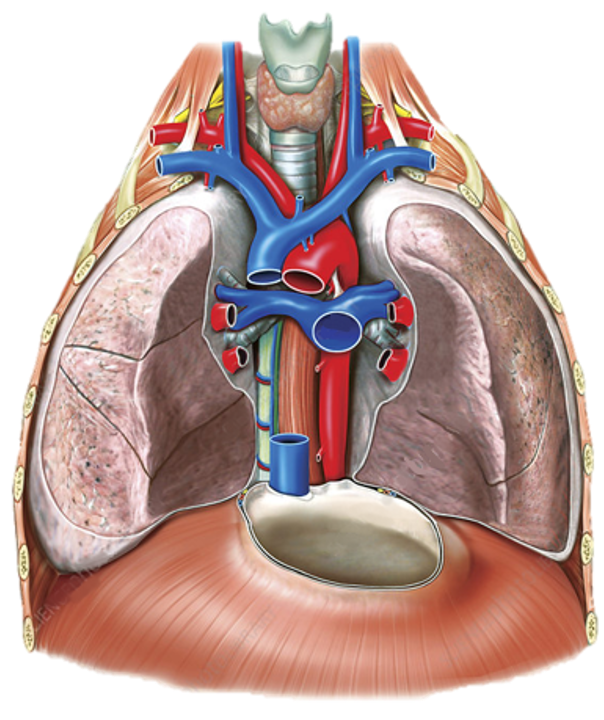
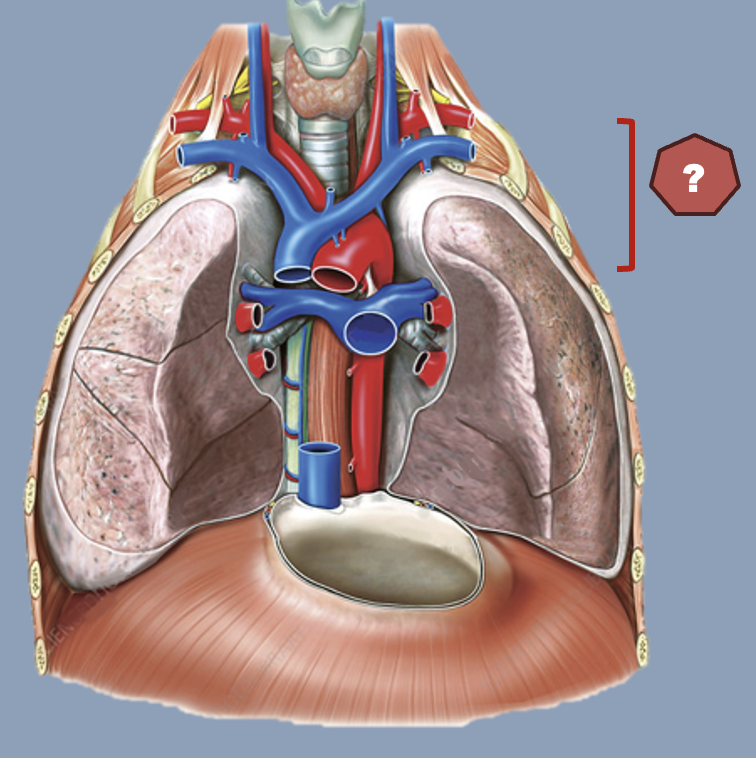
Arterial supply anatomy INCOMPLETE ADD THE LITERAL ARTERIES
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
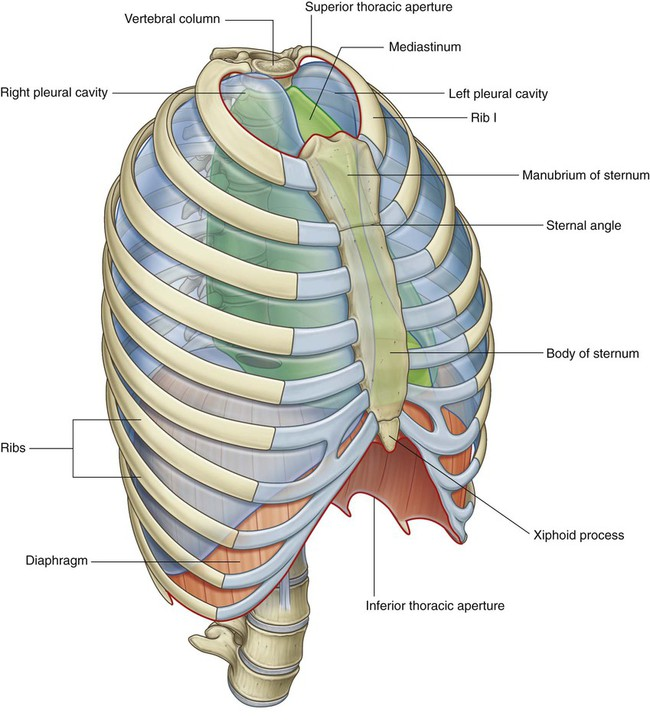
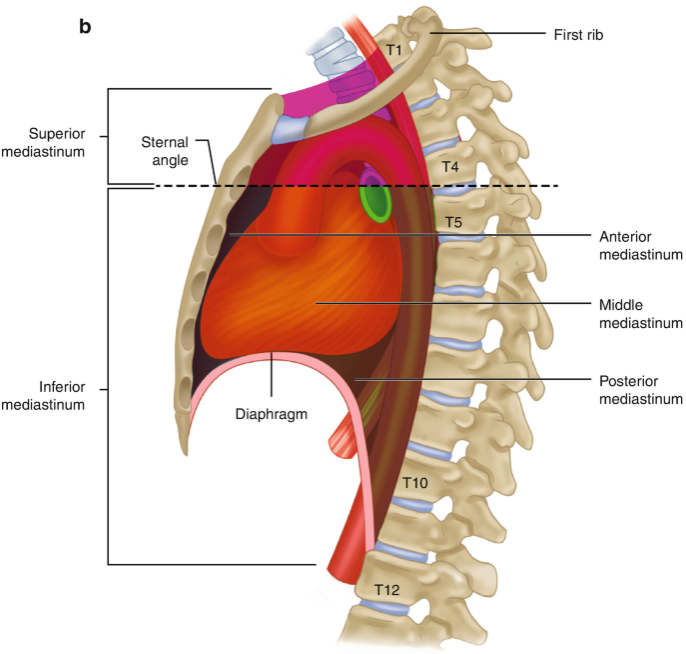
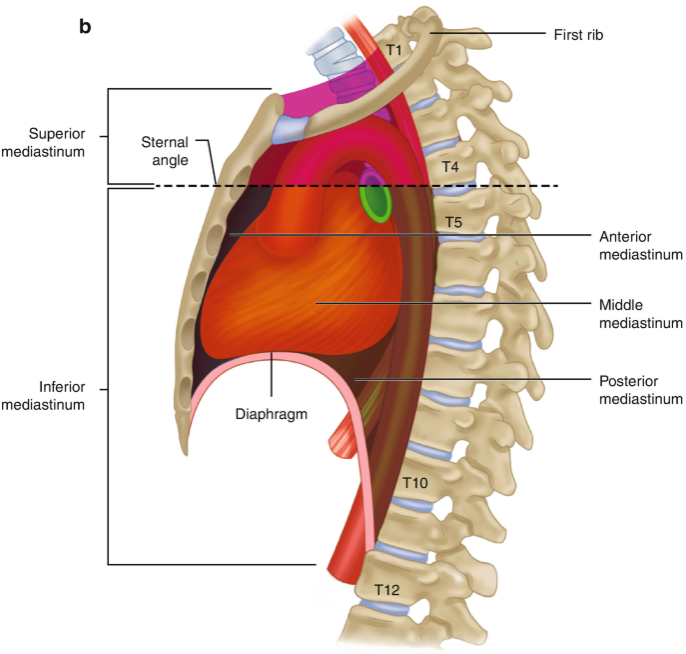
mediastinum
The ‘space’ located between the lungs, bounded anteriorly by the sternum and posteriorly by the vertebral column
divided into superior and inferior
go to gray’s anatomy for students and search “subclavian artery” for good pictures
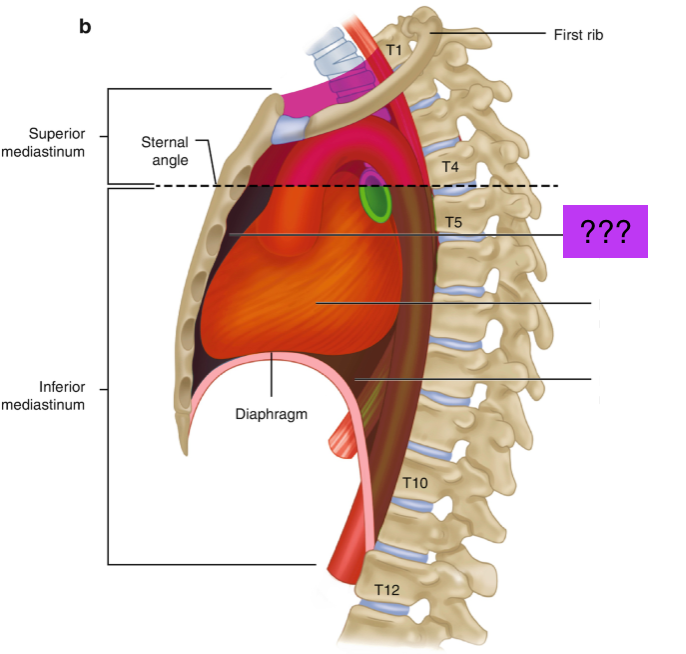
superior mediastinum
boundaries formed by superior thoracic inlet/aperture to transthoracic plane
essentially everything in the thorax above the manubriosternal joint (T4/T5 vertebral level)
contains great vessels of the heart

superior thoracic inlet/aperture
forms upper border of superior mediastinum
upper opening of the thoracic cavity through which major vessels emerge:
Aortic arch and its branches
Superior vena cava (SVC)
Brachiocephalic veins
Trachea and esophagus
transverse thoracic plane
forms lower border of superior mediastinum and upper border of inferior mediastinum
line from the sternal angle anteriorly → IV disk between T4 and T5 posteriorly
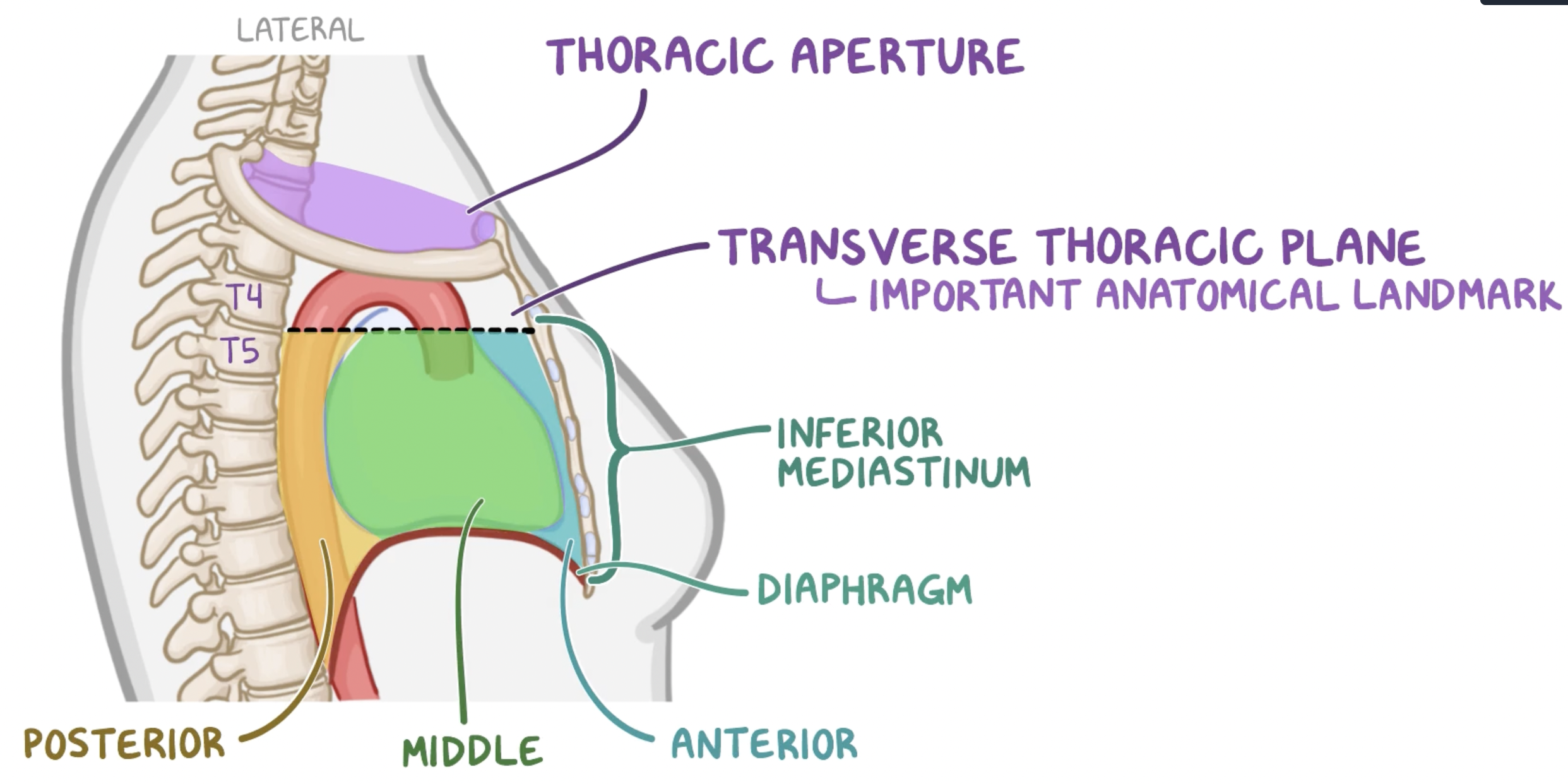
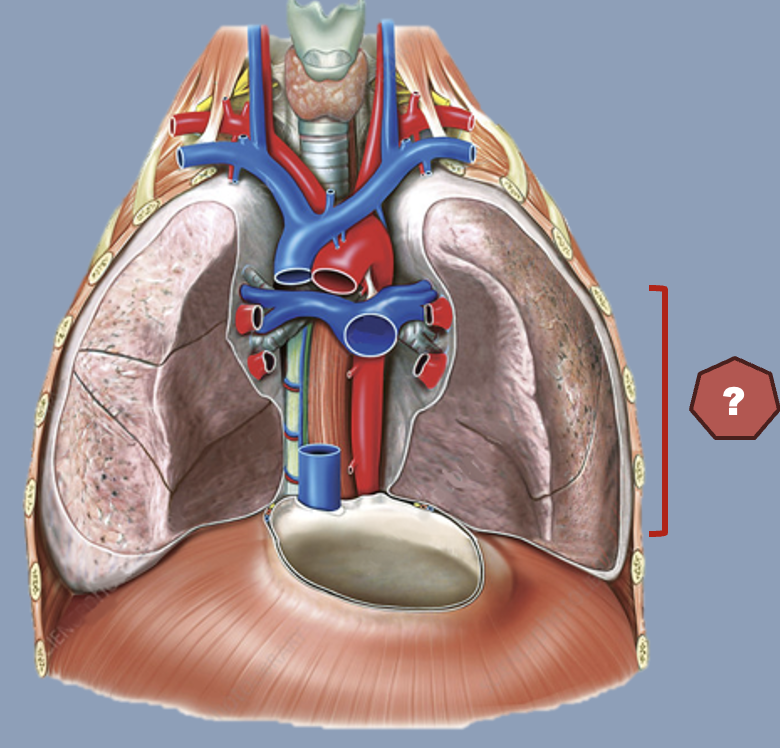
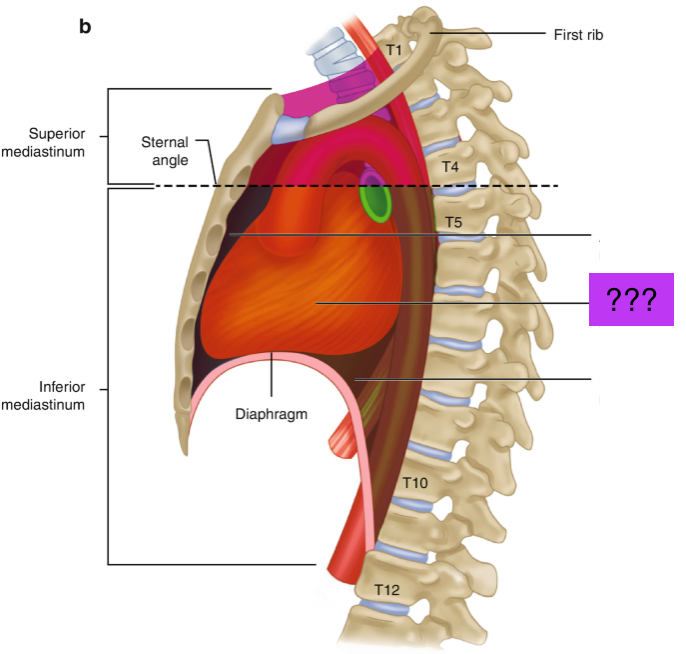
inferior mediastinum
Extends from transverse thoracic plane to diaphragm
divided into anterior, middle and posterior

anterior mediastinum
Prevascular compartment
Potential space with thymus, lymph nodes, fat and nerves
middle mediastinum
Visceral compartment
Contains the heart, pericardium and origins of great vessels
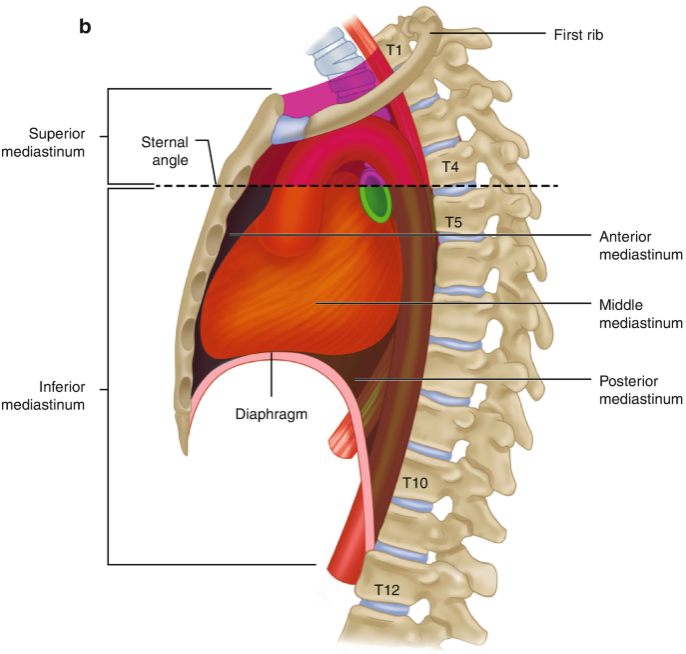
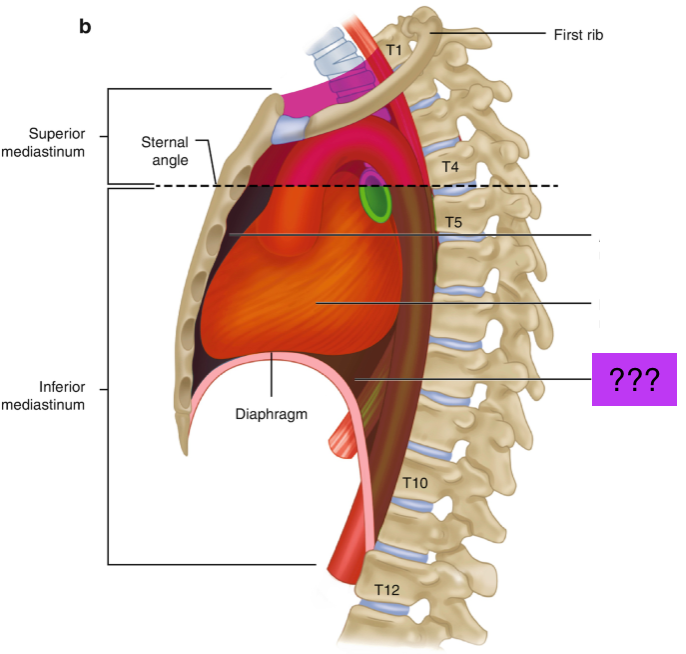
posterior mediastinum
Posterior to pericardial sac and anterior to mid/low thoracic vertebrae
Contains esophagus, descending aorta and thoracic duct
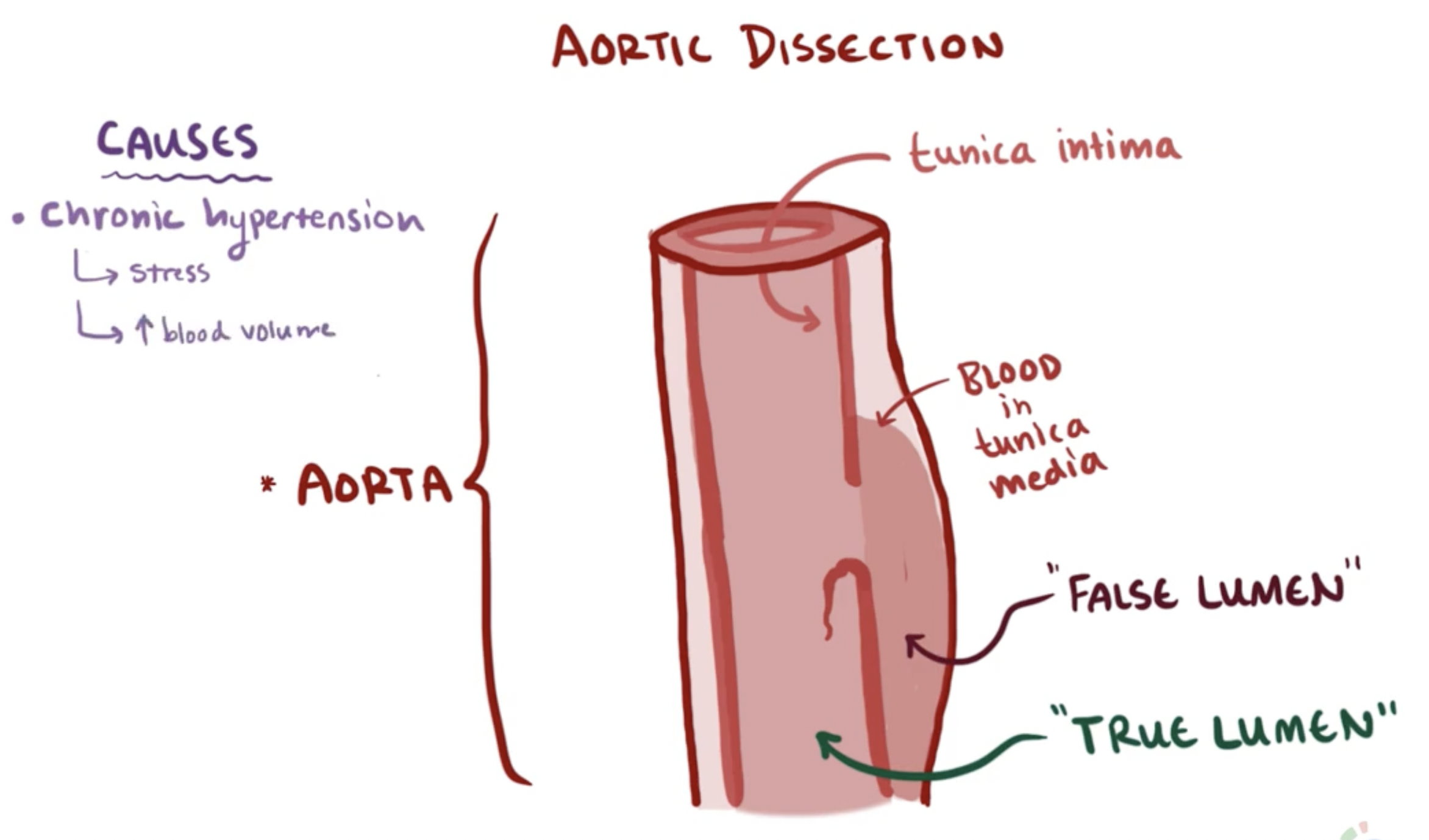
aortic dissection (definition, pain, consequences)
tear in the tunica intima (innermost layer) creating a false lumen/second passage for blood to flow through
centralised, sharp chest pain radiating to their back
Consequences:
organ ischemia/infarction:
If blood flow in the false lumen diverts flow away from branch vessels (e.g., renal arteries → kidney ischemia)
Cardiac tamponade:
If the dissection is in the ascending aorta or aortic arch (inside the pericardial sac)
→ blood leaks into the pericardial cavity, accumulating around and compressing the heart
→ heart can't pump properly
→ death
Hemothorax:
If the aorta ruptures into the thoracic cavity
→ rapid internal bleeding
→ sudden death
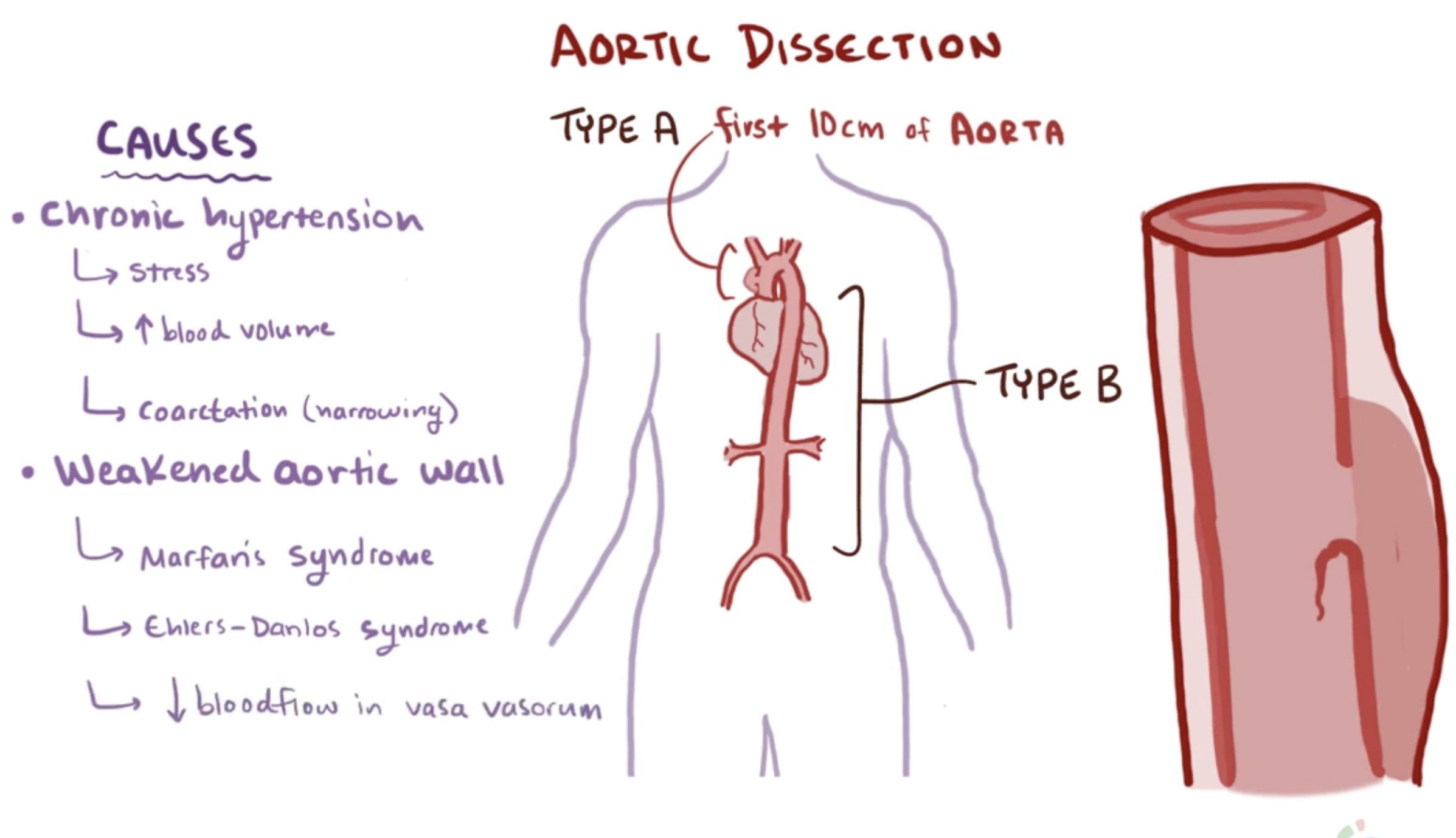
aortic dissection predisposing factors
Chronic hypertension (2/3rds all cases)
arteries in tunica adventitia become artheroslcerotic
→ tunica media + intima integrity at risk
Connective tissue disease (e.g. Marfan syn)
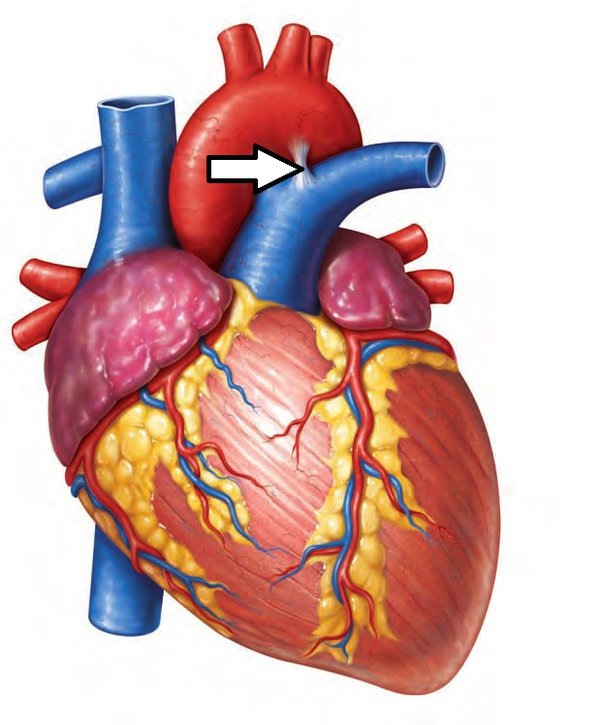
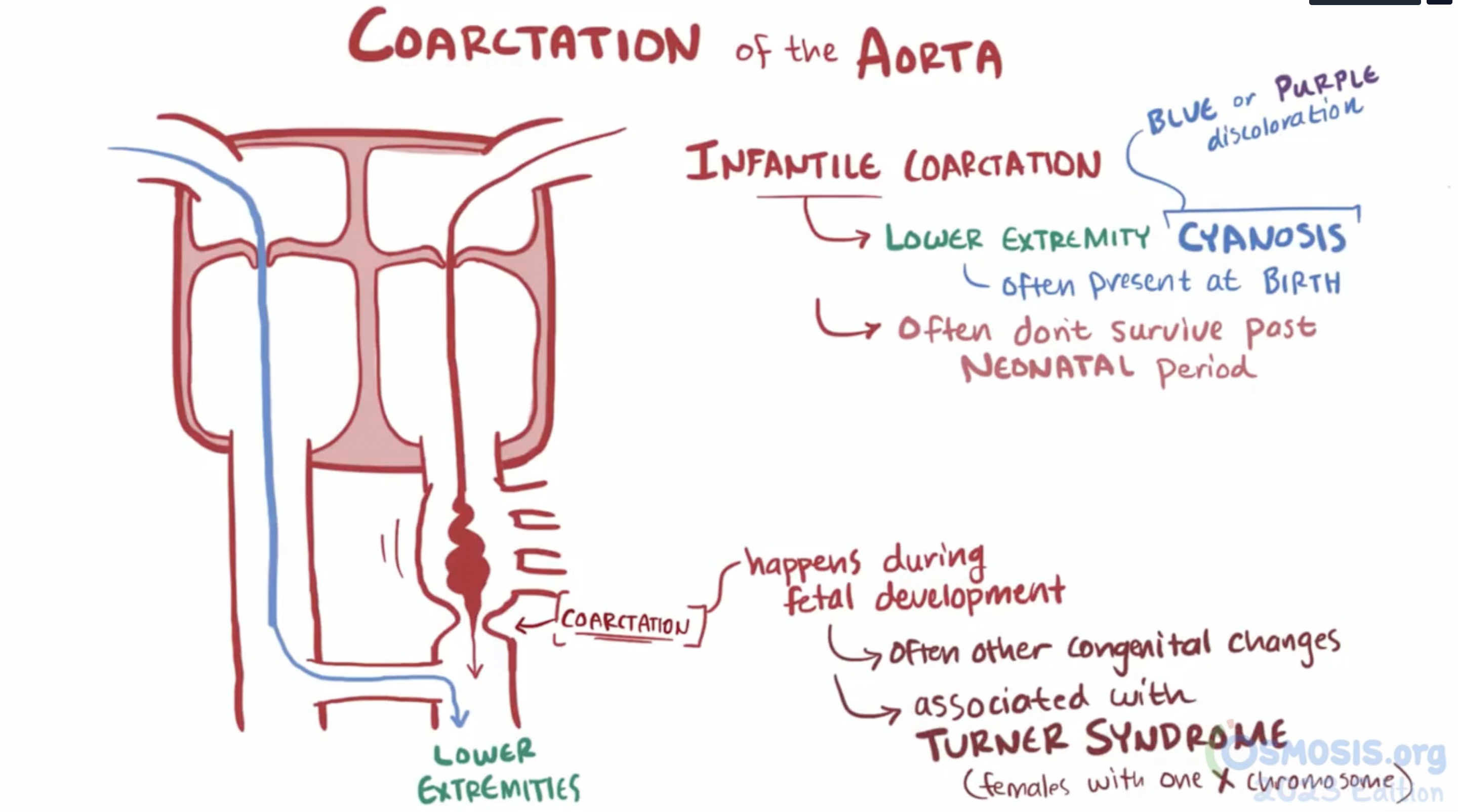
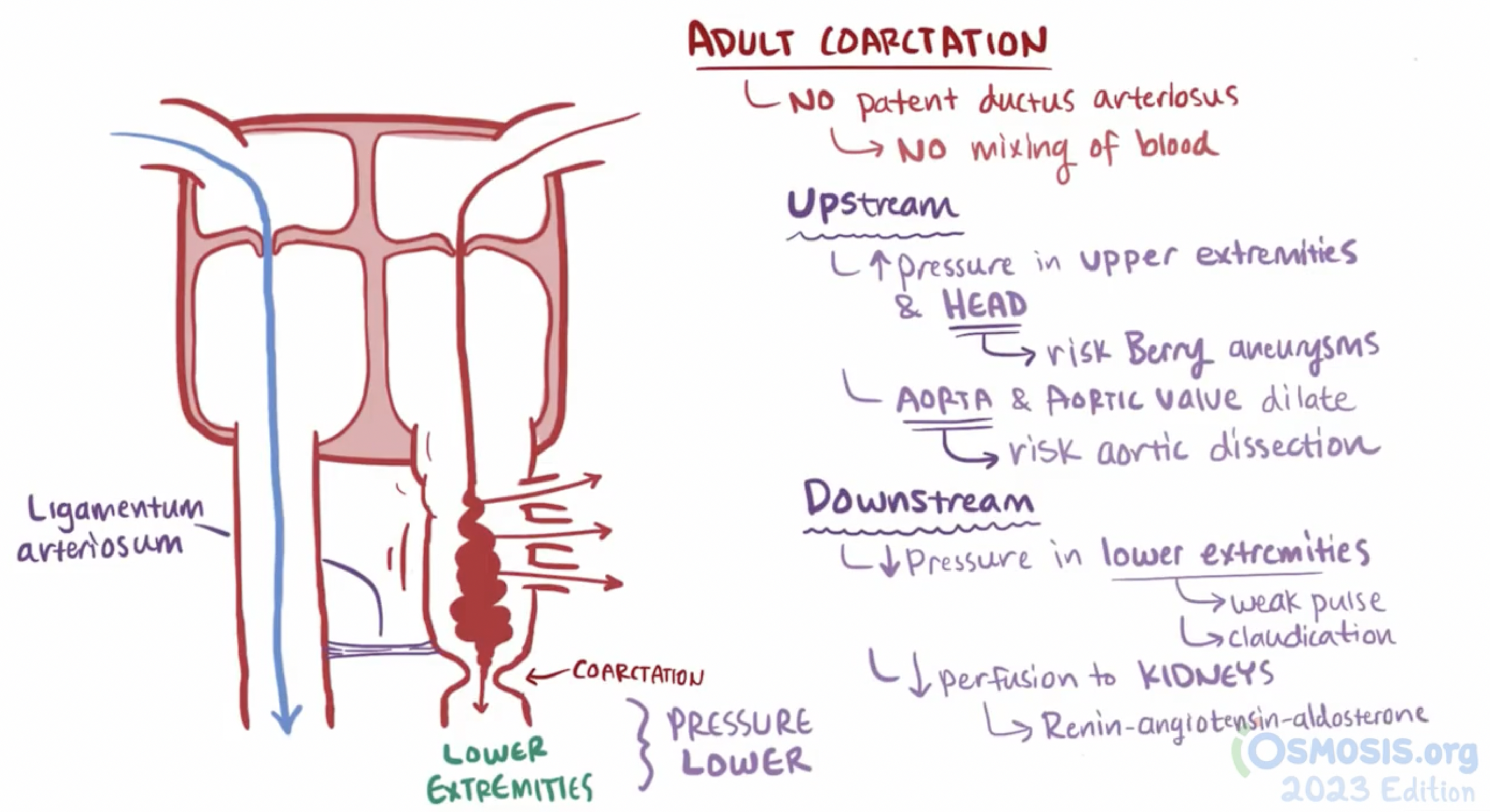
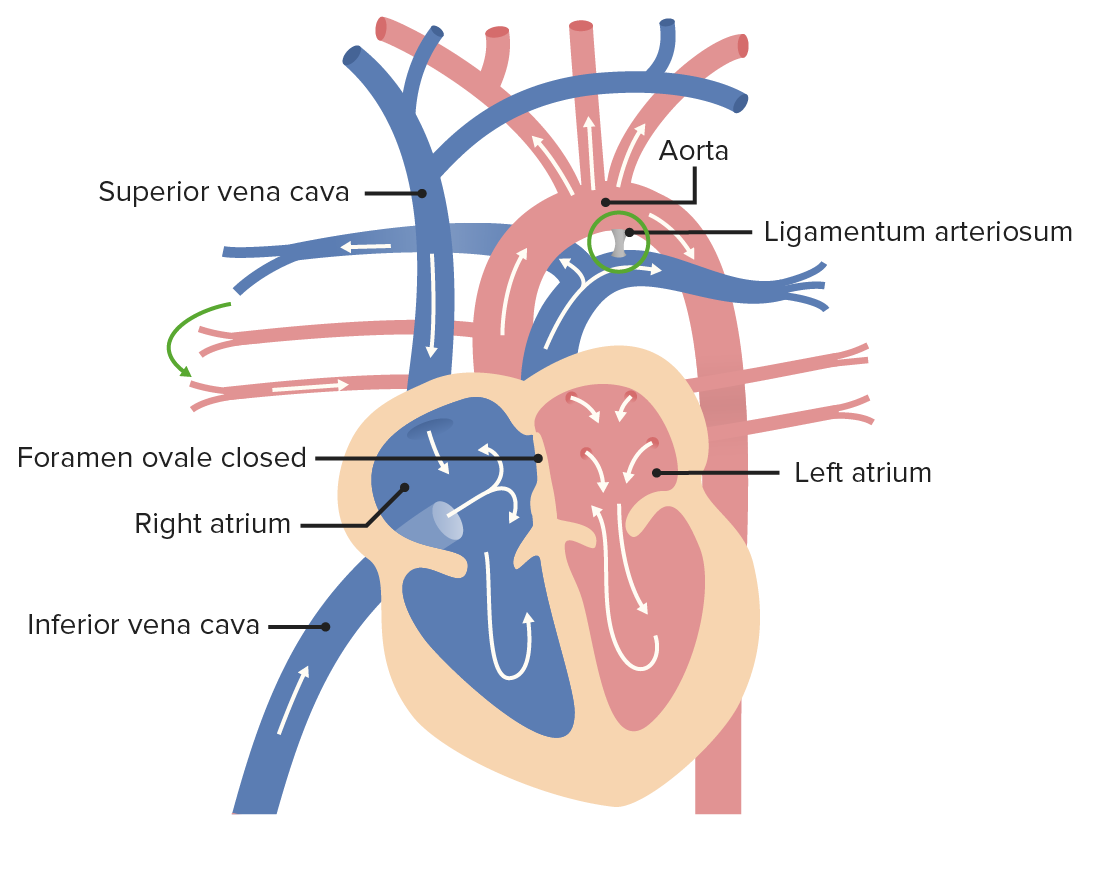
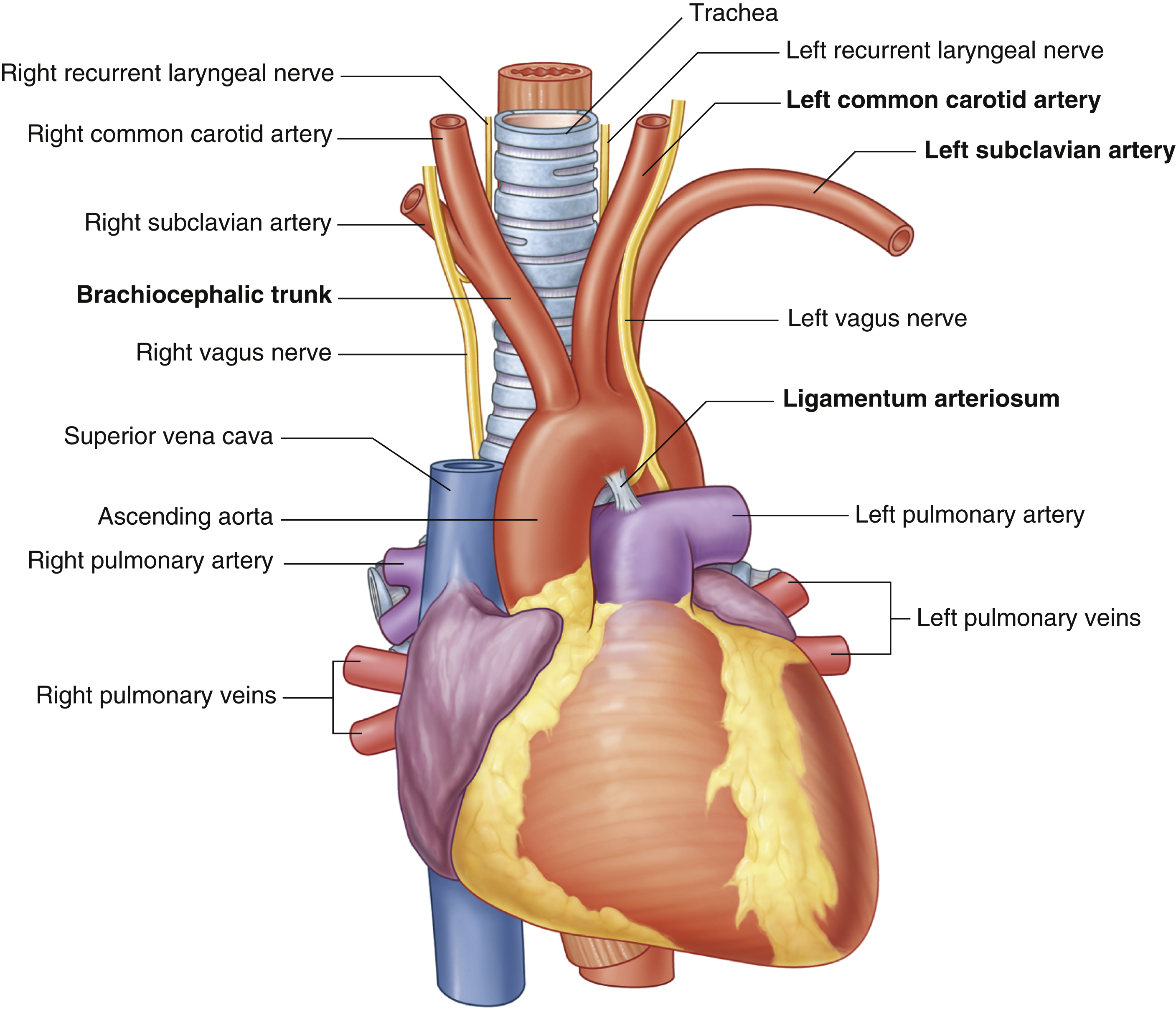
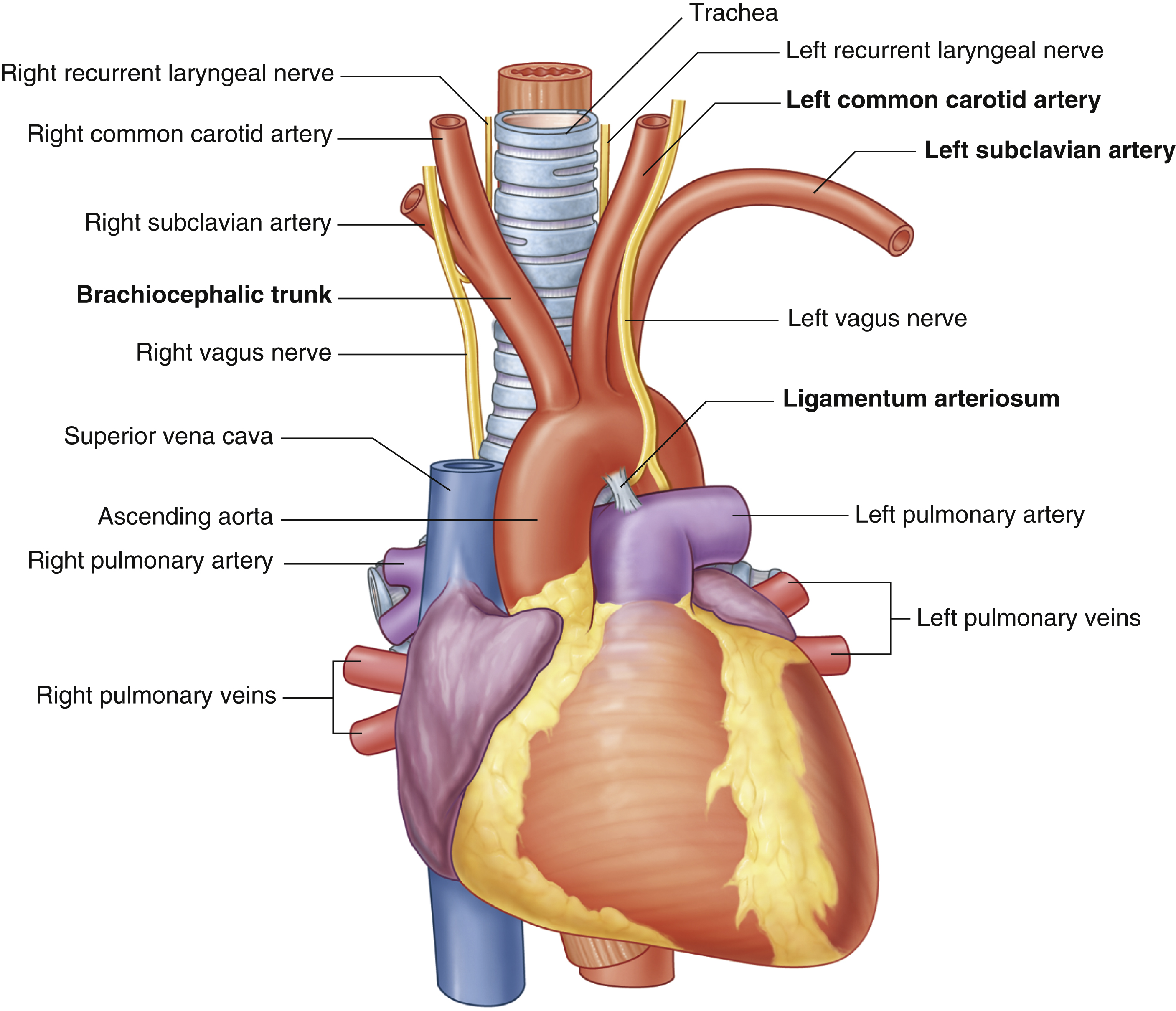
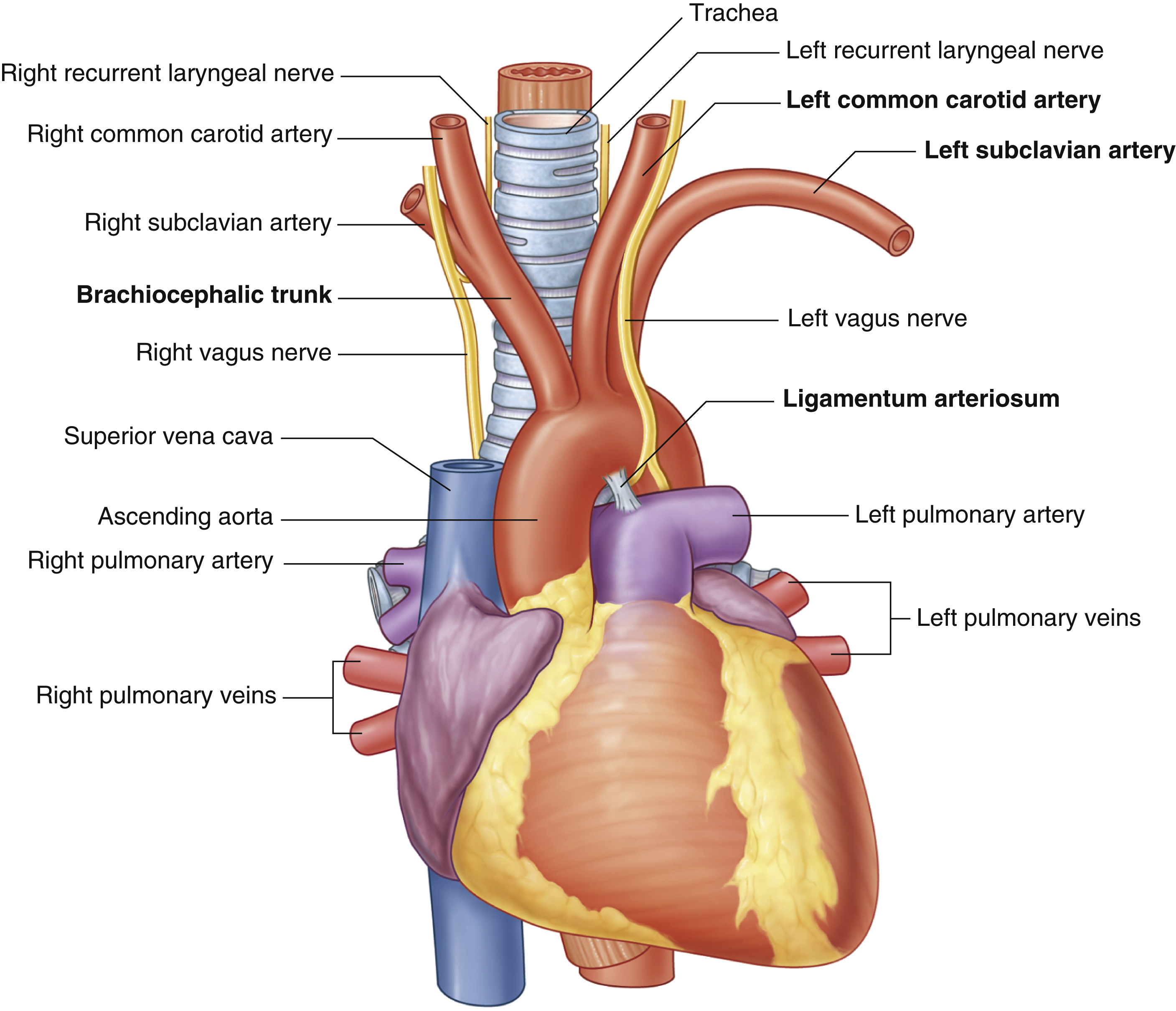
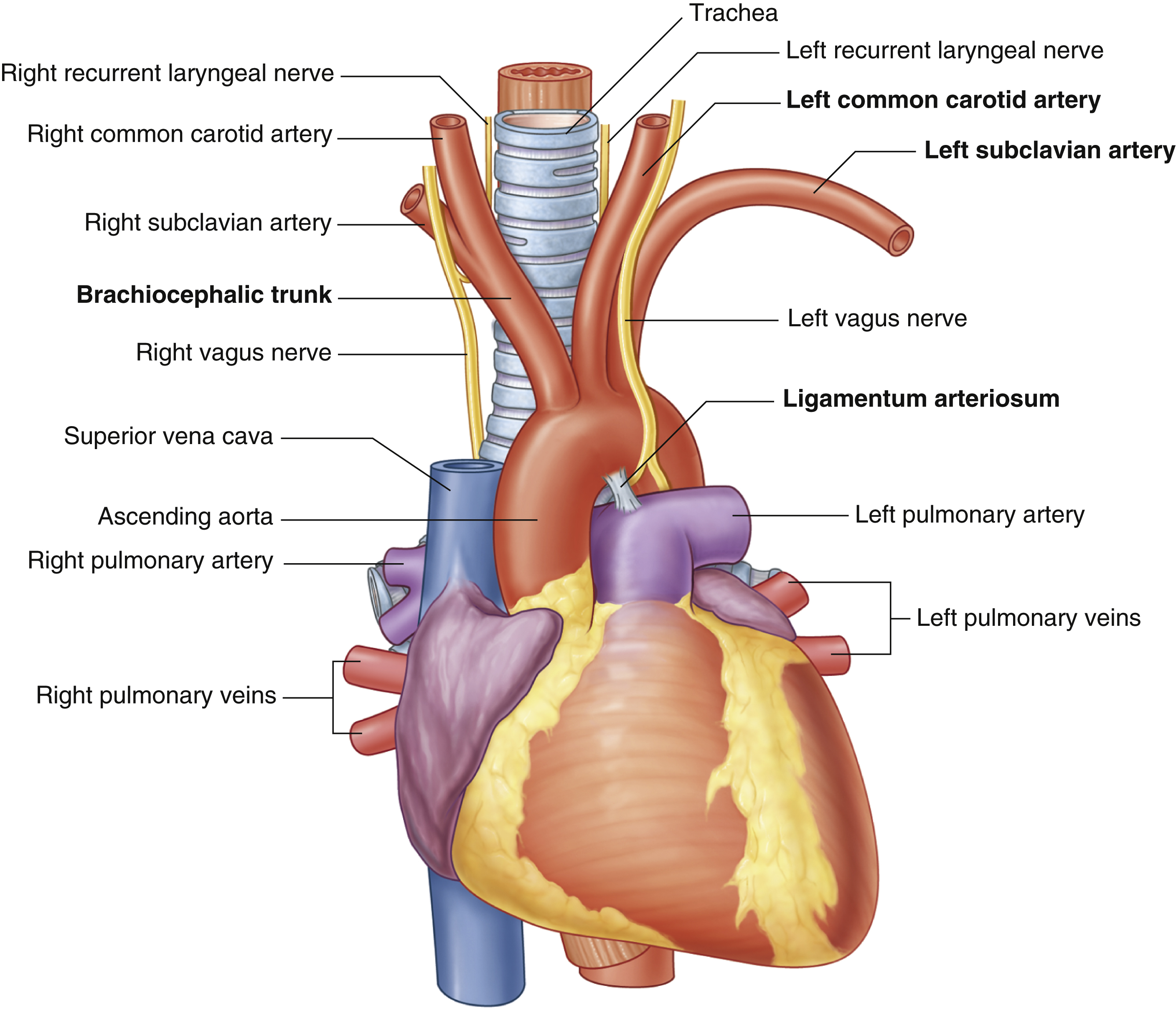
ligamentum arteriosum
remnant of the fetal ductus arteriosus, a vessel connecting the pulmonary trunk to the aorta in the developing fetus
thickening of tunica media, distal to ligamentum arteriosum leads to aortic coarction

