HEALTH ASSESSMENT EXAM 3
1/216
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
217 Terms
solid viscera
- maintain characteristic shape.
- some palpable (liver/right kidney)
- liver, pancreas, spleen, adrenal glands, kidneys, ovaries, uterus
hollow viscera
- shape depends on contents
- usually not palpable
- stomach, gallbladder, small intestine, colon, and bladder.
position of kidneys
- retroperitoneal (behind abdominal contents) and pancreas (behind stomach).
abdominal anatomy
- 4 quadrants = RUQ, RLQ, LLQ, LUQ (midpoint is belly button).
- 9 quadrants = right hypochondriac, epigastric, left hypochondriac, right lumbar, umbilical, left lumbar, right iliac, hypogastric, left iliac
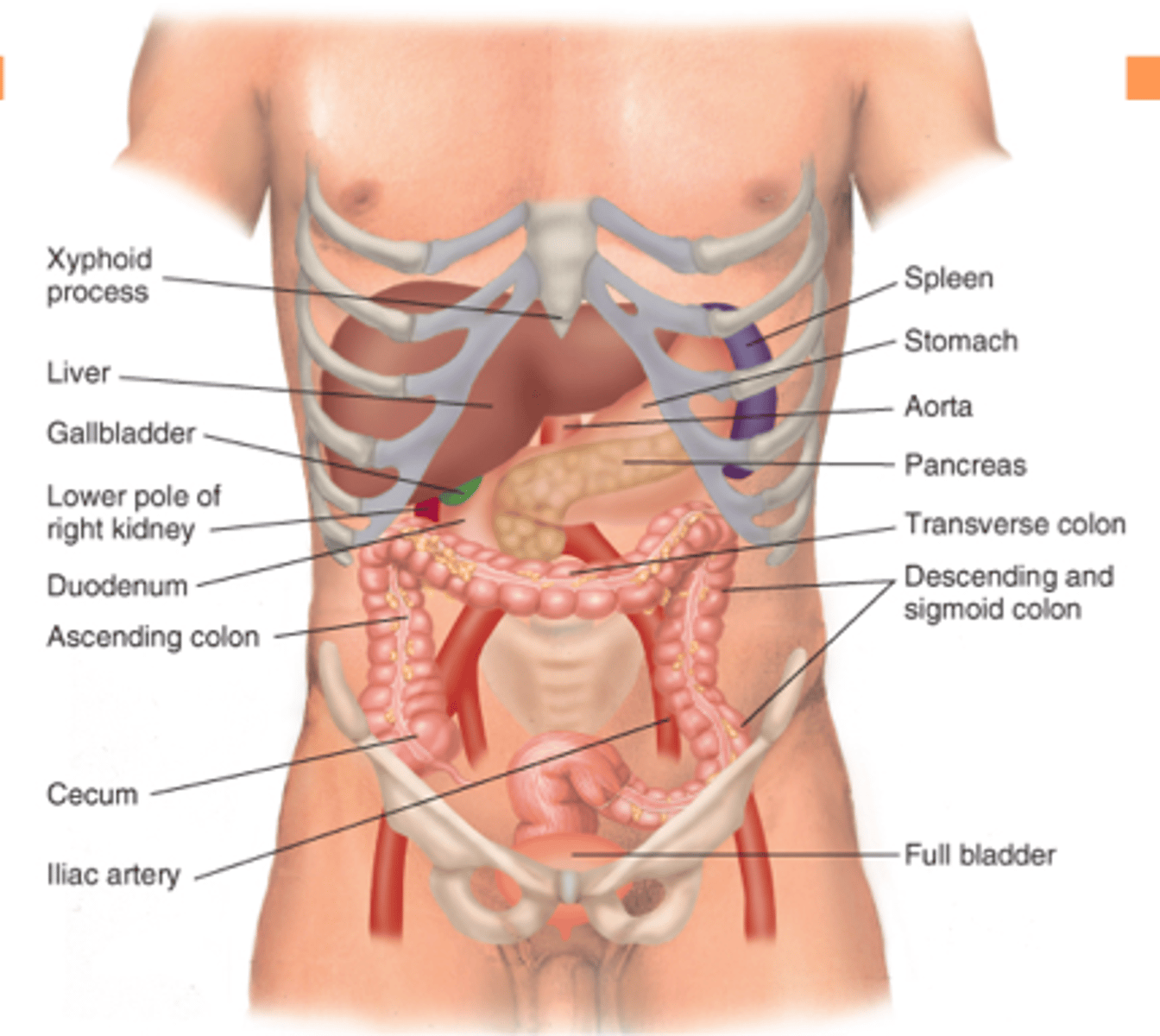
right upper quadrant (RUQ)
liver, gallbladder, duodenum, head of pancreas, right kidney, adrenal gland, part of ascending colon.
