Exam 2: Greek - Islamic Art & Vocab
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Greek through islamic art for Art History Exam 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Cycladic
3000-1600 BCE
Minoan
1900-1375 BCE
Mycenaean
1600-1100 BCE
Geometric
900-700 BCE
Archaic
600-480 BCE
Classical
480-338 BCE
Hellenistic
338- (roman conquest) 31 BCE

What: Bull leaping
When: 1550-1450 BCE
Where: Greece - Minoan
How made: Wall painting
Why/Significance? The act of bull-leaping is significant to Minoan culture and this piece gives expression to that act, this piece also relates to the idea of human triumphing of animal.
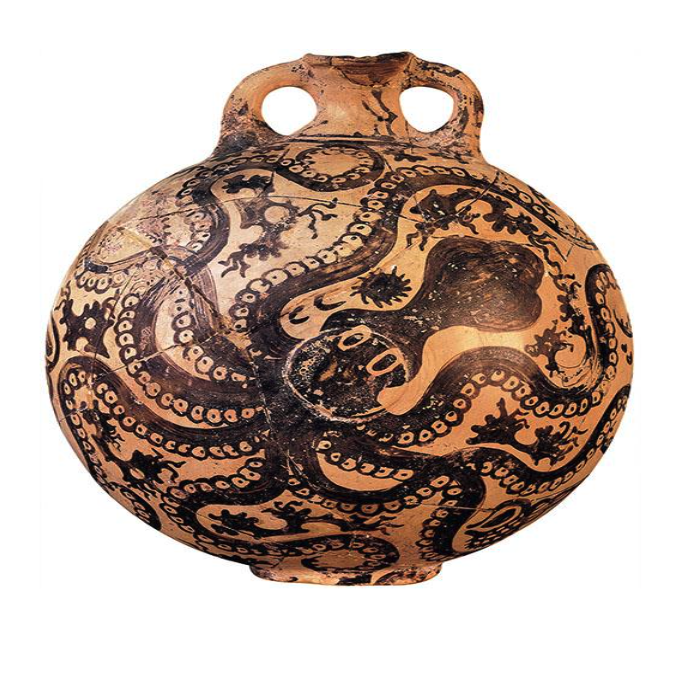

What: Octopus Flask
When: 1500-1450 BCE
Where: Palaikastro, Crete — Minoan
How made: Ceramic
Why made/Significance? This Minoan style of painting pottery was later picked up in greek art forms. The octopus is also hand painted onto the pottery suggesting some appreciation for the sea to take up the entire space and hand paint this piece.

What: Interior of Tholos tomb (Treasury of Atreus)
When: 1350-1250 BCE
Where: Mycenae, Greece
How made: Corbeling— Corbeled vault
Why made/Significance? This displays the way that Mycenaean’s would bury their dead because it is from a tomb. Specifically, the Treasury of Atreus was built for the burial of a Mycenaean king.
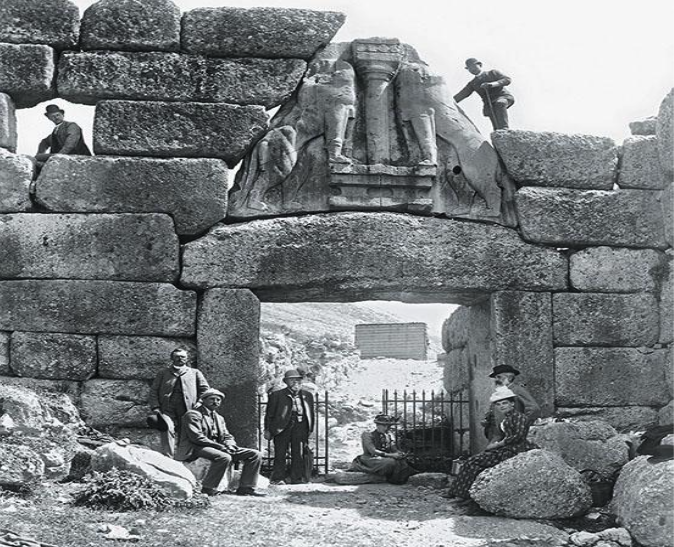

