Lecture 10-11 Tools for analyzing gene expression (copy)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Model Organisms
Features
cheap and common
easy to propagate
easy to manipulate
Bacteriophage lambda
The bacterium Escherichia coli

Transient and stable transfection assays
plasmid DNA remains extrachromosomal or integrated
Transient transfection
intro of DNA into cells for little time
Stable transfection
cells selected for stable integration of plasmid into chromosome by drug resistance
Transient transfection
common
not stable
less predictable
less long-term seconday effects
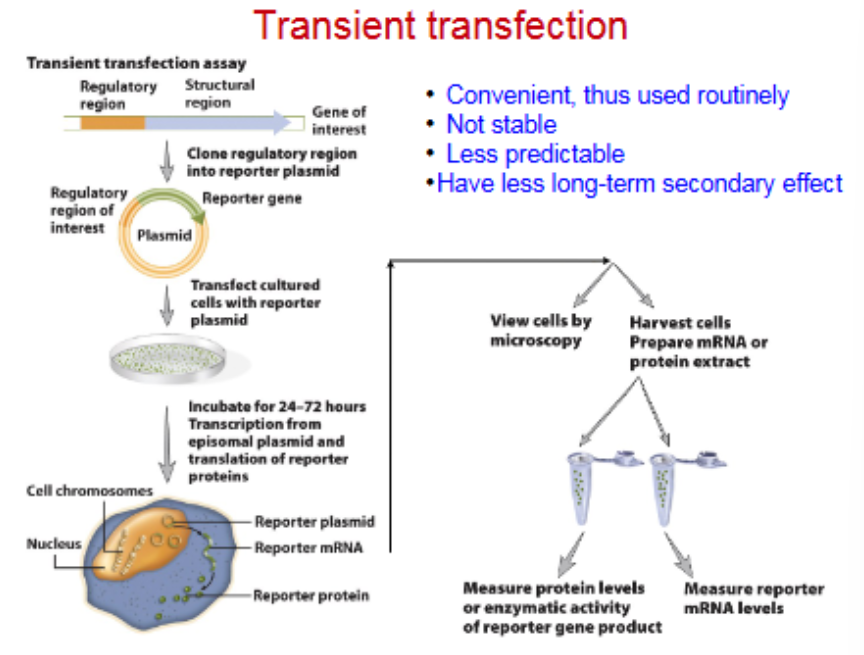
Stable transfection
Drug resistance mRNA
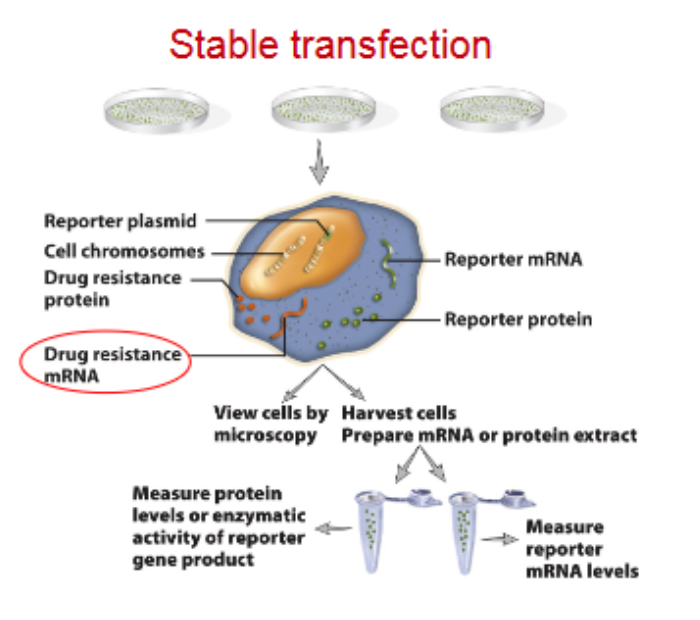
Reporter Genes
Def
known gene whos RNA or protein level can be measure easily/accurately
used to replace other codign regions whs protein products are difficult to measure quantittively
Application
study regulatory elements of genes
effeciencey of gene delivery system
GFP- intracellular fate of gene product
FRET- Protein-Protein interactions
