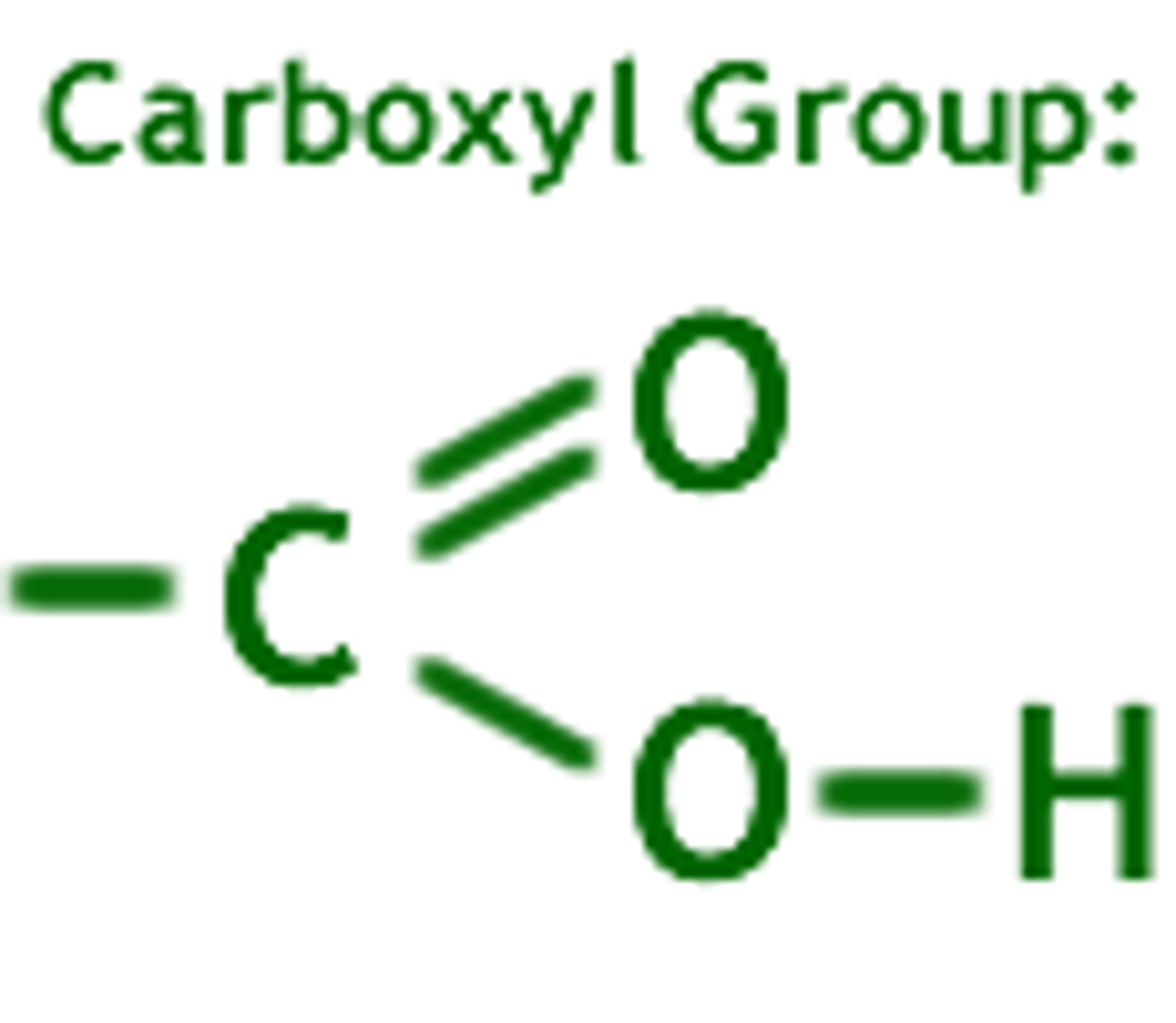Nutrition Exam 1 Study Guide (FSW HUN1201)
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
The Gastrointestinal (GI) tract
A convoluted tube that runs throughout the length of the body, from the mouth to the anus
Sphincters
Segments of the GI tract are separated from each other by circular muscles called?
