Chapter 9: Continuity of Care
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Chapter 9: Continuity of Care
Role of Community Health Nurses
Maintain continuity of care as clients transition from acute → outpatient settings
Address challenges from chronic disease prevalence (more clients moving in/out of acute care)
Provide support through community agencies for:
Medical needs
Financial needs
Personal/social needs
Use technology to coordinate and maintain continuity of care
Community Partnerships
Essential for improving and maintaining healthy communities
Nurses should facilitate development of partnerships within the community
Partnerships enable collaborative health outcomes
Management of Care
Case Management
Provide discharge information for home or community setting
Client Rights
Advocate for client rights and needs
Ethical Practice
Practice according to nursing code of ethics
Referrals
Identify and connect clients with community resources
Concepts of Management
Act as liaison between client and others
Performance Improvement (Quality Improvement)
Define and participate in quality assurance/performance improvement activities
Health Promotion and Maintenance
Self-Care
Assess client’s ability to manage care at home
Plan care accordingly
Consider self-care needs before developing/revising care plan
Community Partnerships
Essential for improving and maintaining healthy communities
Nurses should facilitate development of partnerships within the community
Partnerships enable collaborative health outcomes
Examples of Partnering Entities
Individuals
Families
Community agencies
Civic organizations
Citizen groups
Educational settings
Political offices
Employment bureaus
Faith-based organizations
Characteristics of Successful Partnerships
Shared power (equal voice among partners)
Shared goals (common objectives)
Integrity (honesty and ethical collaboration)
Flexibility (adaptability to needs/situations)
Negotiation (problem-solving and compromise)
A nurse is creating partnerships to address health needs within the community. The nurse should be aware that which of the following characteristics must exist for partnerships to be successful?
Select all that apply.
a
Being a leading partner with decision-making authority
b
Flexibility among partners when considering new ideas
c
Adherence of partners to ethical principles
d
Varying goals for the different partners
e
Willingness of partners to negotiate roles
b Flexibility among partners when considering new ideas
c Adherence of partners to ethical principles
e Willingness of partners to negotiate roles
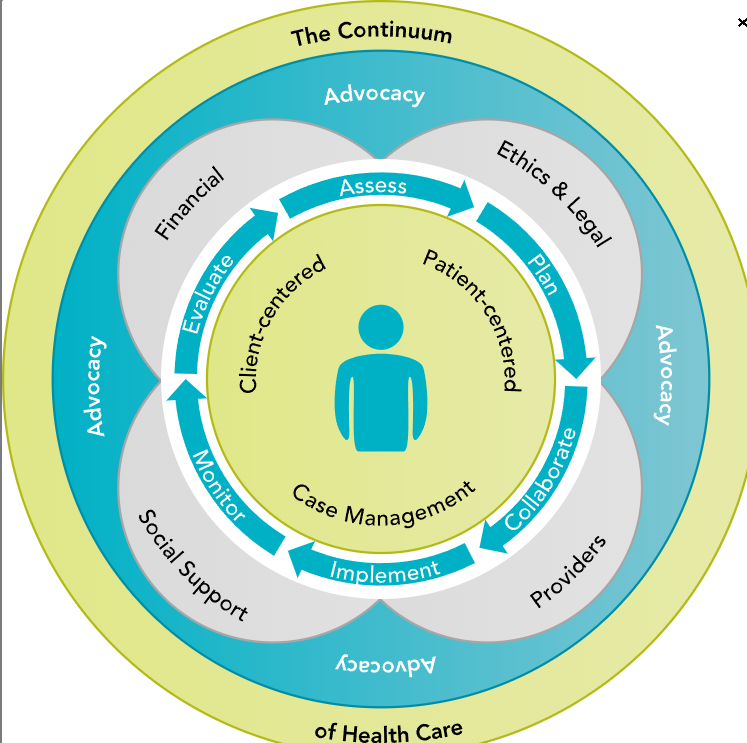
Case Management Continuum of Health Care (Image)
Continuum of Care
Ensures individualized health services are delivered without disruption
Nurse helps client transition smoothly between levels of care
Case Management Process (Patient-Centered)
Assess – evaluate client needs
Plan – develop care strategies
Collaborate – coordinate with providers
Implement – put plan into action
Monitor – track progress and outcomes
Evaluate – review effectiveness and adjust as needed
Support Areas in Continuum
Financial
Social support
Ethics & legal considerations
Advocacy
Community Health Nurse Role
Provide case management services (supervision, individualized care, follow-up)
Make referrals to appropriate resources (medical, social, financial, etc.)