What: Lion Gate
When: 1250 BCE
Where: Mycenae
How made: Limestone relief carving with corbeling surrounding
Why made/Significance? The Lion gate was made as part of the defensive walls and location that was Mycenae. The choice of lions would also be used to ward off evil or terrify enemies because it is a powerful animal and this imagery is used at a gate/entrance. Evidence of early greek art —> Minoan style column v.s. Greeks later use of columns.
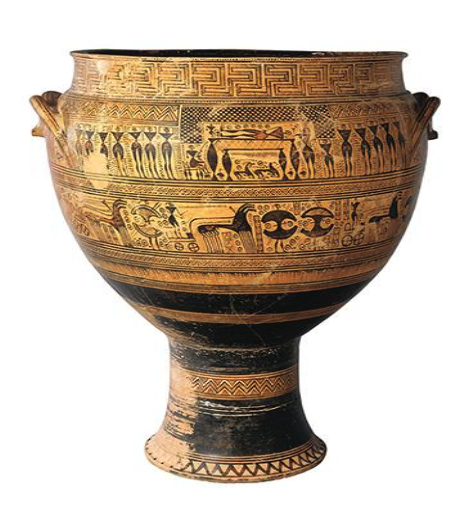

What: Funerary Vessel (krater)
When: 750-735 BCE
Where: Athens, Greece
How made: Ceramic, pottery with black paint
Why made/Significance? Funerary vessel used to mark a grave site because of the friezes painted on the pot. The opening in the pot could be used for an offering or to empty rain water

What: Kouros
When: 600 BCE
Where: Greece
How made: sculpture
Why made/Significance? Kouros were often grave markers. They depicted male youths and sometimes gods.

What: Peplos Kore
When: 530 BCE
Where: Acropolis, Athens, Greece
How made: Sculpture
Why made/Significance? Kore were often grave markers. They depicted female youths and sometimes goddesses.

What: Achilles and Ajax playing a dice game
When: 540-530 BCE
Where: Greece
Artist: Exekias
How made: Black figure vase painting/black slip, red clay
Why made/Significance? Relaxed interaction between the two major players in the Trojan war as told in the Illiad(Achilles and Ajax as noted by text near them), piece of greek history for this depiction. (different view with knowledge of the Illiad: foreshadowing for the two characters)
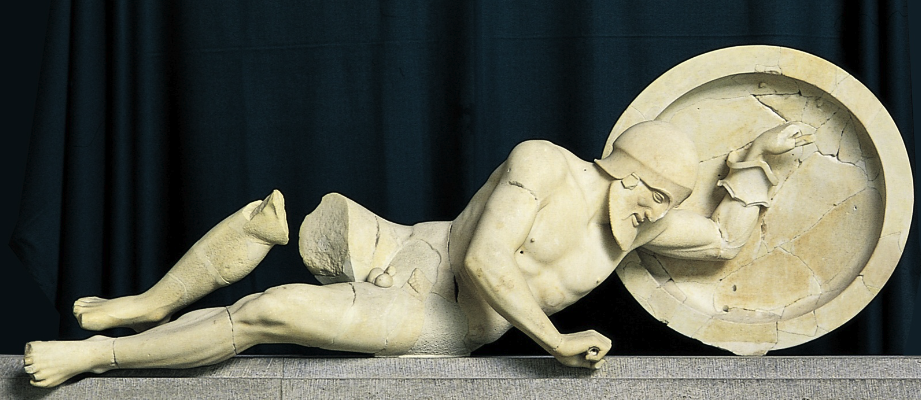

What: Dying warrior
When: 480 BCE
Where: Easy pediment of the temple of Aphaia; Aegina, Greece
How made: Marble sculpture
Why made/Significance? Dying warrior on east pediment shows the transition from archaic style into classical style. The statue still has the archaic smile, but has more tense and naturalistic features rather than rigidy and abstraction of previous styles.