Sphincters function
They can open and close when needed, so the food material does not slush around randomly from one segment to the other.
Saliva
Is secreted by the salivary glands, and its main role is to prepare the bolus.
Several enzymes in saliva?
Lysozyme & Amylase
Function of Lysozyme
Bacteria killing enzyme
Has antiseptic properties?
Saliva
HCl
Hydrochloric acid and digestive enzyme
Function of Amylase?
Breaks down complex sugars (starches).
Function of Lipases.
Breaks down lipids/fats
Function of Mouth
Mechanically breaks down food and mixes it with saliva
Bolus
Chewed food ready to be swallowed
Parotid pair is what and is located where?
Salivary gland located in front of the ears.
Sublingual pair is what and is located where?
Salivary gland located under the tongue
Submandibular pair is what and is located where?
Salivary gland located on the sides, under the jawbone.
Epiglottis
Guardes the Trachea
Pharynx
Food cavity in the back of the mouth
Trachea
Windpipe in fornt of the the esophagus, closed under the skin of the neck. It is always open and built of cartilaginous rings.
Esophagus
Food way behind the trachea, it is soft and rubbery- made of muscle. It stays closed when not in use.
The lower esophageal sphincter connects the esophagus to the.....
Stomach
GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease)
When the stomach contents can spill back into the esophagus.
Boluses are turned into a paste-like material called
Chyme
The stomach secretes a special protein that are important for the absorption of vitamin B12 called
Intrinsic factor
Role of the stomach
To kill microorganisms
Denaturation
When proteins loose their 3D shape in the stomach.
How many digestive enzymes are in the stomach and what are they?
2 / Pepsin & Gastric lipase
Pepsin is what?
An enzyme that cuts up proteins.
Gastric lipase function / found where?
'chews' on lipids / in stomach
The lower part of the stomach finishes in what?
Pyloric sphincter.
The pyloric sphincter connects the stomach to the first portion of the small intestine called what?
The duodenum
Duodenum, jejunum, and Ileum.
The small intestine is divided into three parts named what?
to digest foods and absorb the nutrients into the blood stream.
The main role of the small intestine is ?
The 1st level of folding in the small intestine are circular folds or pleats, then on the surface of the folds there are
Villi
Villi are what and have what on the surface?
Villi are fingerlike protrusions. There are microvilli on the surface of the Villi.
What is inside the villi?
lacteals
Microvilli is called what?
Brush border
Pancreas has two functions .....
Endocrine and Exocrine
Endocrine does what?
Secretes hormones into the blood circulation.
Exocrine does what?
Secreting digestive enzymes into the duodenum.
Location of the pancreas is
Under the liver, gallbladder, and behind the stomach. Nested in the curve of the duodenum.
The liver constantly secretes what and is stored where?
Bile / stored in the gallbladder
Bile is made from what?
Cholesterol
All nutrients absorbed in the small intestine will go where first?
The liver
What processes nutrients and then sends them to the required organs.
The Liver
Stores bile and releases them through bile ducts to the small intestine...
The Gallbladder
The large intestine is connected to what through what?
The Ileum through the ileo-cecal sphincter
What has 4 distinct sub-segments named after their shape and position in the body.
The large intestine
The first segment of the large intestine moves upward so its called?
The Ascending colon.
The second segment of the large intestine moves across and back so its called?
The Transverse colon
The third segment of the large intestine moves downward and back so its called?
The Descending colon.
The fourth segment of the large intestine makes a sigmoid curve before it becomes the rectum so its called?
The Sigmoid colon.
The final straight segment of the large intetsine is called ?
The Rectum
The rectum is closed by 2 anal sphincters called?