Build ongoing relationships between client and health care providers → improves health outcomes
Consultations
An expert who provides specialized knowledge, advice, services, or information.
Nursing Actions
Initiate necessary consults, or notify provider so they can initiate.
Seek expertise from health care professionals in various disciplines.
Request expert opinions from key community members, agency leaders, and professionals.
Collaborate with specialty nurses (psychiatric, school, gerontological, diabetes management, etc.) and advanced practice nurses (PMHNP, gerontological NP).
Incorporate consultant recommendations into the client’s plan of care or community program planning.
Coordinate recommendations from multiple consultants (providers, APNs, pharmacists, dietitians, therapists, holistic providers) to ensure client safety.
Serve as expert witness in legal proceedings.
Act as consultant for the health care needs of individuals, families, and groups in the community.
Referrals
In acute care are usually based on medical diagnosis or clinical information.
Resources help restore, maintain, or promote health.
Nurse responsibilities:
Link client with appropriate community resources
Know individuals/organizations that can serve as resources
Match assistance to client’s personal beliefs and values
Educate clients about community resources and self-care measures
Health Care Services
Providers
Acute-care settings
Primary care sites
Health departments
Transitional and long-term care facilities
Home care services
Rehabilitation services
Physical therapy services
Occupational therapy services
Pharmacies
Specialty Service Agencies
Support services
Psychological services
Faith community centers
Support groups
Life care planners
Medical equipment providers
Health insurance companies
Meal delivery services
Transportation services
Barriers to the Referral Process
Client
Lack of motivation
Inadequate knowledge about resources
Inadequate understanding of need for referral
Accessibility needs
Priorities
Finances (SDOH)
Cultural factors (SDOH)
Resource
Attitudes of health care personnel
Cost of services (SDOH)
Physical accessibility of resources
Time limitations
Limited expertise with culturally diverse populations (SDOH)
Steps in the Referral Process
Engage in a working relationship with the client
Establish criteria for referral
Explore available resources
Accept client’s decision on chosen resource
Make the referral
Facilitate the referral
Evaluate the outcome
Follow-Up Considerations
Monitor referral completion
Assess whether outcomes were met
Determine if client was satisfied with referral
A nurse developing a community health program is determining barriers to community resource referrals. Sort the examples of barriers into client barriers or resource barriers.
Costs associated with services
Decreased motivation
Inadequate knowledge about resources
Limited number of service providers
Lack of interpreters
Client barrier
Resource barrier
Client barrier
Decreased motivation
Inadequate knowledge about resources
Resource barrier
Costs associated with services
Limited number of service providers
Lack of interpreters
Discharge Planning
Essential part of the continuum of care → anticipates client’s future needs.
Requires ongoing communication among:
Client
Nurse
Providers
Family
Interprofessional team
Goal: enhance client well-being by identifying appropriate options for meeting health care needs.
Begins at admission (not just at discharge).
A case management nurse is initiating referrals for a client as part of discharge planning. Place in order the actions the nurse should plan to take.
Provide information about the client to the referral agencies.
Monitor client satisfaction with the referral.
Identify referrals the client needs.
Review available resources with the client.
1
2
3
4
1 Identify referrals the client needs.
2 Review available resources with the client.
3 Provide information about the client to the referral agencies.
4 Monitor client satisfaction with the referral.
Case Management
Indications/Role
Used in a variety of health care settings to:
Promote interprofessional services & client/family involvement
Decrease costs through improved outcomes
Provide education for health participation
Reduce gaps/errors in care
Apply evidence-based protocols & pathways
Advocate for quality services and client rights
Collaboration
Involves clients, families, community resources, payer sources, and health care professionals
Requires strong communication skills to articulate client needs across systems
Promotes effective care coordination and successful outcomes
Ethical Challenges
Nurses may face dilemmas balancing client needs vs. provider/system decisions
Liability Risks in Case Management
Care Management – mismanagement: incomplete records, inappropriate delegation, no alternative treatments
Referrals – mismanagement: incompetent providers, low-quality/substandard care, poor communication
Experimental Treatments – mismanagement: failure to notify client of experimental nature or make timely recommendations
Confidentiality – mismanagement: HIPAA violations, sharing protected information
Fraud & Abuse – mismanagement: false claims, inaccurate data, billing for unnecessary/substandard care, compensation for referrals/treatments
Nursing Process in Case Management
Guides assessment, planning, implementation, and evaluation of client’s health care
Scope of Role
Coordinates care among providers (nursing staff, rehab, OT/PT, home health, community resources)
Advocates across all aspects of health care system
Acts proactively: balances client needs, prevents complications, and ensures continuity from acute → community-based care
Focus on early discharge planning and smooth transition across settings
Liability Risks in Case Management
Care Management – mismanagement: incomplete records, inappropriate delegation, no alternative treatments
Referrals – mismanagement: incompetent providers, low-quality/substandard care, poor communication
Experimental Treatments – mismanagement: failure to notify client of experimental nature or make timely recommendations
Confidentiality – mismanagement: HIPAA violations, sharing protected information
Fraud & Abuse – mismanagement: false claims, inaccurate data, billing for unnecessary/substandard care, compensation for referrals/treatments
A nurse is working with a client who has systemic lupus erythematosus and recently lost their health insurance. Which of the following actions should the nurse take in the implementation phase of the case management process?