What: Doryphoros
When: 450-440 BCE
Artist: Polykeitos
Where: Greece
How made: Original - Bronze, Roman copy - Marble
Why made/Significance? Established Polykleitos’ canon of proportions and shifted to contrapposto.
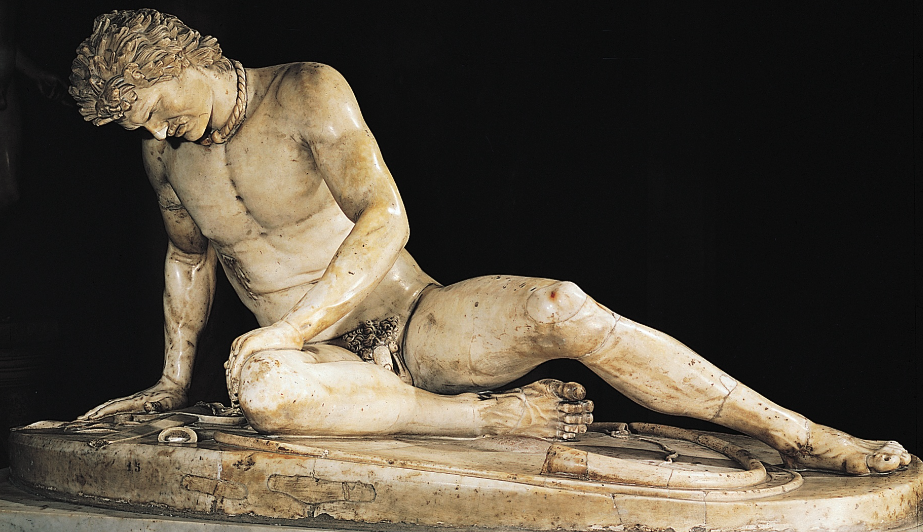

What: Dying Gaul
When: 230-220 BCE
Artist: Epigonos
Where: Greece/Rome(copy)
How made: Bronze(original)/Marble(roman copy)
Why made/Significance? Depicts the defeat of the Gauls. The sculpture has more realisim in it's depiction but also has the dramatasism of the hellenistic era
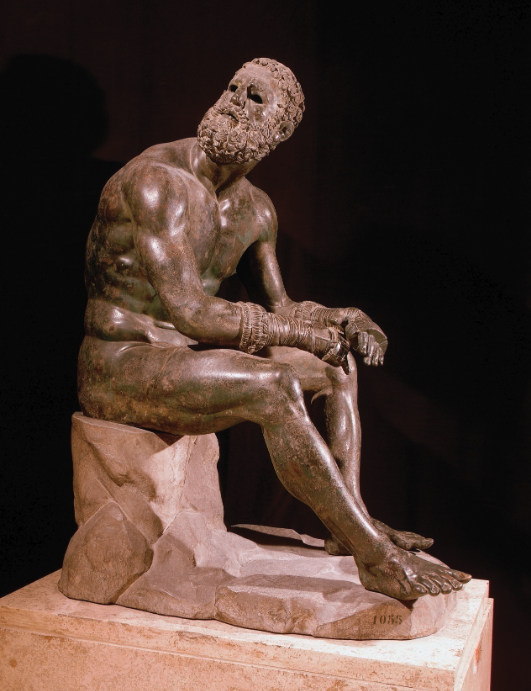

What: Seated boxer
When: 100-50 BCE
Where: Greece
How made: Bronze sculpture
Why made/Significance? Represents a shift to more emotional and diverse subjects of greek sculpture
necropolis
A large ancient cemetery with elaborate tomb monuments
Sarcophagi
stone coffins, usually adorned with sculptures or inscriptions
Patricians
Aristocratic families or noble class who held power and influence in the Roman Republic
Verism
A style of Roman sculpture characterized by hyper-realistic portrayal of subjects, emphasizing age and imperfection
Roman arch
Roman construction that allowed for larger and more stable structures
aqueduct
Roman watercourse constructed to get water from one location to another over a long distance
arcade
A series of arches used in architecture

voissoirs
Wedge-shaped stones used to form an arc (used w/ keystone)
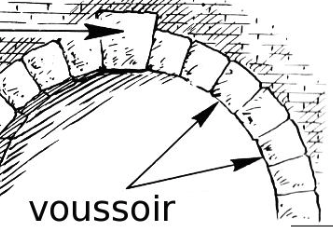
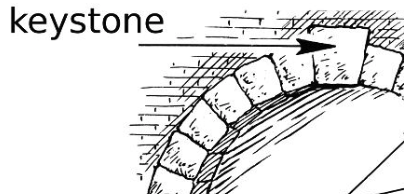
keystone
the central stone at the top of an arch; locks arch together and allows it to bear weight
frieze
A decorative strip or horizontal band on a wall, often w/ reliefs or ornamentation