The internal anal sphincter & the external anal sphincter.
The internal anal sphincter functions?
Reflexively
The external anal sphincter functions?
Voluntarily
The main role of the colon is to?
Absorb water
Review: The List of Accessory Organs ---->
3 pairs of salivary glands are:
- parotid
- submandibular
- sublingual
Review: The List of Accessory Organs ---->
Pancreas and its exocrine and endocrine functions.
Liver and gall bladder.
Review: The List of GI segments ---->
- Mouth
- Esophagus
- Stomach
Review: The List of GI segments ---->
3 sub-segments of the small intestine
Duodenum, jejunum and ileum
Review: The List of GI segments ---->
Large intestine with 4 sub-segments:
-Ascending, transverse, descending and sigmoid
- Rectum and anus
The List of Sphinters ----> *Hint 4
- Lower esophageal
- Pyloric
- Ileo-cecal
- Anal: one reflexive and one voluntary (trainable)
The general formula of all carbohydrates
CH2O
Is brain food (Main fuel for the human body). Hexagonal ring structure. Another name for glucose is DEXTROSE,
Glucose (Monosaccharide)
Milk sugar. It forms a 6 atom (hexagonal) structure similar to glucose
Galactose
Fruit sugar that forms a 5 atom (pentagonal) structure.
Fructose
Milk sugar; this is made of 1 glucose linked to 1 galactose
Lactose
Malt sugar (found in brewing malts - not all sugars are sweet tasting); this is made of 1 glucose linked to 1 glucose
Maltose
Table sugar; this is made of 1 glucose linked to 1 fructose.
Sucrose
Amylose is what type of starch & Examples
Fact: Amylase can only break down the amylose from its 2 ends. The enzyme cannot attack the starch in the middle of the molecule.
Linear starch
Found in white potatoes: Russet potato, Long-grain rice, & Bananas.
Amylopectin is what type of starch & Examples
Fact: Has numerous ends that can be simultaneously attacked by amylases. This leads to a much faster break down and absorption than that of amylose starch.
Branched starch
Found in red potatoes: Red Bliss / also called 'waxy' potatoes, short-grained, sticky rice (Sushi rice).
The meaning of the glycemic index.
Glycemic Index is the measurement of how long it takes carbohydrates to turn into glucose in the blood stream.
The longer it takes the better. Sugars that digest faster get a higher score those that digest slower get a lower score.
The reference sugar for the glycemic index
Over 70 = High GI
55-69= Moderate GI Healthy cooked foods
Less than 54- Low GI= Veggies
The basics of fiber: how many calories? its role in removing cholesterol; what foods contain fiber?
Fact: Fiber is an important tool in removing cholesterol: 1. Cannot be digested 2. Stimulates peristaltic motion in intestine and esophagus.
NO CALORIES
Removes cholesterol by binding onto bile & removes it from the system.
Broccoli and cauliflower stems (or stalks).
Glycogen storage: where is it stored? for how long will the stores last?
Fact: When the body needs glucose the glycogen reserves are raided. Not found in plant products.
Polysaccharide stored in animal and human muscles and liver. Glycogen reserves last 8-12 hours in humans.
Hormone regulation of blood sugar: insulin vs glucagon.
Explain in your own words Hyperglycemia & Hypoglycemia
Hyper: When the blood sugar is too high- The body's blood sugar should remain in between 70-100mg/dl if a deviation occurs either insulin will push the levels back to normal.
Hypo: When the blood sugar level is dangerously low. The body's blood sugar should remain in between 70-100mg/dl if a deviation occurs either insulin will push the levels back to normal.
What secretes insulin?
- Pancreatic Beta cells
What secretes glucagon?
-Pancreatic alpha cells
What is the message of insulin?
-Insulin tells the body that there is too much sugar in the blood- All cells but mainly the muscles and liver cells take in sugar.
What is the message of glucagon?
