Glaciers
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
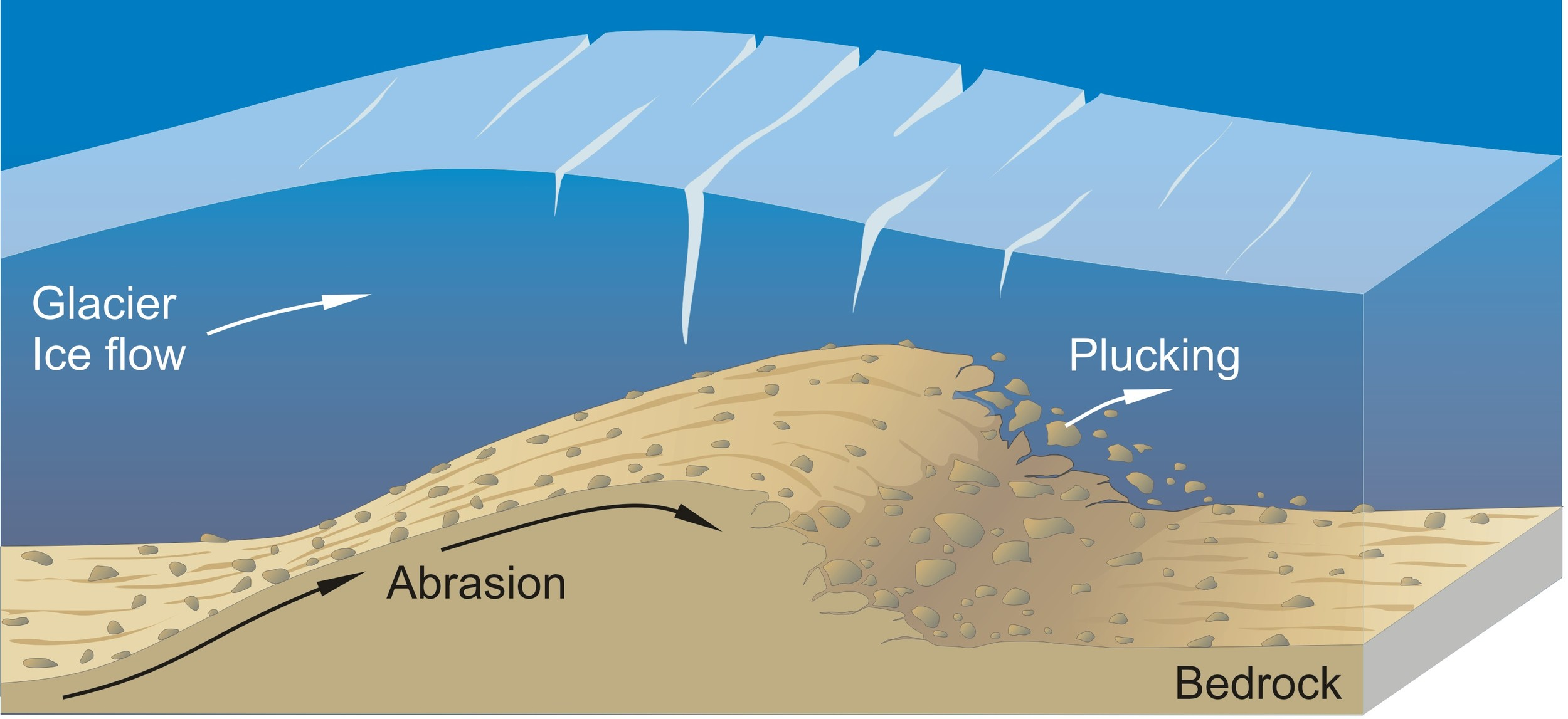
What are the two ways glaciers erode landscapes?