tufa
a type of rock used extensively for temples, tombs and walls in Etruscan and Republican Roman times.
concrete
A building material made from a mixture of broken stone or gravel, sand, cement, and water that can be spread or poured into molds and later hardens into that form
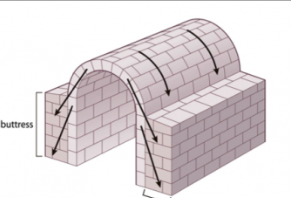
barrel vaults
A type of vault with a continuous arch/tunnel shape
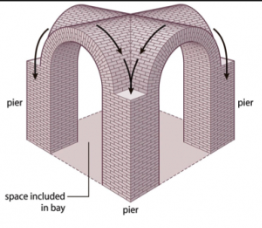
groin vaults
A type of vault formed by the intersection of 2 barrel vaults at right angles
triumphal arch
A monumental structure pierced by at least one arched passageway and created to honor an important person or event

rotunda
A large circular building or room often topped w/ a dome

portico
A structure consisting of a roof supported by columns at regular intervals, usually open on one or more sides

facade
The front or face of a building
drum
The circular or cylindrical wall that supports a dome
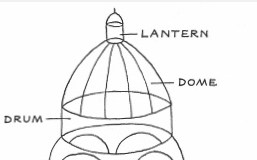
oculus
A circular opening at the top of a dome, allowing light and air to enter the space

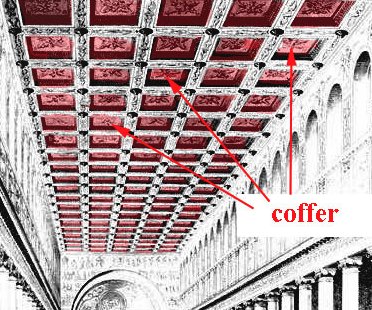
coffers/coffering
a series of recessed panels in a ceiling or dome, often used for decorative purposes and to reduce the weight of the structure

What: Apulo (Apollo) of Veii
When: 510-500 BCE
Artist: Vulca
Where: House at Veii
How made: Painted terracotta sculpture
Why made/Significance? This statue tells the story of the golden hind between Hercules (Heracles) and Apollo. This work was also used to decorate the Temple of Minerva.
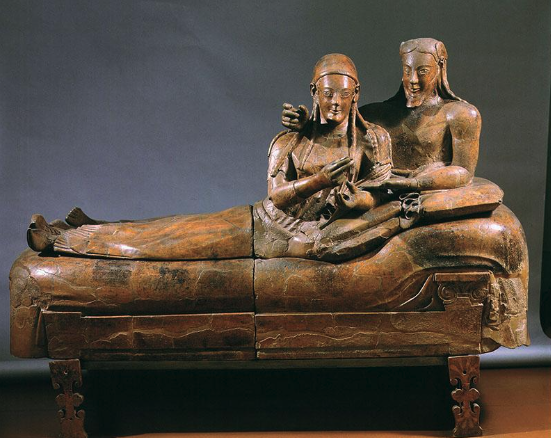

What: Reclining Couple on Sarcophagus
When: 520 BCE
Where: Cerveteri
How made: Terracotta sculpture
Why made/Significance? Despite the archaic smile, the sculpture by this time had become more lifelike.
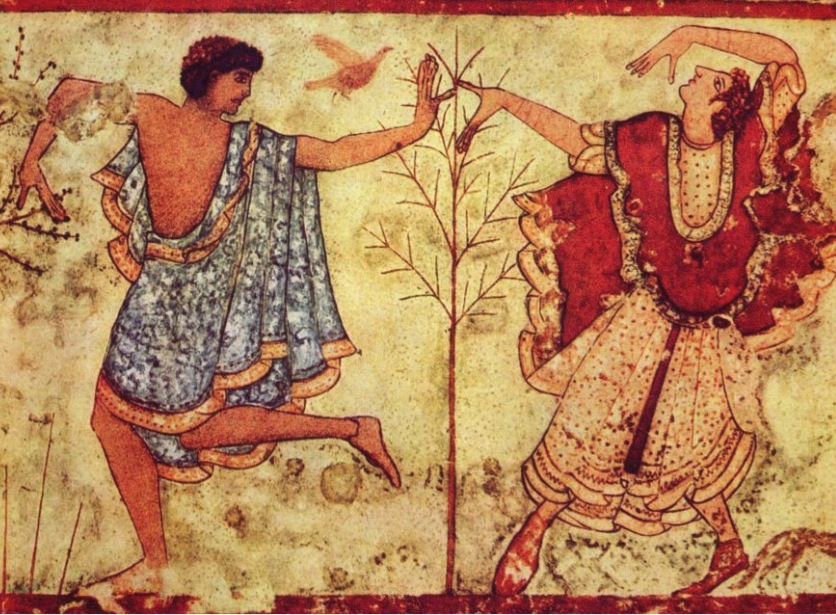

What: Tomb of the Triclinium
When: 470 BCE
Where: Etruscan Chamber tomb
How made: Fresco
Why made/Significance? Depicts Etruscan funeral traditions which was a time of celebration and festivity rather than the somber funerals of other periods.