left upper quadrant (LUQ)
stomach, spleen, left lobe of liver, body of pancreas, left kidney, adrenal gland, and part of transverse and descending colon.
right lower quadrant (RLQ)
cecum, appendix, right ovary+tube, right ureter, and right spermatic cord
left lower quadrant (LLQ)
part of descending colon, sigmoid colon, left ovary+tube, left ureter, and left spermatic cord
midline structures abdominal
aorta, uterus, bladder
GI tract order
mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum), large intestine (cecum, colon, rectum), anus
subjective adbonial with eating
appetite, dysphagia (solids/liquids), food intolerance, lactose intolerace (Sx), abdominal pain (PQRSTU)
subjective nausea/vomiting
frequency, hematemesis (bloody), timing, associated symptoms, reflux?
subjective bowel habits
- COCA = color, odor, consistency, amount.
- changes in BM, laxative use, bleeding
- melena (bloody), black-tarry (old blood/occult) = upper GI
- red, frank blood = lower GI
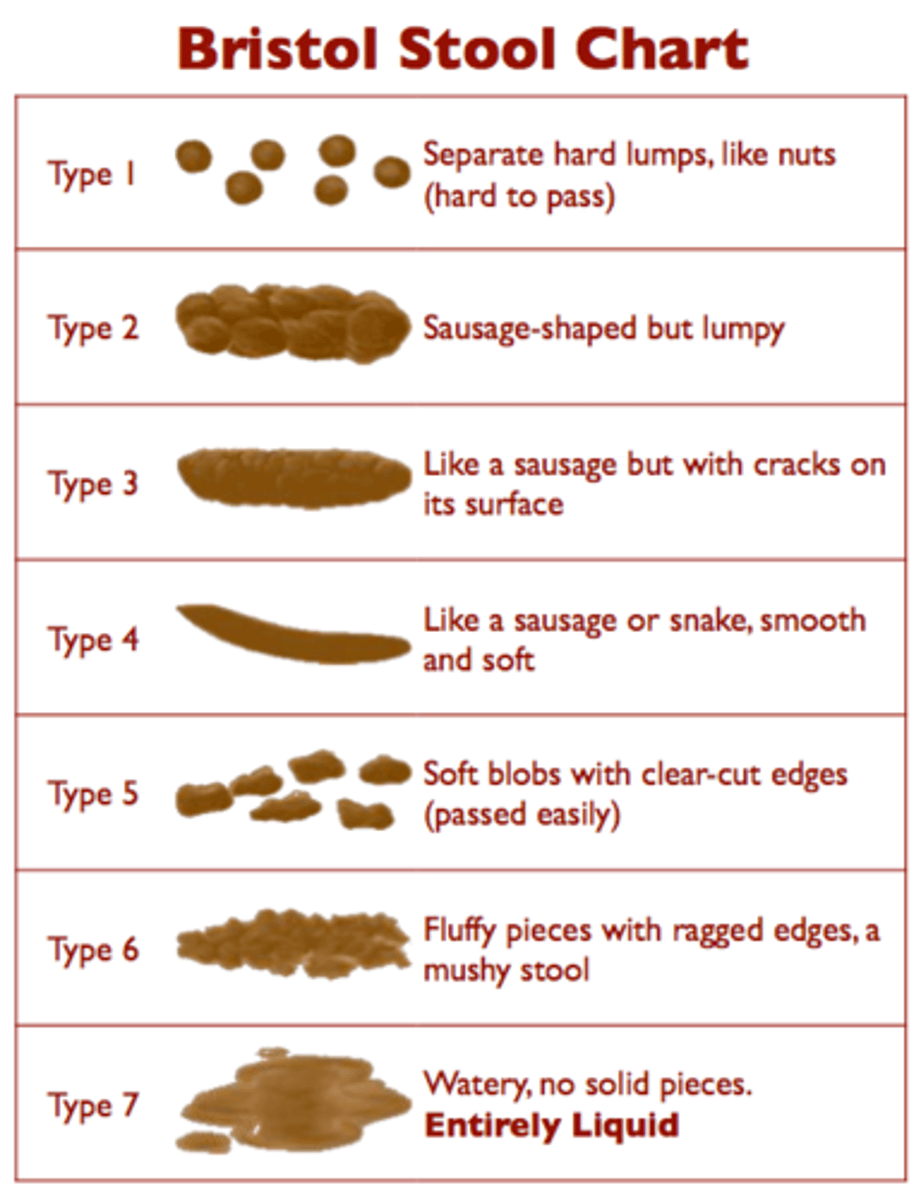
bristol stool chart
medical aid to classify stool
past history abdominal
surgeries, other GI problems, gallbladder disease, uclers, appendicitis, and hepatisis
family history abdominal
cancer, polyps, IBD, IBS
medication history abdominal
antiacids, NSAIDS (aspirin), iron supplements (stain black/green)
nutritional assessments abdominal
24 hour diet recall useful, tobacco, ETOH (alcohol), caffeine
developmental abdominal for infants/children
breast/formula, whole milk 1yr, intro of solids, constipation, # stools/day + liquid in diet, overweight, pain.