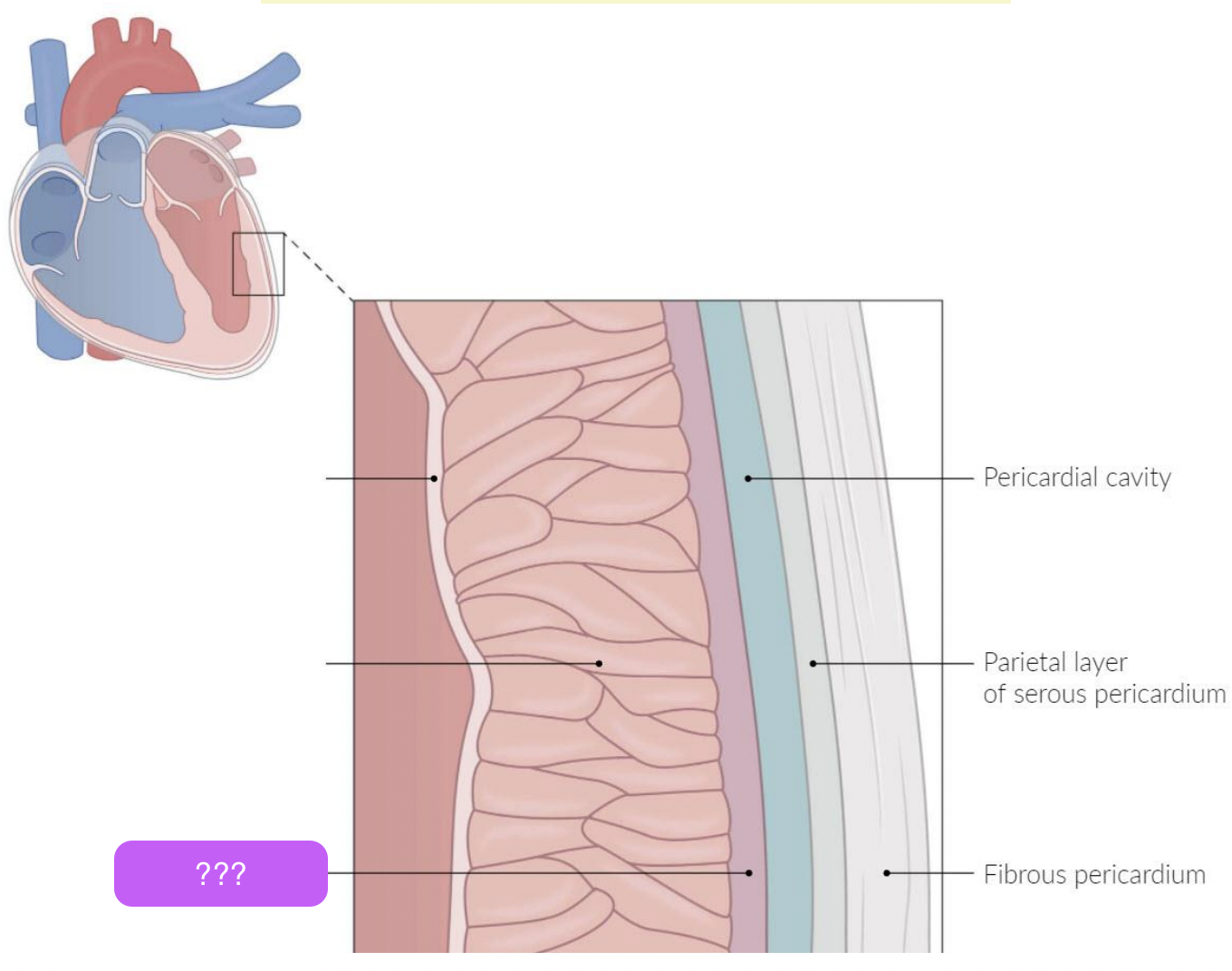
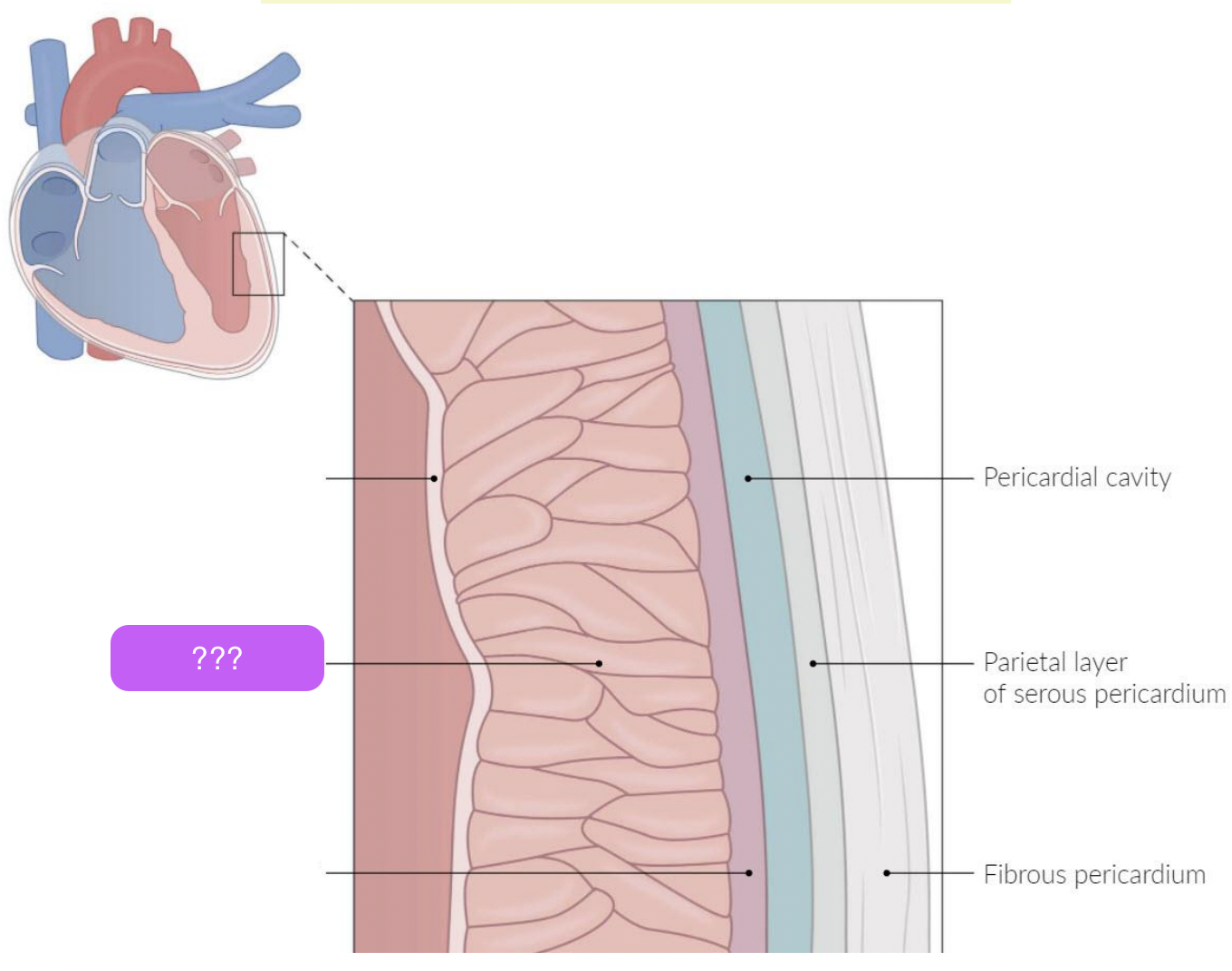
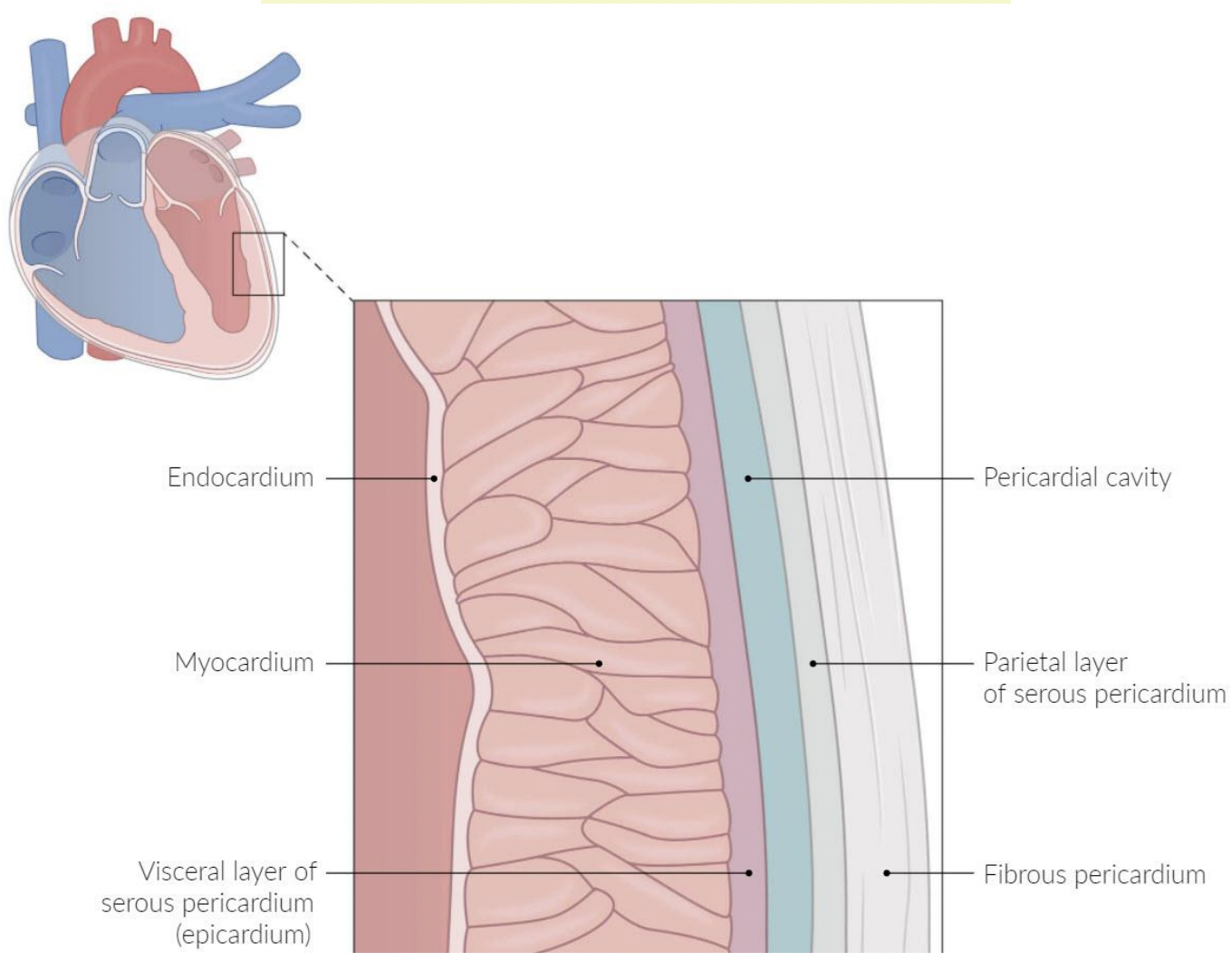
pericardium
A fluid-filled membranous sac that encloses the heart and roots of the great vessels
protects the heart & provides lubrication to reduce friction between heart and surroundings
three layers:
fibrous pericardium
Serous pericardium
Pericardial cavity
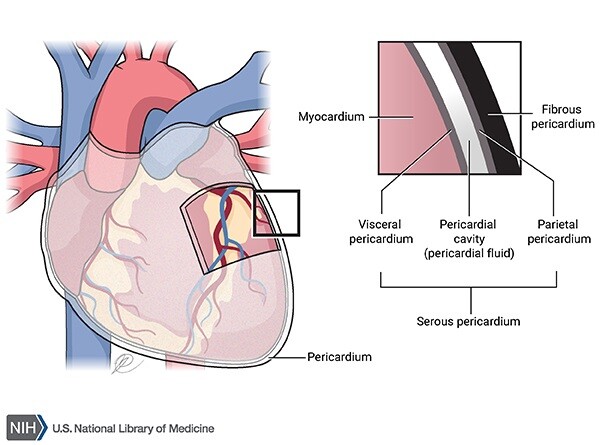

fibrous pericardium
fibro-serous sac continuous with the central tendon of diaphragm
Encloses heart & roots of great vessels
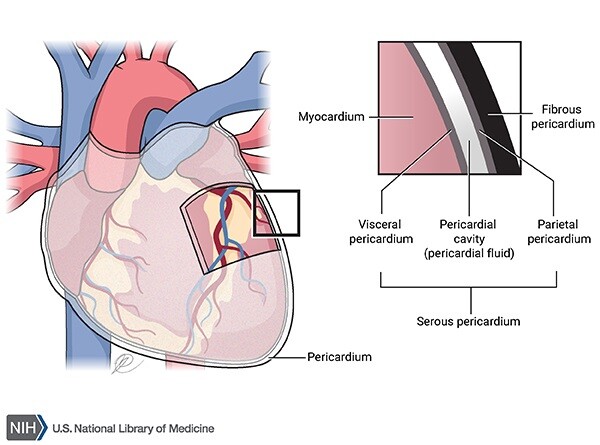
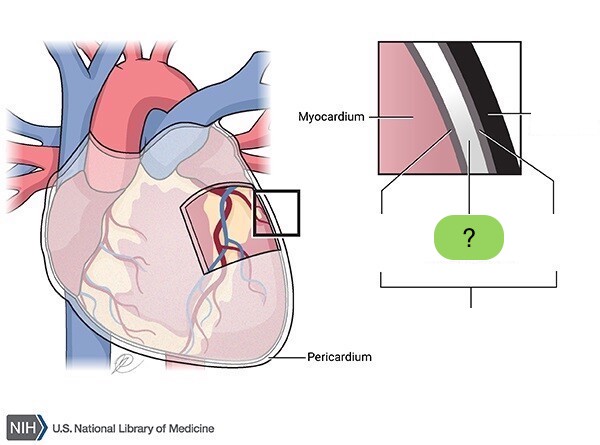
pericardial cavity
space between parietal & visceral layers of serous pericardium
Contains thin film of fluid
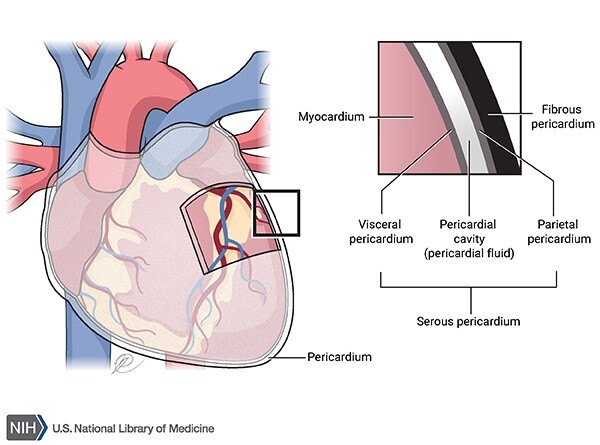
serous pericardium
visceral (epicardium) and parietal
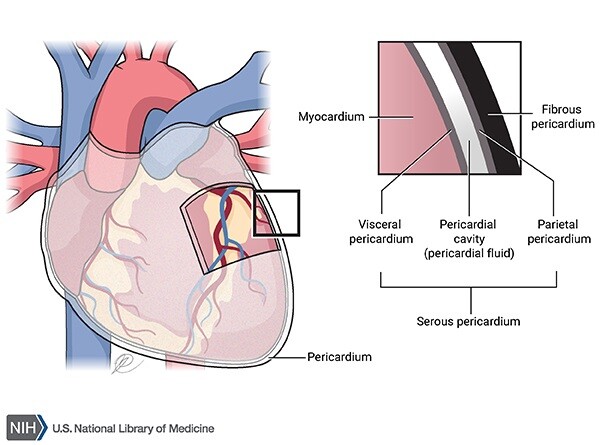
acute pericarditis
inflammation of layers of the pericardium
Sharp pain localised to middle or left thorax - radiates to neck or shoulders
cardiac tamponade
pericardial cavity becomes overly filled with fluid (pericardial fluid or blood)
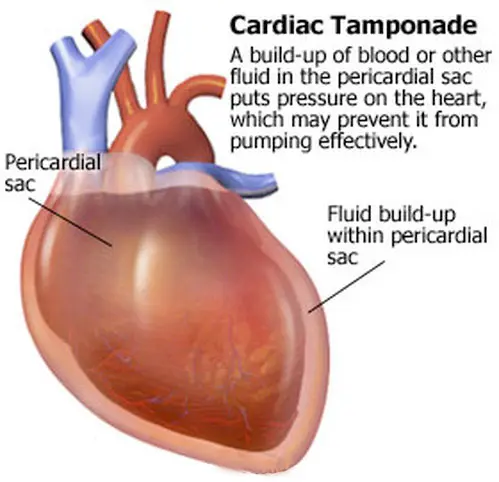
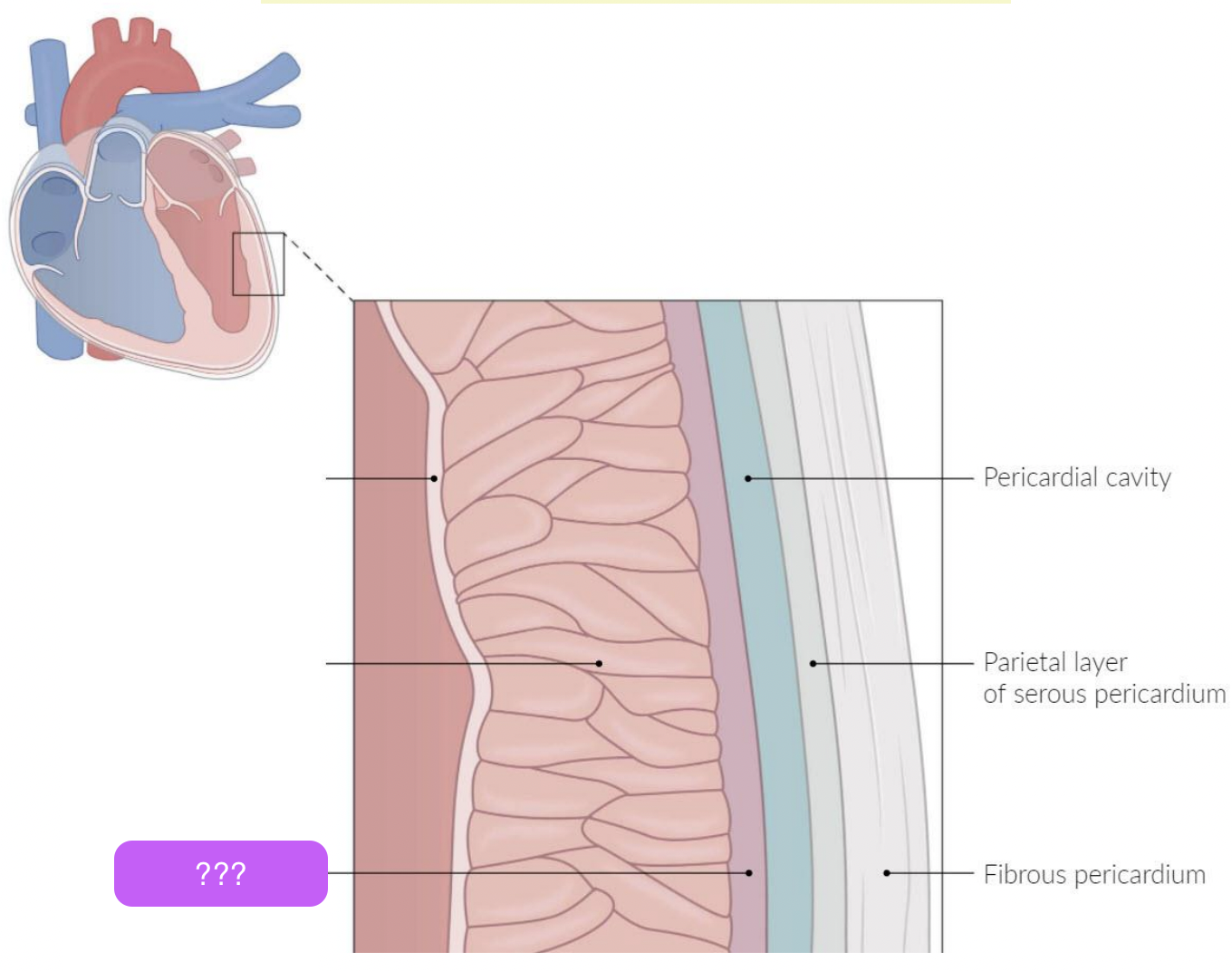
pretend the box is two lines up
endocardium
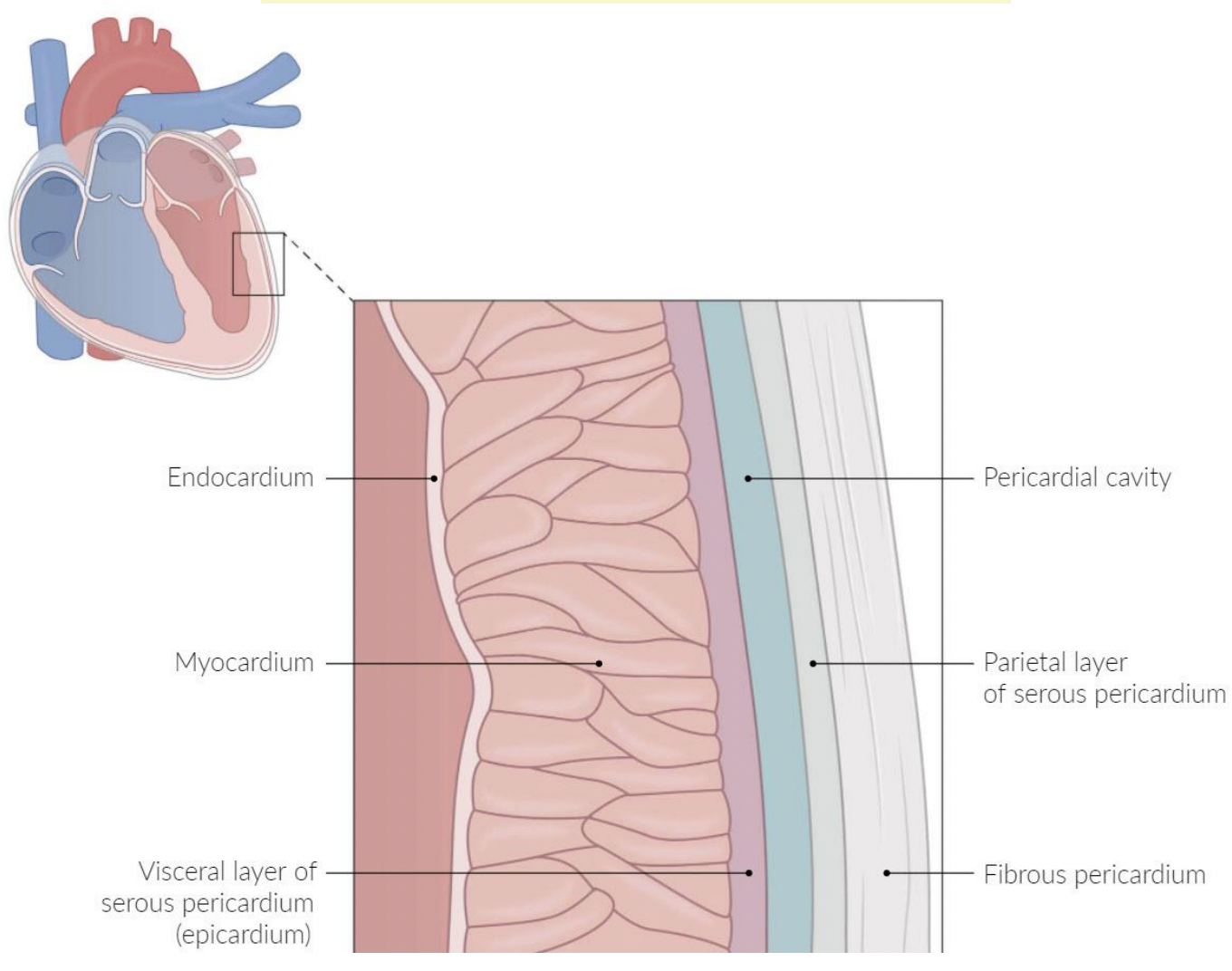
epicardium/visceral serous
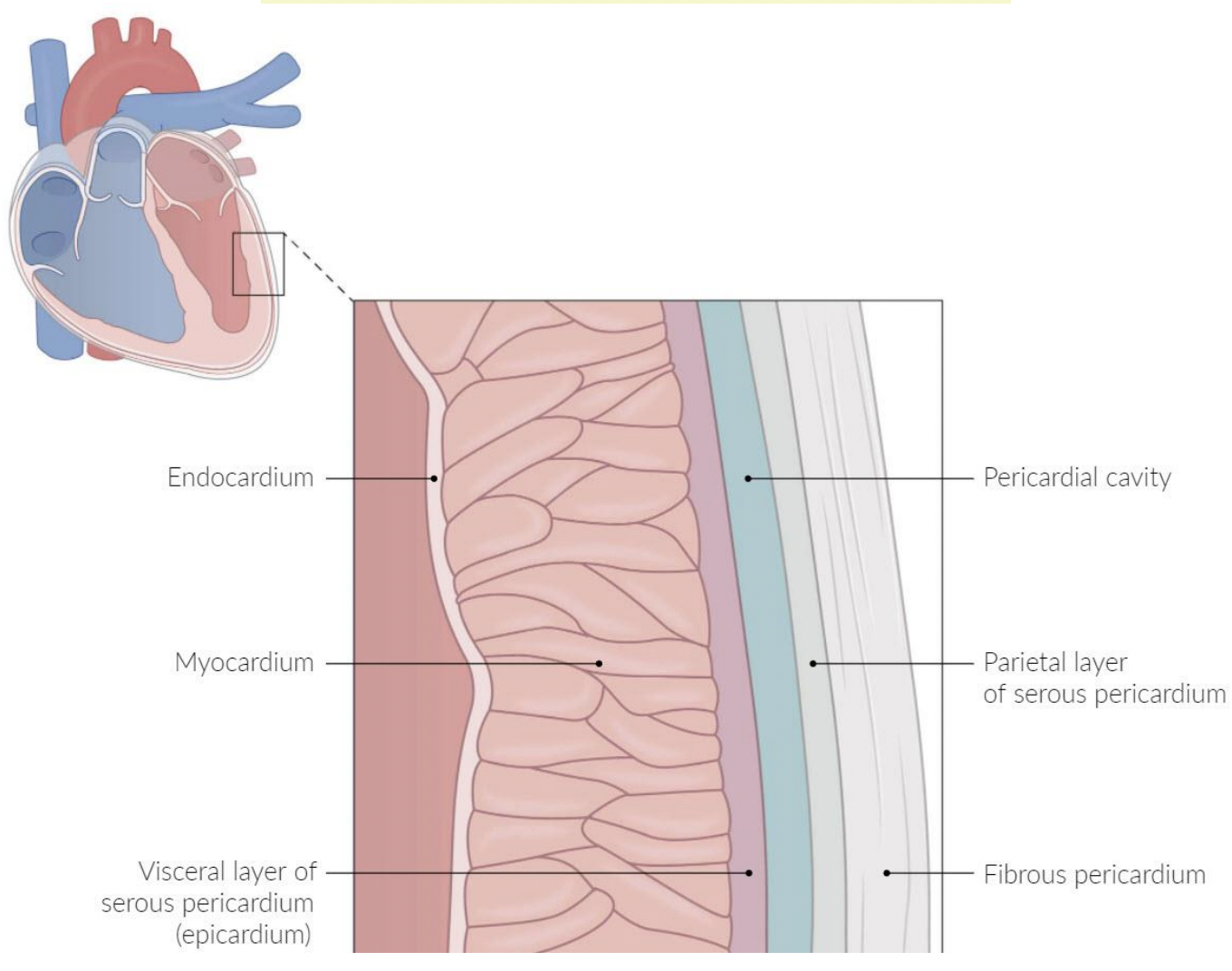
myocardium
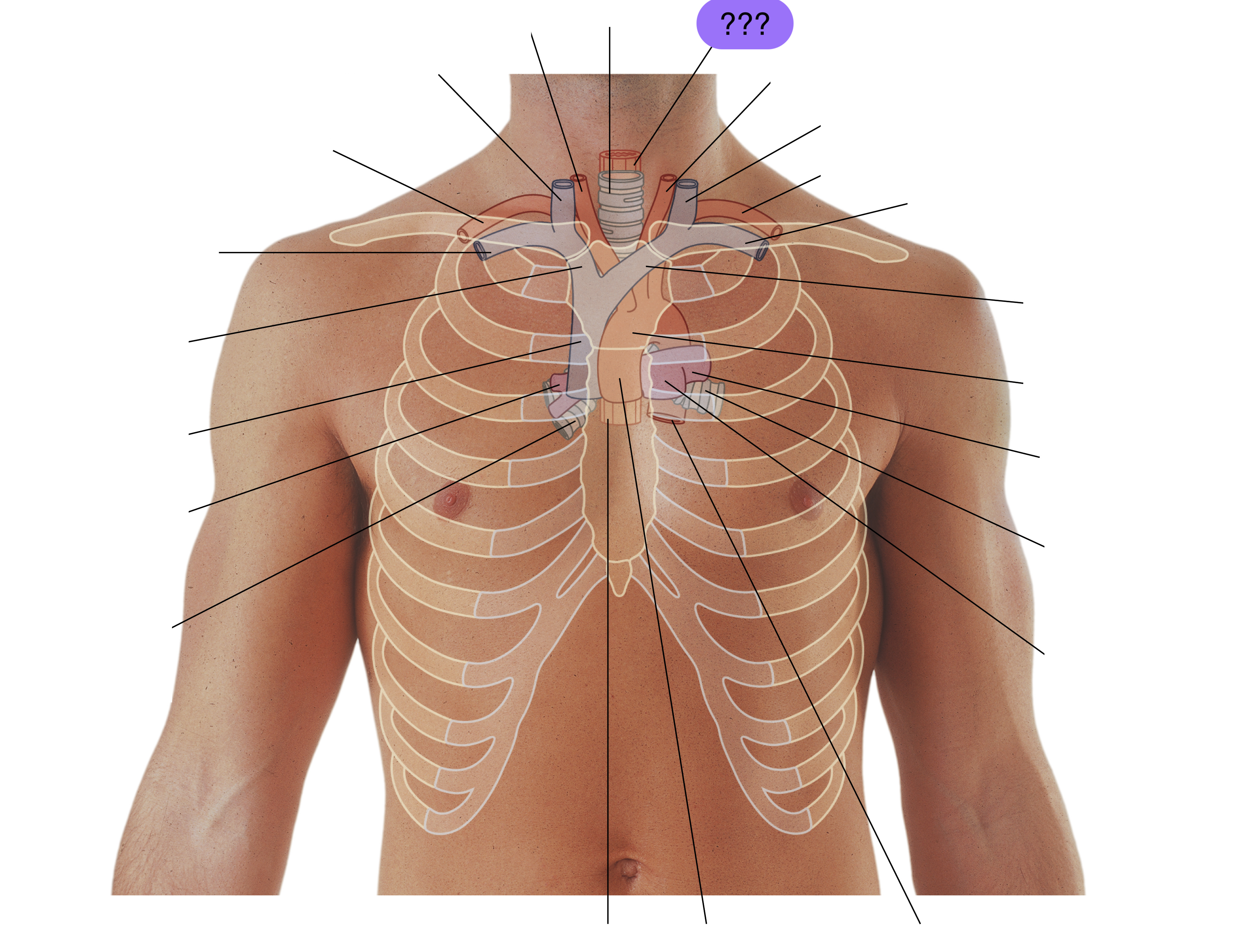
esophagus
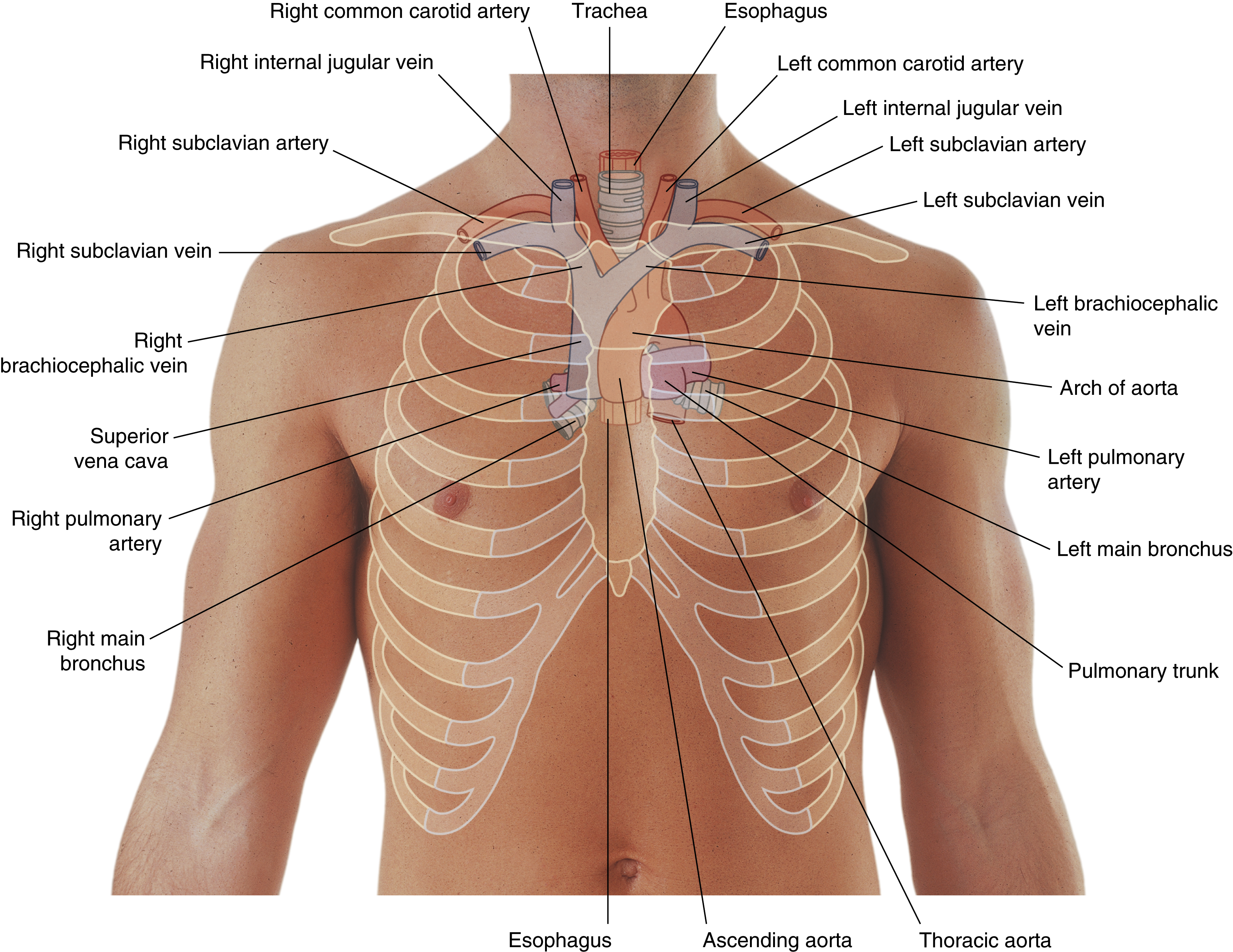
(superior mediastinum)

