2 - LIPOPROTEINS
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
130 Terms
Phospholipids
Main Types of Lipids from Most Abundant to Least Abundant
Most abundant lipid derived from phosphatidic acid
Phospholipids
Main Types of Lipids from Most Abundant to Least Abundant
Form cellular membranes and lipoprotein surfaces
2
1
Main Types of Lipids from Most Abundant to Least Abundant
Phospholipids
Composed of _ fatty acids + _ polar head group
Choline & Ethanolamine
Main Types of Lipids from Most Abundant to Least Abundant
Phospholipids
Main types of head groups: (2)
Cholesterol
Main Types of Lipids from Most Abundant to Least Abundant
Precursor of steroid hormones
4
hydroxyl group
Main Types of Lipids from Most Abundant to Least Abundant
Cholesterol
Steroid alcohol with _ rings and a _ _
Unesterified (Free) and Cholesterol Ester
Main Types of Lipids from Most Abundant to Least Abundant
Cholesterol
Main types (2)
Triglycerides
Main Types of Lipids from Most Abundant to Least Abundant
Main storage lipid in humans
Composed of 3 fatty acids + 1 glycerol molecule
Main types: Saturated (Animal), Unsaturated (Plant)
3
1
Main Types of Lipids from Most Abundant to Least Abundant
Triglycerides
Composed of _ fatty acids + _ glycerol molecule
Saturated (Animal), Unsaturated (Plant)
Main Types of Lipids from Most Abundant to Least Abundant
Triglycerides
Main types: (2)
Fatty acids
Main Types of Lipids from Most Abundant to Least Abundant
Long C-H chains with a terminal carboxyl group
Rarely free in plasma; mostly in phospholipids or TAG
Lipoproteins
Complex of lipids and apolipoproteins for transport of TAG and cholesterol
Chylomicrons (CM)
Major lipoprotein classes
Largest, least dense; cause of milky plasma
Chylomicrons (CM)
Major lipoprotein classes
Transport exogenous (dietary) triglycerides
Chylomicrons (CM)
Major lipoprotein classes
Cleared by LPL, forming remnants taken up by the liver
Very Low Density Lipoprotein (VLDL)
Major lipoprotein classes
Transport endogenous triglycerides made in the liver to peripheral cells during fasting
Very Low Density Lipoprotein (VLDL)
Major lipoprotein classes
Cause plasma turbidity but no creamy layer
Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL)
Major lipoprotein classes
End product of VLDL catabolism
Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL)
Major lipoprotein classes
“Bad cholesterol”; most cholesterol-rich
Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL)
Major lipoprotein classes
Transport cholesterol to peripheral cells
High Density Lipoprotein (HDL)
Major lipoprotein classes
Smallest, most dense; synthesized in liver & intestine
High Density Lipoprotein (HDL)
Major lipoprotein classes
“Good cholesterol”: most protein-rich
High Density Lipoprotein (HDL)
Major lipoprotein classes
Transport cholesterol excess to the liver
Intermediate Density Lipoprotein (IDL)
Minor lipoprotein classes
Transient VLDL remnants; normally short-lived
Contain intermediate levels of TAG and cholesterol
Lipoprotein (a)
Minor lipoprotein classes
