hosa anatomy and physiology
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
four main groups of tissues
epithelial, connective, nerve, and muscle
epithelial tissue
•cover body
•line body cavities
•form glands
connective tissue
•supporting fabric of organs and body parts
•classified as soft or hard
soft connective tissue
•adipose:food reserve for energy, insulate body, pad body, and fill in between tissues
•fibrous:help hold body structures together
hard connective tissue
•cartilage:elastic, between bones, at end of long bones, shock absorber, allows flexibility
urinary system includes which organs?
-kidneys -ureters -urinary bladder -urethra
organs of the lymphatic system
lymph nodes, lymph vessels, spleen, tonsils, and thymus gland
organs of the endocrine system
pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, and thymus glands; pancreas, ovaries, and testes
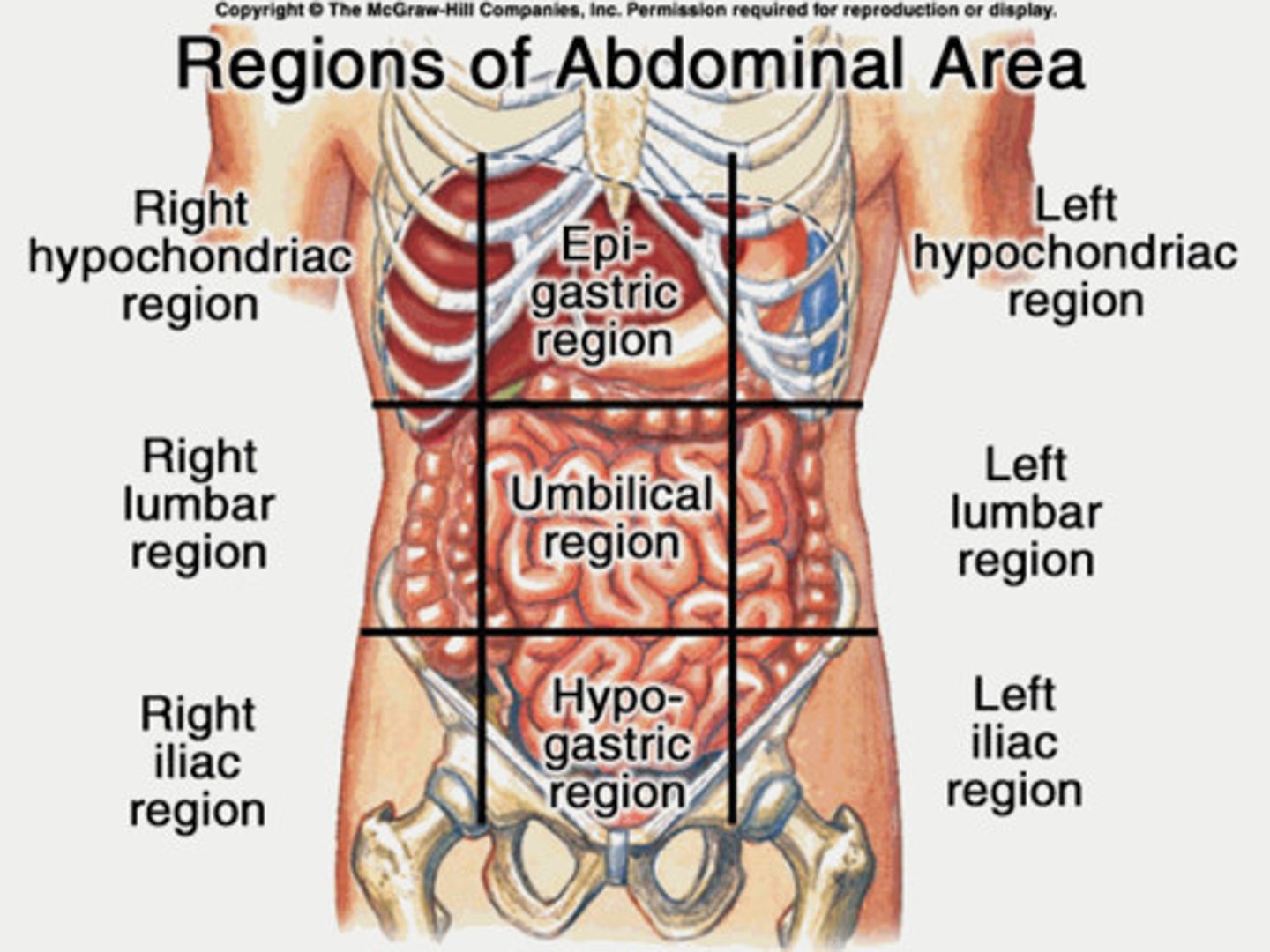
What are the nine division of the abdominal regions?
