Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - Chapter 39
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
asexual reproduction
involves only one parent and produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent
sexual reproduction
involves the union of two sex cells and shows variations in offspring
gametes
haploid cells capable of fusion
stamen
male parts of the flower (anther and filament)
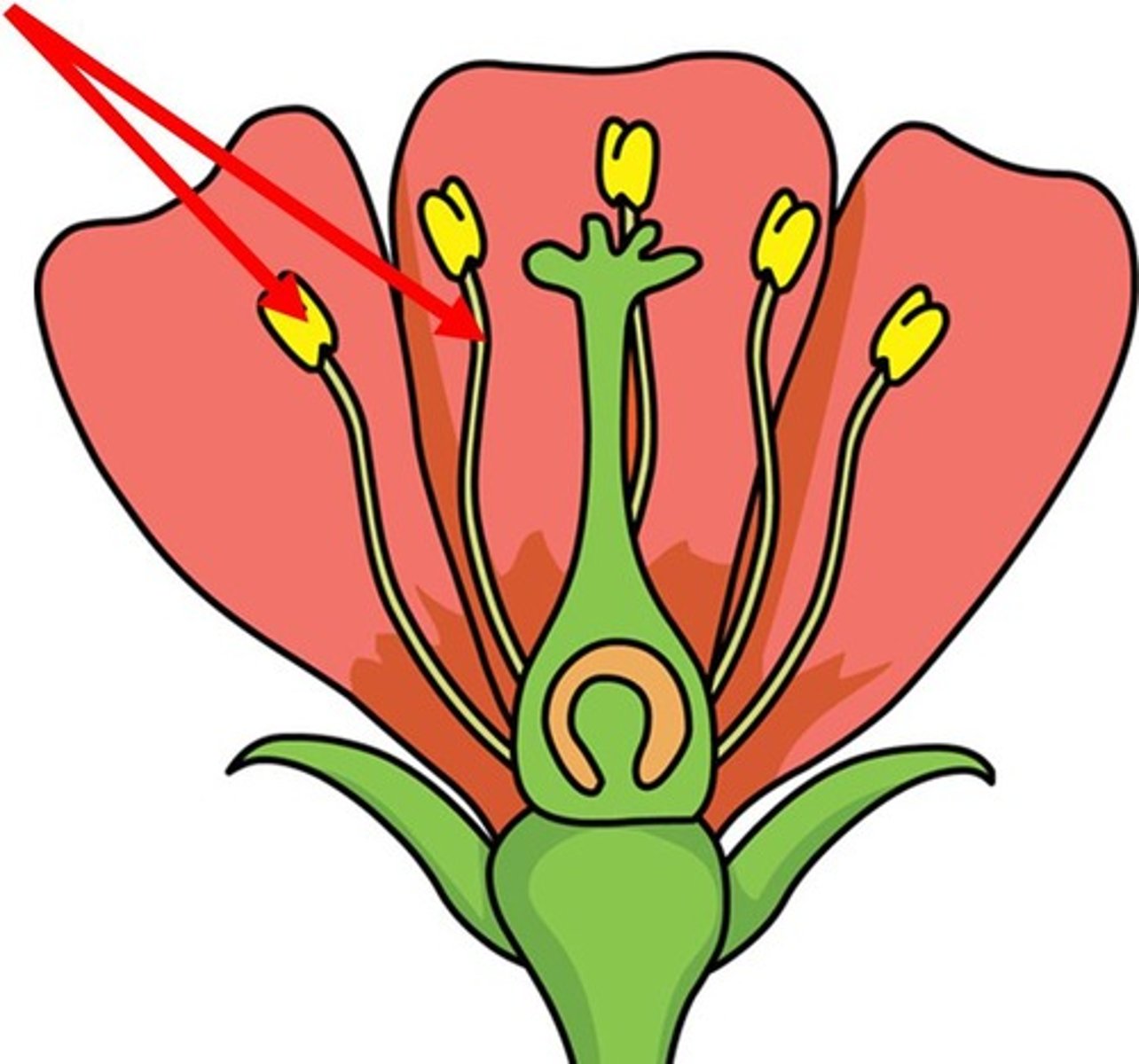
carpel
female parts of the flower (stigma, style and ovary)

filament function
bring food and water up to the anther
anther function
produces pollen
receptacle function
