CMS II Final: Neuro
1/274
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
275 Terms
which spinal cord disorder causes immediate flaccid paralysis and loss of sensation at/below the level of the injury?
spinal cord transection
what develops from the neural tube and neural crest?
tube = CNS (brain and spinal cord)
crest = all other neural structures (including spinal roots)
which medication is essential for treating spinal cord injury?
methylprednisolone → don't use if penetrating/multisystem trauma or TBI
LMN injury vs UMN injury: upward positive Babinski?
UMN
LMN vs. UMN injury: decreased tone and atrophy?
LMN
which type of motor neuron injury is spastic paralysis seen in?
UMN
LMN = flaccid
Where does the communication between the upper motor neuron and lower motor neuron occur?
anterior grey horn
following a MVA, your patient reports no sensation of light touch and pressure in their right leg. which tract is damaged?
Left anterior spinothalamic tract
a patient reports not feeling their phone vibrate in their left buttock pocket. Specifically, which tract has been damaged?
dorsal white column → left f. gracilis!
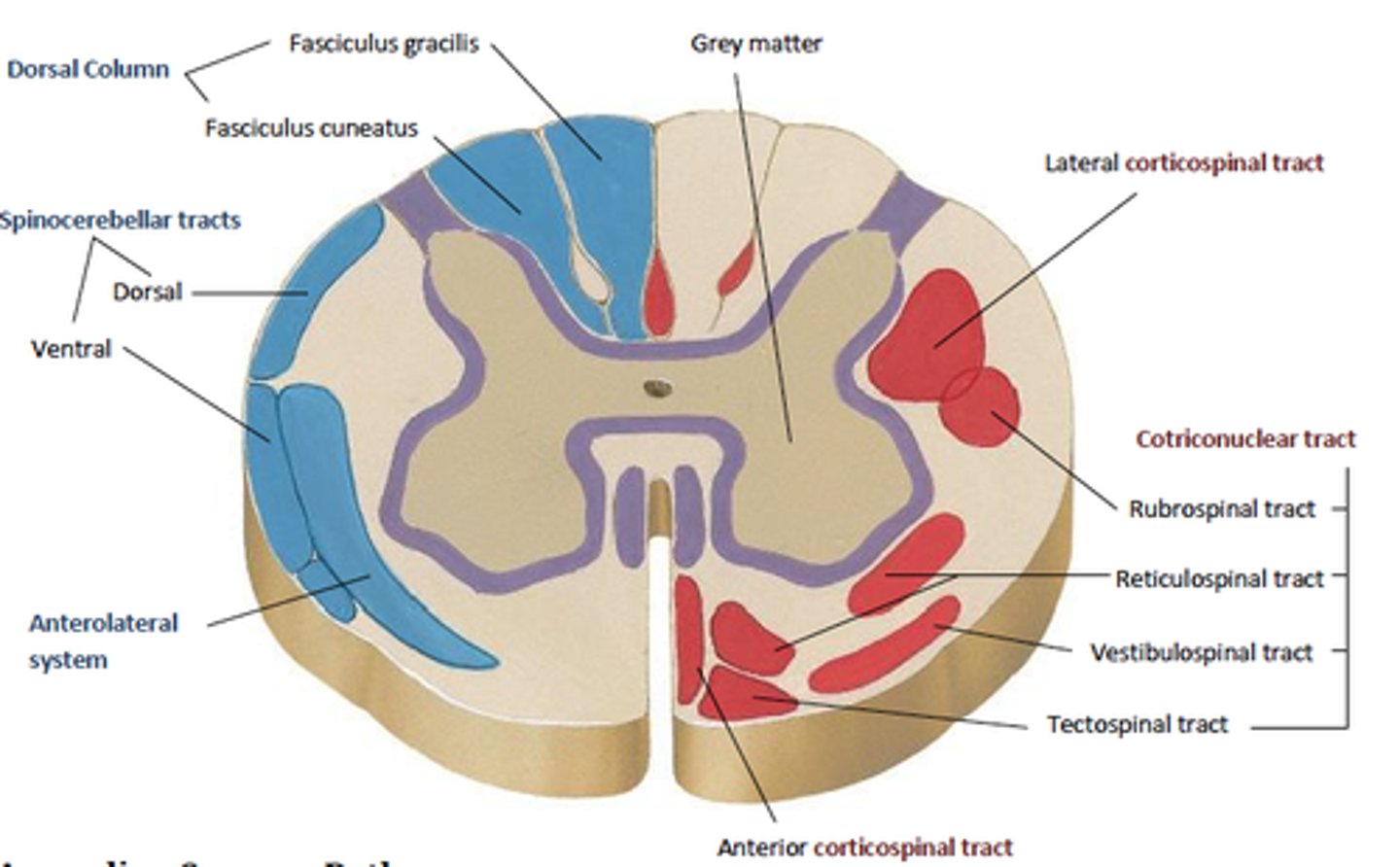
f. gracilis vs. f. cuneatus
make up the dorsal white column
gracilis = sacral and lumbar
cuneatus = thoracic and cervical
an inmate is shanked in their lower back and their dorsal white column was injured. where do you expect them to have deficits?
in their neck
dorsal white column: outermost cervical → thoracic → lumbar → sacral innermost
what connects the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord?
UMN
LMN connects the spinal cord to target muscle
damage to which motor neuron can cause fasciculation d/t degenerative process?
