Med Chem 2 - 04/12 General Anesthetics
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Analgesia
Loss of consciousness
Relax muscles
Reduce reflex
Reversible CNS depression
What are the functions of general anesthetics and basically how does it occur?
Inhaled (volatile liquid, gas)
Inj
What are the types of general anesthetics?
Mostly structurally nonspecific: no specific receptor, activity based on physicochemical props
Highly lipophilic
What are the characteristics of inhaled anesthetics?
NOT USED ANYMORE
Meyer-Overton
Anesthetic action directly related to partition coeff
Mullins
Anesthetic action related to lipophilicity + volume it occupies
Critical volume causes membrane fluidization and ion channel distortion leading to NT depression
What are the lipid hypotheses of general anesthetics?
Anesthetics interact w/ or near inhibitory NT receptors like GABA-A
Explains why anesthetic potency increases to a certain point and then decreases though log P continues to increase b/c size of molecule > receptor pocket
What is the protein hypothesis of general anesthetics?
1: analgesia
2: excitement/delirium w/ amnesia, irregular resp, vomiting
3: surgical w/ regular resp
4: medullary depression w/ resp stop
What are the stages of general anesthesia?
NONE OF HAVE ALL
Nonflammable
Good chem and metabolic stability (dont want toxic metabolites)
Low myocardial effects
Rapid induction and emergence from anesthesia
Low hepatic/renal damage
Adequate SkM relxation
Wide margin of safety
What are the ideal inhaled anesthetic properties?
Blood-gas partition coefficient (BGPC): conc of blood/gas; want low value b/c faster recovery
Minimum alveolar conc (MAC): conc of drug in alveoli needed for 50% of pt to have no motor response as ATM; want low value b/c more potent b/c need less drugs
What are the important parameters of inhaled anesthetics and what do they relate to?
N2O
Cyclopropane
Ethylene
What are the gas inhaled general anesthetics?
Nitrous oxide (laughing gas)
Gaseous inhaled general anesthetic
BGPC: 0.47 (VERY QUICK RECOVERY)
MAC: 104% (LEAST POTENT)
Quick onset and recovery
Very safe
No SkM relaxation
Given w/ other anesthetic
Name?
Type?
MAC?
Advantages?
Disadvantages?
Use?
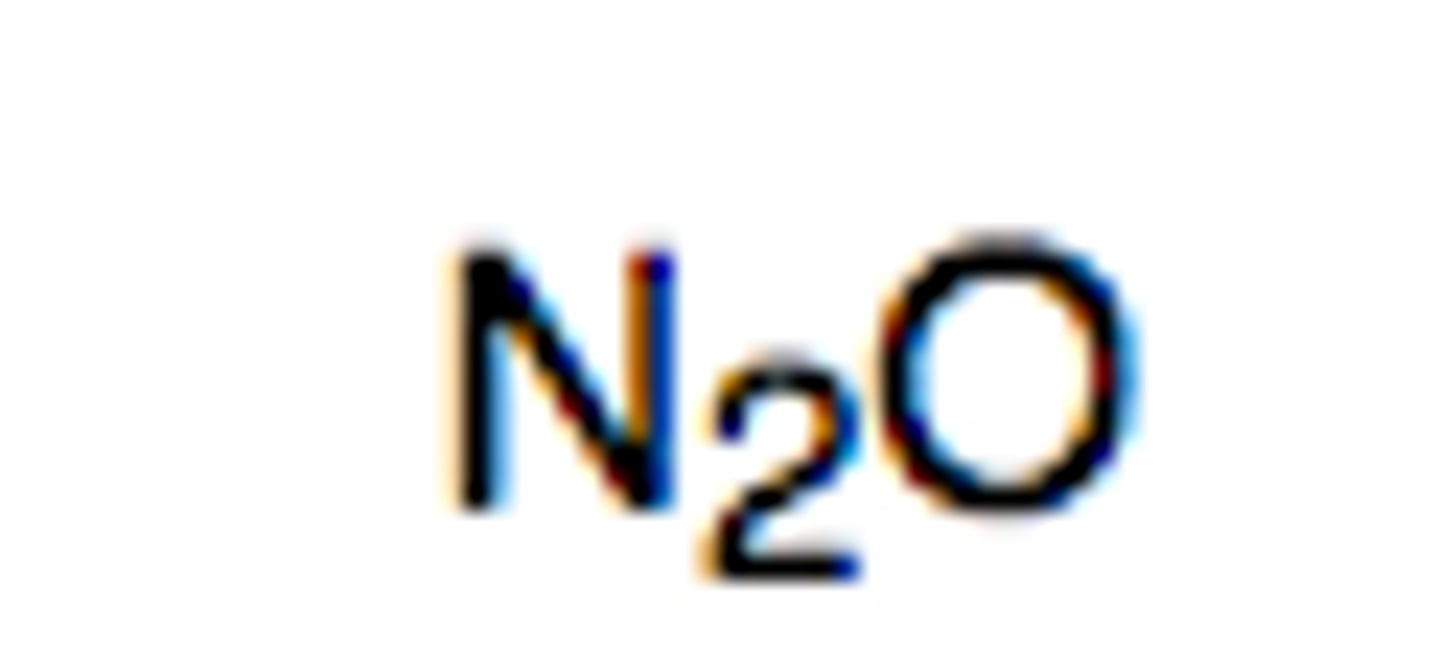
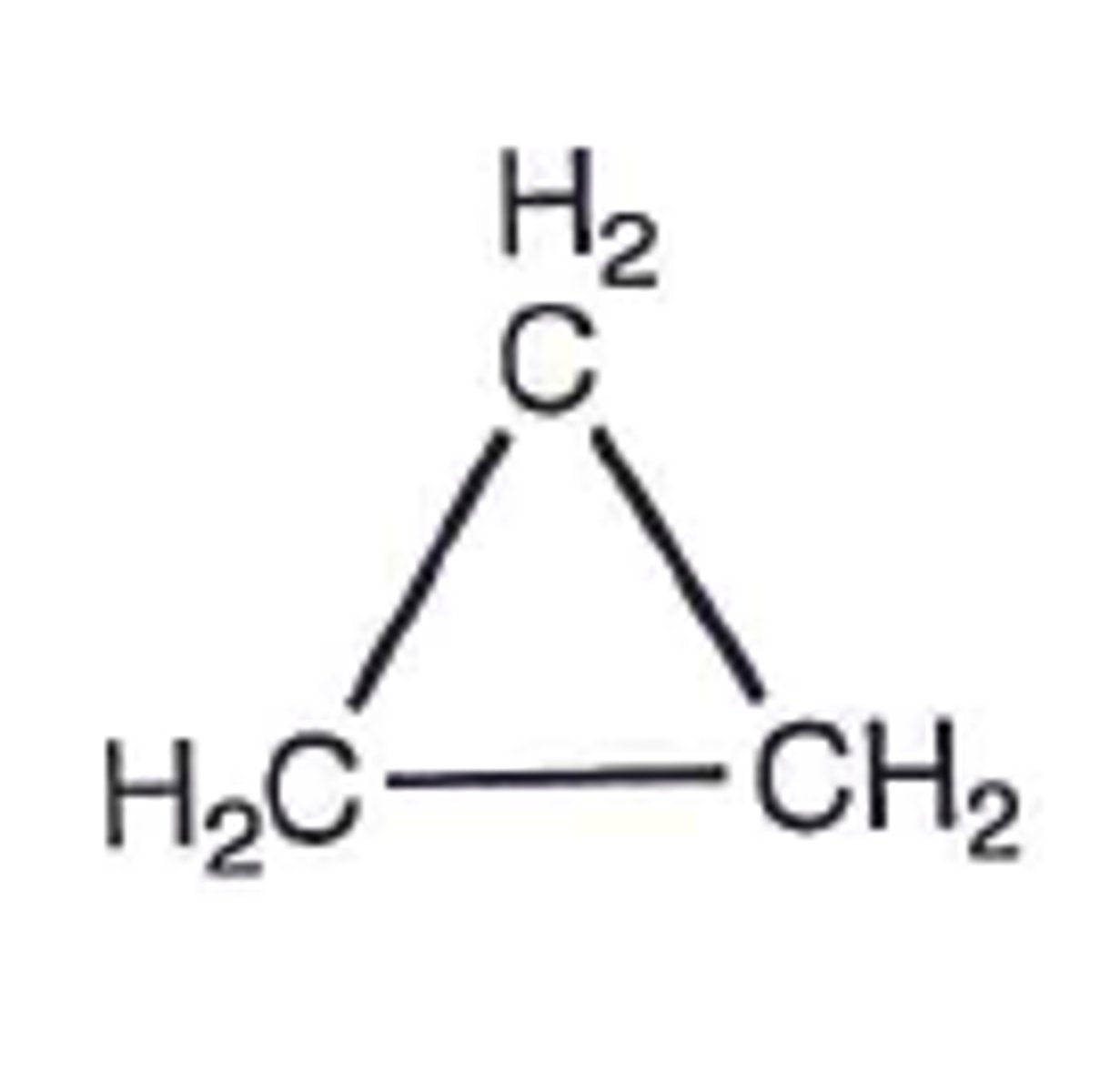
Cyclopropane
Gaseous inhaled general anesthetic
MAC: 17% (MOST POTENT GASEOUS)
Quick onset and recovery
SkM relaxation
Explosive
Not used anymore
Name?
