Anatomy Test III
1/284
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
285 Terms
What is the purpose of the autonomic nervous system (ANS)
The purpose of the autonomic nervous system is to regulate functions that are carried out without conscious intent or awareness (involuntary). it maintains homeostasis. It adjusts the functions of effectors
Where does the ANS innervate
it innervates glands as well as cardiac and smooth muscle
What type of areas does the ANS control (5)
1) thoracic organs (heart/lungs)
2) abdominopelvic organs (digestion, urine production, reproduction)
3) skin
4) other glands
5) other blood vessels
What are the two pathways of the autonomic nervous system (ANS)
1) sympathetic division
2) parasympathetic division
What branch of the nervous system is the ANS a part of (CNS or PNS)
the PNS
What are the inputs of the ANS (2)
1) sensory
2) Premotor
Describe the sensory input of the ANS
They are visceral afferent neurons projected into the spinal cord dorsal horn or brainstem nuclei. also includes somatic sensory neurons
describe the premotor input of the ANS
The hypothalamus, pons, and medulla oblongata (the brainstem) that have inputs from brain regions including brainstem and hypothalamus, amygdala, basal ganglia, anterior cingulate cortex, insular cortex, visual centers, and ventromedial pre-frontal cortex
BASICALLY COMES FROM EVERYONE IN THE BRAIN
What is the GENERAL composition of an autonomic neuron
specific compositions change based on if its a parasympathetic or sympathetic neuron but generally there is a preganglionic neuron that comes from the CNS that meets with an autonomic ganglion to pass the signal onto a postganglionc neuron that is close by a target tissue.
How is the ANS controlled or regulated
the hypothalamus is the main control center for the ANS, but the brainstem also sends outputs to the ANS to help maintain homeostasis
Describe the structure of a SYMPATHETIC motor neuron
The sympathetic motor neuron has a short myelinated axon preganglionic fiber from the CNS to the sympathetic ganglion which transfers the signal to the postganglionic fiber that is fairly long and unmyelinated.
SHORT MYLINATED —> LONG UNMYLINATED
Describe the structure of a PARASYMPATHETIC motor neuron
The parasympathetic motor neuron has a long myelinated preganglionic axon which reaches a parasympathetic ganglion that is close to the target cell. The signal gets transferred to the postganglionic axon which is short and unlmylinated
LONG MYLINATED —> SHORT UNMYLINATED
What is the third not talked about much pathway for the autonomic pathway
the adrenal sympathetic pathway
Describe the composition of the adrenal sympathetic pathway
The CNS sends a signal the kidneys which has a receptor in the center of the kidney (adrenal medulla) this releases a mass amount of epinephrine into the bloodstream, this is considered a hormone
Where is the sympathetic division located in the spinal cord
the thoracic to lumbar vertebrae, located in the lateral horns
Where is the parasympathetic division located in the spinal cord
in the cervical and sacral regions of the spinal cord
What causes sympathetic activation
stress
What are the effects of sympathetic activation (7)
1) increased metabolism (increases ATP)
2) increases glycogenolysis and lipolysis (increases blood glucose)
