MKTG Chapter 7 Understanding and Researching Global Consumers and Markets
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
United States, China, Germany
Who are the leaders in the global merchandise trade?
International Firm
take marketing strategy from HOME country and they duplicate it in other countries
Multinational Firm
view the world as consisting of unique parts and markets to each part differently
Transnational Firm
view the world as one market and emphasizes cultural similarities across countries or universal consumer needs and wants rather than differences
The type of company firm is Multinational Firm
Which type of company firm utilizes a multidomestic marketing strategy?
The type of company firm is Transnational Firm
Which type of company firm utilizes a global marketing strategy?
Multidomestic Marketing Strategy
they have as many different product variations, brand names, and advertising programs as countries in which they do business
Ex: Changing aspects of the product based on the cultural preferences of the country (different 4 P’s in each country)
Global Marketing Strategy
the practice of standardizing marketing activities when there are cultural similarities and adapting them when cultures differ
600 billion dollars a year
How much money does the U.S firms spend on economic espionage?
seller
seller’s international marketing headquarters
channels between nations
channels within foreign nation
final consumer
What are the channels of distribution in global marketing?
Counter Trade:
is the practice of using barter rather than money for making global sales
Exporting:
A global market-entry strategy in which a company produces products in one country and sells them in another country.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP):
is the monetary value of all products and services produced in a country during one year
Balance of trade:
the difference between the monetary value of a nation's exports and imports
Globalization:
is the focused on creating economic, cultural, political, and technological interdependence among individual national institutions and economies
Protectionism:
is the practice of shielding one or more industries within a countries economy from foreign competition through the use of tariffs or quotas
Tariffs:
Government taxes on products or services entering a country that primarily serve to raise prices on imports
Quota:
is a restriction placed on the amount of a product allowed to enter or leave a country
Multidomestic Marketing Strategy:
involves multinational firms that have as many different product variations, brand names, and advertising programs as countries in which they do business
Global Marketing Strategy:
involves transnational firms that employ the practice of standardizing marketing activities when there are cultural similarities and adapting them when cultures differ
Global Brand:
is a brand marketed under the same name in multiple countries with similar and centrally coordinated marketing programs
Cross Cultural Analysis:
involved the study of similarities and differences among consumers in two or more nations societies
Values:
are a society’s personally or socially preferable modes of conduct
Customs:
are what is considered normal and expected about the way people do things different in a specific country
Cultural Symbols:
are things that represent ideas and concepts in a specific culture
Back Translation:
is the practice where a translated word or phrase is restranslated into the original language by a different interpreter to catch errors
Cultural Ethnocentricity:
the tendency for people to view their own values, customs, symbols, and language and other aspects of one's culture are superior to another
Consumer ethnocentrism:
is the tendency to believe that it is inappropriate, indeed immoral, to purchase foreign made products
Currency Exchange Rate:
is the price of one country’s currency expressed in terms of another countries currency
Exporting:
is a global market-entry strategy in which a company produces products in one country and sells them in another country
Joint Venture:
is a global market-entry strategy in which a foreign company and a local firm invest together to create a local business in order to share ownership, control, and profits of the new company.
Direct Investment:
is a global market entry strategy that entails a domestic firm
Dumping:
occurs when a firm sells a product in a foreign country below its domestic price or below its annual cost
Gray Market:
is a situation where products are sold through unauthorized channels of distribution also called parallel importing
Italy currently has a limit on the number of motorcycles that can be imported from Japan
What is an example of a quota
quota
Is a quota or tariff a straight up number?
tarrif
is a quota or tariff a dollar amount/percentage?
protect and industry: “protectionism”
What are quotas and tariffs designed to do?
Unilever markets its Snuggle fabric softener differently to different parts of the world
What is an example of a multinational firm?
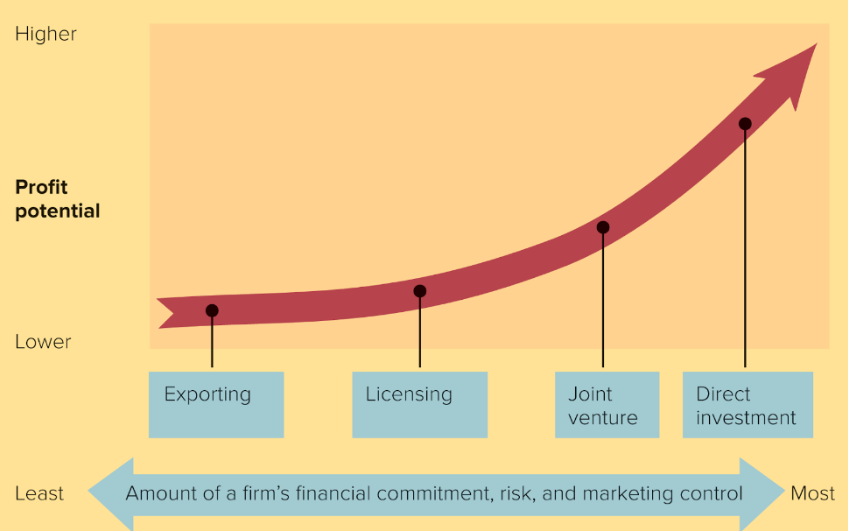
exporting
licensing
joint venture
direct investment
What is the order of the 4 types of global marketing strategies
where a domestic firm owns foreign subsidiary
What is an example of direct investment?
