Relational Databases (Ch. 4, 5, & 7)
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 4 & 5 & 7
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
no - can be broken down into two attributes firstname and lastname
Given the value “Jeremy Brown” is this value atomic? Why?
R1 = (orderID, supplierID, productName, dateOrdered)
R2 = (supplierID, supplierName, city, state)
R3 = (city, state, zip)
Given the relation R and the functional dependencies below, decompose R to be in 3NF. State all foreign and primary keys.
R = (order_id, supplier_id, productName, supplierName, dateOrdered, city, state, zip)
supplierID → {supplierName, city, state, zip}
{city, state} → zip
relation
In a relational database, a table is also called a
1NF
What normal form ensures all attributes are atomic (no multi-valued attributes)?
3NF
What normal form removes transitive dependencies?
foreign, candidate, primary, super
Name the four types of keys in a relational database?
no
Is a super key a minimal candidate key?
Boyce-Codd Normal Form
What does BCNF stand for?
domain
What specifies the allowed values for an attribute type?
2NF
What normal form removes partial key dependencies?
a. selection
Which of these is not a type of anomaly we try to prevent with normalizing?
a. selection
b. insertion
c. modification
d. deletion
CREATE TABLE car (
vin CHAR(20) PRIMARY KEY,
model VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
constraint c1 FOREIGN KEY(model) REFERENCES model(id),
cost FLOAT(5, 2),
code INT NOT NULL)
Write a SQL statement to make a table called car based on the following:
a string of length 20 vin that can be used to uniquely identify a car
a string of up to length 10 called model. This is required. This is a reference to the model table’s id
a number that can be of length 5 and have 2 decimal places called cost
an integer called code. This is required
SELECT * FROM book WHERE name > “Databases”
Write a SQL query to get all rows from a book table such that you want all books with a name greater than “Databases” where name is an attribute of the book table.
…ORDER BY level DESC, hit_points DESC
Complete the query below to return all heroes sorted first by level in descending order, and then by hit points in descending order.
SELECT name, hit_points, level FROM hero …
SELECT COUNT(*)…
Complete the query below to return the total number of heroes stored in the table.
…FROM hero
distinct
What keyword do you use in a select to ensure you won’t get duplicate values in a select query?
not null
What constraint do you use in a create table to ensure an attribute must have a value?
0 to 20
An attribute of type varchar(20) means that the attribute can contain how many characters?
no
Does a when clause in SQL restrict the number of rows returned?
unordered
Are SQL results ordered or unordered?
all rows of foo
What will this return:
SELECT * FROM foo
DROM TABLE bar
Write a SQL statement to remove the table bar from the database?
the value of each attribute type A must be an atomic and single value from the domain dom(A)
What does the domain constraint state?
a subset of attribute types of a relation R with the property that no two tuples in any relation state should have the combination of values for these attribute types
What is a superkey?
attribute types that make up the primary key should always satisfy a NOT NULL constraint
What is the entity integrity constraint?
a foreign key F has the same domain as the primary key P attribute type(s) it refers to and either occurs as a value of P or as null
What is the referential integrity constraint?
when you don’t update everything
What is an update anomaly?
the value of X uniquely determines the value of Y
What does the functional dependency X → Y imply
an attribute type that is part of a candidate key
What is a prime attribute type?
R1(SSN, ename, dnumber, dname)
R2(SSN, pnumber, pname, hours)
Put the following in 1NF form:
R(SSN, ename, dnumber, dname, project(pnumber, pname, hours))
partial
if an attribute type can be removed from a functional dependency X → Y and the dependency still holds, is it full or partial?
R1(SSN, pnumber, hours)
R2(pnumber, pname)
Put the following into 2NF:
R(SSN, pnumber, pname, hours)
Assumption: many people can work on the same project and a project has a unique name
transitive
What type of dependency X → Y in a relation R has a set of attribute types Z that is neither a candidate key nor a subset of any key of R and both X → Z and Z → Y hold
R1(SSN, ename, dnumber)
R2(dnumber, dname, dmgrssn)
Put the following in 3NF:
R(SSN, ename, dnumber, dname, dmgrssn)
Assumption: an employee works in one department, a department can have many workers, and a department has one manager
BCNF
Which normal form guarantees that for every non-trivial functional dependency X → Y, X is either a candidate key or a superset thereof
trivial
In which type of functional dependency X → Y is Y a subset of X?
