Unit 5: Land and Water Use
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/106
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
1
New cards
Soil
renewable resource that can be depleted plant-supporting system
disintegrated rock, organic matter, water, gases, nutrients, microorganisms
disintegrated rock, organic matter, water, gases, nutrients, microorganisms
2
New cards
Sustainable agriculture
agriculture practice in same way/place far into the future
3
New cards
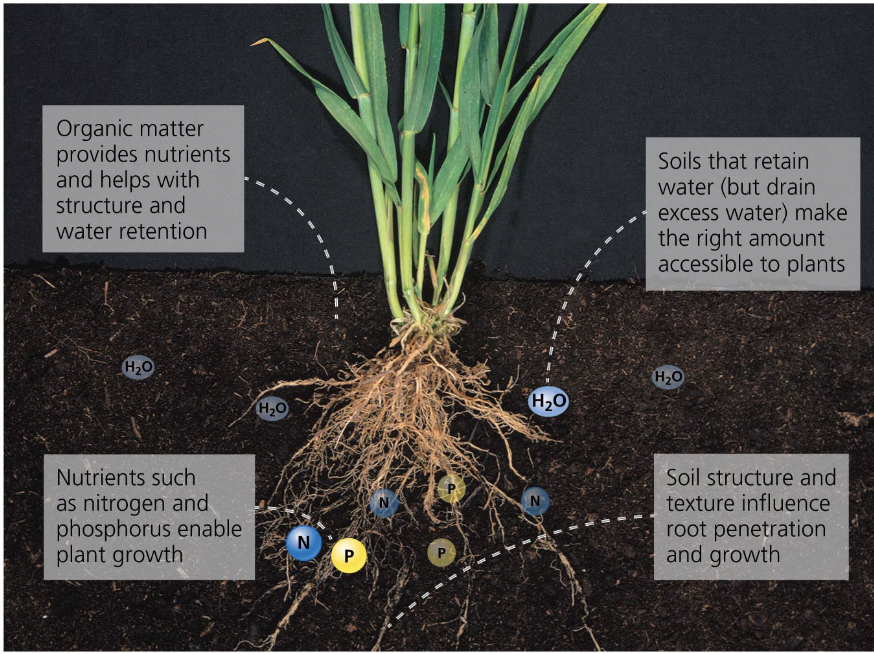
soil supporting agriculture
Provide nutrients
Have a structure that allows roots to penetrate deeply
Retain water
Livestock
Have a structure that allows roots to penetrate deeply
Retain water
Livestock
4
New cards
soil effect chart
Soil is teeming with bacteria, algae, fungi, and protists and provides habitat for earthworms, insects, mammals, reptiles, and amphibians
Since soil is composed of interacting living and nonliving matter, it is considered an ecosystem
Since soil is composed of interacting living and nonliving matter, it is considered an ecosystem
5
New cards
Parent material
the base geologic material of soil
Lava, volcanic ash, rock, dunes
Lava, volcanic ash, rock, dunes
6
New cards
bedrock
solid rock comprising the Earth’s crust
7
New cards
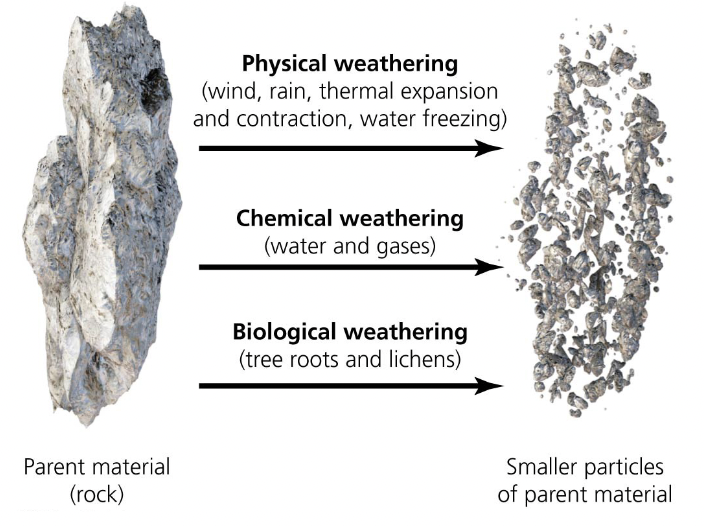
Weathering
processes that break large rock particles down into smaller ones
8
New cards
Physical (mechanical) weathering
wind and rain; no chemical changes in the parent material
9
New cards
Chemical
parent material is chemically changed
10
New cards
Biological
organisms produce soil through physical or chemical means
11
New cards
Humus
spongy material formed by partial decomposition of organic matter; holds moisture
12
New cards
Soil on Climate
soils form faster in warm, wet climates
13
New cards
Soil on organism
plants and decomposers add organic matter
14
New cards
Soil on Topography
hills and valleys affect exposure to sun, wind, and water
15
New cards
soil on Parent material
Influences properties of resulting soil
16
New cards
Soil on time
soil can take decades to millennia to form
17
New cards
horizon
each layer of soil (up to 6)
18
New cards
soil profile
the cross-section of soil as a whole
weathering & organic matter decrease in lower horizons
weathering & organic matter decrease in lower horizons
19
New cards
Leaching
process whereby dissolved particles move down through horizons, may end up in drinking water
20
New cards
Topsoil
inorganic/organic material most nutritive for plants
21
New cards
Soil horizon charts
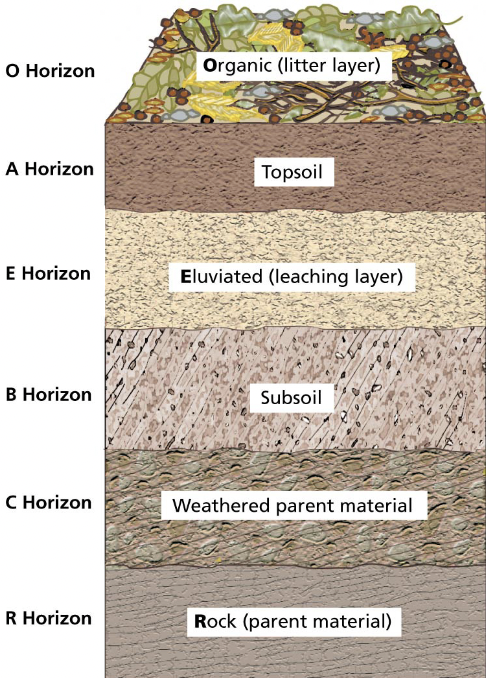
22
New cards
Soils color
color indicates its composition and fertility
Black or dark brown soil is rich in organic matter
Pale gray or white soil indicates leaching
Black or dark brown soil is rich in organic matter
Pale gray or white soil indicates leaching
23
New cards
soil texture
size of particles
smallest to largest: clay, silt, sand
Loam = soil with an even mixture of the three
Affects how easily air and water travel through the soil
Influences how easy soil is to cultivate
smallest to largest: clay, silt, sand
Loam = soil with an even mixture of the three