Type?
MAC?
Advantages?
Disadvantages?
Use?
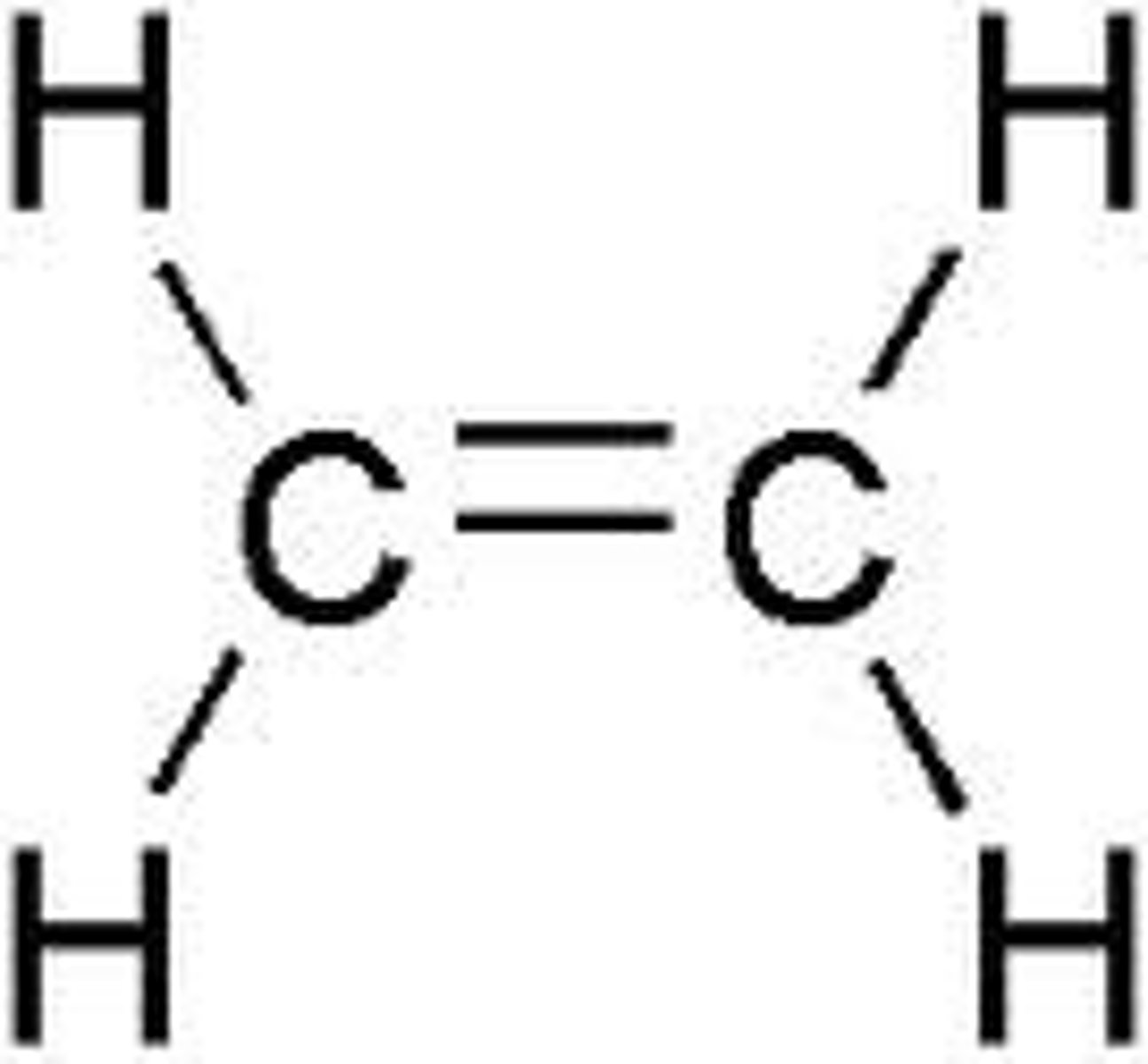
Ethylene
Gaseous inhaled general anesthetic
MAC: 80% (LESS POTENT THAN CYCLOPROPANE)
Quick onset and recovery
NoSkM relaxation
Explosive
Not used anymore
Name?
Type?
MAC?
Advantages?
Disadvantages?
Use?
Halothane
Enflurane
Isoflurane
Desflurane
Sevoflurane
What are the liquid inhaled general anesthetics?
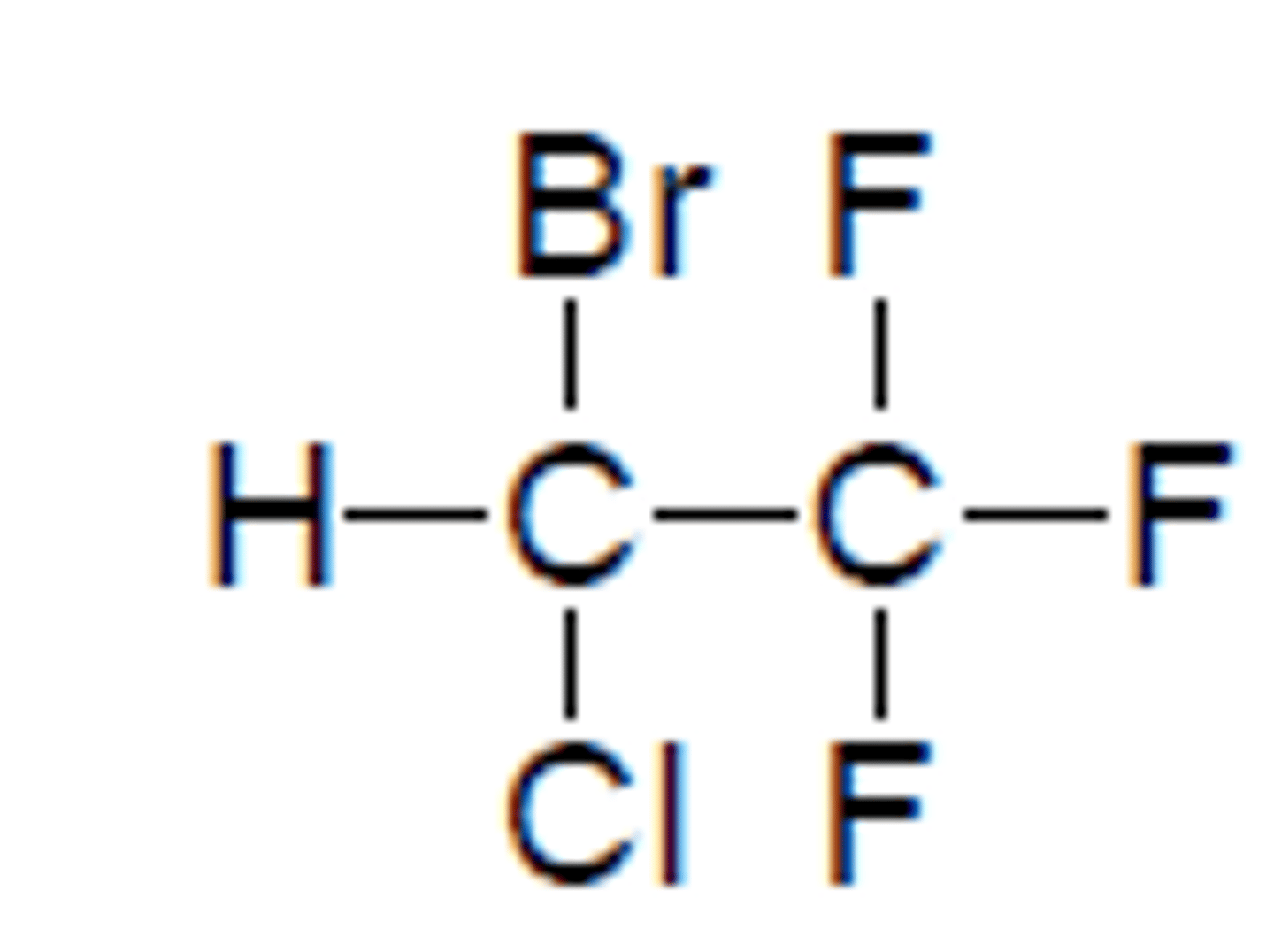
Halothane
Liquid inhaled general anesthetic
Prototypical
RACEMIC
BGPC: 2.5 (SLOWEST ONSET)
MAC: 0.74% (MOST POTENT)
BP: 50.2C
Quick onset and recovery
Potent
20% metabolism releasing Br, Cl, F, TFA
TFA: strong acid
Br & Cl: arrhythmias
F: kidney/renal problems
Not used anymore
Name?
