Ch 24: Bacteria, Archaea, Viruses
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
For Biol 130
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
father of microbiology
discovered bacteria
1st microscopist & microbiologist
What are the 3 domains of life?
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
ALL domains have… (3 things)
plasma membranes & ribosomes
common set of metabolic pathways
use DNA to encode proteins, same genetic code & similar DNA sequences
What do the shared features of the 3 domains help support?
the idea that all living organisms share a common ancestor & show monophyly of life
3 characteristics of prokaryotes
divide by binary fission
DNA not enclosed in a membrane (circular molecule)
no membrane-enclosed organelles
3 characteristics of Bacteria
membrane-enclosed nucleus - absent
Membrane-enclosed organelles - few
peptidoglycan in cell wall - present
3 characteristics of Archaea
membrane-enclosed nucleus - absent
Membrane-enclosed organelles - absent
peptidoglycan in cell wall - absent
3 characteristics of Eukarya
membrane-enclosed nucleus - present
Membrane-enclosed organelles - many
peptidoglycan in cell wall - absent
Does the gram stain method do?
it separates bacteria through stains
What color are gram-POSITIVE bacteria?
they retain violet dye
What color are gram-NEGATIVE bacteria?
they retain red dye
Why do gram-positive & gram-negative stain differently?
they stain differently due to the structure of their cell walls
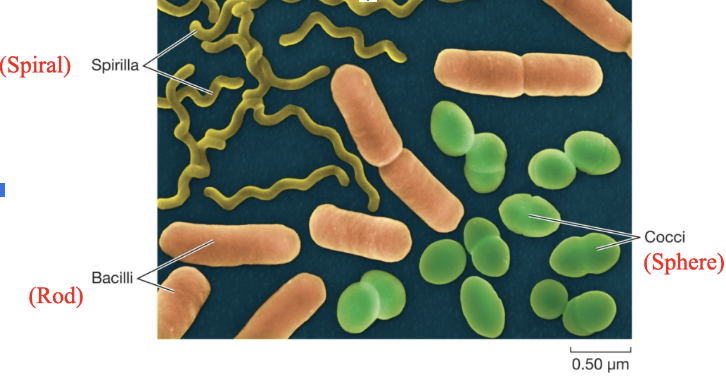
What are the 3 bacteria cell shapes?
Spiral, rod, sphere
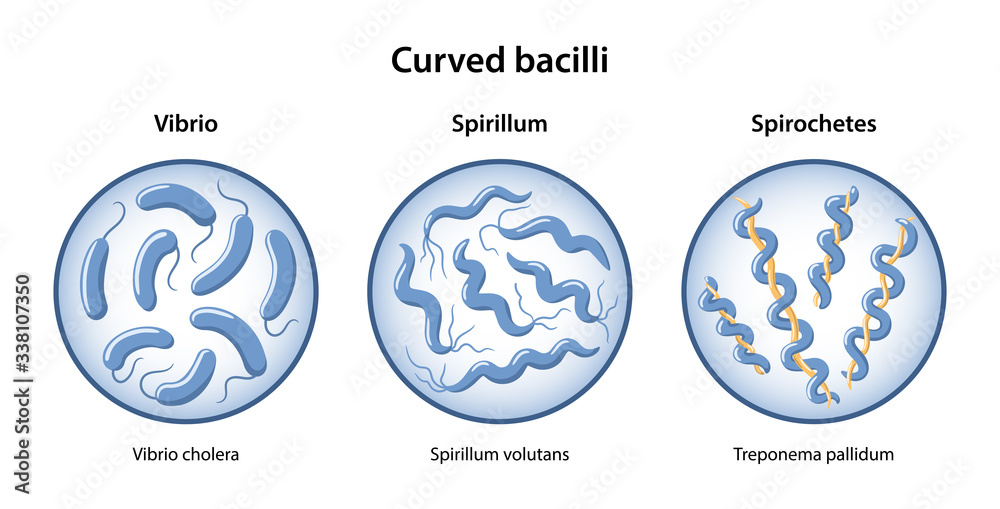
What are the 3 forms of bacterial spiral cells?
Vibrio, spirillum, spirochete
What are the 4 types of bacterial groupings?
Diplococcus - pair
Staphylococcus - clusters
Streptococcus - chain
Tetracoccus - 4 in 2 planes to make squares of four
How are evolutionary relationships clarified?
by sequencing rRNA genes
3 important details of rRNA
rRNA is evolutionary ancient
in all free-living organisms
evolved slowly, similarities easily found
What is lateral/horizontal gene transfer?
lateral gene transfer is when genes from one species become incorporated into the genome of another.
“moving sideways in a tree”
True or false? Lateral gene transfer can occur between domains?