Affects how easily air and water travel through the soil
Influences how easy soil is to cultivate
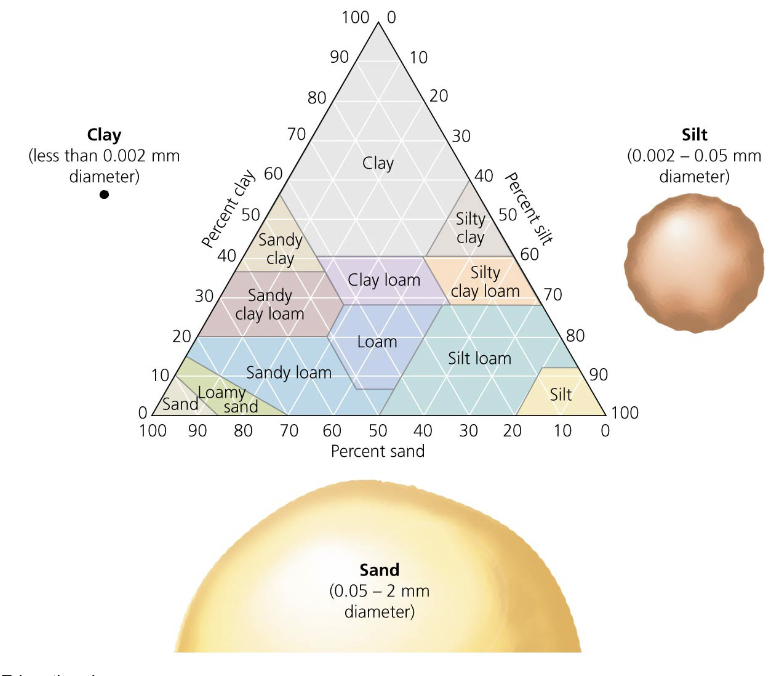
24
New cards
soil structure
“clumpiness" best 4 plants
Repeated tilling compacts soil, decreasing its water-absorbing capabilities
Repeated tilling compacts soil, decreasing its water-absorbing capabilities
25
New cards
Soil pH
too acidic or basic can kill plants
pH influences the availability of nutrients for plants
pH influences the availability of nutrients for plants
26
New cards
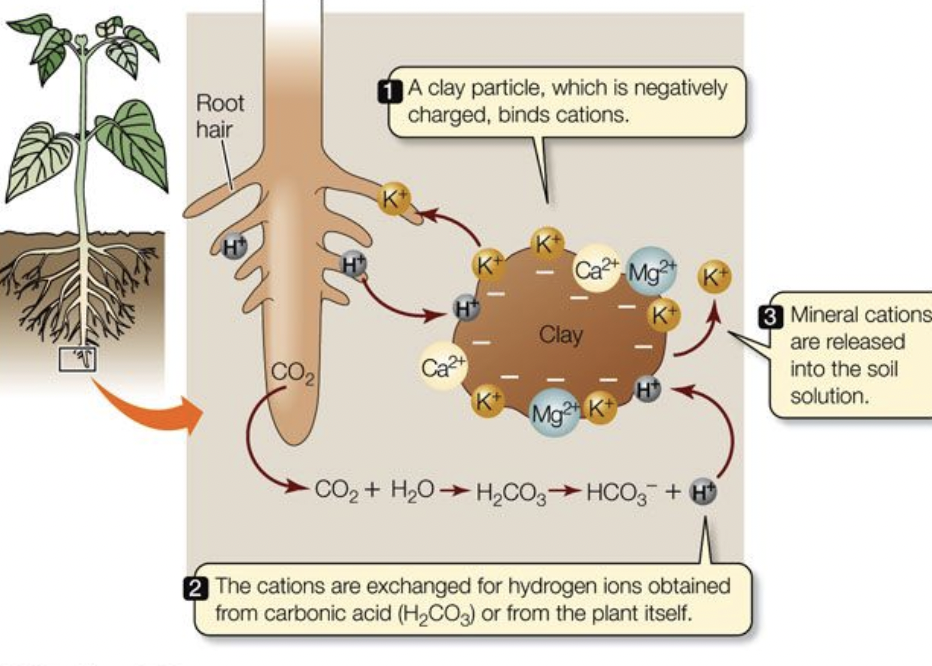
Cation exchange
allows plants to gain nutrients
Negatively charged soils hold cations (positively charged ions) of calcium, magnesium, and potassium
Roots donate hydrogen to soil in exchange for these nutrients
Negatively charged soils hold cations (positively charged ions) of calcium, magnesium, and potassium
Roots donate hydrogen to soil in exchange for these nutrients
27
New cards
Cation exchange capacity
a soil’s ability to hold cations
Cations that don’t leach are more available to plants
A useful measure of soil fertility
Greatest in fine textured or richly organic soils
Decreases with lower pH
Cations that don’t leach are more available to plants
A useful measure of soil fertility
Greatest in fine textured or richly organic soils
Decreases with lower pH
28
New cards
regional soil
rainforests the nutrients are in plants, not the soil
leaches minerals and nutrients, reducing their accessibility to roots
Rapid decomposition of leaf litter results in a thin topsoil layer with little humus
leaches minerals and nutrients, reducing their accessibility to roots
Rapid decomposition of leaf litter results in a thin topsoil layer with little humus
29
New cards
Swidden agriculture
traditionally used in tropical areas
cultivation, a plot is left to grow back into forest
Soils are depleted if not enough time is given
Temperate prairies have lower rainfall and less nutrient leaching and are able to build rich topsoil
cultivation, a plot is left to grow back into forest
Soils are depleted if not enough time is given
Temperate prairies have lower rainfall and less nutrient leaching and are able to build rich topsoil
30
New cards
Soil degradation
decline in soil quality and productivity
Primarily from deforestation, cropland agriculture, overgrazing
Primarily from deforestation, cropland agriculture, overgrazing
31
New cards
Land degradation
a general deterioration of land, decreasing its productivity and biodiversity
Erosion, nutrient depletion, water scarcity, salinization, waterlogging, chemical pollution
Erosion, nutrient depletion, water scarcity, salinization, waterlogging, chemical pollution
32
New cards
Erosion
removal of material from one place to another by wind or water
topsoil—the most valuable layer for plant growth
overfarming
topsoil—the most valuable layer for plant growth
overfarming
33
New cards
Deposition
arrival of eroded material at a new location
34
New cards
floodplains
deposits nutrient-rich sediment in river valleys and deltas
35
New cards
Desertification
a form of land degradation with more than a 10% loss of productivity