GFP- DNA0protein interactions
Purification and detection protein using epxression tags
reporter gene attached t other sequence so that reporter protein is synthesized and fused to another person
often shrt peptide sequence that acks as affinity or epitope tag (antigenic determinant)
Commonly used affinity tag:
Histidine (His) tag: 6-histidine
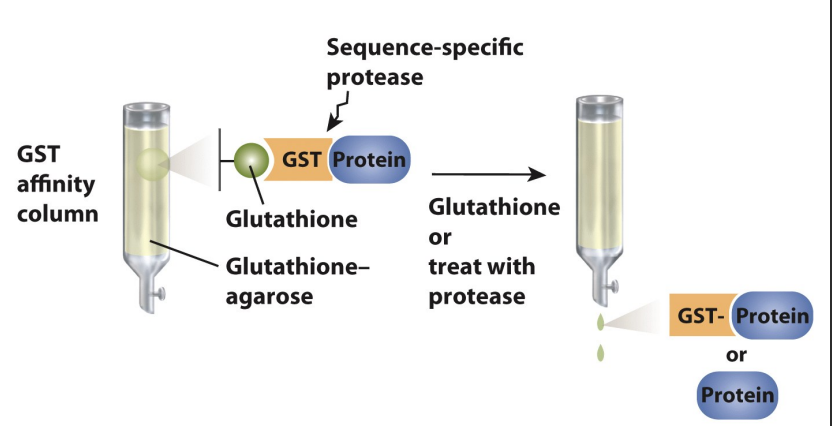
GST tag: gluthathione-S-transferase
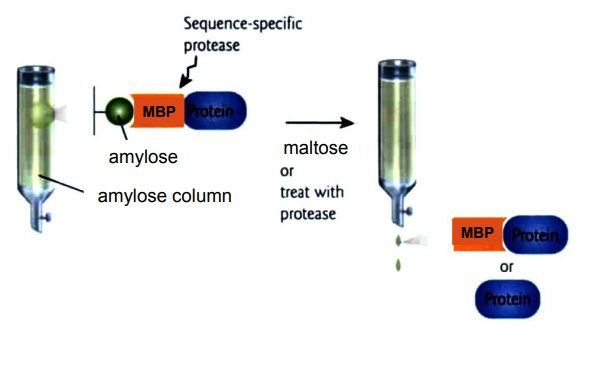
MBP tag: maltose-binding protein
Application:
Protein purifiicaion
Protein localization
FRET- Protein-protein interactions
His tags
small tag
easy to add
not interfere with protein functions
GST tag
can interfere with protein function
can remove enzymatically
MBP (maltose binding protein)
increase protein solubility
interfere with protein function
removed enzymatically
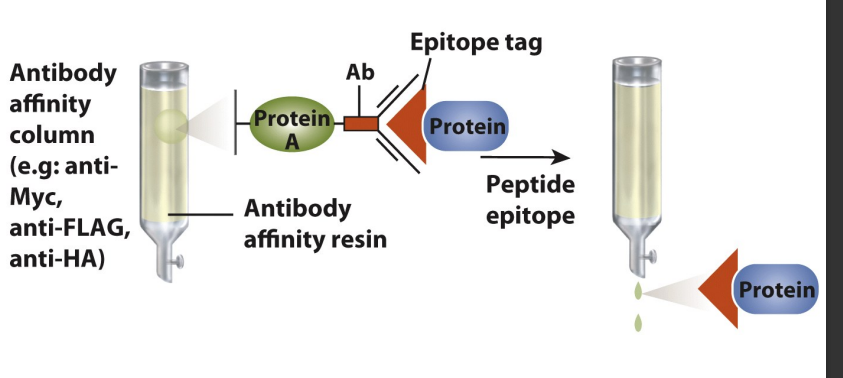
Immunotags
c-Myc
FLAG
HA
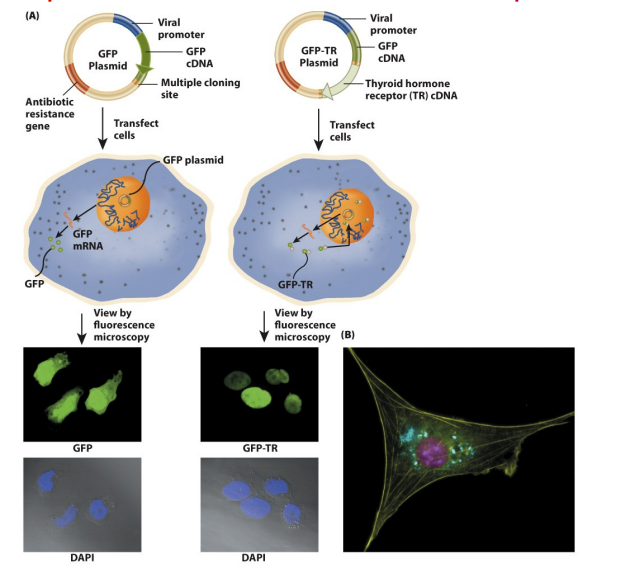
Fluorescent protein tags
Fluorescence of GFP detected in vivo and can be expresed everywhere
application