right/left hypochondriac regions, epigastric region, right/left lumbar regions, umbilical region, right/left iliac regions, and hypogastric region
what are macules?
FRECKLES or flat spots on the skin (freckles, macules-kinda sounds the same)
What are wheals?
itchy,irregular, elevated areas; hives or insect bites ("I WHEAL KILL A BUG IF IT BITES ME" it helps me)
what indicates basal cell carcinoma?
-elevated pink/yellow/white area on skin with a depressed center
-grows slowly and doesnt spread
-from basal cell in epidermis
what indicates squamous cell carcinoma?
-lesions that do not heal
-thin cells of the epithelium are affected and spread quickly
What is ringworm and how do you treat it?
-highly contagious fungal infection
-identified by flat/raised central area with surrounding RING of itchy scales/crusts
-TX: antifungal meds
What is verrucae and how do you treat it?
-it's a WART
-TX: removed with electricity, liquid nitrogen,acids, chemicals, or lasers (VERUCAE ARE TOUGH LITTLE BUGGERS)...or they just fall off on their own
how many cranial bones are there?
-1 frontal
-2 parietal
-2 temporal
-1 occipital
-1 ethmoid
-1 sphenoid
(8 in all)
How many facial bones are there?
-mandible and maxilla (jaw)
-nasal
-lacrimal (inner eye)
-palatine (top of mouth)
-zygomatic (cheeks)
(14 bones in all)
How many bones make up the spinal column?
-7 cervical
-12 thoracic
-5 lumbar
-1 saccrum
-1 coccyx
(26 in all)
How any true ribs do we have?
7 pairs
how many false ribs do we have?
5 pairs
(first three=cartilage
last two=floating)
What are the three parts of the sternum?
-manubrium
-gladiolus
-xiphoid process
What is a colles fracture?
breaking of radius (remember RADius) that causes bulge at wrist
what do fascia attach together?
muscles to bones
What is contracture?
the severe tightening of a flexor muscle
what is the function of the midbrain?
-conduct impulse between brain parts for certain eye/auditory reflexes
what is the purpose of the 4 ventricles of the brain?
-contain cerebrospinal fluid in subarachnoid space as shock absorber and nutrients deliverer
-drains waste out through the arachnoid villi
What is ALS and how is it treated?
-chronic degenerative neuromuscular disease, mental acuity not affected=trapped in progressively paralyzed body
-no treatment exists,Riluzole may slow progression, usually fatal 4-6 years after onset
What is cerebral palsy and how is it treated?
-distrubance of voluntary muscles movement due to brain damage
-three kinds: spastic (most common), athetoid, and atactic
-S/S: contracture, stiff muscles, tremors/seizures, exaggerated reflexes, speech impairment, mental retardation
-TX: relaxants, anticonvulsive drugs, casts/braces, orthopedic surgery, physical/occupational/speech therapy
What is multiple sclerosis and how is it treated?
-chronic degeneration of myelin sheath caused possibly by genetics or virus
-S/s: diplopia, fatigue, paralysis speech impairment, emotional swings, incontinence
-no cure
-TX: steroids, relaxants, counseling, pt
What is the name of the mucous membrane that lines the eyelid to protect the eye?
conjunctiva
What part of the sclera is visibly seen and what is its purpose?
