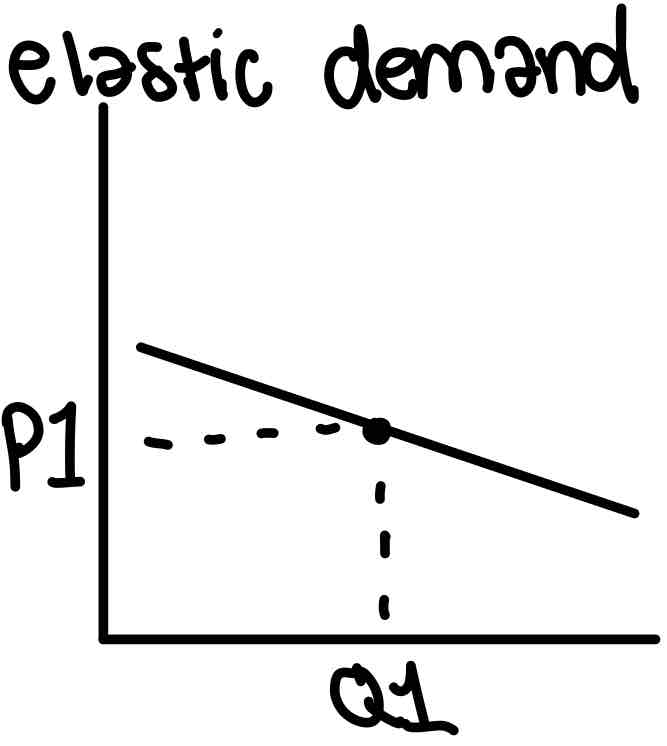
Elastic demand
Quantity demanded is very responsive to a change in price
Determinants of price elasticity of demand
H - habits forming, brand loyalty
I - income/expenditure
T - time the buyer has
S - substitutes for this good
PED =
% change in QD / % change in P
Income elasticity of demand
the responsiveness of quantity demanded due to a change in the real income
Elasticity value
1+
Inelasticity value
More than 0, less than 1
Cross elasticity of demand
Responsiveness of the quantity demanded for one good due to a change in the price of another
XED =
% change in QD (good A) / % change in P (good B)
Substitutes carry a positive/negative XED?
POSITIVE, price of B goes up so demand for A will go up
Complements carry a positive/negative XED?
NEGATIVE, price of B goes up, demand for A goes down
When XED=0
There is no relationship between the goods
PES =
% change in QS / % change in P
PES is always positive/negative?
Positive
Short-run PES
Period of time where at least one factor of production is fixed. Technology is also fixed
Long-run PES
Period of time where all factors of production can be varied. Technology is fixed.
Production lag (PSSST)
Longer production lag so more price inelastic
Stocks (PSSST)
Larger stocks so more price elastic
Spare capacity (PSSST)
Large spare capacity so more price inelastic
Sustainability of factors of production (PSSST)
More sustainability means more price elastic
Time (PSST)
Short run=price inelastic, long run=price elastic
PES is important because…
Opportunity to make sales if demand in a market rices
Quickly move resources out of a market id demand drops
Affects decision whether to buy or rent equipment and what type of contracts to offer
Bounded rationality
Idea that cognitive, decision-making capacity of humans cannot be fully rational because of the number of limits we face
Limits faced when being rational
information failure - may not be enough information, or its unreliable, or not all possibilities/consequences have been considered
The amount of time that we have to make our decisions
The limits of the humans brain to process every piece of information and consider every possibility
Market failure
Markets failing to allocate resources efficiently or a situation where the free market mechanism doesn’t lead to a socially optimal allocation of resources
Evidence of market failure
the free market fails to produce a desirable good or service
Persistent shortages or surpluses
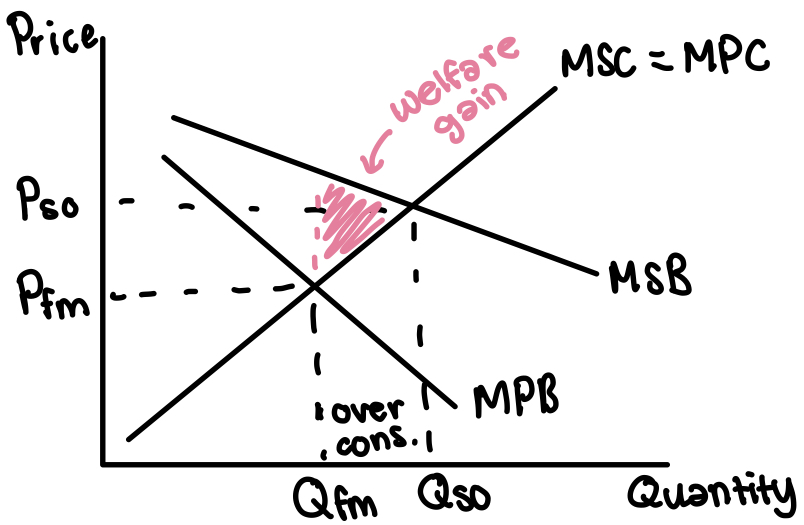
Over consumption/production compared to the socially optimal level
Under consumption/production compared to the socially optimal level
Inequitable allocation of resources
Reasons fro market failure
Negative externalities - factory pollution
Positive externalities - goods and services under consumed
Over consumption/production of de-merit goods
Under consumption/production of merit goods
Information failures - causing people to make suboptimal choices
Failing to provide sufficient quantity of public goods
Monopoly leads to economic efficiency
Immobility of factor of inputs - stops labour market working efficiently
3 types of rationality in market failure
Consideration of the influence of others behaviour : social norms, herd behaviour, peer pressure
Habitual behaviour and inertia : addiction to substances or reluctant to change banks
Consumer weakness at computation / bounded rationality : consumers not being willing or able to make comparisons between princes and different goods on offer
Private goods
Excludable - once its provided it’s possible to stop other individuals from using them
Rivalrous - consumption of the good by on person reduced the amount available for consumption by others
Public goods
Non-excludable - once the good has been provided no one can be prevented from enjoying its benefits
Non-rivalrous - one person consuming the good wont reduce the amount available for another person
Quasi-public goods
Mix of public and private (a playground, congested roads, toll bridge)
Free rider problem
Private firms cannot force consumers to pay for suing public goods due to non-excludability. So they wont make profit from them so the free-market wont provide public goods leading to market failure.