Abrasion - The grinding of rock surfaces by the movement of glacial ice
Plucking - Meltwater of a glacier freezes onto rock and as the glacier moves, it pulls it out
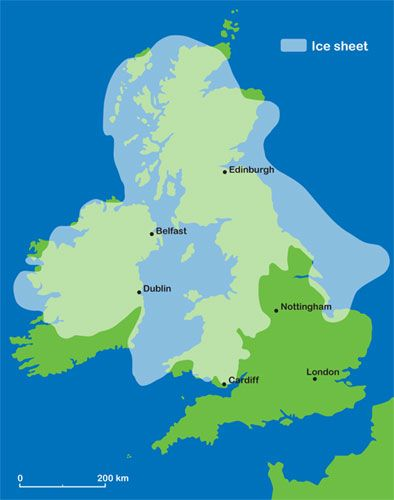
Describe Ice Coverage in the UK?
There have been many glacial periods over the last 2.6 million years in the UK. During these periods, large parts of the UK were covered by ice sheets, particularly in Scotland and Northern England, significantly shaping the landscape.
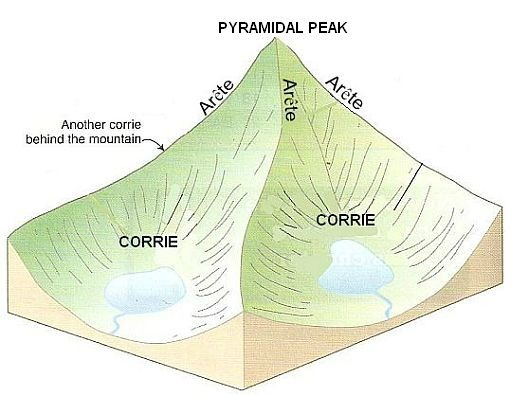
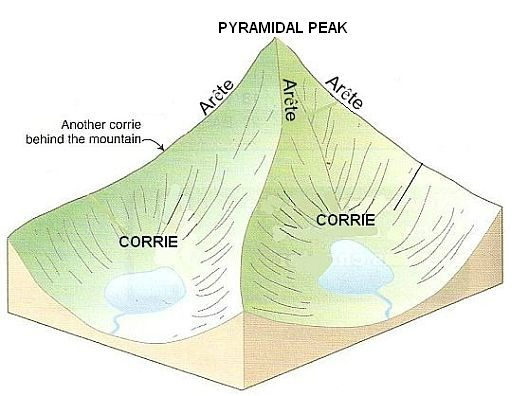
What are Arêtes?
A sharp ridge formed between two glaciers that have eroded the landscape on either side.
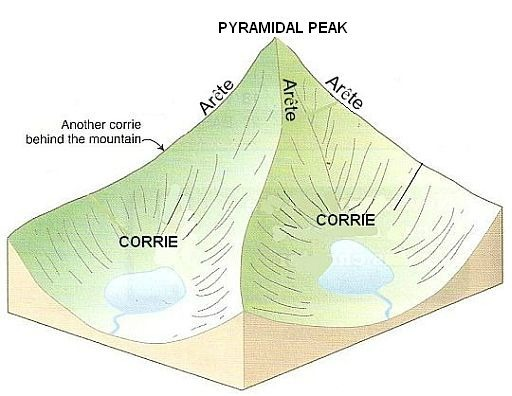
What are Corries?
A bowl-shaped hollow, often containing a lake, located at the head of a valley. Rotational slip causes the hollow to erode deeper and wider, creating a distinctive landform.
What are Ribbon Lakes?
A long, narrow lake that forms after a glacier retreats. They form in hollows where softer rock was eroded more than the surrounding hard rock.
What are Pyramidal Peaks?
A mountain peak with at least three sides. It is formed when three or more back-to-back glaciers erode a mountain.
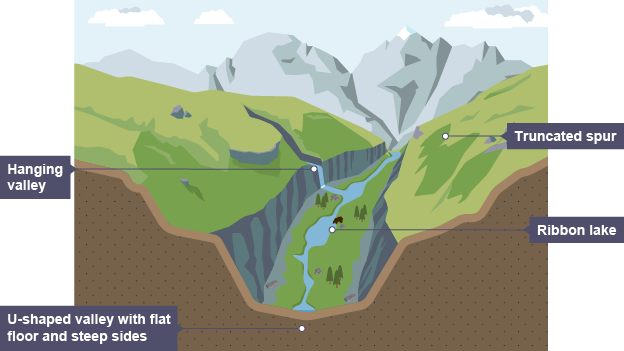
What are Truncated Spurs?