LMN
why does prominent weakness and atrophy occur when LMN is damaged?
there is nothing stimulating the muscle to contract bc LMN connects spinal cord to muscle
your patient complains of visual hallucinations and is found to have an arterial thrombosis in their brain. which artery would you expect the clot to be in based on their symptoms?
posterior cerebral artery → feeds occipital lobe → location of visual cortex
big thinker question !
what are the functions of the frontal lobe?
- behavior, emotions, problem solving
- planning/attention
- primary motor region on precentral gyrus
what are the functions of the temporal lobe?
language
hearing
decoding
short term memory
smell identification
what are the functions of the parietal lobe?
touch, primary sensory region on postcentral gyrus
lesions here cause sensory deficits of astereognosis, hemispatial neglect, inability to copy figures
your patient is recovering from a stroke. they report olfactory hallucinations. which artery was likely affected by the stroke?
middle cerebral artery → temporal lobe
which artery feeds the trunk, legs, feet, and genitals?
anterior cerebral

which artery are you concerned of stroke in if your patient reports paresthesia in their hands and tongue?
middle cerebral
precentral or postcentral gyrus: motor?
precentral
if a patient has abnormal gait a difficulty balancing, which area of the brain may be damaged?
cerebellum
which part of the brain is responsible for vitals?
medulla → brain stem
controls HR, RR, vessel diameter (BP), vomiting, coughing
a lesion in which brain structure could cause extrapyramidal syndromes?
basal ganglia + cerebellum
what diagnosis is defined as partial spinal cord transection?
brown-Sequard
what score on the glasgow coma scale would prompt intubation?
<8 = intubate
what are the first signs of autonomic failure?
postural hypotension
impotence
disturbance of micturition
if a patient has an injury at T10, what motor symptoms would you expect to see below the injury?
UMN below injury
LMN at the level (bc synapse is disrupted)
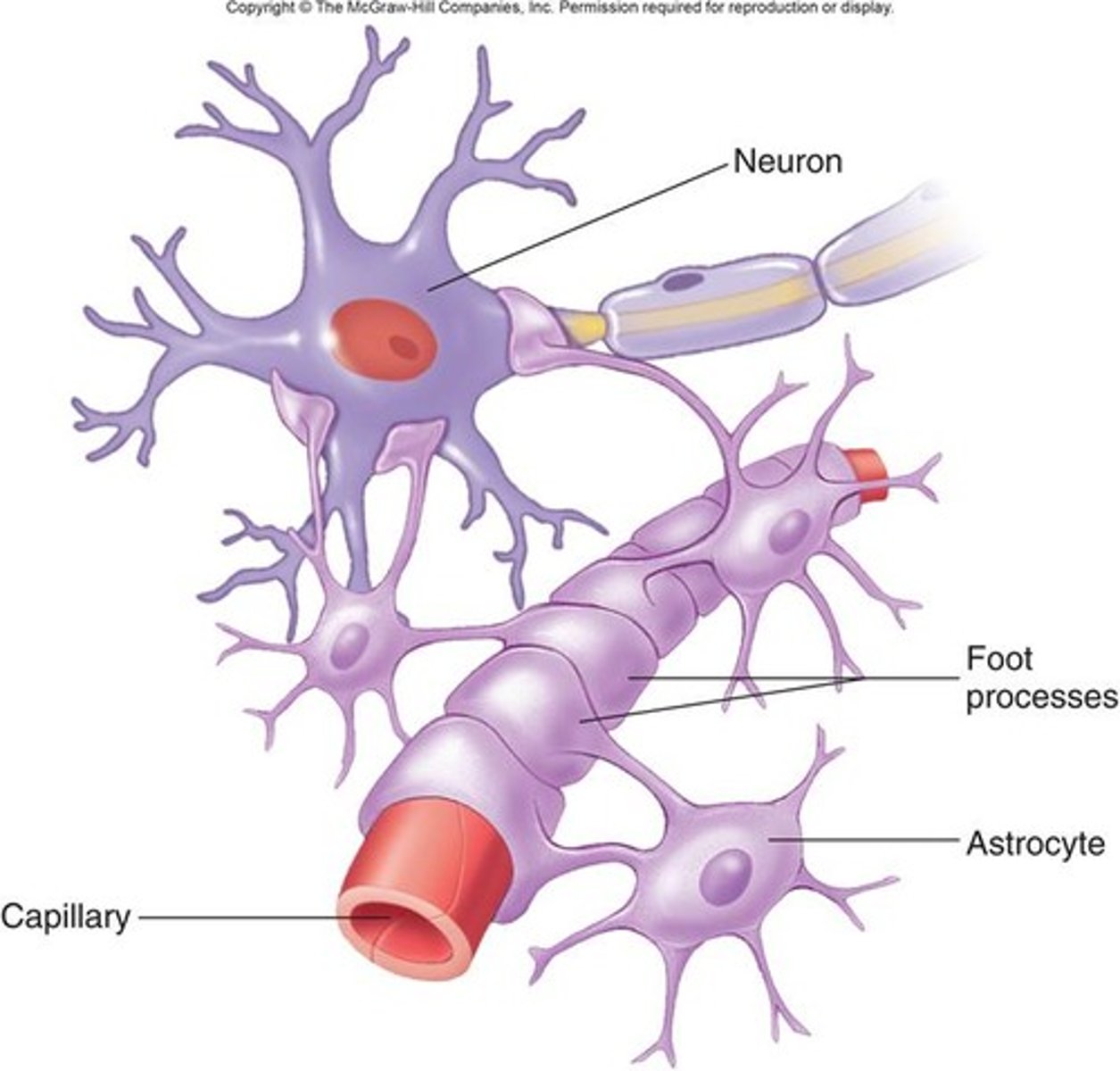
which glial cell attaches to nerves and blood vessels, anchoring neurons to capillaries?