Type?
BGPC?
MAC?
BP?
Advantages?
Disadvantages?
Use?
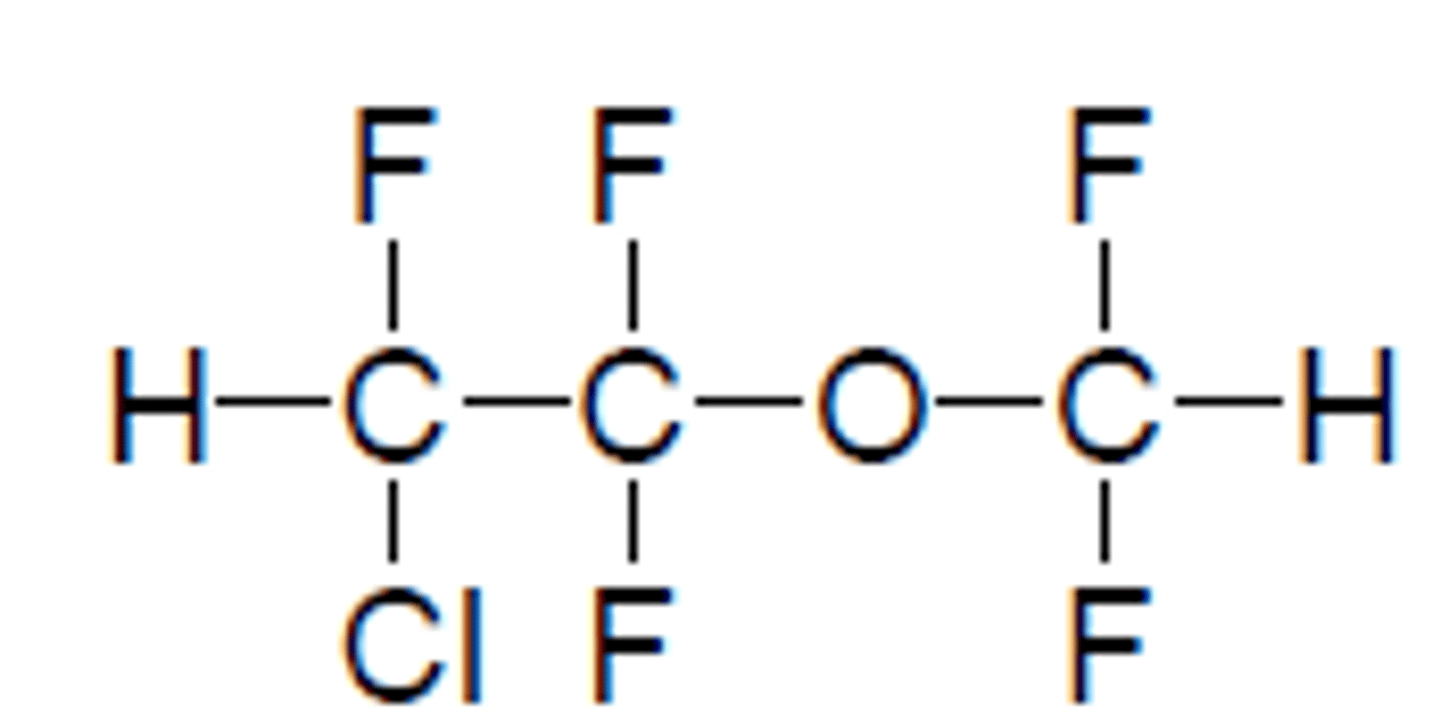
Enflurane
Liquid inhaled general anesthetic
RACEMIC
Orange cap
BGPC: 1.9 (MORE RAPID THAN HALOTHANE)
MAC: 1.7% (LESS POTENT THAN HALOTHANE)
BP: 56.5C
Quick onset and recovery
Potent
SkM relaxation
5% metabolism releasing Cl, F (< halothane)
F: kidney/renal problems
Cl: arrhythmias
Name?
Type?
Cap?
BGPC?
MAC?
BP?
Advantages?
Disadvantages?
Use?
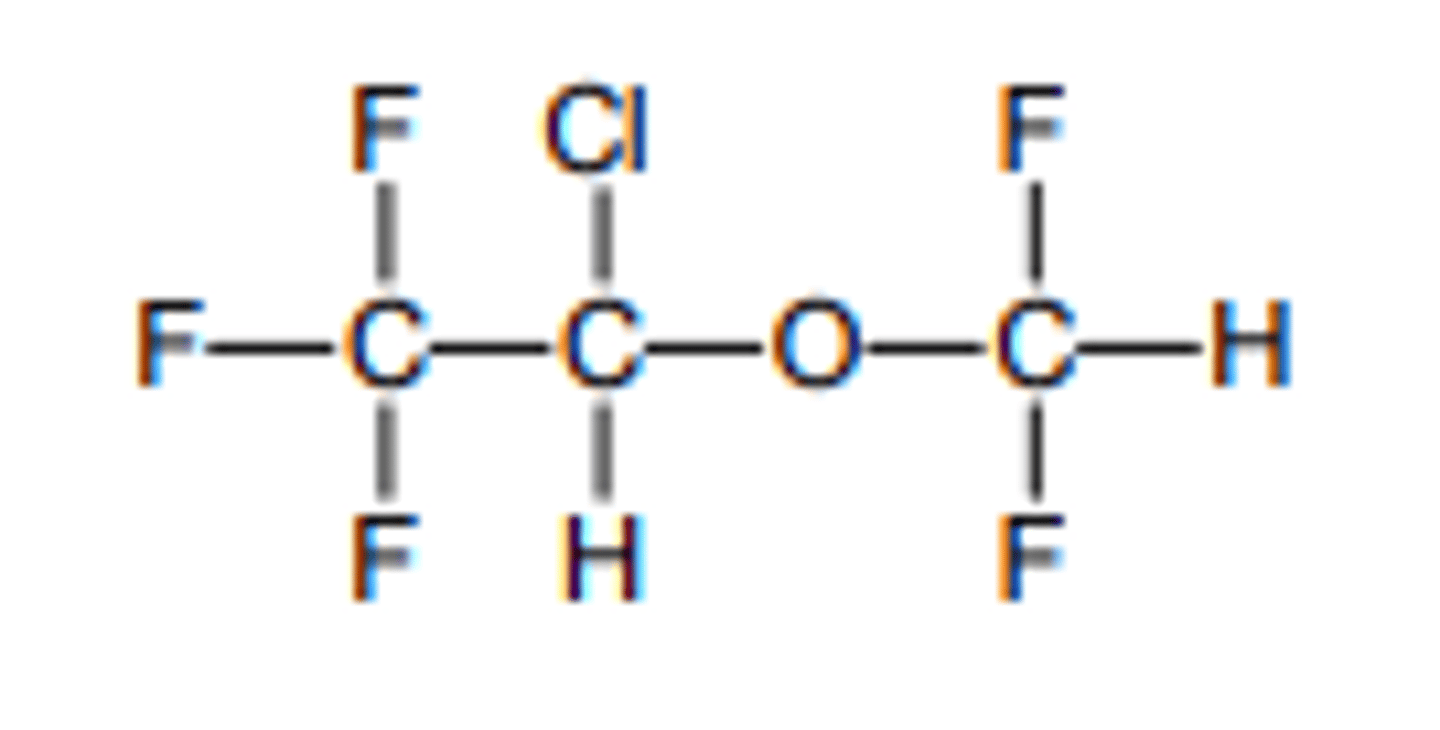
Isoflurane
Liquid inhaled general anesthetic
RACEMIC
Isomer of enflurane
Purple cap
BGPC: 1.4 (MORE RAPID THAN ENFLURANE)
MAC: 1.17% (MORE POTENT THAN ENFLURANE)
BP: 48.5C
Quick onset and recovery
Potent
SkM relaxation
0.2% metabolism releasing F, Cl (< enflurane)
F: kidney/renal problems
Cl: arrhythmias
Name?