-cornea: transparent to allow light to enter the eye
what layer of the eye provides nourishment through blood vessels
choroid coat
Which eye layer transmits light impulses to the optic nerve?
retina: innermost eye containing cones and rods
how does the eye maintain its forward curvature?
aqueous humor
how does the eye maintain its overall shape?
vitreous humor
What is an astigmatism and how is it treated?
-irregular curvature of cornea causing man different focus points on the retina
-TX: glasses
What is the leading cause of blindness and how can it be treated?
-glaucoma: excess pressure in due to extra aqueous humor
-S/S: loss of peripheral vision, limited night vision, mild aching, halos around lights
-TX: medications and surgery
What is macular degeneration and how is it treated?
-dry:fat or wet:blood deform retina, obstructing central vision but peripheral vision stays the same
-TX: none for dry, coagulants and laser surgery for wet
What is the weird curved part of the ear and what is its purpose?
-pinna/ auricle: leads sound to auditory canal
what structure separates the outer and middle ear?
-tympanic membrane/eardrum: vibrates to transmit sound waves to middle ear
What are the three bones that transmit sound from the tympanic membrane to the inner ear?
-ossicles: malleus, incus, and stapes
What allows equal pressure between the both sides of the tympanic membrane?
-eustachian tube the connects the ear to the pharynx
What translates sound waves to the auditory nerve?
-organ of corti: hairlike structures in the cochlea
What part of the ear allows sense of balance and equilibrium?
-semicircular canals
What is the difference between sensory hearing loss and conductive hearing loss?
-sensory hearing loss is caused by damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve treated by cochlear implants
-conductive hearing loss is cause by damage to out or middle ear structures treated by a hearing aid or surgery
what is Meniere's disease and how is it treated?
-excess fluid in inner ear, ruining hair cells
-S/S:vertigo, falling,n&v,tinnitus
-TX:antihistamines, surgery to destroy cochlea
Which cavity is the heart located?
mediastinal cavity
what is the difference between the endocardium, myocardium, and pericardium of the heart?
-endocardium: inner most layer, in heart and veins for smooth bloodflow
-myocardium: muscle middle layer
-pericardium: double-layered membrane covering outside of heart,pericardial fluid in between to prevent friction
What are the four valves of the heart and where are they located?
-tricuspid valve: between right atrium and right ventricle
-pulmonary valve: between right ventricle and pulmonary artery
-mitral valve: between the left atrium and the left ventricle
-aortic valve: between the left ventricle and the aorta
What is the difference between diastole and systole?
-diastole:activity of atrium
-systole: resting of atrium
(remember it's the ATRIUM, not ventricles)
what is the conductive pathway of the heart?
-electrical impulse reaches sinoatrial node (SA node) contracting the atriums
-then atrioventricular nodes (AV nodes), then bundle of his, then purkinjie fibers to contract the ventricles
-occurs every 0.8 seconds
what are the five types of leukocytes?
-neutrophils: secrete lysozyme
-eosinophils: produce antihistamines
-basophils: produce histamine
-monocyte: phagocytize foreign materials
-lymphocytes:develop antibodies
What is an aneurysm and how is it treated?
-ballooning or sac on artery wall, if damaged= hemorrhage=death
-S/S: pain/pressure, but symptoms may not be present
-TX: surgery to remove area and replace with plastic graft
What is the difference between arteriosclerosis and artherosclerosis?
-arterio: hardening/ thickening of the actual cell wall; danger= high blood pressure
-arthero: building of plaque (usually cholesterol) on the artery walls; danger= low blood flow
What is congestive heart failure and how is it treated?
-heart muscles to beat adequately enough to supply body with essentials
-TX: cardiotonic drugs, diuretics, elastic support hose, low-sodium diet
What is hemophilia, why is it dangerous, and how is it treated
-inherited disease, almost exclusively in men
-lack plasma protein to clot blood=excessive bleeding
-TX: transfusion of blood or plasma
What factors influence hypertension and what is considered hypertension?
