AP Biology: Unit 3 - Cellular energetics
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Focuses on Photosynthesis, Cellular Respiration, Fermentation, and Enzymes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
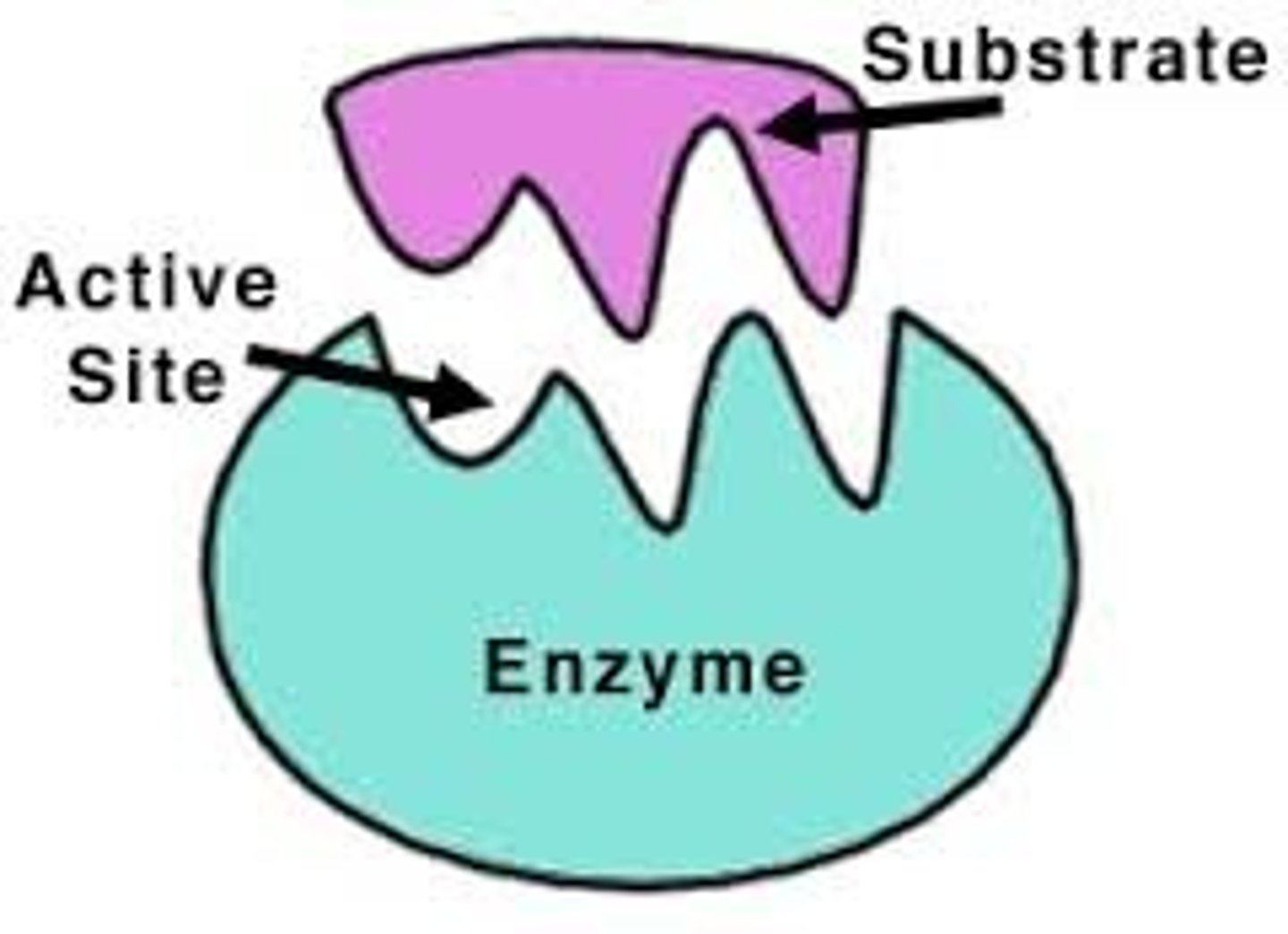
Enzyme
A type of protein that speeds up a chemical reaction (breaking down or putting together molecules) by decreasing the activation energy needed for the reaction to occur
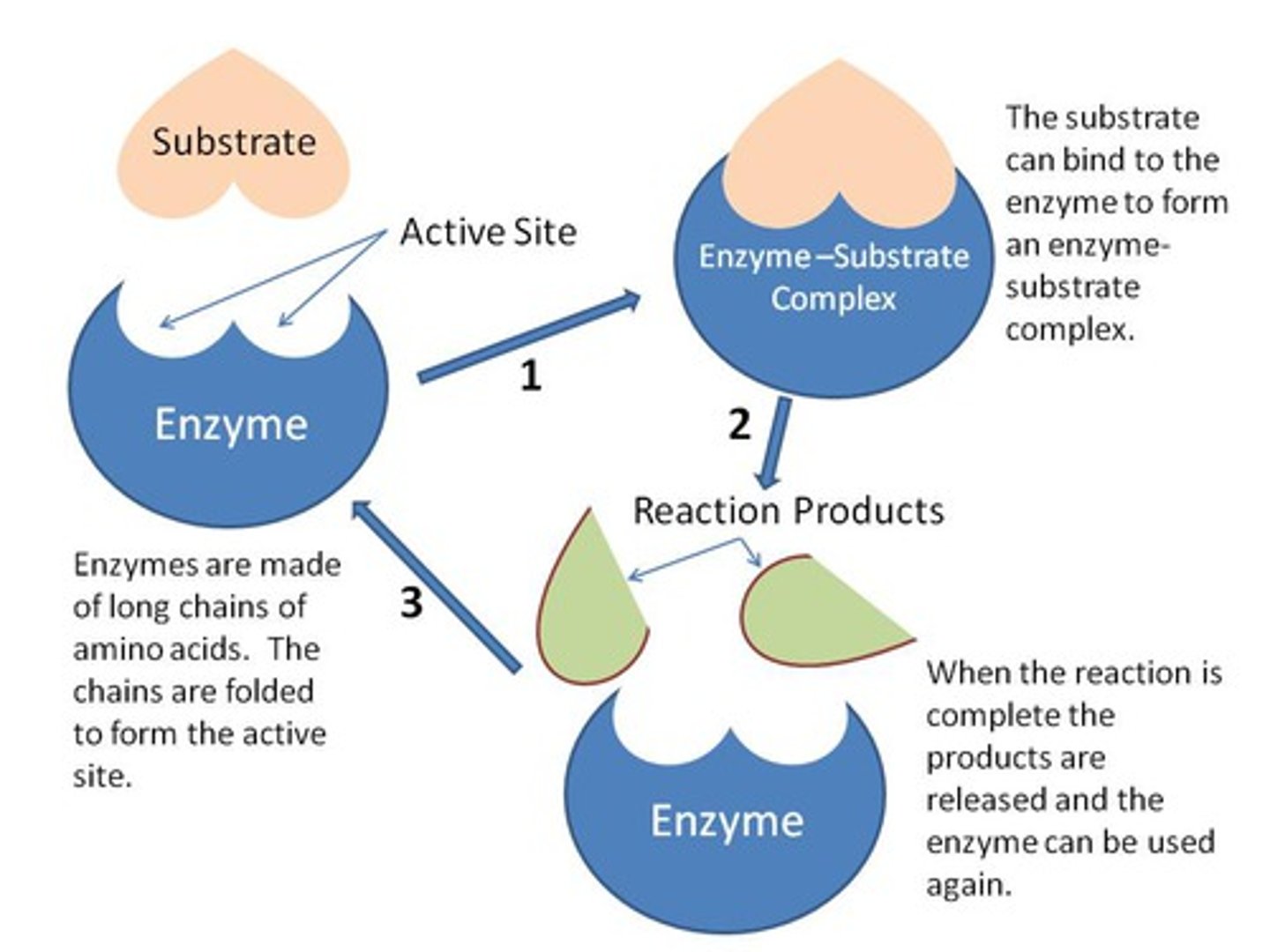
Subtrate
a substance on which and enzyme acts during a chemical reaction.
enzyme-substrate complex
A temporary complex formed when an enzyme binds to its substrate molecule(s).
Products
The elements or compounds produced by a chemical reaction (whether or not a enzyme is used)
Active site of an enzyme
the region of an enzyme that attaches to a substrate
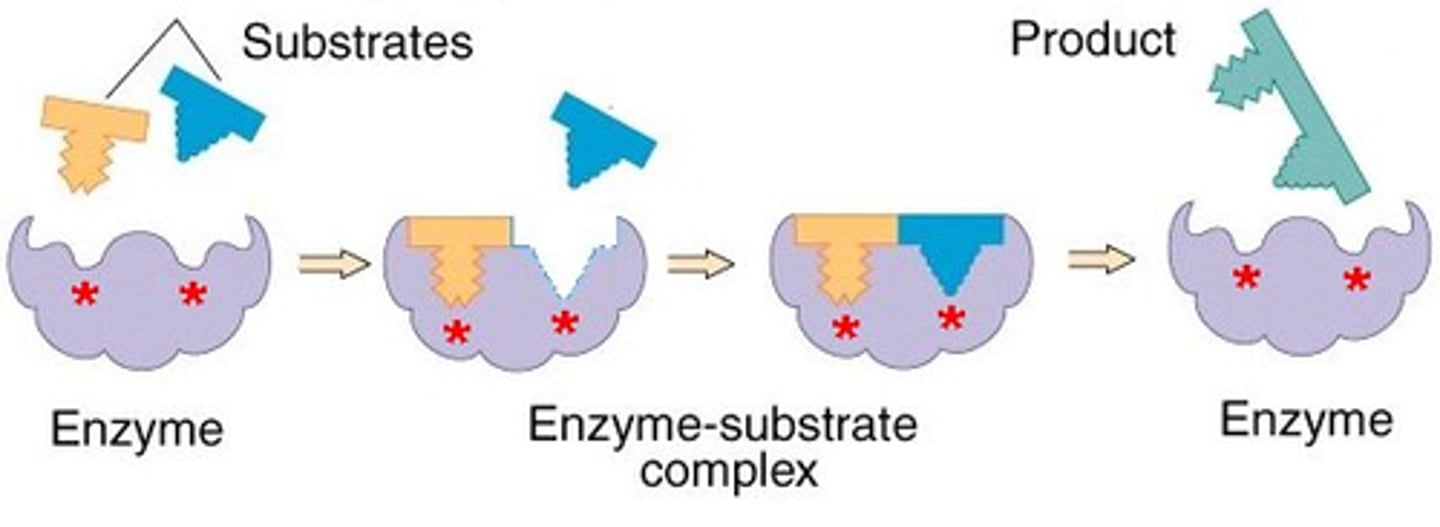
induced fit model of enzymes
theory that enzyme changes slightly to accommodate an incoming substrate in order to break it into smaller components
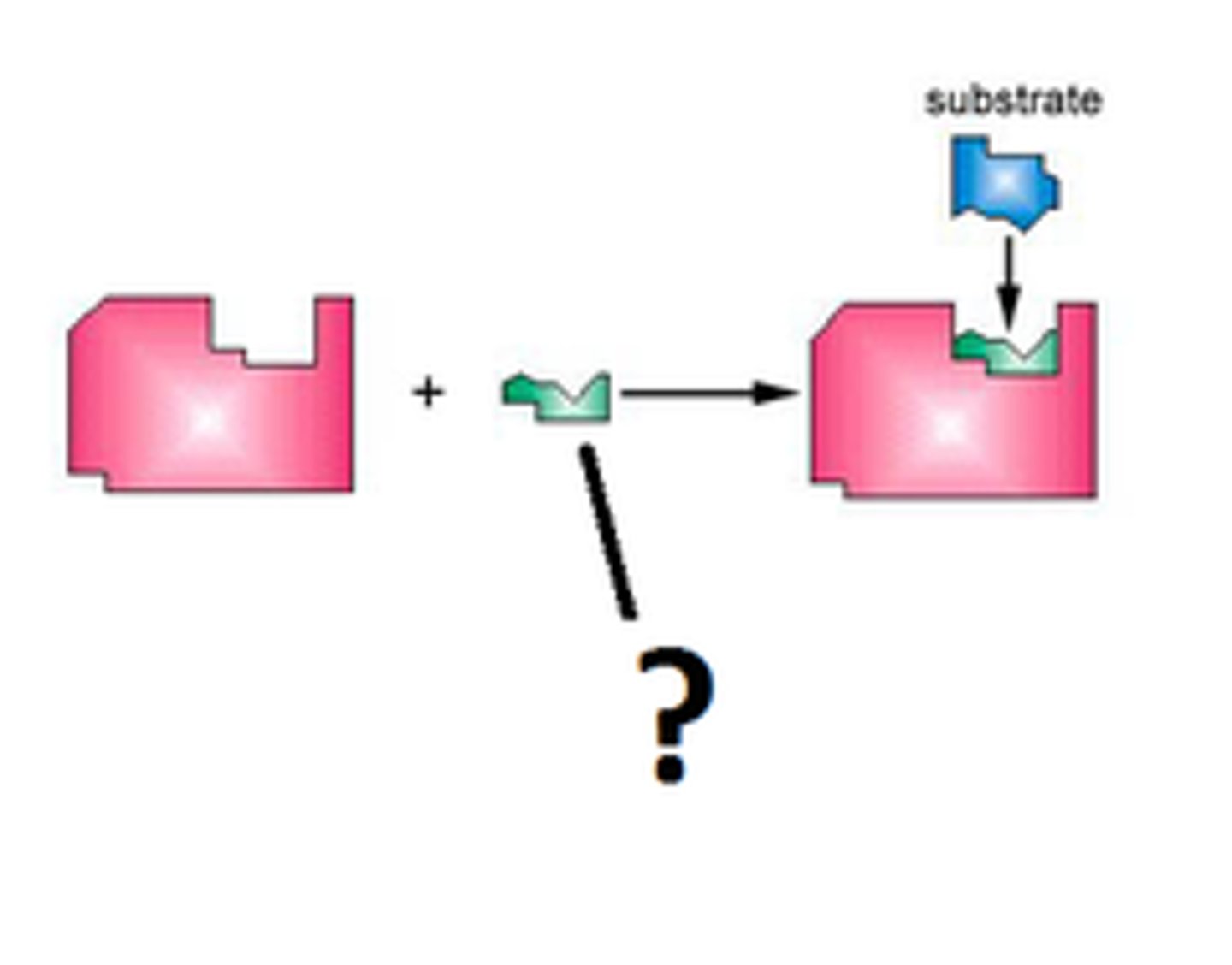
coenzyme
a organic molecule that is needed for a reaction to occur with an enzyme
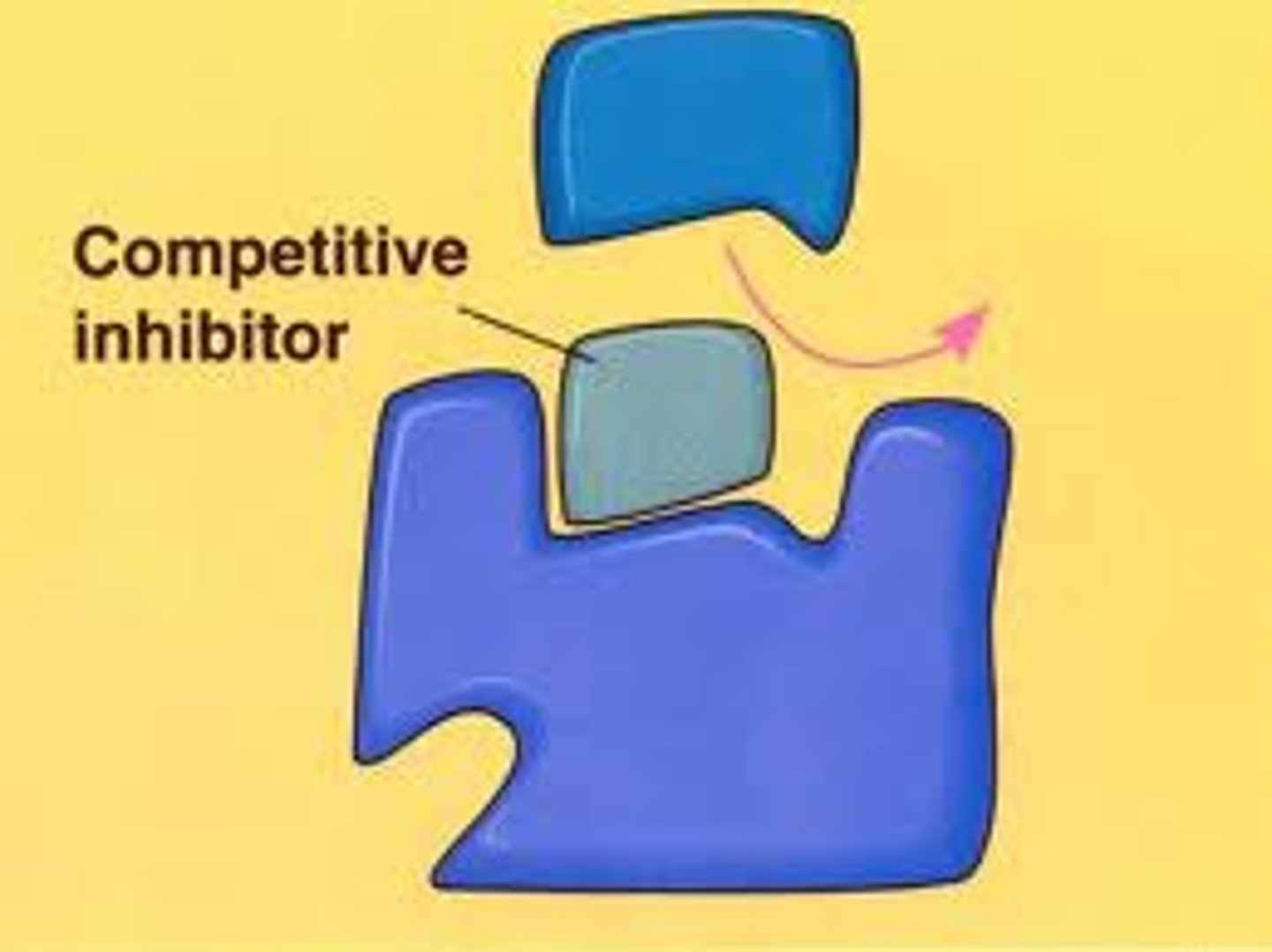
competitive inhibitor
A substance that reduces the activity of an enzyme by entering the active site in place of the substrate whose structure it mimics.