left brachiocephalic vein
(superior mediastinum)
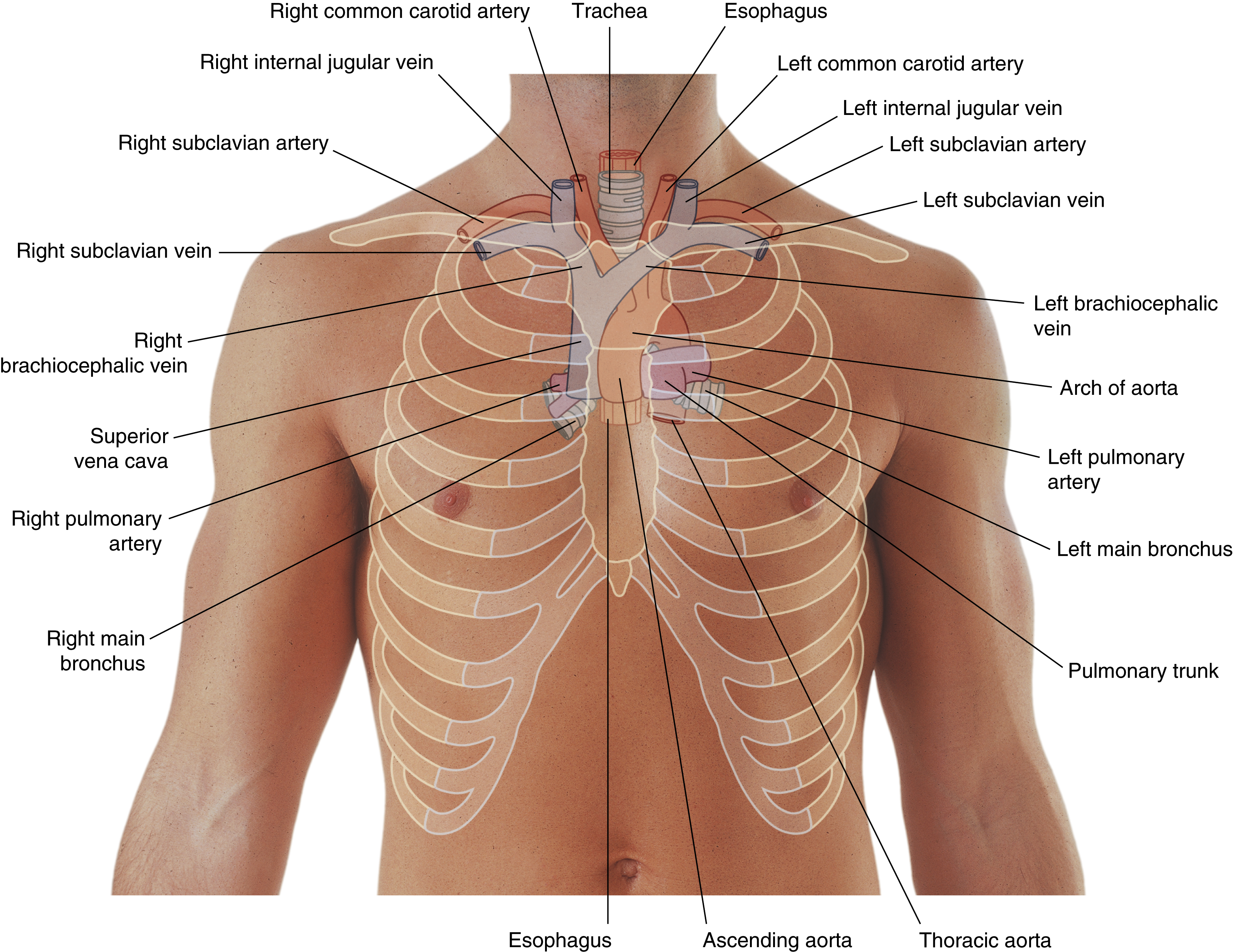
trachea
(superior mediastinum)
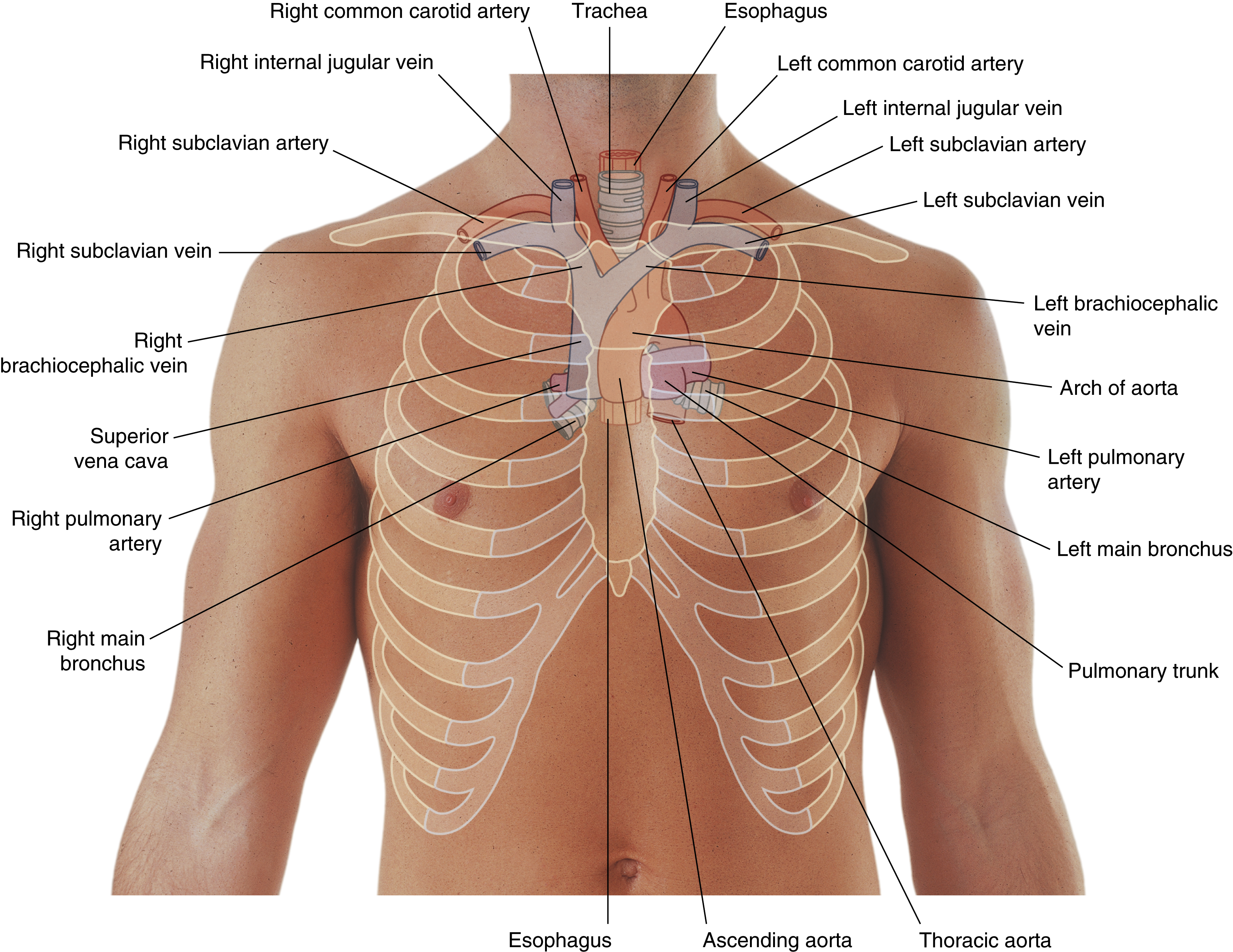
right brachiocephalic vein
(superior mediastinum)
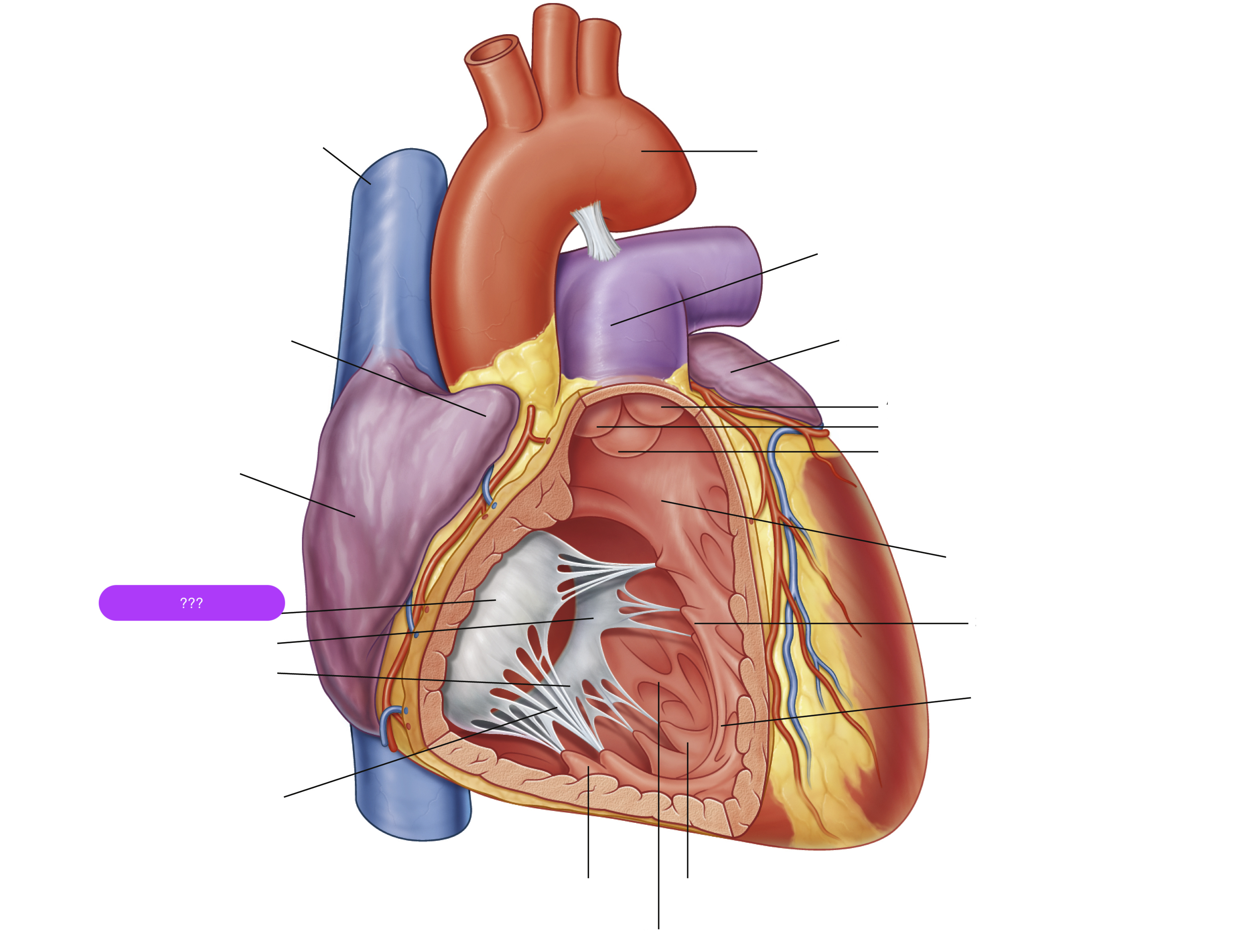
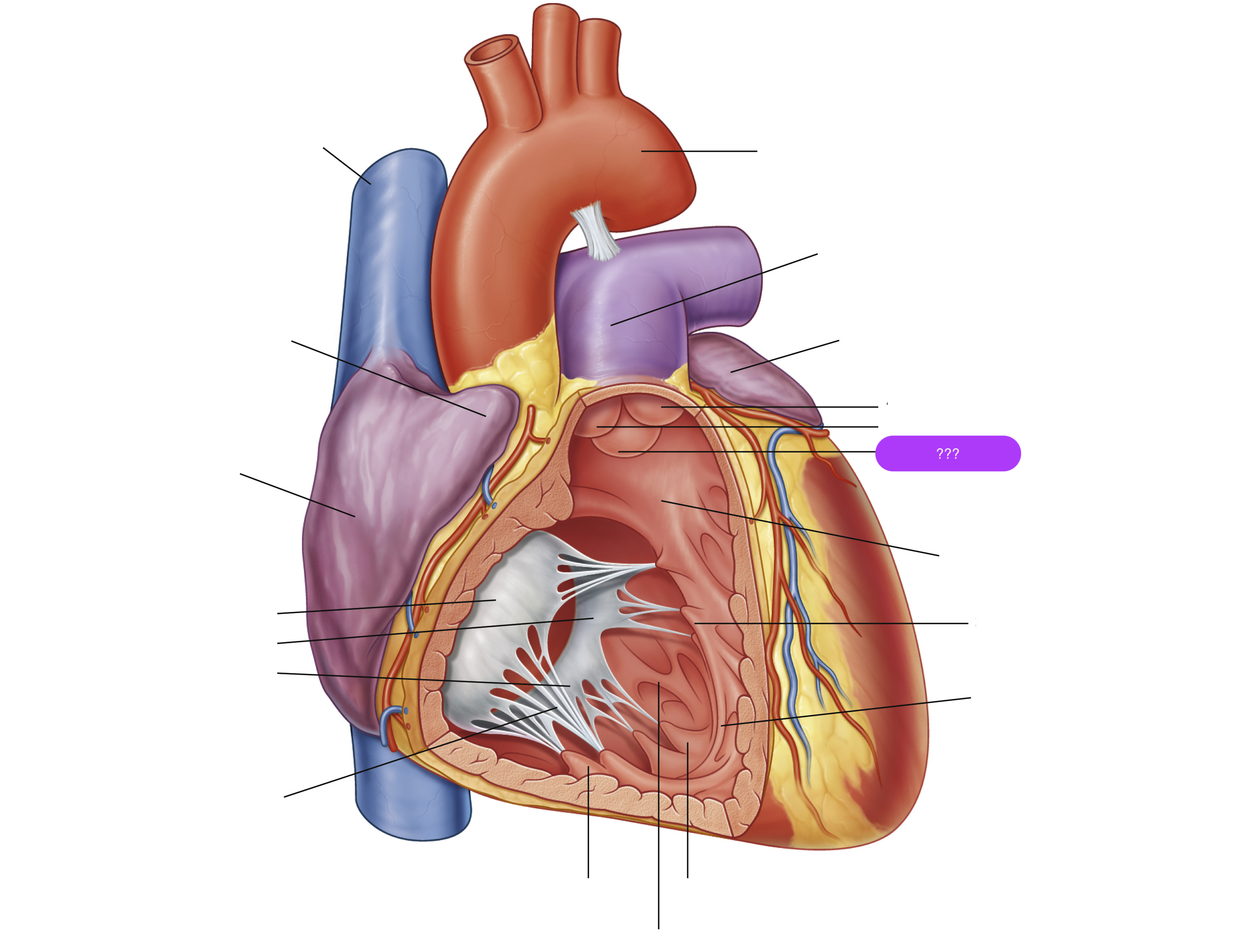
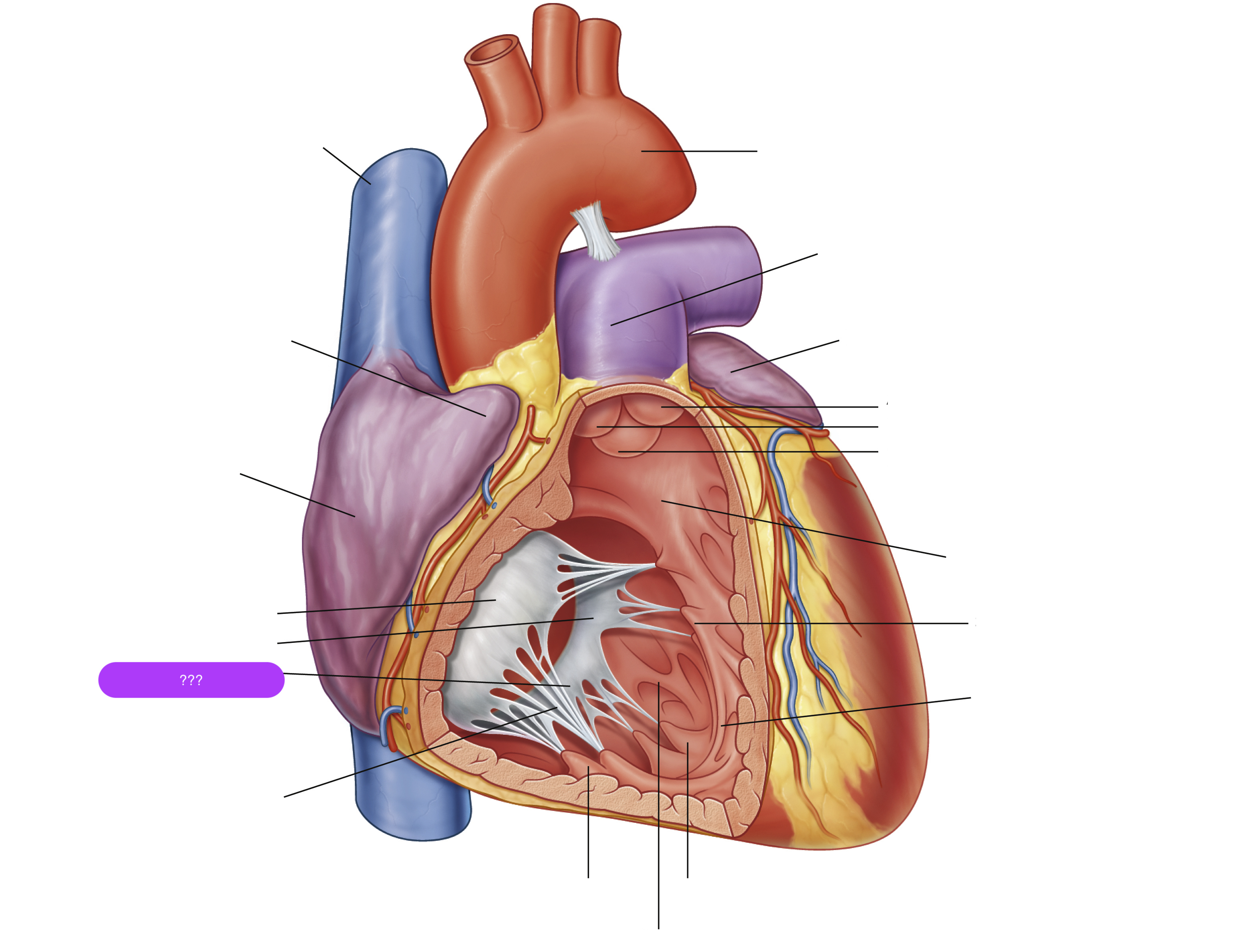
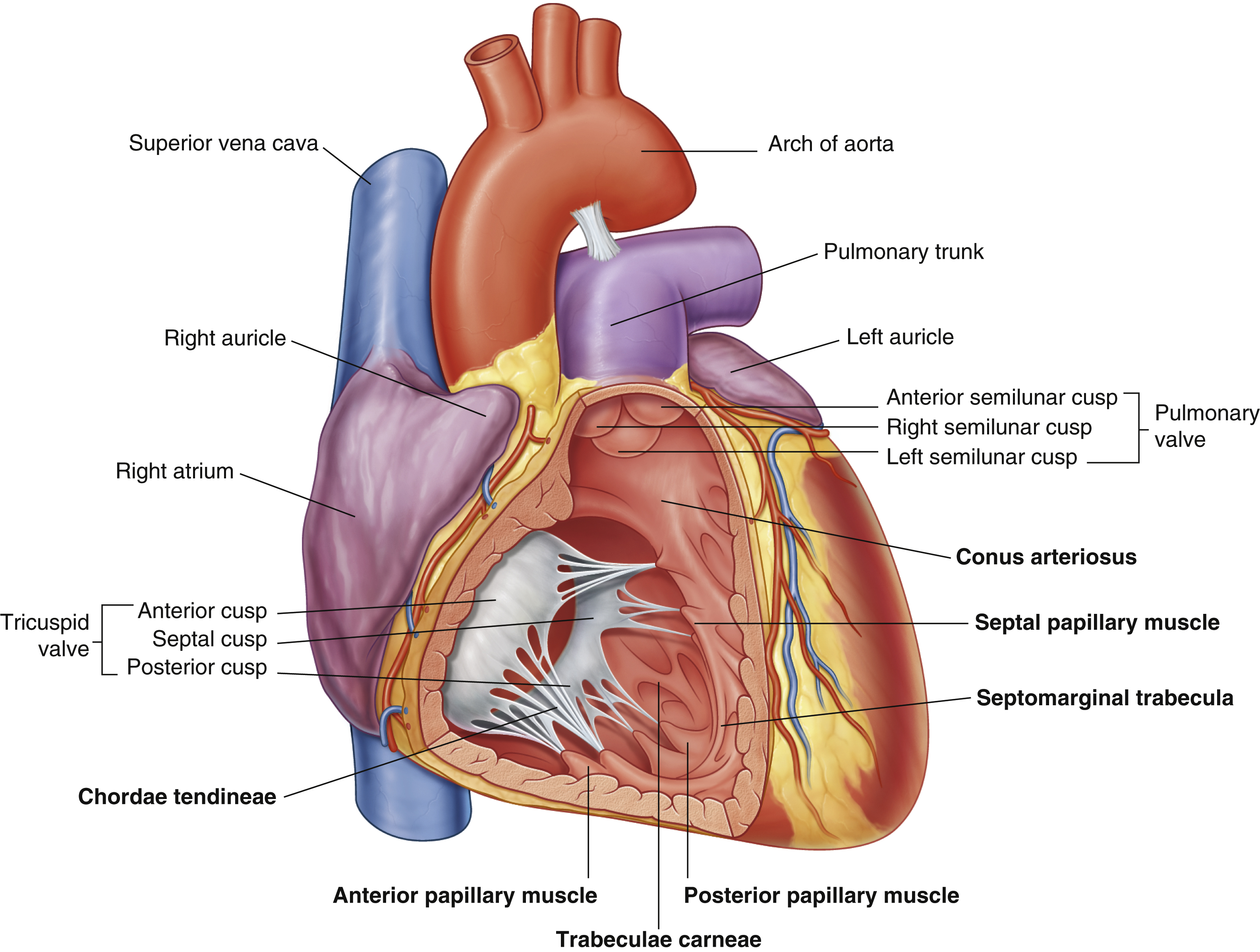
anterior cusp (tricuspid valve)
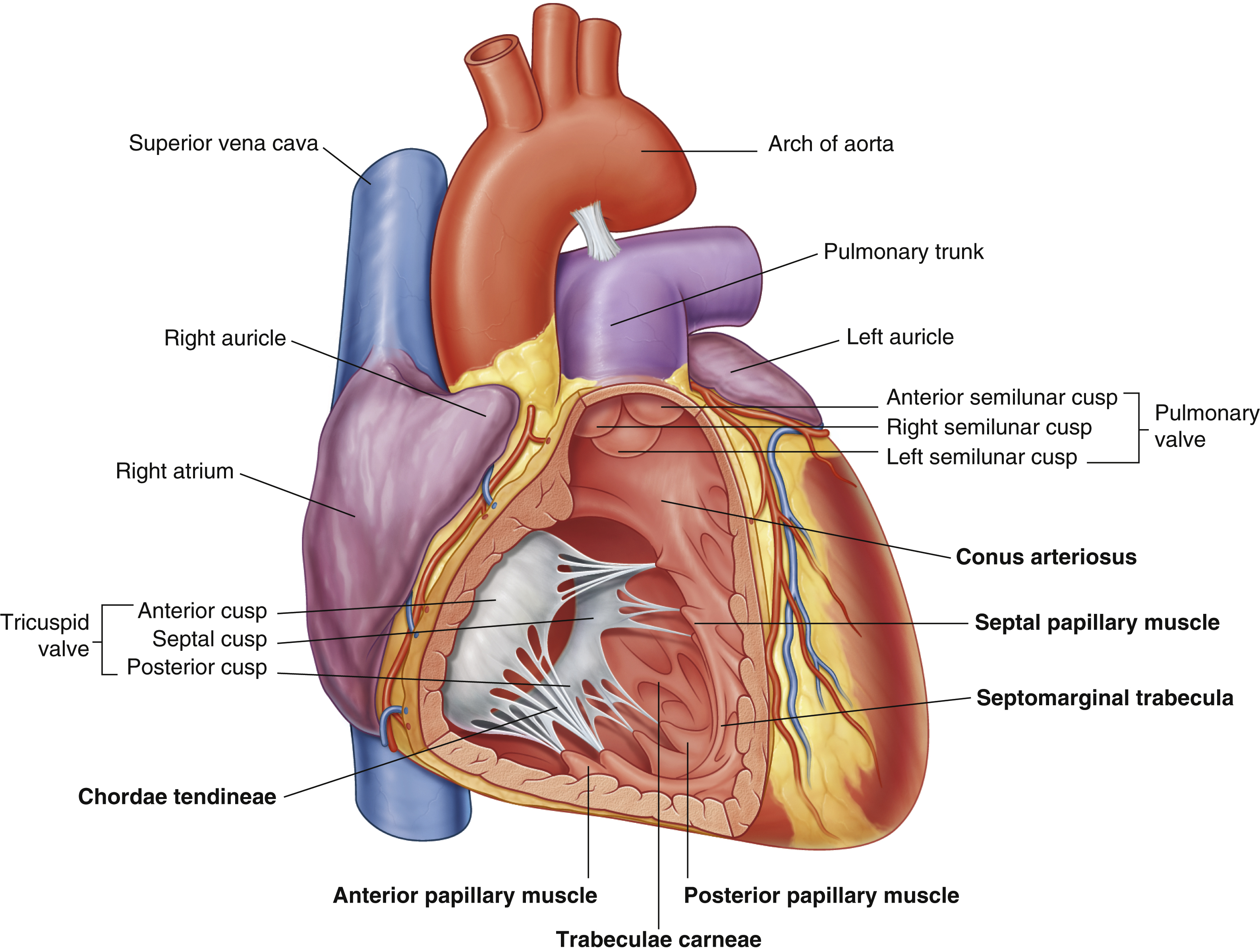

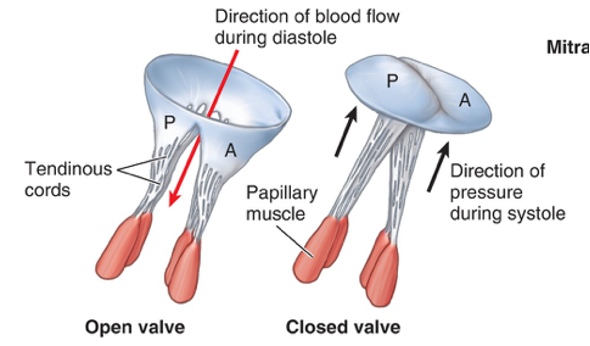
anterior papillary muscle
pulls on chordae tendineae when contracted to keep tricuspid valve closed
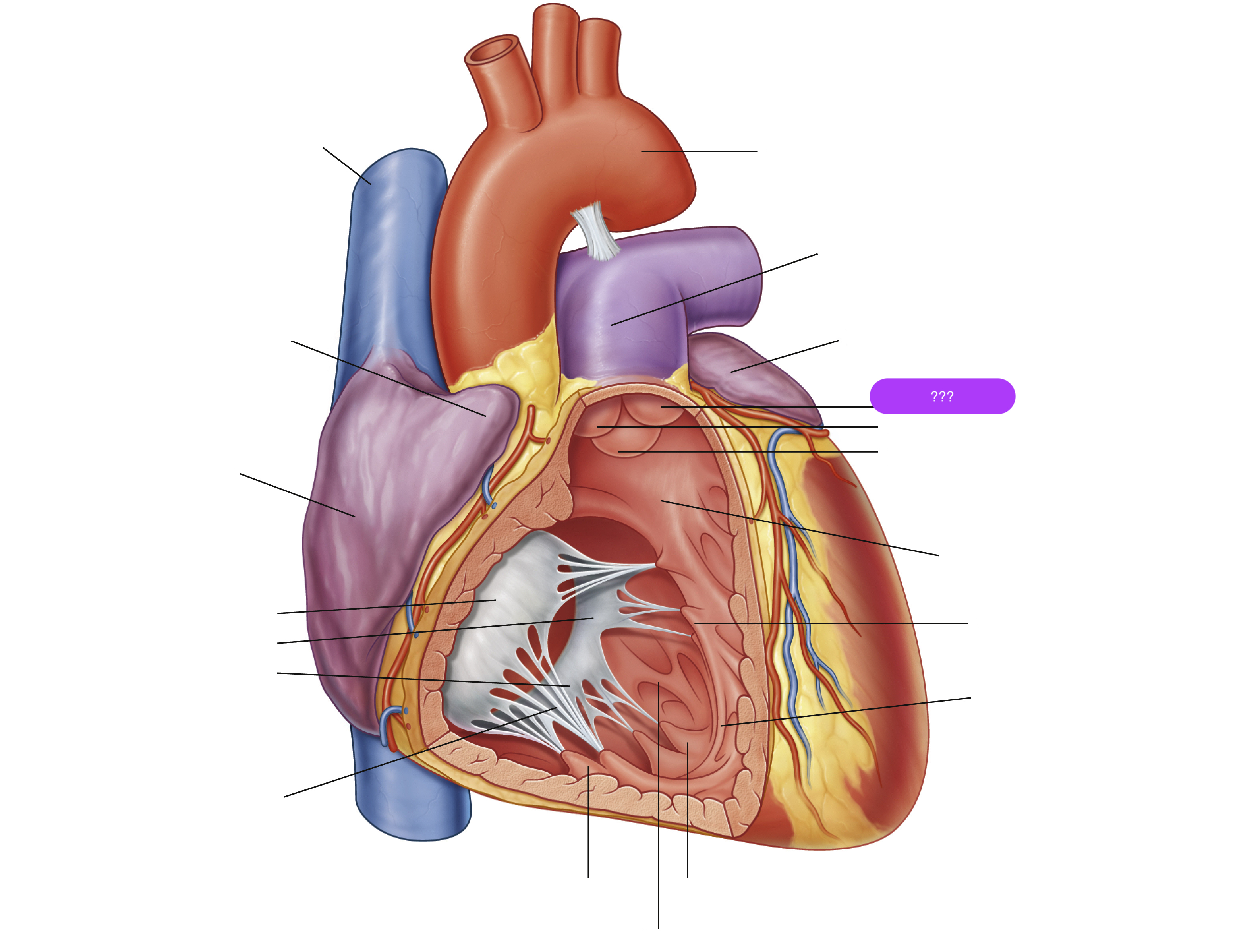
anterior semilunar cusp (pulmonary valve)
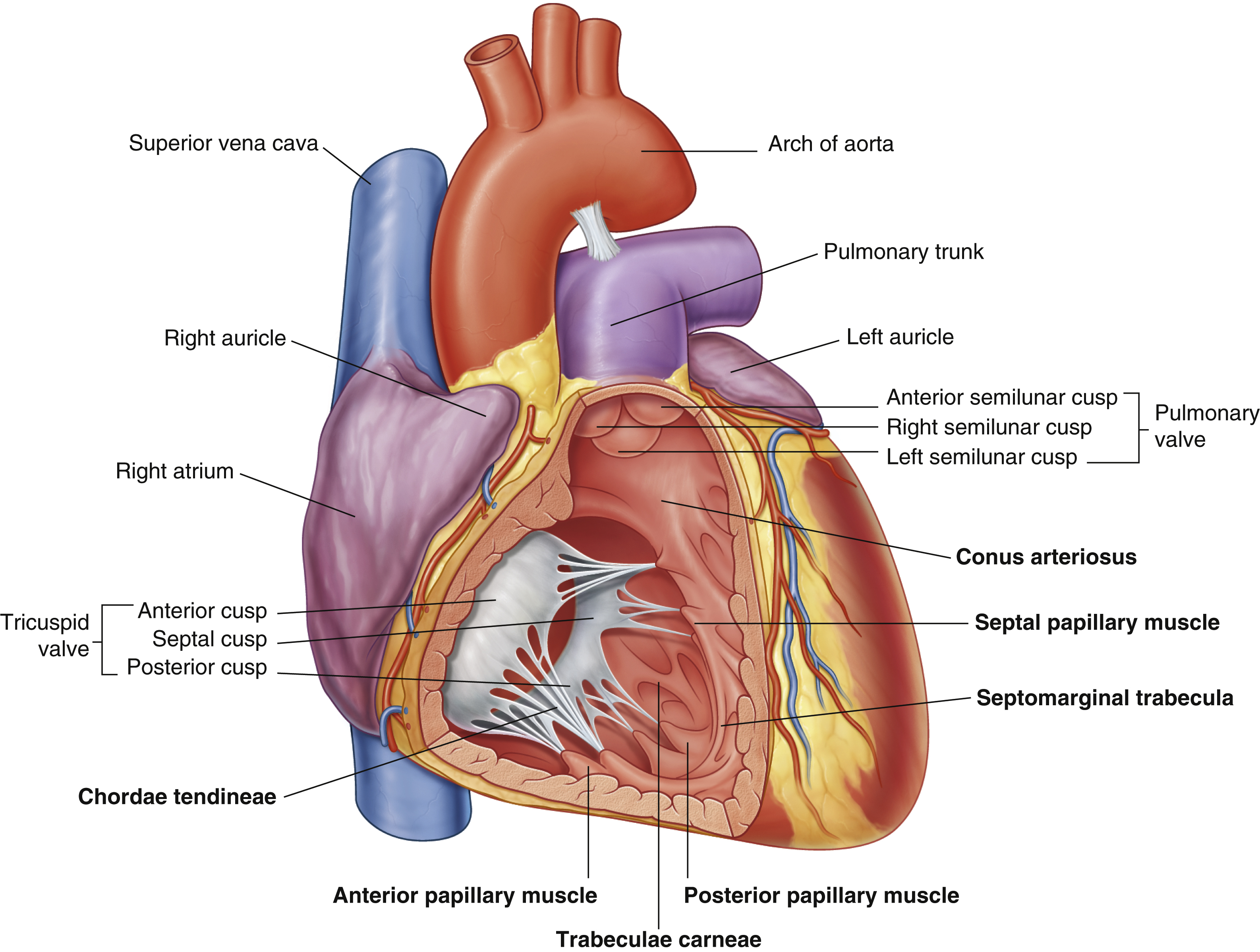

arch of aorta
arches predominantly in the sagittal plane (front to back)
(superior mediastinum)
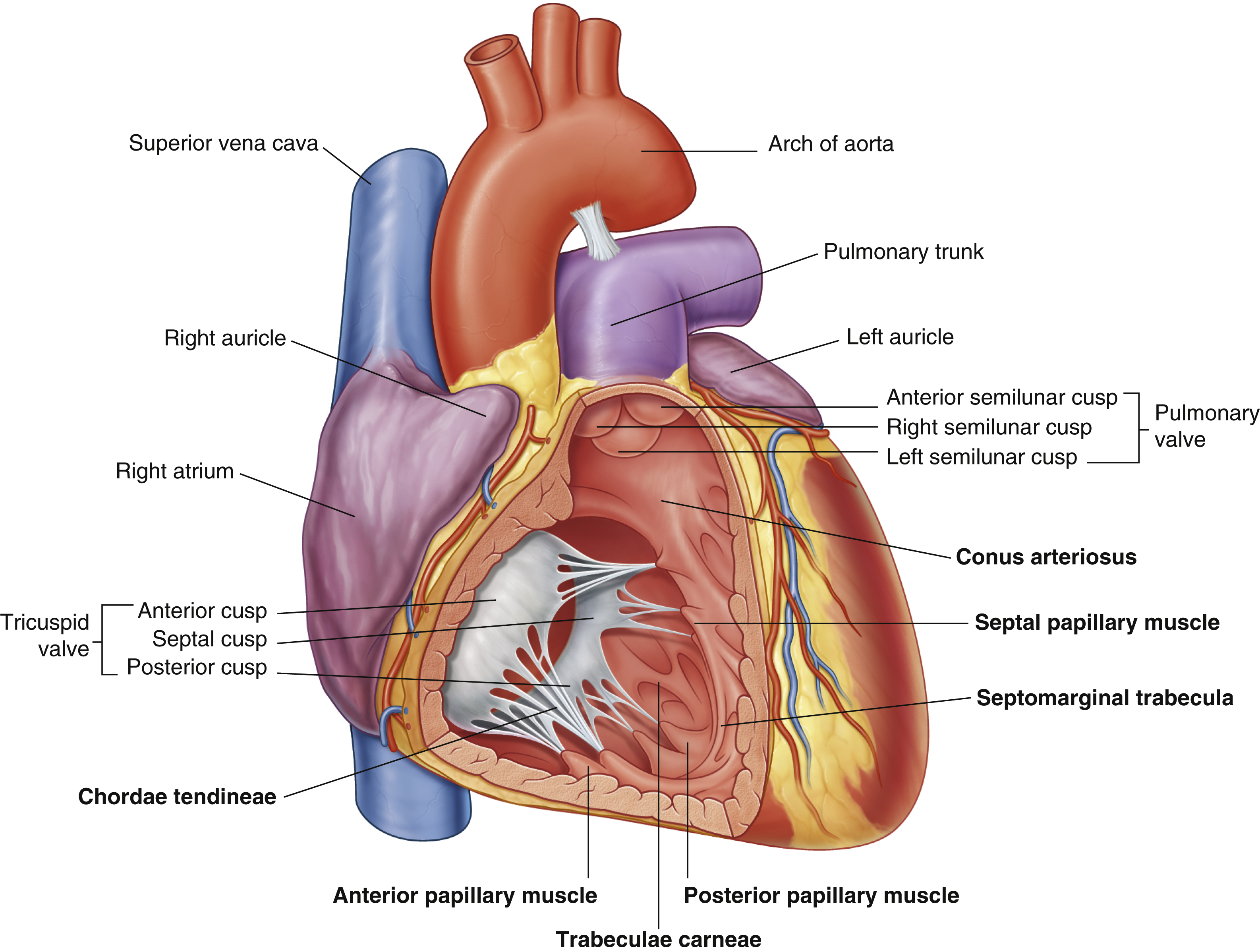
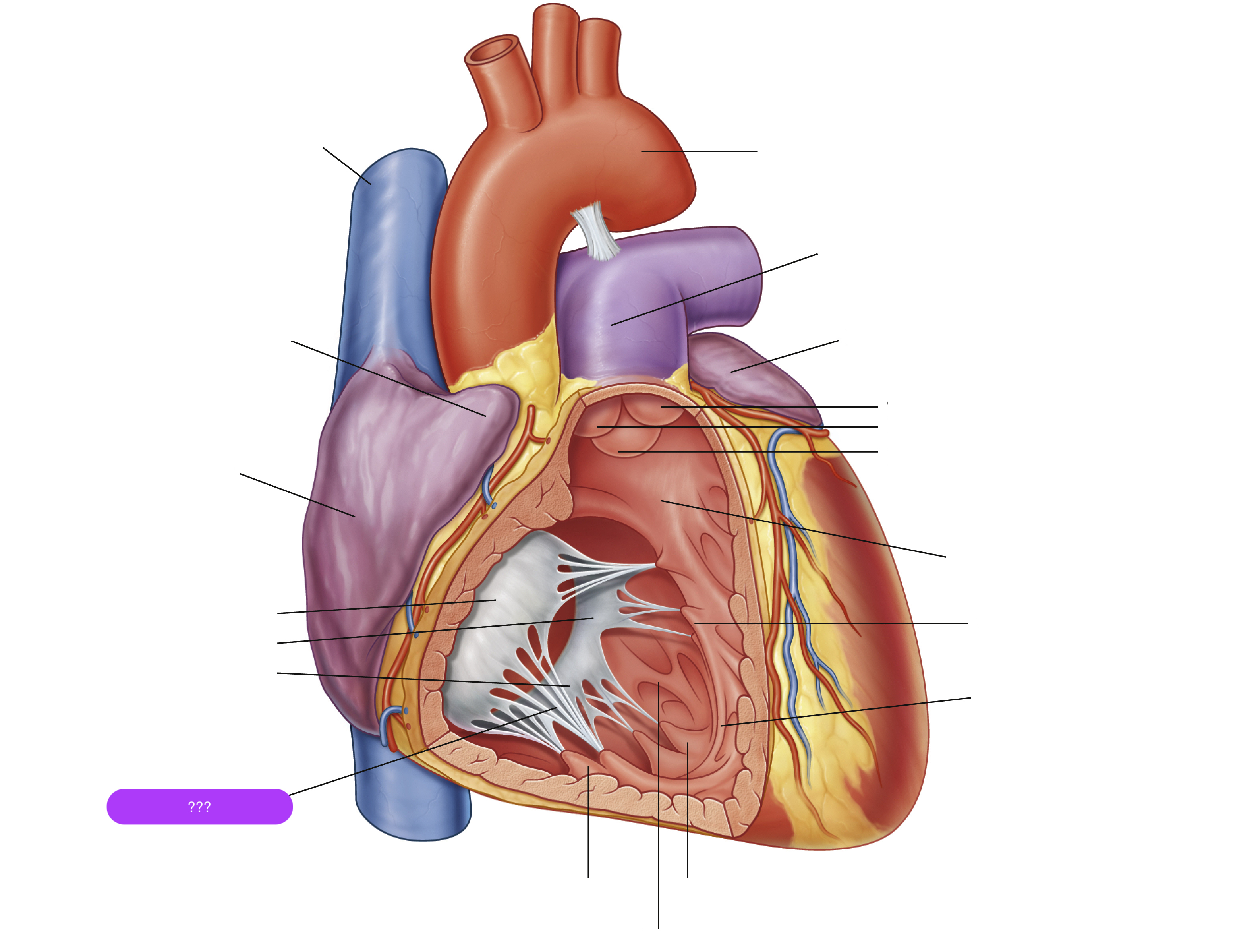
chordae tendineae
made from collagen
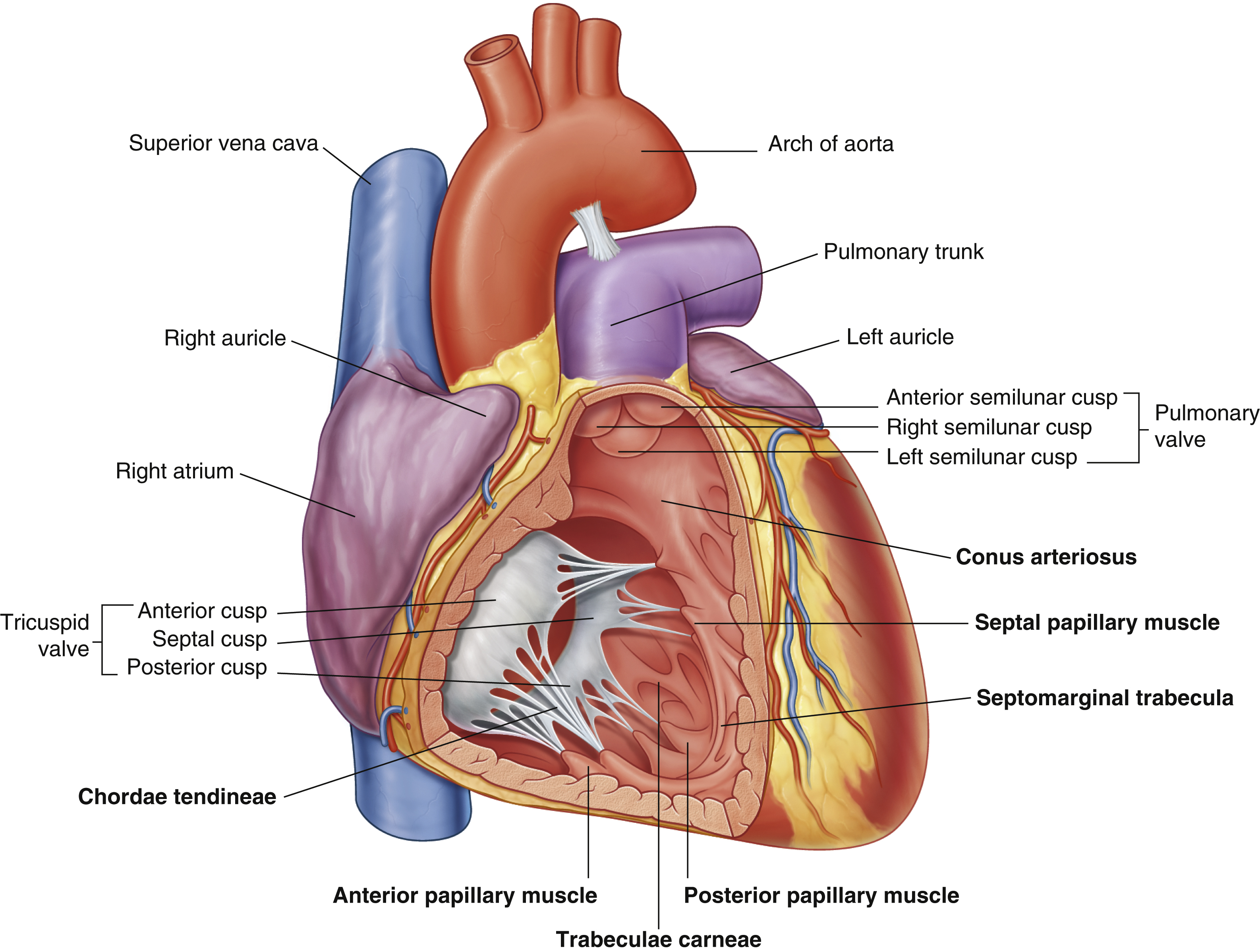
conus arteriosus
funneling structure for pulmonary valve
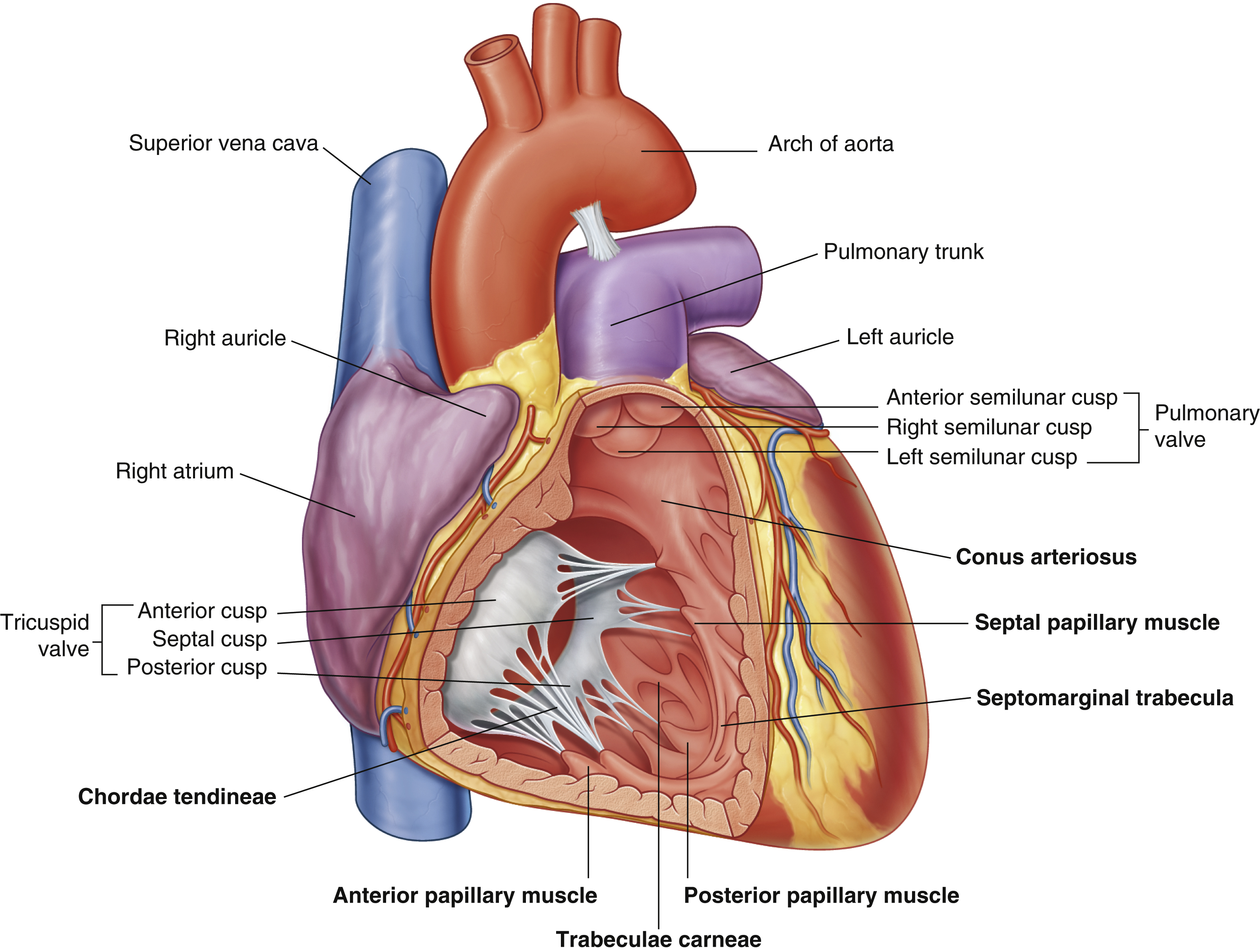
left auricle