What: Aule Metele/Aulus Metellus
When: Early 1st Century BCE
Where: Rome
How made: Bronze sculpture
Why made/Significance? Through the person and pose depicted, this introduces a change in the socio-political landscape as Rome expanded and absorbed other cultures.

What: Man w/ portrait busts of his ancestors
When: Late 1st Century BCE
Where: Rome
How made: marble sculpture
Why made/Significance? Signifies the importance of family in Roman times
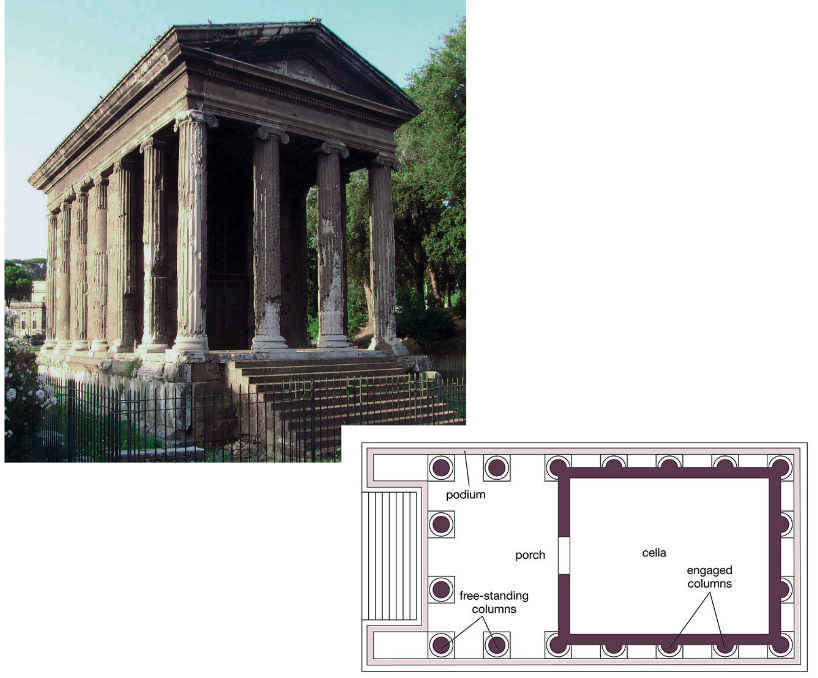
What: Temple of Portunus
When: 75 BCE
Where: Rome
How made: Construction/Architecture
Why made/Significance? The piece shows how Romans absorb other cultures because of the combination of Greek and Etruscan architecture. The temple has a single entrance like in Etruscan culture, but also features Greek columns/orders surrounding the temple.
Roman Monarchy
753-509 BCE
Roman Republic
509 - 27 BCE
Roman Empire
27 BCE - 476 CE (EMPEROR - Augustus)

What: Portrait of Augustus as general
When: 20 BCE
Where: Rome — Primaporta Italy
How made: Sculpture
Why made/Significance? propaganda for Augustus as emperor
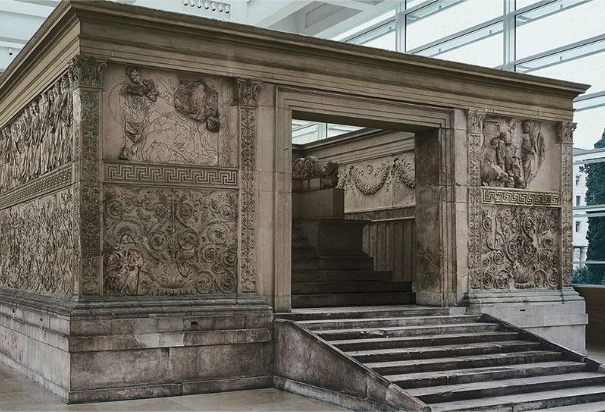