Cliff-like edges on the valley side formed when ridges of land that stick out into the main valley are cut off as the glacier moves past.
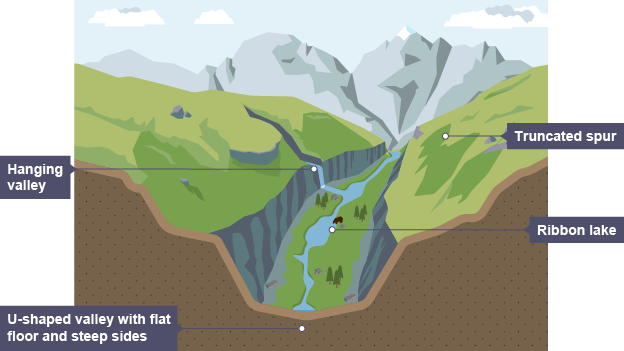
What are Hanging Valleys?
Valleys formed by small tributary glaciers that flow into a main glacier. The glacial trough of the larger glacier is eroded much more deeply, so when all of the glaciers melt the tributary glacier’s valleys are left at a higher level.
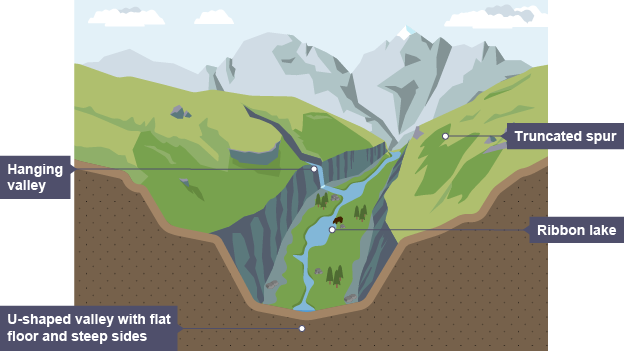
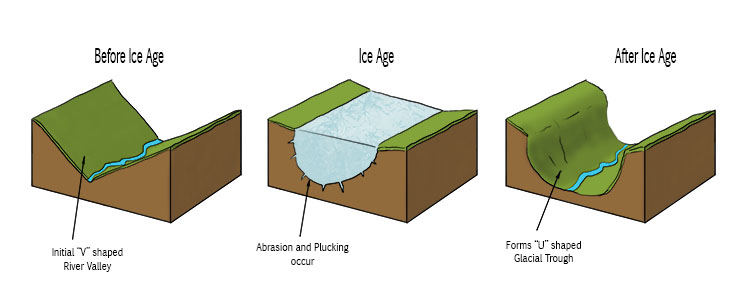
What are Glacial Troughs?
Steep-sided valleys with flat floors. They start off as a V-shaped river valley but change to a U-shape as the glacier erodes the sides and floor, making it deeper and wider.
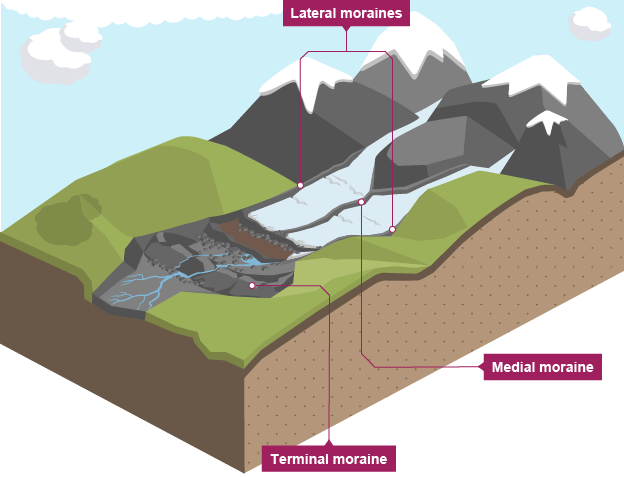
What are the 4 types of Moraines?