- There is too little sugar in the blood start taking reserved sugar from the body mainly the muscle & liver. Release sugar from glycogen resources.
Diabetes-I ?
-Diabetes-I is not irreversible and was not caused by a persons bad habits. People can be born with Diabetes-I. The insulin system is broken and the blood glucose levels cannot be regulated. In some people the body doesn't recognize the beta cells as part of the body and attacks and kills them. If there are no beta cells then insulin cannot be made. Insulin must be injected artificially.
Diabetes-II?
-Diabetes-II is caused by a person's bad habits. Insulin is being made however, the signaling mechanism is broken. Cells are basically deaf and cannot 'hear' the message being sent leading to insulin resistance. Preventable and reversible.
List and explain the typical pathologies found in diabetic patients. *Hint 3
-Diabetic Retinopathy- Retina slowly dies out causing blindness.
-Diabetic Nephropathy- Kidney filtration units slowly die out preventing Kidneys from filtering out the toxins in blood.
Maintenance: Dialysis/ hemodialysis regularly.
-Healing process is slowed down or stopped. Capillaries in the body (especially the feet) degenerate if wounded the body requires capillaries to heal the injury. However, capillaries are negatively affected therefore healing process is off. This possibly leads to gangrenous infections and amputations.
What type of fuel will the brain use?
Brain is picky and only accepts glucose.
How is glucose distributed throughout the body
Glucose is used in a hierarchal system the brain is the most important organ in the human body. Everything else will sacrifice just so that the brain can have its fill.
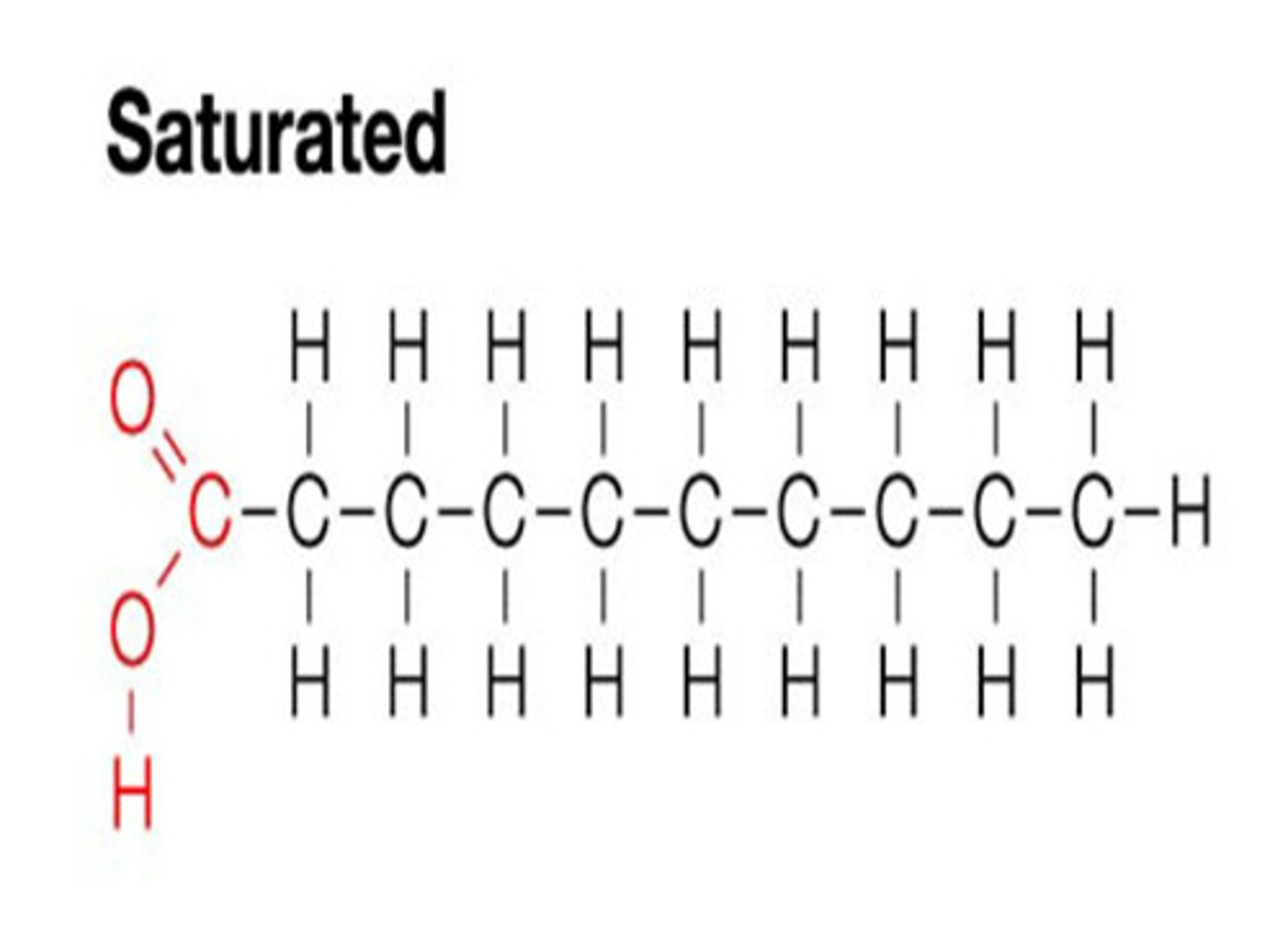
Meaning of saturated