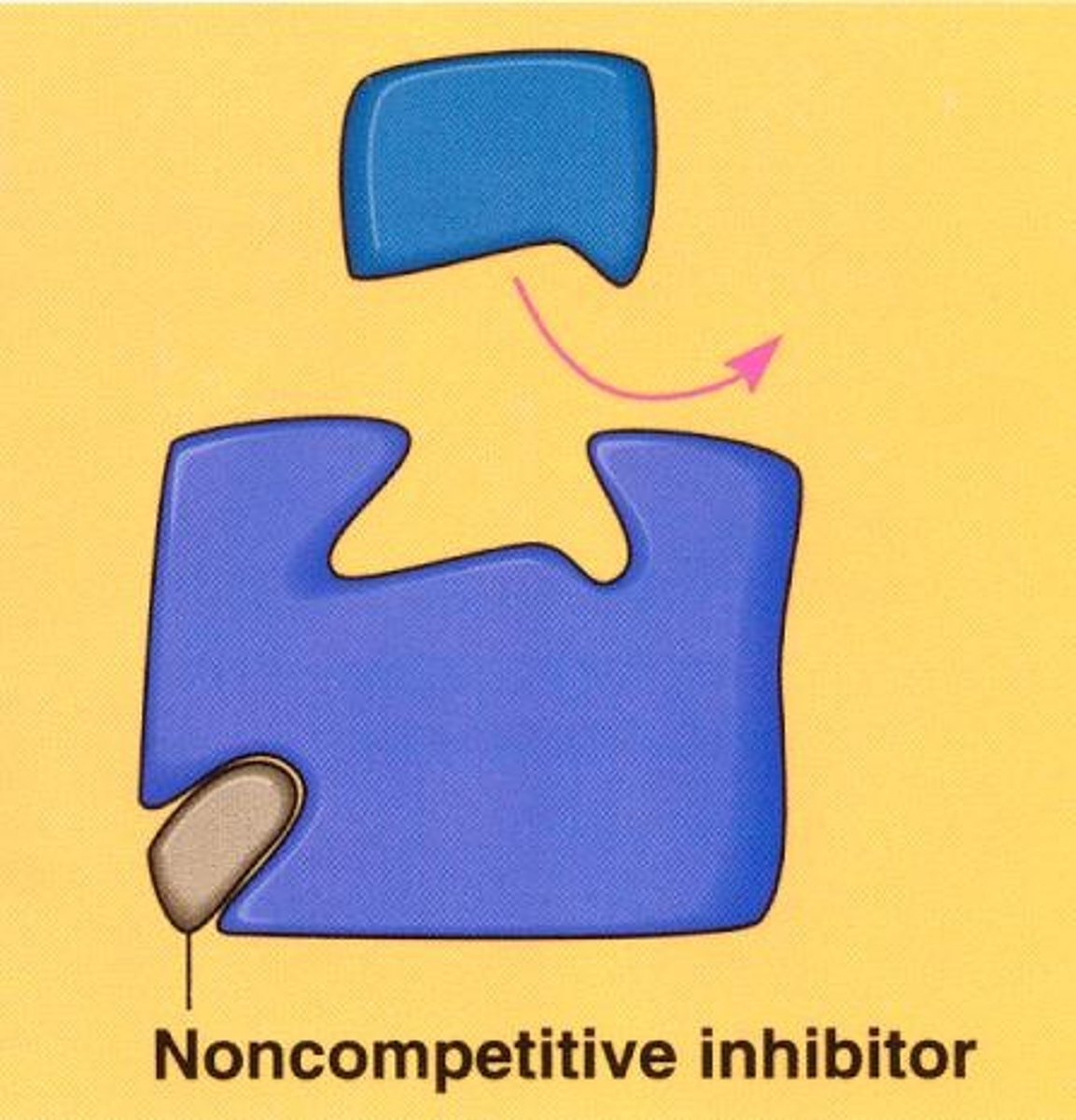
noncompetitive inhibitor
A substance that reduces the activity of an enzyme by binding to a location remote from the active site, changing its conformation so that it no longer binds to the substrate.
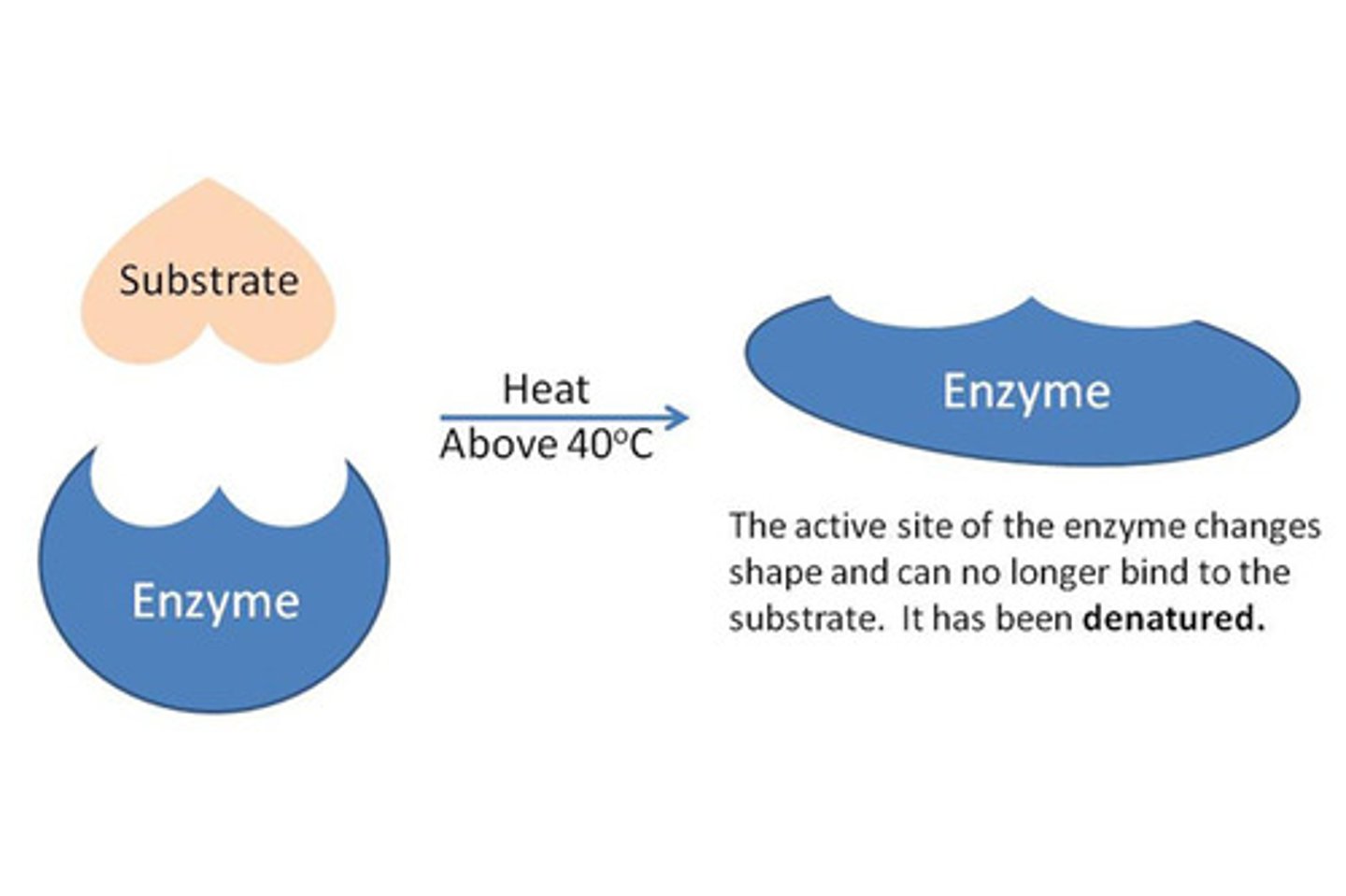
Denaturation
loss of normal shape of a protein due to heat, pH, or other factors.
if an enzyme denatures, it is no longer able to catalyze the reaction because the active sit will have changed shape and therefore the substrate will not be able to bind.
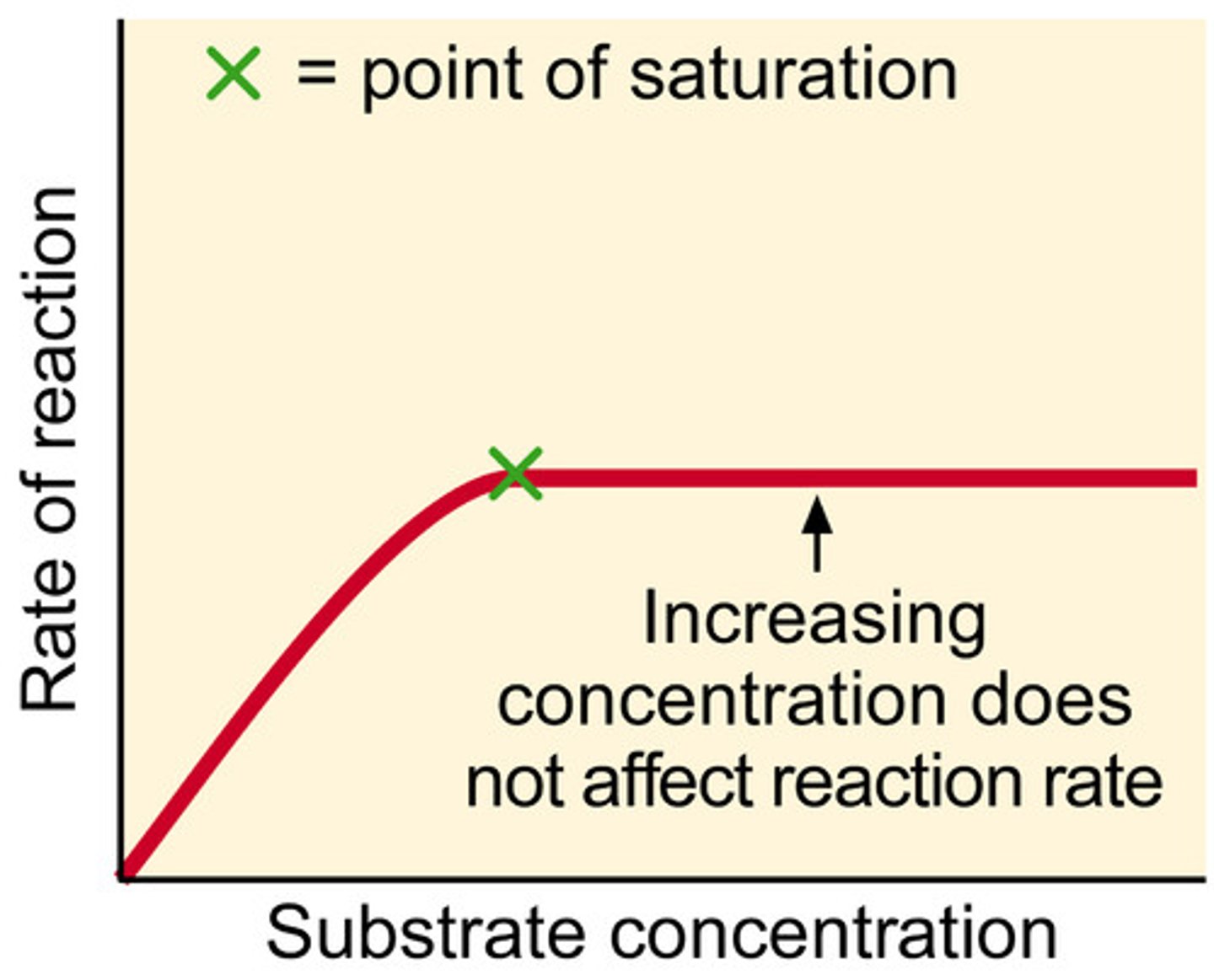
Substrate Concentration on Enzyme Activity
• Increasing the concentration of substrate increases the rate of reaction (True up to a saturation point).
• Collisions are more likely so more Enzyme-Substrate complexes form.
• The concentration will decrease over time therefore the rate of reaction will also decrease.