-family history, race (african american higher), obesity, stress, smoking, diet, aging
- >140/90
What causes varicose veins?
-loss of elasticity in veins=stasis/ decreased blood flow
What is the job of lacteals?
-lymph capillaries in small intestine to pick up digested fats (chyle if mixed with lymph)
What are the three pairs of tonsils and where are they located?
-palative:on soft palate
-phryngeal/ adenoids: in nasopharynx
-lingual tonsils: on back of tongue
Where is the spleen and what is its function?
-beneath left diaphragm, back of upper stomach
-produce: leukocytes
-destroy: old erythrocytes
-store: erythrocytes in case of excessive bleeding
-filter: metabolic wastes
what is the thymus and what is its function?
-lymph tissue in center chest that atrophies after puberty
-produce: antibodies and leukocytes
-function taken over by lymph nodes
what is adenitis?
-inflammation/infection of lymph nodes
-occurs when large quantities of harmful substances infect the tissue
-swelling or abscess may occur
What is hodgkin's disease?
-chronic malignant disease of lymph nodes
-painless swelling of lymph nodes, fever, weight loss, itching, night sweats
-chemo and radiation treat it
What is the adam's apple?
-thyroid cartilage of the larynx (there are nine layers)
What helps keep the trachea open?
-c-shaped cartilage that is open at the back
What prevents alveoli from collapsing?
-surfactant: fatty inner layer of the alveoli
What is pleura and what makes it up?
-membrane enclosing the lungs
-visceral (on lungs surface) and parietal (on chest wall)
what is emphysema?
-chronic, noninfectious deterioration of alveoli walls=poor gas exchange
What is the leading cause of cancer deaths in men and women?
-lung cancer
what are the two things that make up the digestive system?
-alimentary canal(mouth to anus)
-accessory organs(tongue, teeth, liver,gallbladder, pancreas)
What is the difference between the hard palate and the soft palate?
-hard palate: separates mouth from nasal cavity