Caused primarily by wind and water erosion, but also by:
Deforestation, soil compaction, and overgrazing
Drought, salinization, water depletion
Climate change
Caused primarily by wind and water erosion, but also by:
Deforestation, soil compaction, and overgrazing
Drought, salinization, water depletion
Climate change
36
New cards
Dust Bowl
massive dust storms from erosion of millions of tons of topsoil in the 1930s
37
New cards
**Conservation districts**
districts that promote soil conservation practices at the county level
\
* Operate with federal direction, authorization, and funding and are organized by the states
\
* Operate with federal direction, authorization, and funding and are organized by the states
38
New cards
**Crop rotation**
* **growing different crops from one year to the next**
* **Returns nutrients to soil**
* **Prevents erosion, reduces pests**
* **Like crop rotation, no-till farmers may alternate wheat or corn with nitrogen-fixing soybeans**
* **Returns nutrients to soil**
* **Prevents erosion, reduces pests**
* **Like crop rotation, no-till farmers may alternate wheat or corn with nitrogen-fixing soybeans**
39
New cards
**Contour farming**
**plowing furrows sideways across a hillside perpendicular to its slope**
* Sides of furrows trap water and prevent erosion
* Sides of furrows trap water and prevent erosion
40
New cards
**Terracing**
* **cutting level platforms into steep hillsides**
* **The steps of this “staircase” hold water**
* **The steps of this “staircase” hold water**
41
New cards
**Intercropping**
* **planting different crops in alternating bands or mixed arrangements**
* **Increases ground cover, preventing erosion**
* **Decreases pests and disease**
* **Replenishes soil**
* **Increases ground cover, preventing erosion**
* **Decreases pests and disease**
* **Replenishes soil**
42
New cards
**Shelterbelts** **(windbreaks)**
* **rows of trees planted along edges of fields to slow the wind**
* **Can be combined with intercropping**
* **Can be combined with intercropping**
43
New cards
**Conservation tillage**
* **strategies that reduce the amount of tilling relative to conventional farming**
* **Leaves at least 30% of crop residues in the field**
* **No-till farming disturbs the soil even less**
* **Leaves at least 30% of crop residues in the field**
* **No-till farming disturbs the soil even less**
44
New cards
**Overgrazing**
* **occurs when too many animals eat too much of the plant cover**
* **Impedes plant regrowth**
* **Impedes plant regrowth**
45
New cards
**Irrigation**
* **artificially providing water to support agriculture**
* **Unproductive regions become productive farmland**
* **Can grow water-intensive crops like rice and cotton**
* **Unproductive regions become productive farmland**
* **Can grow water-intensive crops like rice and cotton**
46
New cards
**Waterlogging**
**experienced by overirrigated soils when the water table rises to cover and suffocates roots**
47
New cards
**Salinization**
* **the buildup of salts in surface soil layers**
* **Worse in arid areas**
* **Evaporation pulls salts up from lower soil horizons**
* **Worse in arid areas**
