IS LAB: WEEK 3 DILUTION AND ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY REACTION
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
DILUTION
To make weaker solutions from stronger solutions. Indication of relative concentration.
DILUTION FACTOR
Used to correct concentration after using a diluted sample. The result using the dilution must be multiplied by the reciprocal of the dilution made.
SINGLE DILUTION
Used when concentration of sample is too great to be determined accurately or there is low sample size available.
SERIAL DILUTION
For obtaining concentrations of solutions, multiply the original concentration by the first dilution, then by the second and third until the desired concentration is known.
ZONE OF EQUIVALENCE
Occurs when the number of multivalent sites of antigen and antibody are approximately equal.
FALSE-NEGATIVE REACTIONS
Failure to achieve the zone of equivalence may be cause by ___________
PROZONE PHENOMENON
ANTIBODY EXCESS
POSTZONE PHENOMENON
ANTIGEN EXCESS
SERUM DILUTION
REMEDY FOR PROZONE PHENOMENON
REPEAT TESTING AFTER 1-2 WEEKS
REMEDY FOR POSTZONE PHENOMENON
PRECIPITATION
Binding of antibodies + soluble antigens resulting to insoluble complexes
AGGLUTINATION
Binding of antibodies + particulate antigens forming cellular aggregates
PRECIPITATION REACTIONS
PRECIPITATION IN A FLUID MEDIUM
PRECIPITATION BY PASSIVE IMMUNODIFFUSION
PRECIPITATION BY ELECTROPHORETIC TECHNIQUES
NEPHELOMETRY
More sensitive than turbidimetry. Can be used to detect either antigen or antibody.
NEPHELOMETRY
Measures the amount of light that is scattered at a particular angle from the incident beam as it passes through a suspension.
HIGHER
The lower the light intensity, the _______ the concentration of complexes
TURBIDIMETRY
A detection device is placed in direct line with an incident light, measures the reduction in light intensity caused by reflection, absorption or scatter.