developmental abdominal for teens
eating patterns, exercise patterns, weight loss/gain, body image (anorexia/bulimia).
developmental abdominal for aging adults
how do they get their food, who grocery shops, eat alone, weight changes, bowel preoccupations.
apple/android shape
- excess fat on abdomen
- common in men
- has significant correlation with metabolic syndrome
pear/gynoid shape
- excess fat on the things and buttocks
- common in women
- not signifciant correlation with metabolic syndrome
low fat diets
- polysaturated/monsaturated fats +
- trans fats low/eliminated
- cholesterol in diet ONLY comes form animal products (reduced)
low sodium
- DASH diet = dietary approach to stop hypertension by department of health.
renal diet
- lower protein and Na, K, phosophate, and calcium
BRAT diet
- bananas, rice, applesauce, toast
- for nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
low residue diet
- intended to put less stress on GI system and bowel
- low fiber
- avoid seeds, nuts, berries, popcorn, caffeine, and tough meats.
lactose intolerant diet
- no dairy
- lactaid pills and products can be helpful for these patients
carb control diet
- ADA diet = reduced simple sugars, reduced carbohydrates
- for people with diabetes and glucose control concerns.
gluten free diet
- for those with celiac disease (CD)
- avoid wheat, rye, breads, cereals, crackers, cookies, flour tortillas, gravy, ice cream cones, and pancakes.
marasmus
protein-calorie malnutrition caused by starvation, cancer, anorexia, or bowel obstructions.
failure to thrive
- lower than expected weight and growth (kids).
- profound weight loss (elderly).
kwashiorkor
- protien malnutrition
- high calories and low protein.
objective abdominal assessments
lighting, empty bladder (specimen), warm room+stethoscope+hands, supine w/ knees flexed.
order of GI assessment
inspect, auscultation, percuss, palpate
inspection for abdominal cavity
- demeanor relaxed or agitated
- contour of abdomen = scaphoid, flat, rounded, protuberant, distended.
- symmetry
- pulsation = aortic pulsation
- visible masses
- umbilicus
- skin
- JP drain or ostomies
scaphoid
concave or sunken
rounded
slightly rounded
protuberant
bulging or stretched
distended
fat, air, gas, ascites, pathology (cysts/tumor), stool
umbilicus
- midline, inverted, no discolroation
- inflammmation or hernia (typically harmless).
umbilical hernia
part of gthe intestine protrudes through an opening or weak spot in the abdominal muscles
skin
lesions, rashes, scars, ostomies, tubes, drains.
JP drain
- jackson-pratt drain
- suction drain w/ tubing inside the body and pulls fluid out of the body for after abdominal surgery
ostomies
operations to remove part of the small or large intestine resulting in the need to create an artificial opening in the body for the elimination of bodily wastes
ostomy assessment
- stoma should be pink/red and moist
- stoma should not be black or purple.
- assess ostomy bag for COCA.
- consider placement and output (small intestine has more liquid than colon)
auscultate abdominal
- press lightly with diaphragm
- all 4 quadrants
- begin in RLQ (ileocecal valve) and go clockwise = RLQ, RUQ, LUQ, LLQ
bowel sounds
- air/fluid moving thorugh small intestine.
- high pitched, irregular, gurgling, or cascading sounds from 5-40 times/minute.
- you judge if they are normal, absent, hypoactive or hyperactive.
- listen for 5 minutes
-
borborygmus
stomach growls sounds
causes of absent/hypoactive bowel sounds
- peritonitis, or infection/inflammation of peritoneum
- surgery/manipulation of bowel/meds used during surgery/late bowel obstruction.
causes of hyperactive bowel sounds
diarrhea, laxative use, early bowel obstruction, gastroenteritis.
characteristics and frequency of abdomen
- normal = 5-30X/min
- absent = 0X5'
- hyperactive
- hypoactive
auscultating vascular sounds or bruits on abdomen
use bell
- vascular sounds not normal.
percuss
- all 4 quadrants
- typmany predominates (air rises to surface when patient lays down)
- dull = solid organ
- use a smooth, systemic pattern; be sure to get all 4 quadrants
liver span
- going down chest's MCL = resonance to dull (ICS 5th).