True
Why are prokaryotes so diverse/abundant?
prokaryotes are most successful in terms of # of individuals
8 groups of bacteria have broadest phylogenetic support
Explain what biofilms are
Biofilms
formed by many microbial communities
difficult to kill cells in biofilm - many be impenetrable to antibiotics
bacteria in biofilms communicate using chemical signals
How is Archaea separated?
rRNA sequencing
True or false? Much is known about the shapes of Archaea.
False - little is known of Archaea shapes, many never been seen and only known from DNA samples
What are the known Archaea species?
cocci, bacilli, triangular, square
Where do Archaea grow?
on surfaces
What is the environment of Archaea? (3)
Many are extremophiles
some not extremophiles (common in soil)
many live in ocean depths
What are some traits of Archaea?
lack peptidoglycan in cell walls
liquids in cell membranes using ether linkages
What are the categories of Archaea? (4)
Methanogens - energy from H2 - produces methane as waste & poisoned by O2
Extreme halophiles - salt tolerant to salt dependent
Extreme thermophiles - hot environments, metabolism based on sulfur
Nonextreme Archaea - same environment as bacteria - soil
Why are prokaryotes important to health? (3 ideas)
many prokaryotes live in/on organisms
human health depends on microbiome health
every surface of body covered with bacteria
What is a microbiome?
bacterial communities that live in & on our bodies
What are pathogens?
pathogenic prokaryotes shown to cause disease
True or false? Majority of bacteria are pathogens.
False - minority of bacteria are pathogens
What are Koch’s postulates? 4 rules.
set of rules to establish a particular organisms that causes a disease
microorganism always found in infected person
can be taken from host and grown in pure culture
sample of culture causes disease in a new host
new host also yields a pure culture
What is required for an organism to become a pathogen? (5 steps)
arrive at body of surface of a host
enter hosts body
evade hosts defenses
multiply inside host
infect new host
Explain what the consequences of the host depend on. (2)
Invasiveness of pathogen (its ability to multiply in host)
toxinogenicity (ability to produce toxins)
When are endotoxins & exotoxins released? How fatal are they?
Endotoxins - released when lysed (rarely fatal)
Exotoxins - released by living bacteria (often fatal)
List and describe the 4 prokaryotic metabolic pathways.
Obligate anaerobe - poisoned by oxygen
Facultative anaerobes - shift between anaerobic & aerobic
Aerotolerant anaerobes - not damaged by oxygen, but don’t use oxygen for cellular respiration
Obligate aerobes - have to use oxygen to survive
Nutritional categories of prokaryotes (4)
Photoautotrophs - use photosynthesis for energy
Photoheterotrophs - use light energy & get carbon from compounds made by other organisms (carbohydrates, fatty acids, alcohols)
Chemoautotrophs - get energy by oxidizing inorganic compounds & use energy to fix CO2
Chemoheterotrophs - obtain both energy & carbon from complex organic compounds that were synthesized by other organisms
How do prokaryotes impact environments? (3 kinds)
decomposers - metabolize organic compounds in dead organisms & other organic materials
denitrifiers - use ntirate as an electron receptor in anaerobic conditions & N into the atmosphere N2
Nitrifiers - chemoautotrophic bacteria (fix nitrogen for plant use, important for plant growth)
Are viruses cellular?
viruses are NOT cellular
derived from other cells
DNA & RNA
infect all cellular forms of life
Why is virus phylogeny difficult? (4)
viral genomes are tiny (restricts analyses)
no known viral fossils
diverse and may have evolved rapidly
raid mutation rate/evolution clouds evolutionary relationships
How do retroviruses reproduce? Explain the process.
Reverse transcriptase
in host nucleus, viral reverse transcriptase produces cDNA from the viral RNA genome
cDNA is replicated to produce double-stranded DNA
Viral integrase catalyzes the integration of the new double stranded DNA
viral genome is replicated along w the host cell’s DNA
Viral genome is replicated along with the host cell’s DNA; the integrated retroviral DNA is known as a ____
Provirus
Is HIV a retrovirus?
Yes
What happens when cells are infected with retrovirus
they undergo uncontrolled replication
associated with some forms of cancer
How do retrovirus’ infect other cells?
by inserting their genome into the host genome
Humans have about ______ fragments of endogenous viruses
100,000
What are DNA viruses? (3)
start with double-stranded DNA
polyphyletic (many independent origins)
many common phage (bacteriophage)
What is phage therapy?
bacteriophage viruses have been used to fight bacterial infections in humans
What replaced phage therapy?
antibiotics
What is the issue to antibiotics & bacteria? What do we do about it?
bacteria evolve resistance to antibiotics, so research in phage therapy continues
What diseases are DNA viruses? (3)
smallpox, HPV, Herpes