R1(supnr, prodnr, quantity)
R2(supnr, supname)
Put the following in BCNF:
R(supnr, supname, prodnr, quantity)
Assumption: a supplier can supply multiple products, a product can be supplied by multiple suppliers, a supplier has a unique name
4NF
Which normal form ensures that for each non-trivial multivalued dependencies X → Y, X is a superkey - that is X is either a candidate key or a superset thereof
multivalued
What type of dependency X → Y has every X value exactly determining a set of Y values, independently of the other attribute types
R1(course, textbook)
R2(course, instructor)
Put the following in 4NF:
R(course, instructor, textbook)
Assumption: a course can be taught by different instructors, and a course uses the same set of textbooks for each instructor
a foreign key (which is the primary key of the other entity) should be added to the weak entity
What is required when mapping a weak entity to another entity through a weak relationship?
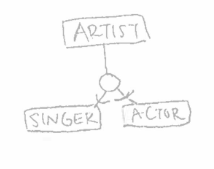
Style I:
ARTIST(anr, aname)
SINGER(anr, musicStyle)
ACTOR(anr, movie)
Style II:
SINGER(anr, aname, musicStyle)
ACTOR(anr, aname, movie)
Style III:
ARTIST(anr, aname, musicStyle, movie)
Map the image to a relational model. ARTIST has two attributes: ANR (primary key) and aname. SINGER has one attribute called musicStyle. ACTOR has one attribute called movie
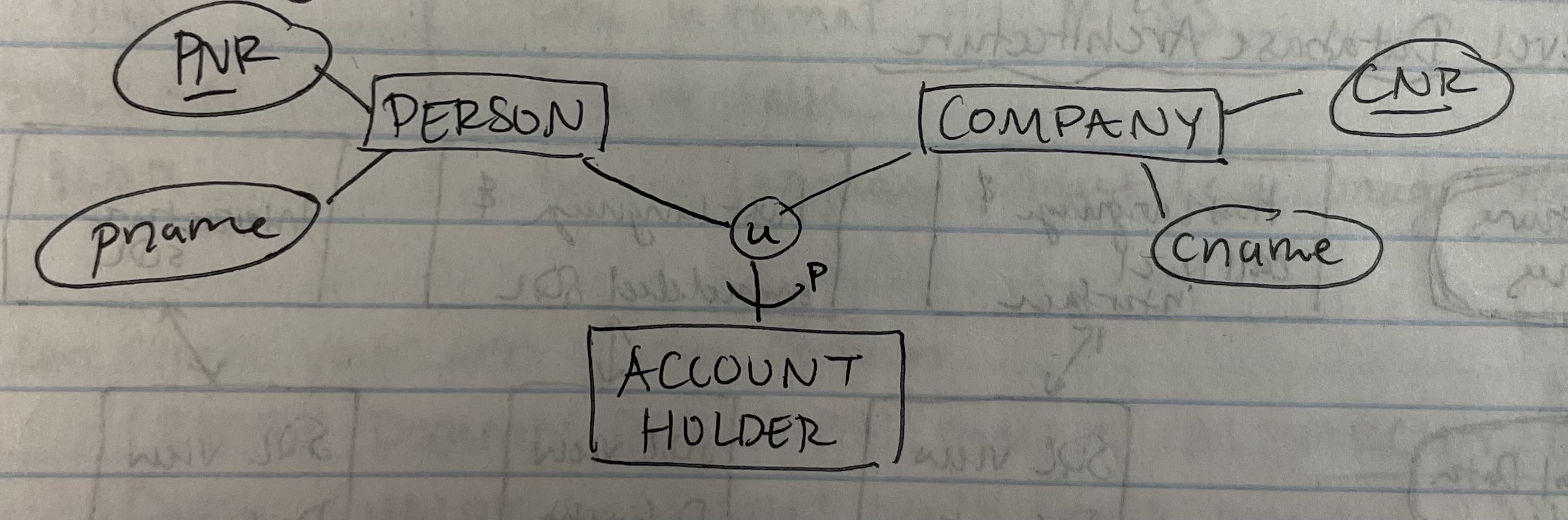
PERSON(pnr, pname, custNumber)
COMPANY(cnr, cname, custNumber)
ACCOUNT_HOLDER(custNumber)
Map the image to a relational model.