left semilunar cusp (pulmonary valve)
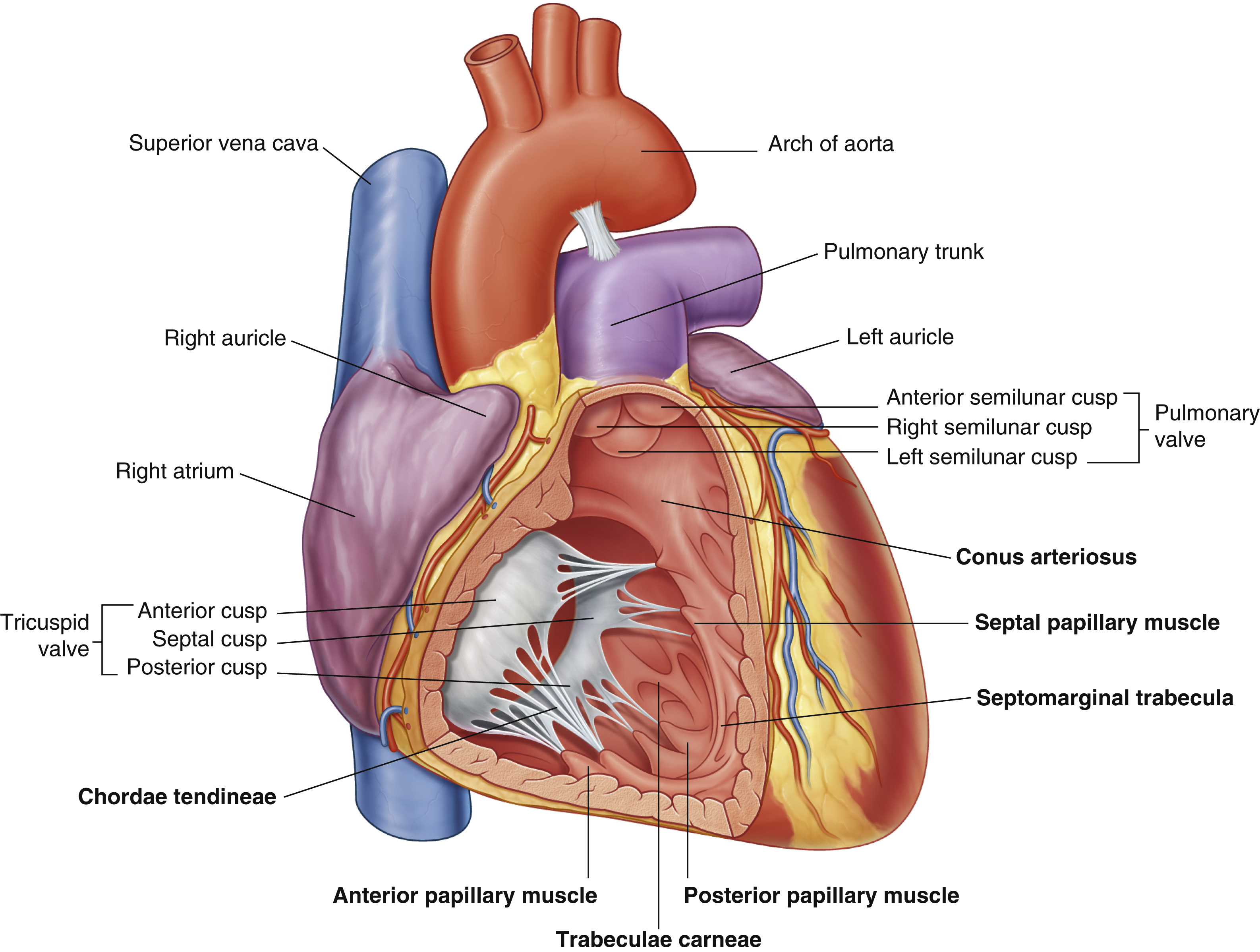
posterior cusp (tricuspid valve)

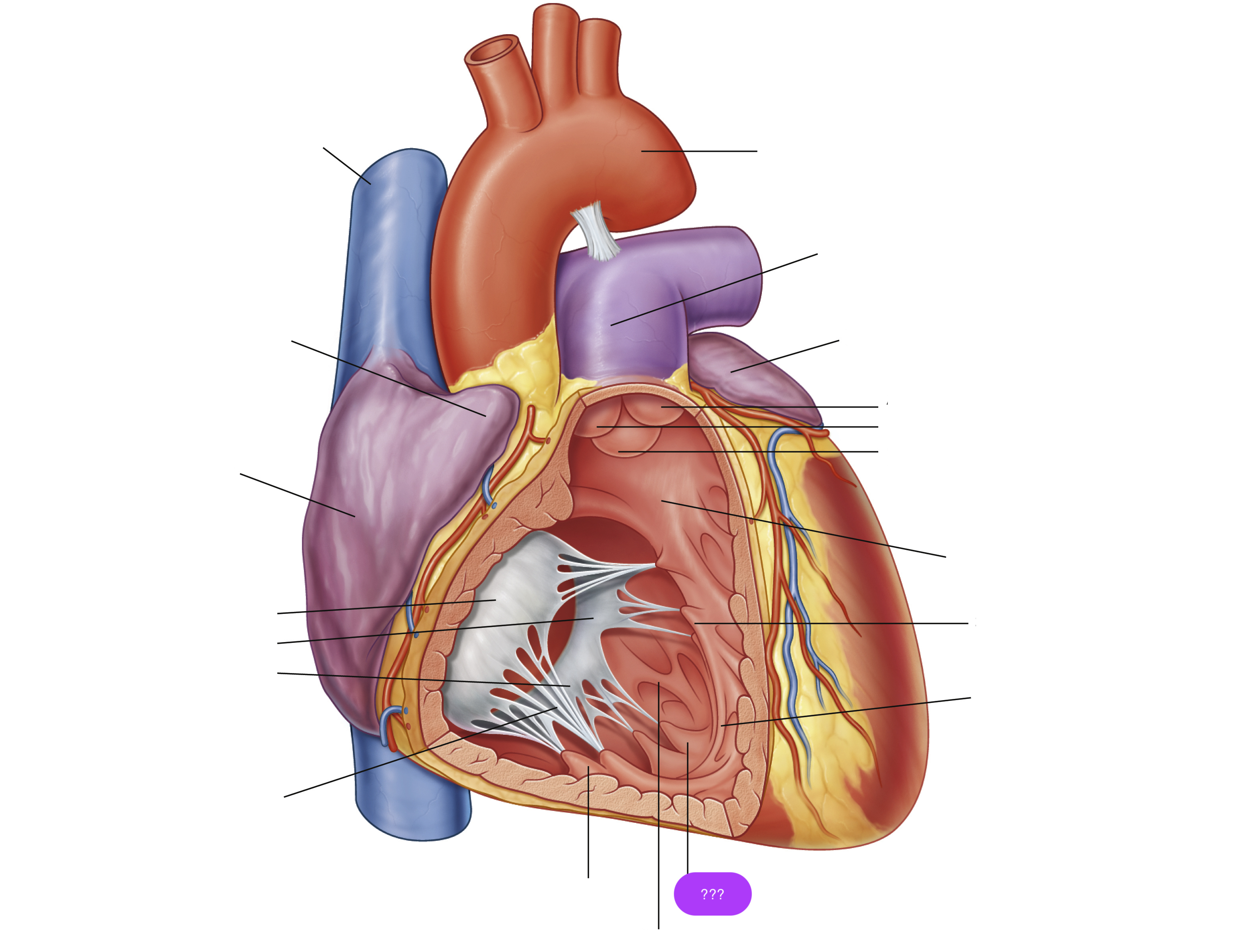
posterior papillary muscle
pulls on chordae tendineae when contracted to keep tricuspid valve closed
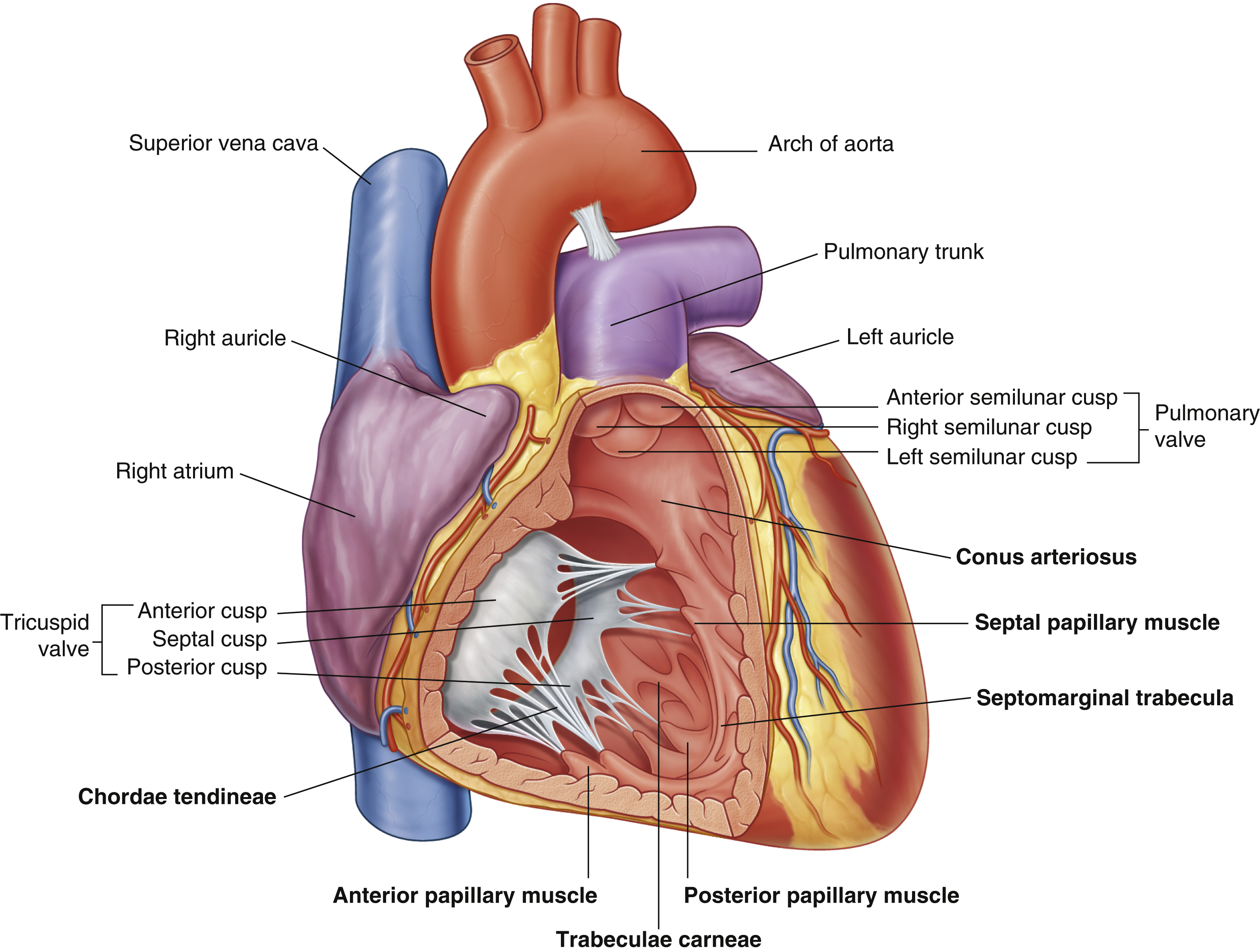
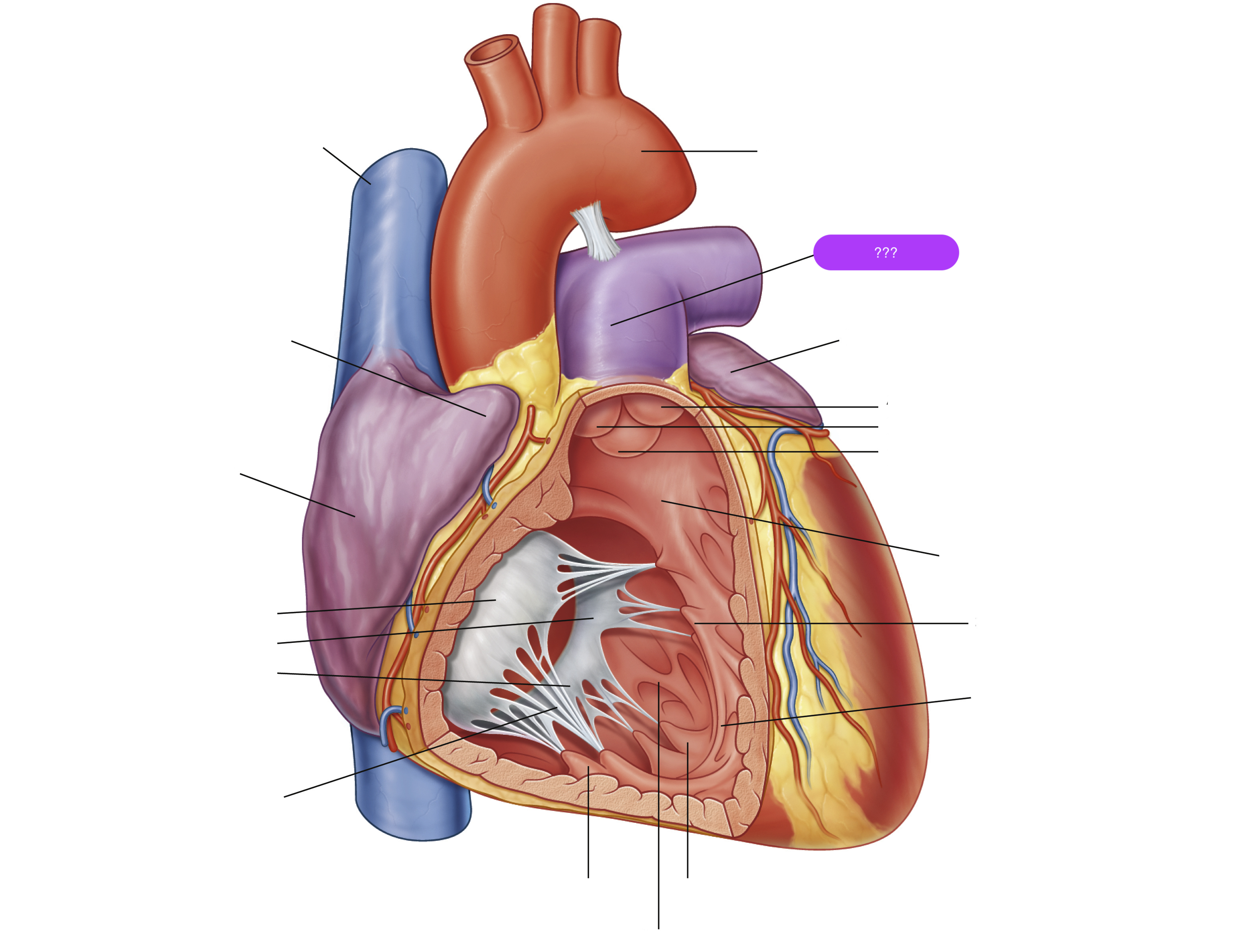
pulmonary trunk
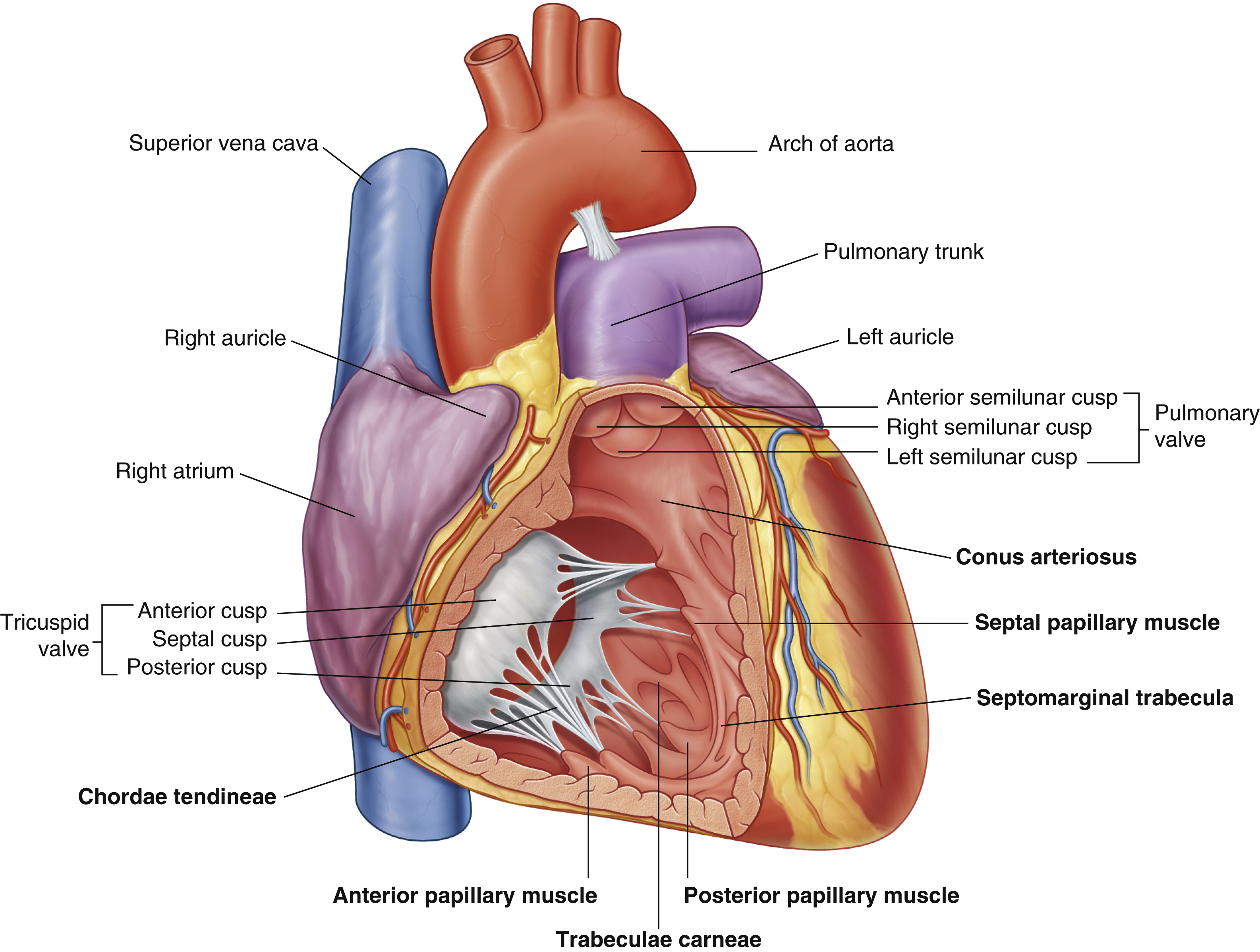

right atrium
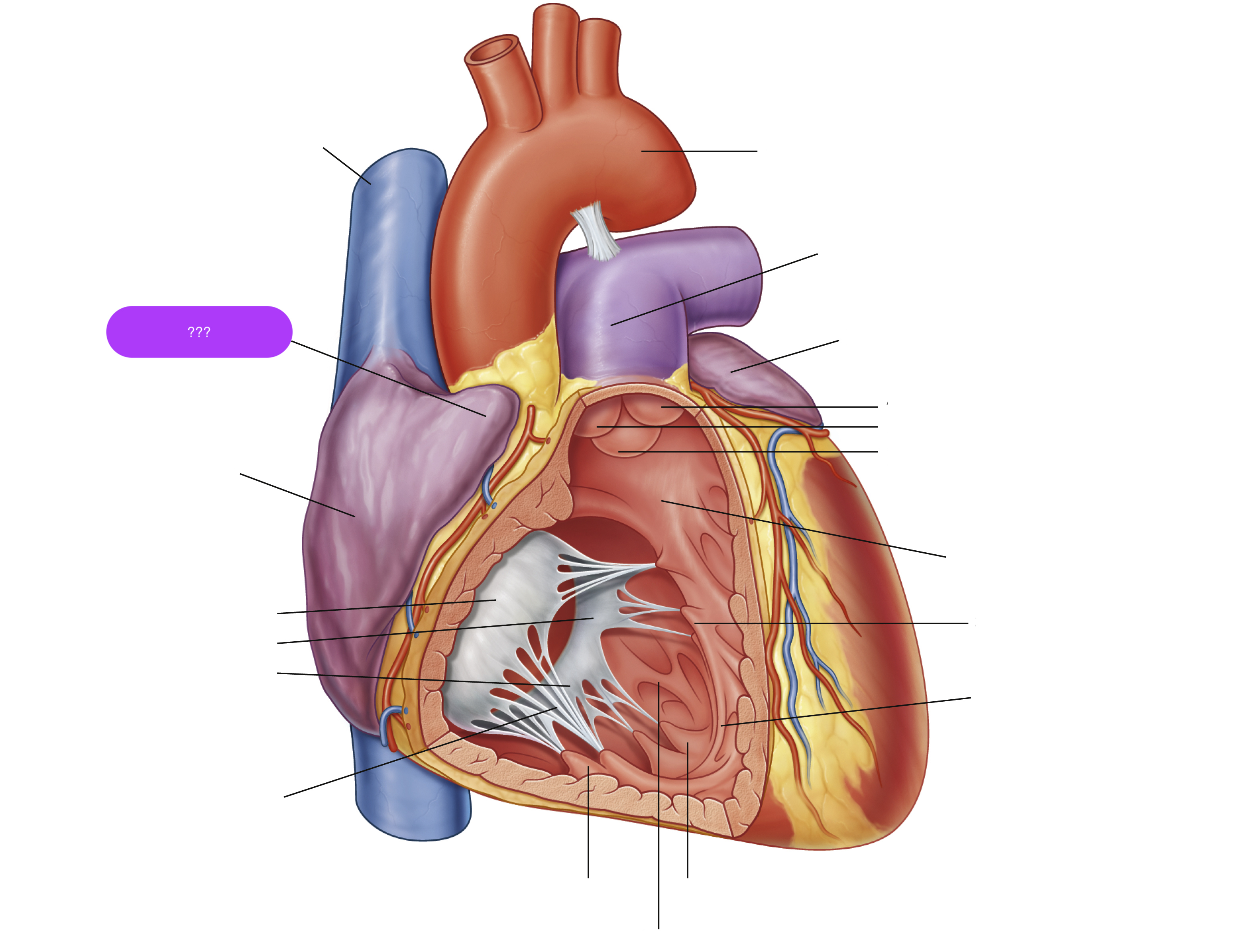
right auricle


right semilunar cusp (pulmonary valve)
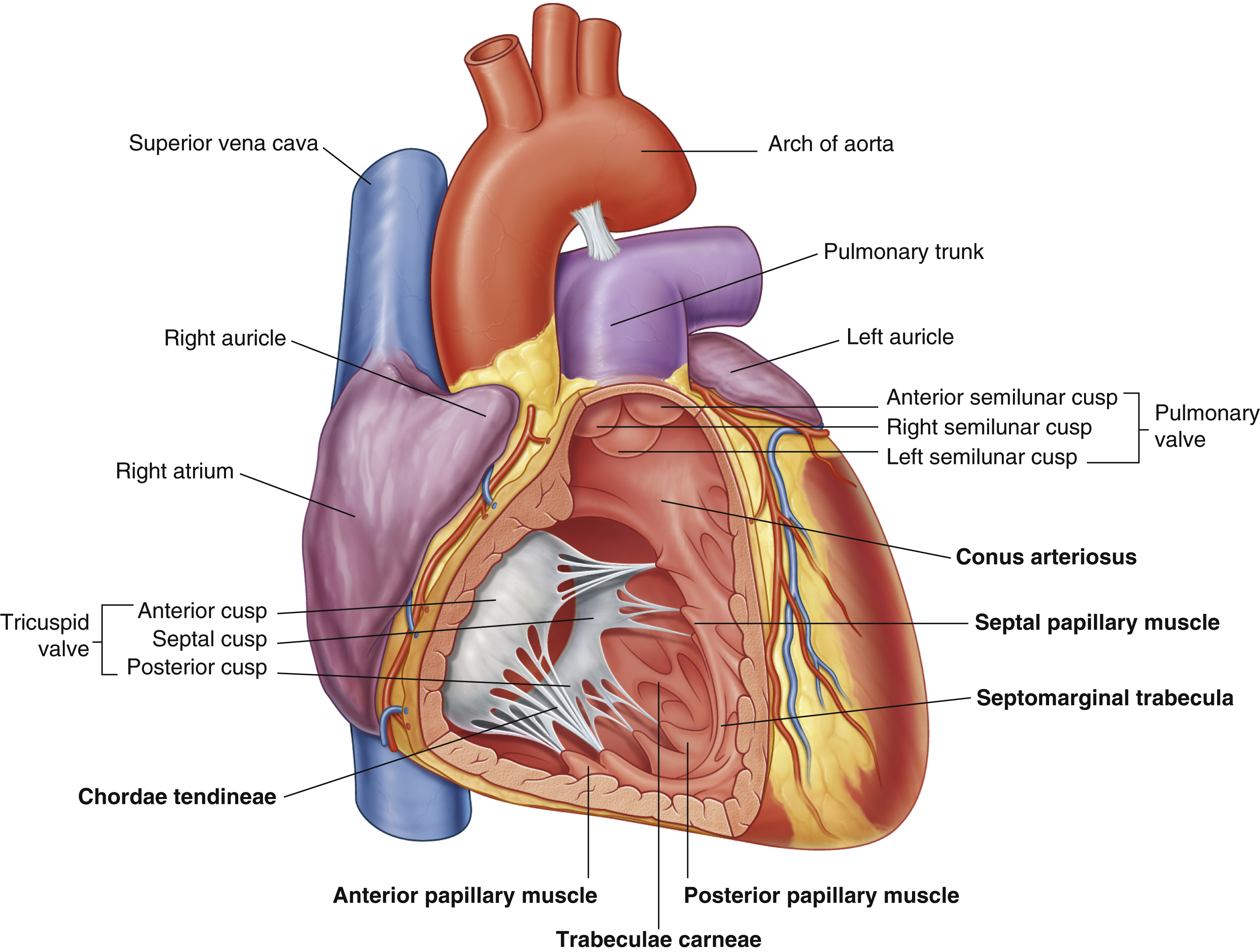
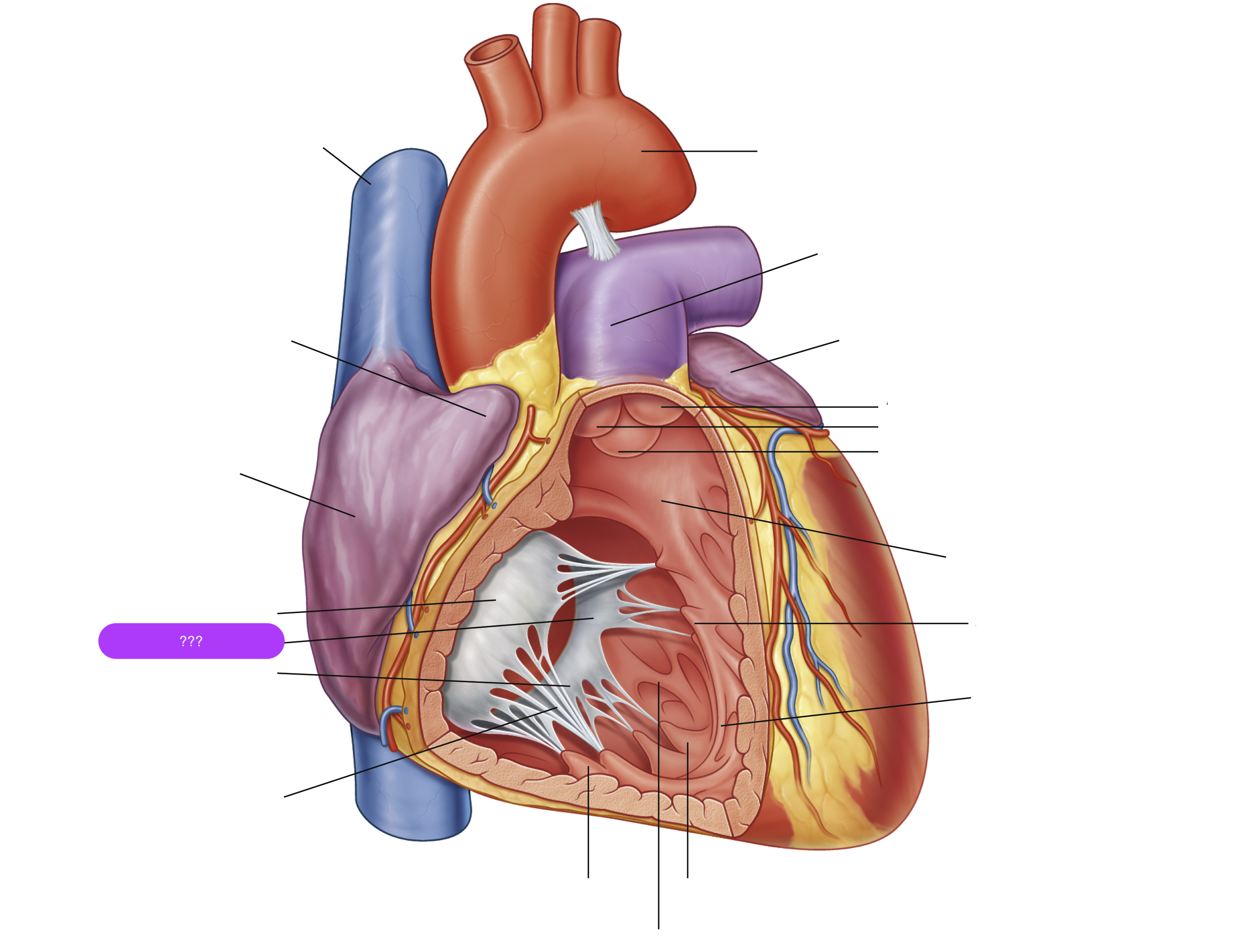
septal cusp (tricuspid valve)
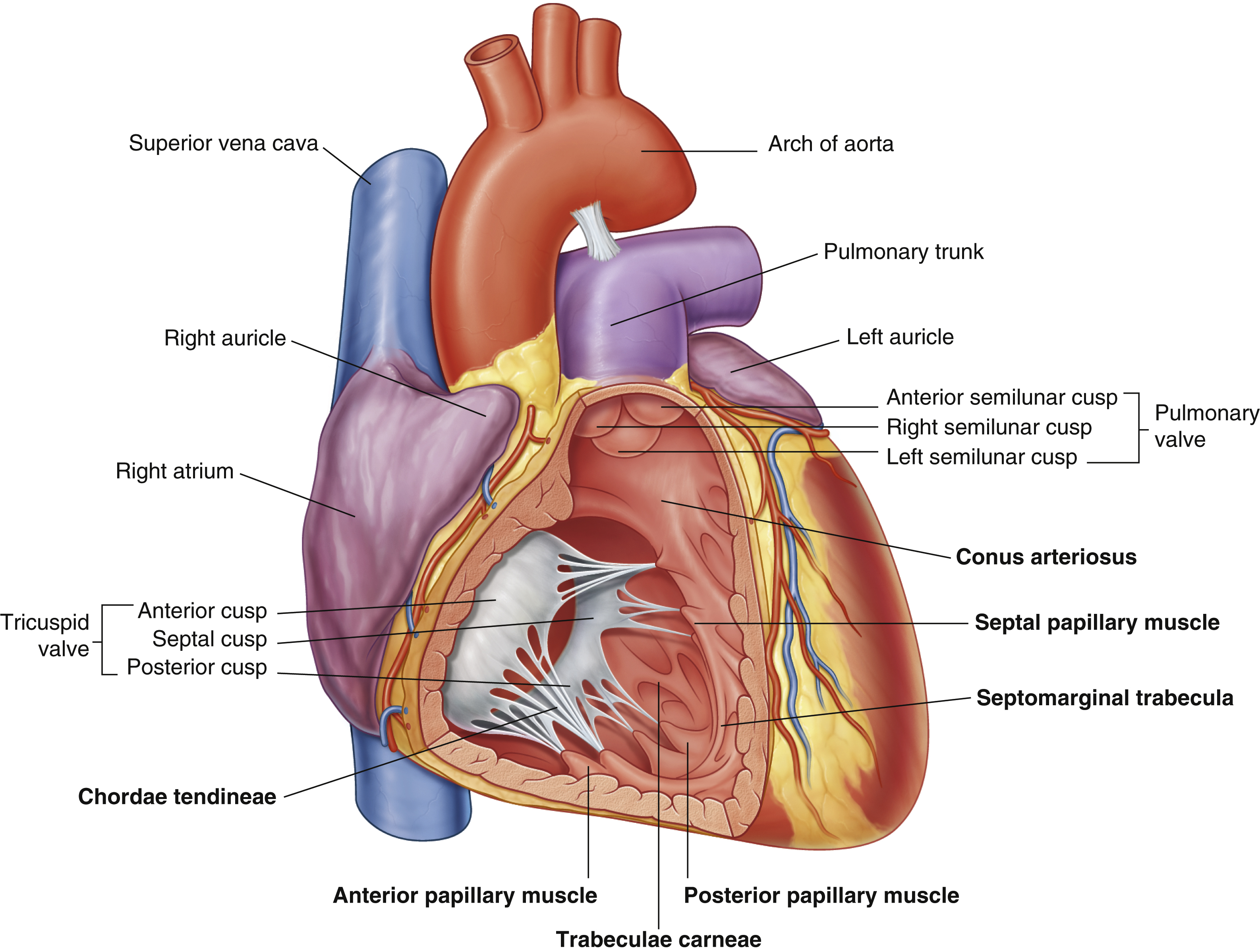
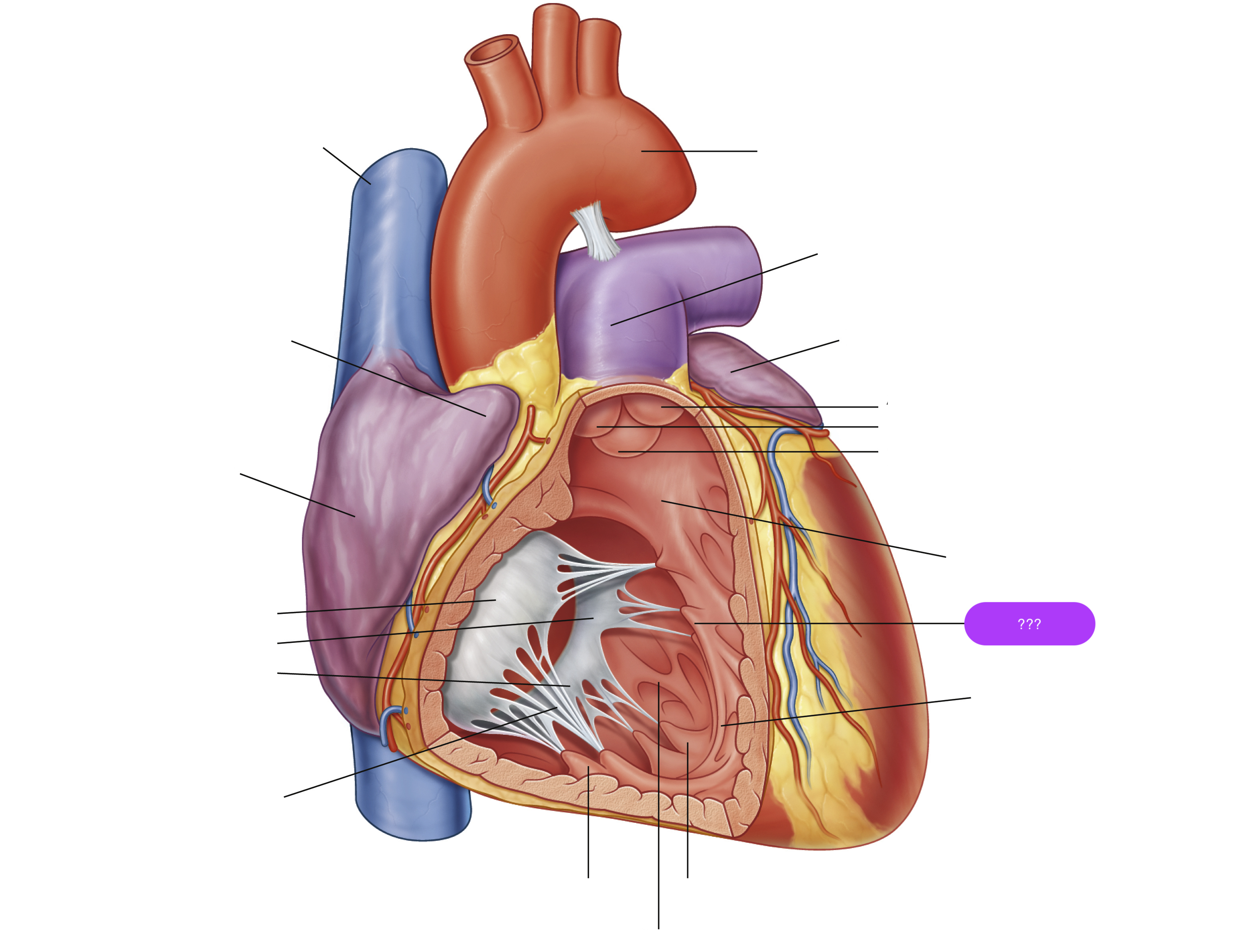
septal papillary muscle