PRECIPITATION IN A FLUID MEDIUM
TURBIDIMETRY
NEPHELOMETRY
PRECIPITATION BY PASSIVE IMMUNODIFFUSION
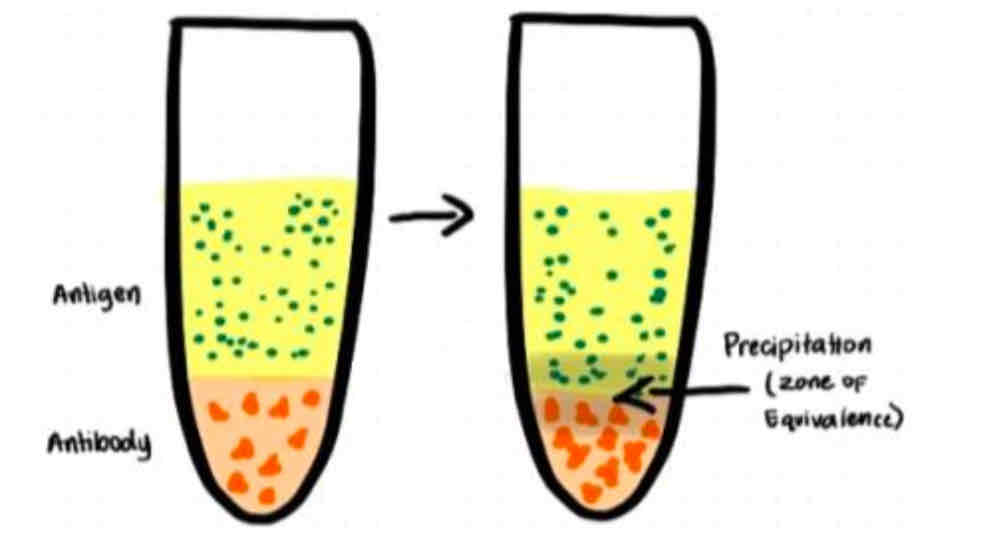
OUDIN’S TECHNIQUE - SINGLE DIFFUSION
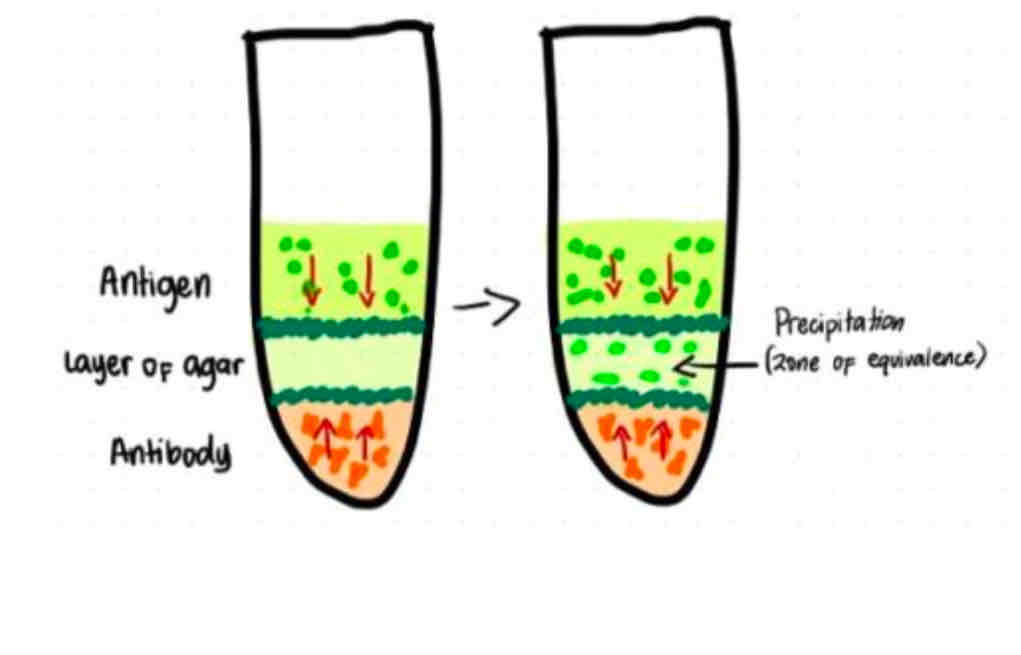
OAKLEY-FULTHORPE TECHNIQUE - DOUBLE DIFFUSION
OUDIN’S TECHNIQUE
Only antigen is diffusing
OAKLEY-FULTHORPE TECHNIQUE
Intervening column plain agar is placed in between. Both antigen and antibody diffusing.
OUDIN’S TECHNIQUE
OAKLEY-FULTHORPE TECHNIQUE
SINGLE DIFFUSION IN TWO DIMENSIONS
Single radial immunodiffusion (SRID). Uses a flat surface petri dish or slide for precipitation reaction. Petri dish allows radial diffusion.
PRECIPITIN RING
SINGLE DIFFUSION IN TWO DIMENSIONS (+) RESULTS
MANCINI METHOD
ENDPOINT METHOD
FAHEY-MCKELVEY METHOD
KINETIC METHOD
MANCINI METHOD
Antigen is allowed to diffuse completely.
ANTIGEN CONCENTRATION
MANCINI METHOD: DIAMETER SQUARED = _________
LOG OF AG CONCENTRATION
FAHEY-MCKELVEY METHOD: INTERPRETATION: d =________
FAHEY-MCKELVEY METHOD
Antigen is NOT allowed to diffuse completely
FAHEY-MCKELVEY METHOD
Measurements taken before the point of equivalence is reached. 18 hours of incubation.
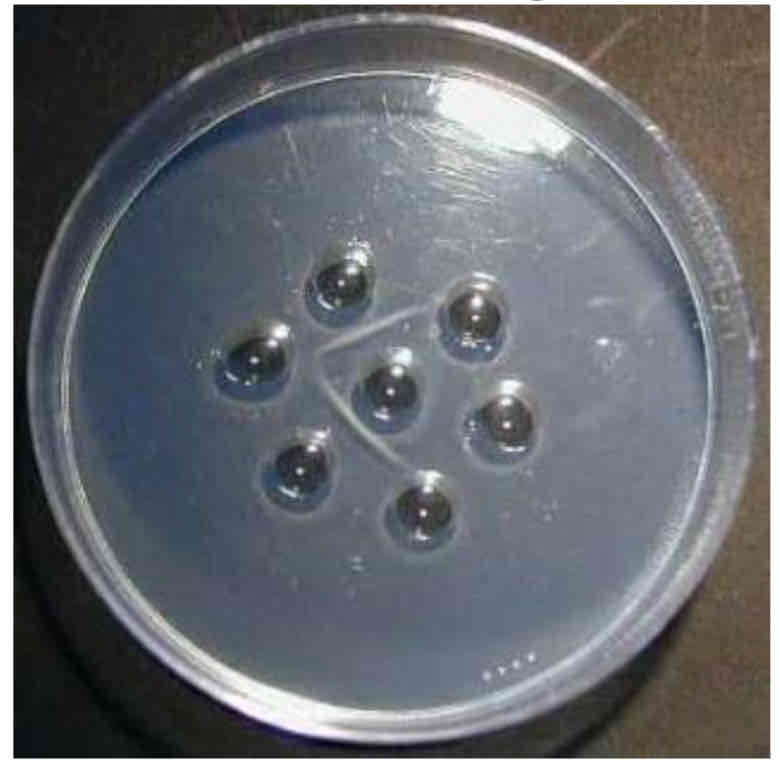
QUALITATIVE OUCHTERLONY TECHNIQUE
Uses a flat surface petri dish or slide for precipitation reaction. (+) Result: Distinct pattern of precipitation
QUALITATIVE OUCHTERLONY TECHNIQUE

IDENTICAL
SMOOTH CURVE
NON-IDENTICAL
CROSSED LINES
PARTIALLY IDENTICAL
SPUR. THE SPUR IS POINTING TO THE SIMPLER ANTIGEN
IDENTICAL, SMOOTH CURVE
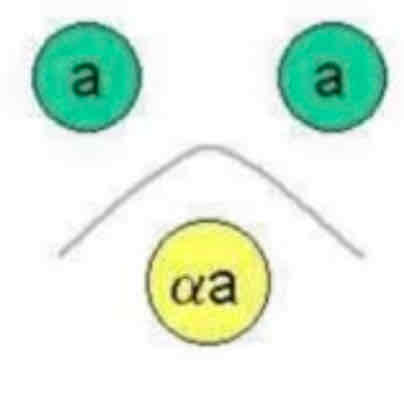
NON-IDENTICAL, CROSSED LINES
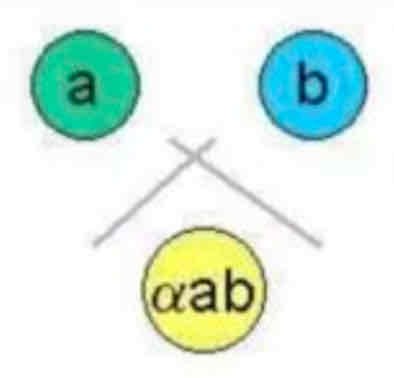
PARTIALLY IDENTICAL, SPUR
IMMUNOELECTROPHORESIS
Antigen: usually from the patient serum
Antibody: placed on trough cut parallel to separated proteins
