7. Infectious diseases of dogs & cats affecting urinary system. Leptospirosis
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What are examples of infectious diseases affecting the urinary system?
Leptospirosis
Cystitis
Pyelonephritis
Prostatitis
Borreliosis
Parasites
What type of bacteria is Leptospira?
Gram-negative, motile, spiral bacteria with flagella
What diseases does Leptospira cause?
Kidney and liver failure
Is Leptospirosis zoonotic?
Yes
What are some Leptospira aetiological agents?
Leptospira interrogans canicola, pomona, bratislava, ausatralis, autumnalis, copenhageni, icterohaemorrhagiae
L. kirschneri grippotyphosa
How is Leptospirosis transmitted?
Urine from infected animals (rodents are infected for life)
Direct contact between animals (bites, vertical, semen, eating infected carcasses)
Contaminated environment (ingestion of contaminated water, damaged and intact skin, MM (eyes, nose)
Which serovar is spread in dog urine (reservoir)?
L. interrogans canicola
What are the main target organs of Leptospira?
Kidneys and liver
What is the pathogenesis of leptospirosis?
Penetrates skin or MM → enter blood & cause → bacteraemia → spread by blood → affinity for kidney, liver → replicates in nephrons → kidney failure, hepatitis, necrosis
Damage of endothelium & lysis of RBC (haemolysin) → haemorrhages. Anaemia
Affinity for pregnant uterus → cross placenta, causes abortions
How can antibody titre affect presentation of leptospirosis?
High Ab titre → no disease
Moderate Ab titre → mild kidney damage → persistent infection → increase Ab & no disease OR mild/no clinical disease
Low/no Ab → replication in liver/nephrons → either renal failure/toxic hepatitis → then severe disease & death OR direct severe disease & death (or increase Ab → persistent infection → mild/no clinical disease)
What are some clinical signs of Leptospirosis?
Peracute: Pyrexia, vomiting, shivering, tachypnoea, dehydration, death
Sub-acute & Acute: Fever, anorexia, vomiting, increased thirst, olig/anuria, rhinitis, cough, ulcers in oral cavity, icterus.
Chronic (Most common): Diarrhoea, vomitus, hepatitis, nephritis, uveitis
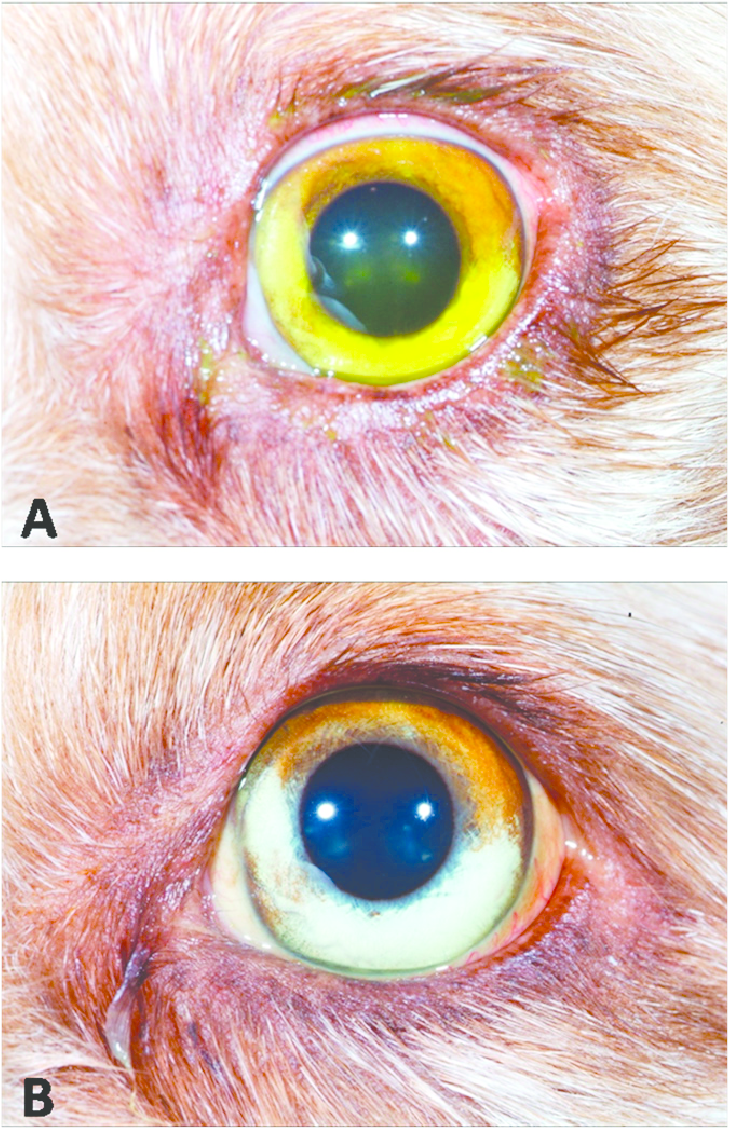
How is Leptospirosis diagnosed?
Serology → Microscopic Agglutination Test - MAT = Gold standard test. (single test is not enough to confirm dx)
NB! Intermittent shedding -may be negative → Paired sampling (to wait for higher values)
Not clinically useful because takes long
Haematology → (non- regenerative anaemia, lymphocytosis, neutrophilia, thrombocytopenia)
Blood chemistry → (elevated liver/ kidney enzymes; LD, GGT, urea, creatinine, SDMA)
Urinalysis → (glucose, protein, blood, pus, bilirubin),
USG → Show changes form of kidney. Cloud shaped/ not smooth edges.