astrocytes → essential for BBB
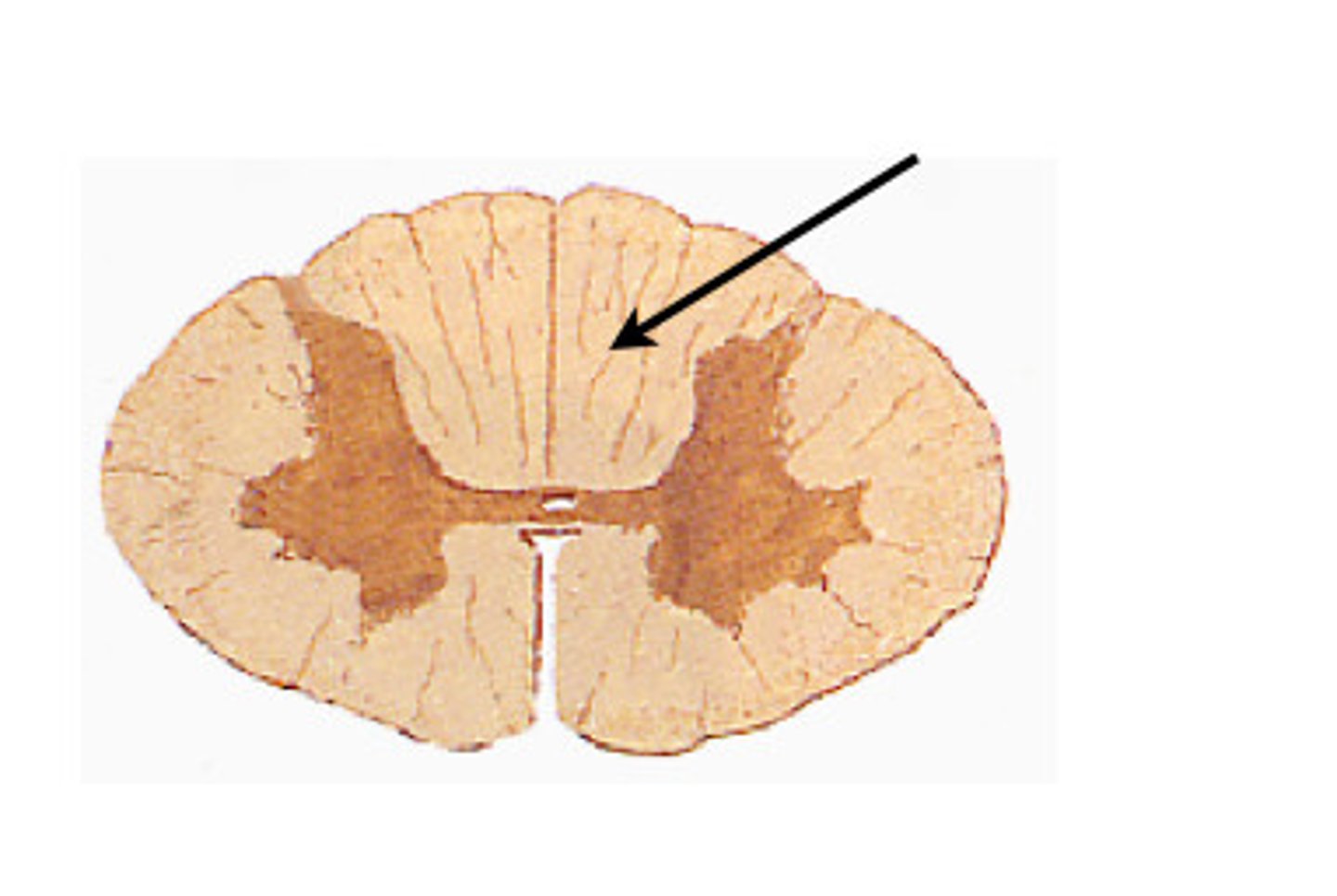
if there is damage to the left lateral corticospinal tract, where would you expect to see deficits?
ipsilateral, UMN below the injury and LMN at the level of the injury --> bc motor neurons cross over in the pyramids
what does the diencephalon differentiate into?
thalamus and hypothalamus
What does the mesencephalon become?
midbrain → visual and auditory reflex centers
if a patient has difficulty problem solving, in which lobe of the brain would you suspect damage?
frontal lobe
where does the first synapse and crossover occur for discriminative touch/vibration/proprioception?
medulla!! → ipsilateral loss of sensation below injury
you sliced your finger and feel immense pain in you left finger. which tract sends this pain signal to your brain?
lateral spinothalamic tract = pain and temp
if a patient with afib suffers a stroke. which artery is likely affected?
middle cerebral
if a patient with incontinence presents with new back pain that worsens when laying down, what should you be suspicious of?
tumor → epidural spinal cord compression → emergent neuro/onc referral
A 42 yo male suffered a fall. Since then he has developed bowel incontinence. He also reports numbness in both buttocks and inner thighs. What is your plan for this patient?
cauda equina syndrome (aka centrally prolapsed disc) → mri and neurosurgery consult
which diagnosis leads to progressive degeneration of corticospinal path down to anterior horn cells?