Marketing Strategies
International-home
Multinational-multidomestic
Transnational- global
are all what?
product extension
the strategy of selling virtually the same product in other countries
product adaptation
changing your products for other countries
product invention
create new products for the countries
international company
This company markets their product the same in every place in the world that they do business
multinational company
This company markets their product different in ever country
transnational company
This company is a brand that you would recognize around the world
Global market entry strategies
What does this graph show?
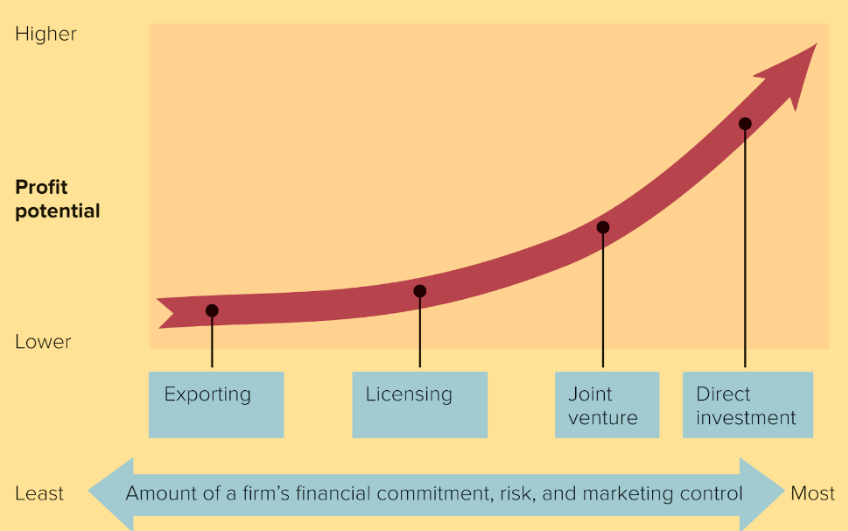
Exporting
Which of global marketing strategies goes in the first box?
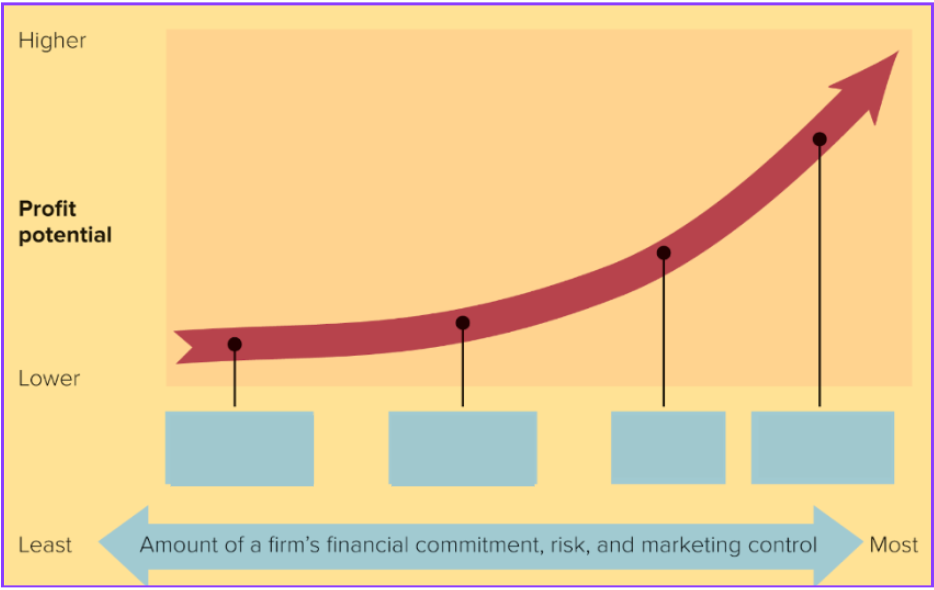
Licensing
Which of global marketing strategies goes in the second box?