3) pupil dilation and lens relaxation
4) increased HR and BP
5) airway dialation
6) vasoconstriction (of skin, GI, kidney)
7) vasodilation (of heart lungs brain muscles etc)
All of the effects of sympathetic activation contributes to what
fight or flight
What are the three types of neurotransmitters used in the sympathetic nervous system
1) norepinephrine (NE)
2) epinephrine (E)
3) ACh
What are the types of inactivation for NE and E (3)
1) diffusion
2) extracellular catechol-O-methyl transverse (COMT)
3) reuptake with mitochondrial monoamine oxidase (MAO)
What are the three main types of receptors and what is their:
1) agonist
2) g-protein
3) 2nd messenger
1) α1, mostly NE, Gq, IP3/DAG (more calcium)
2) α2, mostly NE, Gi, cAMP (decrease)
3) β1-4, NE and E equally, Gs, cAMP (increase)
What are the effects of binding to an α1 receptor (5)
1) vasoconstriction of most vascular smooth muscle
2) pupil dialation
3) contraction of urinary bladder sphincters
4) increased blood glucose levels
5) lower blood pressure
What are the effects of binding to a α2 receptor (2)
1) decrease NE release at presynaptic release sites
2) decrease insulin release (at pancreas)
What are the effects of binding to ACh-M3 receptors (1)
1) merocrine sweat glands increase sweat (focused at the palm and soles of feet)
What are the effects of binding to a β1-4 receptor (10)
1) increased heart rate
2) increased contractibility at the heart
3) higher blood pressure (through kidney)
4) bronchodilation (expanding of the lungs)
5) vasodilation (expanding of blood vessels)
6) decreased motility (contractibility) of the GI tract
7) increase insulin release
8) labor inhibition
9) increase lipolysis (breaking down lipids)
10) decrease micturition (pee)
where is NE released from
varicosities
If the sympathetic nervous system is the fight or flight, what the the parasympathetic nervous system
rest and digest
or
feed and breed
What is the main neurotransmitter involved with the parasympathetic nervous system
ACh
What are the types of responses produced by the parasympathetic nervous system (6)
1) sexual arousal
2) salivation
3) lacrimation
4) urination
5) digestion
6) defection
What are the effects of the parasympathetic nervous system being active (7)
1) decreased metabolism (so less ATP)
2) lower blood glucose levels
3) pupil constriction and lens tension (near sightedness)
4) decreased HR and BP
5) airway constriction
6) vasodilation (of skin GI and kidneys)
7) vasoconstriction (of heart, lungs, brain, muscles)
What is the main nerve involved in the parasympathetic nervous system
the vagus nerve
What are cholinergic neurons in the ANS
they are neurons who’s primary neurotransmitter is ACh
What regions of the ANS are cholinergic neurons (3)
1) All sympathetic and parasympathetic preganglionic neurons
2) all parasympathetic postganglionic neurons
3) sympathetic postganglionic neurons that innervate most sweat glands
What are the types of cholinergic receptors (primarily bind with ACh) in the ANS (2)
1) Nicotinic (ion channels)
2) Muscarinic (G protein coupled receptors)
there are two types of muscarinic receptors what are their names and what is their:
1) agonist
2) g-proteitn
3) 2nd messenger
1) M2, ACh, Gq, IP3/DAG (increases calcium)
2) M3, ACh, Gi, cAMP (decrease)
What are the effects of binding to a M2 receptor (1)
