General Zoology Chapter 12 - Sponges and placozoans
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
advantages of multicellularity
- Low surface area to volume ratio
- Allows individual cells to be more efficient
(instead of being a very large unicellular animal which is inefficient, become an organism with specialized cells)
note: specialized cells = more efficient
which organism was the first multicellular animal
sponge
what makes the organization of cells in sponges very distinct
Cells embedded in very tough extracellular matrix
sponges were not recognized as animals or plants until
19th century
in the tree, animals split off from ________________ which are ____________________
choanoflagellates, algae that are stocks of 2-12 cells that stick out and filter water
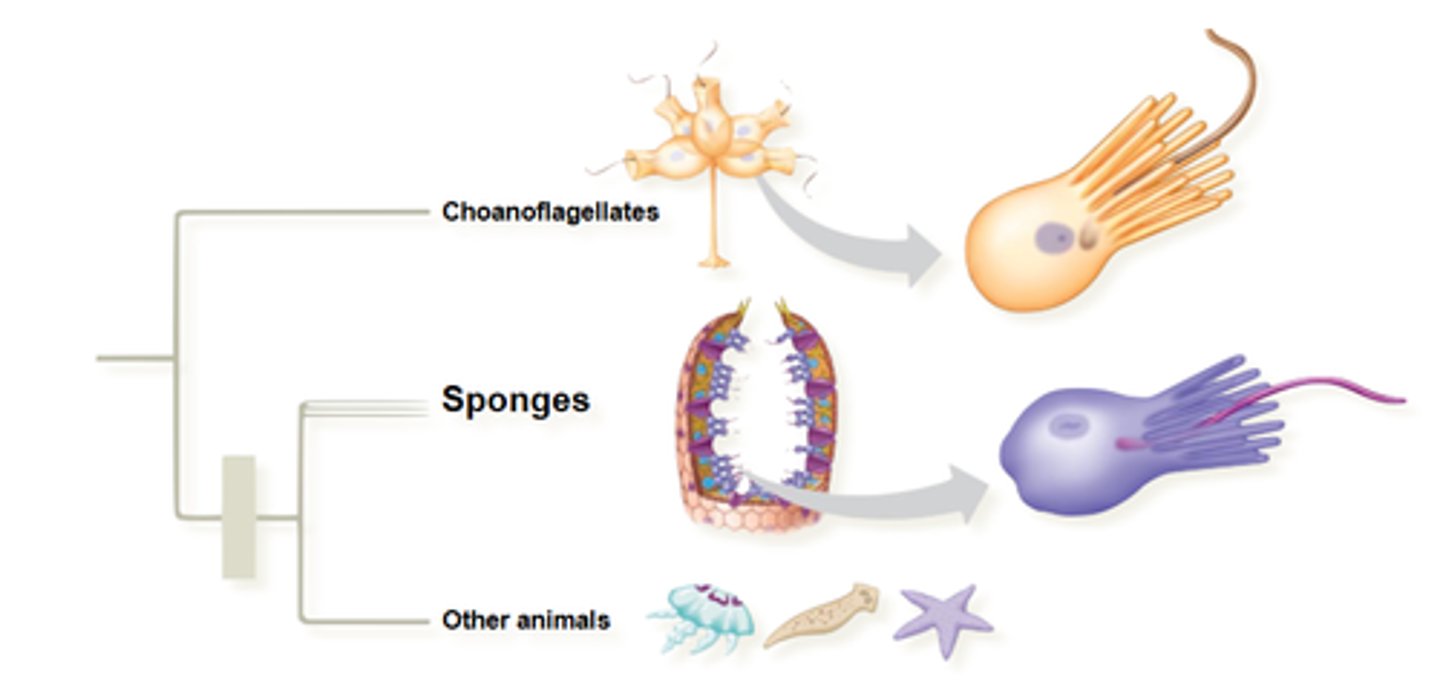
which animal (metazoans) was the first group to branch off of the group "other animals"
sponges
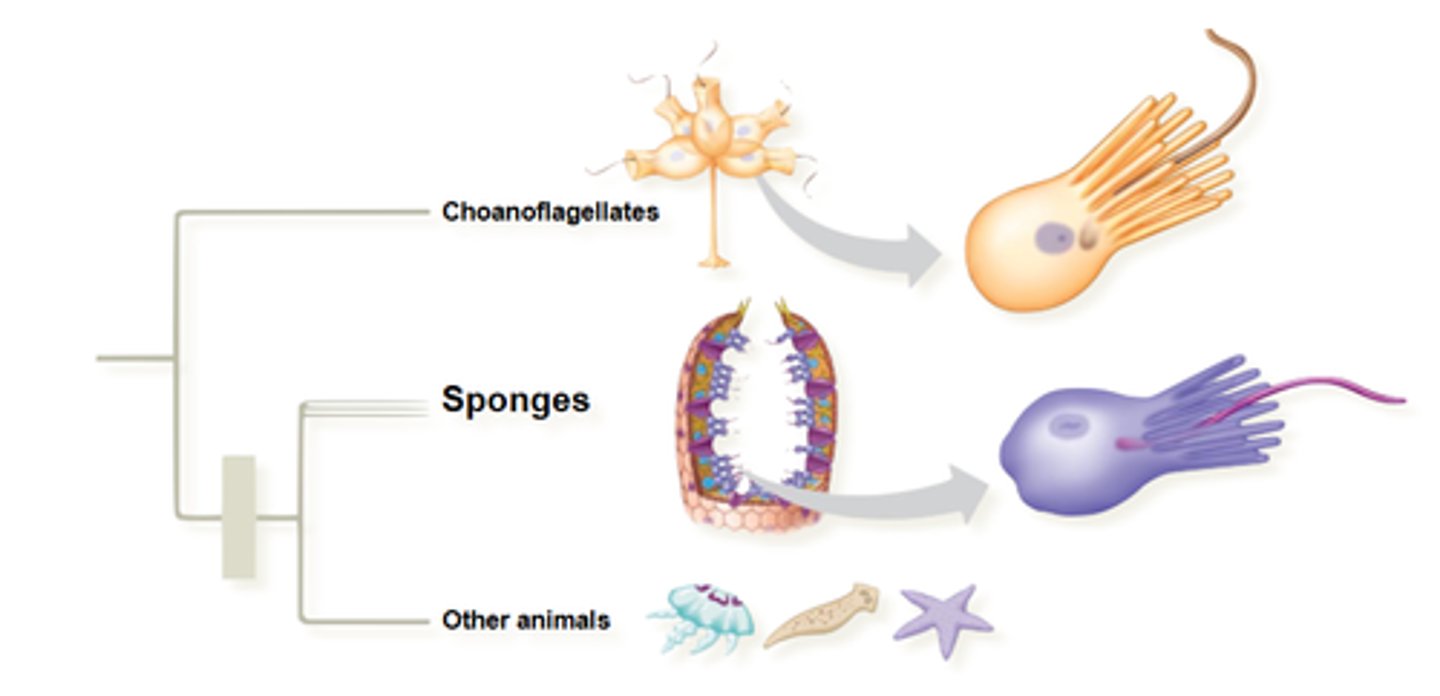
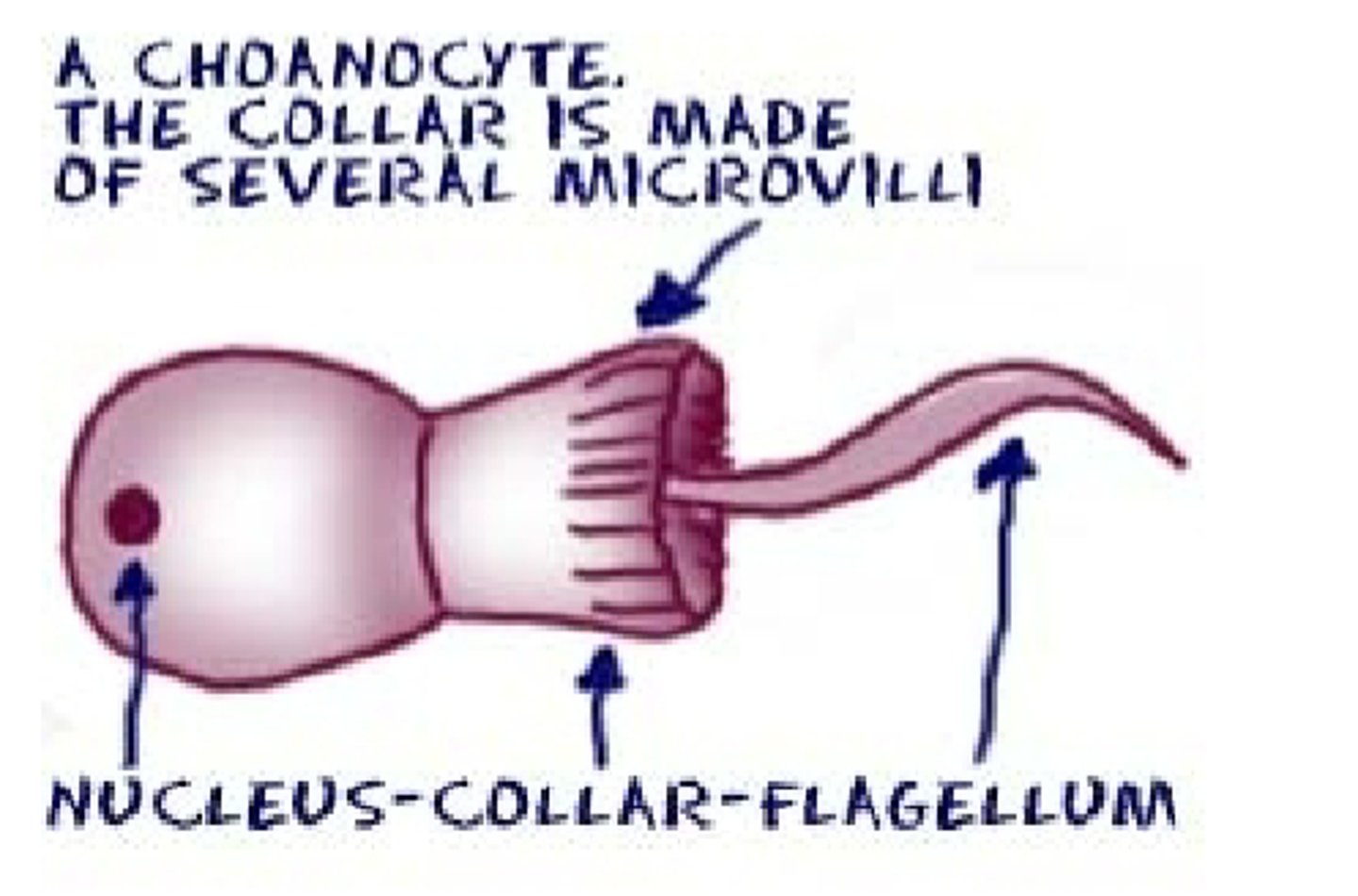
Describe choanocyte cells
- which organisms have them?