ALS → UMN and LMN destruction → NO sensory loss!!!! Steven Hawking
a patient presents with difficulty swallowing and you observe tongue fasciculations. what should you perform for diagnosis?
muscle bx, nerve bx → ALS
Which nerve is compressed in carpal tunnel syndrome?
median
which nerve is responsible for tarsal tunnel syndrome?
posterior tibial nerve
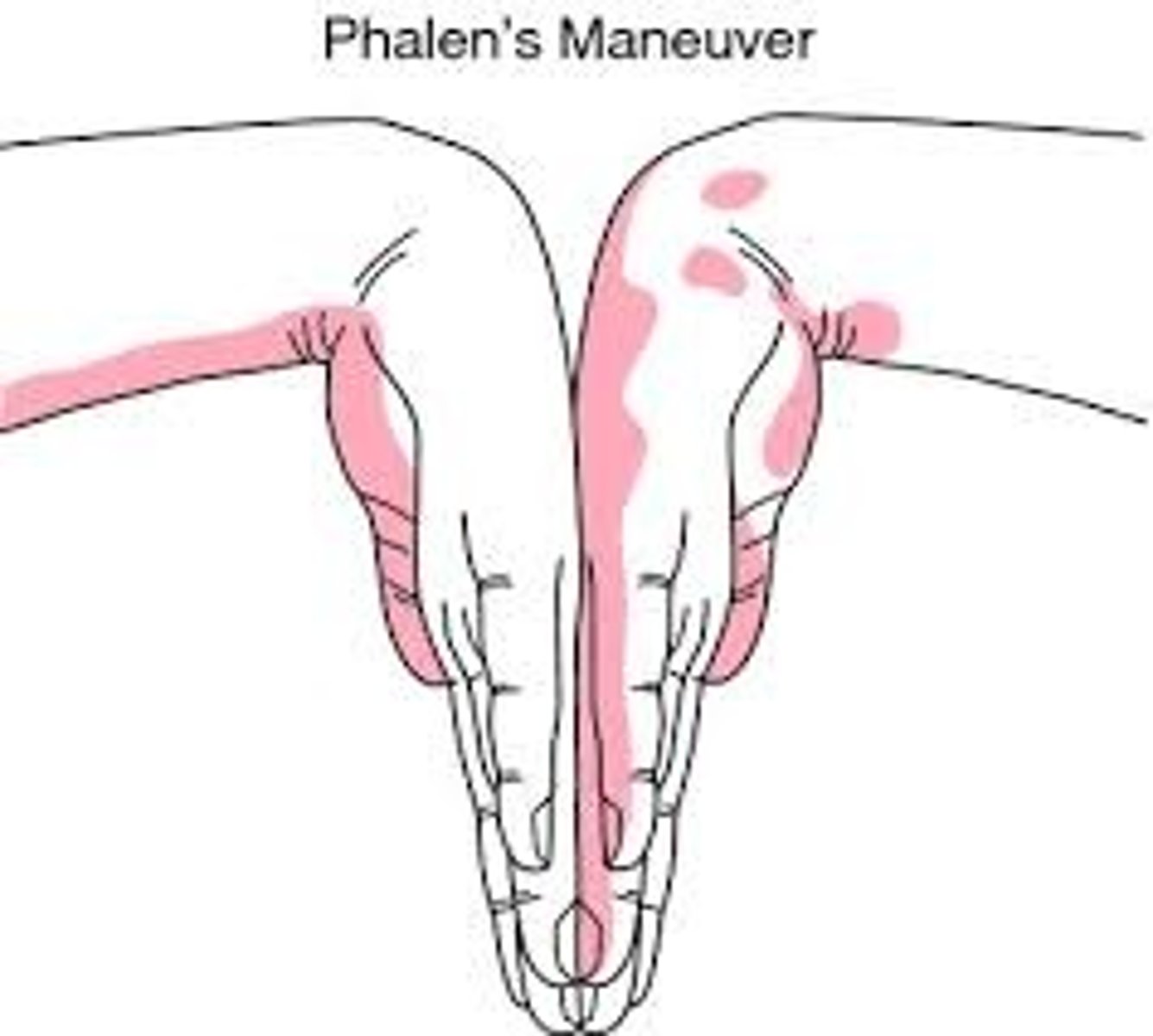
a patient presents with pain/paresthesia in their 1st 3 digits that is worse at night. you perform a test where you have them flex their palm at the wrist and and extend their elbow. what is this test called?
phalen maneuver for carpal tunnel → pain = positive
tinel test is the other one → percussion over median nerve
what are some causes of peripheral neruopathies?
vit B12 deficiency, alcoholism, DM, leprosy
what is the drug of choice for acute MS attacks?
corticosteroids
what drug is used for relapsing MS?
interferon
a 43 year old female presents with complaints of fatigue, urinary retention, and vertigo. she had a positive babinski reflex. what would you expect to see on MRI?
Dawson's fingers (plaques) → MS
symptoms you also would see: unilateral blurred vision, clonus, hand paralysis, loss of vibratory/position sense, dysphagia, dysarthria, ataxia, clumsiness
what criteria is used for diagnosis of MS?