decreased heart rate
What are the effects of binding to a M3 receptor (5)
1) bronchoconstriction
2) increased motility (contractibility) of the GI tract
3) pupil constriction
4) vasodilation (of heart and penis)
5) formation of NO which causes vasodilation in epithelium
What are the three main types of innervation found in effectors
1) antagonistic
2) cooperative
3) sympathetic only
describe antagonistic innervation
it is dual innervation from both the parasympathetic and the sympathetic nervous system, this is the most common type of innervation and each pathway often has opposite (antagonistic) affects
describe cooperative innervation
this is dual innervation but both the parasympathetic and sympathetic are complimentary to each other
How is salivation an example of cooperative innervation
the SNS stipulates mucous membranes while the PNS stimulates serous membranes, they both combine to become saliva
Describe how pupil response is a form of an autonomic reflex
1) sympathetic system causes dilation when light dims
light enters brain, activates preganglionic neuron in the upper thoracic spinal cord, this activates postganglionic neurons in the superior cervical ganglion that releases NE that causes dilation
2) parasympathetic system causes constriction when light brightens
Light bright activates preganlionic neuron in the upper brainstem activates postganglionic neuron in the ciliary, causes constriction
Describe sympathetic only innervation, provide the examples of them (3)
these are the postganglionic receptors that are cholinergic (ACh binding)
examples:
1) skin strictures (sweat glands, hair muscles, blood vessels)
2) adrenal medulla (the thing that releases E as a hormone)
3) many other blood vessels
What is an examples of dual innervation (2)
1) pupil constriction/dilation
2) the heart rate increasing/decreasing
There are some effectors that while duly innervated are mostly controlled by the PNS, what is the example of this
The lacrimal system
Which pathway (parasympathetic or sympathetic) tends to be faster, why is this
the parasympathetic pathway tends to be faster than the sympathetic pathway because it has a long myelinated axon with a short unmylinated axon, this means that the signals travels faster compared to the sympathetic pathway which has a short mylinated axon and a long unmylinated axon
Between the ANS reflexes and the somatic reflexes which is slower and why (4)
the ANS reflexes are slower because there are:
1) more synapses in pathways
2) slower action potential conduction based on diameter and myelination status
3) greater distance between presynaptic release site and postsynaptic membrane (longer diffusion rate)
4) use g-protein coupled receptors which are slower than ion channels
What is autonomic tone
it describes the dynamic balance of homeostasis between the parasympathetic and sympathetic system. the to systems are constantly adjusting to keep the body in homeostasis as well as responding to internal or external stimuli
What is autonomic tone set by
its set by the SNS basal activity
What so important about the vagus nerve
its the longest nerve in the body and there are a bunch of sensory and motor receptors that pass through this nerve, that makes it super important for regulating a multitude of the bodies actions and responses
What is the vagal response