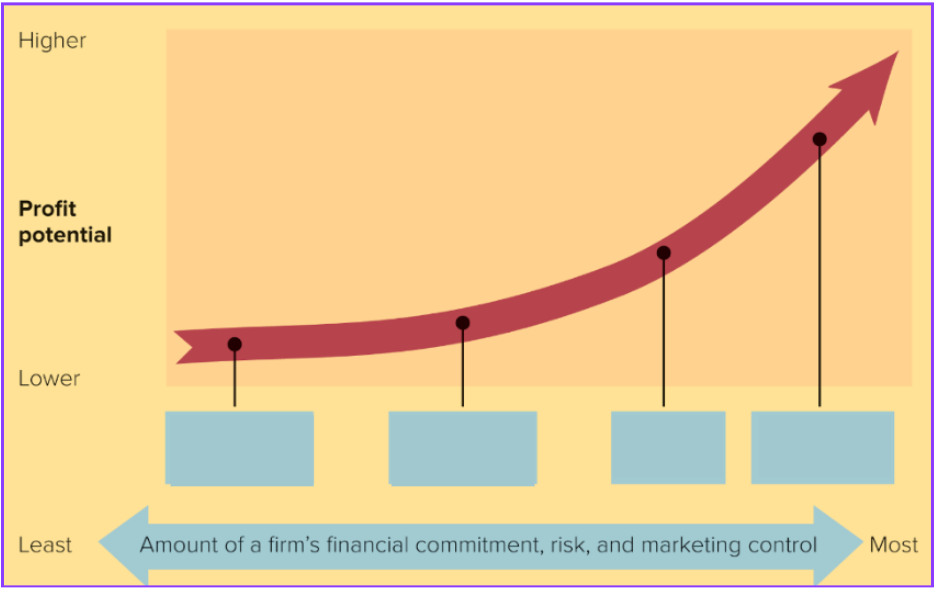
Joint venture
Which of global marketing strategies goes in the third box?
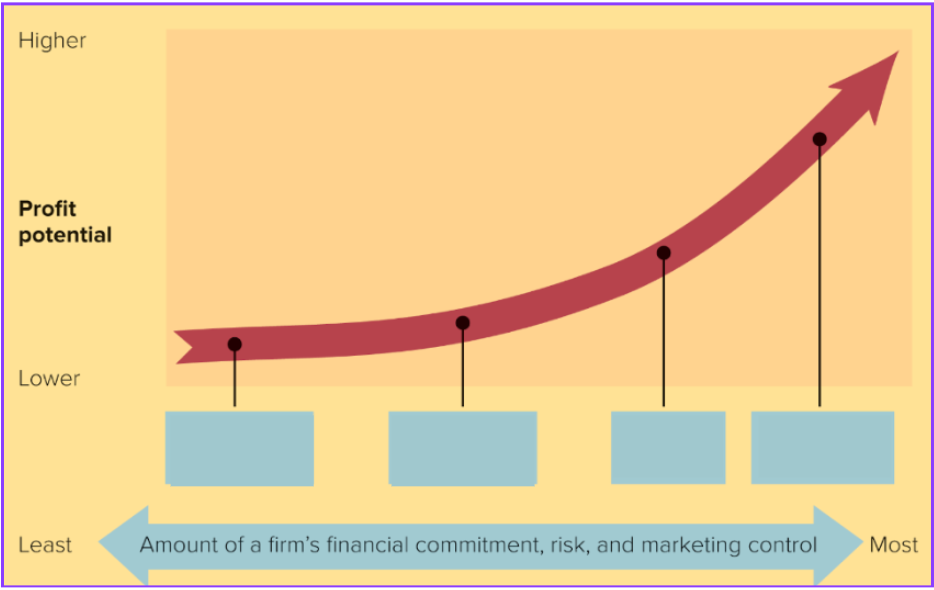
Direct investment
Which of global marketing strategies goes in the fourth box?
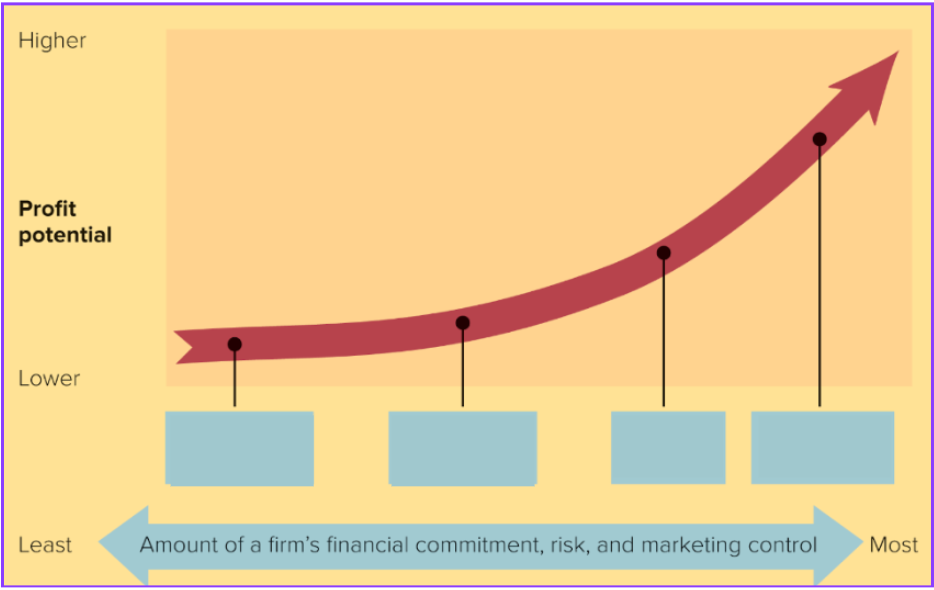
increased profit and increased risk
What happens as we move from left to right?