McDonald criteria****
a patient with recent hx of tibia fracture presents with severe pain and swelling. they are seemingly in severe pain which is not explained by the physical exam. what is the diagnosis?
complex regional pain syndrome → pain out of proportion
follows a fracture → swelling, limited ROM, vasomotor instability, skin changes, patchy bone demineralization
treat with PT/OT, pain management, anticonvulsants (gabapentin), or TCAs
which cells does the polio virus destruct?
anterior horn cells → weakness or paralysis, may effect respiratory muscles
a 73 year old unvaccinated patient presents with complaints of weakness and fatigue. they reported myalgia and URI symptoms that presented 2 weeks ago. what diagnosis are you concerned about?
polio
what indicates ophthalmic involvement of herpes zoster?
hutchinson's sign
which diagnosis has ascending paralysis?
guillan barre syndrome (GBS)
ground to brain
what infection is heavily associated with GBS?
c. jejuni enteritis
what is a concerning symptom of GBS?
respiratory paralysis
what is the first line of therapy for diabetic peripheral neuropathy?
control glucose
then TCAs → amitriptyline, nortriptyline or anticonvulsants → carbamazepine, gabapentin
what drugs are used for gastroparesis d/t autonomic dysfunction
metoclopramide or erythro
which diagnosis occurs when toxin irreversibly binds to receptors in the brain and spinal column?
tetanus → blocks GABA → unchecked excitatory impulses → inc. muscle tone, spasms, rigidity
which diagnosis has symmetric descending paralysis?
botulism
where does the toxin bind to cause botulism?
binds to presynaptic sides of cholinergic synapse at NMJ and irreversibly disrupts ach release
which diagnosis blocks neuromuscular transmission at Ach postsynaptic receptors?
myasthenia gravis
which signs and symptoms are more commonly seen in patients with Myasthenia Gravis?
ptosis, diplopia, dysarthria, dysphagia, generalized weakness
what is lambert's sign?
increased power with muscle contraction (i.e. improvement of power on repeated hand grip) seen in lamber eatons
NOT myasthenia gravis bc it fatigues!!