* **Evaporation pulls salts up from lower soil horizons**
48
New cards
**Fertilizers**
* **substances containing essential nutrients**
* **Plants require nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium and remove them from the soil, possibly limiting growth**
* **Plants require nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium and remove them from the soil, possibly limiting growth**
49
New cards
**Inorganic fertilizers**
* **mined or synthetically manufactured mineral supplements**
50
New cards
**Organic fertilizers**
* **the remains or wastes of organisms**
* **Manure, crop residues, fresh vegetation**
* **Manure, crop residues, fresh vegetation**
51
New cards
compost
* **mixture produced when decomposers break down organic matter**
52
New cards
Wetlands
swamps, marshes, bogs, river floodplains
53
New cards
**No-till** farming
l**eaving crop residue atop the fields**
* **Benefits the soil**
* **Saves time and money**
* **Benefits the soil**
* **Saves time and money**
54
New cards
**Cover crops**
* **= crops planted to hold soil in place between the times that main food crops are growing**
55
New cards
**Agriculture**
* **practice of raising crops and livestock for human use and consumption**
56
New cards
**Cropland**
* **land used to raise plants for human use**
57
New cards
**Rangeland** or **pasture**
* **and used for grazing livestock**
* Land devoted to agriculture covers 38% of Earth’s land
* Land devoted to agriculture covers 38% of Earth’s land
58
New cards
**Soil**
**a complex plant-supporting system**
* **Consists of disintegrated rock, organic matter, water, gases, nutrients, and microorganisms**
* **It is a renewable resource that can be depleted**
* **Consists of disintegrated rock, organic matter, water, gases, nutrients, and microorganisms**
* **It is a renewable resource that can be depleted**
59
New cards
**Sustainable agriculture**
**agriculture we can practice in the same way and same place far into the future**
60
New cards
**Traditional agriculture**
* **biologically powered form of agriculture that uses human and animal muscle power**
* **Hand tools, simple machines**
* **Hand tools, simple machines**
61
New cards
**Subsistence agriculture**
* **form of agriculture in which families produce only enough food for themselves**
62
New cards
**Polyculture**
**different crops are planted in one field**
63
New cards
**Industrialized agriculture**
**form of agriculture that uses large-scale mechanization and fossil fuels to boost yields**
* **Also uses pesticides, irrigation, and fertilizers**
* **Also uses pesticides, irrigation, and fertilizers**
64
New cards
**Monoculture**
**uniform planting of a single crop**
65
New cards
**Green Revolution**
* **new technology, crop varieties, and farming practices were introduced to developing countries**
* **Increased yields and decreased starvation**
* **Degraded the integrity of the soil**
* **Increased yields and decreased starvation**
* **Degraded the integrity of the soil**
66
New cards
*Swidden* agriculture
traditionally used in tropical areas
* After cultivation, a plot is left to grow back into forest
* Soils are depleted if not enough time is given