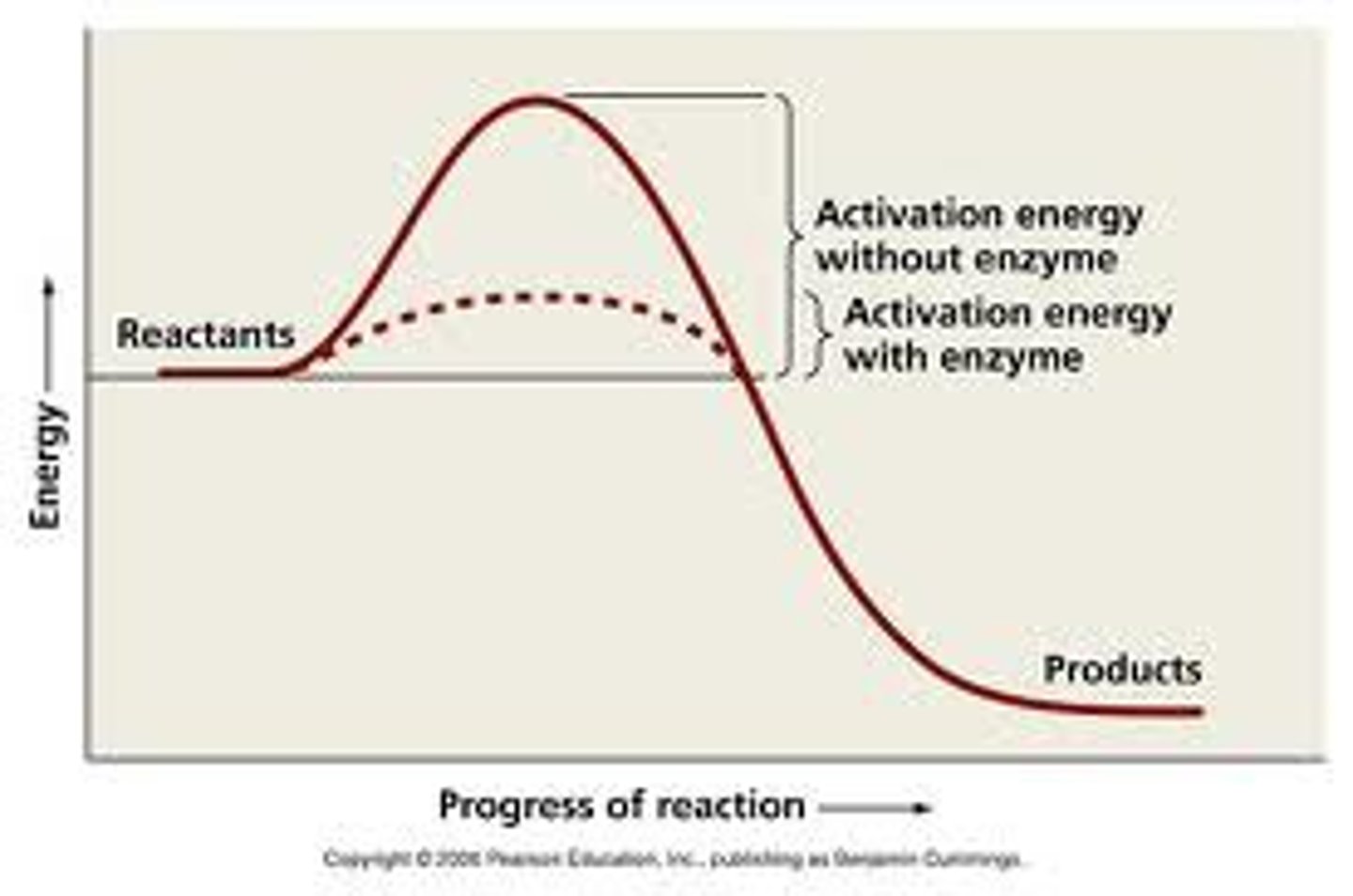
activation energy
energy that is needed to get a reaction started
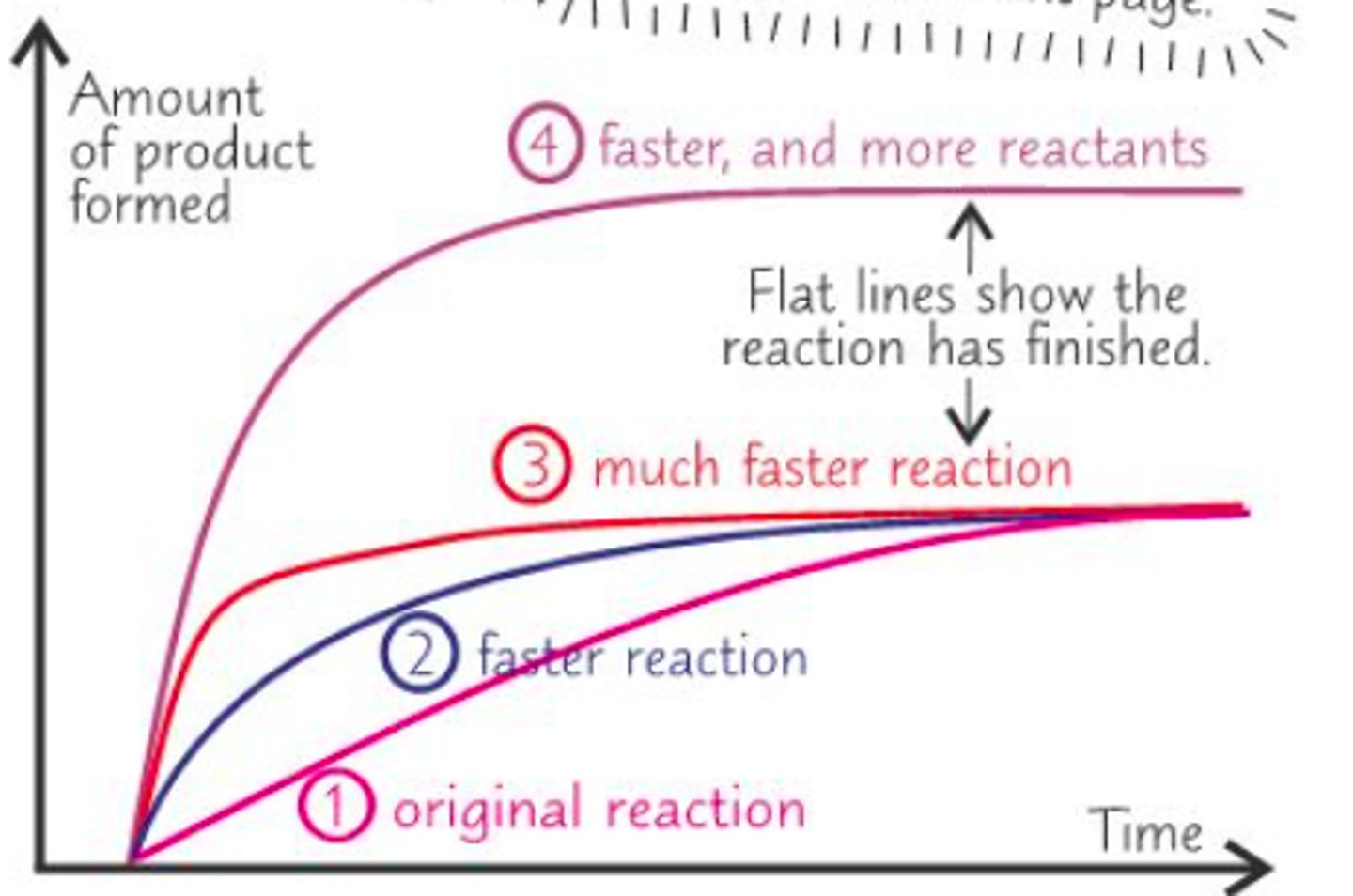
Reaction rate
the rate at which reactants change into products over time
photoautotrophs/phototrophics
organisms that produce their own food using light energy - plants, protists, and algae

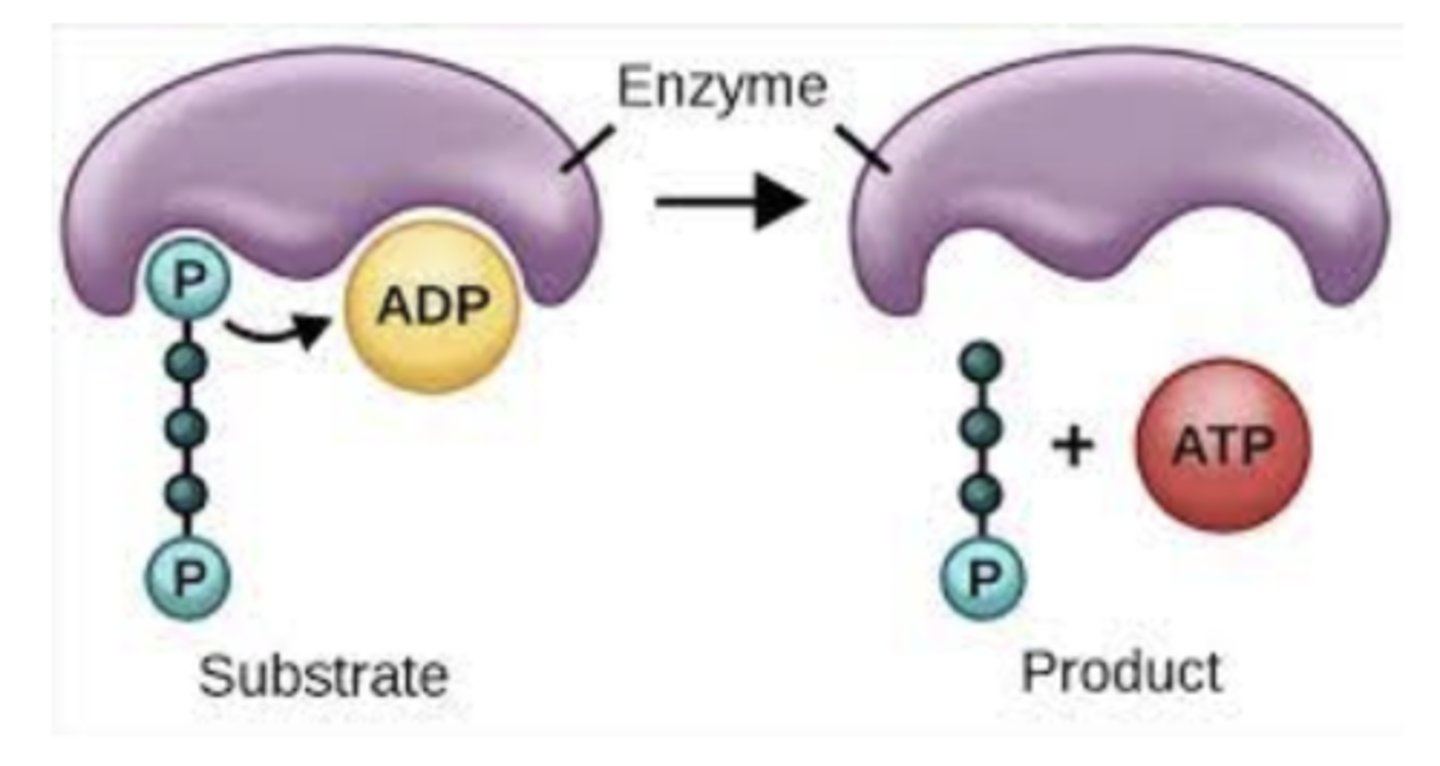
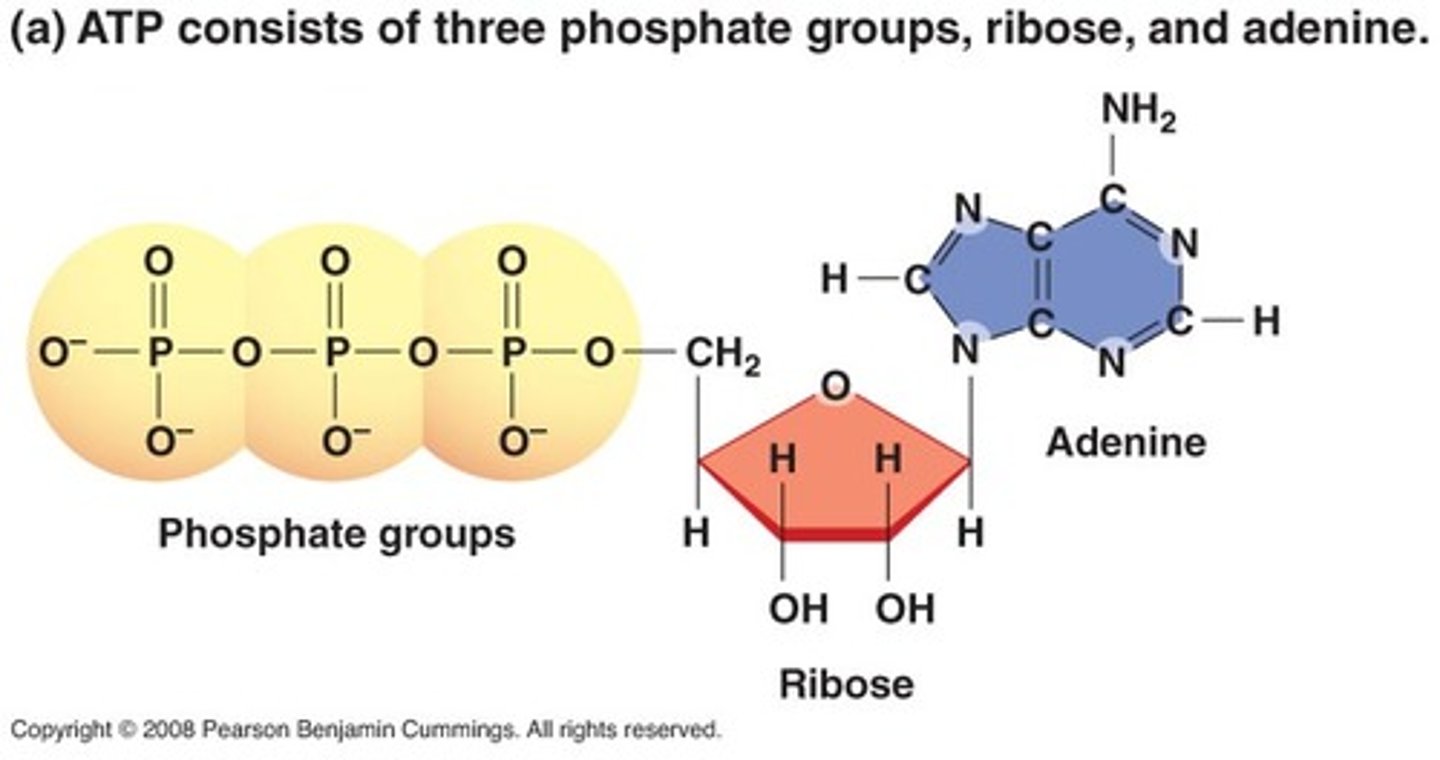
ATP
Adenosine TriPhosphate
- main energy source that cells use for most of their work.
- Product of the light dependent reaction which is then used as a reactant in the Calvin cycle
- In order to release energy, the bond between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate is broken.
- ADP and a Phosphate ion (P) are combined to form ATP.