septomarginal trabecula/moderator band
made of muscular tissue, connected to wall of ventricle
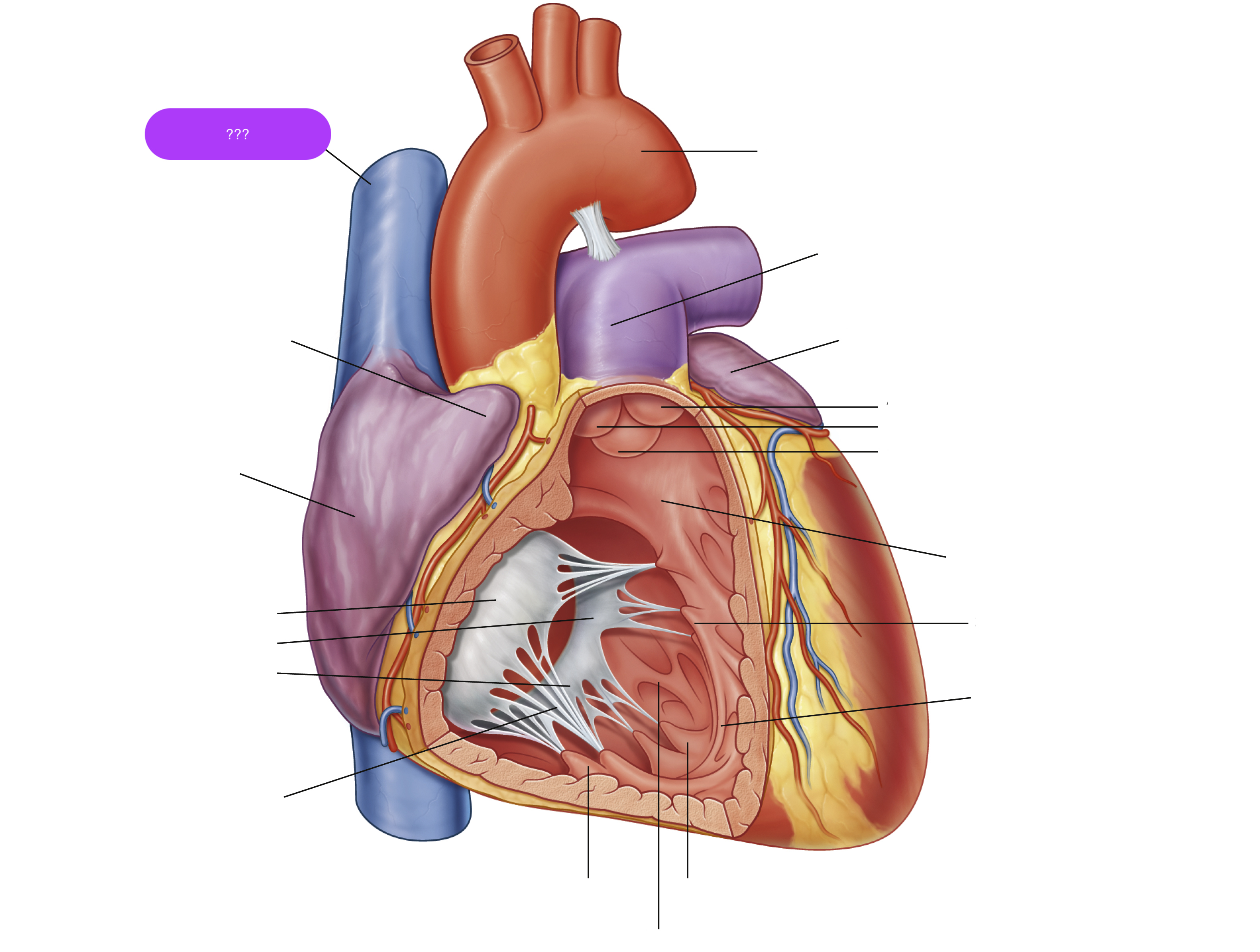
superior vena cava
(superior mediastinum)
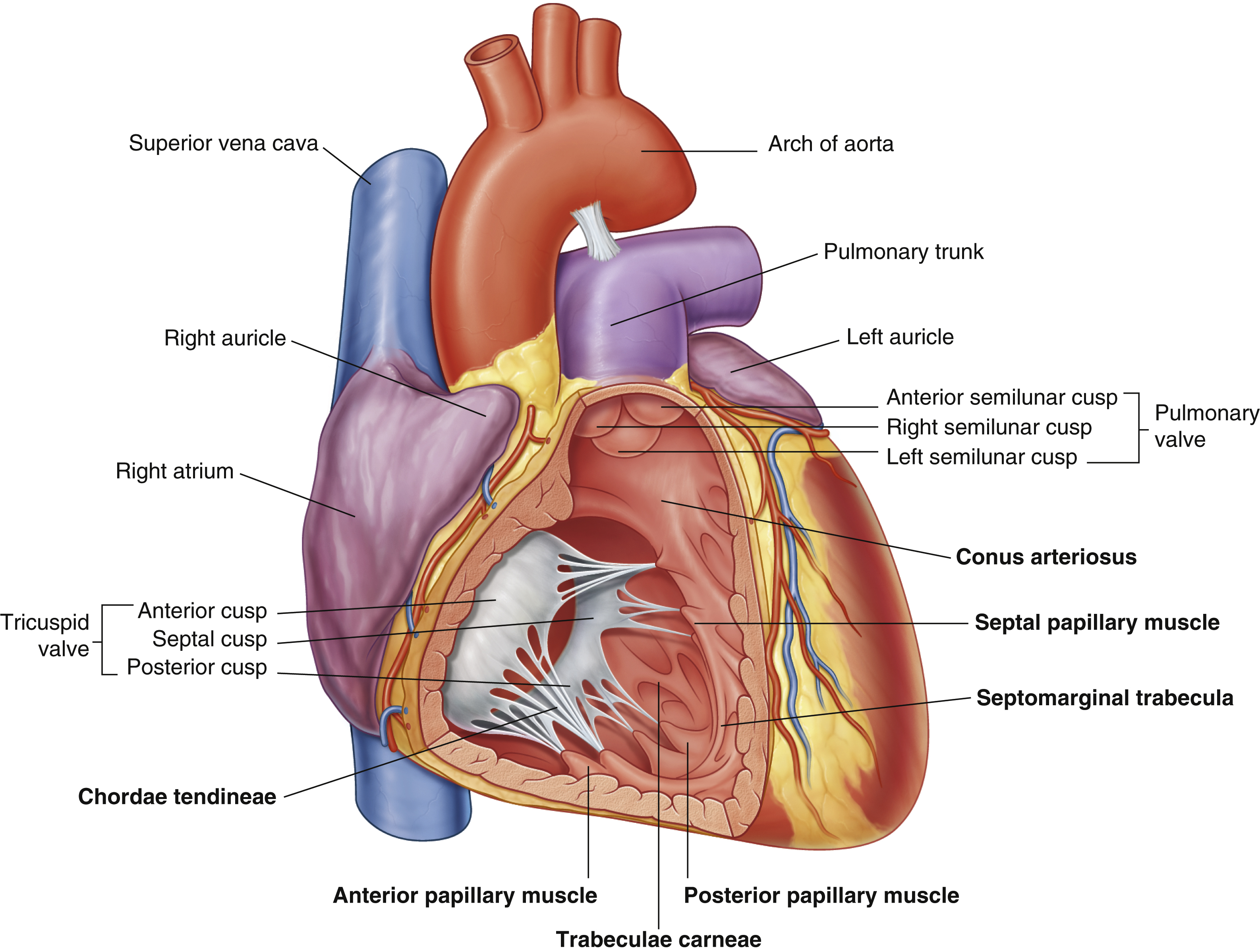
trabeculae carneae
rugous tissue
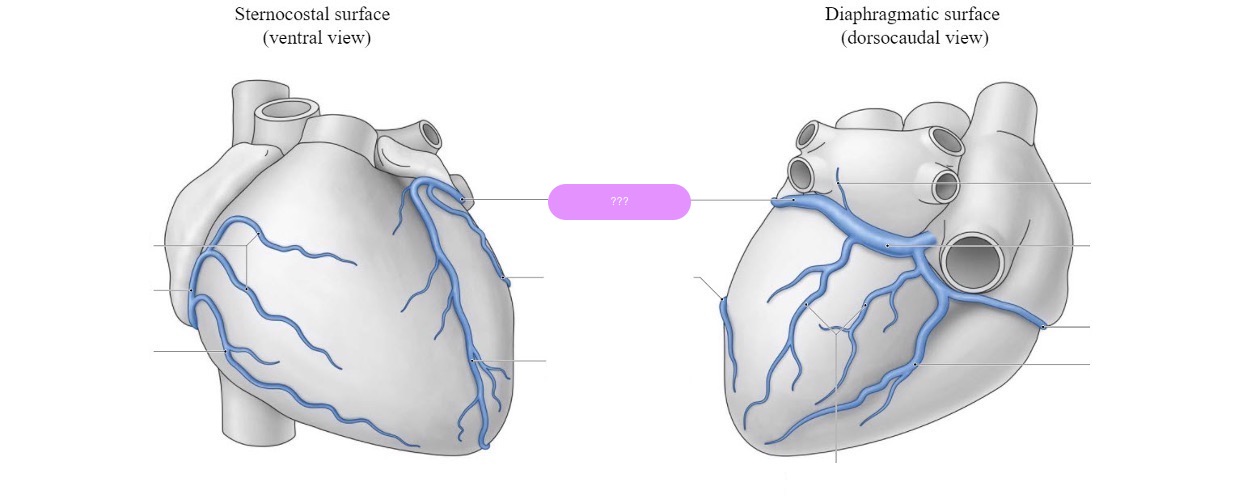
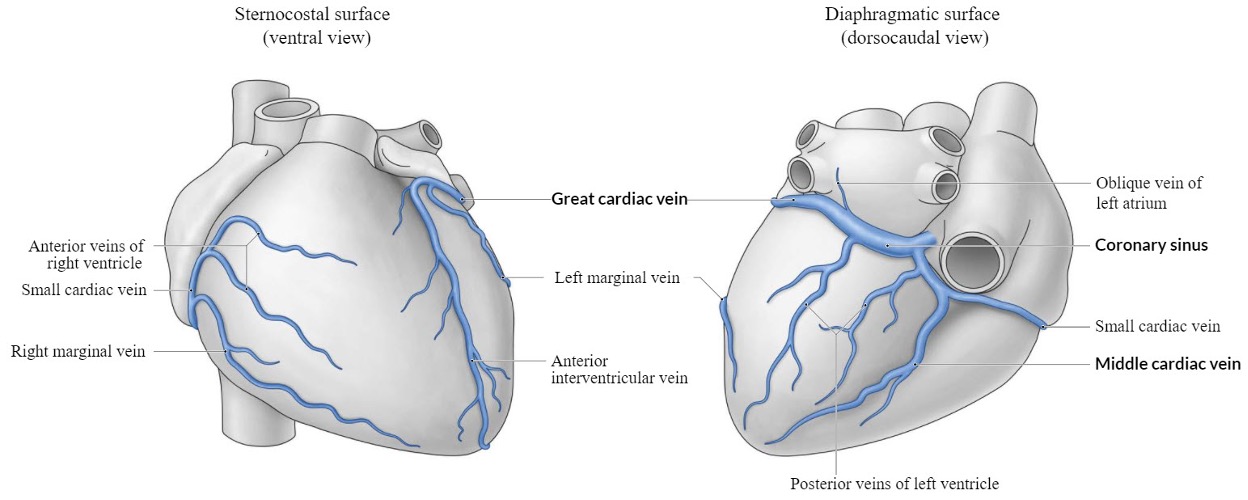
great cardiac vein

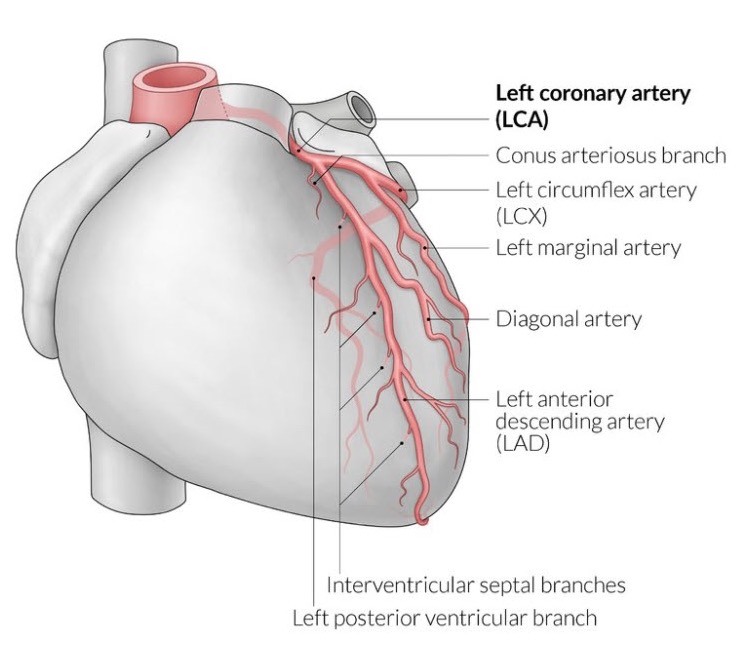
left anterior descending artery (LAD)
supplies:
anterior half of the ventricles
lateral borders of the ventricles
apex of the heart
interventricular septum
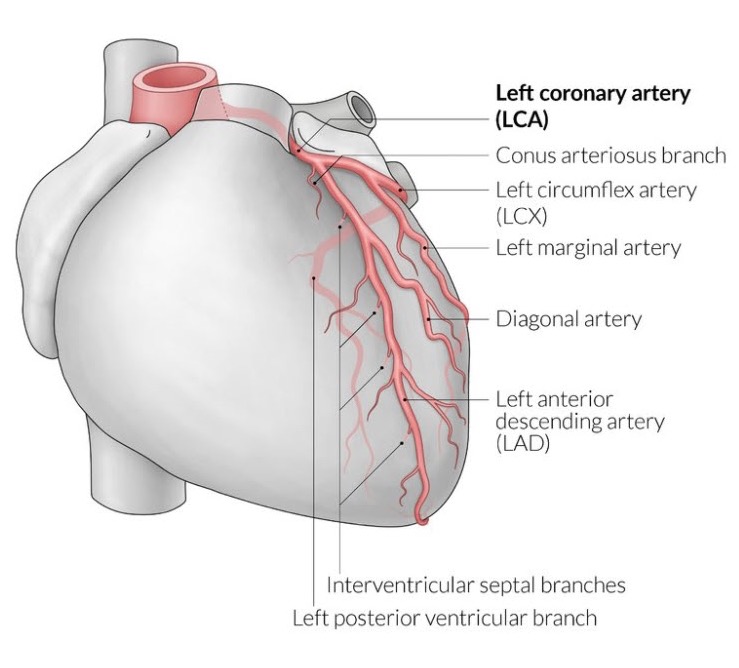

left coronary artery
supplies: left atrium, most of left ventricle, part of right ventricle, anterior two-thirds of IVS (interventricular septum), including the AV bundle
branch from the base of the aorta
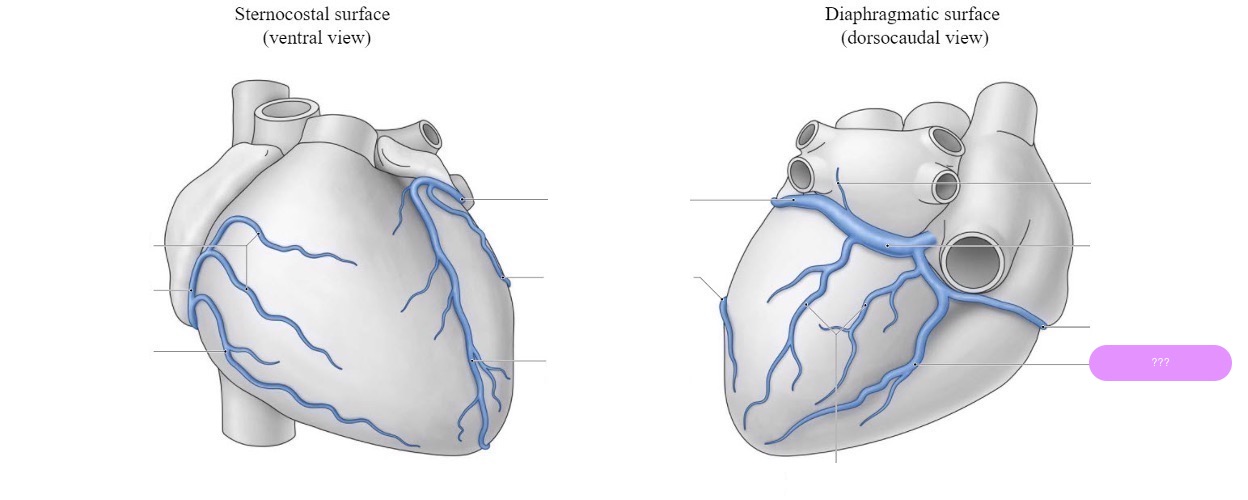
middle cardiac vein
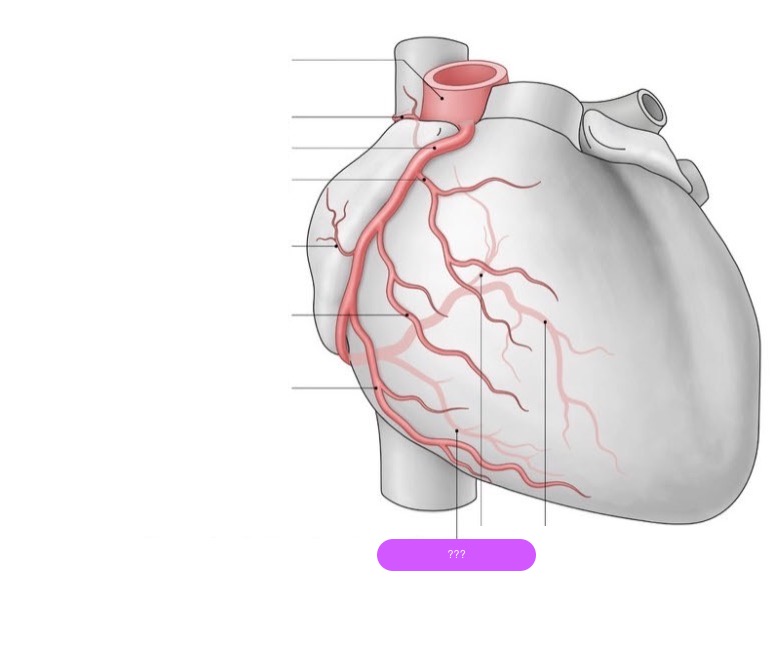
posterior descending artery (PDA)
Right Dominance (70-85% of people):
(PDA) originates from the right coronary artery (RCA).
The right coronary artery supplies both the PDA and the posterior part of the heart.
Left Dominance (10-15% of people):
The PDA originates from the left circumflex artery (LCx), a branch of the left coronary artery (LCA).
The left coronary artery thus supplies most of the heart, including the posterior portion.
Co-Dominance (5-10% of people):
The PDA receives contributions from both the right coronary artery and the left circumflex artery.
Both arteries share responsibility for the blood supply to the posterior part of the heart.
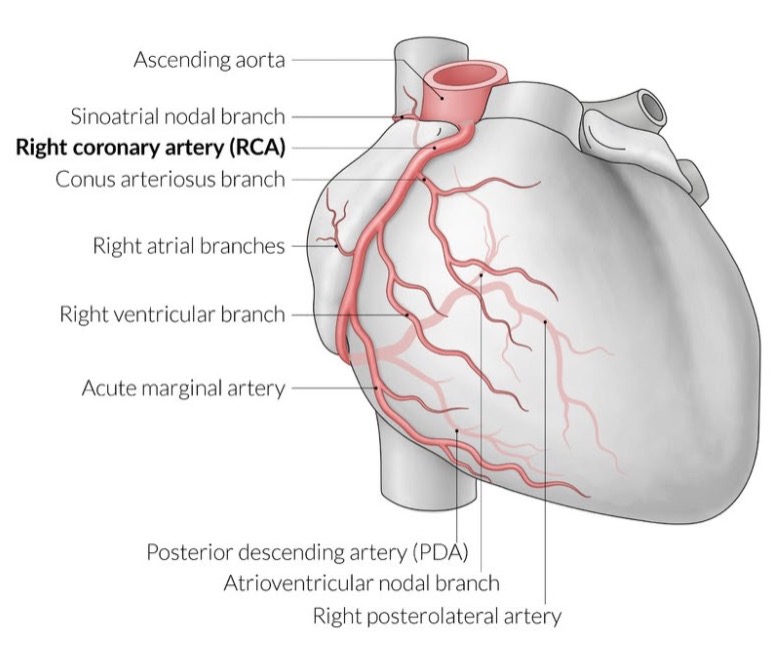

right coronary artery (RCA)
supplies:
diaphragmatic surface of the heart
the right atrium, most of right ventricle, diaphragmatic part of left ventricle, and posterior third of interventricular septum
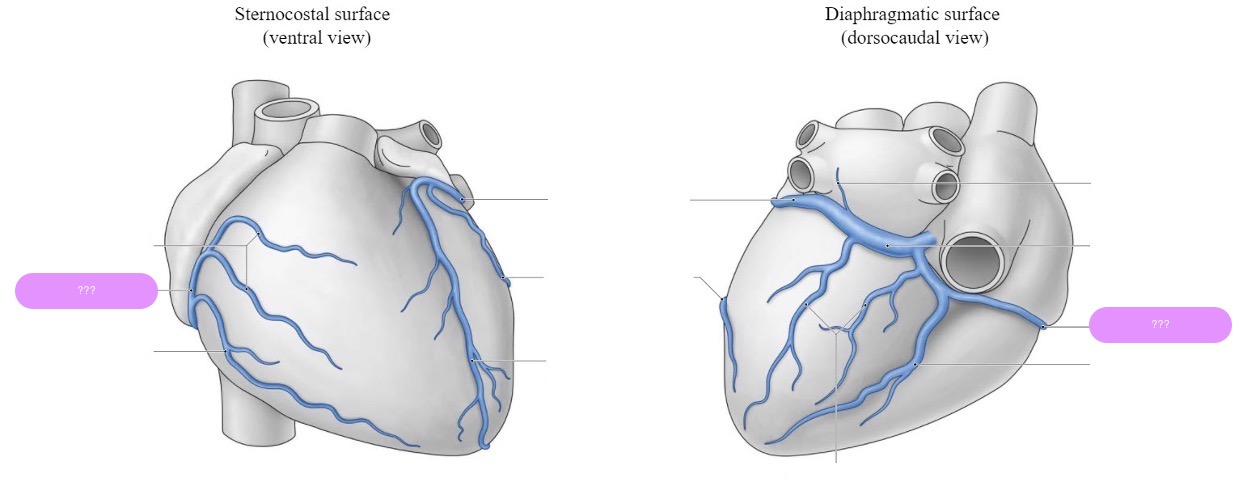
small cardiac vein
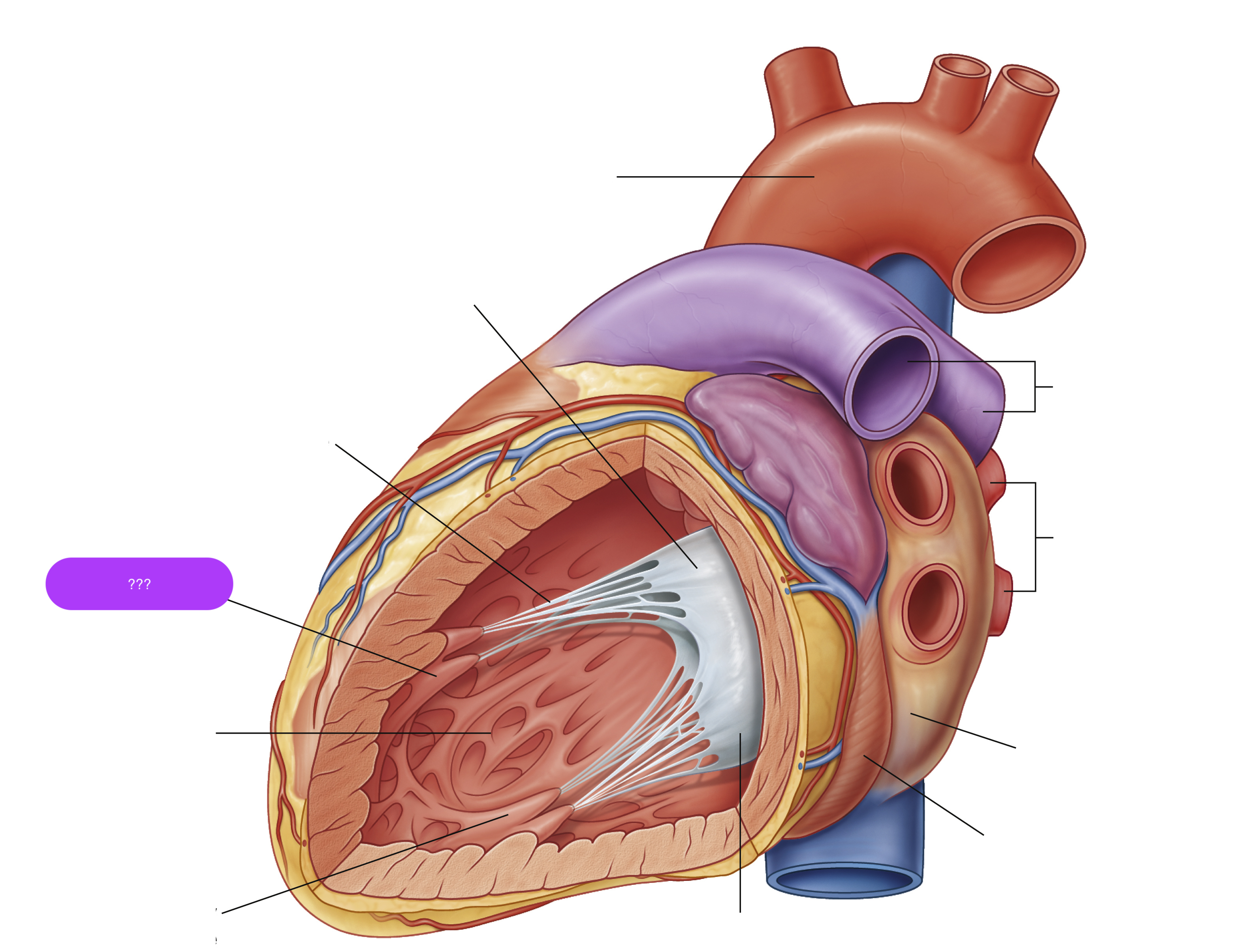
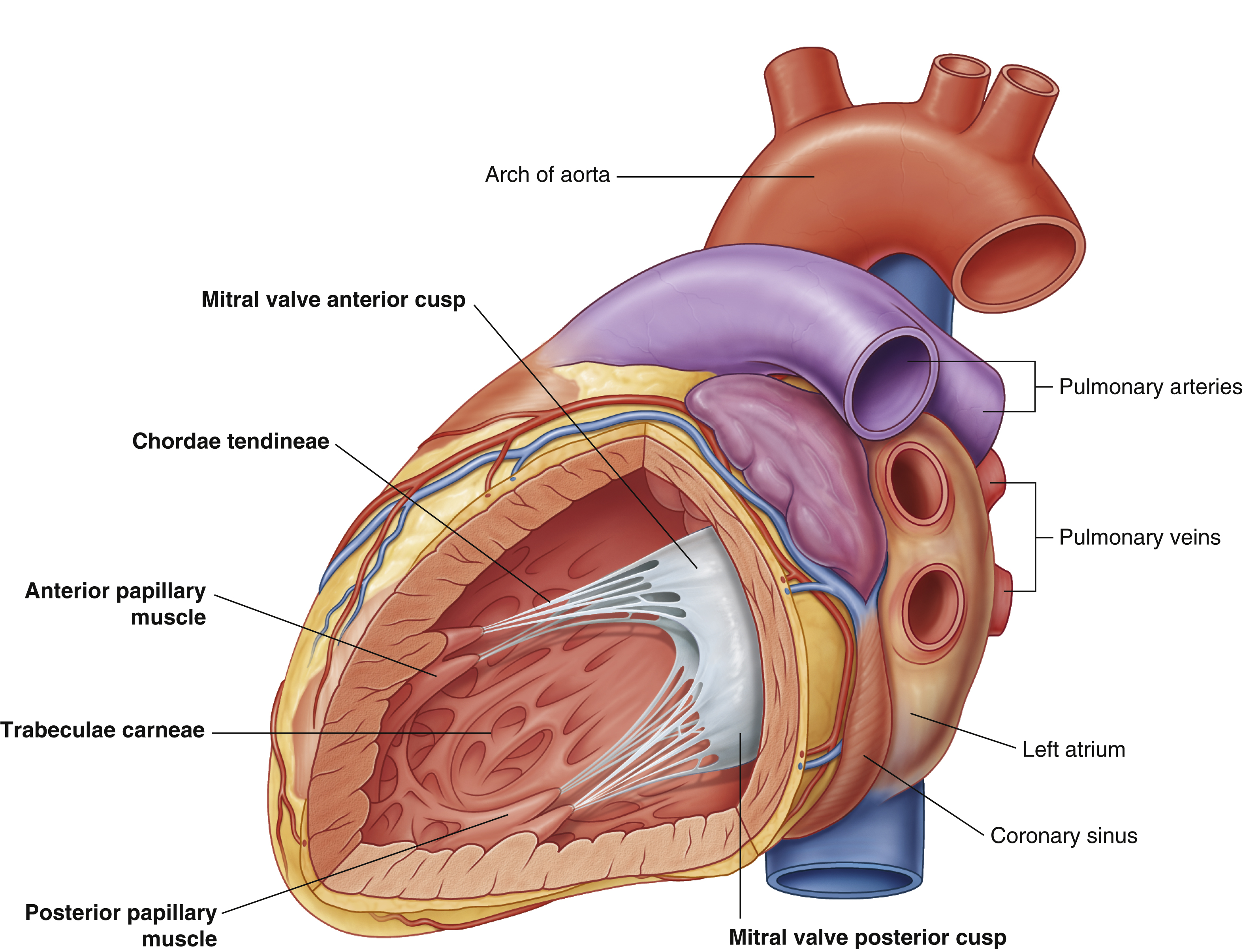
anterior papillary muscle

arch of aorta
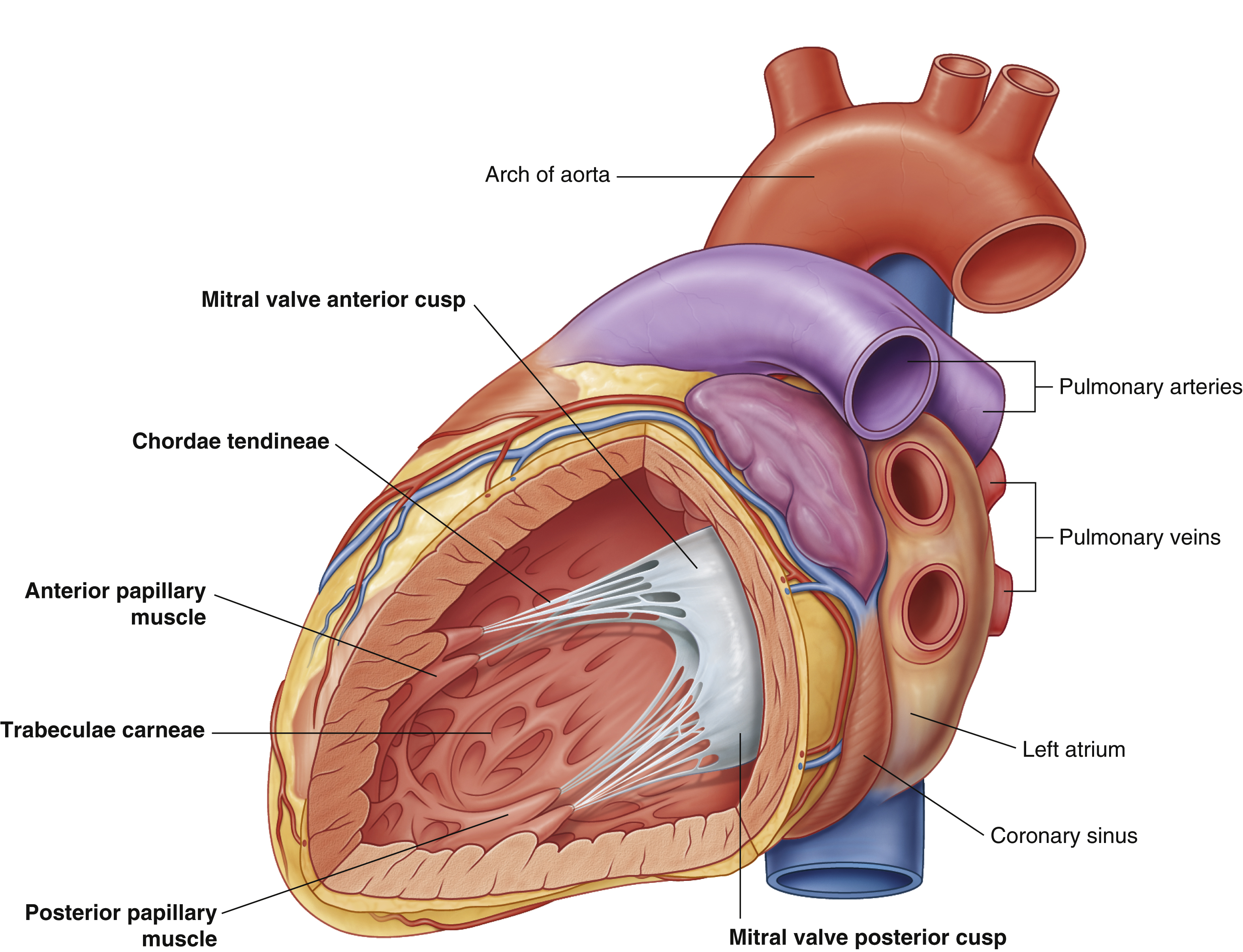

chordae tendineae
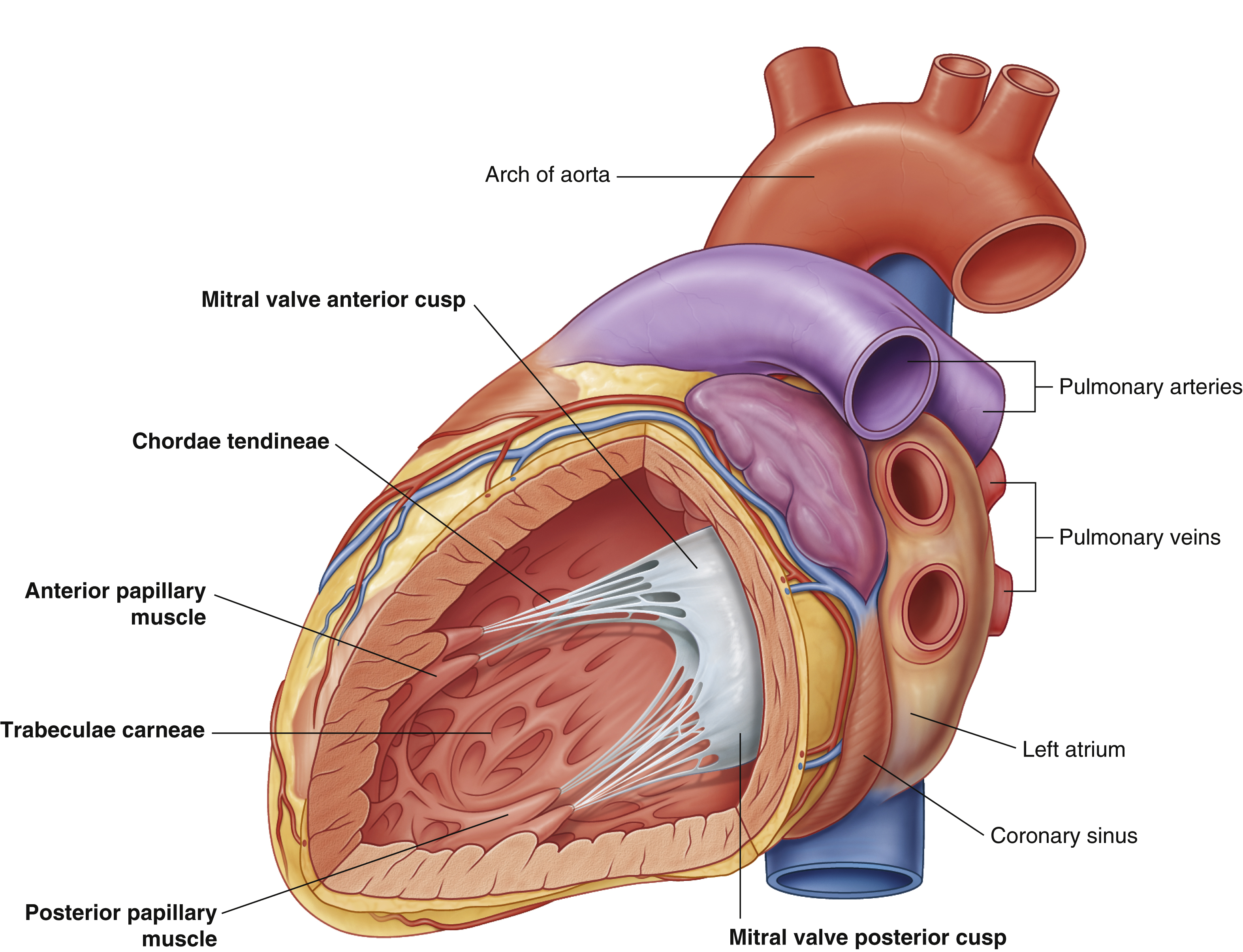
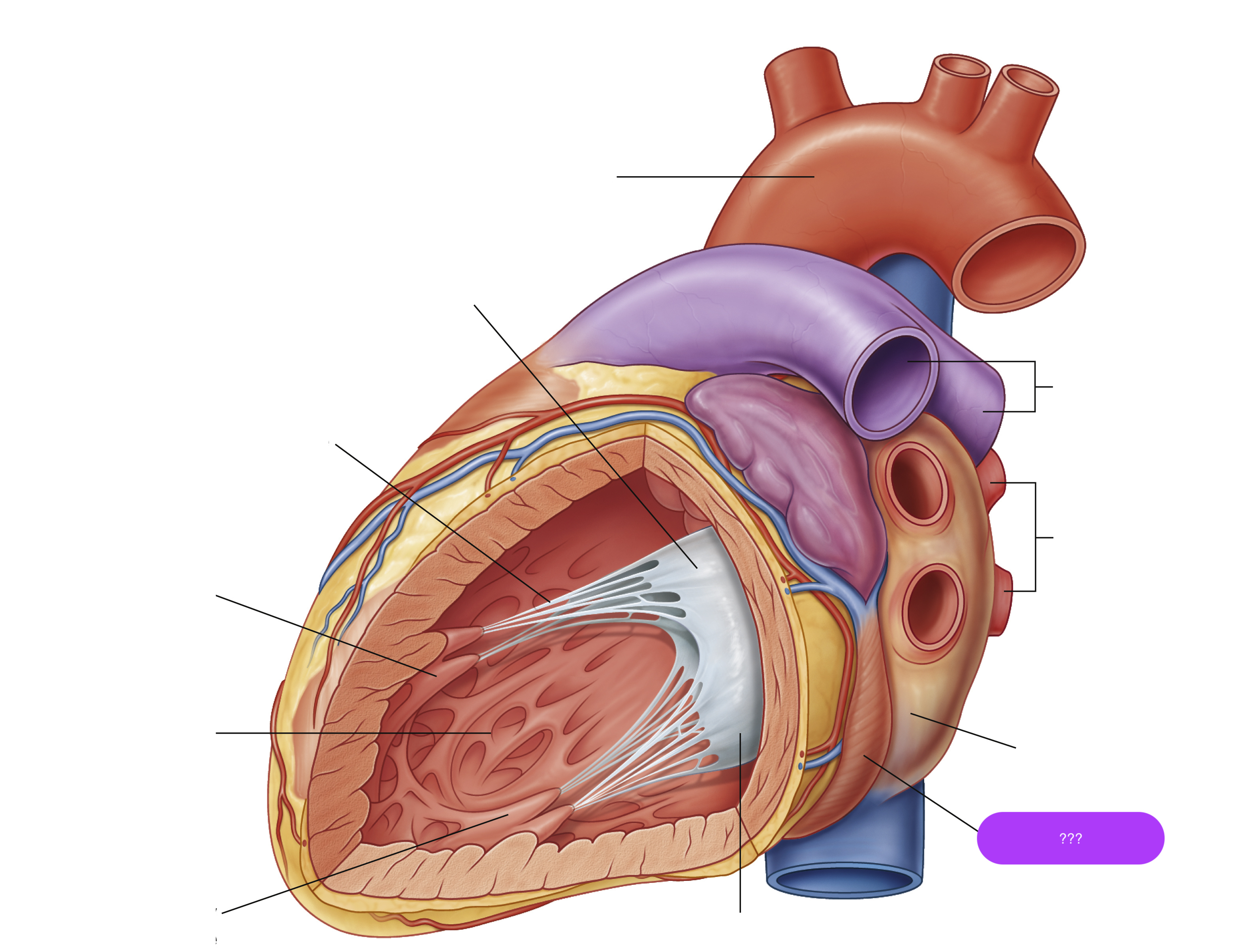
coronary sinus
largest vein of the heart