a reaction that occurs when the vagus nerve is stimulated
what are the symptoms of the vagal response (7)
1) lightheadedness
2) sweating
3) fainting
4) nausea
5) feeling warm
6) cold and clammy skin
7) ringing in ears
What are nonadrenergic and noncholinergic responses
nonadrenergic- uses NE as neurotransmitter
noncholinergic- neither NE or ACh as a neurotransmitter
How are nonadrenergic and noncholinergic responses mediated
they are mediated by cotransmitters
What types of cotransmitters exist in the sympathetic system (2)
1) ATP
2) a bunch of neuropeptides
What types of cotransmitters exist in the parasympathetic system (3)
1) ATP via P2X inotropic
2) vasoactive intestinal peptide
3) Nitric oxide (NO)
What are the effects of caffeine (3)
1) blocks adenosine receptors
2) releases intracellular calcium storage
3) inhibits PDE
What are the characteristics of epithelial tissues (5)
1) Derived from either ectoderm or endoderm
2) cells of endothelial tissues are closely packed, connected by cellular junctions to form sheets of cells
3) thin ECM, the basement membrane
4) avascular, but are associated with vascular-rich connective tissue
5) relatively high rate of mitosis-replacement of cells
What are the functions of epithelial tissues (6)
1) protection from invasion and injury
2) secretion of mucus, sweat, enzymes, hormones etc
3) excretion to remove waste, co2, bile, etc
4) adsorption, absorbs nutrients and chemical from adjacent fluids
5) filtration of blood to the ECF renal tubular fluid
6) sensation with nerve endings, touch, irritation
What is the basement membrane for epithelial tissue and what is its purpose (4)
it is the extracellular matrix that supports and acts:
1) as a support for epithelial cells
2) an anchor for epithelial cells to underlying connective tissue
3) binds growth factors
4) and regulates exchange between epithelium and underlying tissues
What makes up the basement membrane (4)
1) collagen
2) laminin
3) glycoproteins
4) protogylcans
Why do we say that epithelial cells have polarity
Because there are distinct structural and functional regions of cells
What does apical mean for a epithelial cell
oriented away from the basement membrane and toward internal cavity (lumen)
What does lateral mean for a epithelial cell
oriented toward neighboring cells, sites of attachment
What does basal mean for a epithelial cell
oriented toward basement membrane
What are the different classes of epithelial cell (know what they look like) (4)
1) simple
2) psudostratified columnar
3) stratified
4) transitional
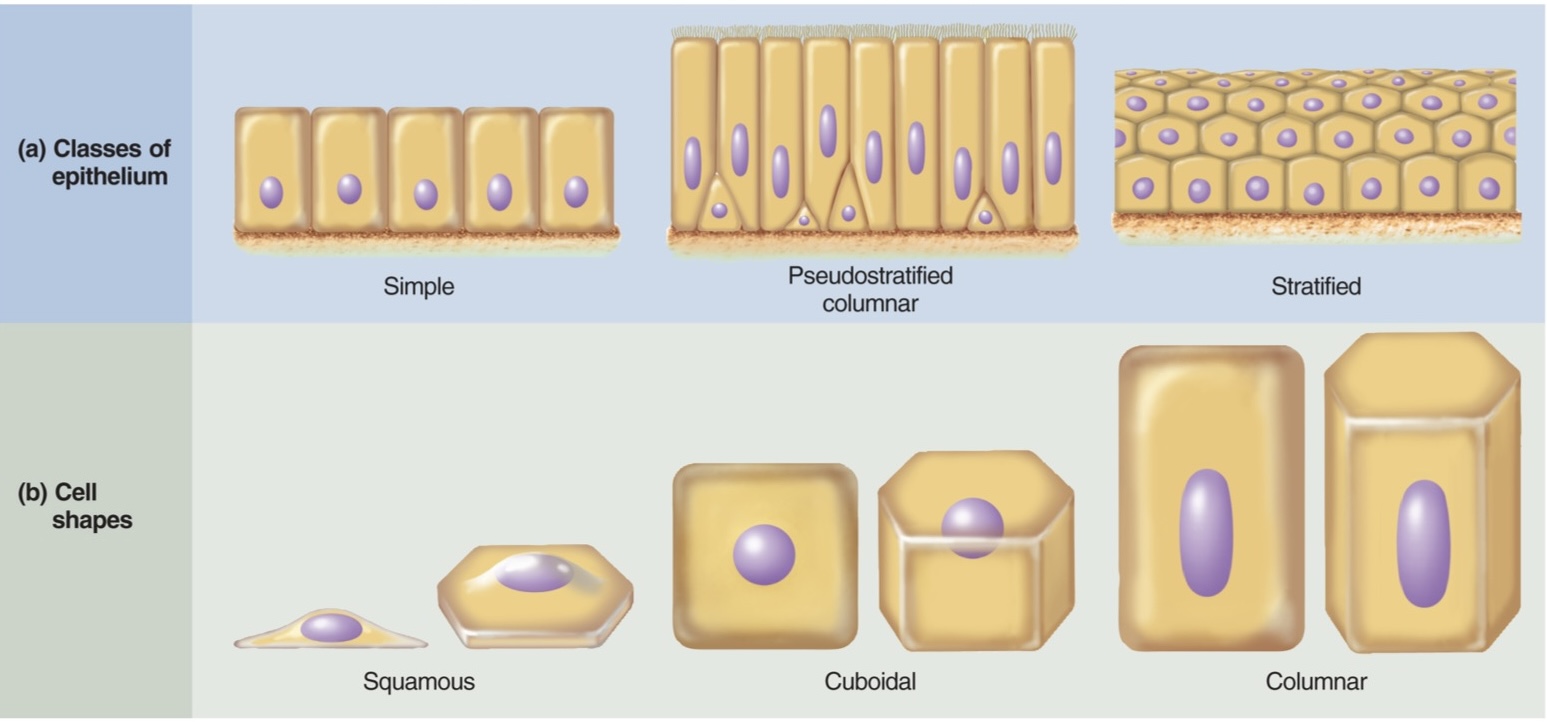
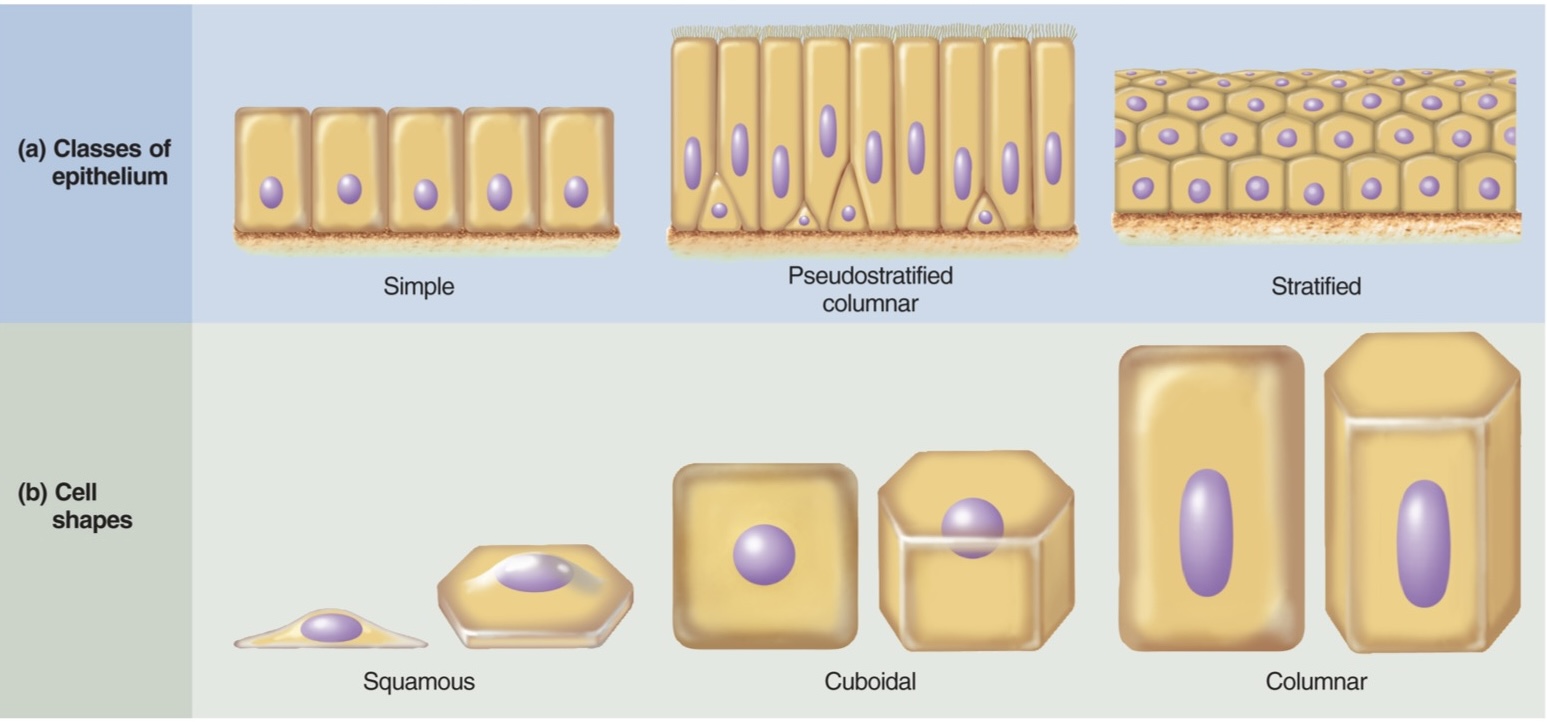
What are the different shapes of epithelial cell (know what they look like) (3)
1) squamous
2) cuboidal
3) columnar
What are the coverings/linings of epithelia (5)
1) cutaneous
2) mucous
3) serous
4) endothelium
5) synovial
What is the structure and function of cutaneous coverings
its the skin, made of stratified squamous epithelium over connective tissue, that serves as a protective barrier against dehydration and infection
What is the structure and function of mucous lining
they line passages open to external environments (respiratory, digestive urinary). They are 2-3 layers of epithelium, areolar lamina propria, and muscular mucosae (sometimes)
What is the structure and function of serous lining