- MAJOR product of cellular respiration
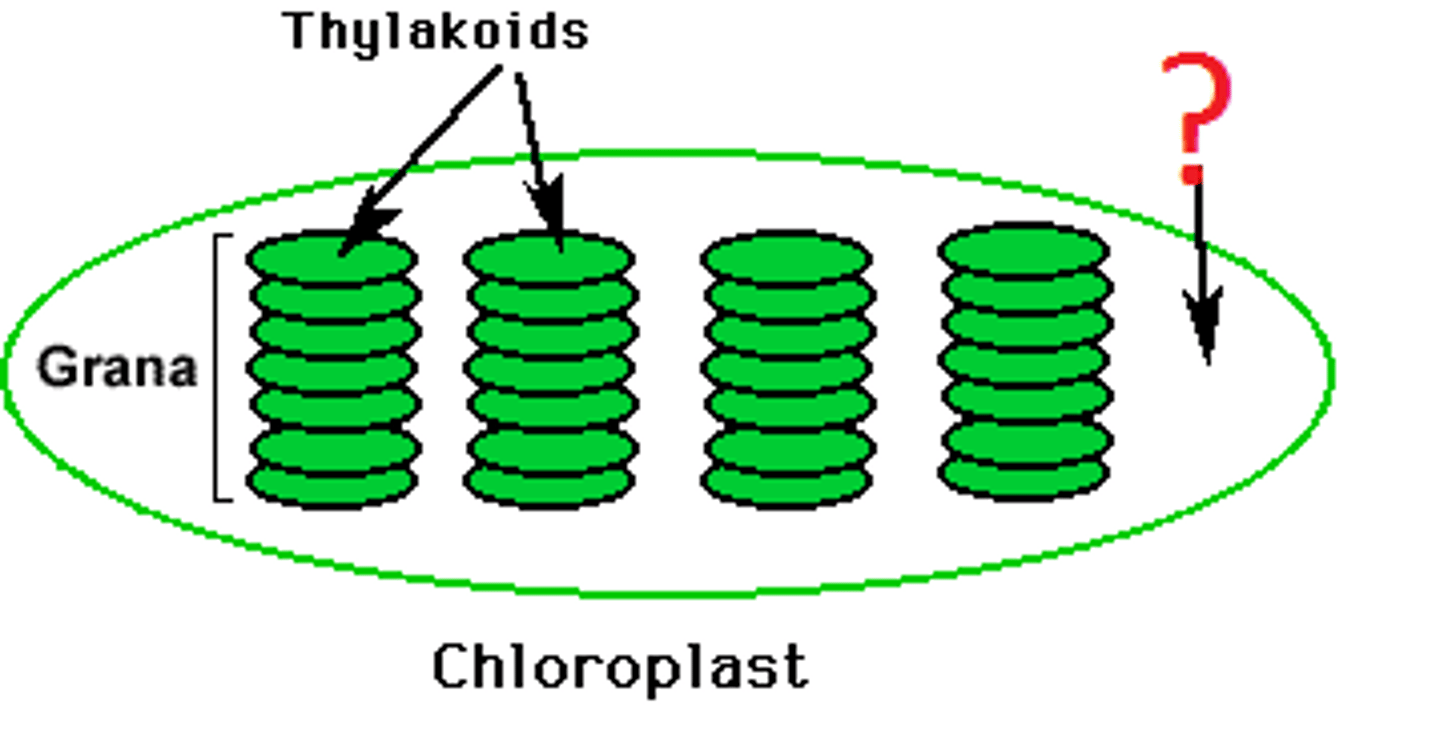
stroma
fluid that fills the inner area of a chloroplast
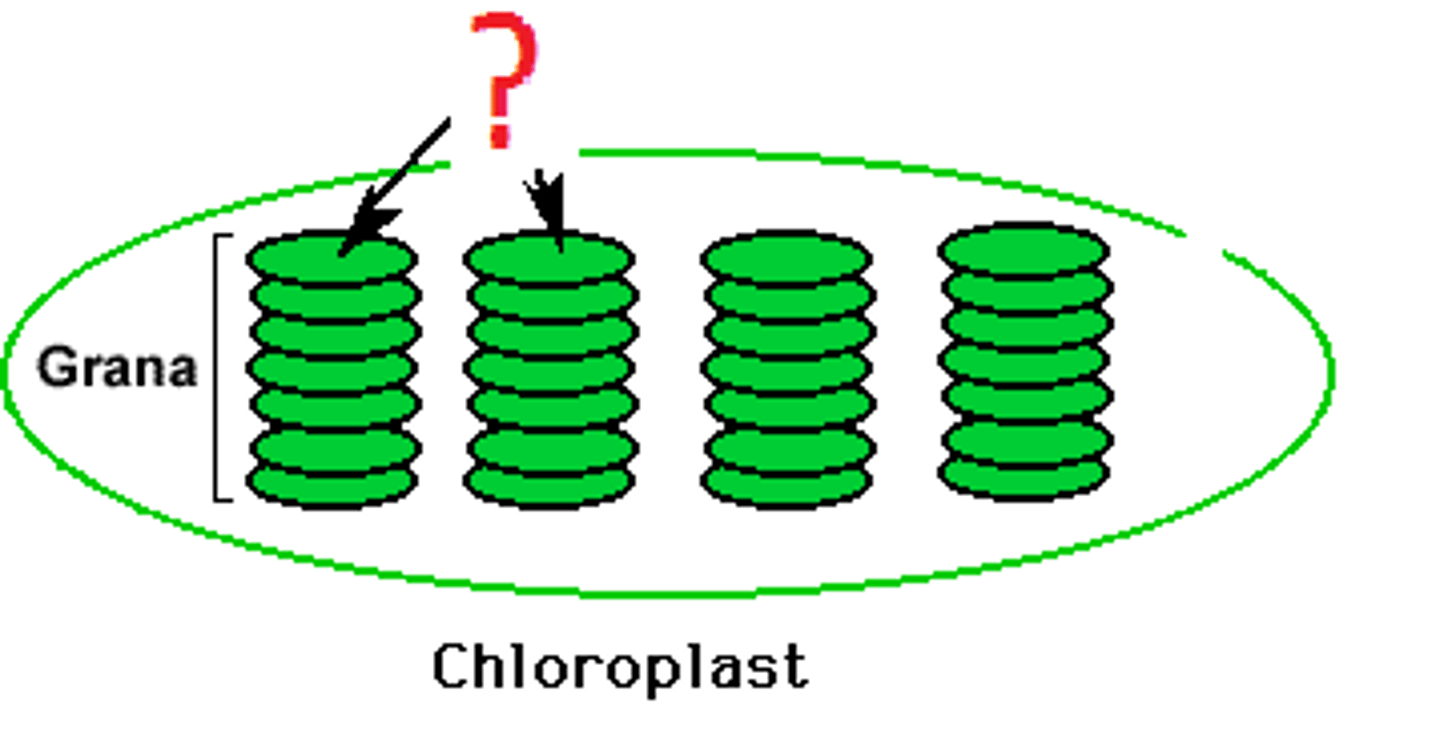
thylakoids
found in stacks in the chloroplast where the light reactions occur
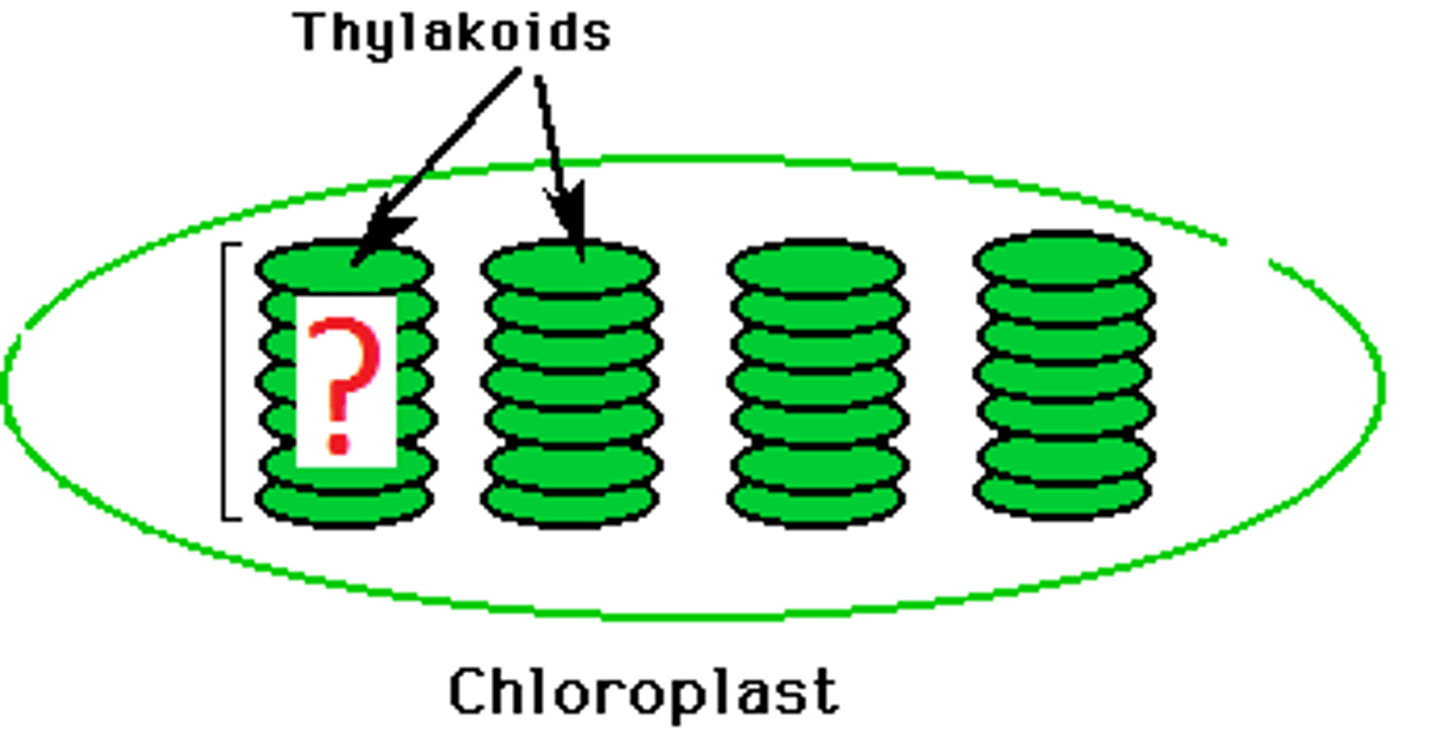
granum
stacks of thylakoids.
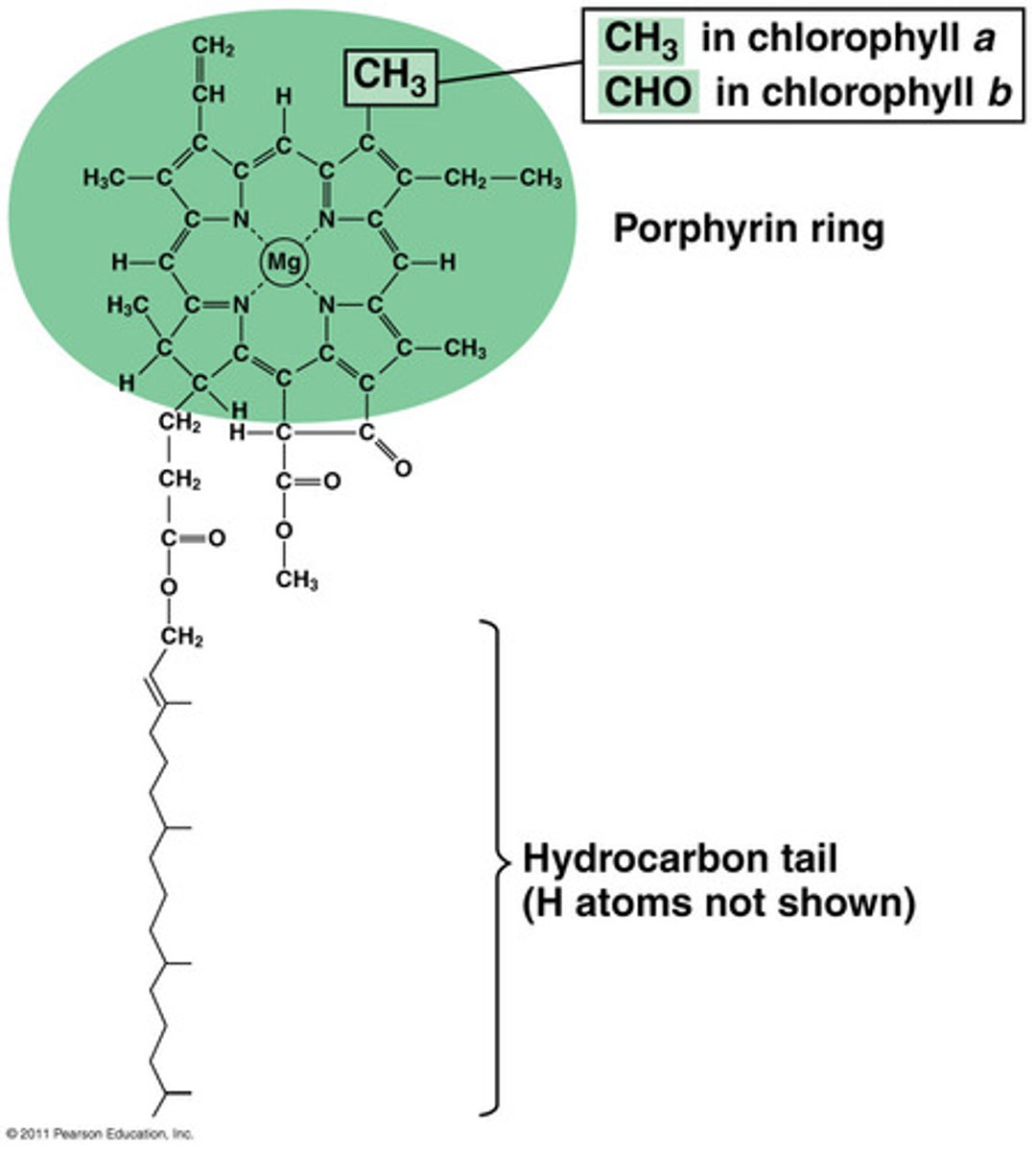
chlorophyll
pigment that absorbs light energy to power the light reactions of photosynthesis
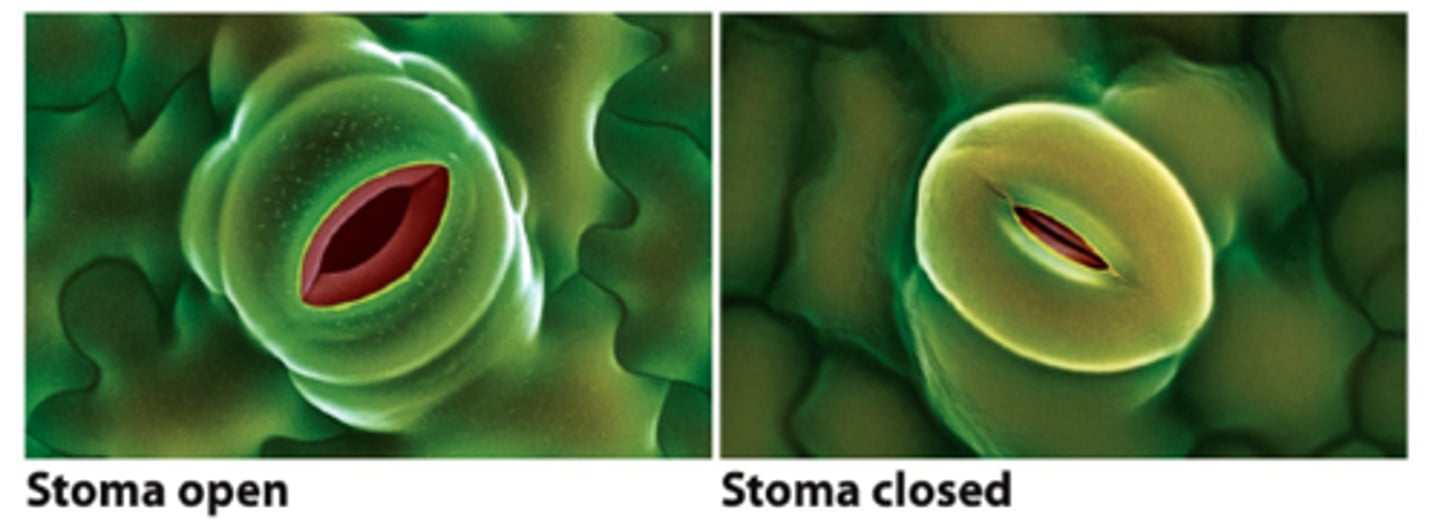
stomata
pores in the epidermis of a leaf that allow water to leave the plant and carbon dioxide to enter it
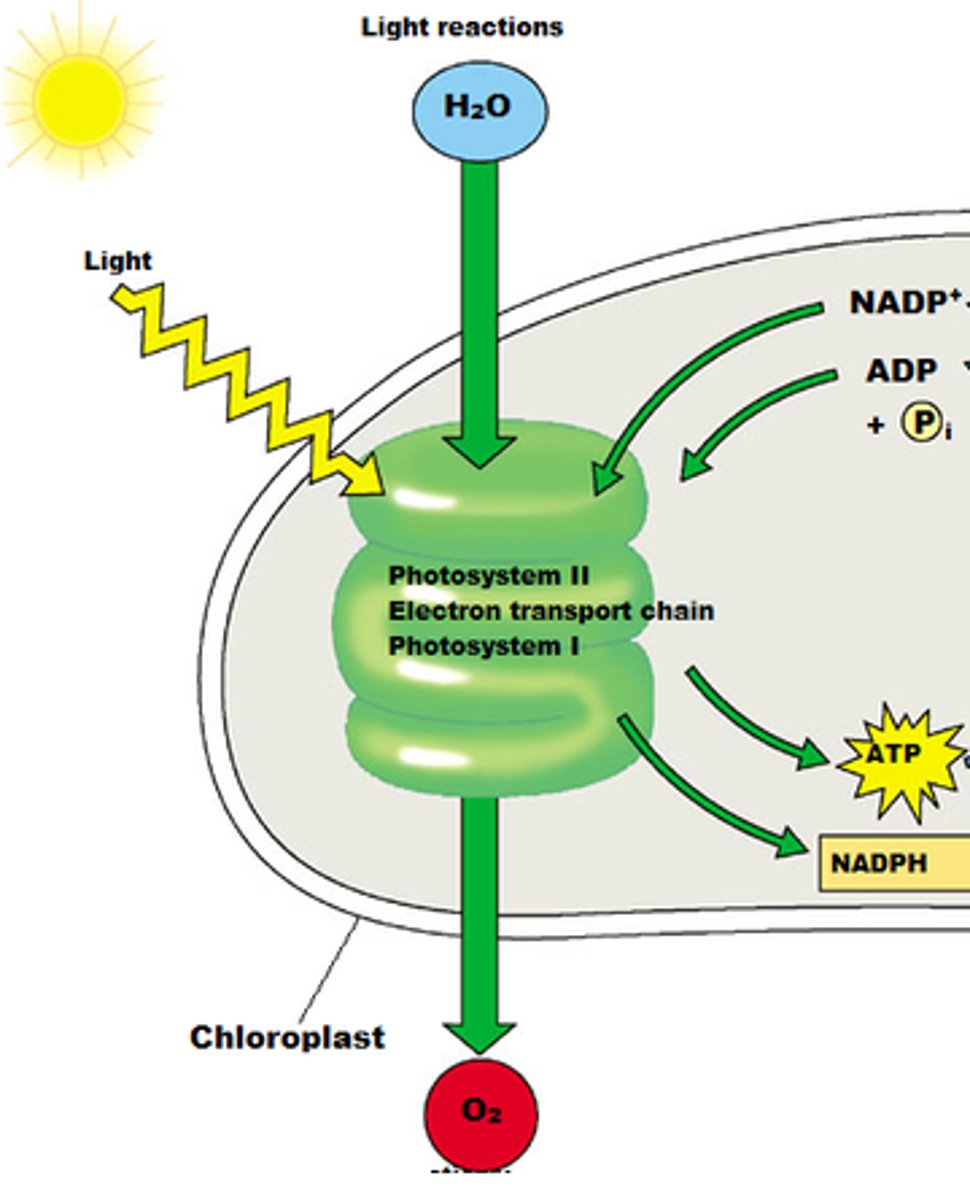
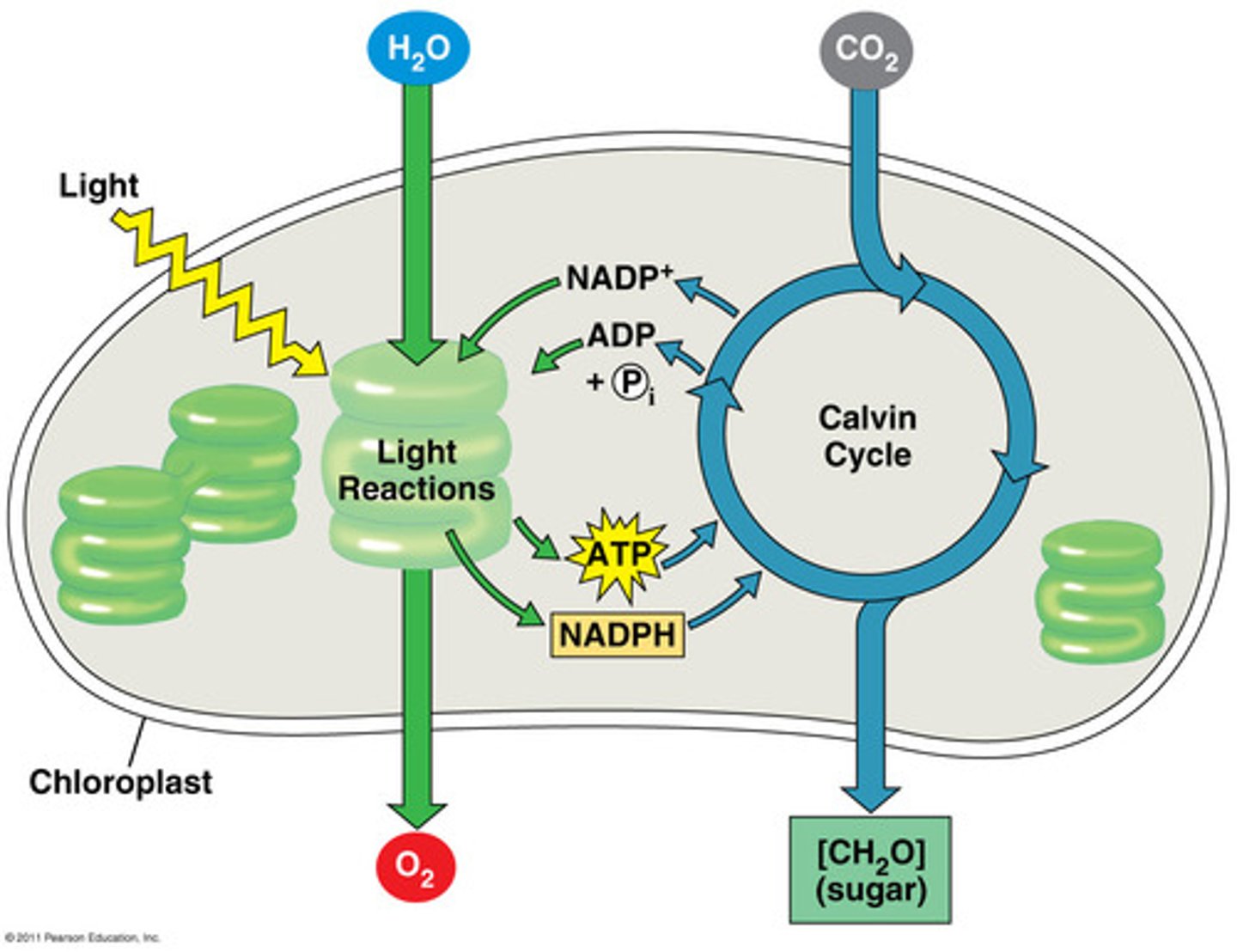
light-dependent reactions
reactions that use water to create ATP and NADPH which are then used in the calvin cycle.