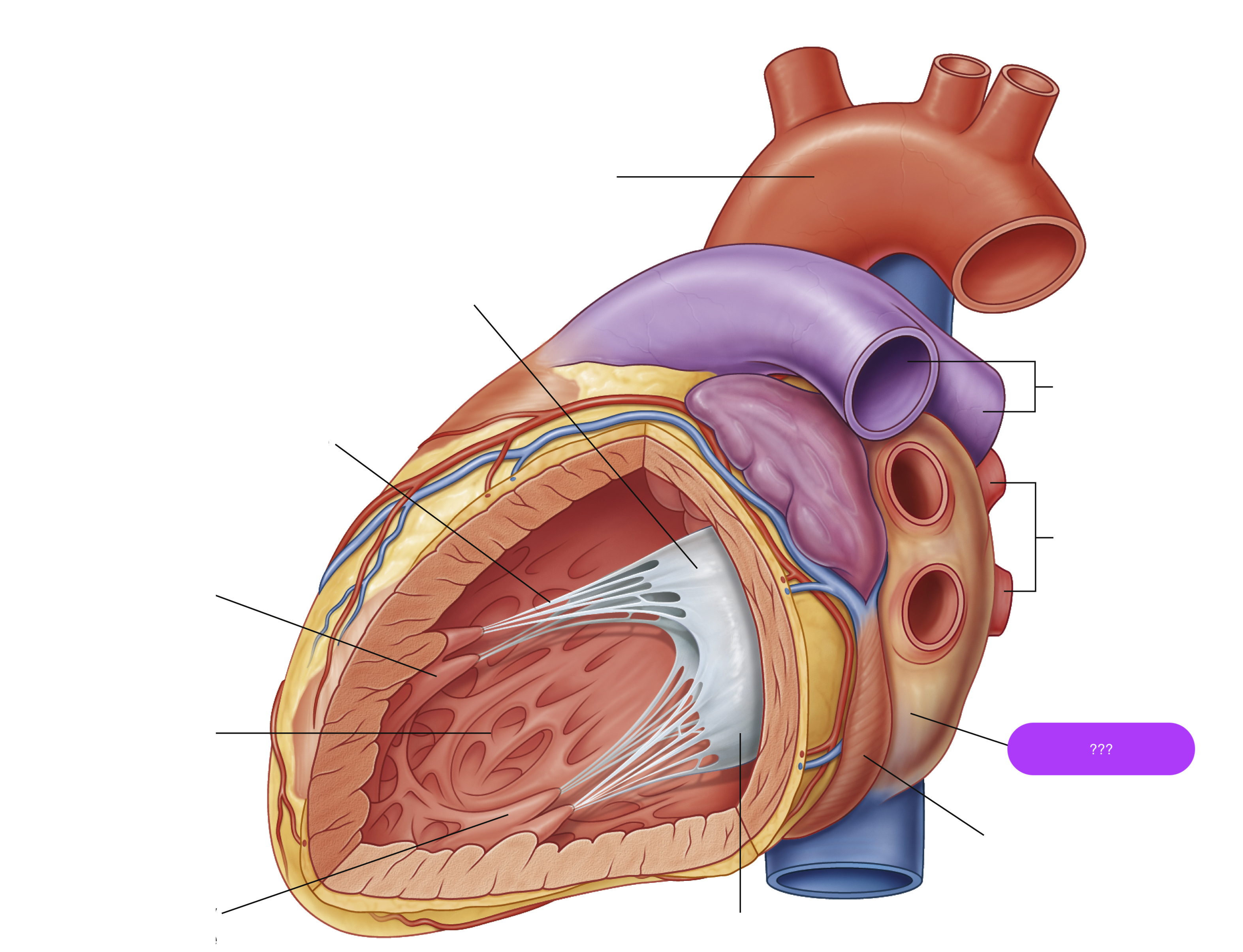
left atrium
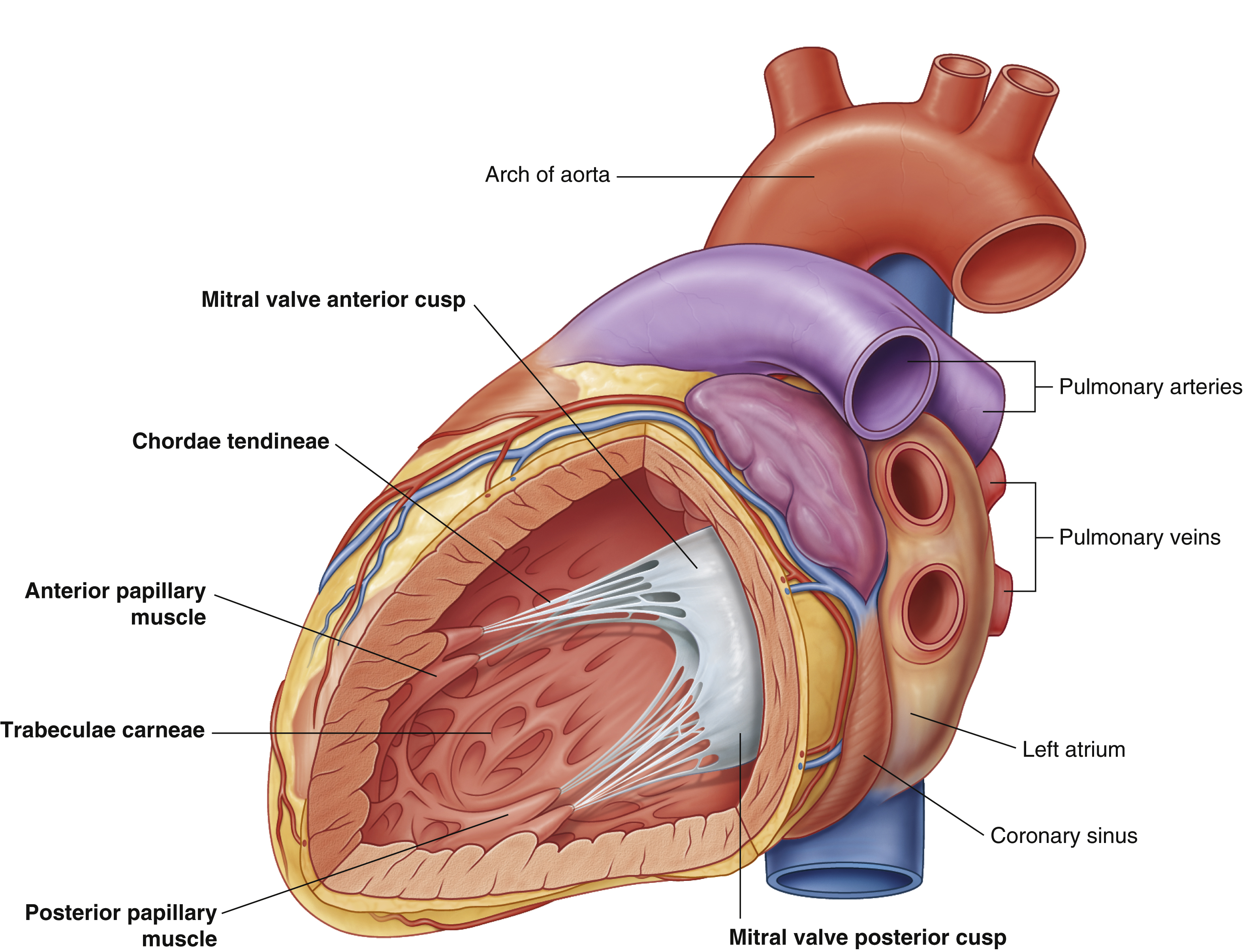
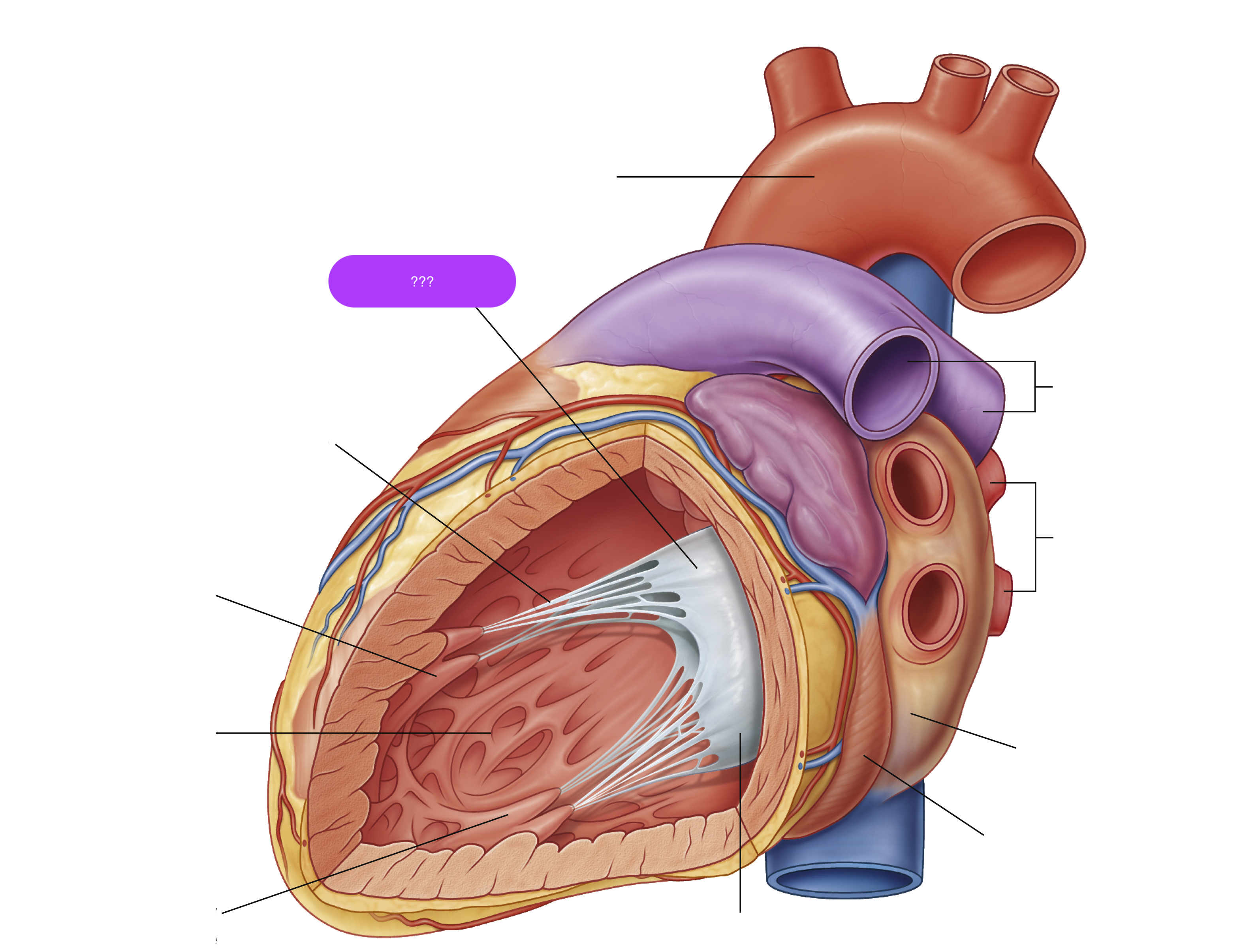
mitral valve anterior cusp
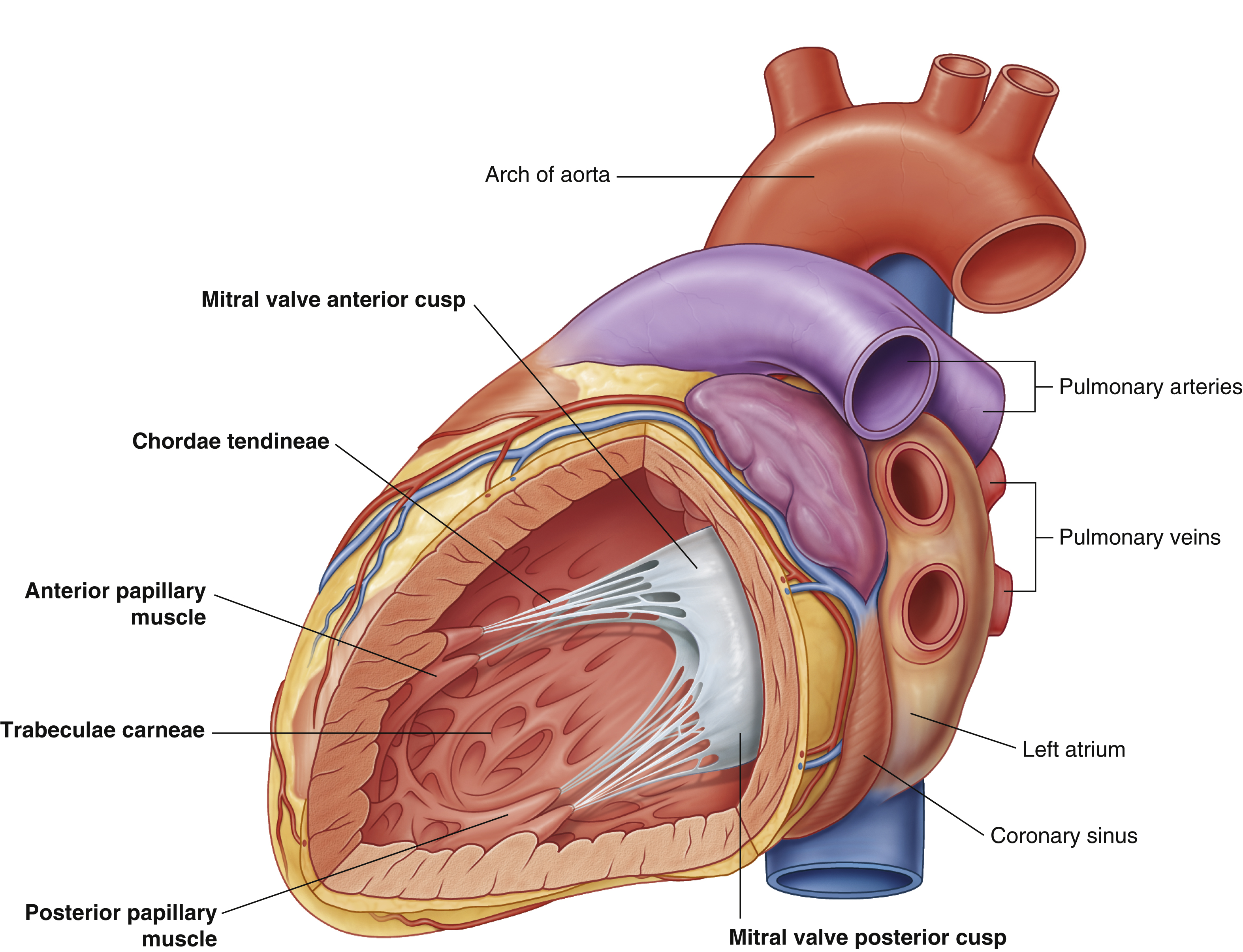
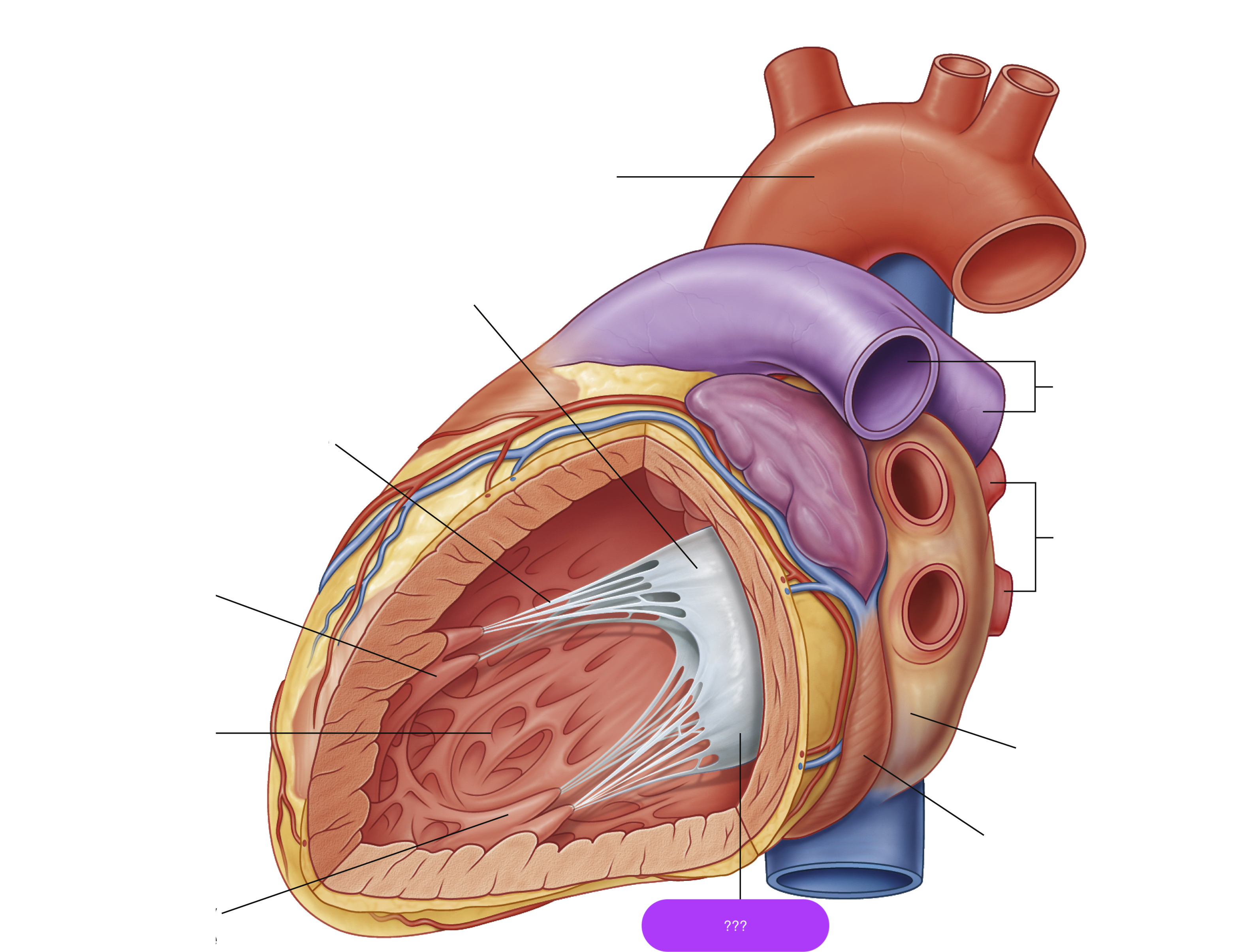
mitral valve posterior cusp
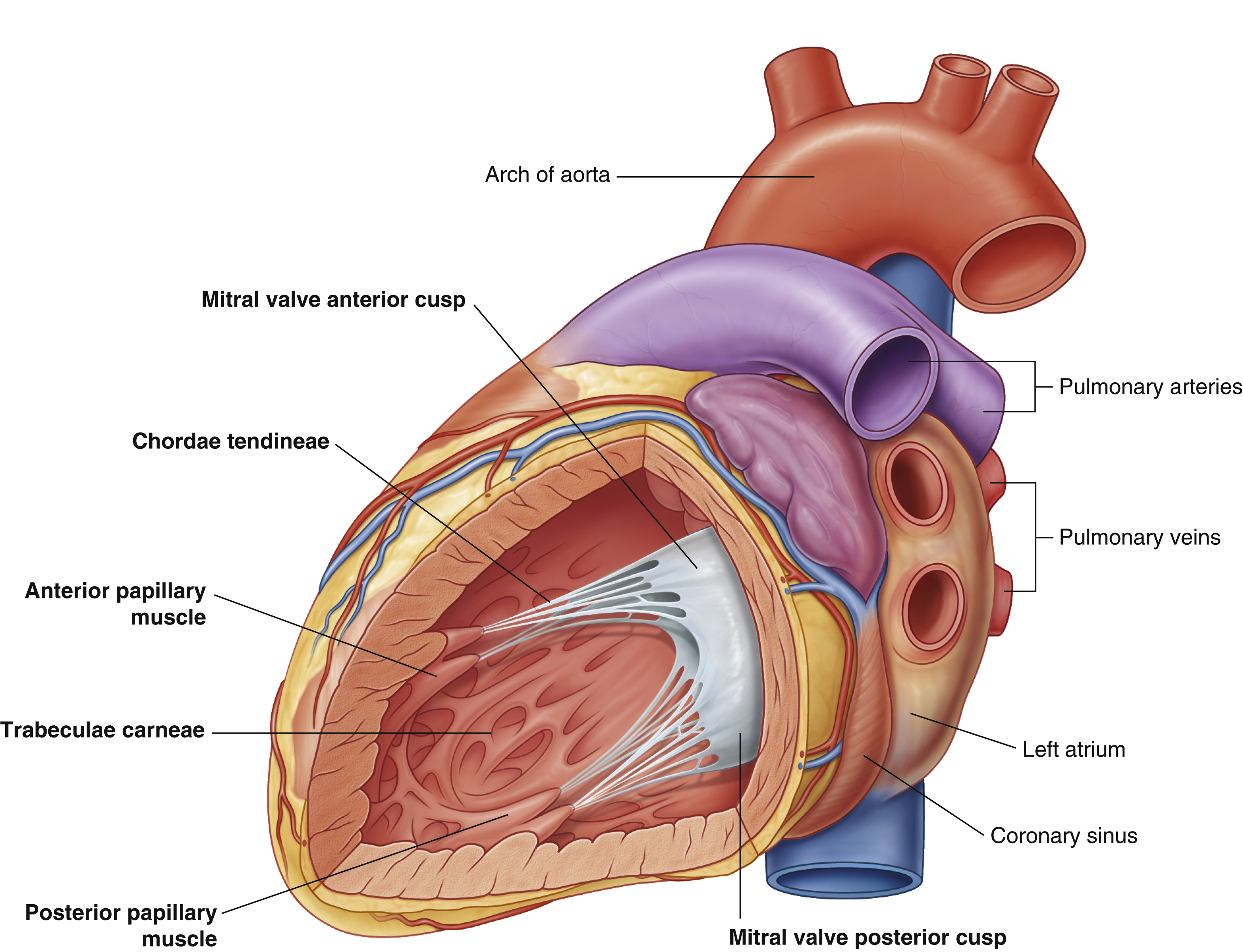
posterior papillary muscle
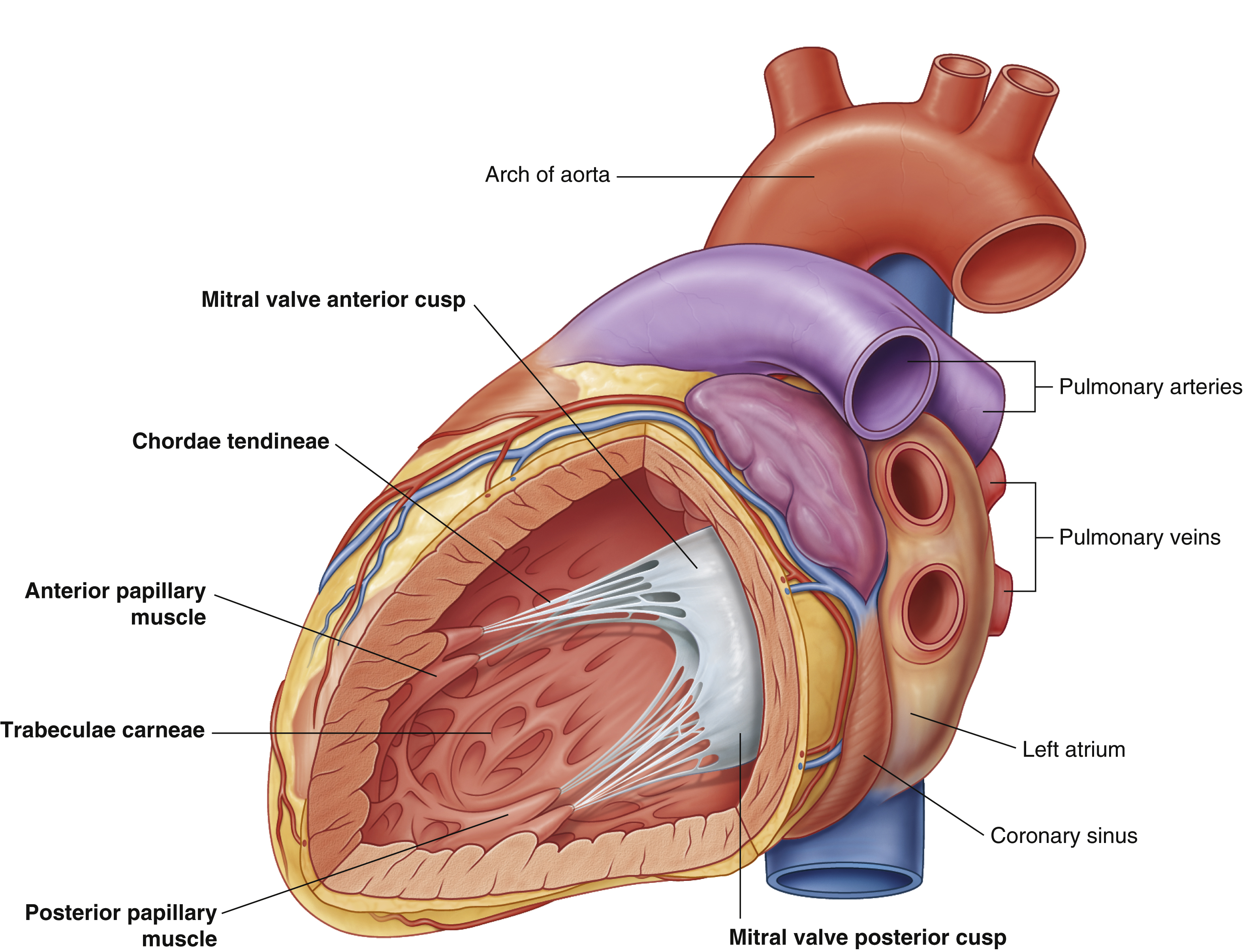
pulmonary arteries
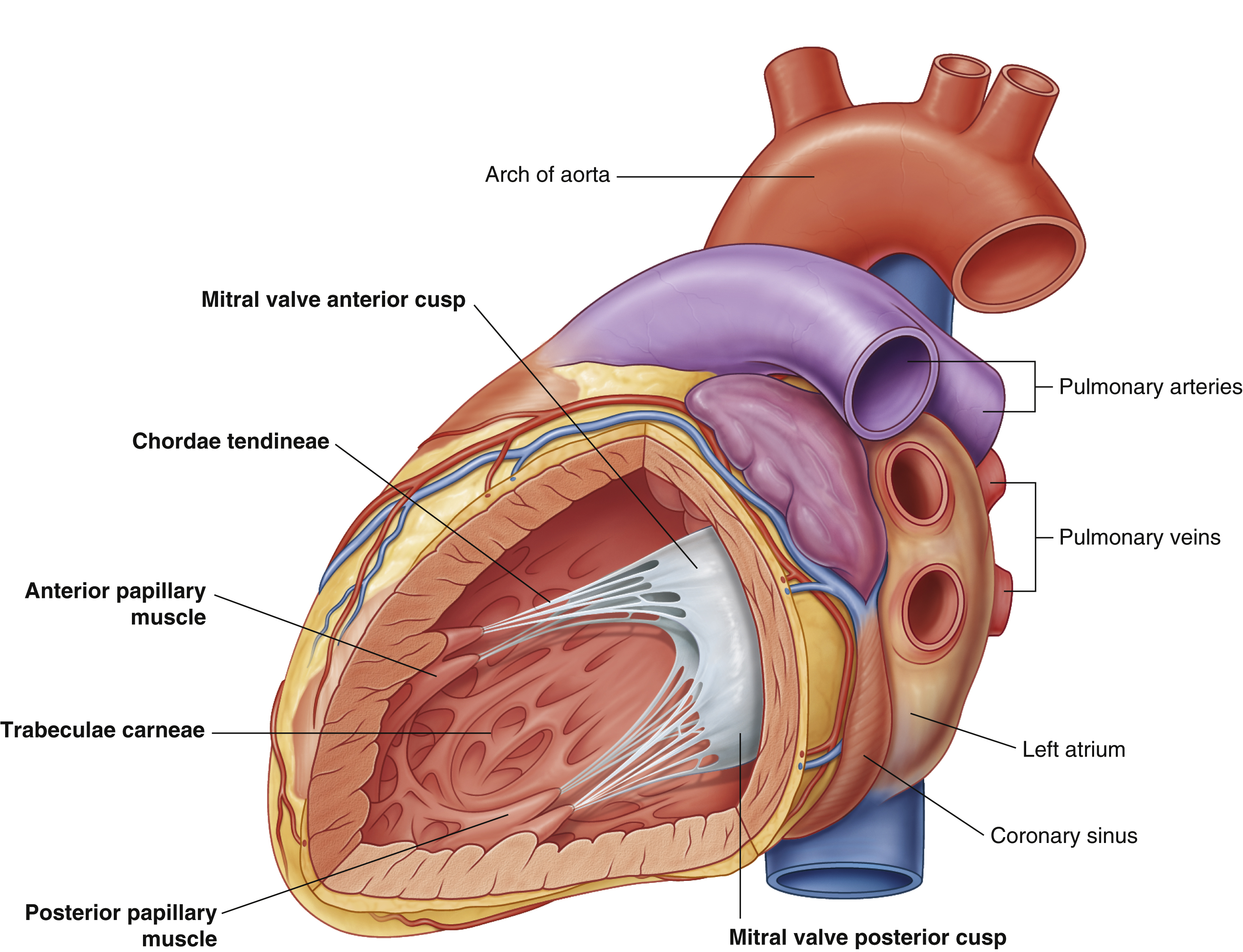
pulmonary veins
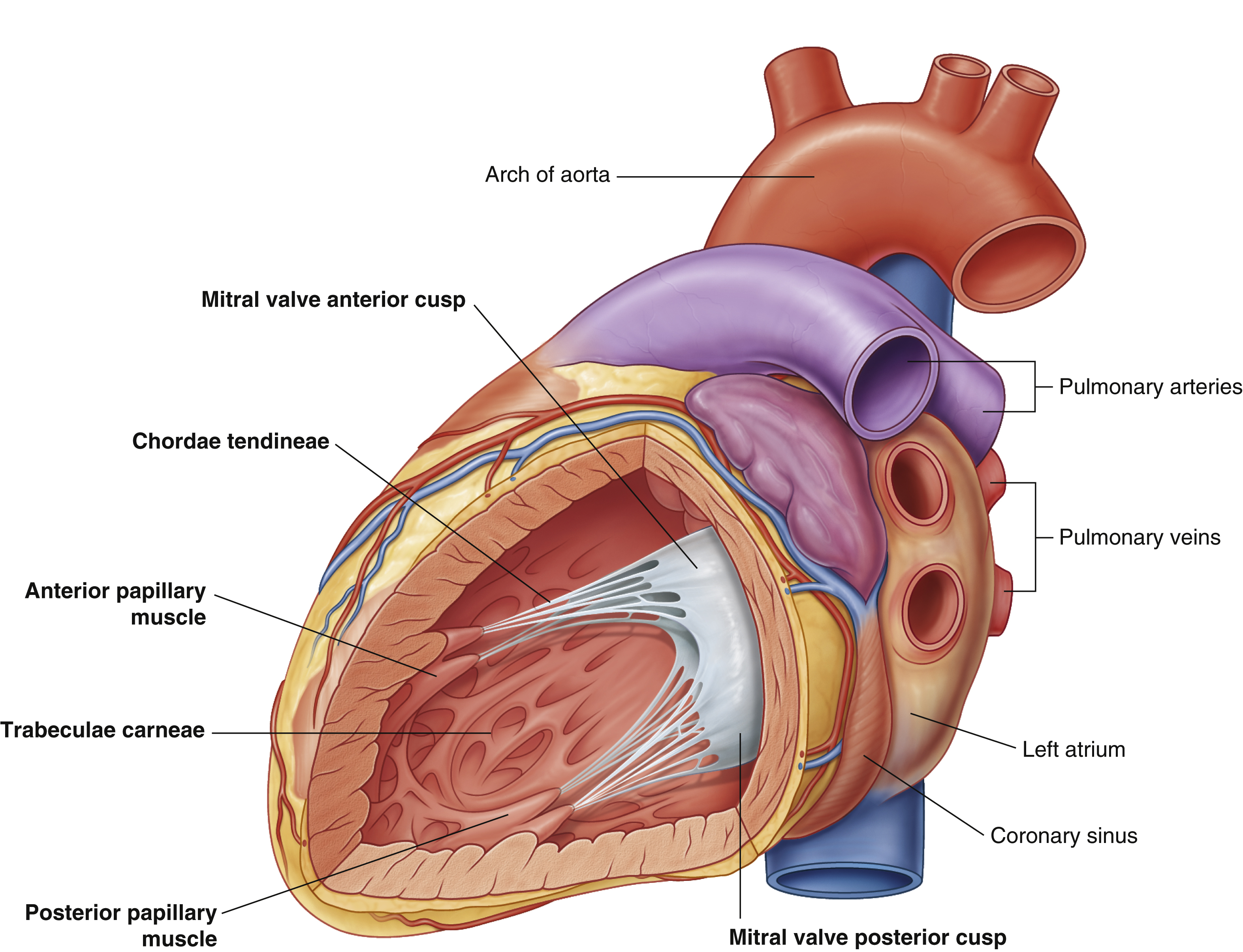
trabeculae carneae
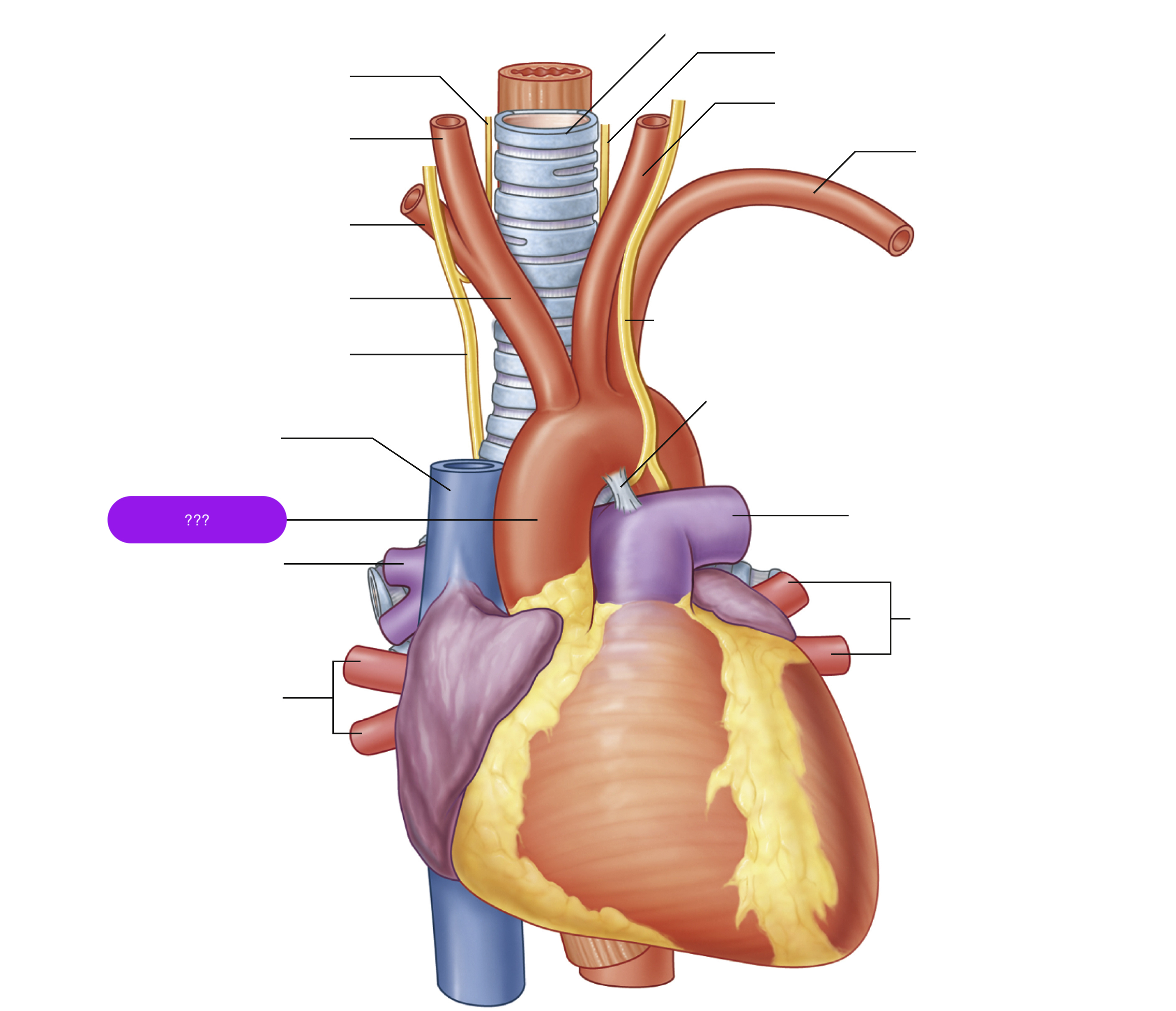
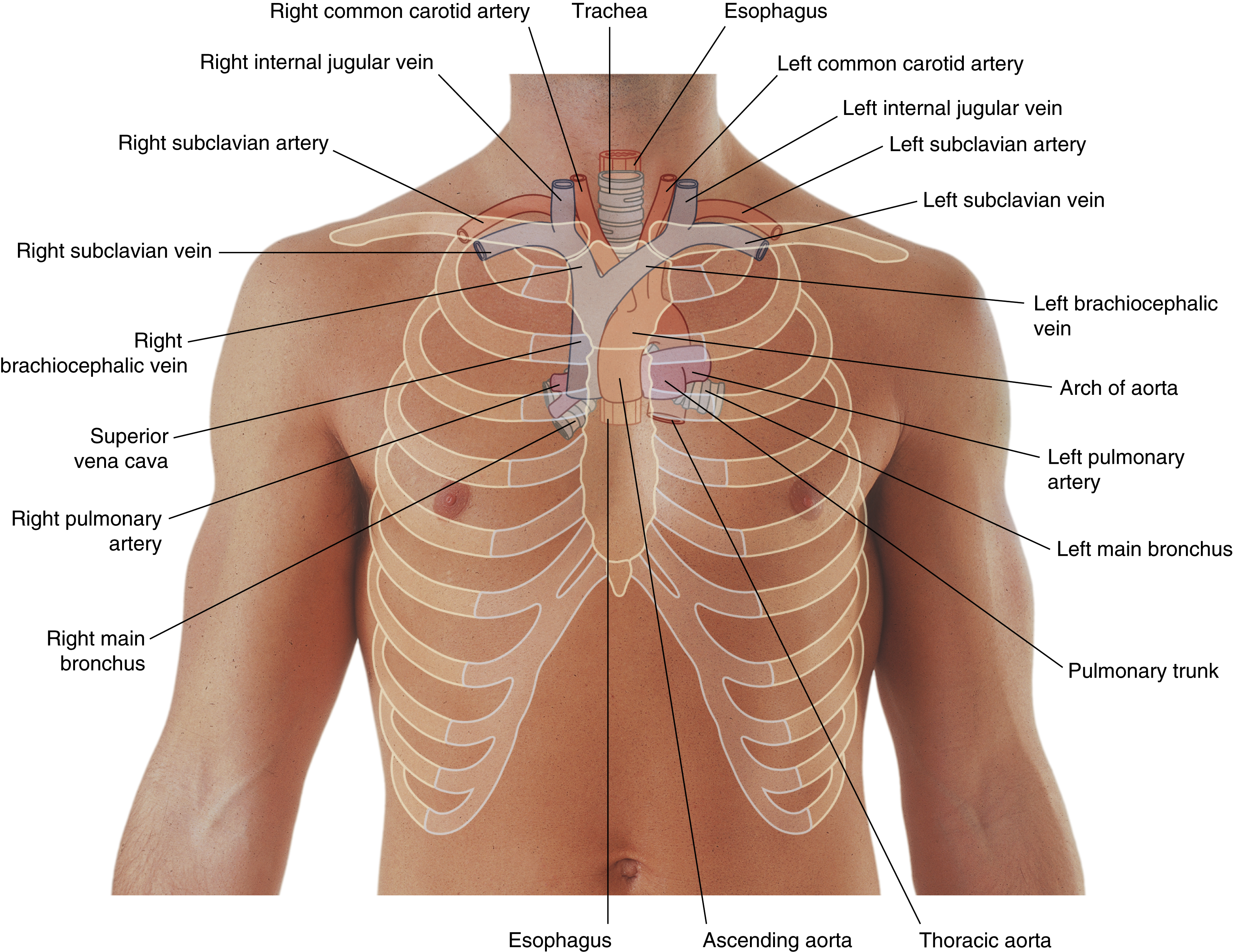
ascending aorta
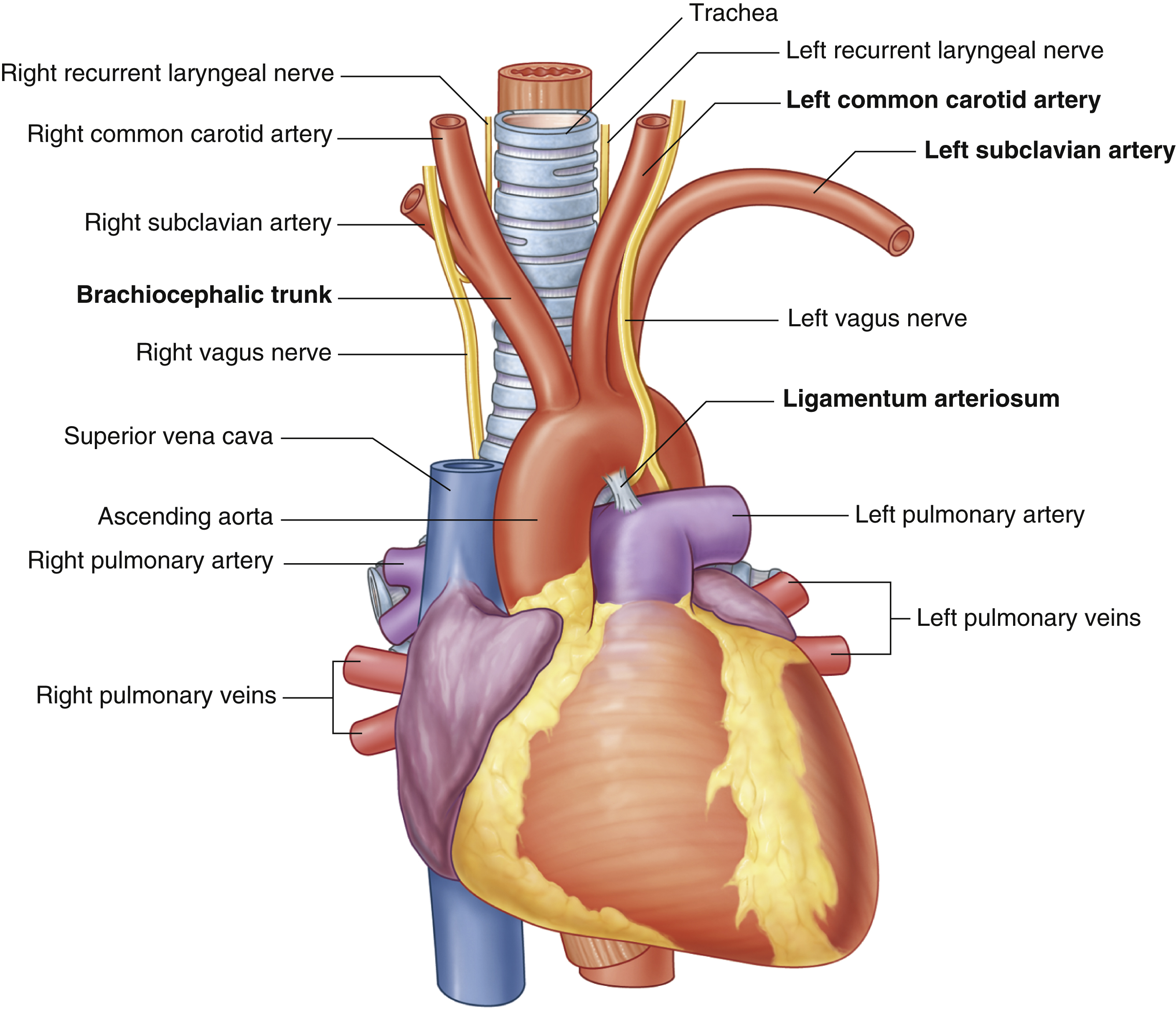
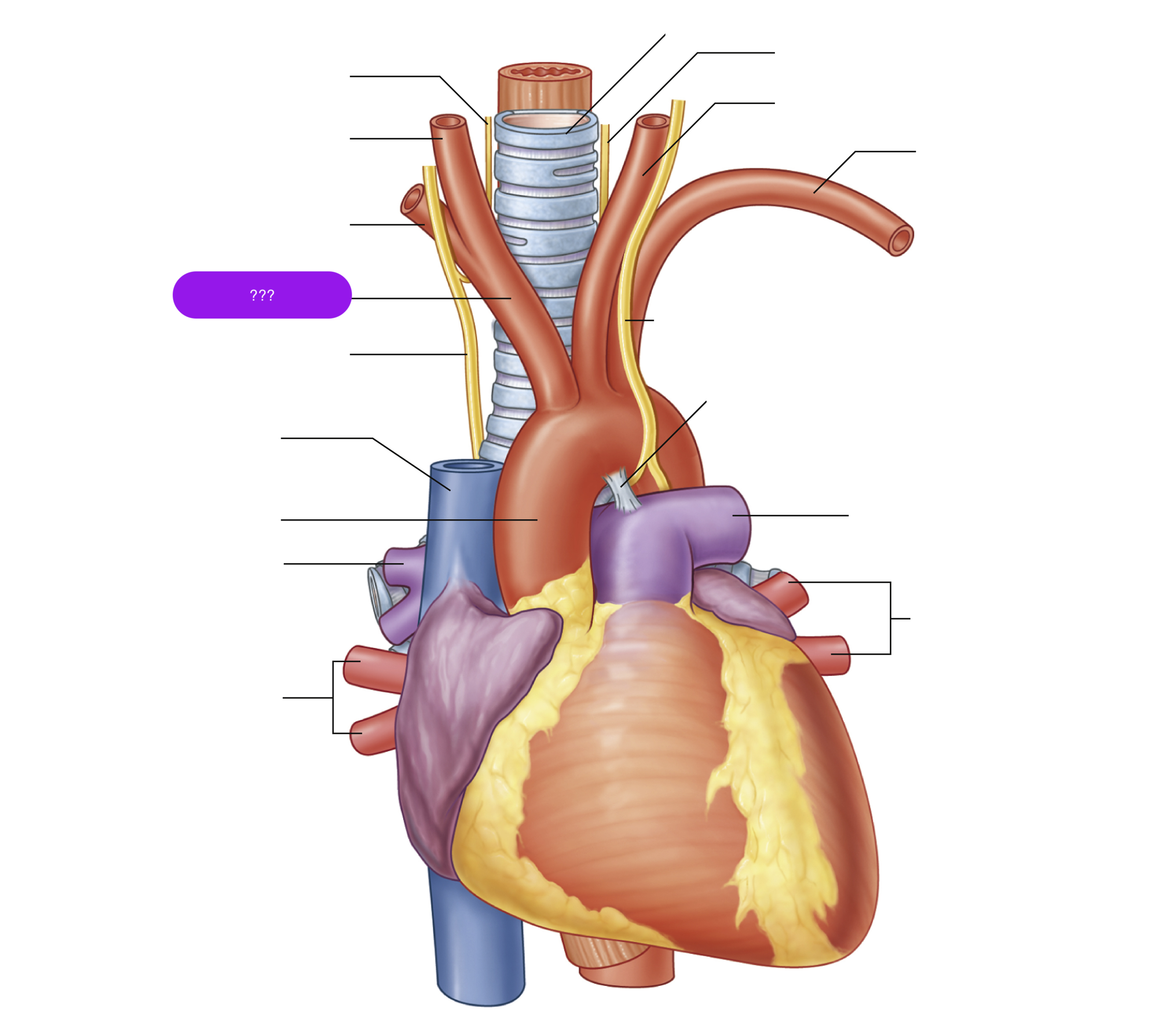
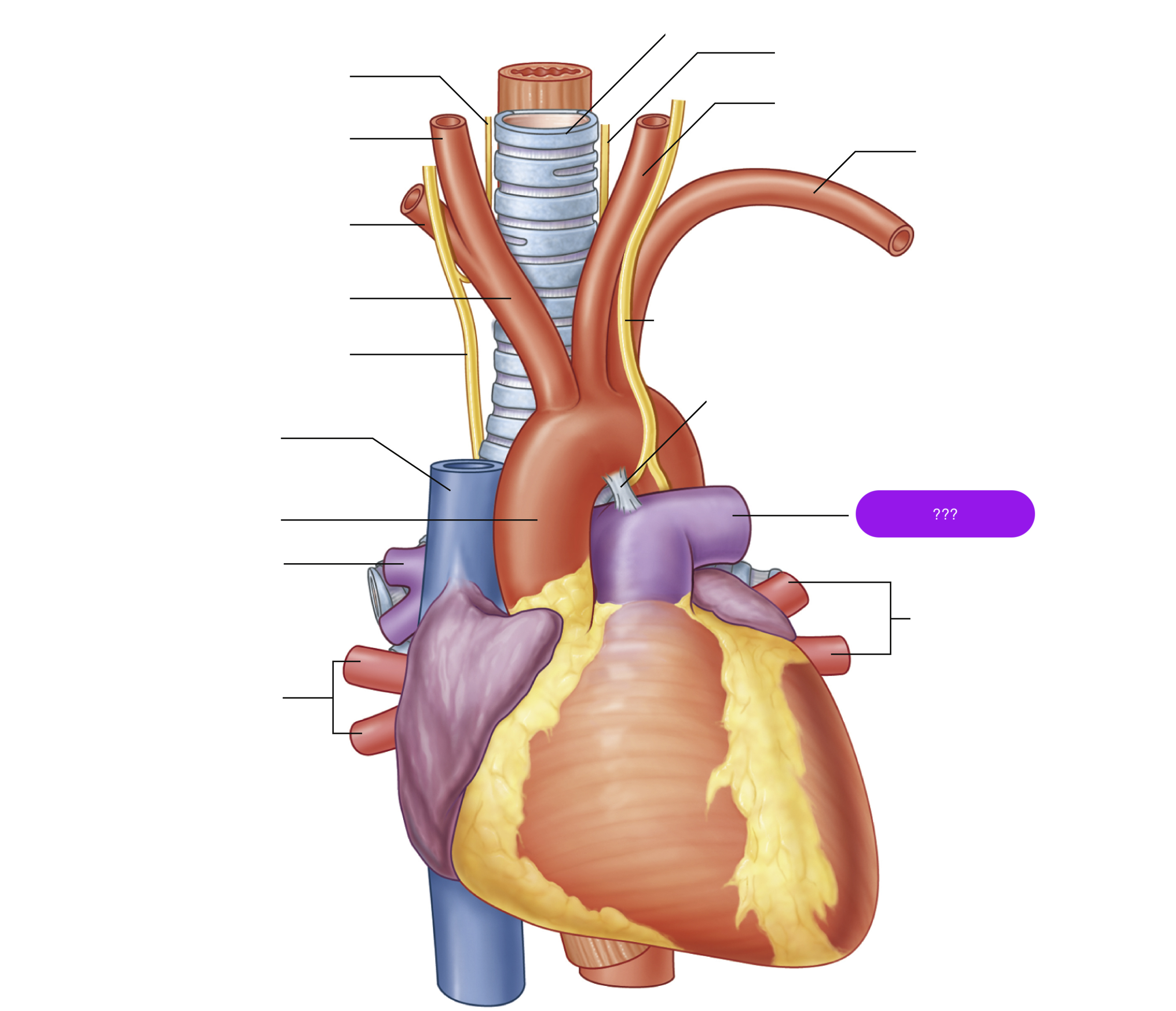
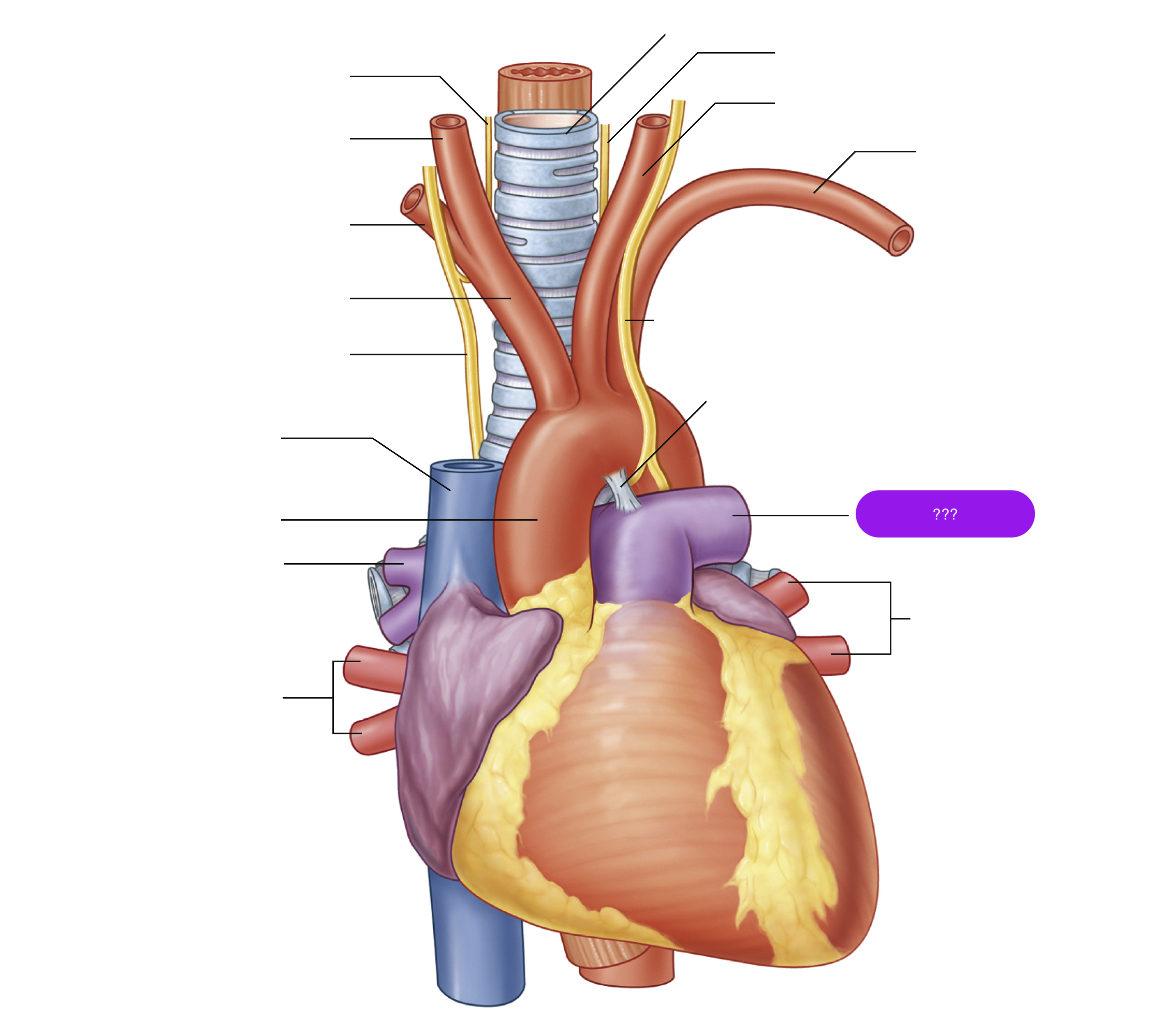
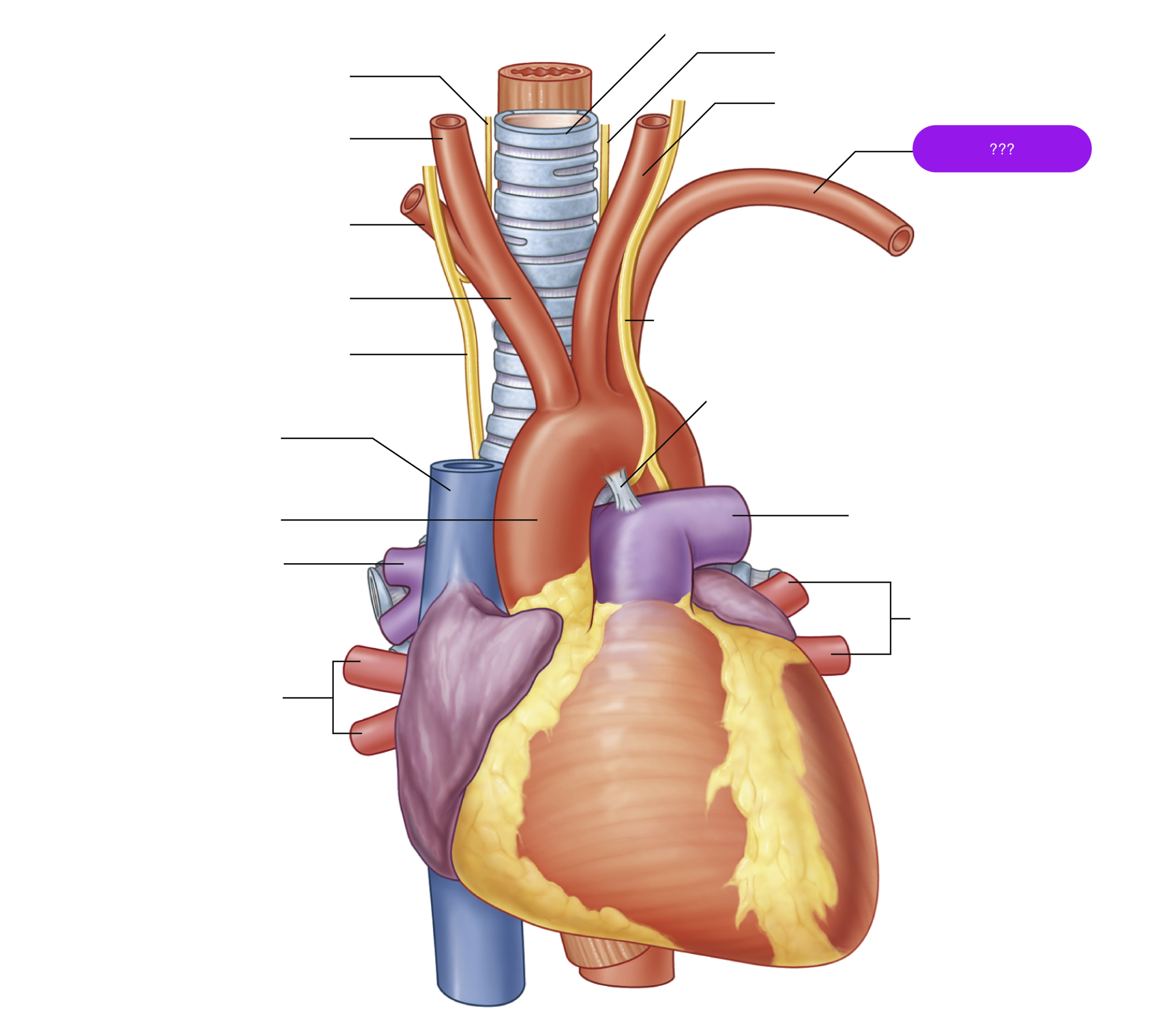
brachiocephalic trunk
first branch of aortic arch → carries oxygenated blood to the upper right side of your body
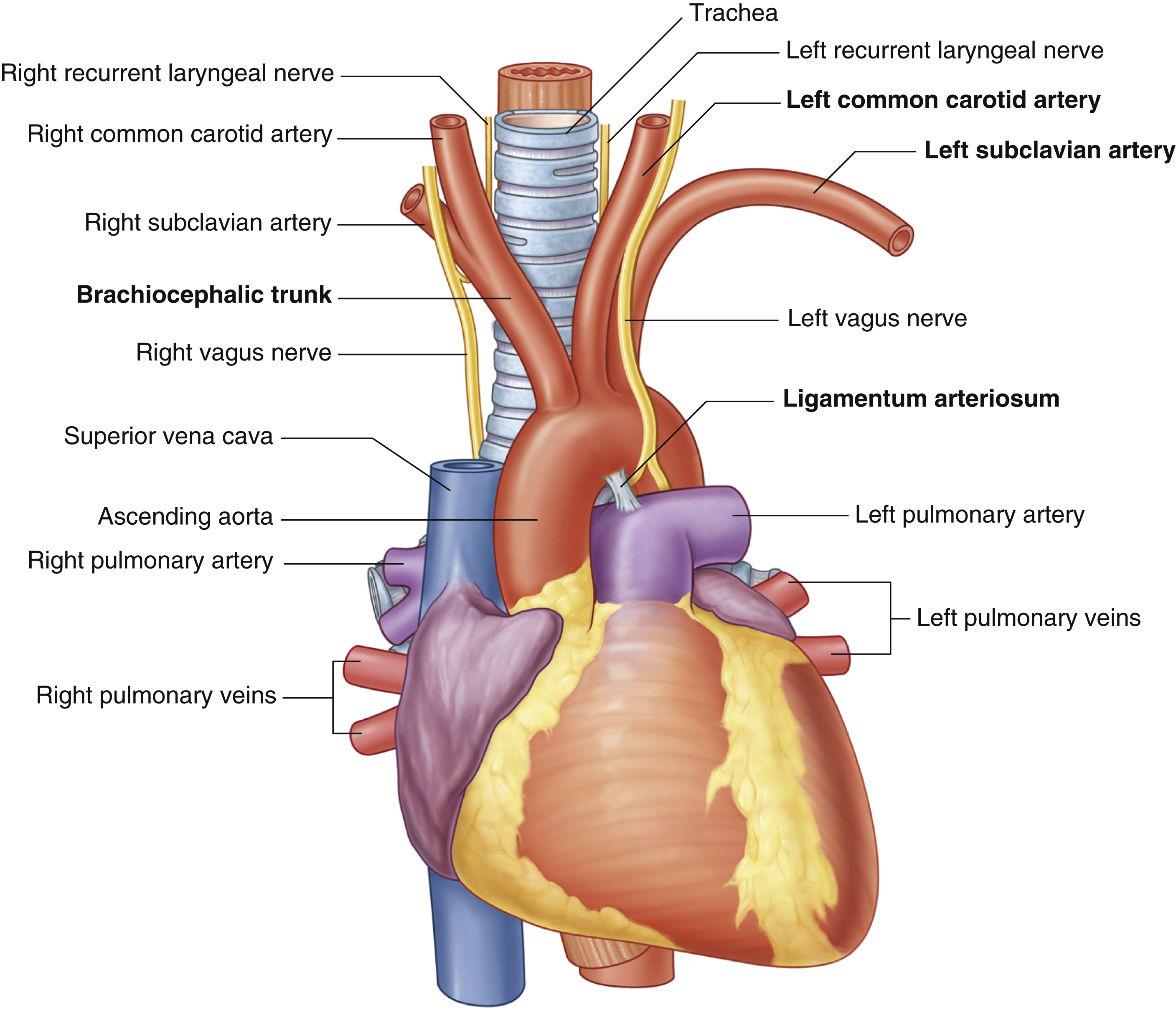
descending aorta
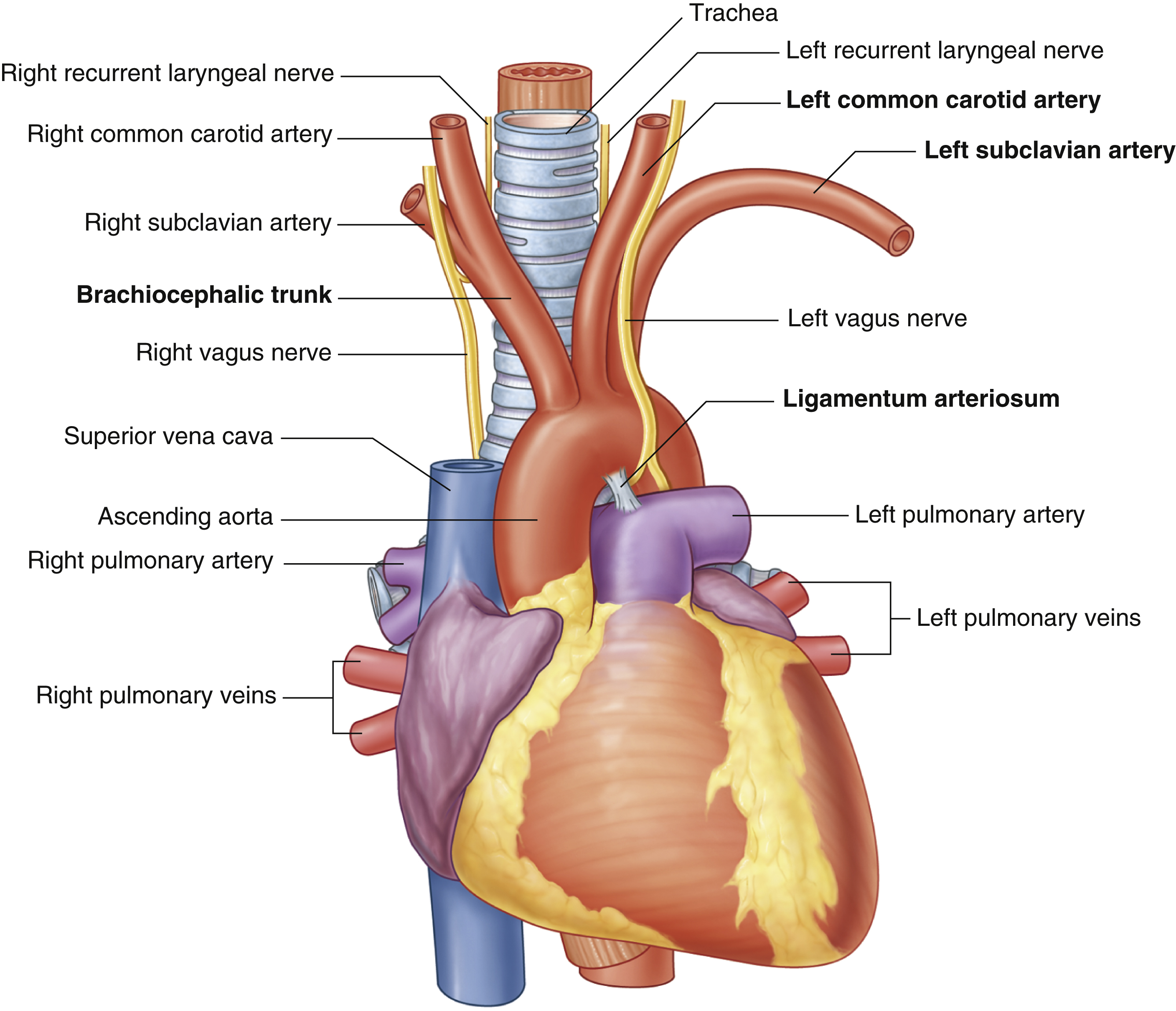