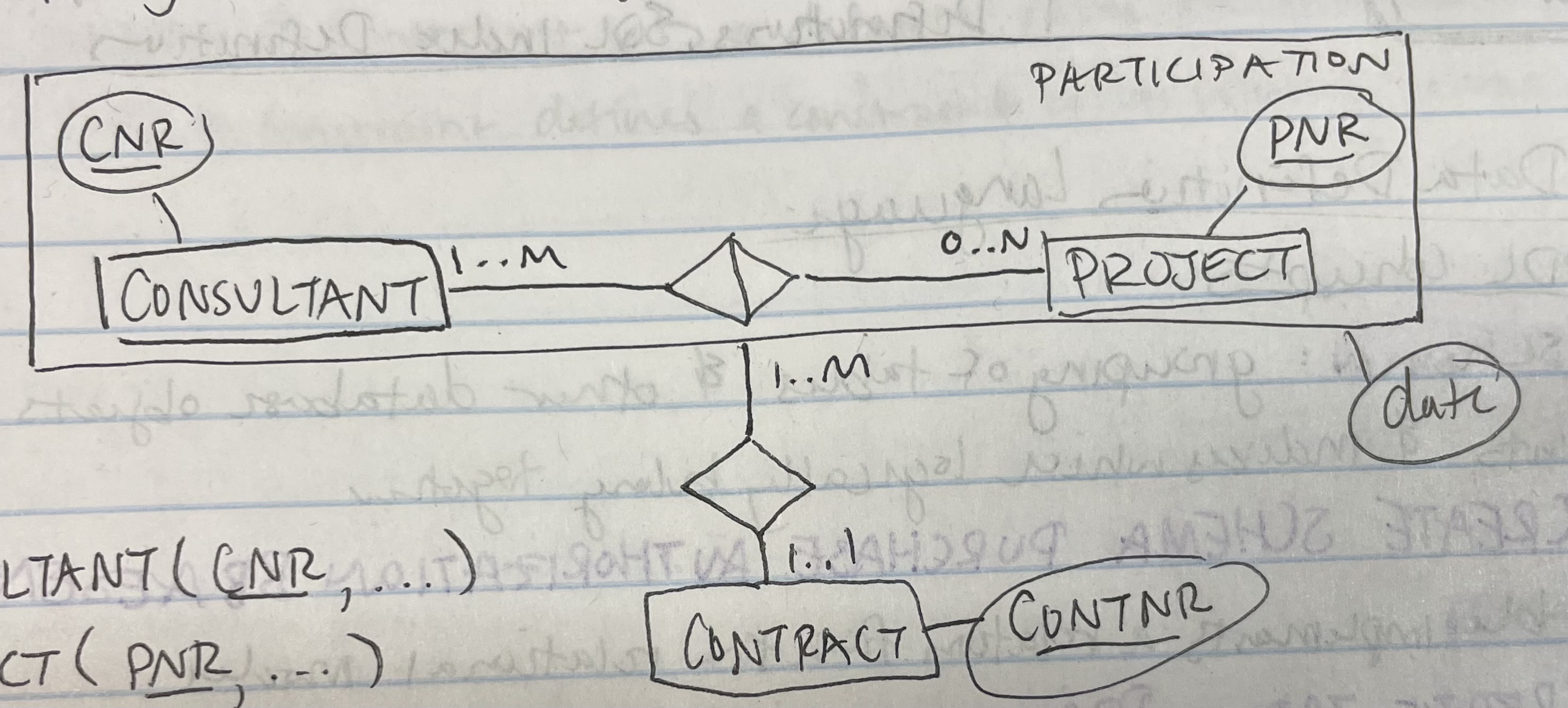
CONSULTANT(cnr)
PROJECT(pnr)
PARTICIPATION(cnr, pnr, contnr, date)
CONTRACT(contnr)
Map the image to a relational model.