Type?
Cap?
BGPC?
MAC?
BP?
Advantages?
Disadvantages?
Use?
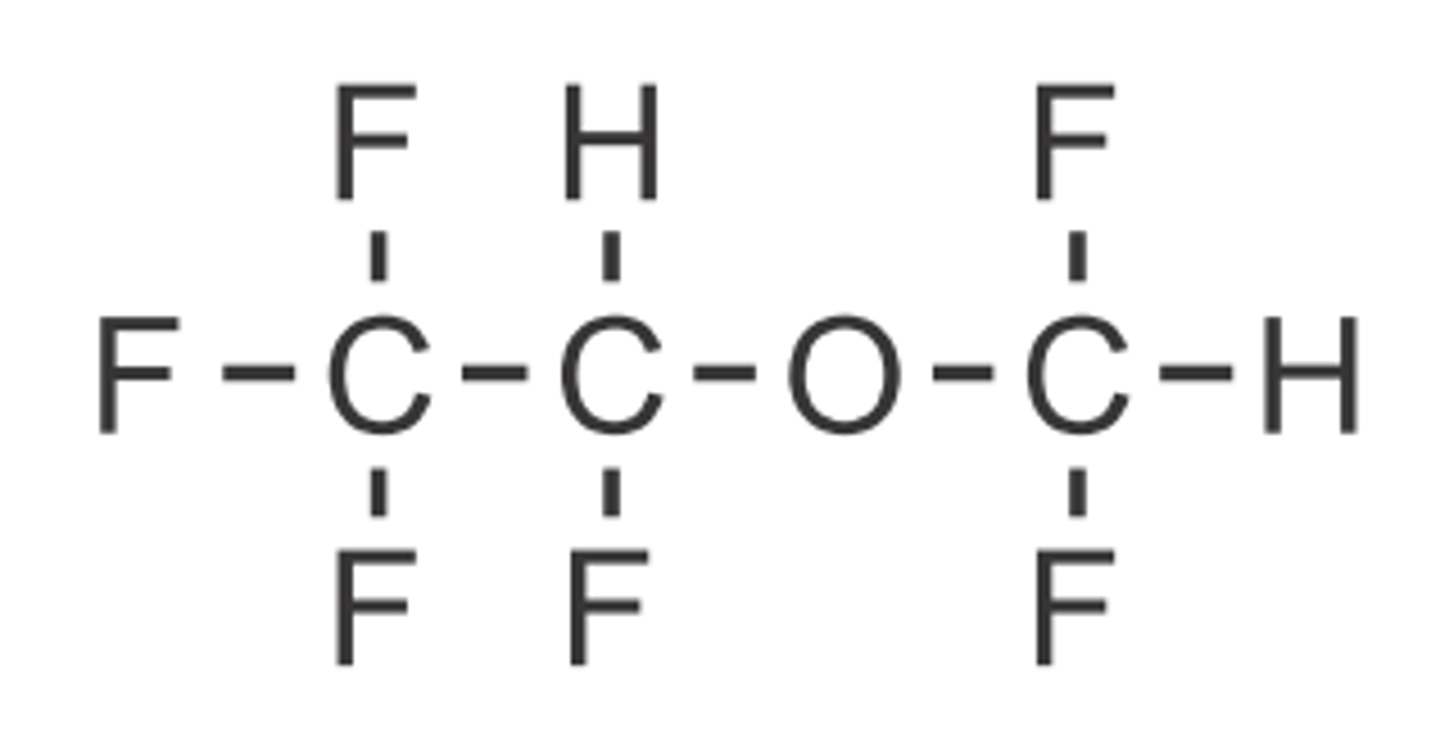
Desflurane
Liquid inhaled general anesthetic
RACEMIC
Blue cap (different b/c very volatile)
BGPC: 0.42 (MOST RAPID OF FLURANES)
MAC: 6% (LEAST POTENT OF FLURANES)
BP: 23.5C (LOWEST REQUIRING DIFF CAP)
Quick onset and recovery
Potent
SkM relaxation
<0.02% metabolism (LOWEST)
Airway irritation: not good for prolonged induction, peds
Name?
Type?
BGPC?
MAC?
BP?
Advantages?
Disadvantages?
Use?
Sevoflurane
Liquid inhaled general anesthetic
ACHIRAL
Yellow cap
BGPC: 0.68
MAC: 2.05%
BP: 58.6C (HIGHEST)
Quick onset and recovery
Very safe
SkM relaxation
Pleasant taste/smell
5% metabolism releasing F
F: kidney/hepatic problems
Usable in peds
Name?
Type?
Cap?
BGPC?
MAC?
BP?
Advantages?
Disadvantages?
Use?
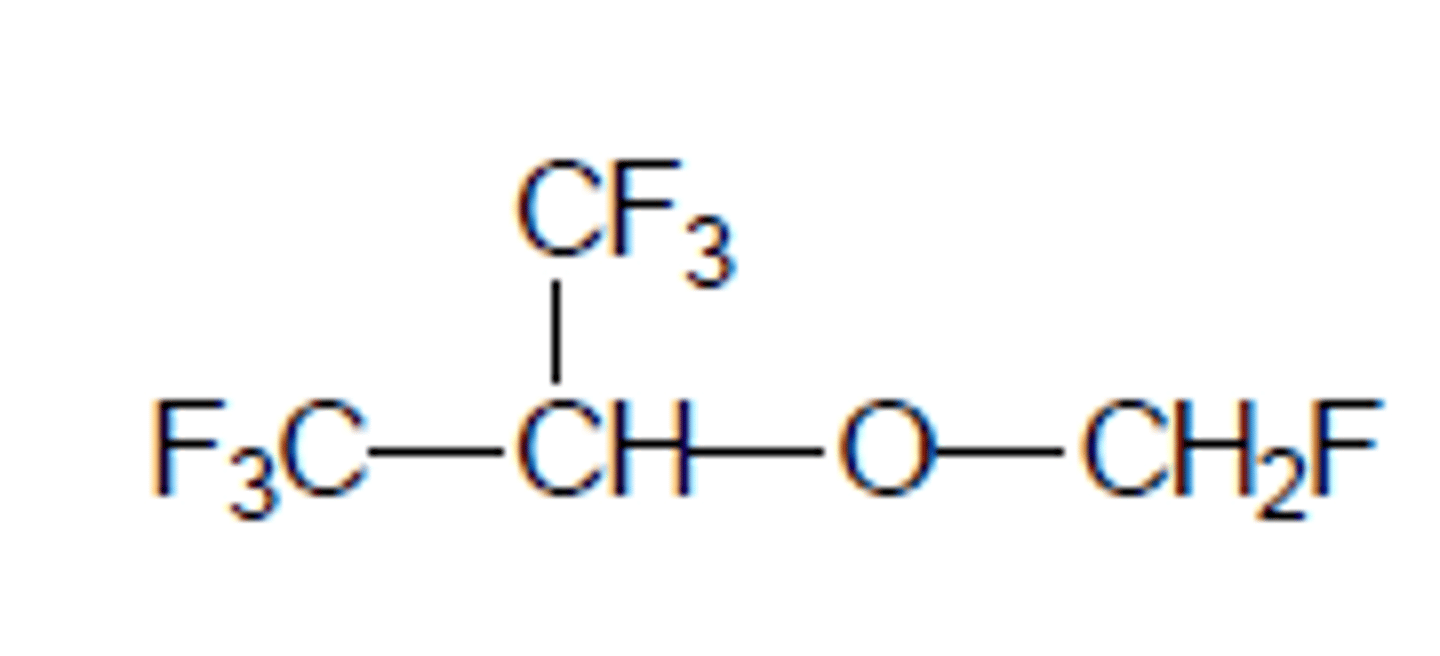
Halide ADRs
Br, Cl: sensitize myocardium to NE and Epi leading to Vfib, arrhythmias
F: kidney/hepatic damage
Low flammability, enhanced partitioning into lipid layers
What are the advantages/disadvantages of halogenated anesthetics?
Halothane >> sevoflurane > enflurane > isoflurane > desflurane
What is the comparative ADR profiles of liquid inhaled general anesthetics?
Halothane > isoflurane > enflurane > sevoflurane > desflurane
What is the comparative potency profiles of liquid inhaled general anesthetics?