localization of protein of interest
reporter assay to study a promoter
FRET- to quantify calcium
gene cloned by Douglas Prasher
Flourescence terminology
Fluorochrome: dye or molecule that exhibits fluorescence
Fluorophore: group of atoms that absord light energy and produce color
Florescent protein with different spectra
Mutated GFP
enhanced GFP (EGFP)
Red flourescent protein
DsRed
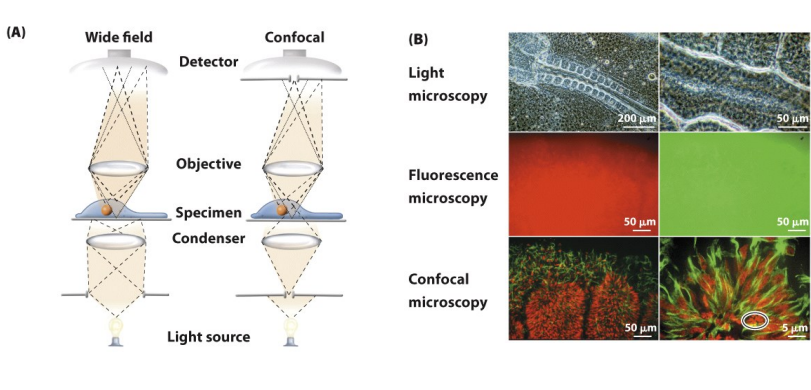
Confocal microscpy
ilumination achieved by scanning one or + beams of light from laser across specimin
Collect Z series to create high resolution 3D images of sample
In Vitro mutagenesis
Site-directed mutagenesis
intro of specific base sub/insertion of defined sited in a cloned DNA molecules
Non-site directed mutagenesis
random mutagenesis
Analysis at level of gene transcription: RNA expression and localization
Constitutive expression: the gene is expressed at all times.
Spatial expression: the gene is only expressed in specific tissues in an organism.
Temporal expression: the gene is only expressed during a specific time in development.