CREATE TABLE supplier
(supnr CHAR(4) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
supname VARCHAR(40) NOT NULL,
supaddress VARCHAR(50),
supcity VARCHAR(20),
supstatus SMALLINT)
Convert the following relational model to a SQL table:
SUPPLIER(supnr, supname, supaddress, supcity, supstatus)
CREATE TABLE po_line
(ponr CHAR(7) NOT NULL,
prodnr CHAR(6) NOT NULL,
quantity INT,
PRIMARY KEY (ponr, prodnr),
FOREIGN KEY (ponr) REFERENCES purchase_order (ponr),
FOREIGN KEY (prodnr) REFERENCES product (prodnr))
Convert the following relational model to a SQL table:
PO_LINE(ponr, prodnr, quantity)
Nore: ponr is the primary key of the purchase_order table
Note: prodnr is the primary key of the product table
DROP TABLE tablename CASCADE/RESTRICT
What command is used to delete a schema or table? What two commands can it combine with?
ALTER TABLE tablename
What command is used to modify a schema or table?
SELECT prodName FROM products WHERE prodName LIKE ‘_COW%‘
Write a SQL statement that takes a products name from the product table. Only return product names that begin with any letter followed by “COW” and then ending in any letters
SELECT COUNT (DISTINCT purchase_price) FROM supplies WHERE prodnr = ‘0178’
Write a SQL query that counts all unique purchase_price’s in the supplies table. The prodnr should be ‘0178’.
SELECT prodnr FROM po_line GROUP BY prodnr HAVING COUNT(*) >= 2
Write a SQL query that returns the prodnr from the po_line table where the number of entries in po_line that have that prodnr is at least 2. Group the results by prodnr.
SELECT r.supname FROM supplier r, supplies s WHERE r.supnr = s.supnr AND s.prodnr = ‘0899’
Write a query that gets the supname from the supplier table where that suppliers supnr = supnr of the supplies table and where the suppplies table prodnr = ‘0899’
SELECT supname FROM supplier WHERE supnr = (SELECT supnr FROM purchase_order WHERE ponr = ‘1560’)
Write a nested query that finds the supname of a supplier whose supnr is equal to the supnr of a purchase_order that has a ponr of 1560
a condition in the WHERE clause of the nested query references some column of a table declared in the outer query
What does it mean for two queries to be correlated?
SELECT p.prodnr FROM product p WHERE 1 < (SELECT COUNT(*) FROM po_line pol WHERE p.prodnr = pol.prodnr)
Write a query to give me the count from po_line where p.prodnr = pol.prodnr…if that count > 1, output prodnr. do this for each product p
EXISTS - checks that any instance occurs
ALL - checks that the condition satisfies every entry in table
ANY - checks that the condition satisfies any entry in table
What do EXISTS, ANY, and ALL do in SQL?
union, intersect, except
What are the three set operations you can perform on queries?
INSERT INTO product VALUES (attr1, attr2, etc.)
Write a SQL statement that adds a row to the product table
INSERT INTO product(name, price, qty) VALUES (‘yoyo’, 5.00, 400), (‘slinky’, 3.50, 200)
Write a SQL statement that adds 2 rows to the product table. The data entered should be a name, price, and qty in that order.
DELETE FROM product WHERE prodnr = ‘1000’
Write a SQL statement that deletes all entries of the product table where prodnr = ‘1000;
UPDATE product SET qty = 26 WHERE prodnr = ‘0185’
Write a SQL statement that updates a product whose prodnr = ‘0185’ and sets its qty to 26.
ALTER TABLE supplier ADD color VARCHAR(10) DEFAULT silver
Write a SQL query that adds a column to the supplier table called color. Set the default value to silver.
CREATE VIEW topsuppliers AS SELECT supnr, supname FROM supplier WHERE supstatus > 50
Write a SQL statement that creates a view called topsuppliers. The values should be supnr and supname from supplier table (only where supstatus > 50)
GRANT select, insert, update, delete ON supplier TO bbaesens
REVOKE to remove
Write a SQL statement that grants selection, insertion, update abilities, and deletion on the supplier table to the user bbaesens.