-soft palate: separates mouth from nasopharynx
what are the three salivary glands?
-parotid
-submandibular
-sublingual
what valve separates the small intestine from the large intestine?
-ileocecal valve
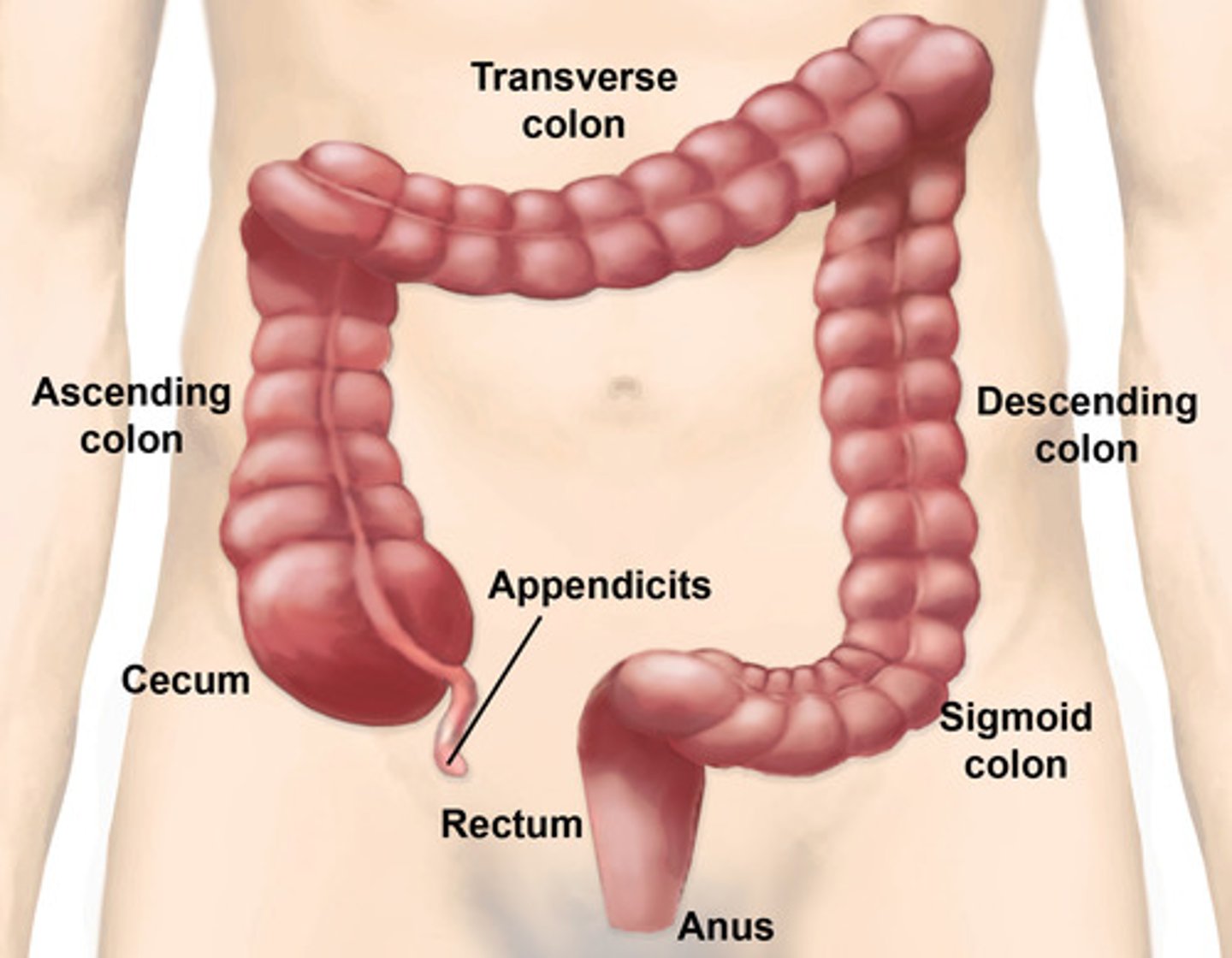
What are the different parts of the large intestine?
-cecum
-colon(ascending, transverse, descending, sigmoid)
-rectum (6-8 in.)
-anus
where is the pancreas and what is its function?
-behind stomach
-produce: pancreatic juices(digestion), amylase (sugar d.),trypsin(protein d.), lipase (fat d.), insulin (regulate metabolism)
what is cirrhosis?
-chronic destruction of liver cells
-formation of fibrous connective and scar tissue
What is diverticulitis and how is it treated?
-fecal matter or bacteria become trapped in the diverticula of the small intestine
- S/S: pain, constipation/diarrhea, abdominal distention, n/v, gassy
-TX: stool softener/high fiber diet, pain meds, antibiotics or surgery
What are hemorrhoids and how are they treated?
-painful dilated varicose veins of the rectum/anus
-TX: sitz baths, anything to soften stool (meds, fiber, water), warm/moist compresses, surgery
what is the difference between HAV, HBV, and HCV?
-HAV: transmitted through food or water contaminated by infected feces; most benign and self-limiting;has vaccine
-HBV: spread through bodily fluids; can lead to chronic hepatitis or cirrhosis;has vaccine
-HCV: no vaccine, transmitted through body fluids, most likely to lead to chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis, TX with high protein and low fat diet or surgery
What are the symptoms of HCV?
-n/v, anorexia, myalgia, dark urine and clay colored feces, and jaundice
Where are the kidneys located and what makes up their structure?
-located in retroperitoneal cavity in upper abdominal cavity= protected by ribs
-covered with fatty capsule then fibrous capsule
-two main section: cortex (outer, full of nephrons)
and medulla (inner mostly tubules)
what are the different parts of a nephron?