oxygen is also released as a product
occurs in the thylakoid's membrane
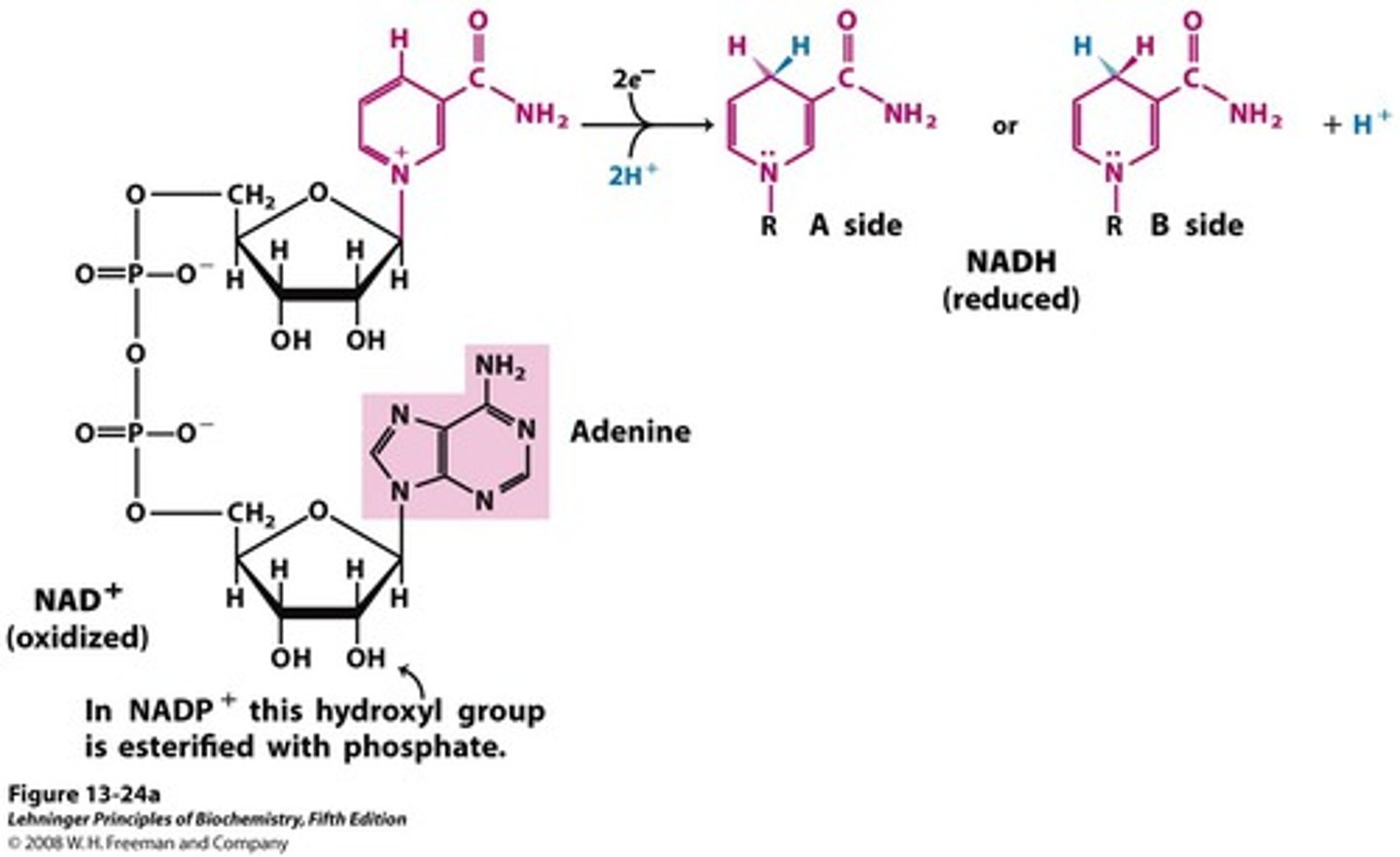
NADP+
an electron acceptor that is reduced and converted to NADPH to be used to in the calvin cycle
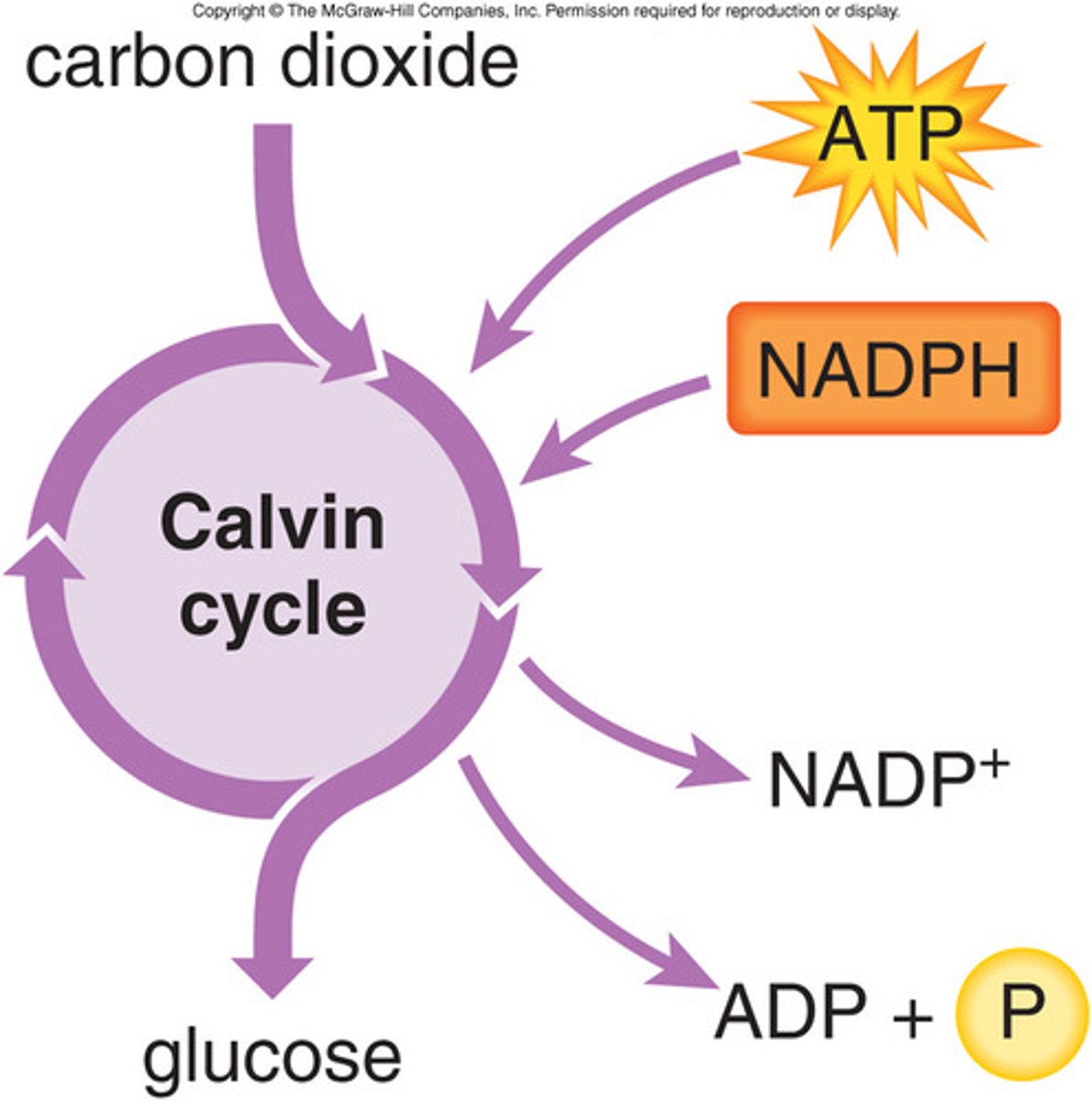
calvin cycle
reactions of photosynthesis in which energy from ATP and NADPH is used to build high-energy compounds such as sugars
carbon fixation
reactions that use CO2 to make glucose (carbon in a solid form)
chloroplast
the organelle where photosynthesis takes place
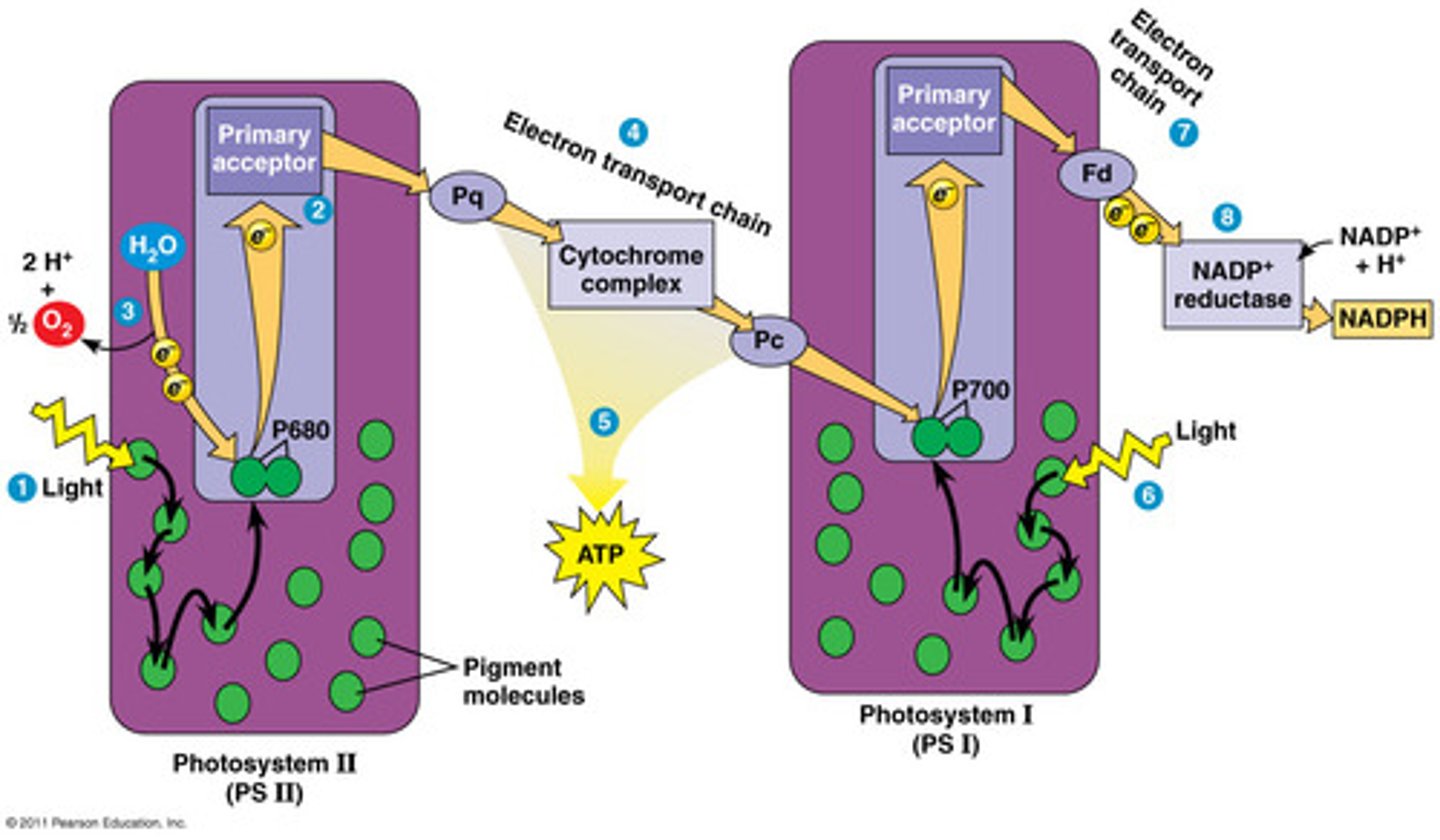
Photosystem II (PSII or P680)
When light is absorbed by one of the many pigments in photosystem II, energy is passed inward from pigment to pigment until it reaches the reaction center.