what is the cause of lambert eaton syndrome?
antibodies against voltage gated calcium channels → decreased calcium in nerve ending → less Ach released from NMJ
which medication can cause vestibular and auditory symptoms?
aminoglycosides are ototoxic!
salicylates
A 28 yo female presents with muscle weakness and fatigue. You do a tensilon test and shows improvement. What type of therapy would you initiate?
anticholinesterase therapy → mestinon or prostigmin
immunosuppressants
thymectomy
a patient presents with proximal muscle pain and weakness. you see papules on their fingers. what is the appropriate treatment?
polymyositis/dermatomyositis → Eteplirsen → slows rate of muscular dystrophy
finger papules = gottrons papules
also heliotrope rash on eyes
what is an inherited set of myopathic disorders characterized by progressive muscle weakness and wasting?
muscular dystrophy is INHERITED!!!
what is the most common cause of cerebral palsy?
abnormal cerebral development likely d/t prenatal care
what is the most worrisome complication of cerebral palsy?
aspiration PNA
peripheral vs. central vertigo: less than one minute and fatigues?
peripheral
central lasts longer than a minute and doesn't fatigue
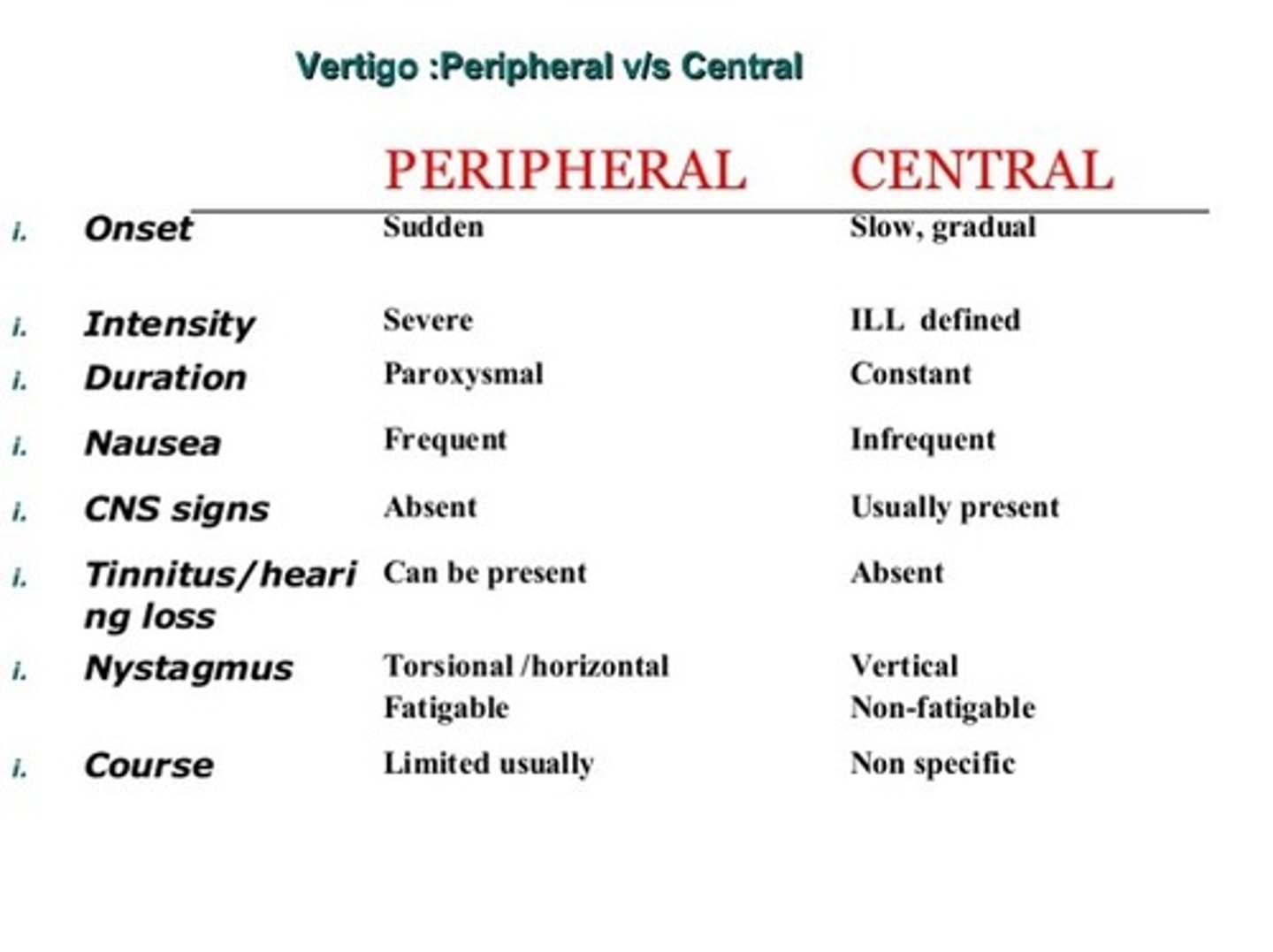
peripheral vs. central vertigo: nystagmus may change direction with head position?
central
peripheral is only one type, usually rotational
if you perform caloric testing on a patient with suspected unilateral vestibular dysfunction, what would you expect to see to confirm the diagnosis?
affected side fails to produce nystagmus
which type of vertigo has severe symptoms?
peripheral
what test is diagnostic for vertigo?
Dix-Hallpike maneuver
what is the treatment for vertigo?
Epley maneuver
meclizine/scopolamine
peripheral or central vertigo: vertical nystagmus?
central
peripheral = horizontal nystagmus
a patient presents with complaints of sudden vertigo attacks that fully resolve between episodes. they deny hearing loss. what is the treatment?
BPPV → epley to dislodge otolith
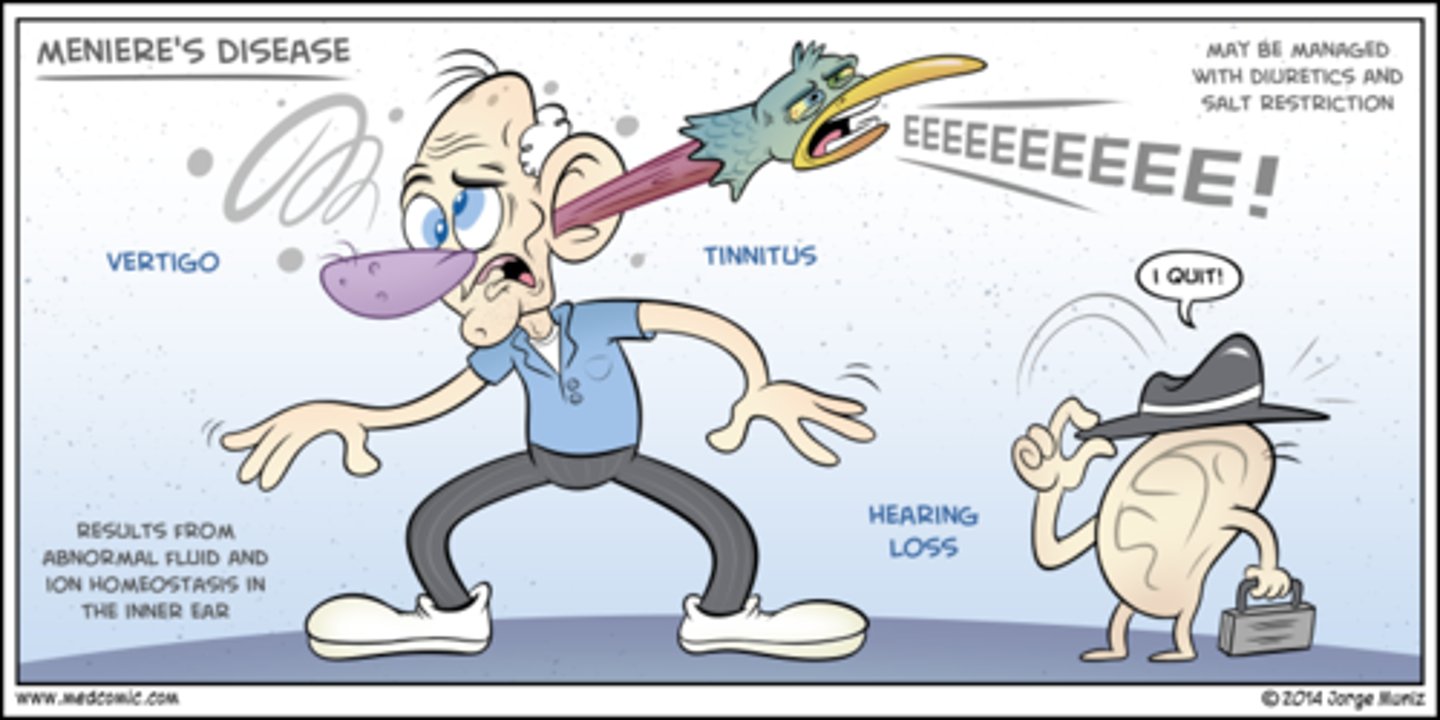
what is the tetrad of Meniere's disease?