Social cost =
Private cost + external cost (negative externality)
Social benefit =
Private benefit + external benefit (positive externality)
Externalities
Third party or spill-over effects arising from the production or consumption of a good or service.
Third party
An individual / entity not involved in an economic transaction but is affected y the activity of buyer / seller
Negative externality of…
Production
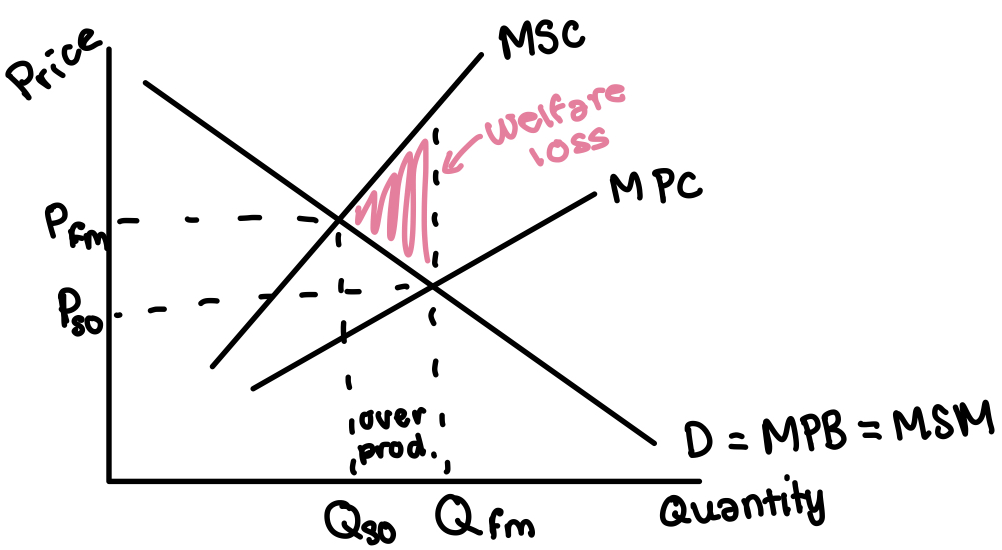
Positive externality of…
Consumption
Incidence of tax
The way in which the burden of paying a sales tax is divided between buyers and sellers
Indirect tax
A tax on expenditure on goods and services
Burden tax
Measures economic effect of the tax measured by the difference between real income or utilities after imposing the tax
2 types of indirect tax
Specific per unit tax
Ad valorem tax (percentage)
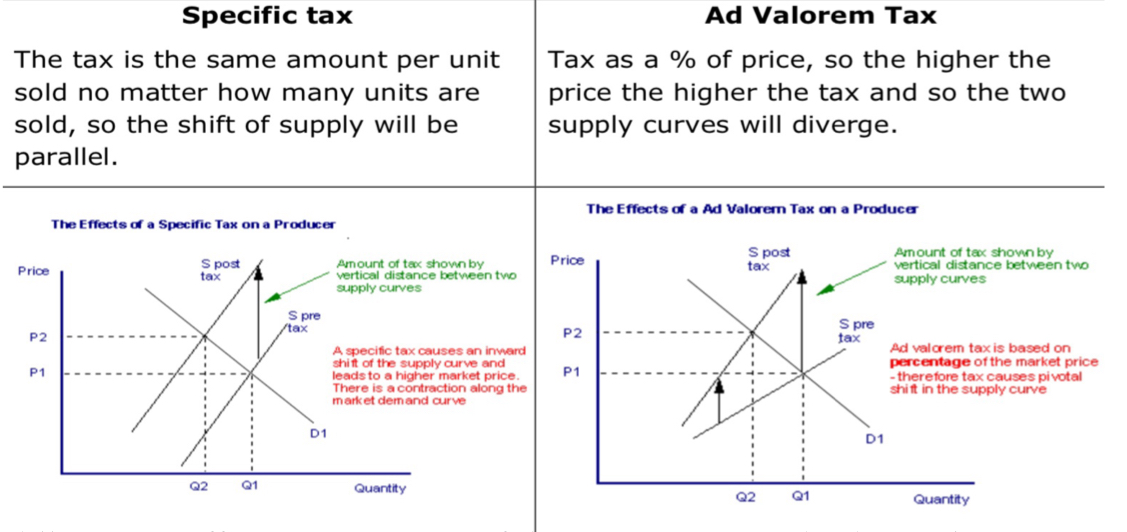
specific tax
The tax is the same amount per unit sold no matter how many units are sold so the sift of supply is parallel
Ad valorem tax
Tax is a % of the price so the high the price the higher the tax so the two supply curves diverge
Allocative efficiency
A state of the economy in which production is aligned with the preferences of consumers and producers
Productive efficiency
The ability of a firm to produce goods or services at the lowest possible cost, given the level of of output and the available technology
Economic efficiency
Every resource is optimally allocated to serve each individual or entity in the best way
Subsidy
A payment from the government to a producer to lower their costs of production and encourage them to produce more
Why do governments intervene by giving subsidies
To encourage economic growth. Subsidies can stimulate economic growth by supporting key inductions. (Market failure correction)