“Sinking pre-β lipoprotein”
Lipoprotein (a)
Minor lipoprotein classes
Electrophoretic mobility like VLDL, density like LDL
Structure similar to plasminogen
Beta-VLDL
Abnormal lipoprotein classes
“Floating β lipoprotein” or “VLDL rich in cholesterol”
Beta-VLDL
Abnormal lipoprotein classes
Electrophoretic mobility like LDL, density like VLDL
Found in Type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia
Beta-VLDL
Abnormal lipoprotein classes
Found in Type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia
LpX
Abnormal lipoprotein classes
Seen in cholestatic disease or LCAT deficiency
<0.93
0.93-1.006
1.019-1.063
1.063-1.21
CHARACTERISTICS OF MAJOR LIPOPROTEINS | ||||
CM | VLDL | LDL | HDL | |
Density | _ | _ | _ | _ |
80-95% TAG
2-4% CE
1-3% FE
1-2% Protein
CHARACTERISTICS OF MAJOR LIPOPROTEINS | ||||
CM | VLDL | LDL | HDL | |
Composition | _ | 45-65% TAG 15-20% PL 6-10% Protein | 45-50% CE 18-22% Protein 6-8% FE | 45-55% Protein 26-32% PL 3-5% FE |
45-65% TAG
15-20% PL
6-10% Protein
CHARACTERISTICS OF MAJOR LIPOPROTEINS | ||||
CM | VLDL | LDL | HDL | |
Composition | 80-95% TAG 2-4% CE 1-3% FE 1-2% Protein | _ | 45-50% CE 18-22% Protein 6-8% FE | 45-55% Protein 26-32% PL 3-5% FE |
45-50% CE
18-22% Protein
6-8% FE
CHARACTERISTICS OF MAJOR LIPOPROTEINS | ||||
CM | VLDL | LDL | HDL | |
Composition | 80-95% TAG 2-4% CE 1-3% FE 1-2% Protein | 45-65% TAG 15-20% PL 6-10% Protein | _ | 45-55% Protein 26-32% PL 3-5% FE |
45-55% Protein
26-32% PL
3-5% FE
CHARACTERISTICS OF MAJOR LIPOPROTEINS | ||||
CM | VLDL | LDL | HDL | |
Composition | 80-95% TAG 2-4% CE 1-3% FE 1-2% Protein | 45-65% TAG 15-20% PL 6-10% Protein | 45-50% CE 18-22% Protein 6-8% FE | _ |
Apo B48, C, E
Apo B100, C, E
Apo B100, E
Apo A-I, A-II, C
CHARACTERISTICS OF MAJOR LIPOPROTEINS | ||||
CM | VLDL | LDL | HDL | |
Apolipoprotein | _ | _ | _ | _ |
Apolipoproteins
Located on surface of lipoprotein particles
Maintain structure, enable receptor binding, and regulate enzymes
Apo A1
Characteristics of Major Apolipoproteins
Major HDL protein; antiatherogenic, LCAT activator
Apo B
Characteristics of Major Apolipoproteins
Found in LDL & VLDL; LDL receptor ligand
Apo E?
Characteristics of Major Apolipoproteins
Chylomicron-specific; Remnant receptor ligand
Apo C2
Characteristics of Major Apolipoproteins
LPL cofactor/activator
Apo C3
Characteristics of Major Apolipoproteins
LPL inhibitor
Apo E
Characteristics of Major Apolipoproteins
LDL receptor ligand; targets CM and VLDL remnants
Apo(a)
Characteristics of Major Apolipoproteins
Plasminogen inhibitor
Lipid Absorption Pathway
Lipoprotein Metabolism Pathways
Dietary lipids are digested into fatty acids, monoglycerides, diglycerides, free cholesterol, and lysophospholipids
Exogenous Pathway
Lipoprotein Metabolism Pathways
Chylomicrons (from intestinal cells) enter blood via thoracic duct and interact with LPL in capillaries
Endogenous Pathway
Lipoprotein Metabolism Pathways
VLDL is produced in the liver using recirculated lipids and converted into LDL via LPL and hepatic lipase
Reverse Cholesterol Transport Pathway