Halothane > enflurane > isoflurane > sevoflurane > desflurane
What is the comparative recovery profiles (decreasing time) of liquid inhaled general anesthetics?
No special equipment
Many w/ faster onset than inhaled (no absorption)
Rapid recovery (suitable for outpatient)
What are the advantages of IV general anesthetics?
Ketamine
Esketamine
Propofol
Midazolam
Remimazolam
Etomidate
Methohexital
Thiopental
What are the IV general anesthetics?
Ketamine
IV general anesthetic
RACEMIC
C3 drug
NMDA receptor antagonist
Oxidative demethylation to norketamine (1/3 as active but can be greater conc than parent)
Alpha-oxidation then glucuronidation or DB creation
No SkM relaxation
Abuse potential
Hallucinations for 24hrs (similar to PCP)
Dissociative amnesia w/o loss of consciousness
Diagnostic and treatment surgery not requiring SkM relaxation
Name?
Type?
Controlled?
MoA?
Metabolism?
Advantages?
Disadvantages?
Use?
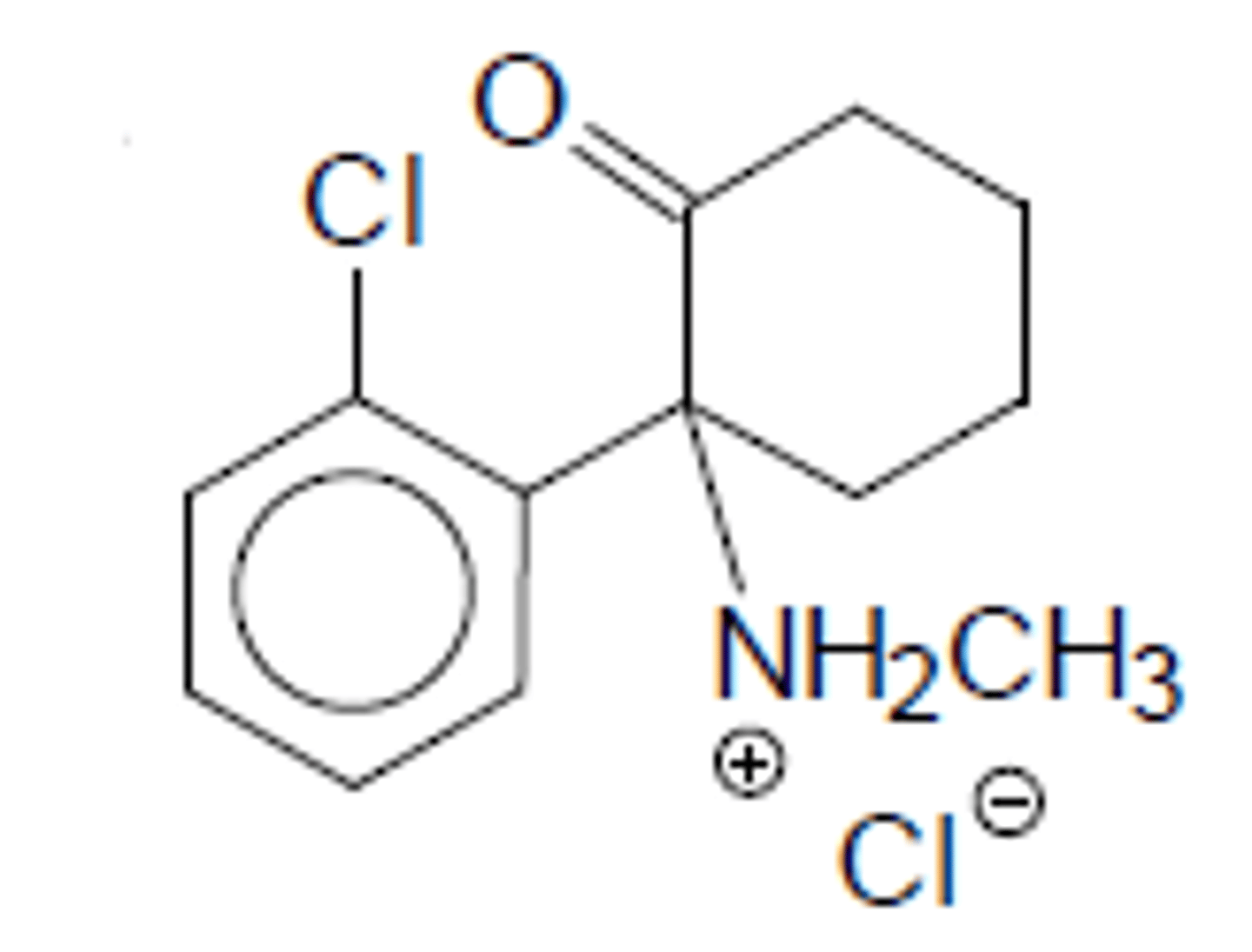
Esketamine
NASAL SPRAY (recently approved)
S-ketamine
C3 drug
Treatment-resistant depression w/ PO antidepressants
Name?
Type?
Controlled?
Use?
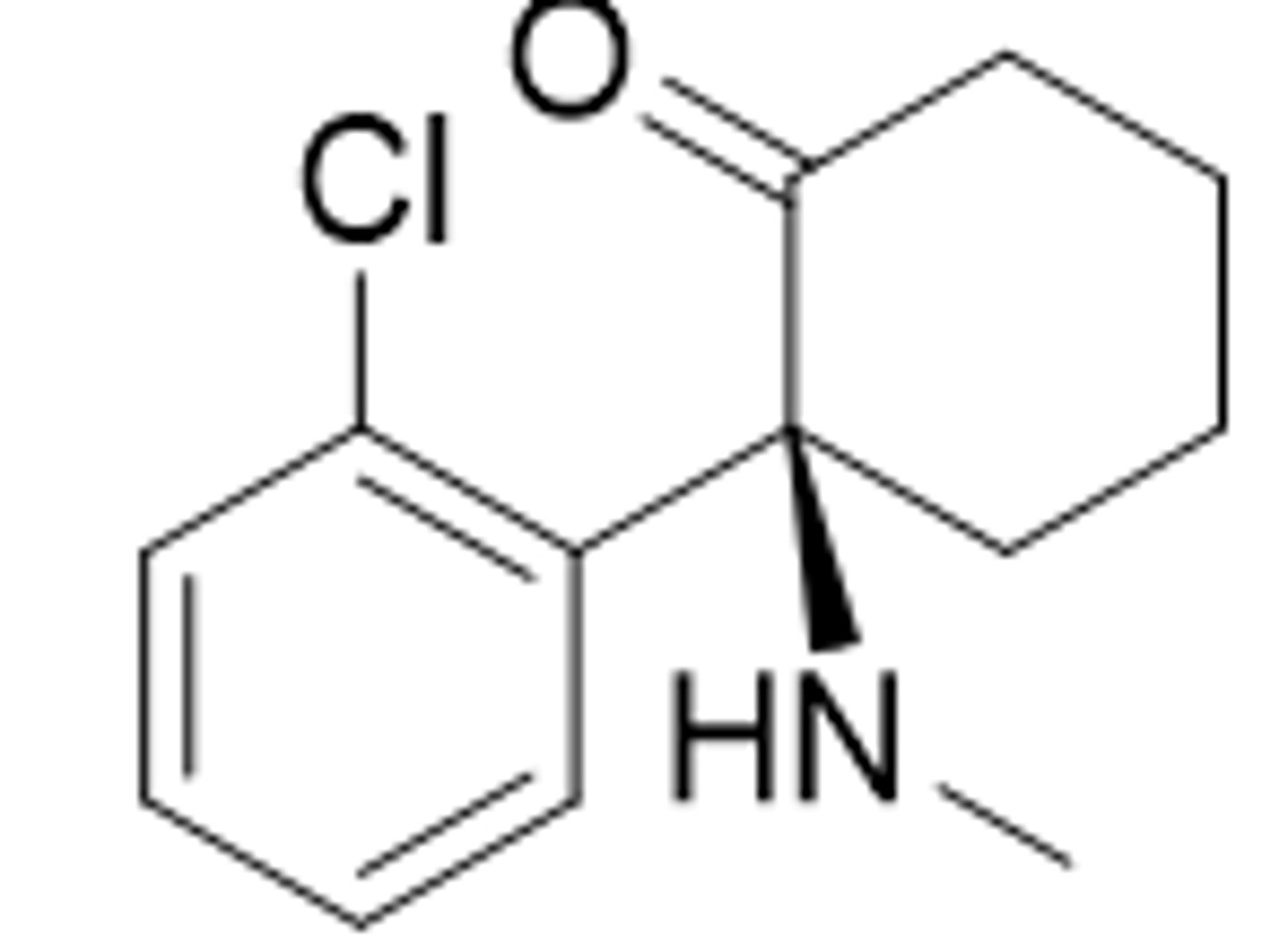
Propofol
IV general anesthetic
Not controlled
Enhance GABA transmission (unsure of exacting binding)
<0.3% unchanged b/c rapid gluc or sulf conjugation
<1min onset
Rapid recovery
Antiemetic properties
SkM relaxation
Needs to be formulated as emulsion b/c very lipophilic which leads to allergies, bacterial growth, etc
Induction/maintenance of anesthesia
ICU
Drug of choice for ambulatory surgery
Name?