supports flower
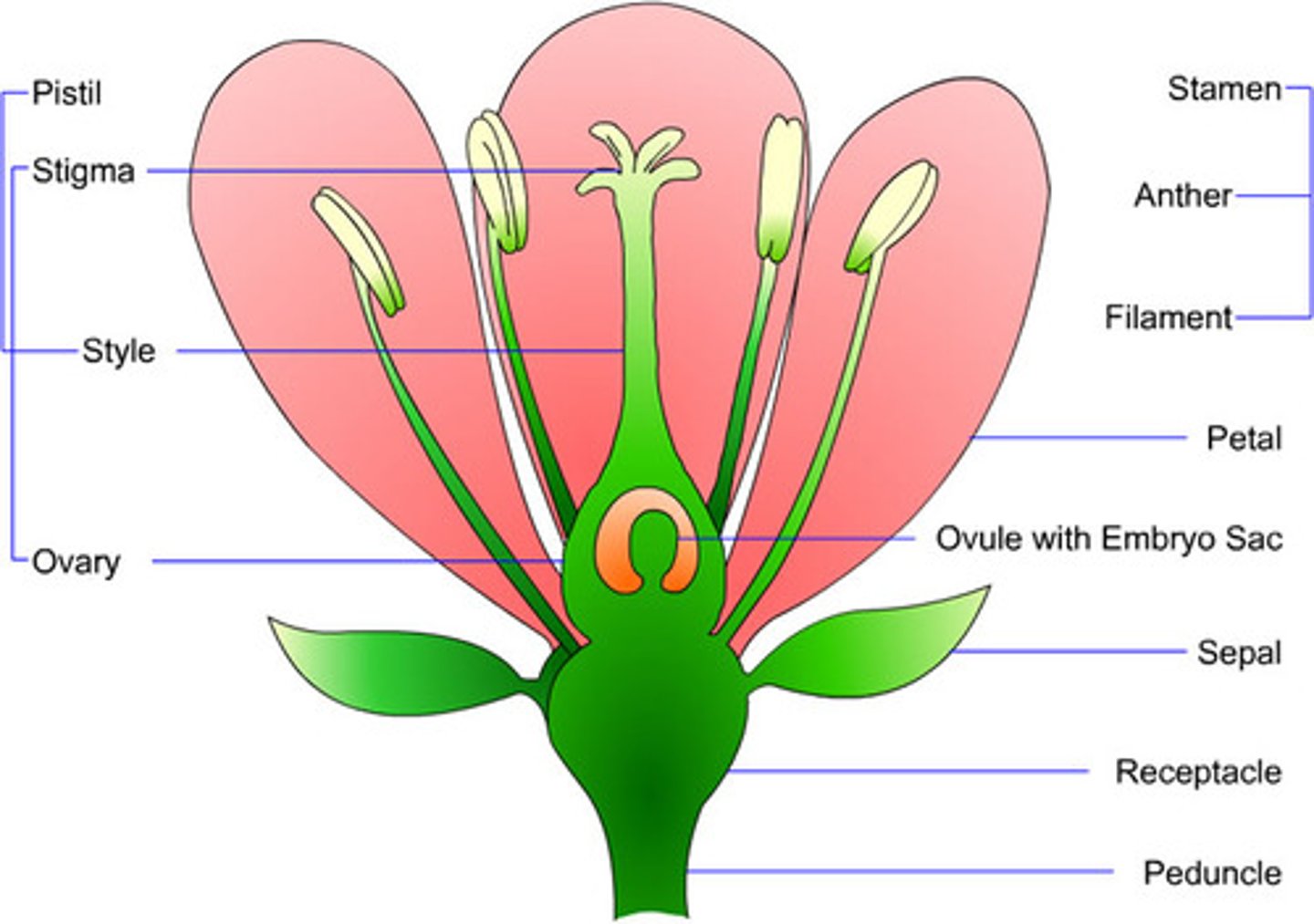
sepal function
protects flower when in bud
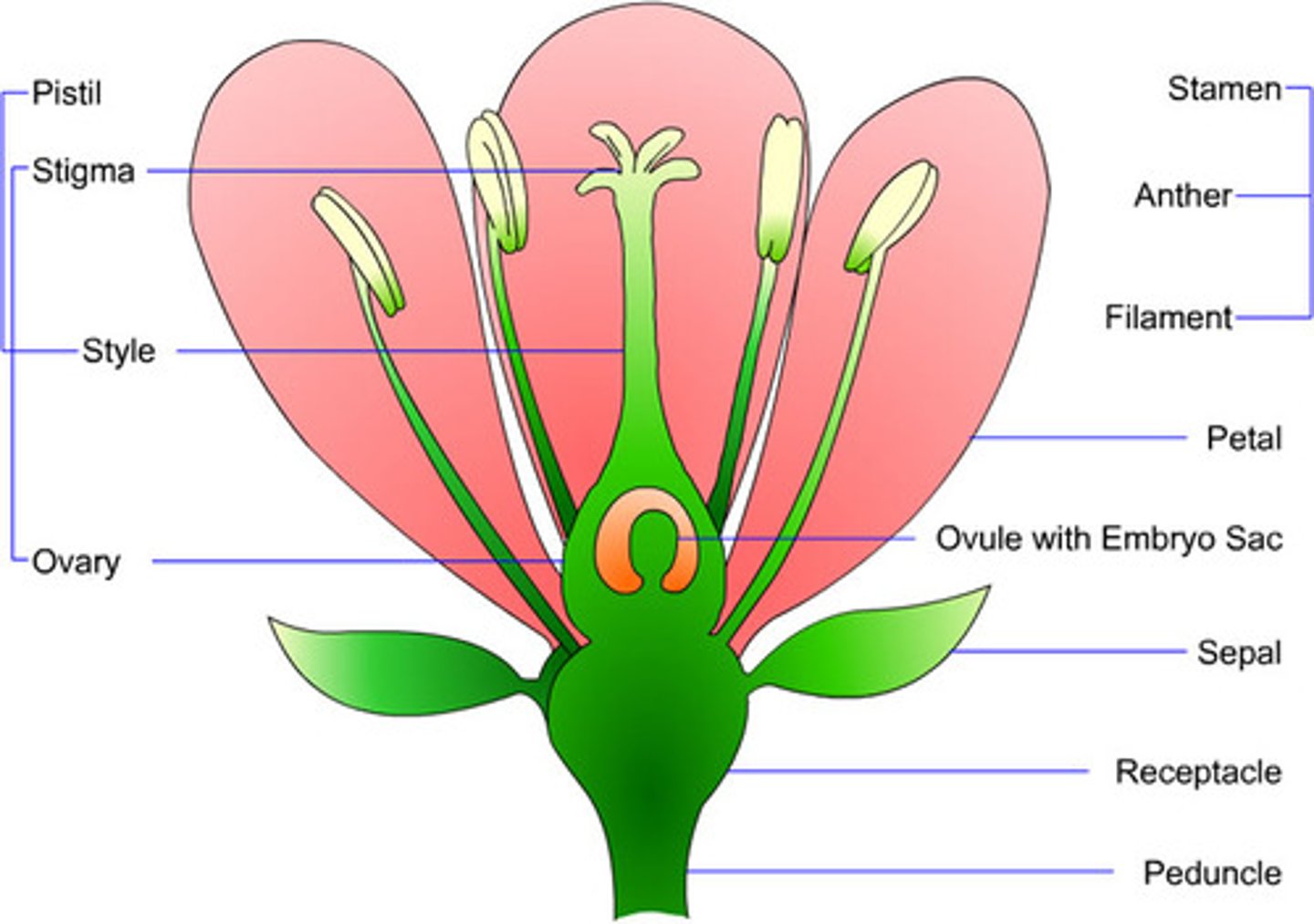
petal function
attracts insects to flower flower pollination
stigma function
where pollen lands
style function
where pollen tube grows
ovary function
contains one or more ovules
pollination
the transfer of pollen from an anther to a stigma of a flower from the same species
self-pollination
involves the transfer of pollen from an anther to a stigma on the same plant
cross-pollination
involves the transfer of pollen from an anther to a stigma on a different plant
fertilisation
the union of the male and female gametes to form a diploid zygote
radicle
the part of the plant embryo that develops into the root
plumule
part of the plant embryo that develops into a shoot
non-endospermic seed
has no endosperm when fully formed
endospermic seed
contains some endosperm when fully formed
fruit
a developed ovary
dispersal
the transfer of a seed or fruit away from the parent plant
dormancy
a resting period when seeds undergo no growth and have reduced cell activity or metabolism
germination
the regrowth of the embryo, after a period of dormancy, if the environmental conditions are suitable