Lipoprotein Metabolism Pathways
HDL removes excess cholesterol from peripheral cells, and delivers cholesterol directly to the liver or transfer cholesterol to LDL/VLDL via CETP for indirect delivery
Lipoprotein Lipase (LPL)
Lipolytic Enzymes
Hydrolyzes TAG into free fatty acids and glycerol
Lecithin Cholesterol Acyl Transferase (LCAT)
Lipolytic Enzymes
Converts free cholesterol into cholesteryl ester on immature HDLs
Acyl-CoA:Cholesterol Acyltransferase (ACAT)
Lipolytic Enzymes
Converts free cholesterol into cholesteryl ester inside cells
Hepatic Lipase
Lipolytic Enzymes
Hydrolyzes TAG and phospholipids in IDL and HDL
Pancreatic Lipase
Lipolytic Enzymes
Hydrolyzes dietary TAGs in the intestine into monoglycerides and free fatty acids
Hormone-Sensitive Lipase (HSL)
Lipolytic Enzymes
Releases FFAs from stored triglycerides in adipocytes during fasting or stress
12-hour
4
Lipid Measurements
Cholesterol
_-_ fast preferred but not highly affected by meals
If delayed analysis, refrigerated at _°C several days
GC-MS and IDMS
Lipid Measurements
Cholesterol
Reference methods (2)
Chemical (Colorimetric)
Lipid Measurements
Cholesterol
Obsolete Methods
Colorimetry
Extraction
Saponification
Precipitation
Lipid Measurements
Cholesterol
Reagents for the steps:
1. Lieberman-Burchardt (_)*
2. Petroleum Ether (_)
3. Alcoholic Potassium Hydroxide (_)
4. Digitonin (_)
Pearson, Stern, Mac Gavack
Bloors
Abell-Kendall
Schoenheimer, Sperry, Parekh, Jung
Lipid Measurements
Cholesterol
General Step Methods:
ж 1-Step (_): C
ж 2-Step (_): C + E
ж 3-Step (_): C + E + S
ж 4-Step (_): C + E + S + P
Lieberman-Burchardt, Green
Salowski, Red
Lipid Measurements
Cholesterol
There are two colorimetric reactions with their end products:
1. _-_: Cholestadienlyl Monosulfonic Acid (_)
2. _: Cholestadienlyl Disulfonic Acid (_)
Enzymatic Cholesterol Oxidase
Lipid Measurements
Cholesterol
Routine Method
Cholesterol + Fatty acid
Lipid Measurements
Cholesterol
Routine Method
Cholesteryl ester + H2O w/ Cholesteryl esterase
Cholestenone + H2O2
Lipid Measurements
Cholesterol
Routine Method
Cholesterol + O2 w/ Cholesteryl esterase
500
Lipid Measurements
Cholesterol
Routine Method
H2O2 + Dye = Color intensity measured @~_ nm
Hemoglobin, plant sterols
Lipid Measurements
Cholesterol
Positive interference (2)
Vitamin C, Bilirubin
Lipid Measurements
Cholesterol
Negative interferences (2)
10-12
Lipid Measurements
Triglycerides
Requires fasting (_-_ hours)
10-20
Lipid Measurements
Triglycerides
Endogenous glycerol increases TAG by _-_ mg/dL
GC-MS
Lipid Measurements
Triglycerides
Reference Method
Chemical
Lipid Measurements
Triglycerides
Obsolete Methods:
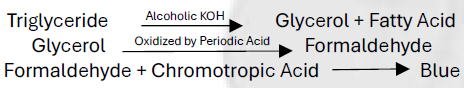
Van Handel & Zilversmith
Lipid Measurements
Triglycerides
Obsolete Methods
Colorimetric
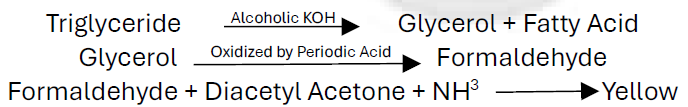
Hantzch Condensation
Lipid Measurements
Triglycerides
Obsolete Methods
Fluorometric
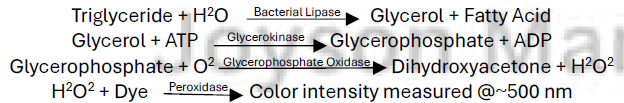
Enzymatic Glycerokinase
Lipid Measurements
Triglycerides
Obsolete Methods
Routine Method