Technique to monitor mRNA levels
Northern blot
one gene per probe
detects RNA,DNA, Protein with Ab
in situ hybridization
localization
abundance
Reverse transcription- PCR
first strand cDNA reandom primer or poly (dT)
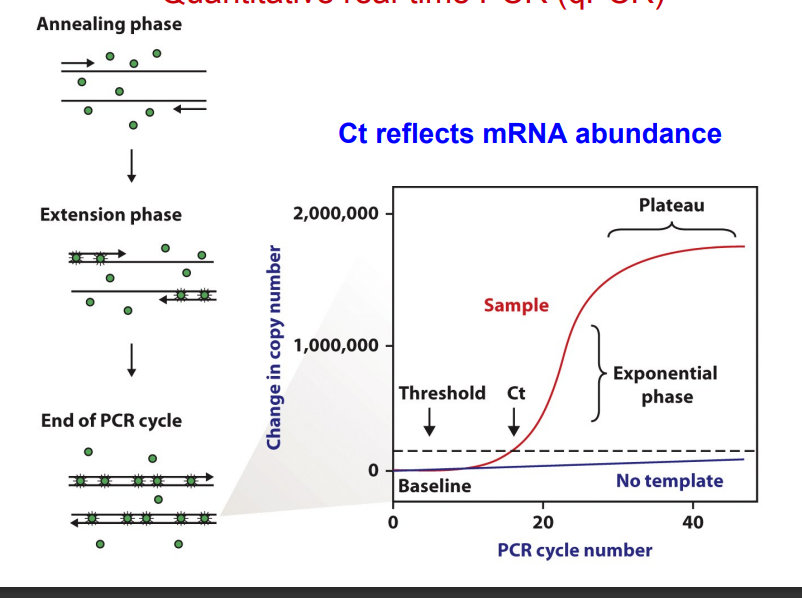
Quantitative real-time PCR (Q-PCR)
Ct reflets mRNA abundance
Next gen sequenceing (systematic)
qpcr (quantitative real-Time PCR
4 steps
denature to create single strand
annel
tention to create product
use Syber green dye to annel with doubel strand DNA to emit light that is detected by machine to check for product
a sample run 10 cycles to create 10,000 molecules (faster bc less amount of cycles)
b sample run 12 cycles to create 10,000 molecules
cycle^(-small cycle-long cycle) => faster and
2^(-(10-12))
curve: product is s
Analysis at the level of translation: protein expression and localization
Protein gel electrophoresis
Polyacrylamide used to make gel for better resolution rather than agarose
AA in proteins not all charged
Negative charge provided by binding socidum dodecyl sulfate (SDS) during sample preparation and running
amount of SDS bound proportional to AA #
One-dimentional (1D) SDS-PAGE
separated proteins by size
2D PAGE
sep proteins by charge and size
Native vs denaturing
Technique for monitoring protein levels
western blot
detects protein via Ab
In situ analysis
indirect immunoflourescene assay
single cell level
using Ab to detect protein
ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) (liquid western blot)
not single cell
use Ab to bind to antigen and another Ab to detect signal
uses 96 well plate
enzyme generates light that is proportiona to the protein binding t antibodies
Constructing fusion proteins with easy-to-detect tag
Antibody
Polyclonal Ab:
antibody made of B cels and recognie multiple pitopes
Monoclonal Ab: made of clonal amp of single B cell and recognise 1 epitope
Analysis of DNA- protein interaction
EMSAL Electrophoretic mobilit shift assay
native gel
look at interaction to look at what gets bigger using native gel
DNase 1(Deoxyribonuclease 1) footprinting (footprint is where the part that wasnt degraded when adding the Dnase is attached to proteins)
special for DNA-Protein interactions
get negative DNa then label 1 strand, then DNase 1 added to cut at random to create a band
end labeling
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay
protein-dna interaction
use ab to pull down protien specifically chromatin
Analysis of protein-protein interaction
pull down assay
yeast two-hybrid assay(in exam)
Coimmunoprecipitation assay (CoIP)
Western
pull down protien x and then use a labeled
Mass spectrometry
pull down spike protein and sequence it
FRET (Fluorescence resonance energy transfer)
yeast 2-hybrit screening
GAL4 is transcription factor
Interaction Present (ON state):
• Protein X (bound to GAL4 DNA-binding domain) and Protein Y (bound to GAL4 activation domain) interact.
• This interaction brings the activation domain close to the DNA-binding domain, enabling the recruitment of RNA polymerase and transcription factors.
• Result: The lacZ gene is expressed, and a color change (e.g., BLUE) is observed.
2. No Interaction (OFF state):
• Protein X and Protein Y do not interact.
• The GAL4 DNA-binding domain and activation domain remain separated, preventing transcription of the lacZ gene.
• Result: No reporter gene expression (e.g., WHITE colony).
FRET
You emit at only wavelength but express a highter wavelenth due to the first protein binding with other protein that leads to transfer of energey and emits at higher template
