Resource Constraints Temp
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
macroclimate
large scale climate patterns that prevail over entire regions
determined by climate cells and topography
microclimate
small scaled climate patterns (can be down to cm)
deviate from the macro
determined by landscape, vegetation, or small topography (elevation, aspect, surface colour, depressions, etc)
elevation on microclimate
the timberline shows a shift with increasing elevation
as mean annual temp decreases trees are less able to survive (need 6.7* for 94 days per year to grow)

aspect on microclimate
north slopes have less solar radiation, more snow and more water leading to more forest growth
south slopes have more solar radiation, less snow, and less water leading for a more dominant grass land type ecosystem
vegetation on microclimate
trees and shrubs can cast shade, understories have colder temps and evaporation is decreased
surface colour on microclimate
lighter colours will reflect light so the surface wont increase in temperature (snow), while darker colours absorb light so the surface increases in temp (bedrock)
albedo
reflectivity of a landscape, how much light is reflected and does not get absorbed
so light coloured surfaces would have a higher __ than dark coloured
boulders and burrows on microclimate
some organisms live under rocks or underground in burrows
these create shade and allow animals to avoid heat during the day
aquatic temperatures
less fluctuation than air temperatures - usually between -4 to 32*
heat is absorbed by water as it evaporates, water gives up heat energy as it freezes
range of tolerance
the range of an environmental condition (abiotic factors) in which an organism can survive, grow and reproduce
species have optimal conditions within environmental thresholds, beyond this survival decreases and physiological stress ovvurs
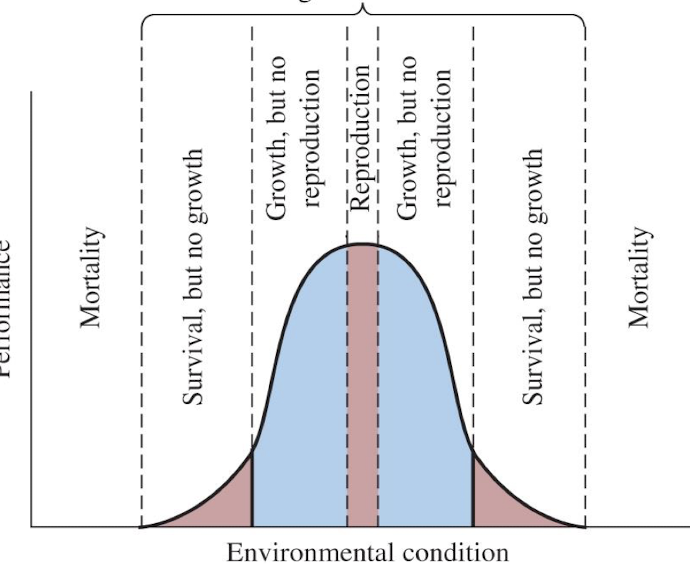
range of tolerance and fundamental niche
one environmental condition such as temperature compared to all environmental conditions where a species may live
law of tolerance
the abundance and distribution of an organism can be determined by the deviation between location conditions (temp) and optimum set of conditions for a species
so the same factors which limit growth will affect abundance and distribution
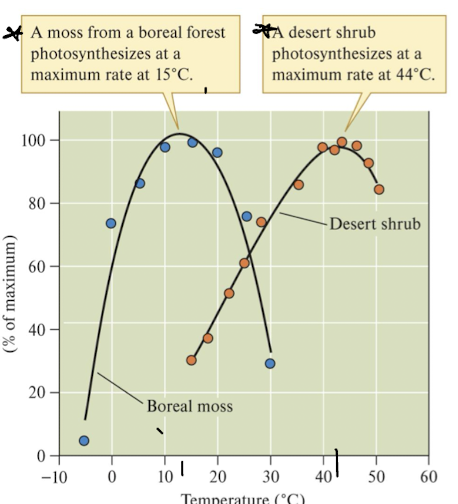
plant range of tolerance
temperature limits photosynthesis in various species who have adaptations to different climates
differently adapted species have different ranges of tolerance and optima
principle of allocation
organisms have limited energy, when an organism allocates energy to one function, it reduces energy available to others