Gel is incubated for 18 to 24 hours.
MONOCLONAL GAMMOPATHY
IMMUNOELECTROPHORESIS ABNORMAL COUNTOUR OF PRECIPITIN ARC MAY INDICATE ____________
IMMUNOFIXATION ELECTROPHORESIS
Used to identify heavy and light chains involved in monoclonal gammopathies
HEAVY CHAINS
gamma, alpha, mu
LIGHT CHAINS
Kappa, lambda
SENSITIZATION
Initial reaction which involves Ag-Ab combination through single antigenic determinants on the particle surface.
SENSITIZATION
Initial reaction follows the law of mass action is rapid and reversible.
LATTICE FORMATION
Formation of cross-links that form the visible aggregates, represents the stabilization of Ag-Ab complexes with the binding together of multiple antigenic determinants.
DIRECT AGGLUTINATION
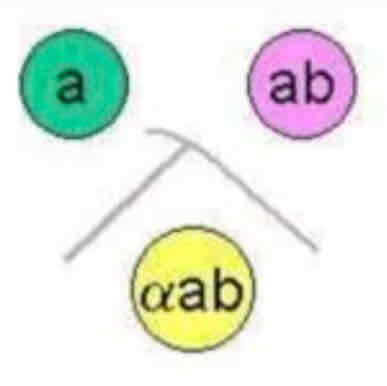
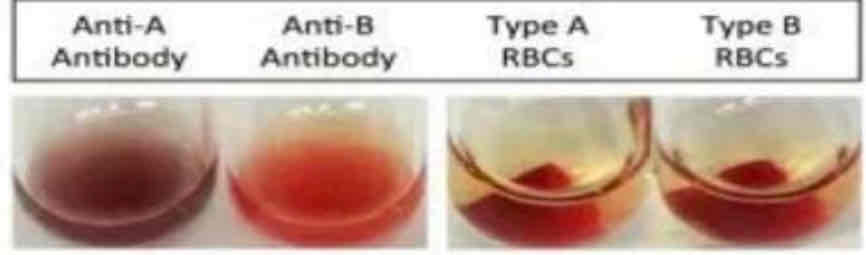
Antigen are found naturally on particle. Example: ABO blood typing, widal’s test for salmonella.
TYPE O
INDIRECT AGGLUTINATION
Employs particles that are coated with antigens not normally found on their surfaces. Example: Latex agglutination test.
REVERSE PASSIVE AGGLUTINATION
Antibodies rather than antigens are attached to a carrier particle. DETECTS ANTIGENS. EXAMPLE: CRP
COAGGLUTINATION
Uses bacterial protein as inert particles to which antibodies are attached. DETECTS ANTIGENS. EXAMPLE: PROTEIN A OF S.AUREUS
AGGLUTINATION INHIBITION
Based on competition between particulate and soluble antigens for limited antibody-combining sites.
LACK OF AGGLUTINATION
AGGLUTINATION INHIBITION: (+) RESULTS:
HEMAGGLUTINATION INHIBITION AND RESPIRATORY SYNCYTIAL VIRUS
EXAMPLE OF AGGLUTINATION INHIBITION:
ANTI-HUMAN GLOBULIN MEDIATED AGGLUTINATION
Employs an antihuman globulin to detect antibody-coated cells.
COOMB’S TEST
AHG TEST
ANTI-HUMAN GLOBULIN MEDIATED AGGLUTINATION EXAMPLES:
24 HRS
IgG
50-72 HRS
IgM
ANTIGEN CONCENTRATION
D2 =