Product Life Cycle
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
What is the product life cycle?
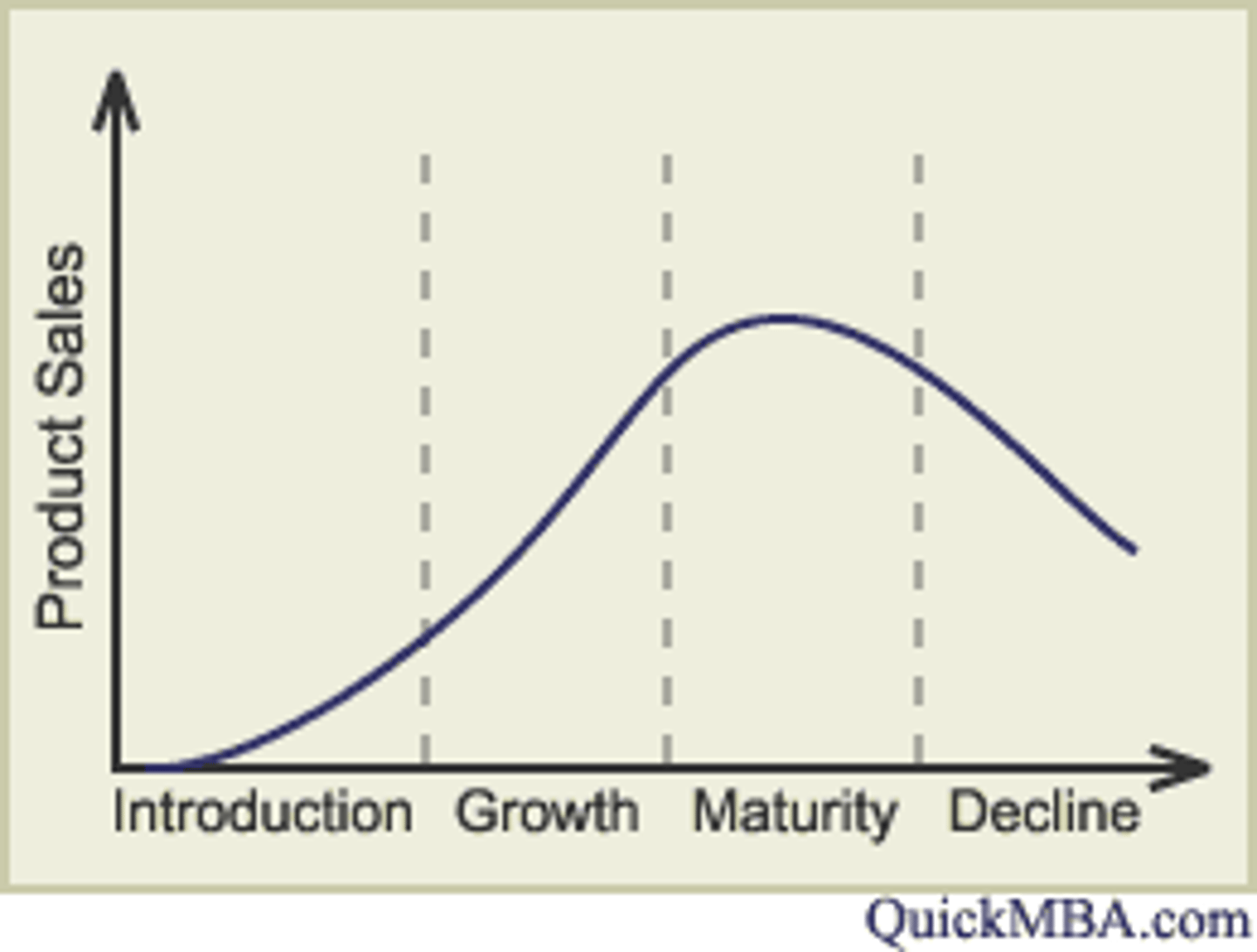
The product life cycle shows the stages which a product passes through over time. The stages show how the demand for the product will vary throughout its lifespan.
What are the stages of the product life cycle?
1. Introduction
2. Growth
3. Maturity
4. Saturation
5. Decline
Some product life cycles also show an additional stage before the product comes onto the market. This is called the...
Development stage.
What is the development stage?
This is where the research and development takes place and can take years for certain products. For example, it can take three years to develop a new model of car. At this stage money is needed to invest in developing and testing the product and no income is received by the business, so costs are high and sales and revenue are zero.
What is the introduction stage?
The product is launched. This is normally backed up by an advertising campaign and other forms of promotion. Sales will begin at this stage. The product is new to the market and few potential consumers know of its existence. Prices can be high and sales may be restricted to early adopters (those that must have new technology, gadgets or fashions first). Profits are often low as development costs have to be repaid and advertising expenditure can often be high.
What is the growth stage?
In the growth stage sales and profits rise and the products are sold in more and more outlets. Marketing will continue to focus on increasing awareness of the product. Advertising tries to establish or strengthen the brand and develop an image for the product. Costs can still be high.
What is the maturity stage?
In the maturity stage the product reaches a peak in sales, and profits should be high. All the research, development and advertising costs have been paid off. Marketing efforts will focus on persuading customers to make repeat purchases. The product is profitable enough to finance the development of other products. The rate of sales will slow down as competitors launch competing products or consumers may be looking for different or new products. A business may consider introducing an extension strategy at this stage to boost sales.
What is the saturation stage?
In the saturation stage very few new customers are gained and sales start to decline as more customers either buy a competitor's product or simply stop buying the product. The product may be established but there is little opportunity for further growth, the business could try to reduce its costs, so that prices can be reduced. The battle to survive is beginning and the market for the product is 'full'. Profits may start to decline.
What is the decline stage?
In the decline stage sales fall fast and profits will decrease. A business may decide to increase advertising costs in an attempt to boost sales or it may reduce advertising and eventually stop selling the product and withdraw it from the market. Prices of products in the decline stage often fall to sell remaining stock quickly
Product Life Cycle Diagram.
When can a business decide to use an extension strategy?
When a product is in the maturity or decline stage of its life cycle, the business may decide to take the product off the market or to prolong its life by carrying out an extension strategy.
Give examples of extension strategies.
Extension strategies include: •
- Bringing out new versions with additional or new features - Changing the packaging
- Lowering the price
- Carrying out more advertising
- Finding new markets
- Finding new uses and persuading consumers to use the product more frequently.