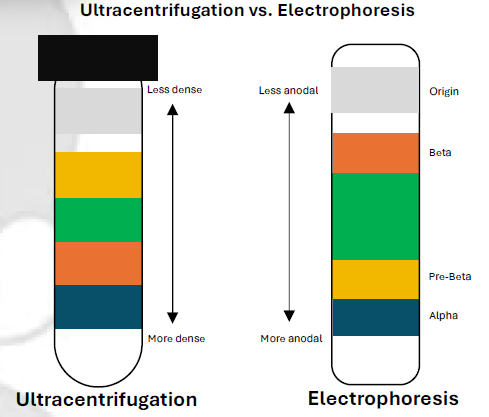
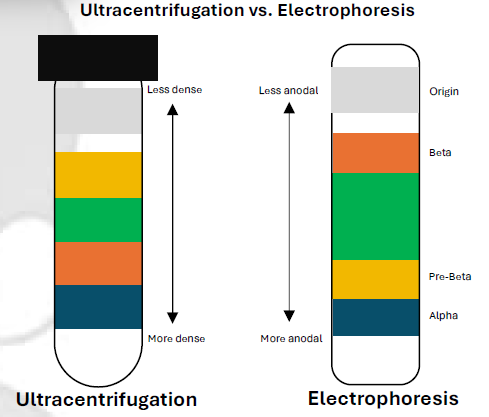
Ultracentrifugation (Density Gradient)
Lipoprotein Separation Techniques
Reference Method
100,000–120,000×g for 18–24 hours
Lipoprotein Separation Techniques
Ultracentrifugation (Density Gradient)
Force & Duration
Potassium Bromide with 1.063 density
Lipoprotein Separation Techniques
Ultracentrifugation (Density Gradient)
Reagent:
Electrophoresis
Lipoprotein Separation Techniques
Charge & Size-Based
Agarose Gel
Lipoprotein Separation Techniques
Electrophoresis (Charge & Size-Based)
Supporting medium
Oil Red O, Fat Red 7B, Sudan Black B
Lipoprotein Separation Techniques
Electrophoresis (Charge & Size-Based)
Staining Dyes (3)
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMRS)
Lipoprotein Separation Techniques
Non-destructive imaging technique for lipoproteins
Chemical precipitation (Dextran sulfate + Magnesium)
Centrifugation
Enzymatic cholesterol assay on supernatant
HDL
Obsolete method
Step 1:
Step 2:
Step 3:
polymers/detergents
HDL
New and routine methods: direct homogeneous assays using _/_ to block non-HDL reaction
3-step precipitation + Abell-Kendall assay
HDL
Reference method:
β-Quantification
LDL
Reference Method:
VLDL
HDL
LDL
Ultracentrifugation (Remove ) + _ Precipitation
Friedewald Equation (If TAG <400 mg/dL)
LDL
Routine Method
5
2.175
LDL
Friedewald Equation
LDL = Total cholesterol – HDL – (Triglycerides/_)*
or
LDL = Total cholesterol – HDL – (Triglycerides/_)**
*If expressed in mg/dL | **if expressed in mmol/L
Turbidimetry, nephelometry, ELISA
Apolipoproteins
(3)
Familial LPL Deficiency
Dyslipidemias
Hyperlipoproteinemias
Fredrickson Classifications of Hyperlipoproteinemias
Type 1
Familial LPL Deficiency
Dyslipidemias
Hyperlipoproteinemias
Fredrickson Classifications of Hyperlipoproteinemias
High CM & TAG
Familial hypercholesterolemia
Dyslipidemias
Hyperlipoproteinemias
Fredrickson Classifications of Hyperlipoproteinemias
Type 2a
Familial hypercholesterolemia
Dyslipidemias
Hyperlipoproteinemias
Fredrickson Classifications of Hyperlipoproteinemias
High Chole & LDL w/ LDL receptor defect
Combined Hyperlipidemia
Dyslipidemias
Hyperlipoproteinemias
Fredrickson Classifications of Hyperlipoproteinemias
Type 2b
Combined Hyperlipidemia
Dyslipidemias
Hyperlipoproteinemias
Fredrickson Classifications of Hyperlipoproteinemias
High TAG, Chole, LDL, VLDL
Familial Dysbetalipoproteinemia
Dyslipidemias
Hyperlipoproteinemias
Fredrickson Classifications of Hyperlipoproteinemias
Type 3
Familial Dysbetalipoproteinemia
Dyslipidemias
Hyperlipoproteinemias
Fredrickson Classifications of Hyperlipoproteinemias
High VLDL, IDL (Apo E2/2 homozygosity)
Familial Hypertriglyceridemia
Dyslipidemias
Hyperlipoproteinemias
Fredrickson Classifications of Hyperlipoproteinemias
Type 4
Familial Hypertriglyceridemia
Dyslipidemias
Hyperlipoproteinemias
Fredrickson Classifications of Hyperlipoproteinemias
High TAG, VLDL
Type 5
Dyslipidemias
Hyperlipoproteinemias
Fredrickson Classifications of Hyperlipoproteinemias
High CM, VLDL, TAG, Chole