Fact: Mainly found in food animal products. Consumption: Low levels are recommended but 100% elimination is OK (Vegan).
- Saturated = Straight chain: 'Saturated' refers to the number of hydrogens added onto the carbons.
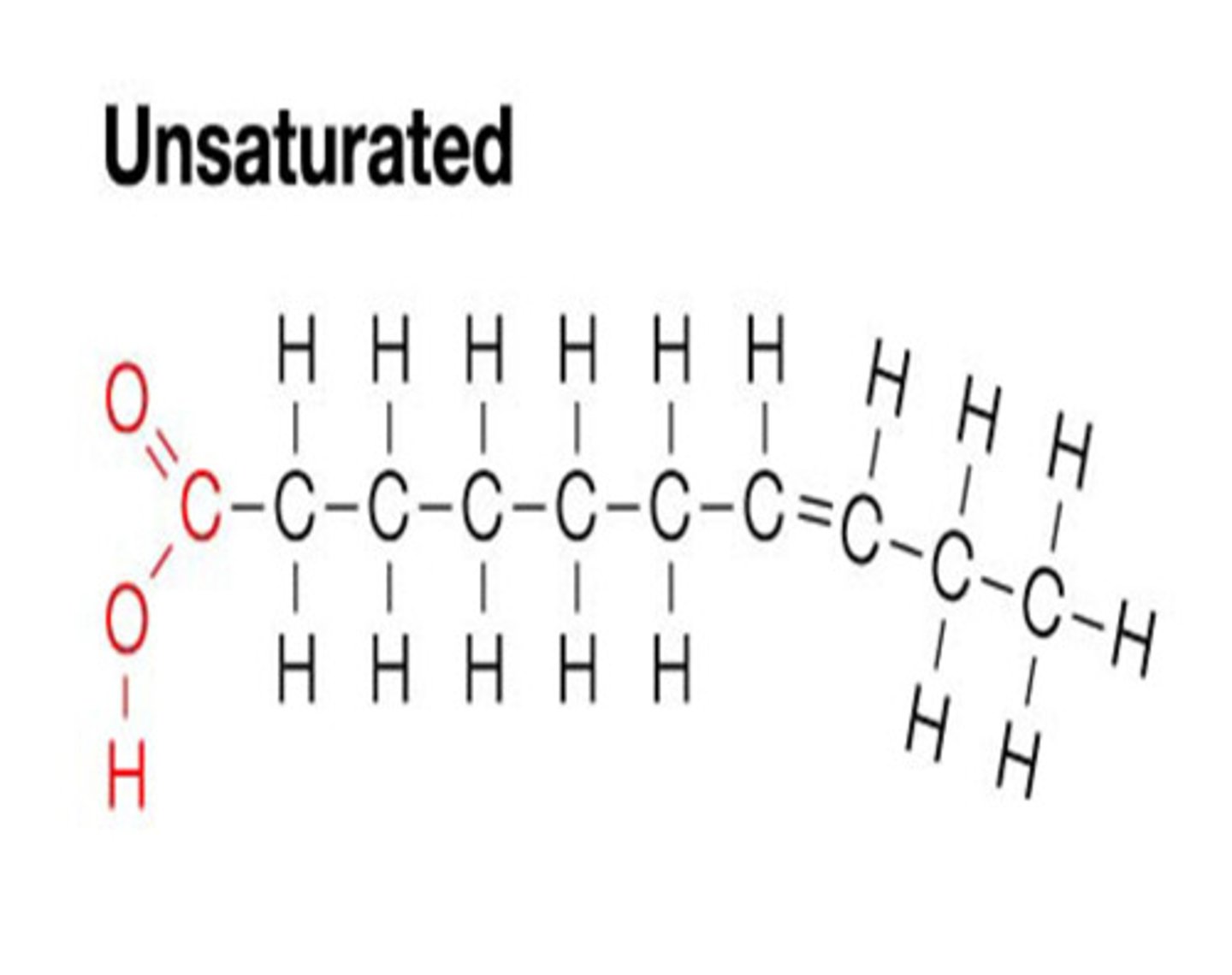
Meaning of unsaturated
Fact: Double bond found mainly in plants-based foods, with fish being an exception.
Unsaturated= Kincked chain: If hydrogens are removed (can be added back), the carbon is 'unsaturated'.
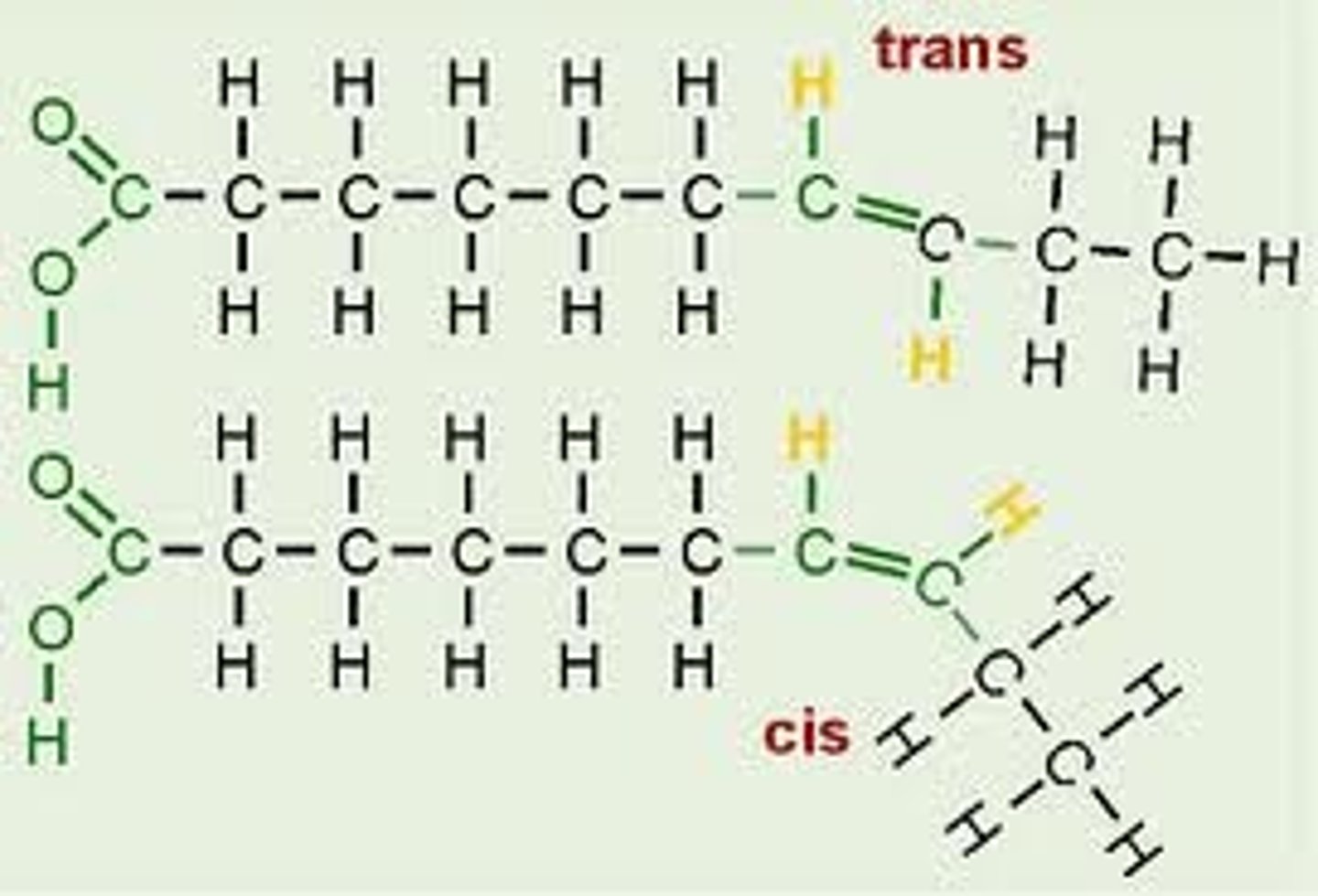
Meaning of Cis
All natural unsaturated fatty acids are healthy.
Cis Configuration: Hydrogen atoms are stuck in either the same side or double bond.
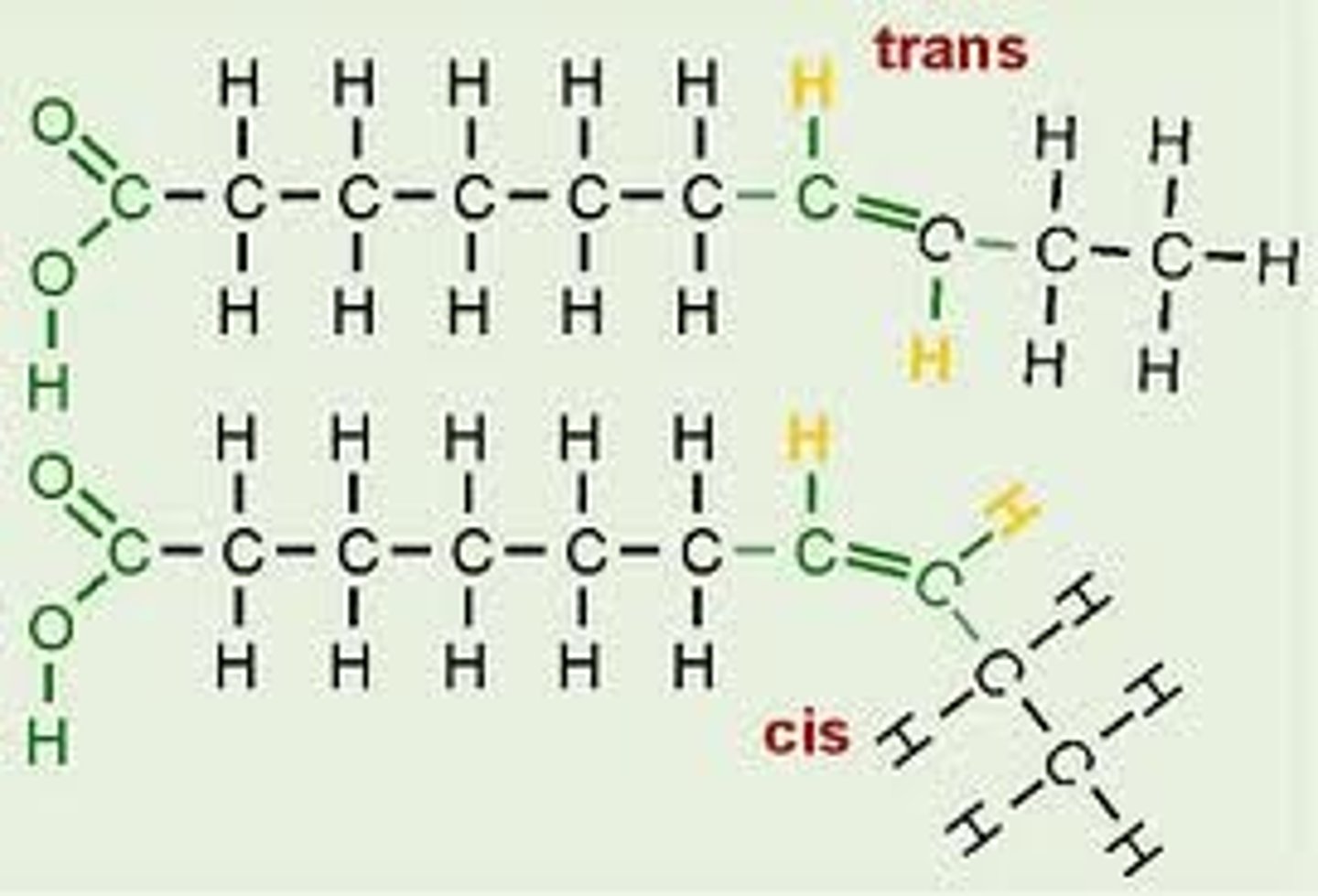
Meaning of Trans
Fact: As it happens, trans-fats are toxic and they should be avoided at all costs.
All artificial/industrial unsaturated fatty acids