There, energy is transferred to P680, boosting an electron to a high energy level.
The high-energy electron is passed to an acceptor molecule and replaced with an electron from water.
This splitting of water releases the oxygen we breathe.
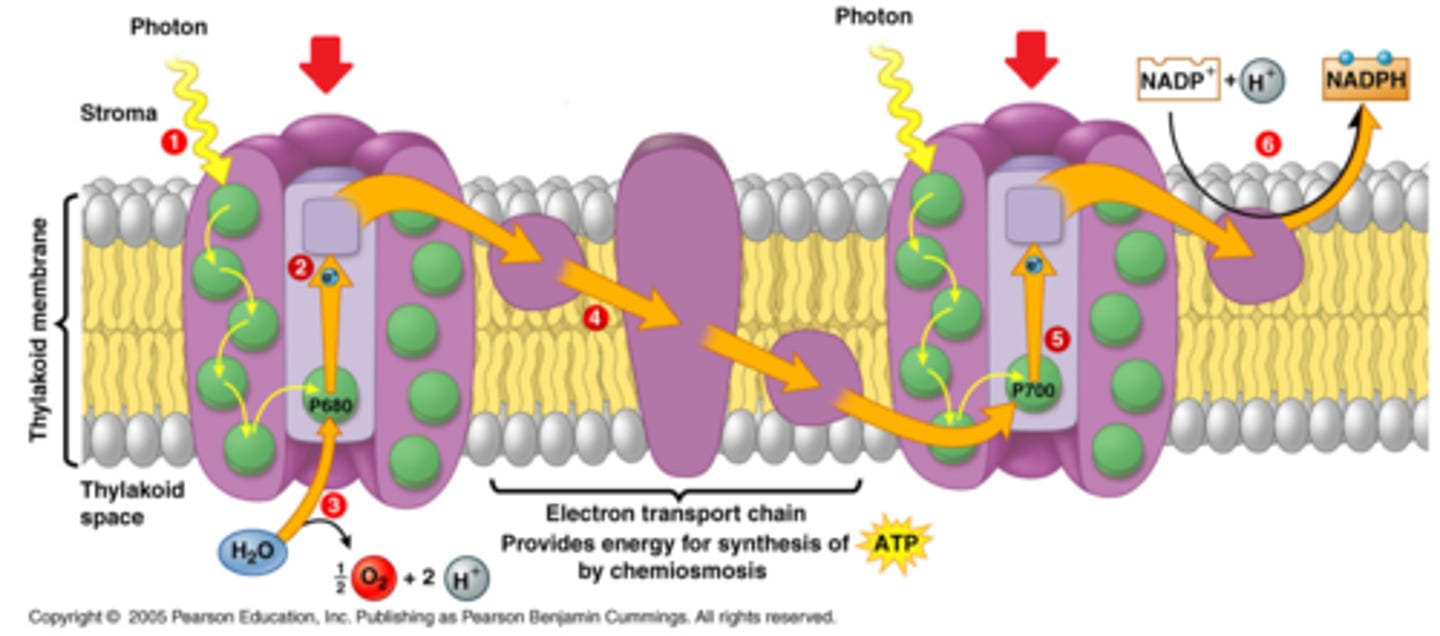
Electron Transport Chain
A sequence of electron carrier molecules (membrane proteins) that shuttle electrons during the redox (reduction) reactions that release energy used to make ATP.
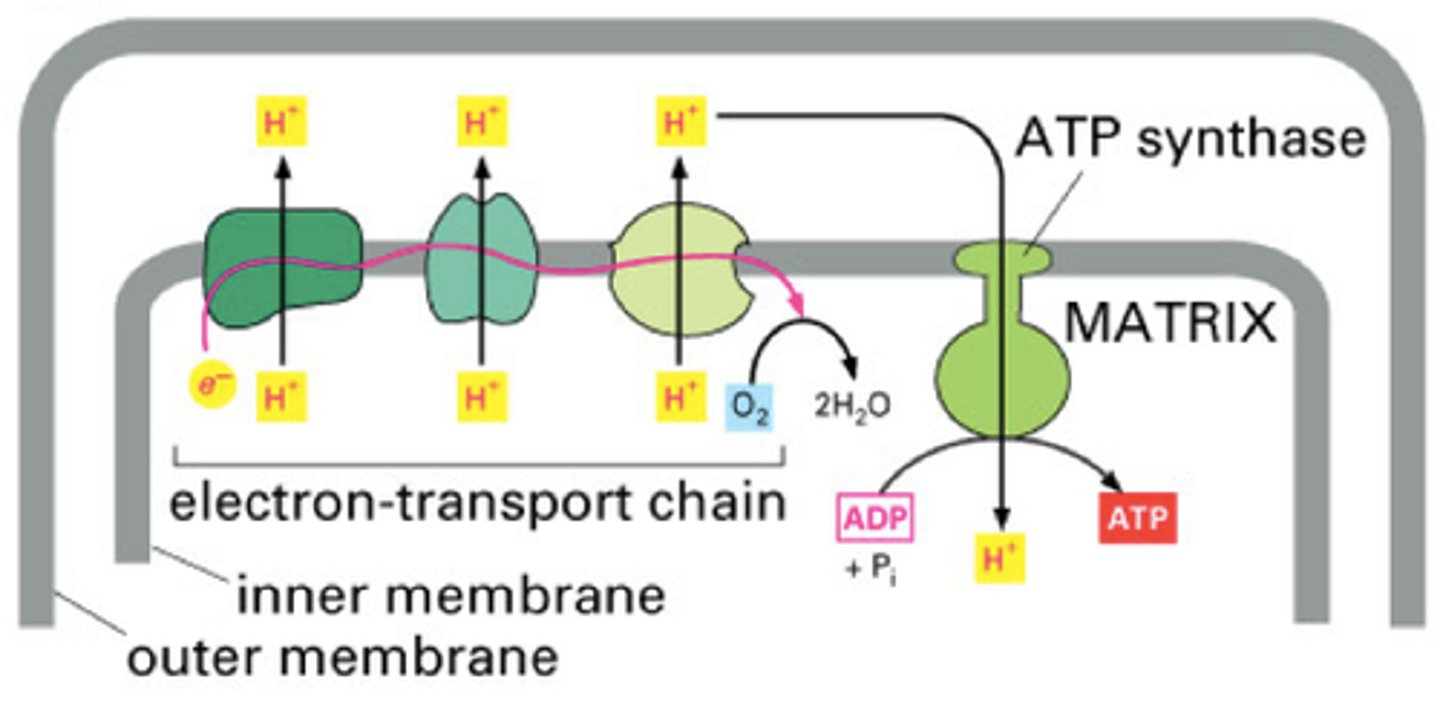
ATP Synthase
Large protein that uses energy from H+ ions to bind ADP and a phosphate group together to produce ATP
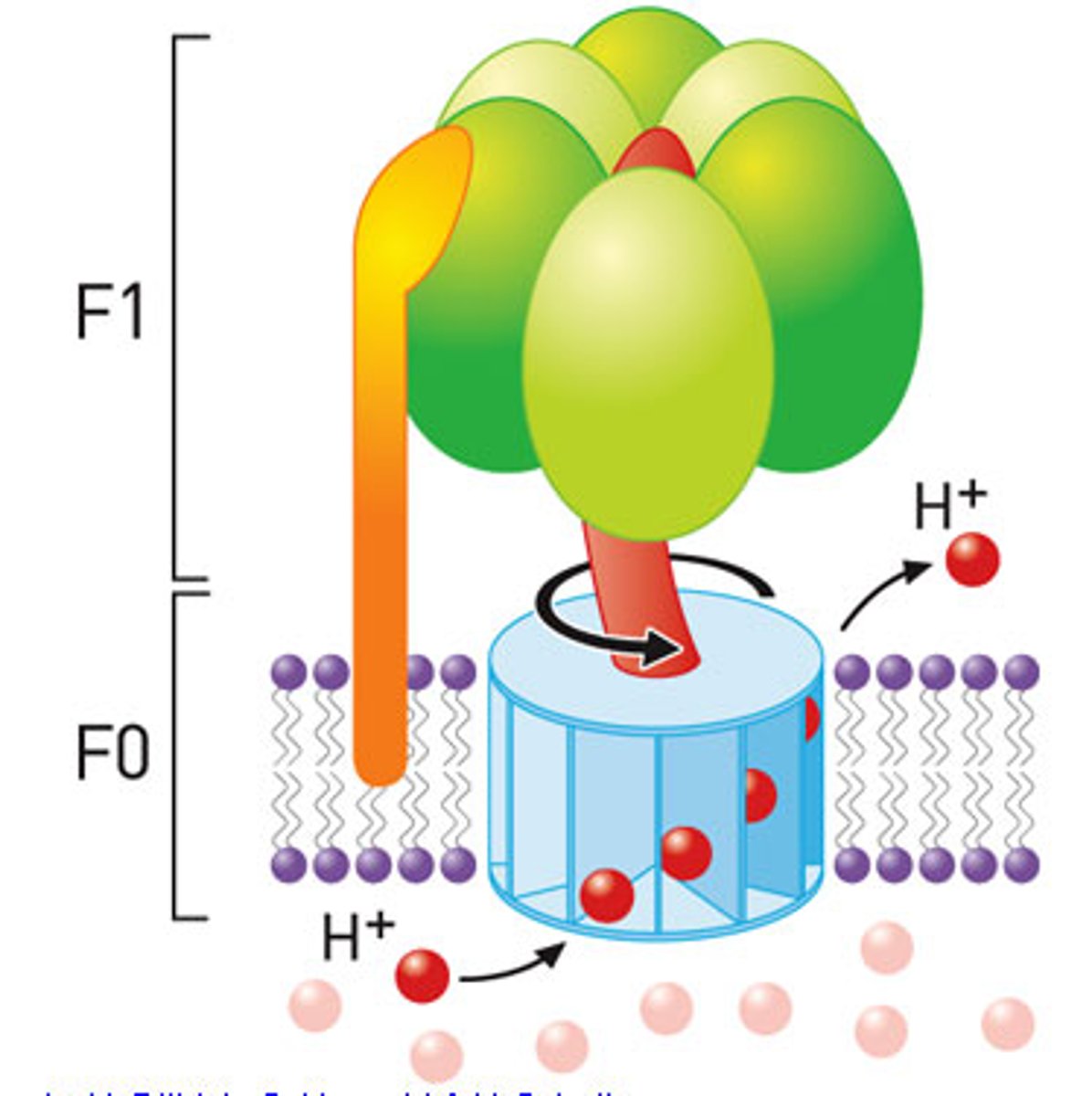
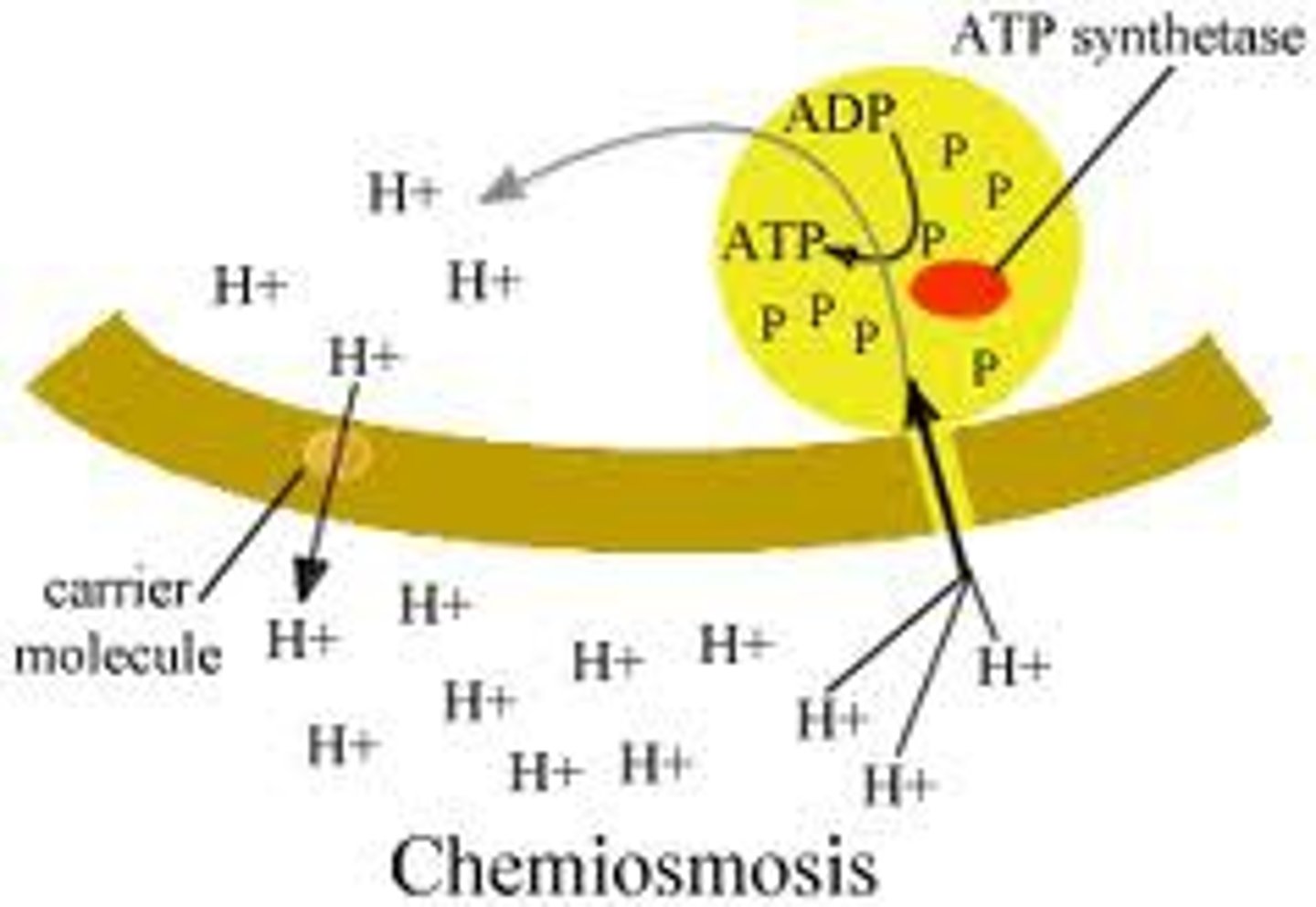
Chemiosmosis
Process by which a Hydrogen pump pumps protons into the thylakoid membrane. H+ passively flows through the ATP synthase which leads to the creation of ATP.
Photosystem I (PSI or p700)
The electron arrives at photosystem I and joins the P700 special pair of chlorophylls in the reaction center.
When light energy is absorbed by pigments and passed inward to the reaction center, the electron in P700 is boosted to a very high energy level and transferred to an acceptor molecule.
The special pair's missing electron is replaced by a new electron from PSII (arriving via the electron transport chain).
electrochemical gradient
The diffusion gradient of an ion, which is affected by both the concentration difference of an ion across a membrane (a chemical force) and the ion's tendency to move relative to the membrane potential (an electrical force).