Lateral moraines - A long mound of material deposited where the side of a glacier was
Medial moraines - Formed where two glaciers meet, creating a ridge of debris in the centre.
Terminal moraines - A ridge of debris at the furthest advance of a glacier, that builds up at the snout
Ground moraines - A blanket of till deposited as a glacier retreats, covering the land beneath
What are Drumlins?
Drumlins are elongated hills formed by glacial action, typically consisting of till, that indicate the direction of ice flow. They often appear in groups and have a tapered shape, with a steeper slope facing the direction from which the glacier advanced.

What are Erratics?
Erratics are large boulders or rocks that have been transported and deposited by glaciers, often found in locations far from their source, differing in composition from the local geology.
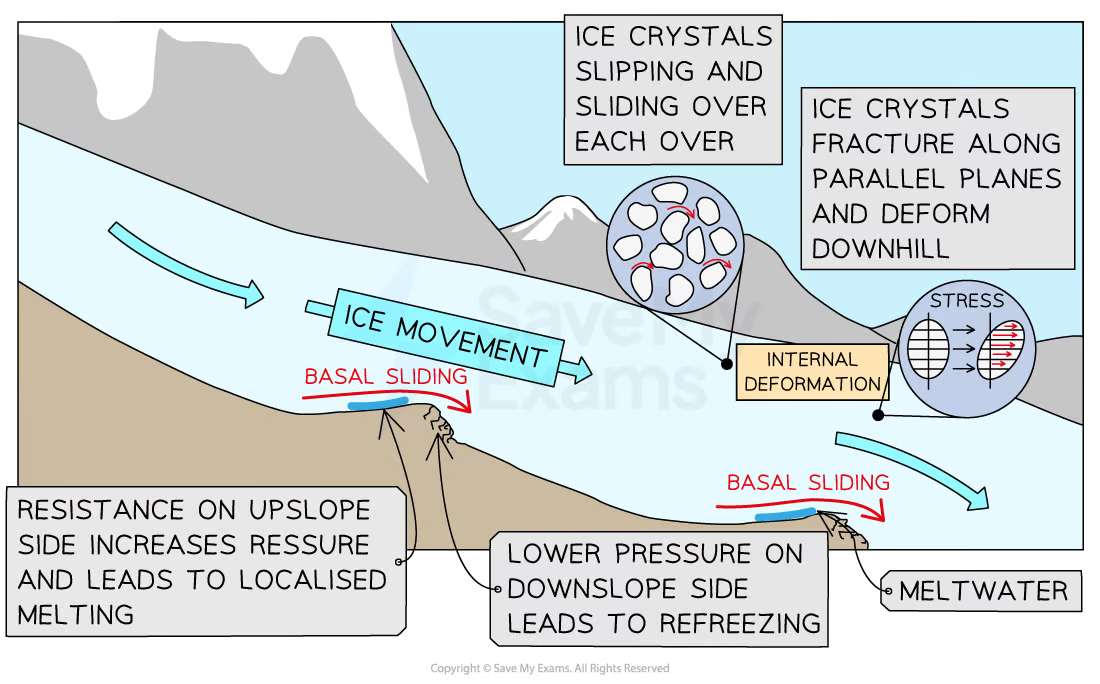
What are the two types of Ice Movement?
Basal Sliding - Meltwater forms under pressure and the meltwater acts as a lubricant and helps ice to flow
Internal Deformation - Ice crystals within the glacier slip and slide over each other. The ice crystals may also become deformed or fractured under pressure
What are the 4 main Opportunities in Glacial Areas?
Farming - Lots of space and fertile soil for agriculture
Forestry - Access to timber resources for logging and wood production
Quarrying - Extraction of minerals and rocks for construction and industry
Tourism - Attracts visitors for activities like skiing, hiking, and sightseeing
What are some Conflicts in Glaciated Areas?
Tourism and Farming - They can damage property and scare away livestock
Locals and Quarrying - Local communities may oppose quarrying due to environmental concerns and disruption of their land
Military Presence and Conservation - Operations can destroy habitats while polluting with things like jet fuel
Energy Production and Logging - Energy production takes up the space where replanting takes place