inferior vena cava

left common carotid artery
oxygenated blood → brain, face, and neck
(left originates from aortic arch)
(superior mediastinum)

left pulmonary artery

left pulmonary artery
left subclavian artery
oxygenated blood → head, neck, arms
pulmonary trunk
right common carotid artery
oxygenated blood → brain, face, and neck
(right originates from brachiocephalic trunk)
(superior mediastinum)

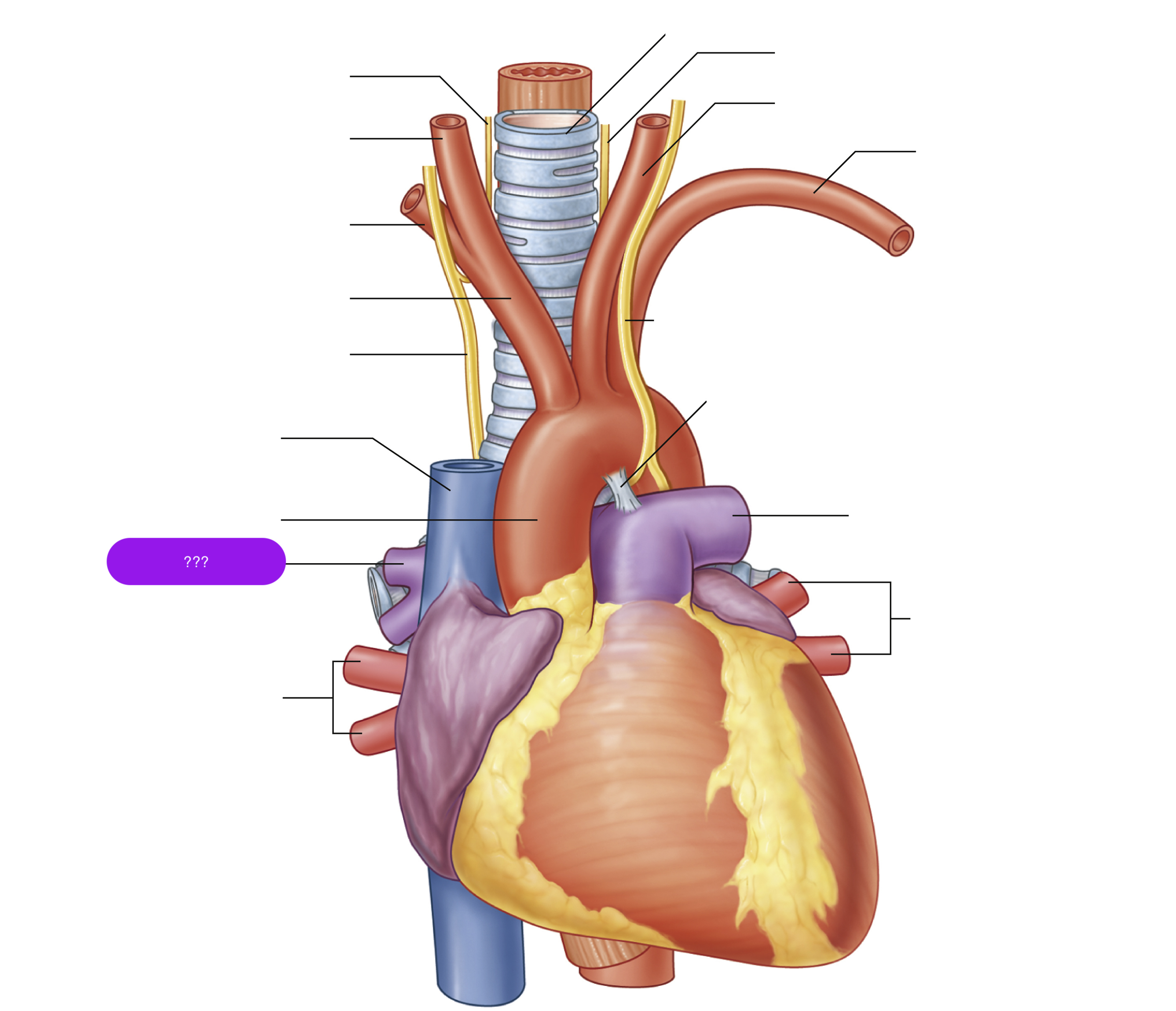
right pulmonary artery
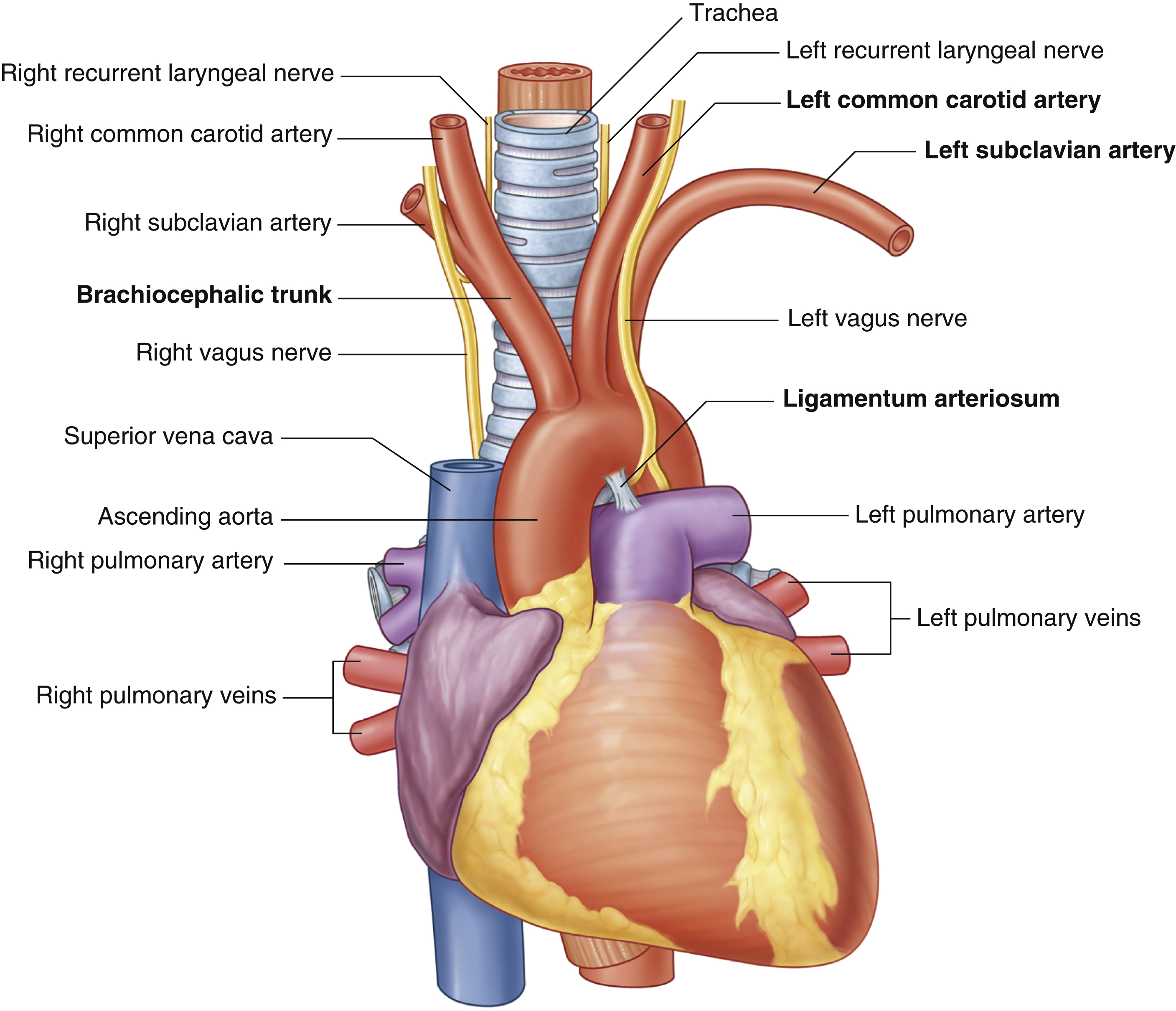
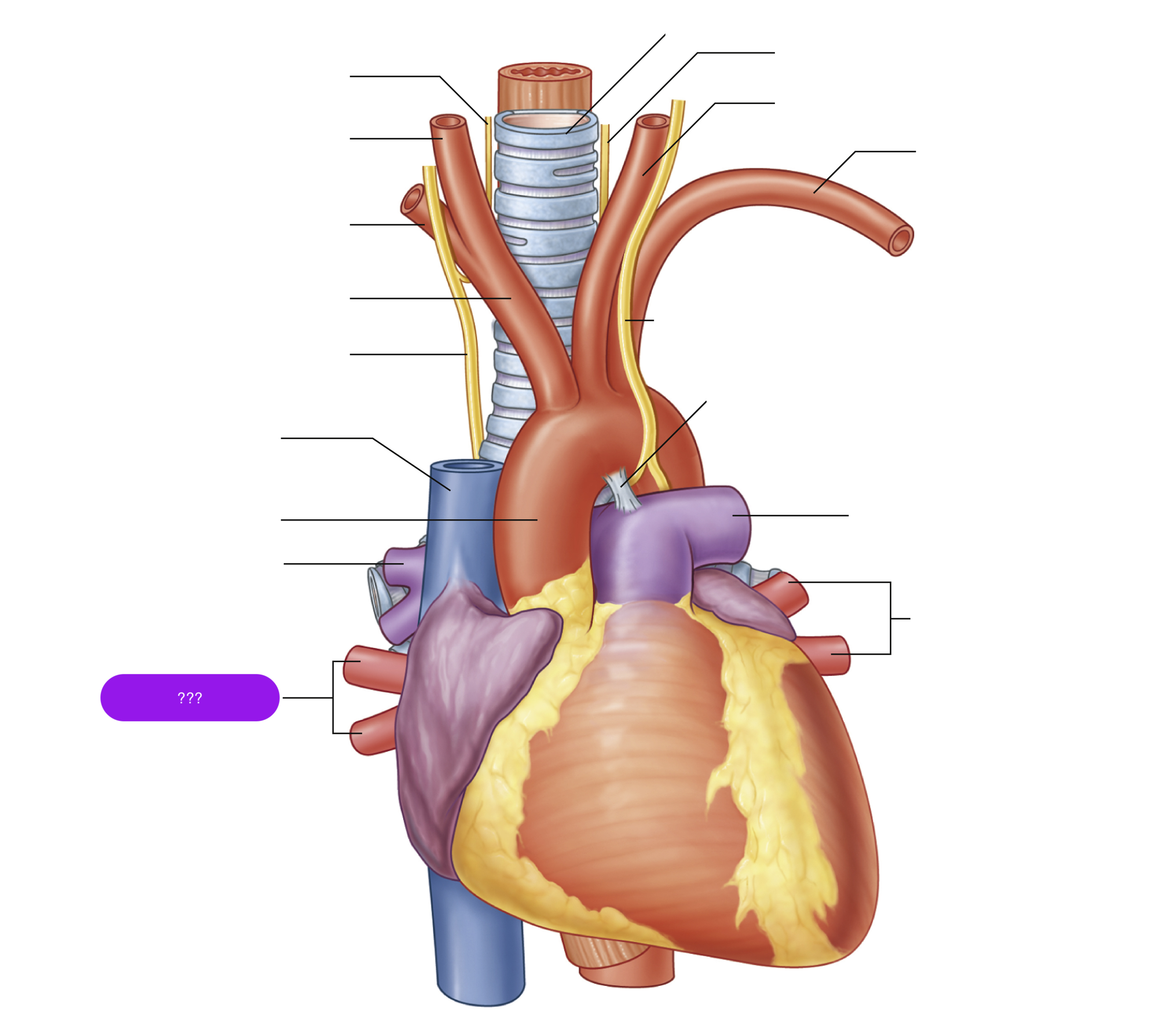
right pulmonary veins
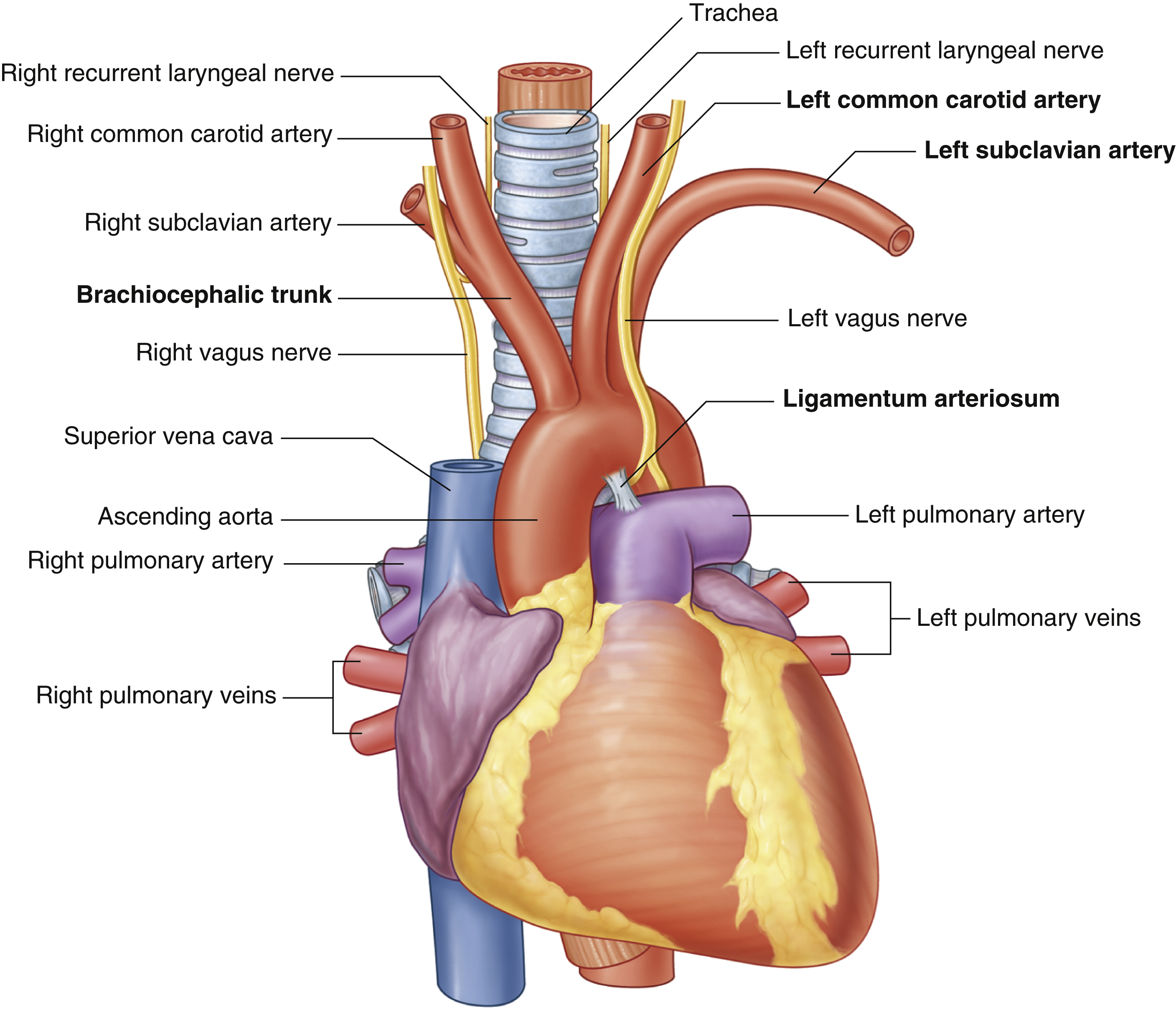
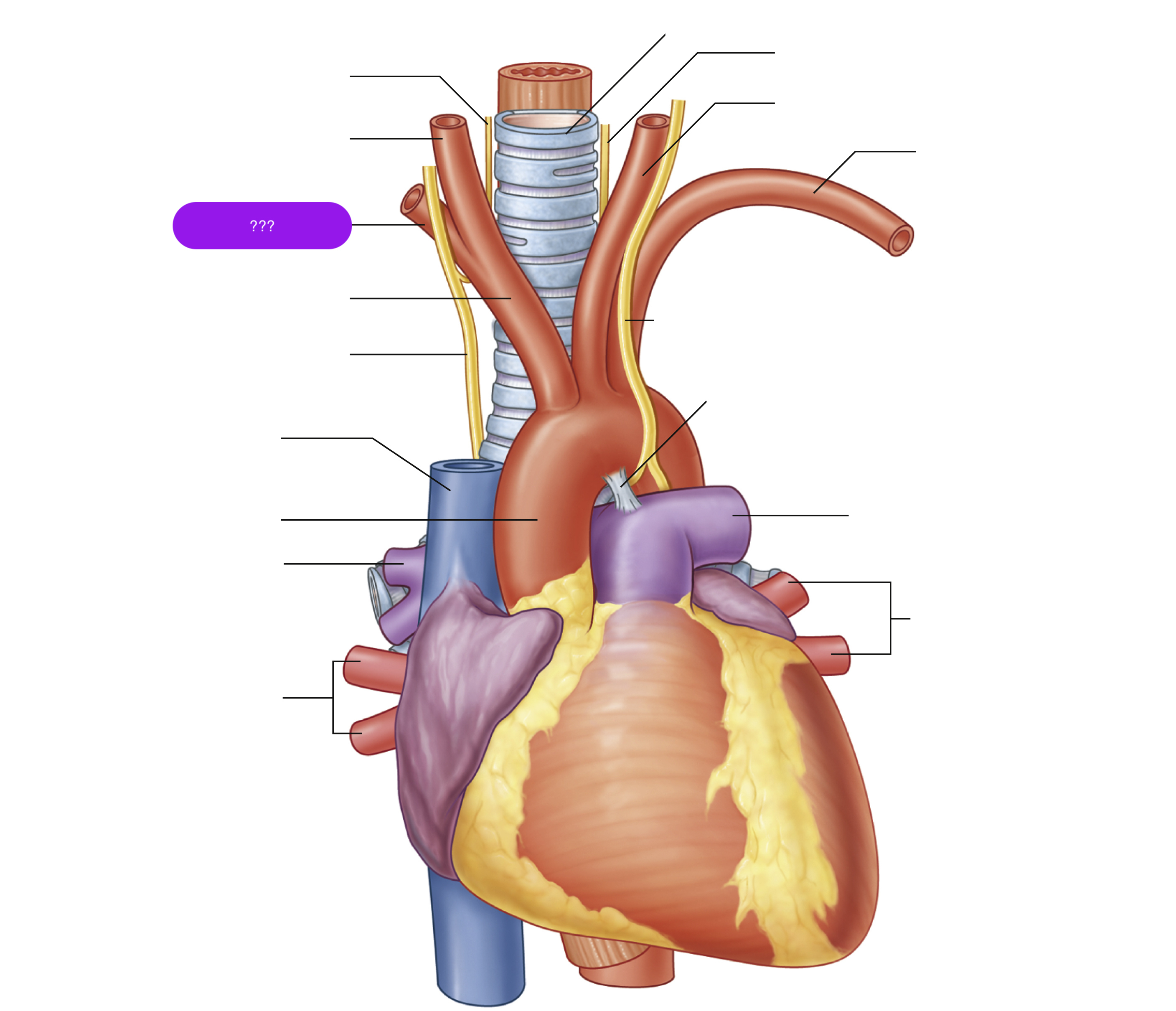
right subclavian artery
oxygenated blood → head, neck, arms
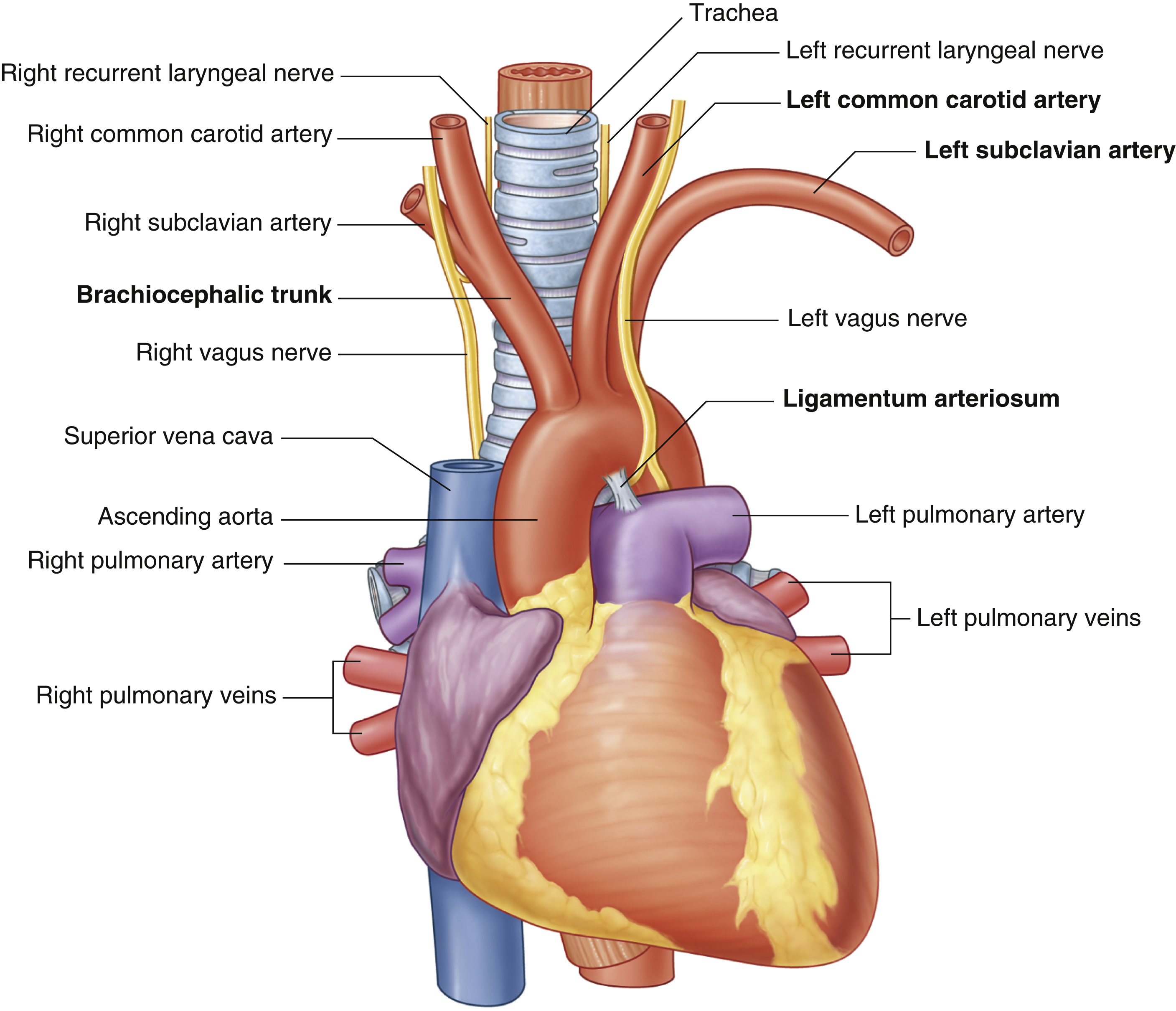
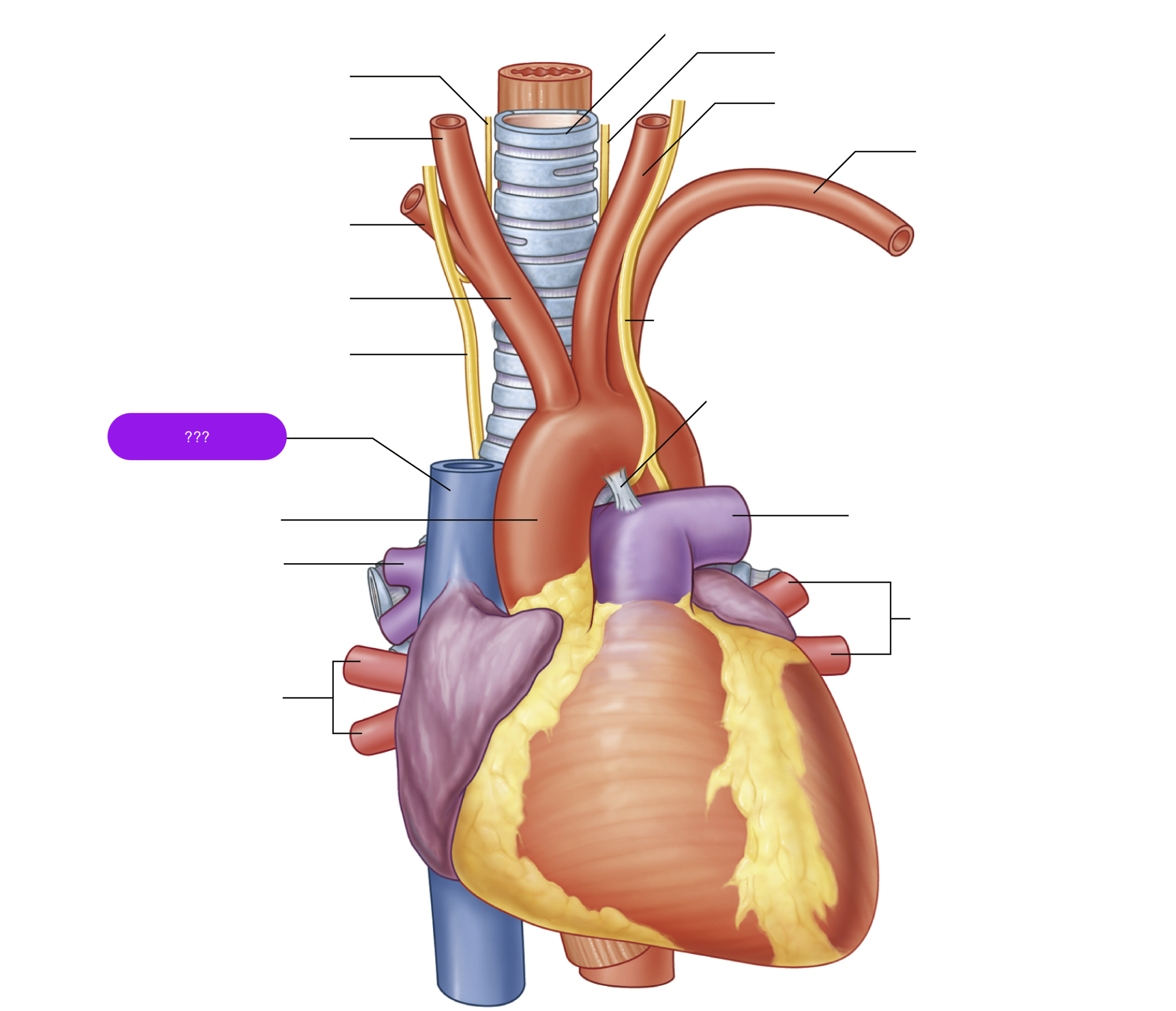
superior vena cava
(superior mediastinum)