Type?
Controlled?
MoA?
Metabolism?
Advantages?
Disadvantages?
Use?
Fospropofol
IV general anesthetic
Prodrug version of propofol
C4 drug
Enhance GABA transmission (unsure of exacting binding)
Activated by alkaline phosphatase which removes phosphate and triggers OCH2 removal
<0.3% unchanged b/c rapid gluc or sulf conjugation
Rapid recovery
Antiemetic properties
SkM relaxation
INCREASED SOLUBILITY
Slower onset than normal (4 to 8min)
Induction/maintenance of anesthesia
ICU
Drug of choice for ambulatory surgery
Name?
Type?
Controlled?
MoA?
Metabolism?
Advantages?
Disadvantages?
Use?
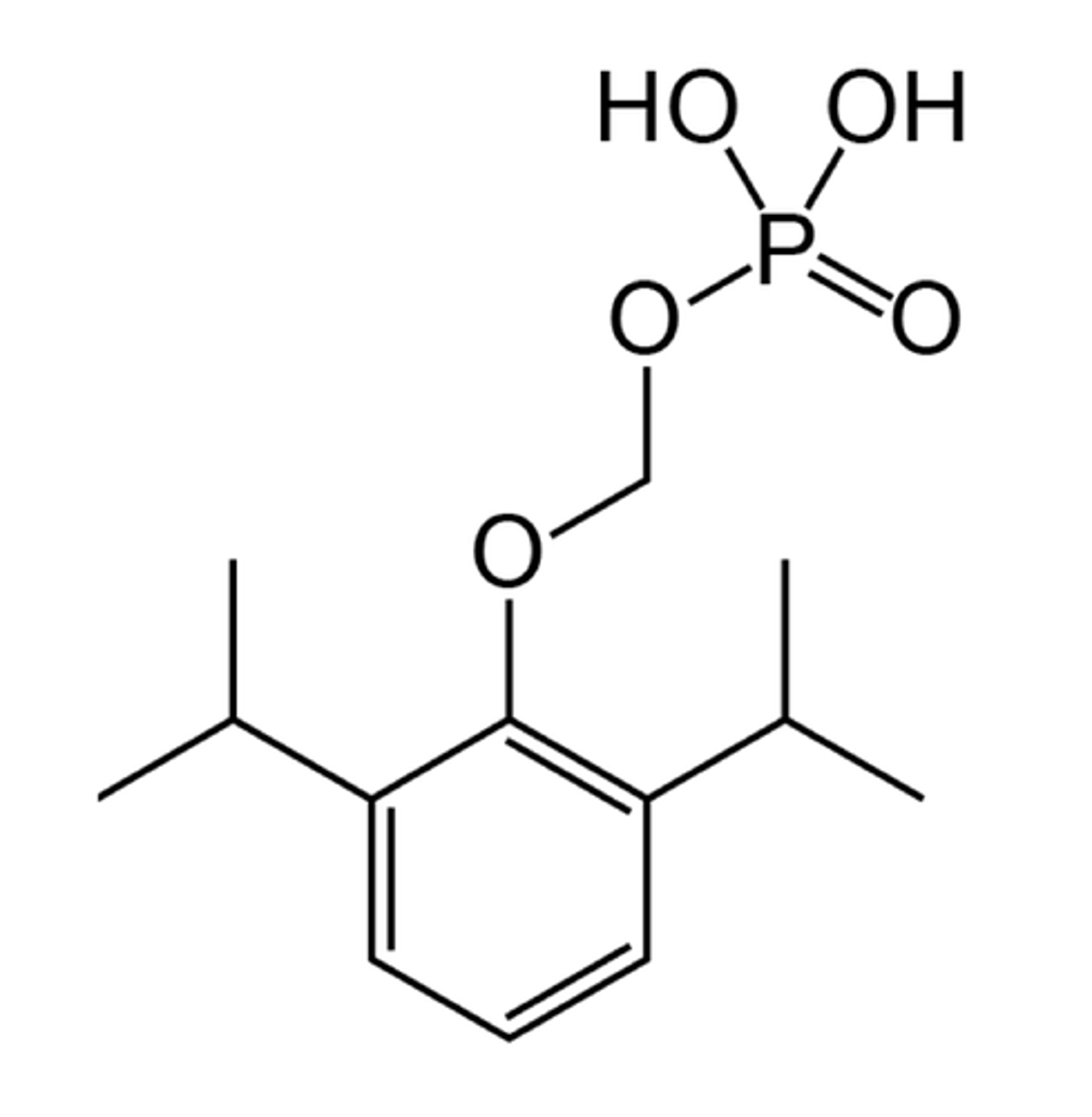
Midazolam
IV general anesthetic (can be PO or IM but 10min onset)
Benzodiazepine
C4 drug
Methyl hydroxylation then conjugation
SkM relaxation
Can reverse prolonged activity w/ flumazenil (benzo antag)
Longer onset than propofol, barbs (<5min)
Long recovery (2 to 7hr HL)
Minor sedation, mechanical ventilator sedation
Name?
Type?
Controlled?
Metabolism?
Advantages?
Disadvantages?
Use?
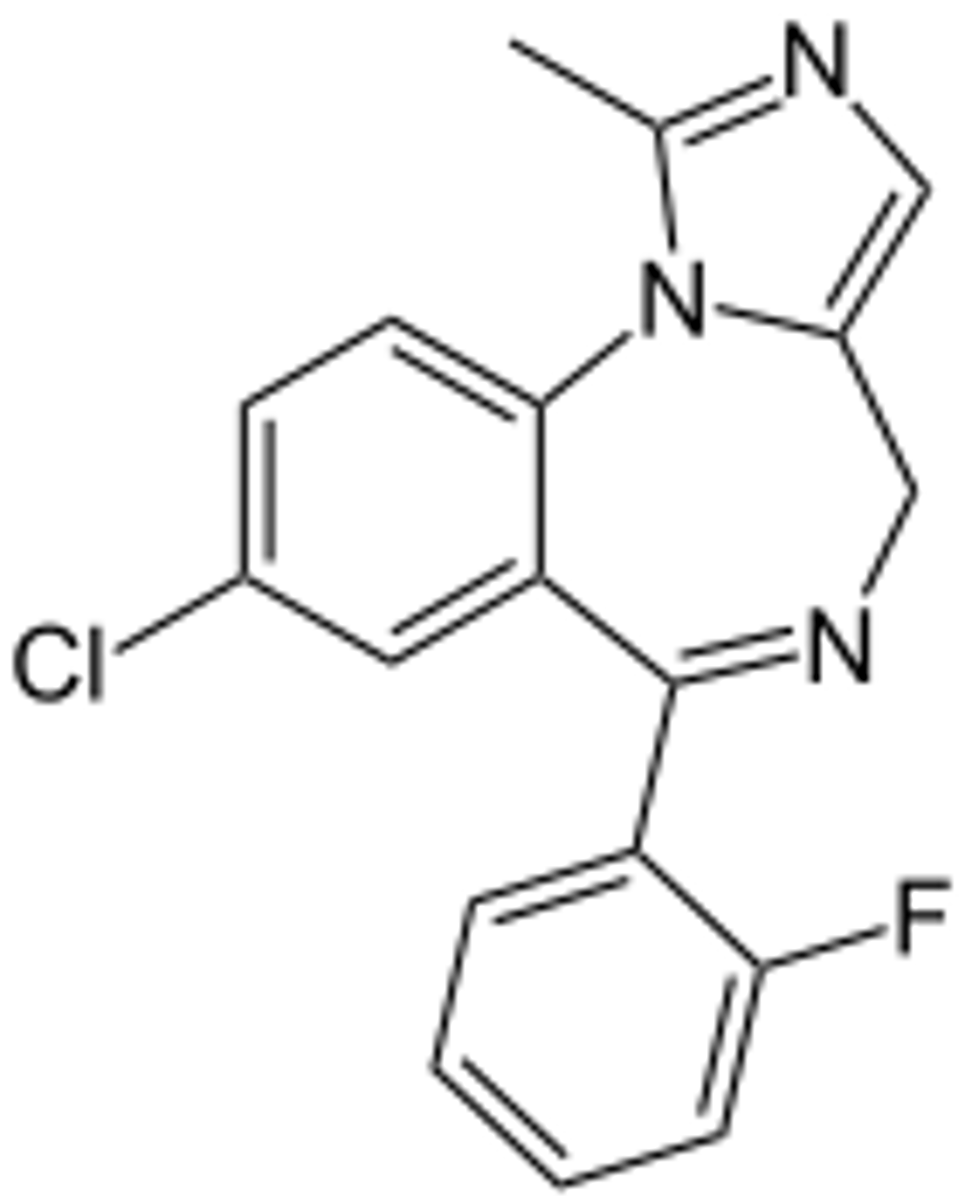
Remimazolam
IV general anesthetic
R-enantiomer only
Benzodiazepine
C4 drug
Esterase hydrolysis to COOH to create 300x less active drug
SkM relaxation
Onset >1m (faster than midazolam)
Duration 15m (lower than midazolam)
VERY SHORT ACTING
Induction (inf over 1 min) and maintenance (over 15sec) of procedures <30min
Name?
