Biology - Evolution and evidences of Evolution
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Adaptation
Inherited characteristics of a species that developed over time in response to an environmental factor, enabling the species to survive.
Artificial Selection
Darwin’s term for the selective breeding of organisms selected for certain traits in order to produce offspring having these traits.
Biogeography
The study of the distribution of plants and animals on Earth.
Biological Fitness
Measure of a trait’s relative contribution to the following generation (the success of an organism’s reproduction).
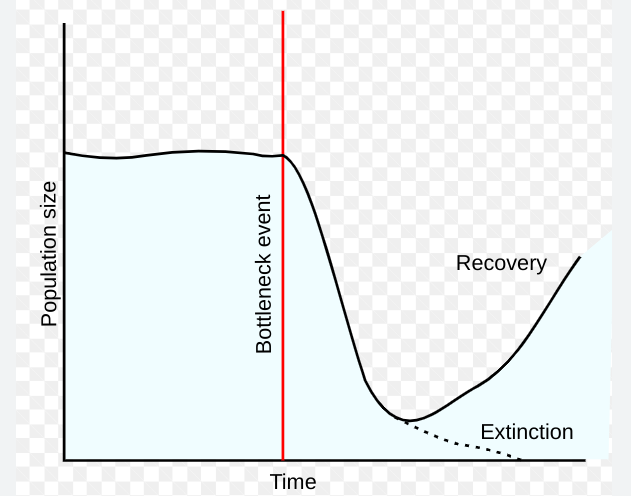
Bottleneck Effect
The process through which a large population declines in number then rebounds.
Directional Selection
The shift of a population towards an extreme version of a beneficial trait. (Drastic changes occur in a few generations).
Disruptive Selection
The process through which those with average traits are removed, creating two populations with extreme traits (black or white colored Oysters -- both can camaflouge well, however there are not gray Oysters present).
Embryology
The studies of embryos and their development.
Evolution
The hereditary changes in groups of living organisms over time.
Fossil Record
A term used to describe the fossils found and used to place important events and species in the appropriate geologic era. (Fossil records may show the presence of different organisms, allowing scientists to better understand the evolution of them).
Founders Effect
The random effect which can occur when a small population settles in an area separated from the rest of the population and interbreeds, producing unique allele variations.
Gene Flow
The movement of organisms and the genetic material that they carry from one population to another.
Gene Frequency
The ratio of a particular allele to the total of all other alleles of the same gene in a given population.
Genetic Drift
The change in the allele frequency of a population.
Gradualism
The hypothesis that evolution proceeds CHIEFLY by the accumulation of gradual changes over time.
Homologous Structures
Body parts in different species that have similar anatomy because they evolved from a common ancestors; they usually have different functions.
Hypothesis
An educated guess based on observations and existing knowledge which can be tested in an experiment.
Inherited Variation
Traits and their variations that are passed down from parent to child.
Isolation
A process by which two species that could produce offspring are prevented from doing so.
Molecular Homology
Similarity in molecular structures like amino acids or DNA between two organisms indicating evolutionary relationships.
Mutation
A permanent change in a cell’s DNA ranging from a single nucleotide change to a deletion of a chromosome.
Natural Selection
A theory of evolution developed by Darwin based on the four ideas: excess reproduction; variations within a population; inheritance; advantages of specific traits in an environment.
Non random Mating
Occurs when the probability of two individuals in a population will mate is NOT the same for all possible combinations of genotypes (certain traits are more favorable).
Phylogenetic Tree
A diagram which depicts the lines of evolutionary descent of different species or organisms.
Punctuated Equilibrium
The hypothesis that evolutionary change is marked by isolated episodes of rapid specialization between long periods of little to no change.
Reproductive Success
Passing of genes onto the next generation in a way that they too can pass those genes on; number of offspring an organism produces.
Speciation
A process by which new species are formed.
Stabilizing Selection
The most common known form of natural selection in which organisms with extreme expression of a trait are removed.
Stasis
A period of equilibrium or stability
Theory
A well supported explanation for a phenomenon based on scientific evidence.