a
Coordinating services to meet the client’s needs
b
Comparing outcomes with original goals
c
Determining the client’s financial constraints
d
Clarifying roles of interprofessional team members
a Coordinating services to meet the client’s needs
Technology and Community Nursing
Advances in technology have changed health care delivery, disrupting old methods and creating new opportunities.
Technology can help with cost control → compare expense vs. potential savings before implementation.
Nurses can use technology to:
Increase awareness and provide education (social media campaigns, surveys, health literature databases)
Collect data for community/public health
Technology increases life expectancy but may also create ethical dilemmas.
Nurses must stay updated on new technologies → affects quality of care and community health outcomes.
Informatics
Combines nursing science + information/communication technology.
Examples:
EHR (Electronic Health Records), EMR (Electronic Medical Records), databases, billing systems
Smartphones, hand-held computers, GIS (Geographic Information Systems), internet tools
Uses:
Support interprofessional meetings (chatrooms, asynchronous discussions)
Alternative delivery methods for client education
Facilitate support groups, peer collaboration, staff training
Telehealth
Delivery of quality health care via technology.
Particularly useful in rural areas → increases access to specialized/skilled nursing care.
Uses include:
Home care services (clients at home, nurses in centralized location)
Must balance telehealth with hands-on care for best outcomes
Agencies use telehealth for electronic health data transmission (ensures confidentiality/security).
Telecommunications support physical, audio, visual data transfer.
Data Types in Telehealth
Physical Data
Blood pressure
Weight
Blood oxygenation
Blood glucose
Heart rate
Temperature
ECG results
Audio Data
Voice conversations
Heart sounds
Lung sounds
Bowel sounds
Visual Data
Images of wounds
Images of surgical incisions
Other Uses for Technology
Outreach/education: ex. public service announcements (e.g., intimate partner violence prevention, resource connection)
Electronic record keeping in public health:
Client records
Document services provided
Maintain financial records
Manage organizational plans
Partnerships with Legislative Bodies
Laws/decisions profoundly affect health outcomes.
Health policy regulates licensing, scope of practice, negligent care, and responsibilities in different settings (e.g., schools, corrections).
Nursing Responsibilities
Stay informed about current policy and laws impacting community & nursing practice.
Advocate for policies that:
Protect public health
Offer solutions to community problems
Communicate with policymakers to present evidence-based solutions to major health problems.
Ensure equitable distribution of resources (SDOH).
Nurses’ Role in Health Policy
Change Agents → Advocate for needed change at the local, state, or federal level.
Lobbyists → Persuade or influence legislators; can be done by individuals or nursing associations.
Coalitions → Facilitate achievement of goals through collaboration between two or more groups.
Public Office → Nurses can serve in public office to advocate for change and influence policy development.
A nurse is reviewing the various roles of a community health nurse. Match each action to the example of the community health nurse function.
Advocate
Consultant
Coalition builder
Lobbyist
Case manager
Counselor
Updating local officials about the need for activities to prevent youth violence
Contributing to policy development for state funding of prenatal programs
Working with a childcare center on handwashing to reduce the spread of communicable diseases
Collaborating with an interprofessional team to provide continuity of care after hospitalization
Bringing together community agencies to implement a community garden
Establishing an interpersonal relationship with a family to enhance their self-care and coping abilities
Updating local officials about the need for activities to prevent youth violence
Advocate
Contributing to policy development for state funding of prenatal programs
Lobbyist
Working with a childcare center on handwashing to reduce the spread of communicable diseases
Consultant
Collaborating with an interprofessional team to provide continuity of care after hospitalization
Case manager
Bringing together community agencies to implement a community garden
Coalition builder
Establishing an interpersonal relationship with a family to enhance their self-care and coping abilities
Counselor