* After cultivation, a plot is left to grow back into forest
* Soils are depleted if not enough time is given
67
New cards
**Soil degradation**
* **a decline in soil quality and productivity**
* **Primarily from deforestation, cropland agriculture, overgrazing**
* **Primarily from deforestation, cropland agriculture, overgrazing**
68
New cards
**Land degradation**
* **a general deterioration of land, decreasing its productivity and biodiversity**
* **Erosion, nutrient depletion, water scarcity, salinization, waterlogging, chemical pollution**
* **Erosion, nutrient depletion, water scarcity, salinization, waterlogging, chemical pollution**
69
New cards
erosion
**removal of material from one place to another by wind or water**
70
New cards
**Deposition**
* **arrival of eroded material at a new location**
* Flowing water deposits nutrient-rich sediment in river valleys and deltas
* Floodplains are excellent for farming
* Flowing water deposits nutrient-rich sediment in river valleys and deltas
* Floodplains are excellent for farming
71
New cards
**Desertification**
* **a form of land degradation with more than a 10% loss of productivity**
72
New cards
**Undernutrition**
* **people receive fewer calories than their minimum requirements**
* **Due to economics, politics, conflict, and inefficiencies in distribution**
Most undernourished live in developing nations
* **Due to economics, politics, conflict, and inefficiencies in distribution**
Most undernourished live in developing nations
73
New cards
**Food security**
* **guarantee of an adequate, safe, nutritious, and reliable food supply**
74
New cards
**Monoculture**
* **large expanses of a single crop**
* **More efficient, increases output**
* **Devastates biodiversity**
* **Plants are more susceptible to disease and pests**
* **More efficient, increases output**
* **Devastates biodiversity**
* **Plants are more susceptible to disease and pests**
75
New cards
**Sustainable agriculture**
* **agriculture that does not deplete soils faster than they form. It does not**
* **reduce the amount of healthy soil**
* **pollute water**
* **decrease genetic diversity**
* **reduce the amount of healthy soil**
* **pollute water**
* **decrease genetic diversity**
76
New cards
**Biofuels**
* **fuels derived from organic materials**
* **Replace petroleum in engines**
* **Replace petroleum in engines**
77
New cards
**Ethanol**
* **a biofuel derived from corn**
\
* Food prices increased
* Farmers sold corn for ethanol, not food
* Farmers planted biofuels, not food crops
* Riots erupted in many nations
\
* Food prices increased
* Farmers sold corn for ethanol, not food
* Farmers planted biofuels, not food crops
* Riots erupted in many nations
78
New cards
**Feedlots**
* ***factory farms*****, also called** ***concentrated animal feeding operations,*** **or** ***CAFOs*****) = huge warehouses or pens that deliver food to animals living at extremely high densities**
* **Increases production**
* **Increases production**
79
New cards
**Seed banks**
* **institutions that preserve seed types as living museums of genetic diversity**
80
New cards
