4 - Synaptic junction
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Define a synapse
junction between two neurons which permits the transmision of a signal from one neuron to another
State the two main types of synapse
electrical
chemical
Electrical synapse
allows for rapid propagation of an action potential between neurons
Chemical synapse (2)
exocytosis of neurotransmitters from pre synaptic membrane bound vesicles to enable communication with a post synaptic cell
neurotransmitter binds to receptors of post synaptic cell
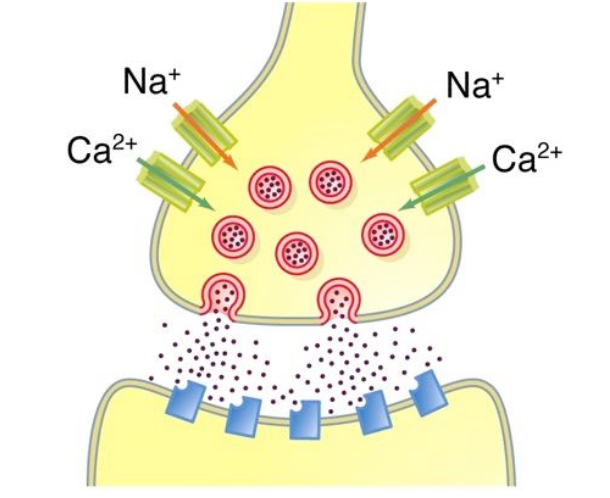
Following action potential (8 points)
action potential arrives at axon terminal
depolarisation of axon terminal
activation of voltage gated axon terminal
influx of calcium down conc gradient into axon
increase of calcium triggers fusion of neurotransmitter containing vesicle with presynaptic membrane
vesicles release neurotransmitter into synaptic cleft by exocytosis
neurotransmitter binds to post synaptic membrane bound receptor
activcation of post-synaptic membrane bound receptor
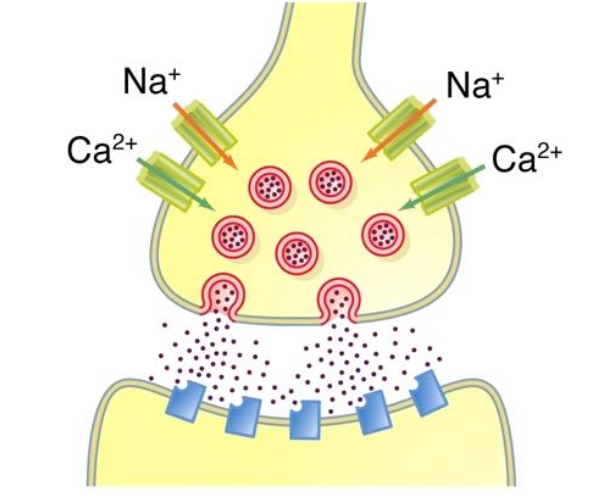
What happens to the neurotransmitter following binding?
can be either degraded or recycled back into the pre synaptic neuron
What do excitatory neurotransmitters do and how?
cause depolarisation of post synaptic cell by triggering an excitatory post synaptic potential (EPSP)
How is an excitatory post synaptic potential formed?
binding to receptors that act as ligand gated ion-channels that are permeable to Na ions
What do inhibitory neurotransmitters do and how?
cause hyperpolarisation of post synaptic cell by triggering an inhibitory post synaptic potential (IPSP)
How is an inhibitory post synaptic potential formed?
binding to receptors that act as ligand gated ion-channels that are permeable to Cl ions
List two excitatory neurotransmitters and what they do
acetylcholine (common in vertebrates)
glutamine (main excitatory neurotransmitter in brain)
List two inhibitory neurotransmitters and what they do
GABA (main inhibitory neurotransmitter in brain)
Glycine (main inhibitory neurotransmitter in spinal chord)
Define spatial summation
stimulatiuon of multiple neurons at the same time
Define temporal summation
stimulatiuon of multiple neurons in repeat succession