Vertigo
Hearing loss
Tinnitus
Aural pressure
in meniere's disease, vertigo ___________ as hearing loss worsens
resolves
what is the cause of meniere's disease?
endolymphatic hydrops → low Na diet and diuretics help lower pressure
a patient presents with unilateral sensorineural hearing loss, tinnitus, and facial weakness. what should you order to confirm your diagnosis?
MRI WITH contrast → acoustic neuroma
What is the cause of Wernicke's encephalopathy?
thiamine deficiency
what is the triad of symptoms associated with Wernicke's encephalopathy?
gait ataxia
ophthalmoplegia
confusion
all pts with undiagnosed AMS, oculomotor disorders, or ataxia should receive what medication?
parenteral thiamine
which population is Wernicke's more prevalent in?
alcoholics
what is the cause of alcoholic cerebellar degeneration?
alcohol abuse that leads to toxic degeneration of Purkinje cells
is nystagmus seen in alcoholic cerebellar degeneration?
no! and cognition remains intact
may see alcohol related neuropathy, irreversible :/
what can worsen symptoms of Wernicke's if given prior to thiamine?
glucose bolus! don't give!
what is the first symptom seen in Friedreich's ataxia?
gait ataxia → followed by slurring dysarthria and nystagmus
NO vertigo
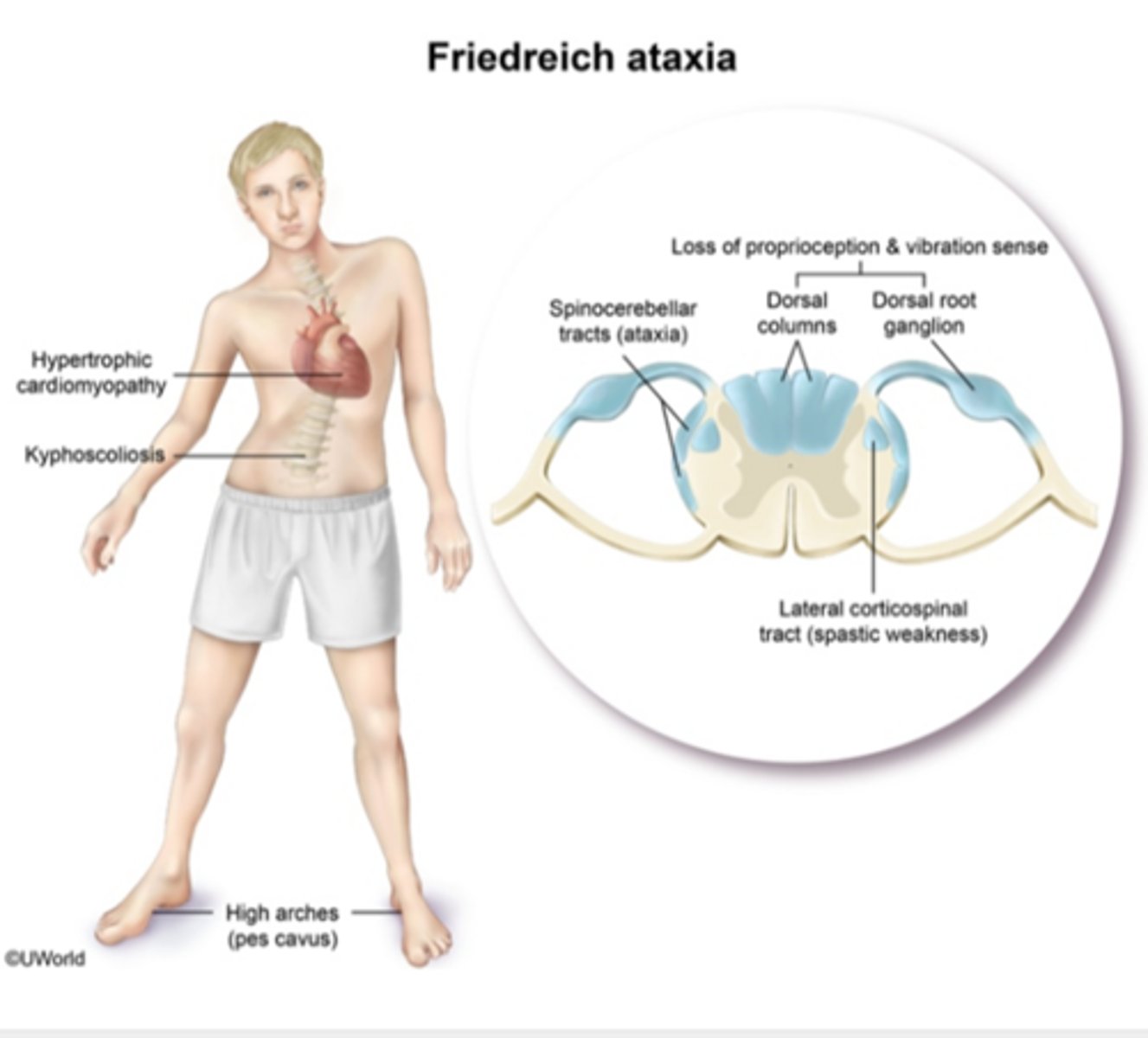
which systemic/metabolic disorders can cause peripheral neuropathy?