- going up from abdomen = tympany to dull.
spleen
not typically palpable and is small unless enlarged due to disease.
percussing costovertebral angle tenderness (CVAT)
direct or indirect
- hit back with fist for kidney pain.
fluid wave
- done when there is suspicion of ascites and differentiate from gas.
- stand of right side and place ulnar edge of someone elses hand in middle of abdomen.
- place your hands on either flank and press left flank and wait for tap
- gas/adipose tissue = no tap.
- ascites = tap on your other hand
- reason = HF, cancers, pacreatitis.
palpation for on abdomen
size, location, shae, consistency, surface, mobility, pulsatility, tenderness
how to palpate with abdomen?
- light then deep 1 cm then 5-8 cm(2-3inches).
- use first 4 fingers make a gently rotary motion.
- lift fingers clockwise around the abdomen.
- use palmar surface fingers.
palpation hints
- palpate known tender area last.
- knees bent.
- voluntary guarding (cold/tense/ticklish) vs. involuntary rigiduty (hardness of muscles).
bimanual technique
- large abdomen
- retroperitoneal organs = duck bills.
hooking method/technique
- face the patient's feet = hooking fingers over costal margin from above
- ask person to take deep breath = feel bump agaist fingertips or not
- palpate lower margin of liver.
gallbladder murphy's sign
- take deep breath inspiration depresses liver/GB for palpation under costal margins
- (+) inspiratory arrest = descending liver pushes inflamed GB onto hand, sharp pain and midway inspiration stops
- normal. = no pain
cholecystitis
GB inflammed causing pain.
palpation spleen
- bimanual
- palpable when 3X normal size
- spleen enlarges with mononucleosis, trauma, leukemia, and lymphomas.
- friable and can rupture easy with over palpatation.
palpation of kidneys/adrenal glands
- bimanual "duck bill" technique
- at right/left flank
- may palpate R lower pole as round/smooth sliding mass (can be normal)
- no changes felt with deep inspiration
- palpating the R lower pole or palpating nothing are both normal findings.
blumberg sign
rebound tenderness in RLQ when pressure is apllied to LLQ indicating appendicitis.
iliopsoas sign
patient supine, lifts right lef straight up, flexing at hip, then pushing down over lower part of right thigh as person holds leg up.
- abnormal = pain felt in RLQ
- normal = no pain with the test.
developmental changes with infants/children
- large liver and most organs palpable
- abdomen protuberant > 4 years.
- BS only, no vascular sounds on auscultation.
developmental changes with geriatric
- increased fatty deposits in abdomen and hips.
- muscle atrophy = organ easily palpable.
- abdominal muscles atrophy so the abdominal wall thinner/softer, so organs more easily felt.
referred pain
pain is not be directly over injured organ; may be referred to where organ was located in fetal development.
function of MS system
support to stand erect, movement, encase and protect inner vital organs, produce RBCs in bone marrow (hematopoiesis), and reservoir to store essential minerals. (calcium+phosphorus).
musculoskeletal system
skeleton, joints, muscles
skeleton/bones
the framework of the body
joints
functional structure needed for mobility
nonsynovial joints
bones united by fibrous tissue or cartilage can be immovable (skull) or slightly moveable (vertebrae)
synovial joints
move freely because bones separate and enclose in joint cavity (knees). the cavity is filled with lubricant or synovial fluid which allows sliding to permit movement
muscles
account for 40-50% of the body weight and made of 3 types skeletal, cardiac, and smooth.
when muscles contract they produce _______.
movement
skeletal muscles
muscle attached to bone by tendons and are under conscious control.
cardiac muscles
under unconscious control.
flexion
bending limb at joint.
extension
straightening limb at joint
abduction
moving limb away from midline of body
adduction
moving limb toward midline of body
pronation
turning forearm palm down
supination
turning forearm so palm is up
circumduction
moving arm in circle around shoulder
inversion
moving sole of foot inward at ankle
eversion
moving sole of foot outward at ankle
rotation
moving head around central axis
elevation
raising a body part
depression
lowering a body part
plantar flexion
pointing toe downward
dorsiflexion
oppoite of plantar flexion, pulling foot upwards.
temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
articulation of mandible and temporal bone; permits jaw function of speaking and chewing; assess for crepitus or pain with TMJ motion or palpation; allow for hinge (open/close), gliding (side/side), and gliding (retraction).
infants musculoskeletal
3 months gestation the fetus has formed skeleton of cartilage; bone growth continues rapidly during infancy.
children musculoskeletal
steady growth and lengthening at epiphyses/growth plates; any trauma can risk bone deformities.