What: Ara Pacis
When: 13-9 BCE
Where: Rome
How made: Marble sculpture
Why made/Significance? monument dedicated to the peace and prosperity that Emperor Augustus had brought to Rome. (propaganda)

What: Pont-du-Gard
When: 16 BCE
Where: Rome - modern day Nîmes, France
How made: Series of arches, slight slope down
Why made/Significance? An important way to get water from one place to another and keep drinking water clean
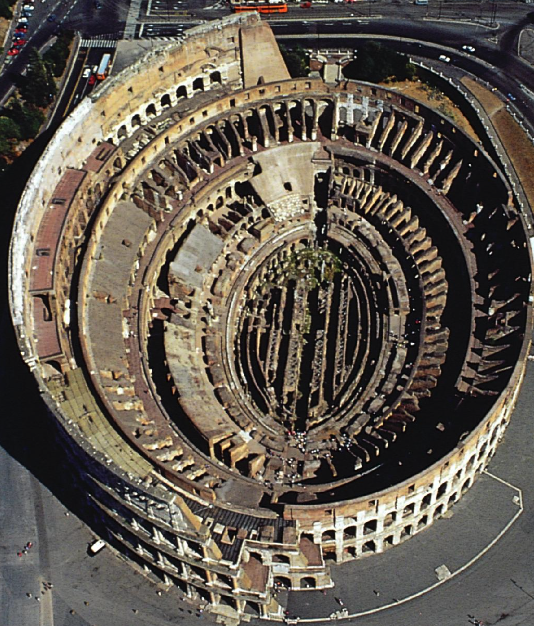

What: Colosseum (Flavian Amphitheater)
When: 70-80 CE
Where: Rome
How made: construction/architecture
Why made/Significance? Entertainment, seating systems, unobstructed viewing, and easy system of entrance and recess

What: Column of Trajan
When: 112 CE
Where: Forum of Trajan, Rome
How made: Sculpture/Architecture
Why made/Significance? One of the remaining elements of the forum of Trajan after Pompeii. The reliefs on the pillar also show the emperor’s victory and serve as a form of early propaganda.
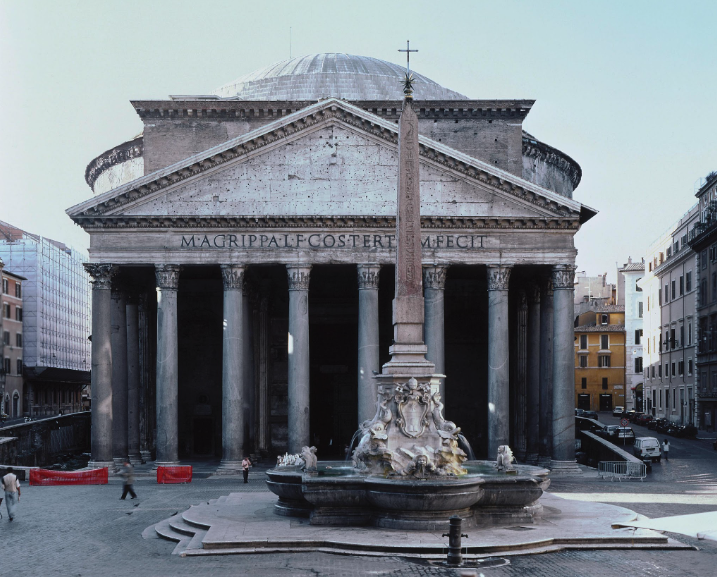

What: Pantheon
When: 118-125 CE
Where: Rome
How made: Architecture/Construction
Why made/Significance? Temple to the pantheon of gods that all people could visit.
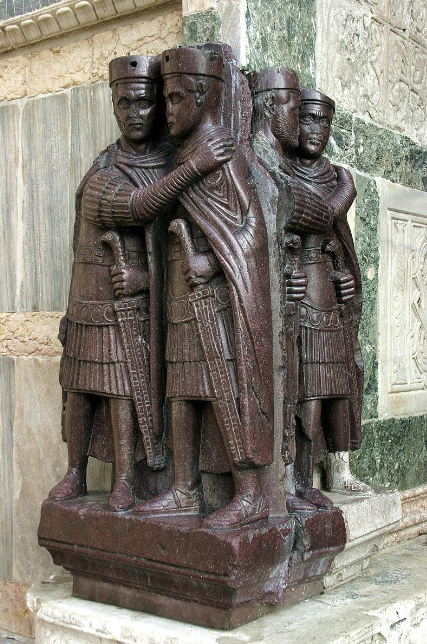