balance of costs vs benefits, adaptation to one set of conditions will reduce fitness in other environments
when you are at the margins of tolerance
die, migrate, acclimate, adaptations to extreme temps
death
avoid extreme temps by funnelling all energy to reproduction - offspring has a chance
ex annual plants seed before winter
migration
avoid extreme temperatures by moving to warmer regions
advantages outweigh the costs
ex birds, insects, mammals
acclimation
physiological or morphological changes in an organism in response to changes in the environment (temp, pH, humidity, etc)
NOT adaptation (but the ability to is an adaptation)
phenotypic plasticity
ex adjustment to high altitudes - generally reversible
physiological/morphological adaptations
to extreme temperatures
freeze tolerance - cryoprotectants
or in a polar bear - thick fur, body fat, short body appendages
freeze tolerance
production of cryoprotectants
example in wood frogs - freeze themselves and rehydrate in the summer
reduced metabolic activity adaptations
to extreme temperatures
hibernation or estivation (hot temps)
adaptation vs acclimation
an evolutionary process changing on the genetic level, not reversible VS and individual changes within an individuals lifetime - reversible
heat balance equation
Hs = Hm ± Hcd ± Hcv ± Hr - He
Hs - total heat stored, Hm - gain via metabolism, Hcd - conduction (ex soil or roots), Hcv - convection (wind), Hr- radiation, He - evaporation
plant heat balance in cold temps
dark coloured leaves, and leaf and flower orientation allow for increase Hr
cushion/compact growth allows for decreased loss from convection (wind)
smaller surface area ratio
plant heat balance in hot temp
decrease contact with ground, open growth form allows for increase loss from Hcv
reduce leaves and light surface and so Hr and Hcd also decrease
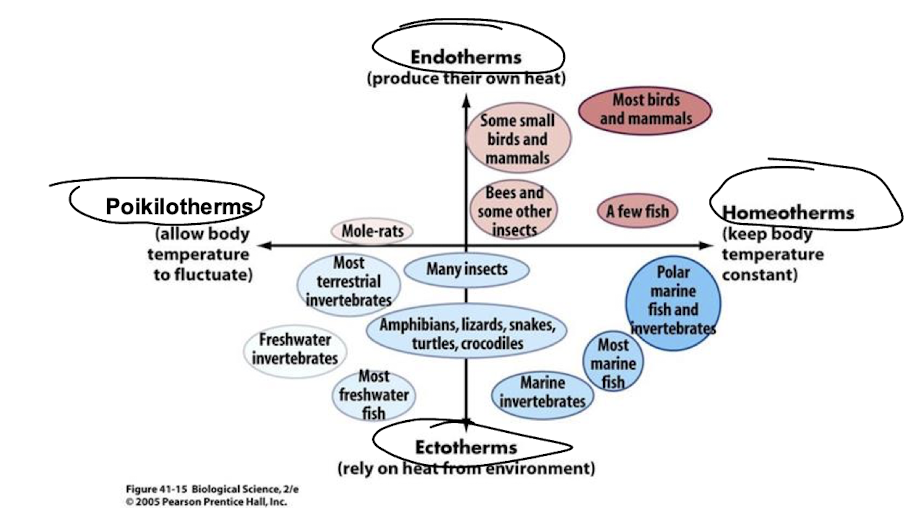
poikilotherms
body temperature varies with the environment
homeotherms
body temperature relatively constant regardless of environemt
ectotherms
control body temp using external energy
ex plants, fish, amphibians, reptiles and inveterbrates
sit in sun for warmth or get out of sun if too hot
low diversity in regions of cold climate
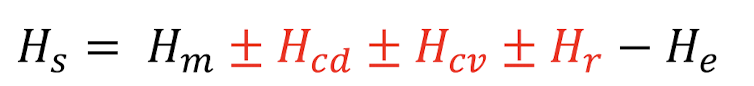
endotherms
control body temperature using internal energy such as metabolism or shivering/sweating
metabolic rate remains constant in neutral zones but increases when too hot or too cold
ex mammals and birds - allows for species to live in regions where temp gets colder than body temperature
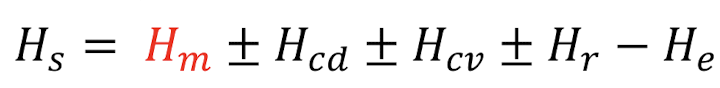
endotherm heating/cooling
shivering to contract muscles and generate heat
sweating or panting will increase convective cooling
temperature regulation