Type?
Controlled?
Metabolism?
Advantages?
Disadvantages?
Use?
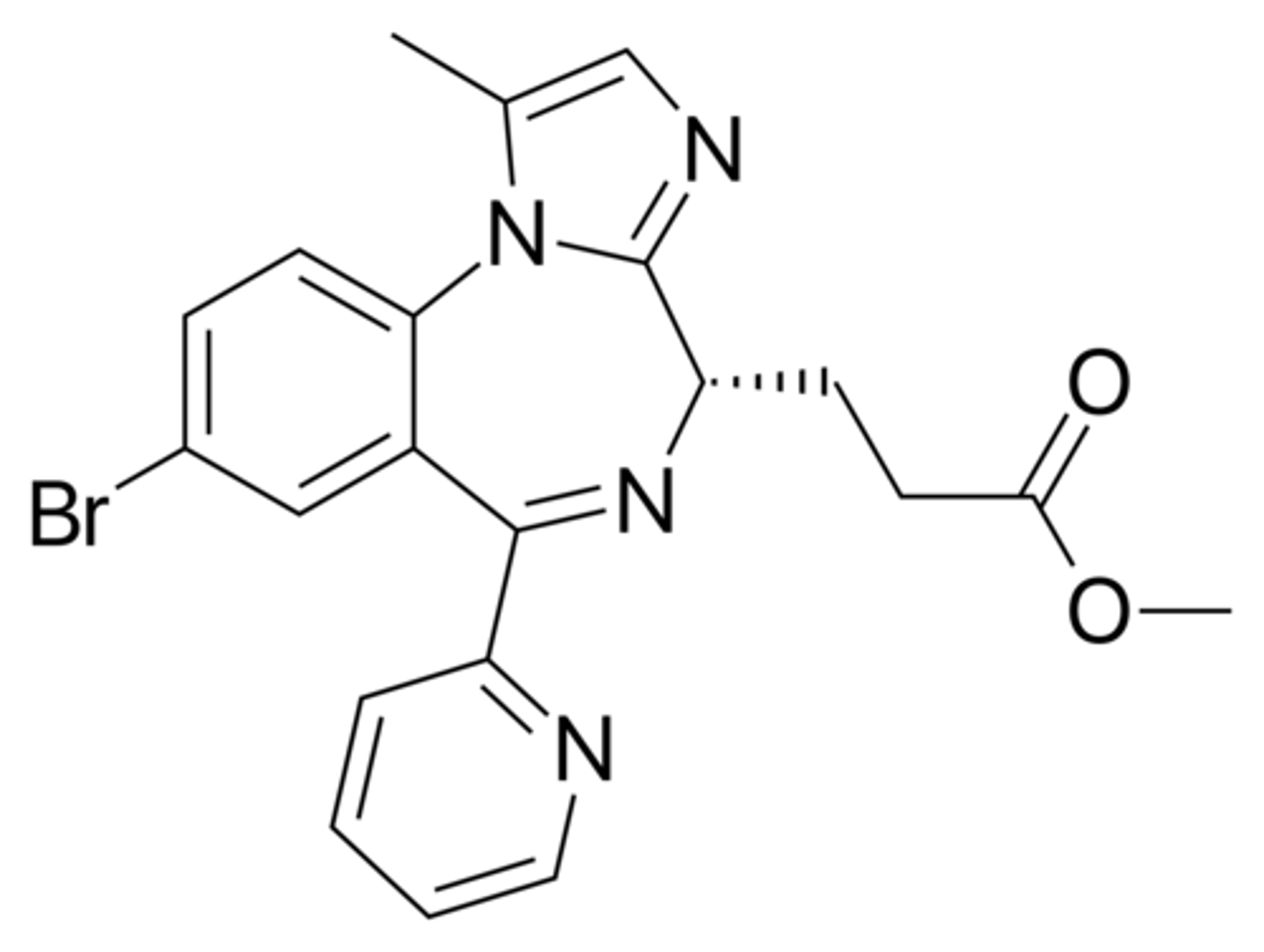
Etomidate
IV general anesthetic
Not controlled
Ester hydrolysis rapidly
Hypnosis w/in 1min
Lasts only 3 to 5min (VERY SHORT)
Less CV tox
No analgesia
No SkM relaxation
Cardioversion
Very short procedures
Name?
Type?
Controlled?
Metabolism?
Advantages?
Disadvantages?
Use?
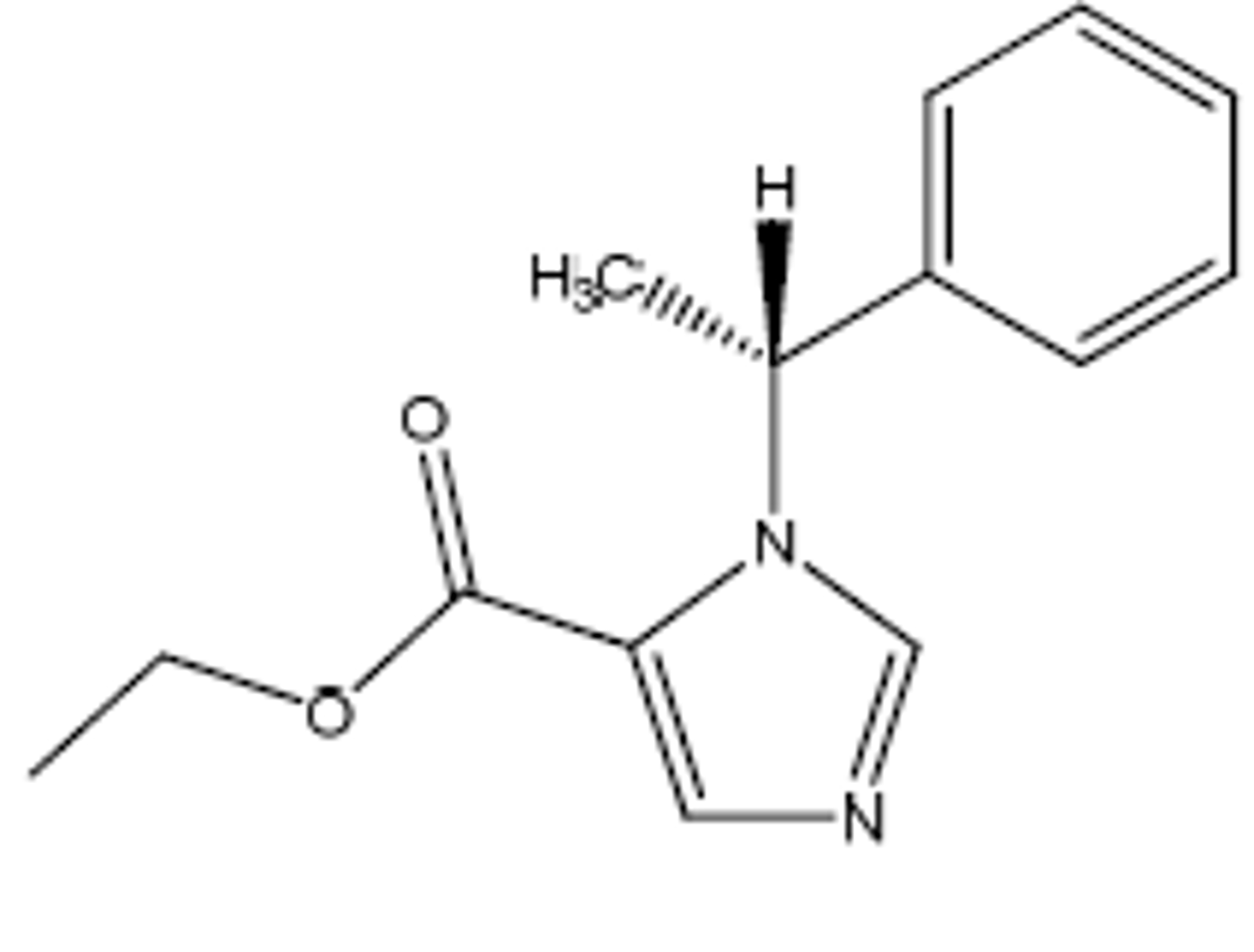
Methohexital
IV general anesthetic
Ultrashort acting barbiturate
C4 drug
<1m onset
C5 branches including DB metabolized: <20min duration
No SkM relaxation
Induction of anesthesia, procedural sedation
Name?