Trans Orientation: Stuck on the opposite side or double bond. (Looks like a saturated chain).
Lipid causes transportation from the small intestine to the peripheral tissue (adipose / outer tissue) = fatty food goes straight to the love handles.
The lipoproteins: Chylomicrons
Very low-density lipoprotein- Transportation of fats from the liver to the peripheral tissues.
The lipoproteins: VLDL
Low density lipoprotein: Remnants of very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL) which are supposed to go back into the liver occasionally wander around dropping cholesterol deposits.
The lipoproteins: LDL
High density lipoprotein: Transports fats from the peripheral tissue to the liver. Trash pick-up cure: Picks up metabolic trash.
The lipoproteins: HDL
Digestive Enzymes: The disaccharides are broken down by enzymes specific for each disaccharide.
Rule of thumb for naming these enzymes is adding the -ASE suffix to the substrate's name.
Sucrose is broken down by ?
Sucrase
Digestive Enzymes: The disaccharides are broken down by enzymes specific for each disaccharide.
Rule of thumb for naming these enzymes is adding the -ASE suffix to the substrate's name.
Maltose is broken down by ?
Maltase
Digestive Enzymes: The disaccharides are broken down by enzymes specific for each disaccharide.
Rule of thumb for naming these enzymes is adding the -ASE
Lactose is broken down by ?
Lactase
Explain the metabolic fat-trap between carbohydrates and lipids
Excess carbohydrates can become lipid stores, but they will never be able to be used as sugars again
The general formulae of the 4 lipid types
- fatty acids
- triglycerides (also called triacylglycerols)
- phospholipids
- cholesterol
Properties of lipids * Hint 2
Hydrophobic & calorie bombs
The simplest form of lipids are the fatty acids.
Carboxyl group