What: Tetrarchs
When: 293 CE
Where: Rome
How made: Poryphory sculpture
Why made/Significance? The statue symbolizes the political unity of the four rulers as shown by their similarities in pose and style to represent the unity between them.
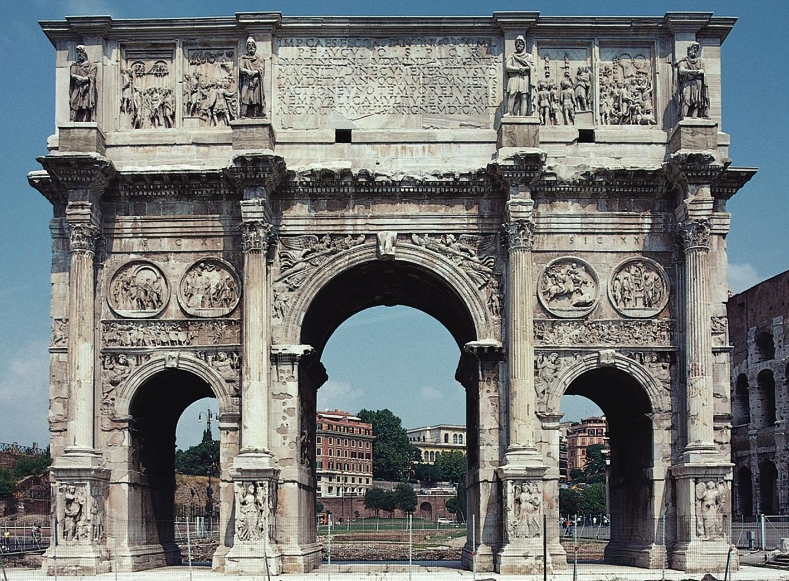

What: Arch of Constantine
When: 312-315 CE
Where: Rome
How made: Architecture/Construction
Why made/Significance? Commemorates the victory of Constantine over Maxentius; Last great monument of Imperial Rome
catacombs
Subterranean burial places comprised of tunnels and chambers for the interment of the dead
Torah
(in Judaism) The law of God as revealed to Moses and recorded in the 1st five books of the Hebrew scriptures.
basilica
a large oblong hall or building with double colonnades and a semicircular apse, used in ancient Rome as a court of law or for public assemblies
apse
A large semicircular or polygonal recess in a church, arched or with a domed roof, typically at the eastern end and usually containing the altar
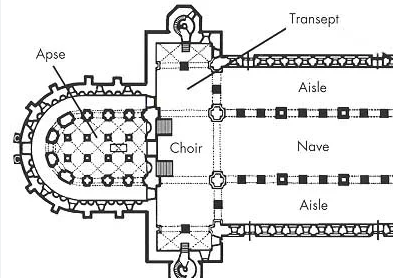
nave
The central part of a church building, intended to accommodate most of the congregation
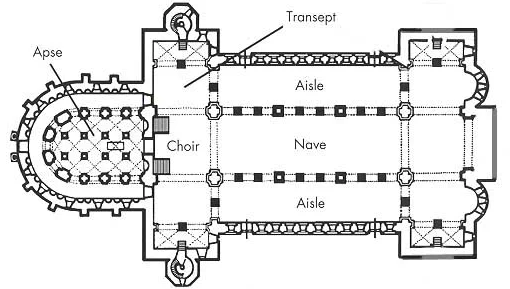
narthex
An antechamber, porch, or distinct area at the western entrance of some early christian churches
central plan
a design that is organized around a vertical axis and can be circumscribed w/in a circle
longitudinal plan
an architectural layout where the building is organized along a central axis w/ a long nave that extends from the entrance to the apse
exedrae
a room, portico, or arcade w/ a bench or seats where people may converse, typically in semicircular in plan
pendentives
A curved triangle of vaulting formed by the intersection of a dome with its supporting arches
illuminated manuscript
a handwritten book that has been decorated with flourishes such as borders, miniature illustrations, and gold or silver leaf
codex (codices)
An ancient book made of stacked, hand-written pages (ancestors of modern books)

