AP Gov Unit 5.6 & 5.7 - INTEREST GROUPS and OTHER GROUPS Influencing Policy Making and Policy Outcomes
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What are interest groups?
Organization that seeks to influence public policy, either for a specific or broad purpose
Example of an interest group focused on a specific purpose
National Rifle Association (NRA) --> Focus on gun rights
Example of an interest group focused on a broader purpose
American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU) --> Focus on a broader set of issues, all related to civil liberties
Although there are thousands of interest groups in the U.S., most of them fall in three categories. Which are those?
- Economic Groups
- Public Interest Groups
- Government Interest Group
Economic Groups (focus, characteristics, and examples)
Economic groups are formed to promote & protect members' economic interests.
- Most have existed for a long time, thus have formed strong ties with legislators/bureaucrats
- Very large, influential, and extremely well funded
- Represent or employ large groups of people
Examples include:
- U.S. Chamber of Commerce
- American Farm Bureau Federation
- American Nuclear Energy Council
- AFL-CIO
- American Medical Association
Public Interest Groups (focus, characteristics, and examples)
Public interest groups are non-profit organizations that usually focus around a set of public policy issues
- Usually the most powerful public interest groups are single-issue groups (NRA/ Mothers against Drunk Driving) due to the intensity of their supporters (use a single issue as a litmus test for candidates)
Examples include:
- Sierra Club (environment)
- Christian Coalition (religious interests)
- NRA (gun rights)
Government Interest Group (focus and characteristics)
Government interest groups focus on bringing the issues of local and state government before Congress and the administration.
- Groups that represent mayors
- Groups that represent the nation's governors
How do interest groups influence public policy?
- GOTV
- Endorsements of candidates
- Testifying before Congress
- Political Donations/PACs
- Court Action
- Direct Lobbying
- Grassroot Lobbying
- Propaganda
Explain the concept of "GOTV" in the context of interest groups
GOTV (Get Out To Vote) refers to the practice of mobilizing voters in order to get them to the polls to vote candidates that support the goals of the interest groups
How does the endorsement of candidates help interest groups influence government?
By endorsing a candidate, an interest group is encouraging their membership/followers to vote for that candidate that is going to go along the policy goals of the interest group
How does "Testifying before Congress" help interest group influence legislation
Interest groups send expert witnesses to committee hearings in order to propose legislation. Doing this allows interest groups to support certain legislation or even write bills than can be later introduced to Congress by a Representative/Senator.
Basically, interest groups can draft legislation favorable to their goals.
How political donations allow interest groups to influence government
Interest groups can donate big chunks of money to candidates and political parties that support their causes.
To do this, corporations, trade groups, and unions form political action committees (PACs) and super PACs.
How can interest groups affect the judiciary in their advantage?
a. By filing lawsuits or class action suits to protect and advance their interests
b. By submitting amicus curiae briefs in lawsuits to which they are not the plaintiff so that judges may consider their advice (has to directly affect the case).
What does "amicus curiae" means?
Friend of the court
What is lobbying?
The practice of persuading political leaders to support the group's position.
Explain how interest groups practice direct lobbying to influence politics
Interest groups representatives meet privately with government officials to suggest legislation and to give arguments that support their position. By doing this interest groups are more likely to receive legislation friendly to their interests.
Lobbyists are policy specialists, while congressmen (gov't official) are policy generalists (TRUE/FALSE)
TRUE
Lobbyists are the ones expert on their policies, and they educate Congressmen/gov't politicians, which know policies but in a more general manner
Explain how interest groups practice grassroot lobbying to influence politics
By practicing grassroot lobbying, interest groups encourage their members to write, phone, or email their legislators in support of a particular program or piece of legislation that goes along with the interest group cause.
The 1946 Federal Regulation of Lobbying Act
Intended to allow the government to monitor lobbying activities by requiring lobbyists to register with the government and publicly disclose their salaries, expenses, and the nature of their activities in DC
Explain how interest groups use propaganda to promote their cause
Interest groups send out press releases and run advertisements promoting their views. They do this through
- TV commercials
- Social Media campaigns
- Advertisements.
Some laws prohibit, for limited amounts of time, certain lobbying activities by former government officials. This is done to prevent the appearance of influence peddling. What does "influence peddling" mean?
It is the practice of using personal friendships and inside information to get political advantage
Explain the issue of the "revolving door"
Former congressmen help interest groups. Ater Congressmen leave the government, those interest groups give jobs to those former congressmen that helped them. Now, the former congressmen become lobbyists and influence Congress.