- vitamin B12 deficiency → distal, symmetric sensorimotor polyneuropathy
- alcoholism → distal, symmetric sensorimotor polyneuropathy
- leprosy
- DM→ stocking glove
if you hit your funny bone, which nerve is affected?
ulnar n.
compartment syndrome involves which nerve?
deep peroneal
what would you expect to see on a lumbar puncture from a patient with MS?
oligoclonal bands, WBCs
GBS doesn't have either of these!!
which drug reduces spasticity in patients with spinal cord transection, MS, and ALS?
baclofen
Which type of CRPS has a known nerve injury?
Type 2
type 1 is without nerve injury
which has a better prognosis: decerebrate or decorticate positioning?
decorticate → flexion of lower arms
decerebrate → extension of lower arms → poor prognosis
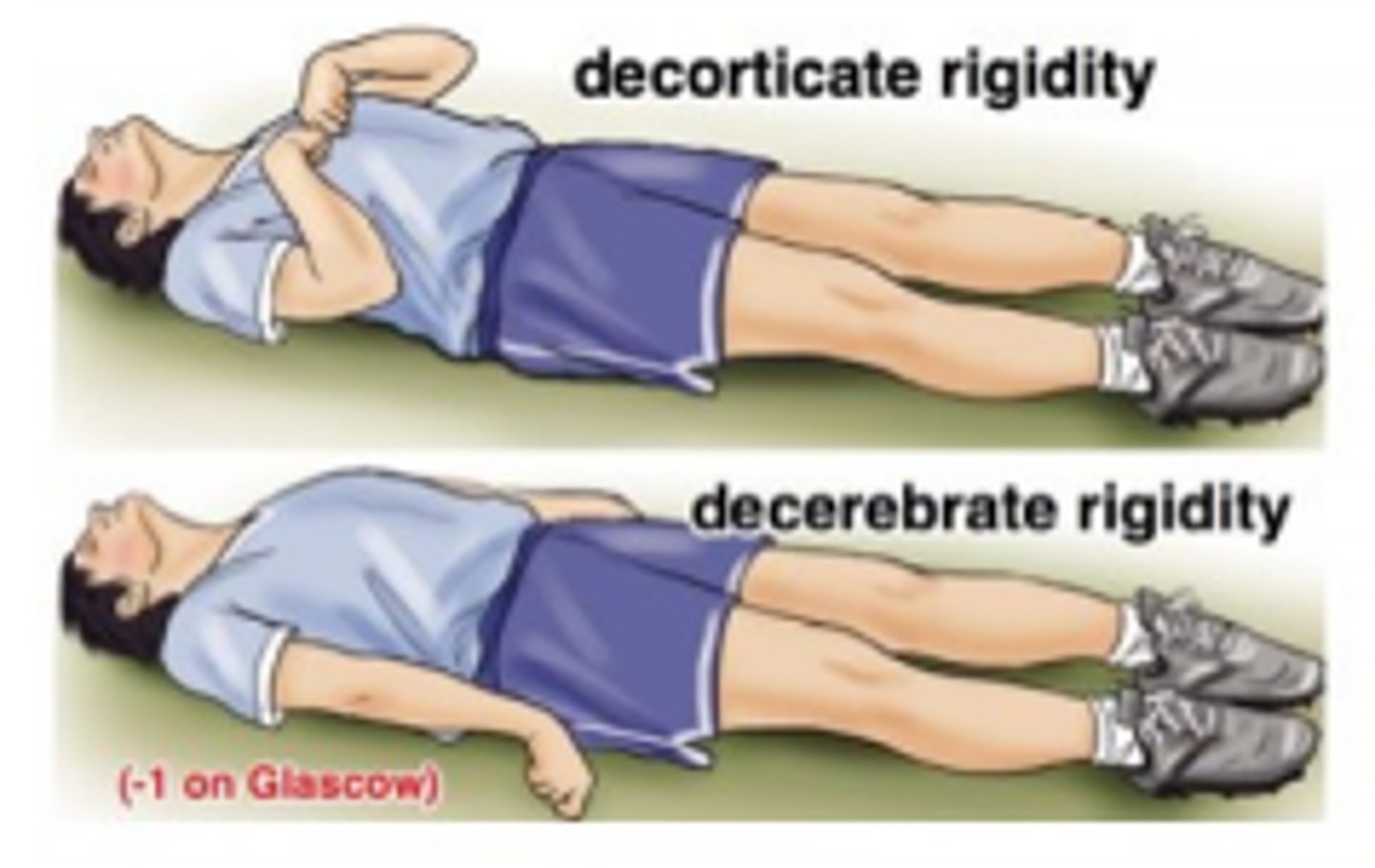
what reflexes are done for suspected brain/spinal cord damage?
abdominal
cremasteric
anal wink
babinski
clonus
Broca's or Wernicke's aphasia: patient can form words easily but there are errors in the content?
Wernicke's → Nickie's nonsense
Broca's = unable to produce words → BRO CAn't talk :P