What: Menorahs & Ark of the Covenant
When: 3rd Century
Where: Jewish catacomb, Villa Torlonia, Rome
How made: Wall painting — Dry fresco
Why made/Significance? —
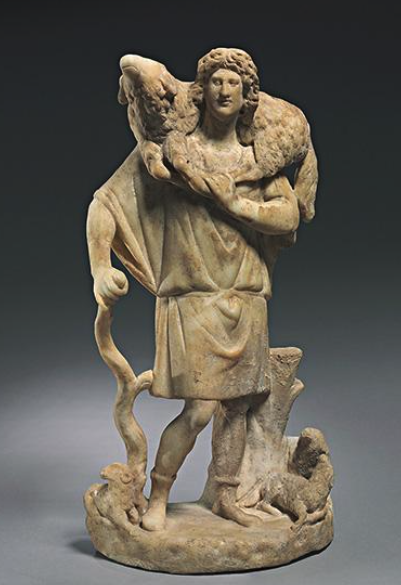

What: The Good Shepherd
When: 3rd Century
Where: Eastern Mediterranean, Antolia
How made: Sculpture
Why made/Significance? Relation to christ and the parable of the lost sheep
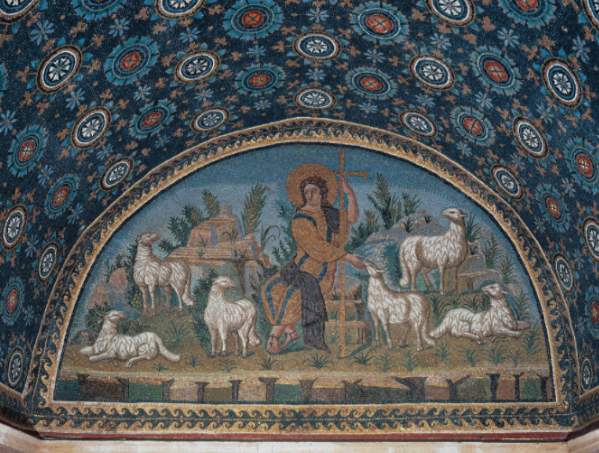

What: Mosaic in the lunette over the west entrance
When: 425-426 CE
Where: Oratory of Galla Placidia, Ravenna
How made: Mosaic
Why made/Significance? The imagery of the mosaic suggests entering into the guidance of Christ and represents a passage from mortal life to eternal life; Christian iconography —> transition from classical to medieval
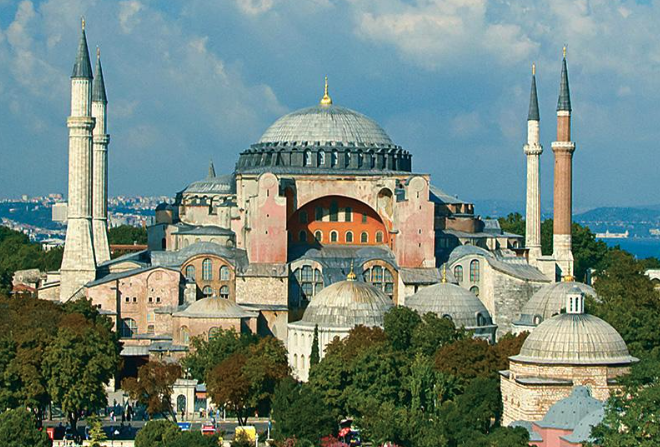

What: Church of Hagia Sophia
Artists: Anthemius of Tralles and Isidorus of Miletus
When: 532-537 CE
Where: Istanbul (Constantinople)
How made: Construction/building
Why made/Significance? The church served as a center of religious, political, and artistic life for the Byzantine world

What: Mosaics of Justinian, Theodora, and Retinue
When: 546 CE
Where: Apse Entry, San Vitale, Ravenna
How made: Mosaic
Why made/Significance? Example of Byzantine architecture and mosaic work; Gives visual testament to the two major ambitions of Justinians reign (christian and roman emperor)

What: Dome of the Rock
When: 688-692 CE
Where: Jerusalem
How made: Construction/Mosaics
Why made/Significance? Important site for all three Abrahmaic religions; The rock at the center of the Dome of the Rock is sacred for various religious reasons.

What: Great mosque
When: 785 CE
Where: Cordoba
How made: Architecture/Construction
Why made/Significance? Represents a big artistic achievement due the the size and boldness of the heaight of its ceilings

What: Qibla Wall
When: 785 CE
Where: Cordoba
How made: Mosaic
Why made/Significance? Marks the direction that muslims face when praying