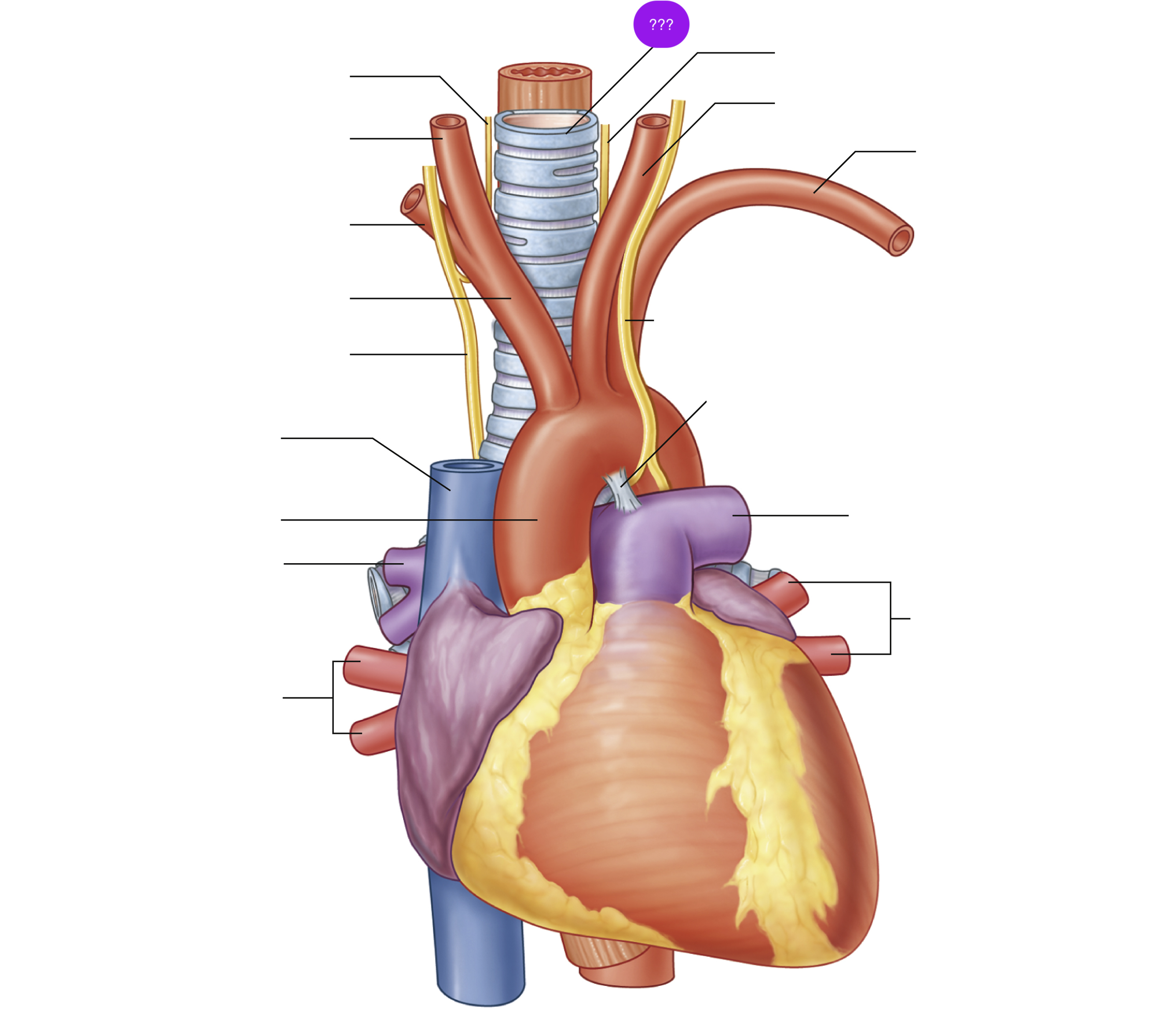
trachea
Atrioventricular valves
between atrium and ventricle
Tricuspid (Right Atrium → Ventricle) (3 cusps)
Mitral (Left Atrium → Ventricle) (2 cusps)
After a ventricular contraction, pressure in the ventricles exceeds the pressure in the atria, so the AV valves shut
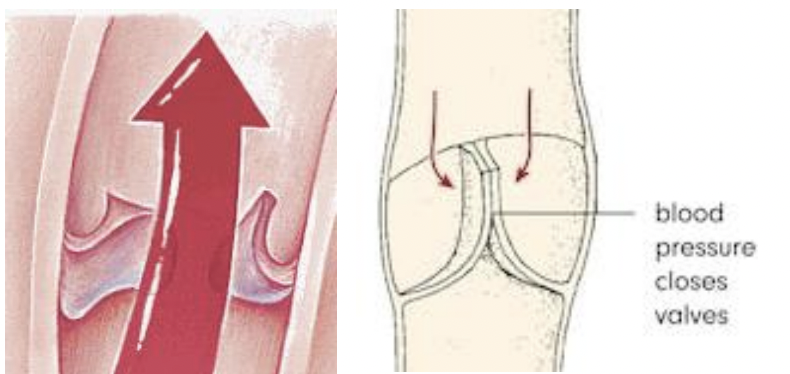
semilunar valves
between ventricles and great vessels
Pulmonary (R.Ventricle → Pulmonary trunk)
Aortic (L.Ventricle → Ascending Aorta)
The semilunar valves are closed because the ventricular pressure is lower than the aorta and the pulmonary artery
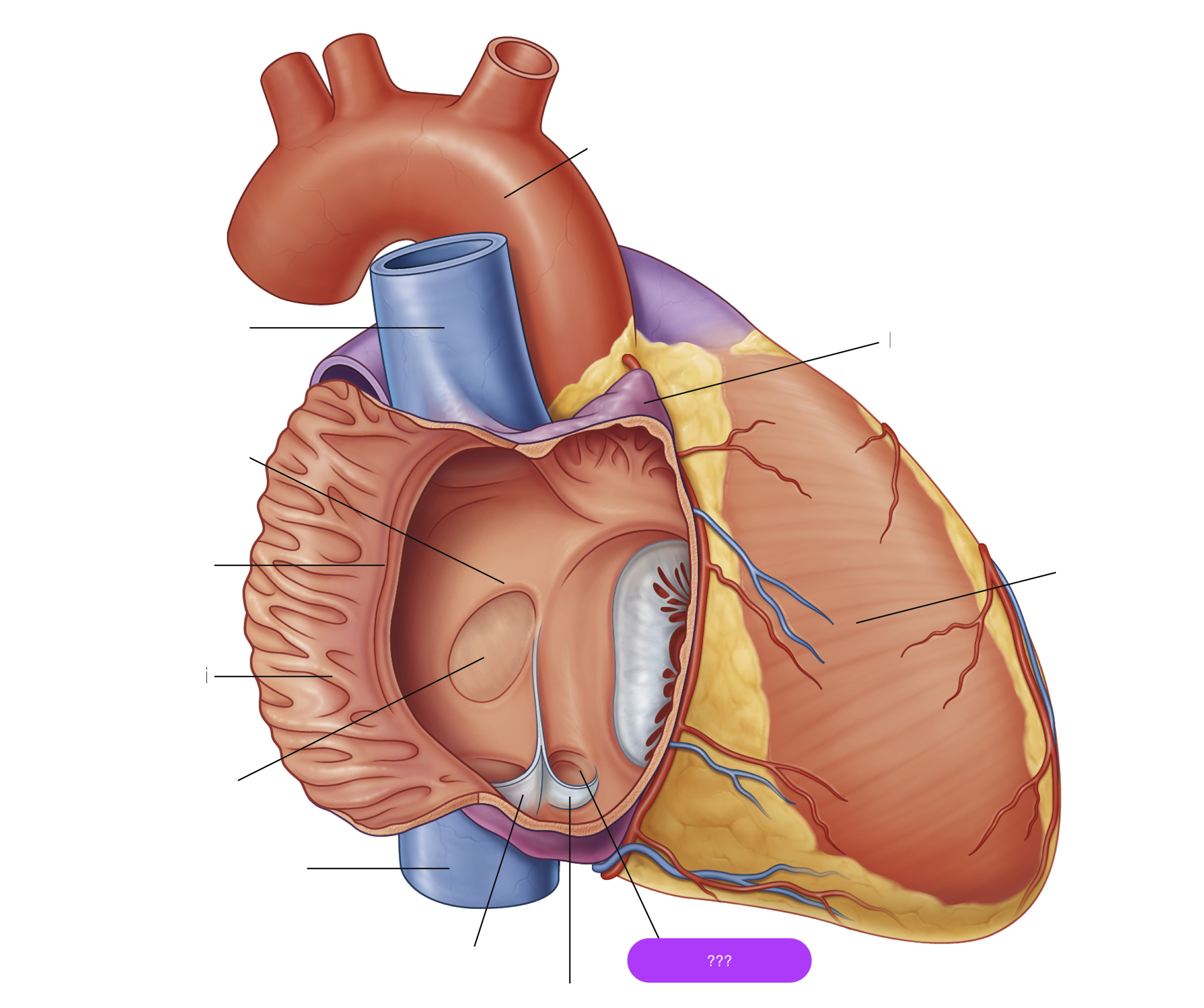
opening of coronary sinus
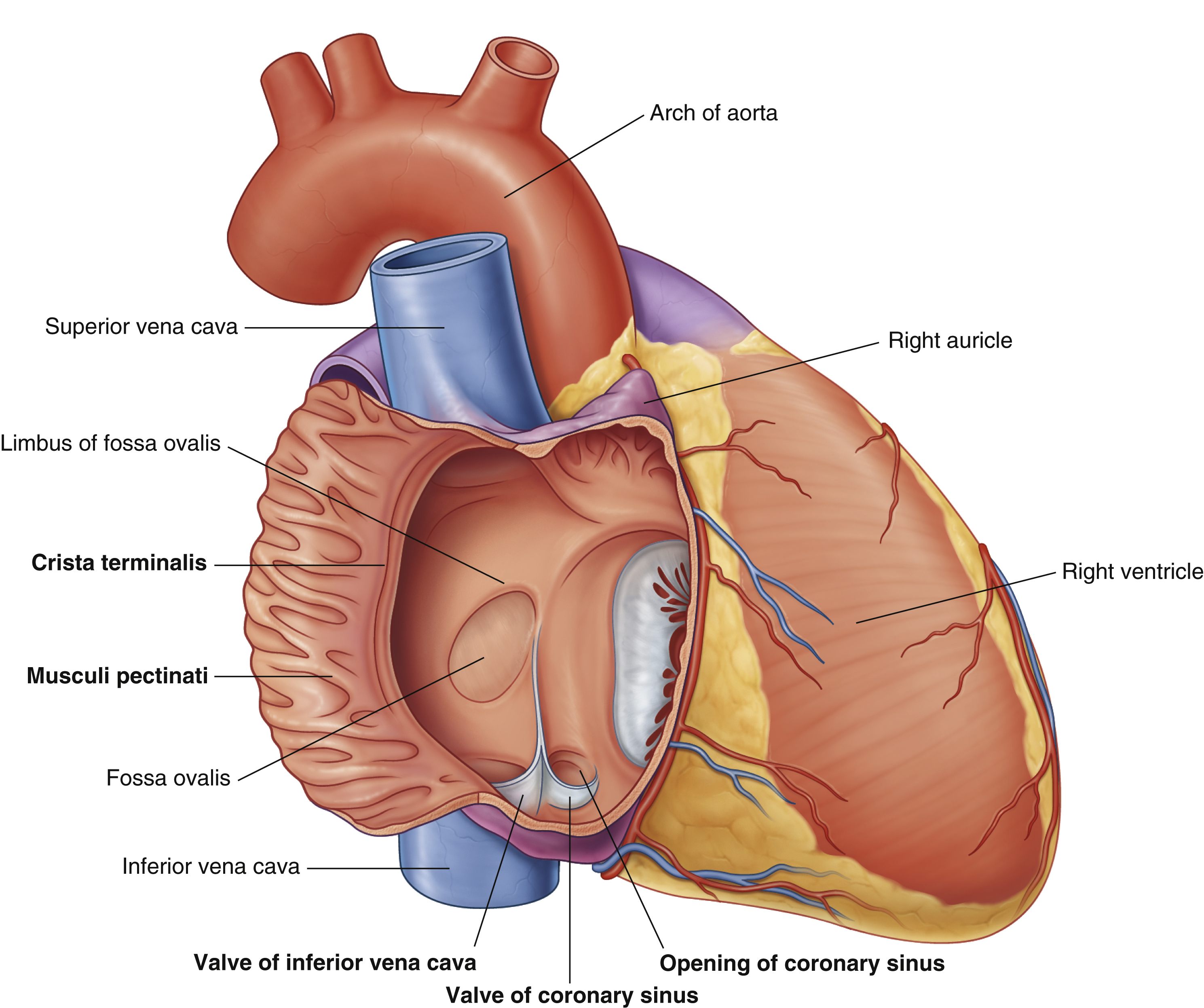
crista terminalis
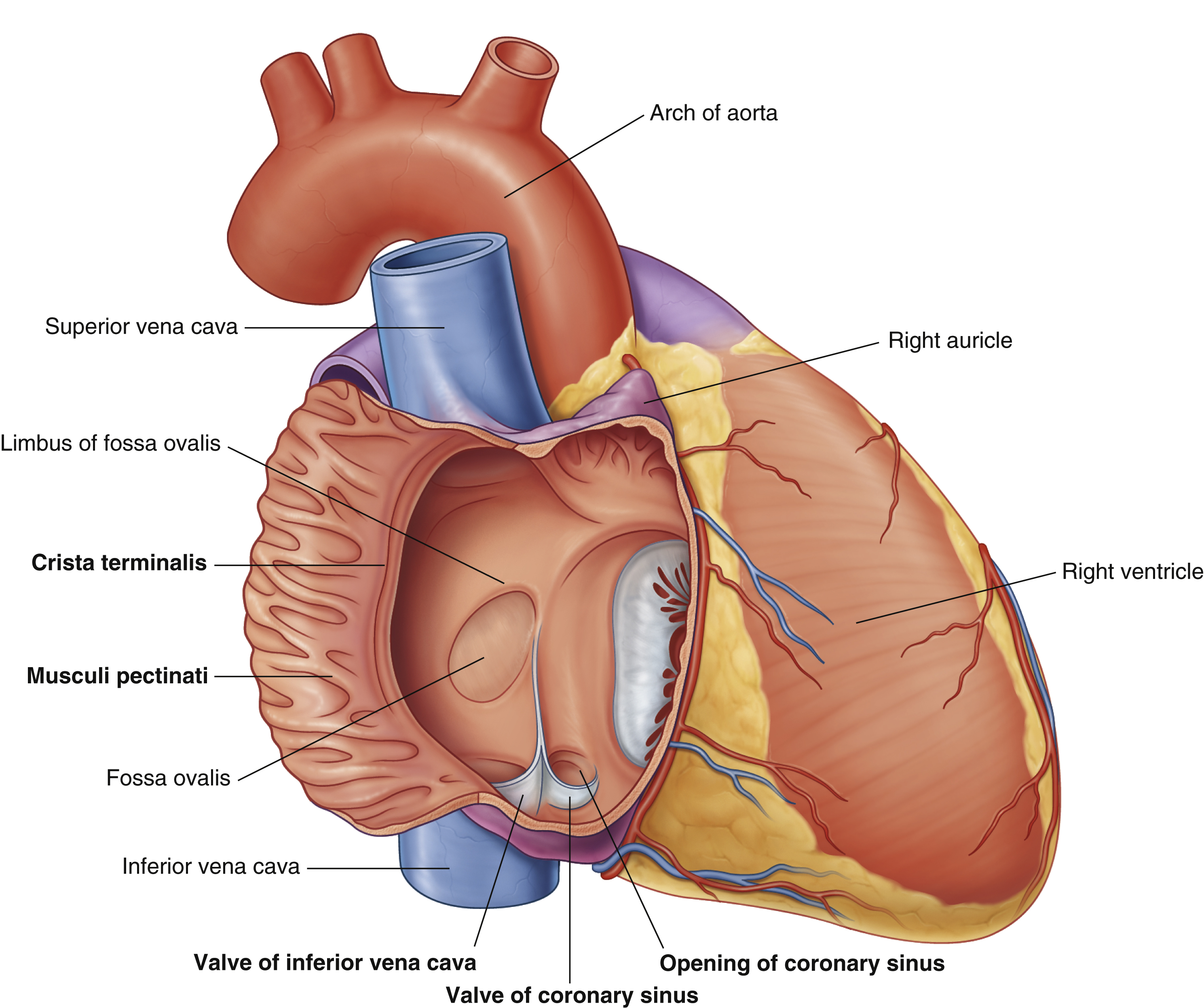
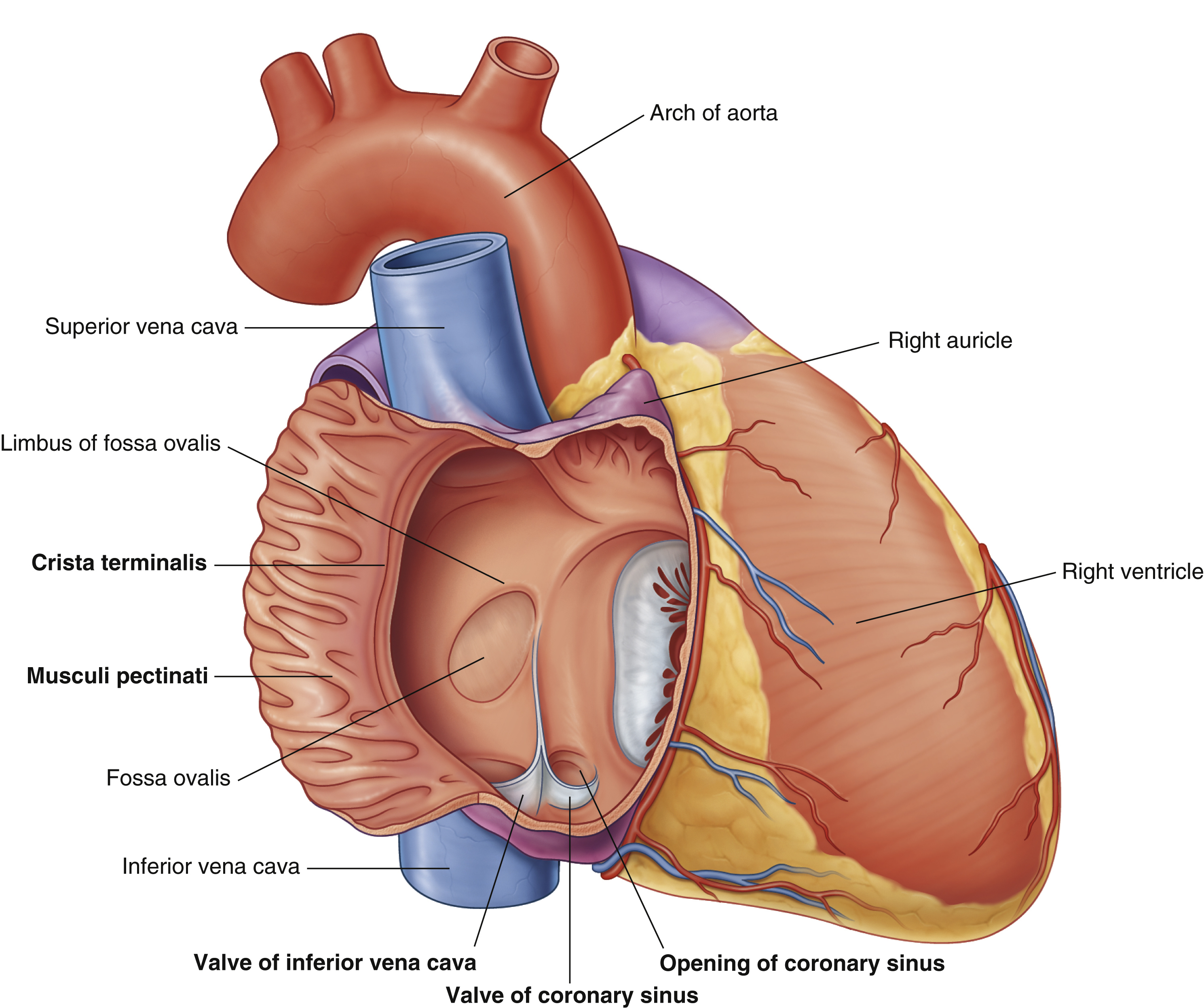
fossa ovalis
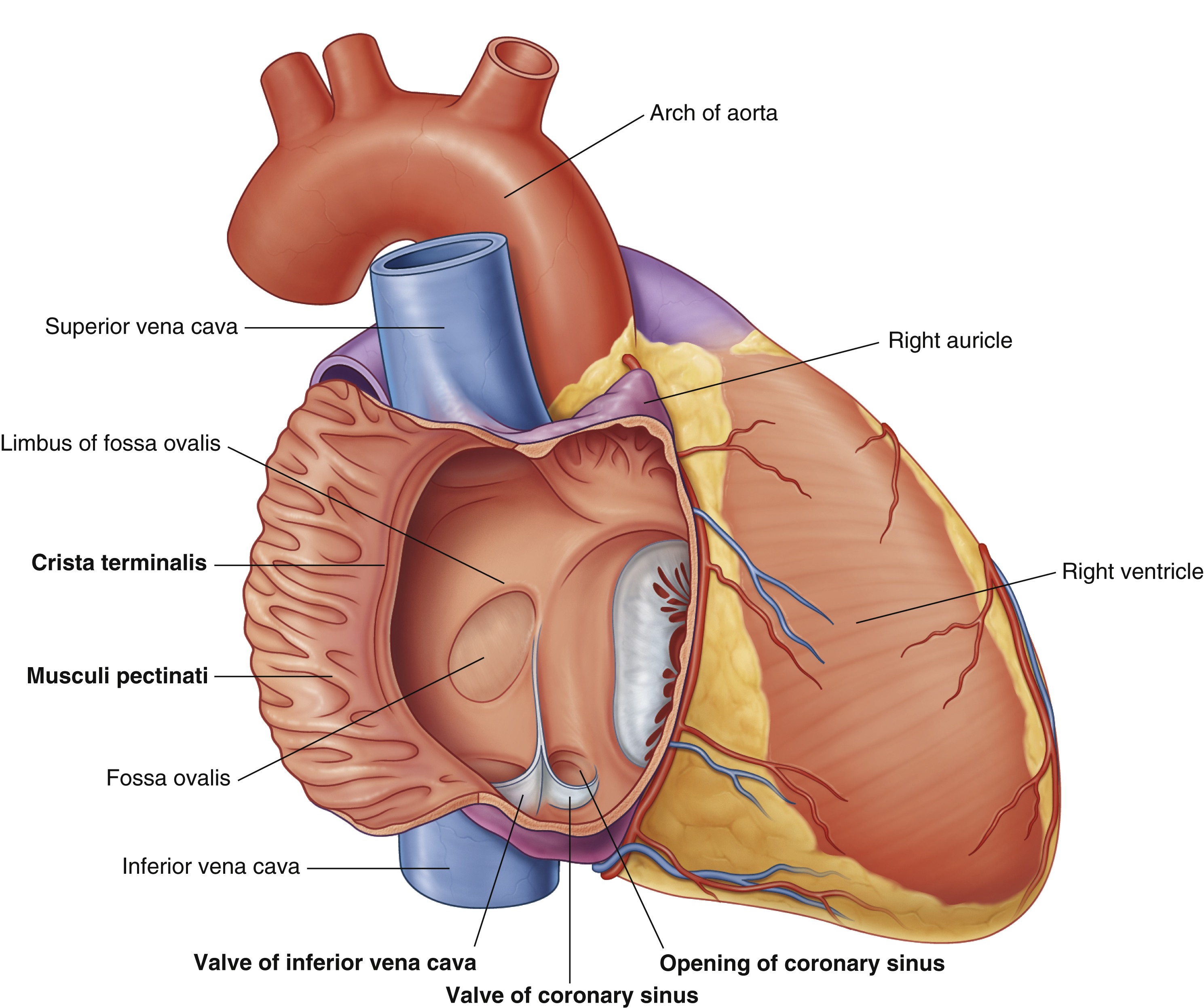
musculi pecinati
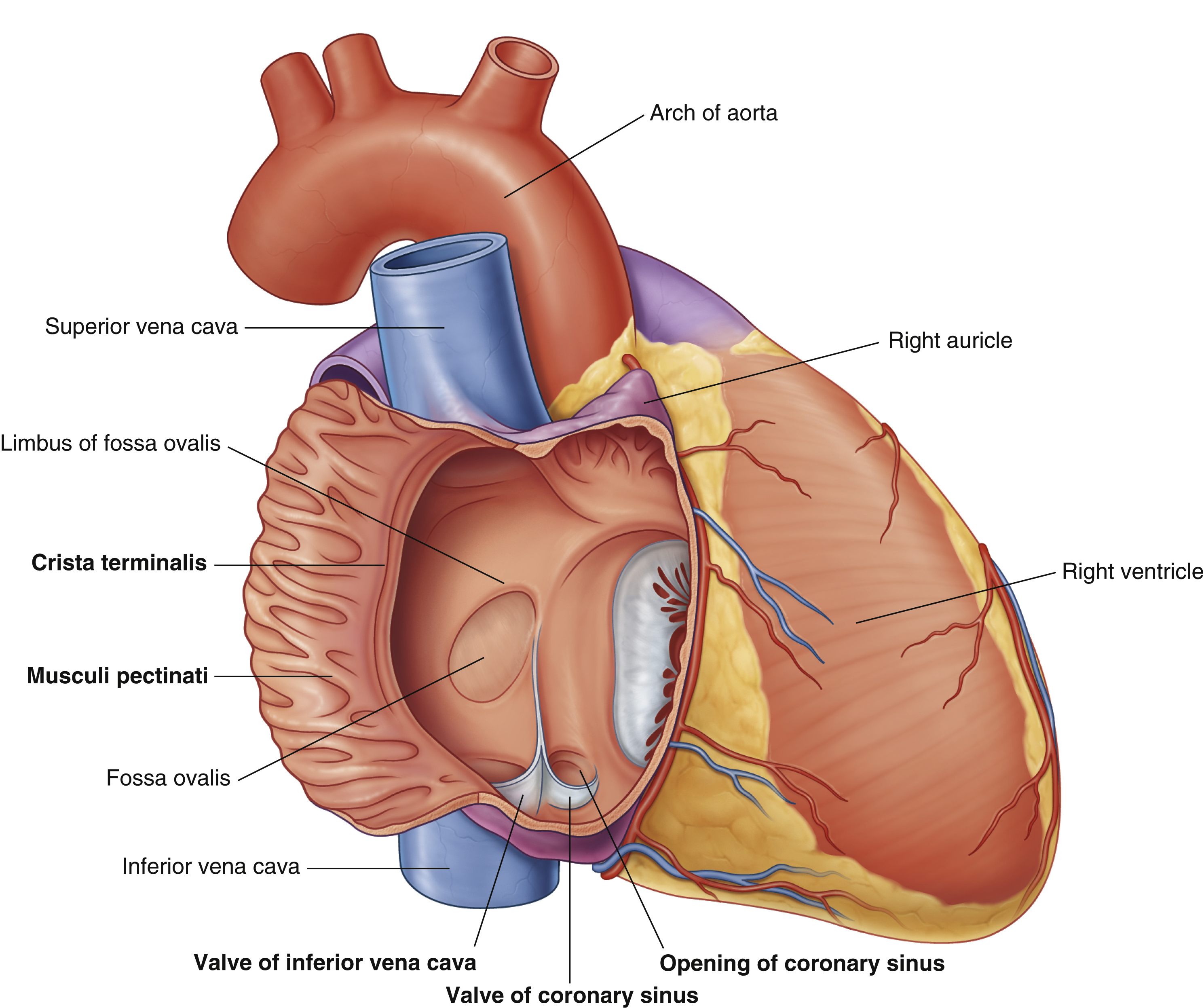
right auricle


right ventricle
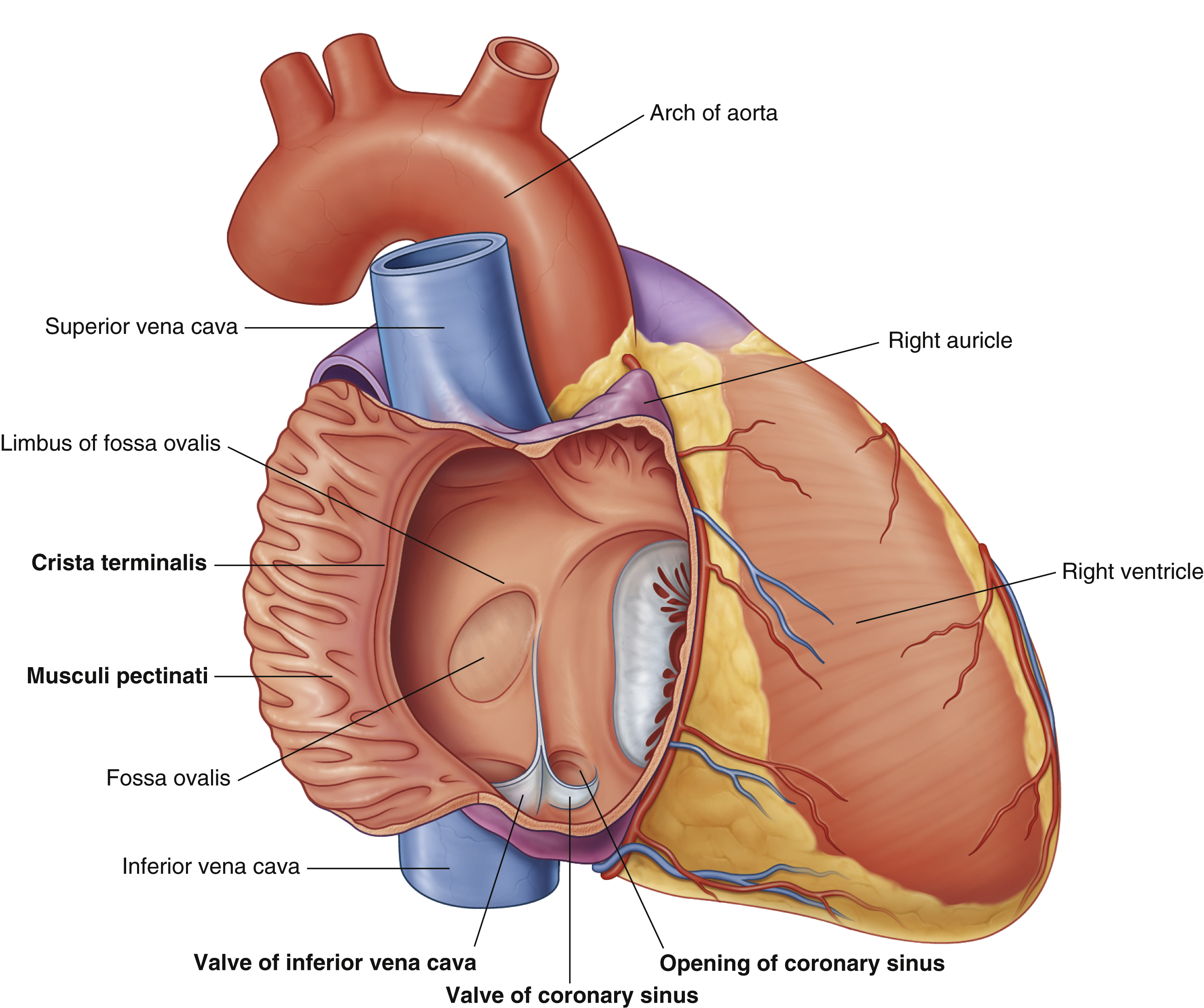
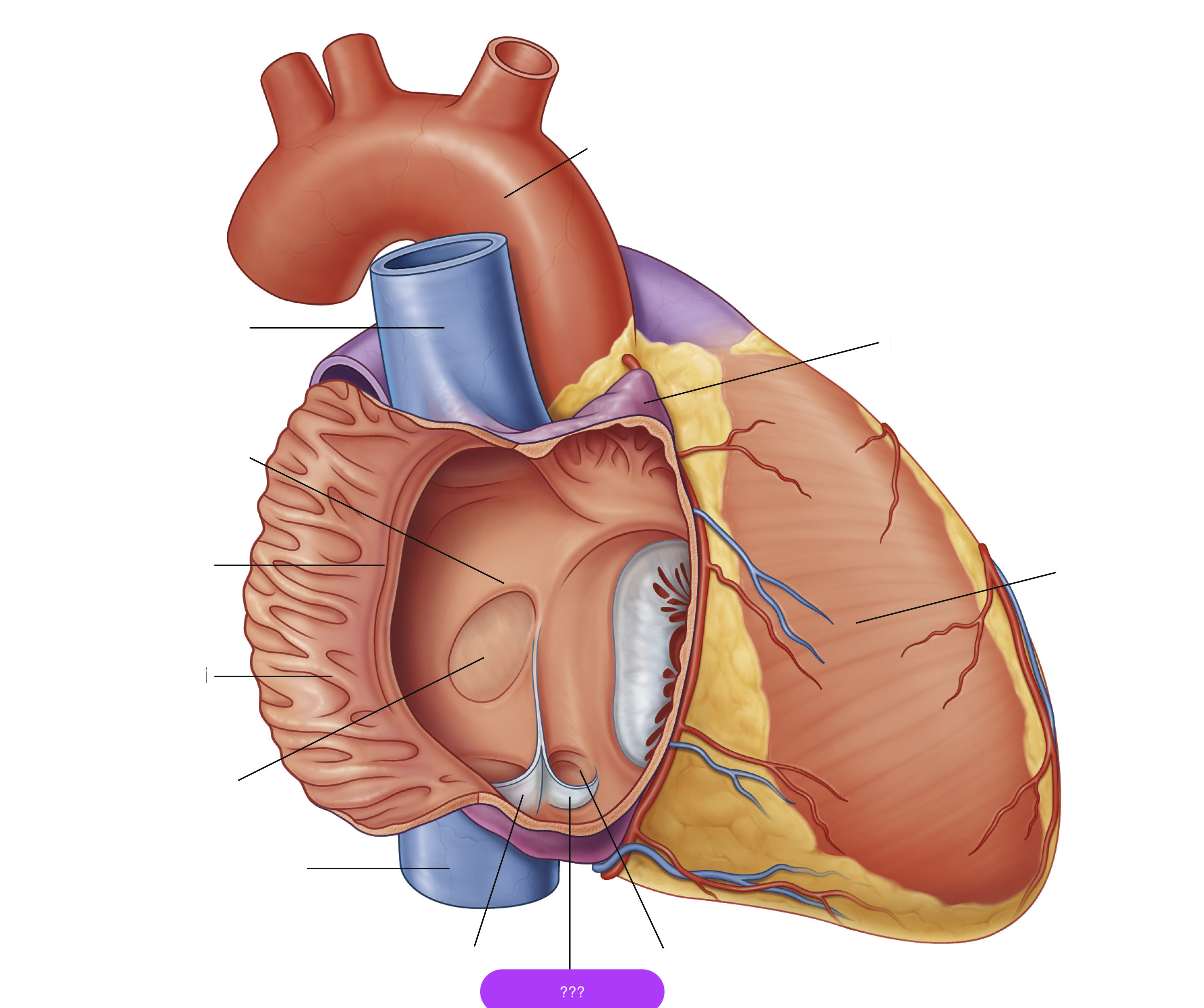
valve of coronary sinus


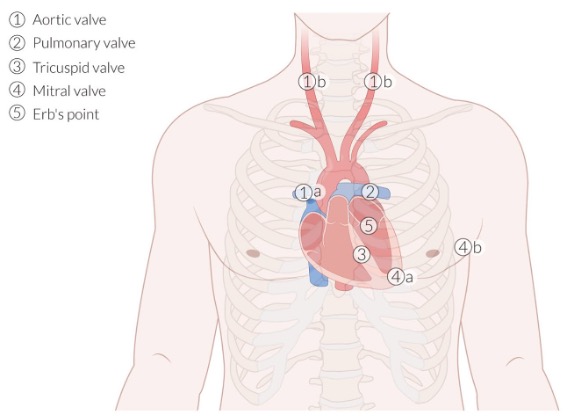
auscultation site 1
aortic valve (APTM)
R. of sternum at 2nd intercostal space

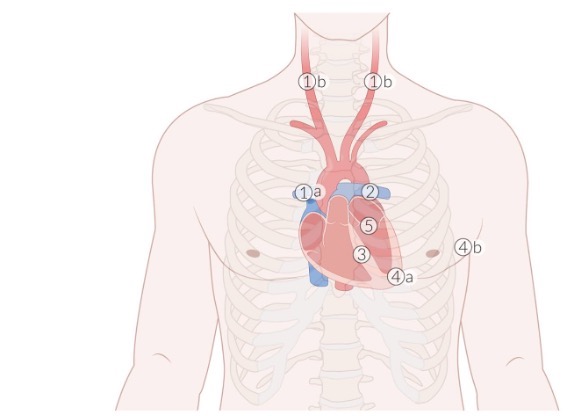
auscultation site 2
pulmonary valve (APTM)
L. of sternum at 2nd intercostal space

auscultation site 3
tricuspid valve (APETM)
L. of sternum at 4th intercostal space
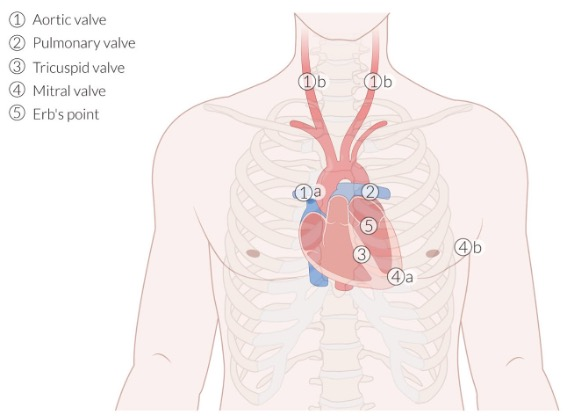
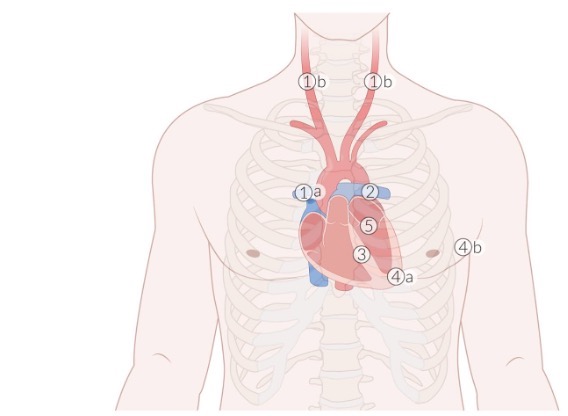
auscultation site 4
mitral valve (APETM)
L. of sternum at 5th intercostal space (midclavicular line)
auscultation site 5
Erb’s point
L. of sternum at 3rd intercostal space

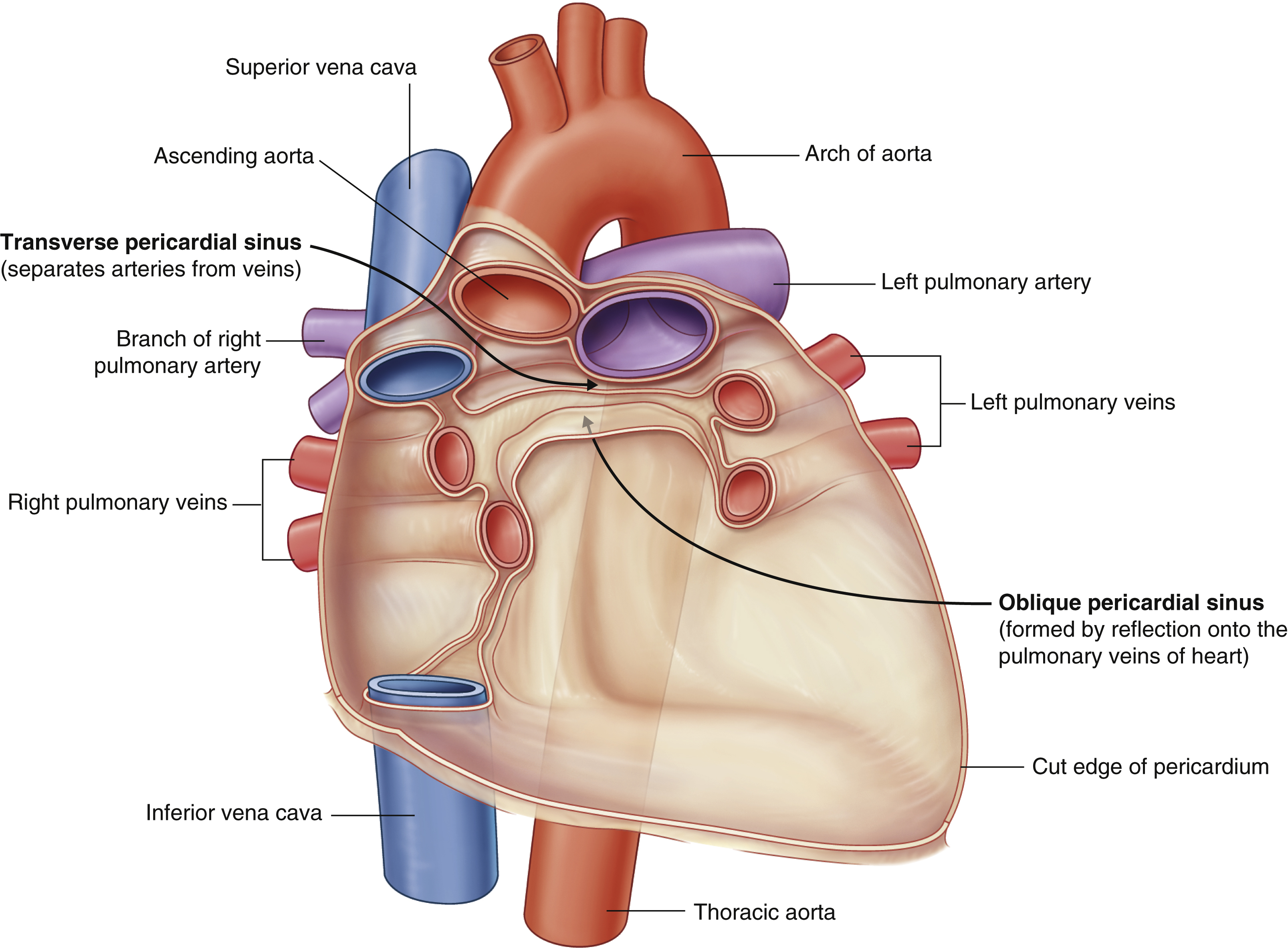
transverse pericardial sinus
(impressions in the pericardial sac formed between the points where great vessels enter it)
Located posterior to the roots of the ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk
Clinical significance: can be used to identify the arteries of the heart during coronary artery bypass grafting
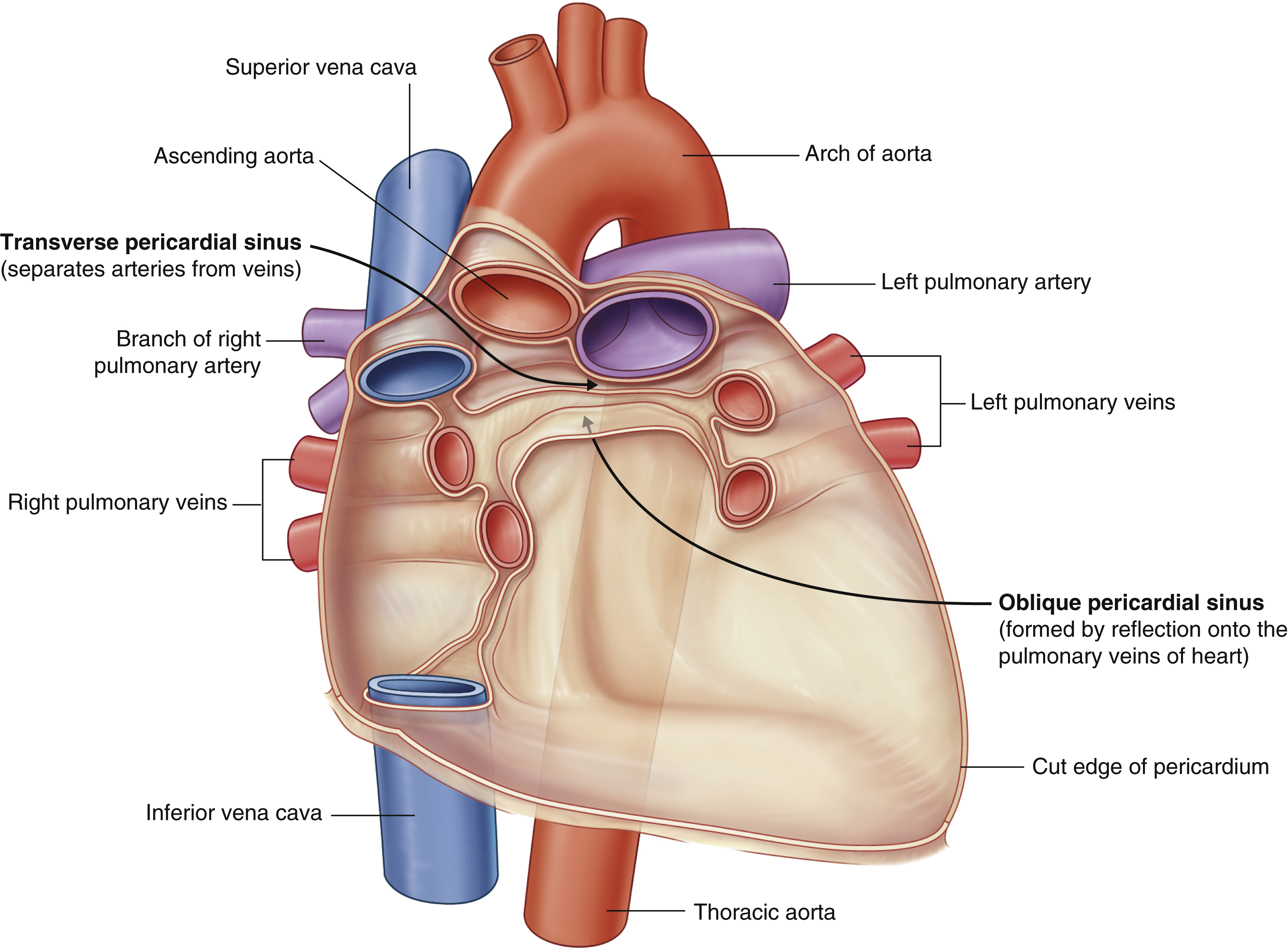
oblique pericardial sinus
(impressions in the pericardial sac formed between the points where great vessels enter it)
Located posterior to the left atrium; between R and L pulmonary veins
No clinical significance.
neurovascular bundle
structure consisting of an artery, vein and nerve bound together by connective tissue
artery types of branching
Terminal branch
artery ends by dividing/bifurcating into multiple branches
Collateral branch
side branch comes off the main artery
Continuation
artery changes name as it passes a landmark (functionally the same vessel)
Anastomosis
artery connects with another artery, forming arches/circles (backup blood supply if there is an occlusion)

aortic coarctation
narrowing of the aorta that occurs near the ligamentum arteriosum just distal to the origin of the left subclavian artery
Infantile (pre-ductal): narrowing before the ductus arteriosus. Presents in infancy with heart failure
radial-radial delay
Adult (post-ductal): narrowing after the ductus. Collateral circulation develops (via intercostal and internal mammary arteries)
radial-femoral delay