How would you take away this ability from bbaesens?
CREATE TRIGGER foo AFTER UPDATE OF dog ON (age)
REFERENCING NEW row AS nrow FOR EACH row WHEN nrow.age == 0 BEGIN ATOMIC UPDATE nrow.age = null END
Write a row level trigger on the age attribute of dog to set the age to null when someone sets the age to 0.
row and statement
Triggers can be performed on a database in multiple ways, for each ___ and for each ___
yes
Can a stored procedure have both IN and OUT variables?
no
Are both relational algebra and SQL pure languages?
no
Can triggers cause deadlocks?
trigger
What is the SQL code that is run when a specific event, such as inserting happens?
procedure
What can be used as a container for several SQL instructions
INSERT INTO Software (Name, OS, Year_Created, Month_Created) VALUES (‘Steam’, ‘Windows’, 2015, ‘March’)
Write SQL statements to insert a new product called Steam into the Software table. Steam was made in March of 2015, and works on Windows and MacOS.
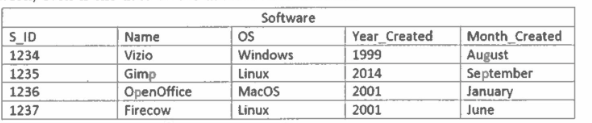
UPDATE Software SET OS = ‘OS X’ WHERE name = ‘Steam’
Write SQL statement(s) to change the OS from MacOS to OS X.
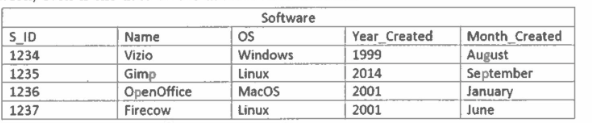
SELECT name FROM Software WHERE year_created > 2002
Write SQL statement(s) to find all the Software created after 2002.
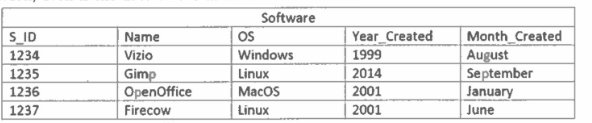
DELETE FROM Software WHERE os LIKE ‘%Linux%’
Write SQL statement(s) to remove all the software that works on Linux.
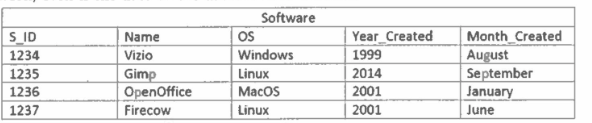
SELECT name
FROM Software
WHERE os =
( SELECT COUNT(os)
FROM Software
GROUP BY os)
Write SQL statement(s) to count all the software items that work on each OS. i.e. (Windows: 5. Mac: 2. etc).
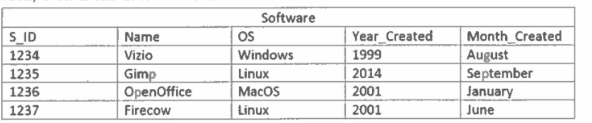
yes
Does the relational model require all relations to be normalized?
tuple and set constructor
What are the 2 types of constructors for the relational model?
atomic
What type of data can tuple constructors be used on?
A piece of SQL code consisting of declarative and/or procedural instructions and stored in the catalog of the RDBMS. A trigger occurs any time an event occurs.
Define a trigger.
CREATE TRIGGER salary_total
AFTER INSERT ON employee
FOR EACH ROW
WHEN (new.dnr IS NOT NULL)
UPDATE department
SET total_salary = total_salary + new.salary
WHERE dnr = new.dnr
Create a trigger called SALARYP_TOTAL that does the following after you insert a new entry into the EMPLOYEE table:
when DNR equals NEW.DNR and NEW.DNR is not null, update the DEPARTMENT to be equal to TOTAL_SALARY + NEW.SALARY in each row.
deadlocks
debugging complexities
performance problems
infinite loop
What are the disadvantages of using a trigger?
A piece of SQL code consisting of declarative and/or procedural instructions and stored in the catalog of the RDBMS.
What is a stored procedure?