This cycle repeats like a revolving door
Review iron triangles
EXAMPLE
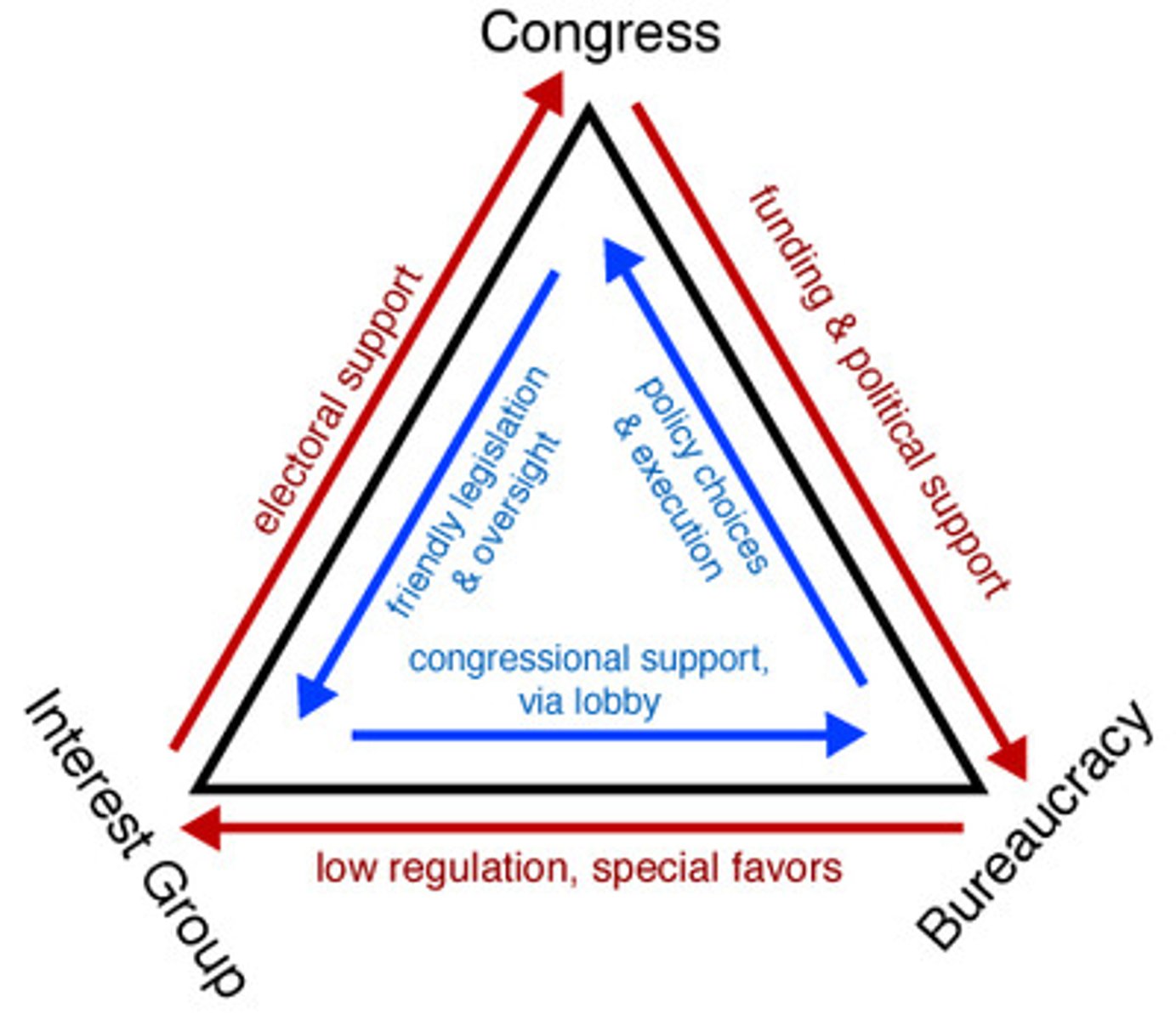
Explain how there is inequality between interest groups and how it affects policy making
Some groups have a larger membership and/or are very well funded, increasing the influence they have, and making it harder for smaller interest groups to promote their policy goals.
Larger groups have a greater access to policymakers, and thus most of the time promoted policies come from this larger groups, not small ones.
As there are interest groups that focus on single issues, there are social movements which focus on...
broad based efforts to achieve major policy change
Social movements are more unified than single-issue interest groups (TRUE/FALSE)
FALSE
Social movements tend to be more diffuse than interest groups
Explain the difference in leadership between interest groups and social movements
In interest groups, a narrow group of people at the top form the leadership, and the people that follow them are members/followers
In social movements, leadership is more disperse
EXAMPLE
- Civil Rights Movement
- Women's Rights Movement
Explain protests movements
Movements that protest and use civil disobedience as a way to call attention to their issues.
EXAMPLES
- Black Lives Matter
- MeToo Movement
Explain civil disobedience
Civil disobedience is intentionally breaking a law to call attention to an injustice (prove the law is unjust
What can affect the success of social/protest movements?
Lack of leadership
Lack of resources and infrastructure
Unclear policy goals
Social/protest movements always fail to meet their policy goals (TRUE/FALSE)
FALSE
Some gather momentum and result in policy changes (e.g. civil right movement)