**Pollination**
* **male plant sex cells fertilize female sex cells**
* **By wind or animals**
* **By wind or animals**
81
New cards
**Pest**
* **any organism that damages valuable crops**
82
New cards
**Weed**
any plant that competes with crops
83
New cards
**Pesticides**
* **poisons that target pest organisms**
84
New cards
**Biological control (biocontrol)**
* **strategy that uses a pest’s predators or parasites to control the pest**
85
New cards
***Bacillus thuringiensis*** **(Bt)**
* ***soil bacterium that kills many caterpillars and some fly and beetle larvae***
86
New cards
**Integrated pest management (IPM)**
* **use of a mix of techniques to suppress pests:**
* **Pest population monitoring**
* **Biocontrol and mechanical pest removal**
* **Chemicals, if necessary**
* **Crop rotation and alternative tillage methods**
* **Use of transgenic crops**
* **Pest population monitoring**
* **Biocontrol and mechanical pest removal**
* **Chemicals, if necessary**
* **Crop rotation and alternative tillage methods**
* **Use of transgenic crops**
87
New cards
**Organic agriculture**
food-growing practices that use no synthetic fertilizers or pesticides but rely on biological approaches such as composting and biocontrol
88
New cards
Criteria

89
New cards
**Biotechnology**
* **the application of biological science to create products derived from organisms**
* **Seeks to scale up the technological aspects of agriculture**
* **Seeks to scale up the technological aspects of agriculture**
90
New cards
**Genetic engineering**
* **direct manipulation of genetic material through adding, deleting, modifying DNA**
91
New cards
**Recombinant DNA**
* **DNA patched together from multiple organisms**
* Biotechnology has created medicines, cleaned up pollution, and dissolved blood clots
* Biotechnology has created medicines, cleaned up pollution, and dissolved blood clots
92
New cards
**Precautionary principle**
* **idea that one shouldn’t undertake a new action until the effects of that action are understood**
93
New cards
**Farmers’ markets**
* **provide meats and fresh fruits and vegetables from local producers**
94
New cards
**Community-supported agriculture (CSA)**
* Consumers pay farmers in advance so farmers get guaranteed income
* Consumers get fresh locally grown food
* Consumers get fresh locally grown food
95
New cards
**Life-cycle analysis**
**analysis of all inputs across all stages of production, transportation, sale, and use**
96
New cards
*Factory fishing*
* *huge vessels use powerful technologies to capture fish in huge volumes*
97
New cards
*Driftnets*
* *transparent nylon mesh nets that drift with the current*
* *Used for herring, sardines, mackerel, sharks, shrimp*
* *Used for herring, sardines, mackerel, sharks, shrimp*
98
New cards
*Longline* *fishing*
* *extremely long (up to 80 km or* \n *50 mi) lines with several thousand baited hooks*
* *Used for tuna and swordfish*
* *Used for tuna and swordfish*
99
New cards
*Trawling*
* *using cone shaped nets with weights at the bottom and floats at the top to catch pellagic fish*
100
New cards
*Bottom trawling*
* *using weighted nets that drag across the seafloor to catch groundfish or scallops*