-glomerulus: capillaries that filter out everything but rbc and proteins
-bowman's capsule: picks up materials filtered in the glomerulus and send it to convoluted tubules
-convoluted tubules: needed materials are reabsorbed and urea and creatinine are left to make urine
after urine is produced where does it go?
-ureters: connect kidney to bladder to transport urine
-bladder: holds 1 cup of urine to signal void, but can hold more
-urethra: tube that carries urine from bladder to outside(1.5 in. for girls and 8 in. for boys)
-urinary meatus: opening where urine is voided
What is uremia and how is it treated?
-kidneys fail=urinary waste products are left in bloodstream
-S/S: ammonia breath, oliguria/anuria,n/v, convulsion, mental confusion, death
-TX: restricted diet, cardiac meds, dialysis, kidney transplant
what is the difference between acromegaly and giantism?
-acromegaly: caused by a tumor (adenoma) in the pituitary gland and oversecretion of somatotropin; hands. feet. and face are abnormally large and tongue swells; leads to short life and cardiac arrest
-giantism: caused by oversecretion of somatotropin;long bones grows unusally tall and sexual development decreases, may cause mental retardation
What is diabetes insipidus?
-lack of vasopressin or adh hormone= water not reabsorbed in kidneys
-S/S: polyuria, polydipsia, dehydration, constipation, and dry skin
-TX: administer adh/vasopressin
What causes dwarfism?
-undersecretion of somatotropin in the pituitary gland, possibly from tumor
-can be reversed if given somatotropin injections for 5 years during growth
What is the thyroid gland and where is it located?
-gland that controls metabolism and calcium in blood
-two lobes around larynx
-requires iodine to produce hormones
what is a goiter?
-enlargement of the thyroid gland to oversecretion= dysphagia, cough, choking feeling
-TX: eliminating the cause
what is hyperthyroidism and how is it treated?
-overactivity of the thyroid= increased bmr
-S/S: rapid pulse, diarrhea, diaphoresis, irritability, tremors, extreme nervousness, heat intolerance, polydipsia, goiter, hypertension, hungry but weight loss
-TX: radiation or thyroidectomy
what is graves disease and how is it treated?
-severe hyperthyroidism more common in women
-S/S: same as hypert. but include, strained expression, exophthalmia
-TX: meds to inhibit thyroxine, radioactive iodine to destroy thyroid tissue or thyroidectomy
What is hypothyroidism?
-underactive thyroid gland
-cretinism: infancy
-myxedema: childhood or adulthood
-S/S: retardation, slow heart rate, edema, weight gain
-TX: oral thyroid hormone taken or iodine in diet
What is the function of the parathyroid gland and where is it located?
-regulate amount of calcium in the blood
-four glands behind the thyroid gland
what is hyperparathyroidism?
-overactivity in parathyroid= hypercalcemia=renal calculi, lethargy, gastrointestinal problems, and possibly osteoporosis
-TX: remove adenoma if it is the cause, low calcium diet
what is hypoparathyroidism and how is it treated?
-underactivity of the parathyroid/thyroid= low levels of calcium in blood
-S/S: tetany, convulsive twitch, can lead to death if larynx and respiratory tract involved
-TX: vitamin D, calcium, and parathormone
What are adrenal glands?
-suprarenal:above each kidney
-separated into medulla (epinephrine and norepinephrine) and cortex (mineral/gluco/gonado-corticoids)
what is addison's disease and how is it treated?
-decreased aldosterone=increased potassium in blood
-S/S: bronzing skin, mental lethargy, edema, weight loss, hypotension, dehydration
-TX: corticosteroid hormones, controlled sodium intake, fluid regulation
what is cushing's syndrome?
-oversecretion of glucocorticoids due to tumor or ACTH excess production
-S/S:hyperglycemia, hypertension, hirsutism, "moon face", obesity
-TX: remove tumor or remove gland and replace with hormonal therapy
What organ is both an exocrine and endocrine gland?
pancreas