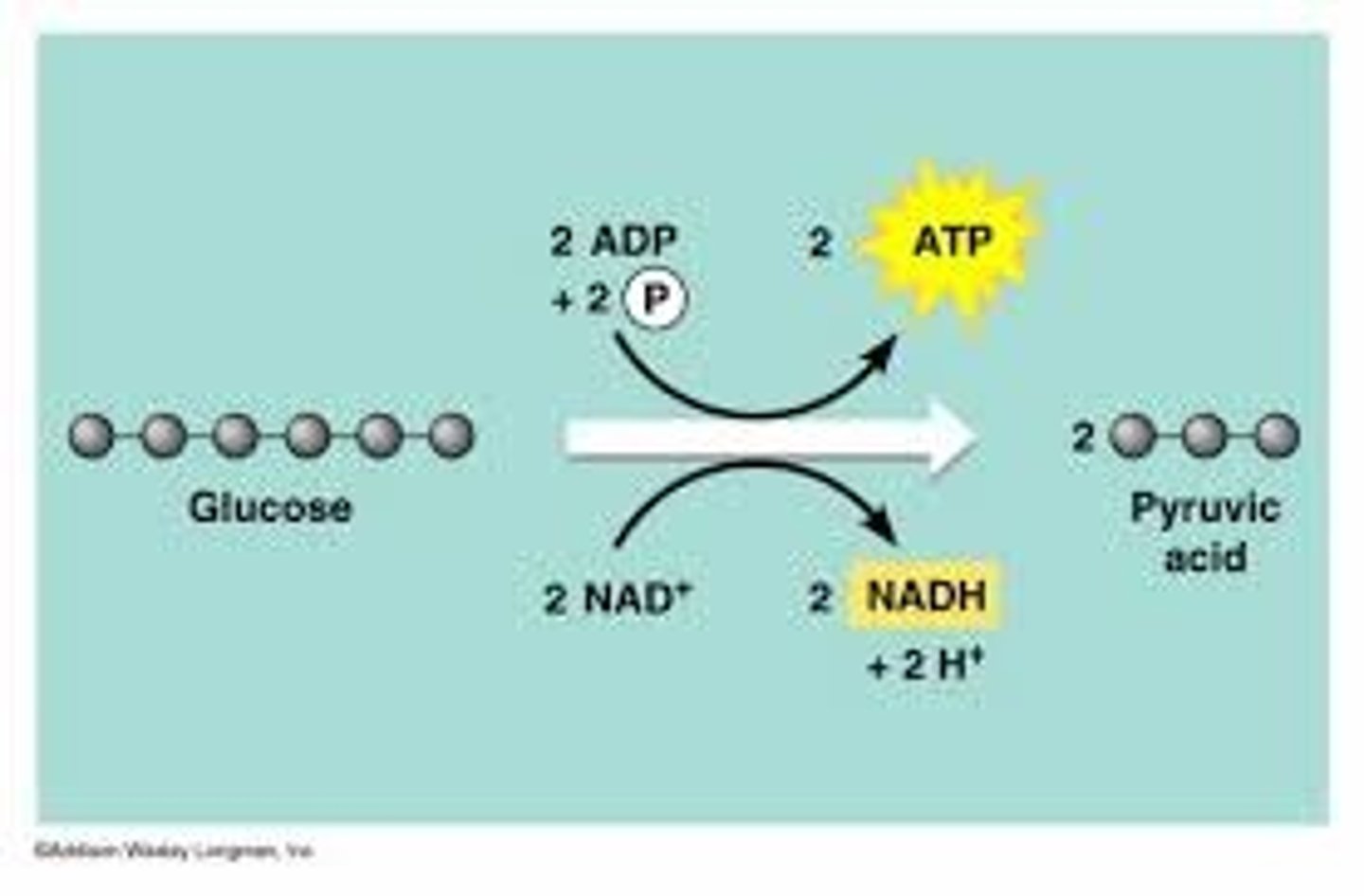
Glycolysis
the breakdown of glucose
Produces pyruvic acid (pyruvate: a carbon molecule), NADH, and ~2 ATP
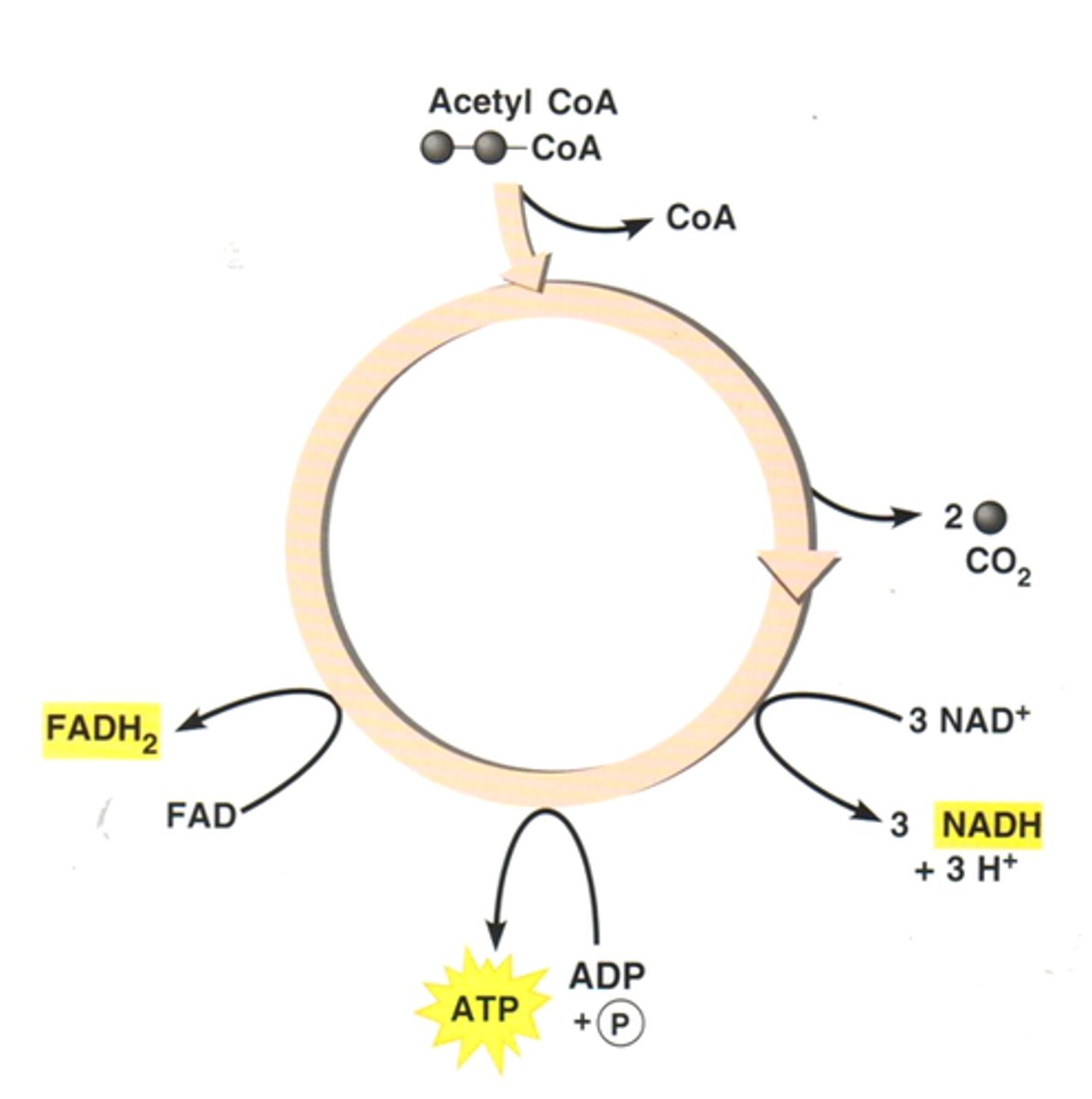
Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
second stage of cellular respiration, in which Acetyl CoA is broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of energy-extracting reactions.
Energy carrying electrons are also transferred from these carbon molecules to NAD+ (becomes NADH) and FAD (becomes FADH2)
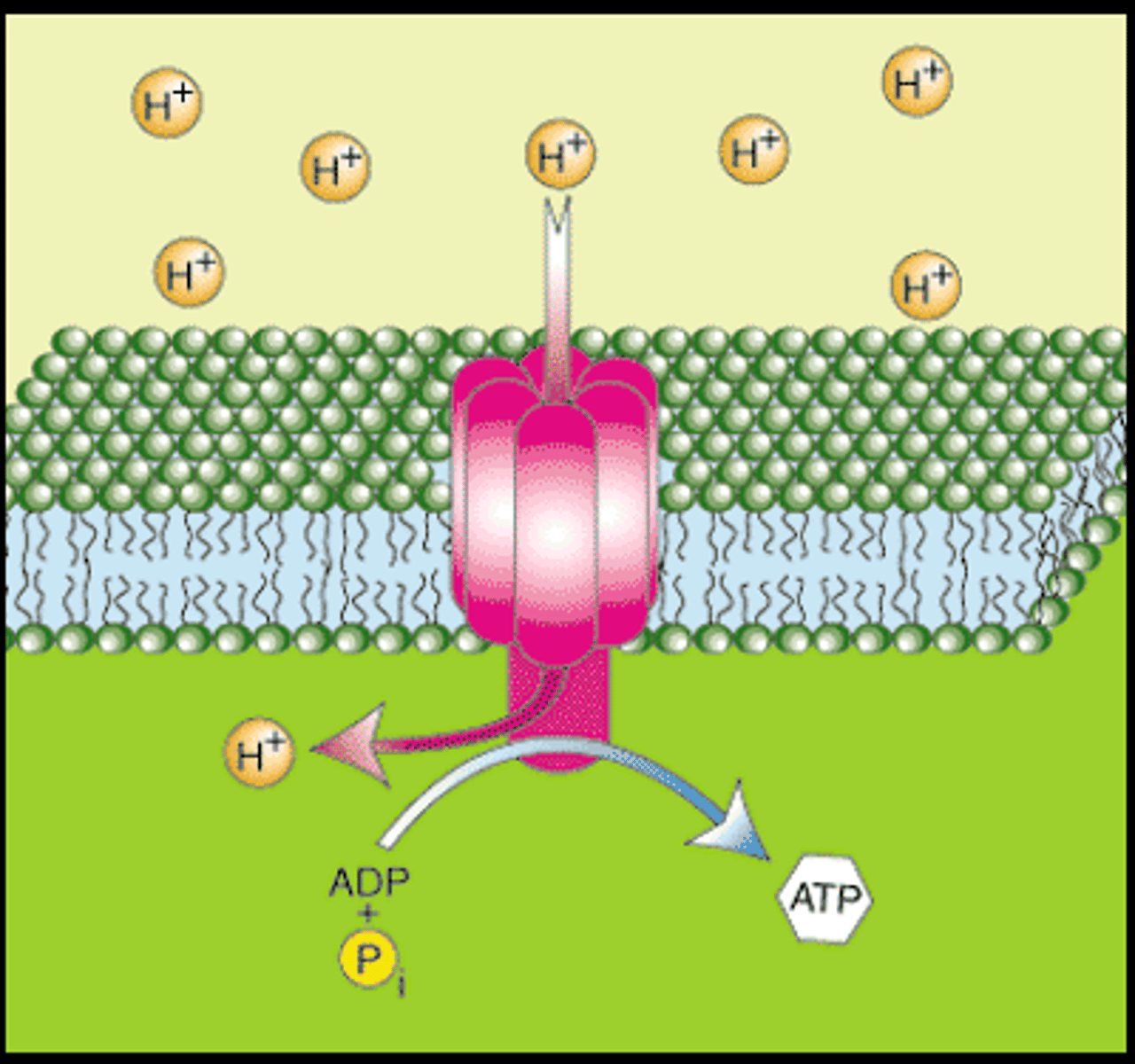
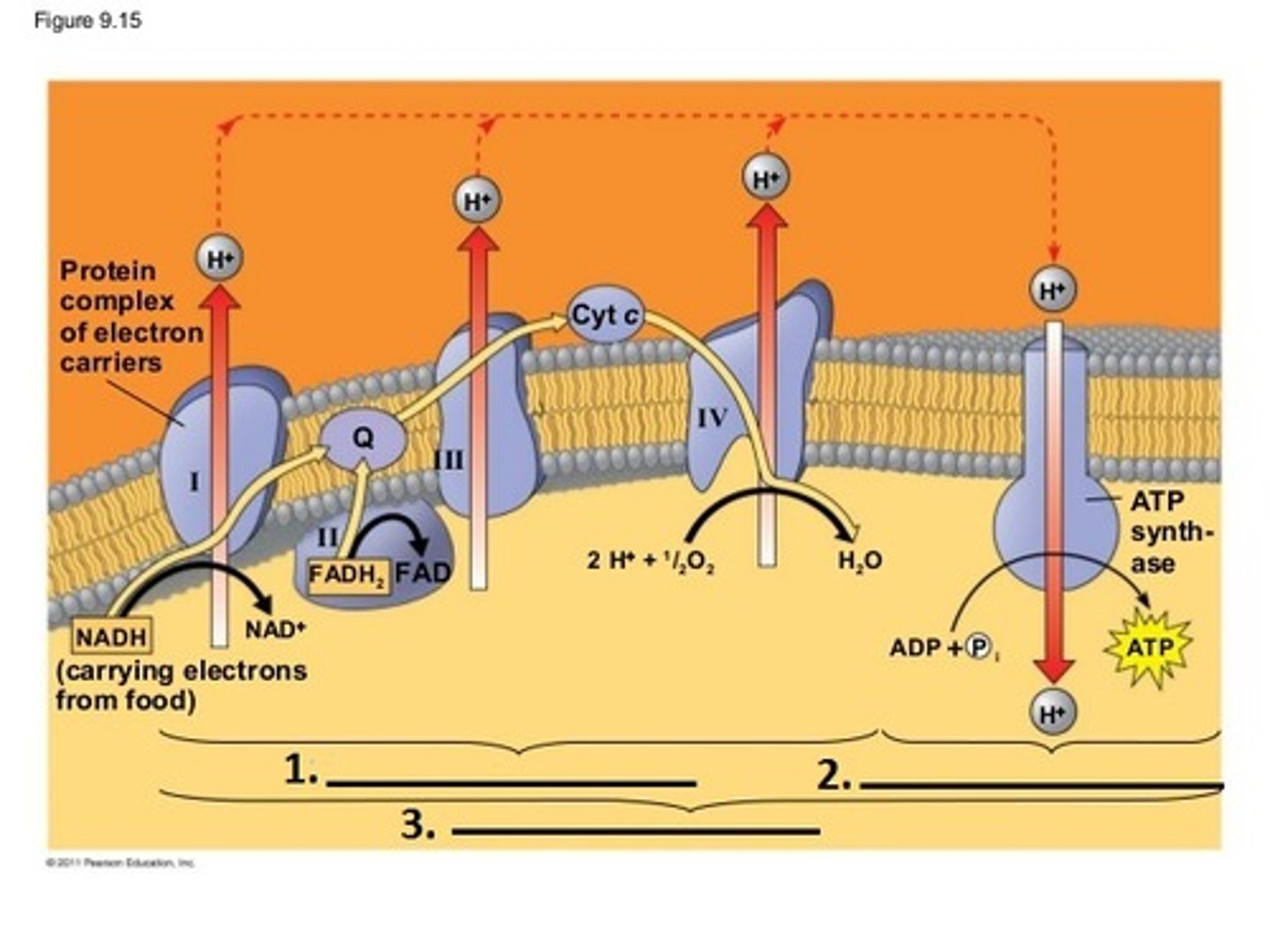
oxidative phosphorylation
The production of ATP using energy derived from the reduction reactions of an electron transport chain; the third major stage of cellular respiration.
Proteins use the energy from the ETC to pump H+ ions creating a proton gradient. These protons (H+ ions) then diffuse from the concentrated area through ATP Synthase to the less concentrated area. This ion movement powers ATP synthase to form ATP using ADP and P.
NADH
the reduced form of NAD+; an electron-carrying molecule that functions in cellular respiration
FADH2
the reduced form of FAD. An electrion carrier.