Type?
Controlled?
Metabolism?
Advantages?
Disadvantages?
Use?
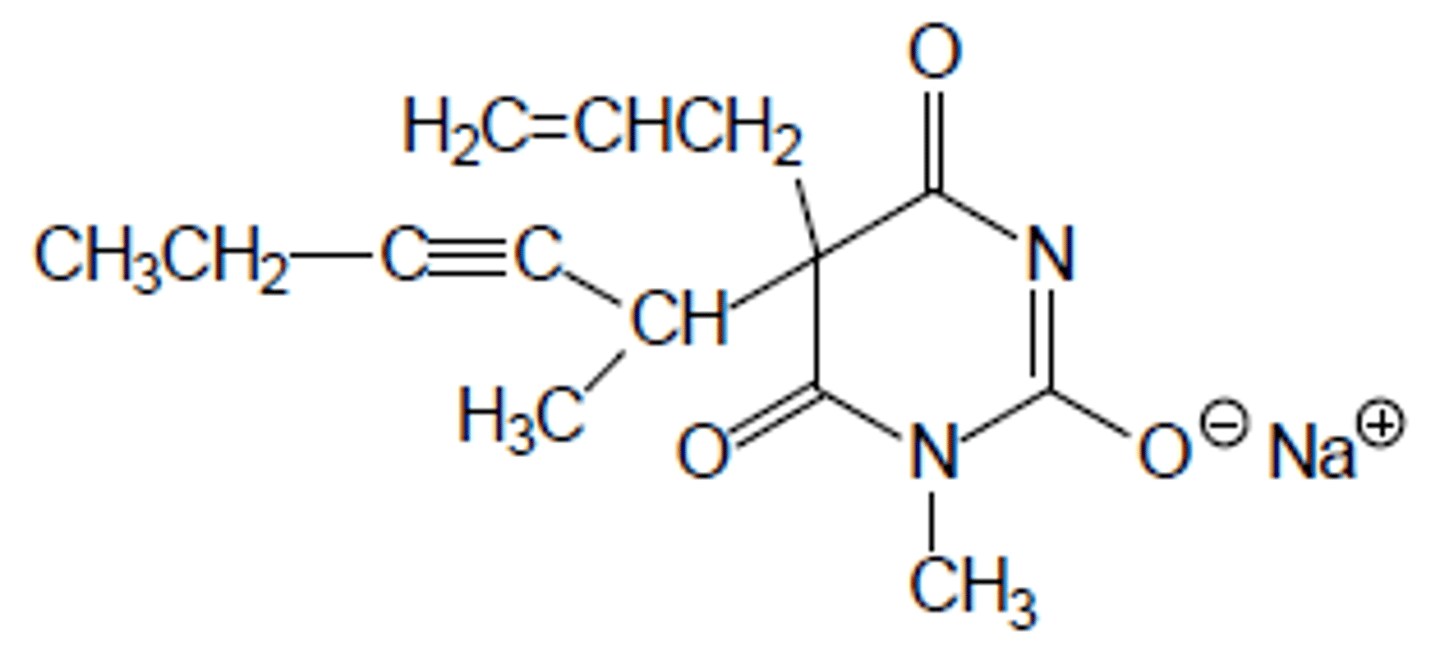
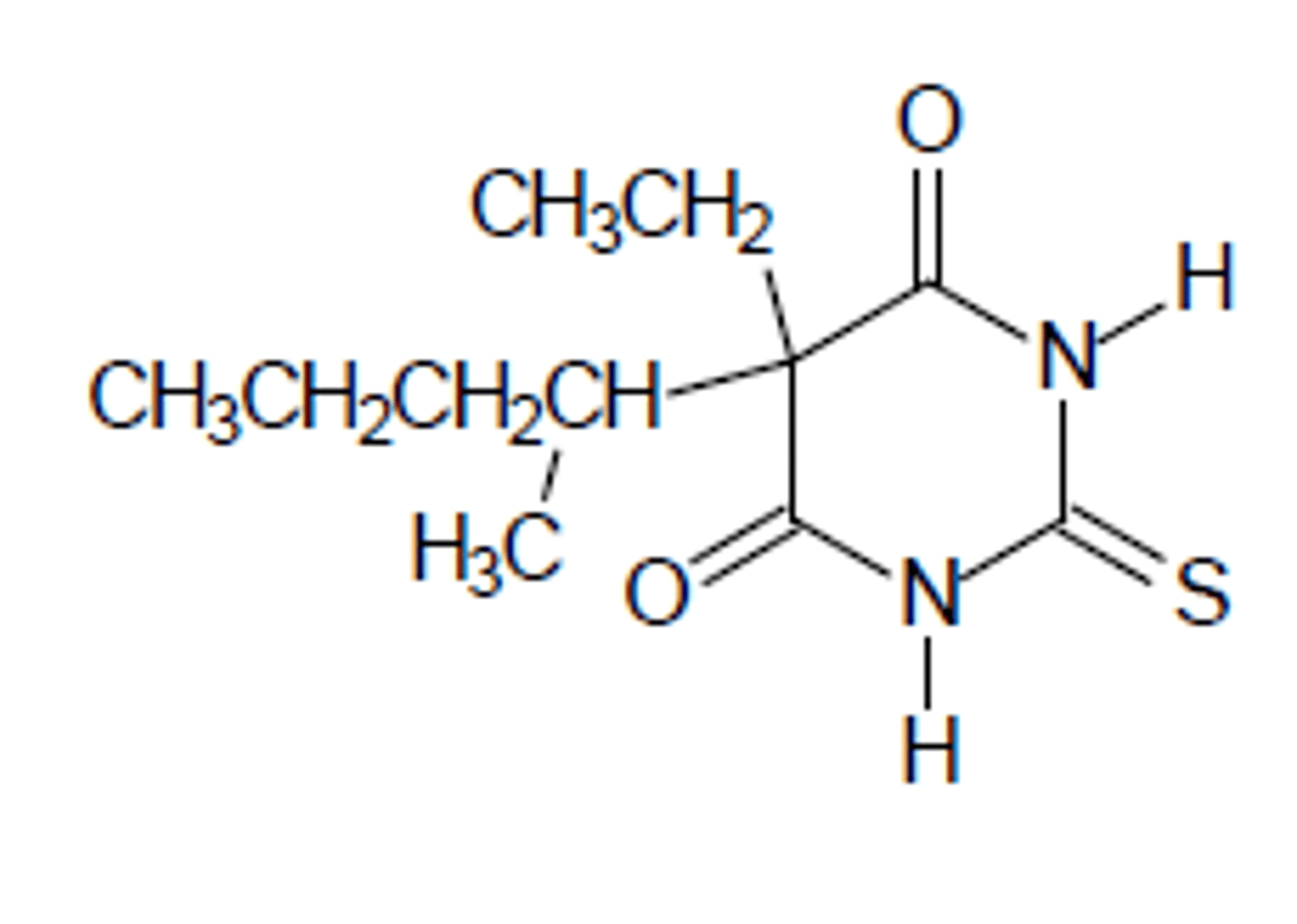
Thiopental
IV general anesthetic
Ultrashort acting barbiturate
C3 drug
Can have S=O metabolized to C=O to create less lipophilic + increased duration product (PENTOBARBITAL)
Longer acting than methohexital
No SkM
Replaced by propofol
Name?
Type?
Controlled?
Metabolism?
Advantages?
Disadvantages?
Use?