PCR, cultivation, Dark field microscopy (spiral-shaped bacteria).
What are some differential diagnoses for Leptospirosis?
Babesiosis, intoxication, Lyme borreliosis, glomerulonephritis, bacterial pyelonephritis, acute pancreatitis, bacterial sepsis
How is Leptospirosis prevented?
Core vaccination. Killed vaccine
1: 12 weeks; 2: 16 weeks) then every 6-12 months
L4 vaccine has 4 serovars, L2 has 2 serovars (No cross-protection)
Rodent control, avoid contact with reservoir hosts and contaminated areas
Inactivation by temperature, UV, disinfection, freezing.
Why is a killed vaccine used for leptospirosis?
Live vaccines cause shedding in urine
What is the treatment for Leptospirosis?
Causal: antibiotics (penicillin G, doxycycline, chloramphenicol, streptomycin, erythromycin)
Supportive: fluids (NB! Kidney damage- slow administration) glucose to support liver function.
Symptomatic (kidney → diet low in protein)
What is the prognosis for leptospirosis?
Depends on early intervention
What is important to tell an owner when their dog has leptospirosis?
Wear gloves and wash hands after touching the dog (Zoonotic)
What is bacterial cystitis?
Infection and inflammation of the urinary bladder
What are some causes of bacterial cystitis?
Bacteria: E. coli, Staphylococcus, Enterococcus, Streptococcus, Proteus, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas, Pasteurella, Mycoplasma
Non-infectious: chronic glucocorticoid administration, hyperadrenocorticism, chronic kidney disease, diabetes mellitus, stress
What is the pathogenesis of bacterial cystitis?
This infection typically ascends from the urethra to the bladder, resulting in colonisation of bladder epithelium. Predisposing factors include abnormalities of urine flow, decreased immunity, inadequate urine concentration, glucosuria, & systemic diseases.
What are some clinical signs of bacterial cystitis?
Pollakiuria, haematuria, dysuria, inappropriate urination, pain on abdominal palpation
How is bacterial cystitis diagnosed?
Urinalysis (cystocentesis or free catch): increased protein, haemoglobin, pH, WBCs, RBCs. Decreased urine specific gravity
Microscopy of sediments (struvite is often seen in bacterial infection)
USG
Bacterial culture
What is the treatment for bacterial cystitis?
Antibiotics (trimethoprim sulphate, penicillin, amoxicillin)
What is pyelonephritis?
Bacterial infection of the renal pelvis
What are some causes of pyelonephritis?
E. coli, Staphylococcus, Enterococcus, Streptococcus, Proteus, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas, Mycoplasma), rhinoliths, ureteroliths
What is the pathogenesis of pyelonephritis?
Ascending bacterial infection
Haematogenous infection
Rhinoliths/ureteroliths → prevent normal flow of urine out of kidneys
What are some clinical signs of pyelonephritis?
Kidney or flank pain, fever, malaise, vomiting, dysuria, haematuria, PU/PD
How is pyelonephritis diagnosed?
Urinalysis: proteinuria pyuria, bacteriuria, &/ or haematuria. WBC cast may be present in fresh urine sediment.
Biochemistry: normal or azotemia (renal/postrenal) &/or hyperglobulinemia. The animal may have kidney failure.
USG: hyperechoic renal cortex, enlarged, dilated renal pelvis
What is the treatment for pyelonephritis?
Broad-spectrum antibiotics, IV antibiotics (fluoroquinolone + beta-lactam is most effective), fluids
What is prostatitis?
Inflammation of the prostate
What are some causes of prostatitis?
E. coli, Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Mycoplasma spp.
What is the pathogenesis of bacterial prostatitis?
Infection may be haematogenous (acute prostatitis) or ascend from the urethra (chronic prostatitis)
What are some clinical signs of prostatitis?
Tenesmus, stranguria, pollakiuria, urine flow blockage, urethral discharge, fever, lethargy, painful gait, pain on abdominal palpation
How is prostatitis diagnosed?
Rectal palpation, ultrasound, radiography, cytology, culture
What is the treatment for prostatitis?
Antibiotics (chloramphenicol, clindamycin, erythromycin, enrofloxacin), castration
What is Lyme disease (borreliosis) caused by?
Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto, Borrelia afzelli, Borrelia garinii
How is borreliosis transmitted?
Ticks
What are some clinical signs of Lyme disease?
Renal disease (uremia, hyperphosphatemia, protein-losing nephropathy)
How is Lyme disease diagnosed?
Serology (Ab: ELISA, IFA)
What is the treatment for Lyme disease?
Antibiotics (penicillin, tetracyclines) for 30 days (IV or PO)
What are some parasites that can affect the urinary tract?
Capillaria plica – urinary bladder & urethra (dog)
Capillaria feliscati – urinary bladder (cat)
Dioctophyme renale – kidney (fish eating mammals)
Why can anaemia be found in leptospirosis?
Decreased erythropoietin produced by the kidneys
What indicators can you use to check the kidneys?
Urea
Creatinine
SDMA
What is a parasite which causes colour changes in the urine?
Babesia