also known as serosa, made of simple squamous epithelium (mesothelium) on a thin layer of areolar connective tissue, produces serous fluid, and lines some body cavities and covers some organs
What is the structure of endothelium lining
simple squamous mesoderm-derived epithelium on a thin sheet of areolar connective tissue
What is the structure and function of synovial lining
only fibrous connective tissue, lines some joints
What is a gland
A cell or organ composed primarily of epithelial tissue that secretes substances for use in other location or for elimination either through secretion or excretion
What are the two things glands secrete
1) synthetic product of glandular cells
2) modified substances removed from tissues
What’s the difference between secretion and excretion
Secretion: useful substances
excretion: waste products
What are unicellular glands
located in epithelial tissues and can be either endocrine or exocrine (goblet cells or g-cells)
describe endocrine glands (3)
1) lose contact with epithelial surface
2) ductless
3) secretion into blood via associated capillaries
describe exocrine glands (3)
1) maintain contact with epithelial surface
2) have ducts
3) secretion into organ lumen or onto body surface
When talking about glands, what two areas could a gland have
1) duct
2) acinus
What is the acinus part of a gland
it is the part of a gland that is secreting the substance into the duct
What are the three types of exocrine glands and an example of each
1) simple coiled tubular: sweat gland
2) compound acinar: mammary gland
3) compound tubuloacinar: pancreas
What are the 3 modes of exocrine secretion
1) Merocrine
2) apocrine
3) holocrine
How does merocrine secretion work
also known as eccrine glands, they release substances from vesicles by exocytosis, includes sweat tear pancreas gastric and others. Most common
How do apocrine glands work
release by exocytosis, but into large lumen with apical portion pinched off, especially mammary and sweat glands
how do holocrine glands work
accumulate product and then cells rupture. includes sebaceous and eyelid meibomian glands
What are the types of exocrine secretions
1) Serous
2) mucous
3) mixed
4) cytogenic
Describe serous secretion
release thin watery serum-like fluids
serum is plasma from blood which contains water and solutes including proteins but not clotting factors
What are examples of serous membranes
1) pleural membranes
2) pericardium
3) peritoneum
describe mucous secretions
release mucin, a glycoprotein that absorbs water and become mucus
describe mixed secretions
glands that include both serous and mucous cells (salivation)
Describe cytogenic secretions
release whole cells- gonads (eggs and sperm)
What are goblet cells
They are single cell exocrine glands found in simple and psedusostratified columnar epithelia, they secret mucous
briefly describe the skin
the bodies largest, heaviest, and most vulnerable organ
Define integument
the skin, covering of the body composed of epidermis and dermis
Define integumentary system
includes both the skin and the accessory organs such as hair nails and glands
define epidermis
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Define dermis
dense irregular connective tissue under the epidermis
hypodermis
connective tissue layer often found below dermis