A molecule that stores energy for harvest by the electron transport chain.
inner mitochondrial matrix
The inside of the inside of the mitochondria.
Location of the Krebs Cycle
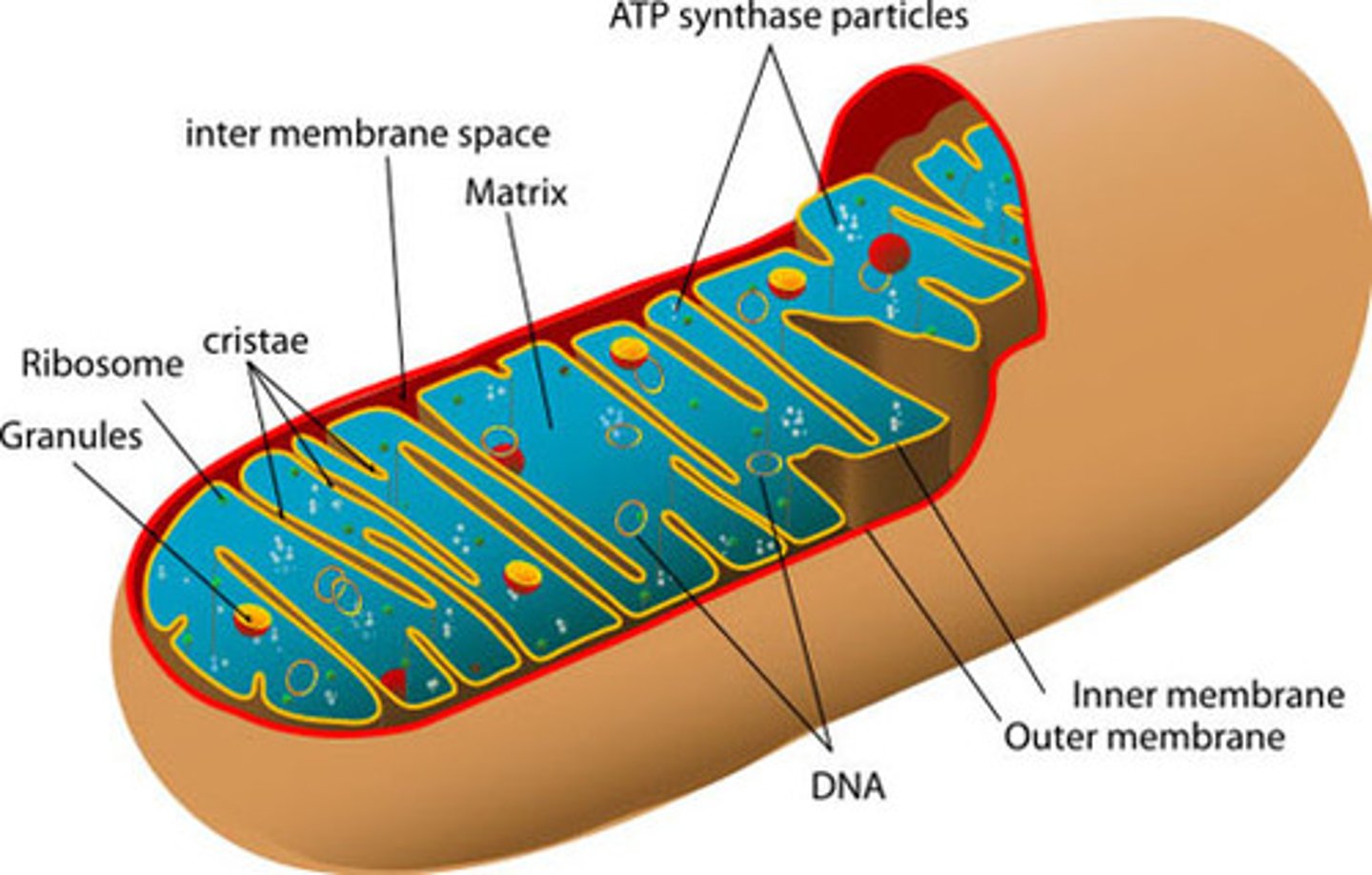
inner mitochondrial membrane
The inner mitochondrial membrane is the innermost membrane of the mitochondria.
Oxidative phosphorylation and chemiosmosis take place at the inner mitochondrial membrane, which produces ATP via the flow of protons across the membrane.
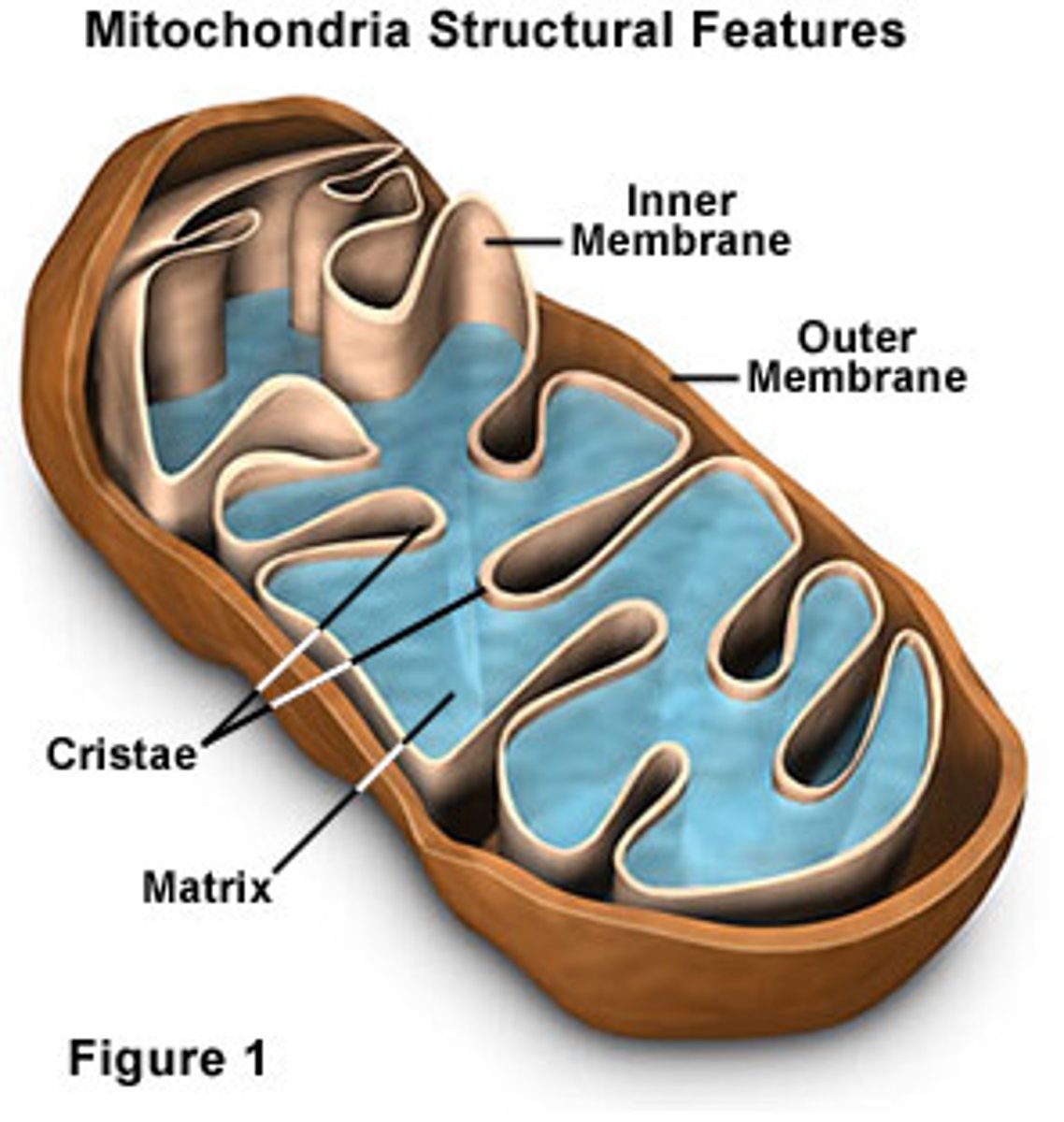
aerobic respiration
Respiration that requires oxygen
anaerobic respiration
Respiration that does not require oxygen
Fermentation is a form of anaerobic respiration
Oxygen (in the context of cellular respiration)
Final electron acceptor in the ETC.
Accepts electrons and gets converted into H20.
Oxidation/oxidized
loss of electrons
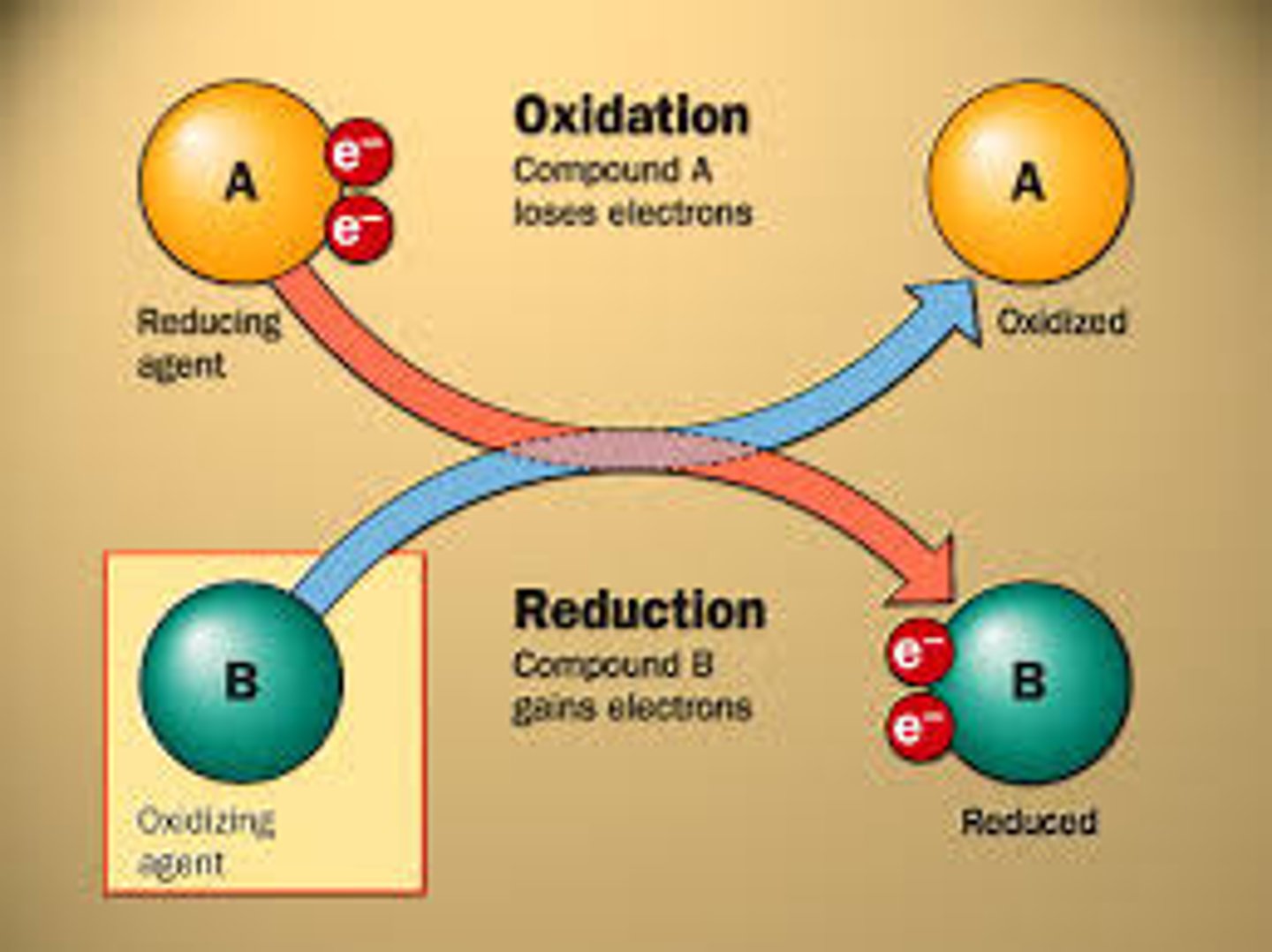
Reduction/Reduced
gain of electrons
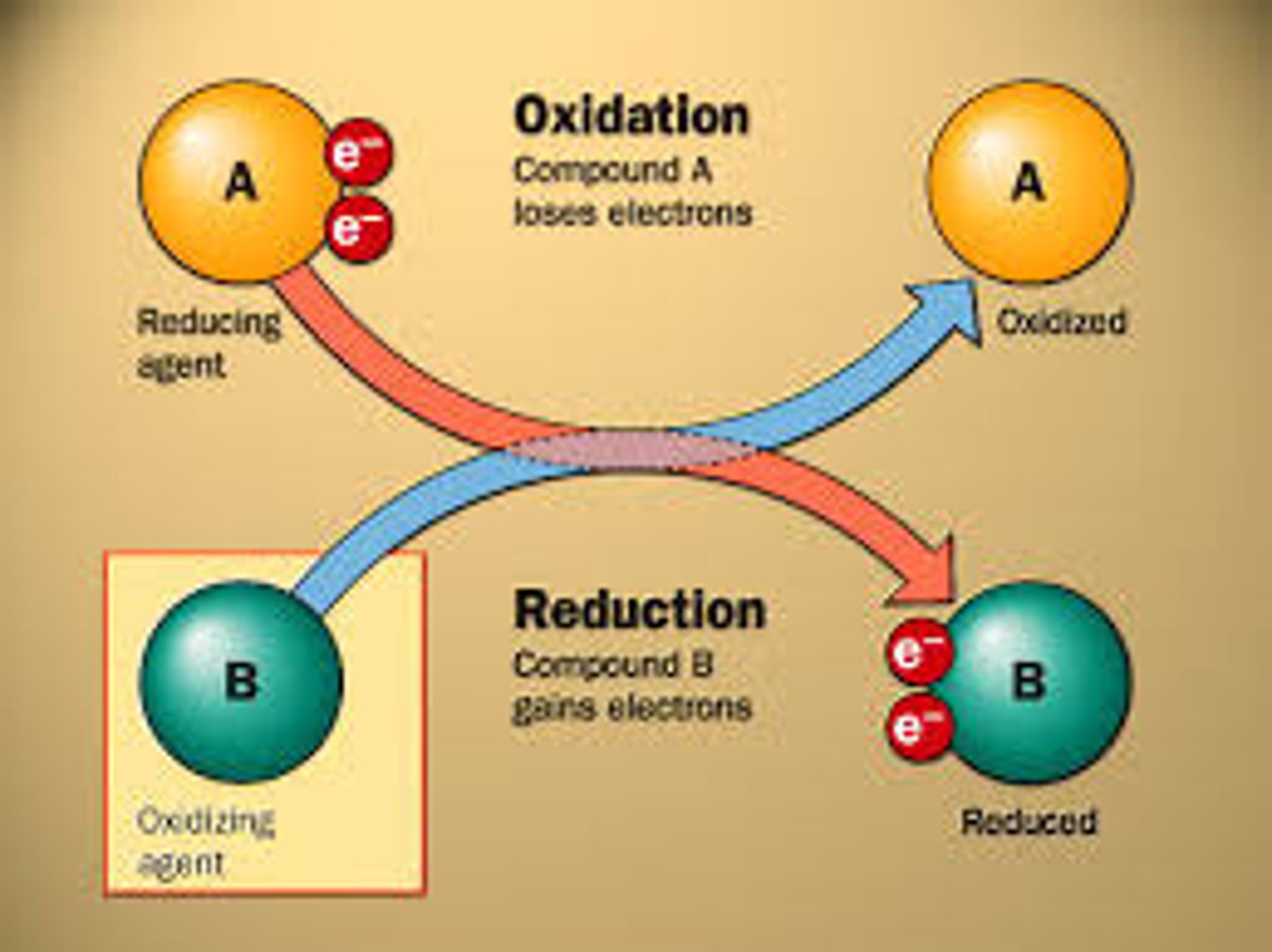
Carbon Dioxide
A product of CO2.
Produced in the intermediate step before the Krebs cycle and in the Krebs cycle