- structure and function of structure
- most organisms who have these cells are ___________ and ______________________
- choanoflagellates and sponges
- flagellum surrounded by collar of microvilli which collect particles for filter feeding, usually bacteria
- sessile (immobile or fixed to one place) and attach to hard surfaces
What is evidence for the common ancestors of metazoans being "colonial"
colonial makes sense as a "Prototype" multicellular organism
Similar cell communication mechanisms exist between
choanoflagellates and sponges
What is evidence against the common ancestors of metazoans being "colonial"
Choanocytes only in adult sponges, not in the larval form
Not seen in other phylogenetic groups, lost or suppressed (this is not surprising)
What has more evidence? for or against common ancestors of metazoans colonial
for
describe the latin name for sponge phylum
Porifera
porus (pore)
fera (bearing)
sponges ranges in size from _____ to ____
Range in size from a 2 mm across to 2 m across
Describe Sponge Structure
- Spicules imbedded in spongin for support
- Pinacoderm – incurrent pores on cells
- Dermal ostia – incurrent pores for the sponge
Phylum Porifera
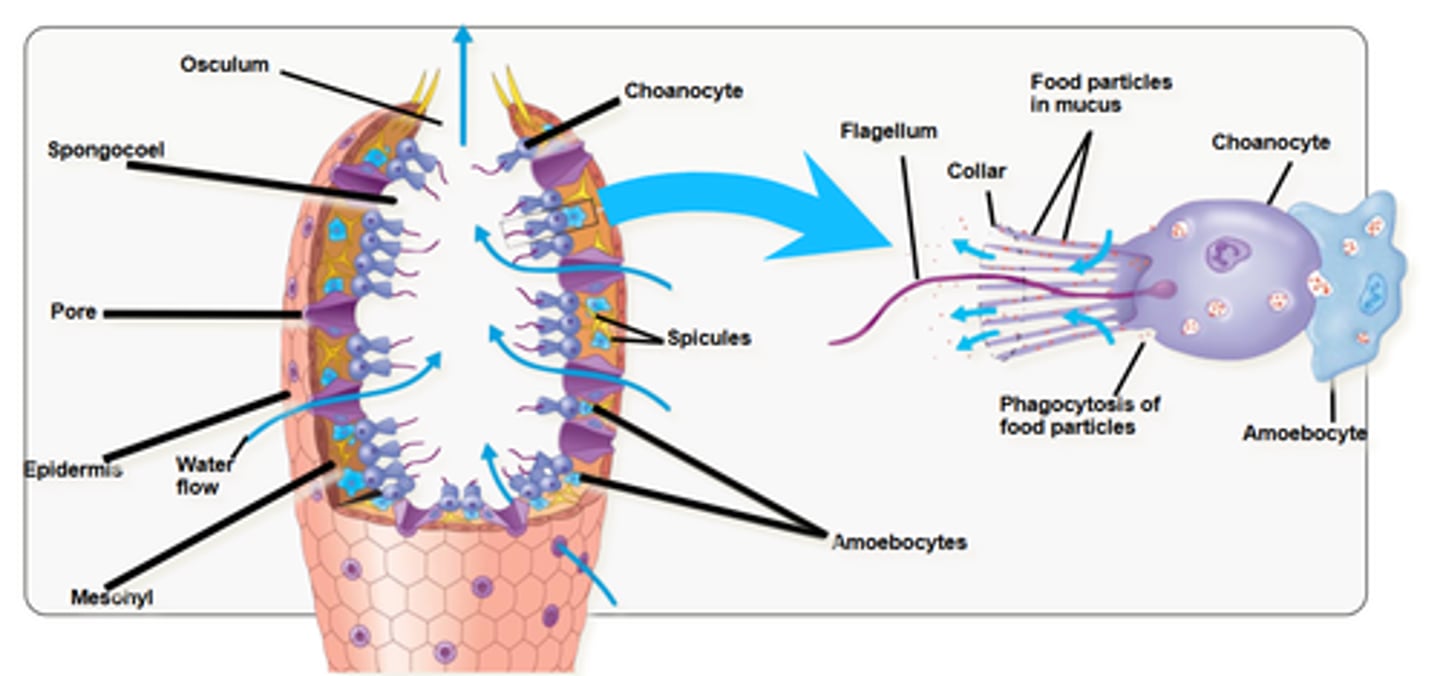
Describe how sponges "eat"
- suspension feeders
- phagocytosis for small food particles
- pinocytosis for smaller proteins
Phylum Porifera
Organ System
- digestion is intracellular, no organs or true tissues
- nervous system absent or very primitive
Phylum Porifera
How do they live/where do they live
aquatic
stays in one spot
Phylum Porifera
Structure
- radial symmetry
- body with pores that facilitate water movement
- 3 types of body types
Phylum Porifera
Structure (body parts/symmetry)
- radial symmetry
Spongocoel - large central cavity
Ostia - tiny pores for water to enter
Osculum - a large aperture in a sponge through which water is expelled.n the surface of sponges that allow
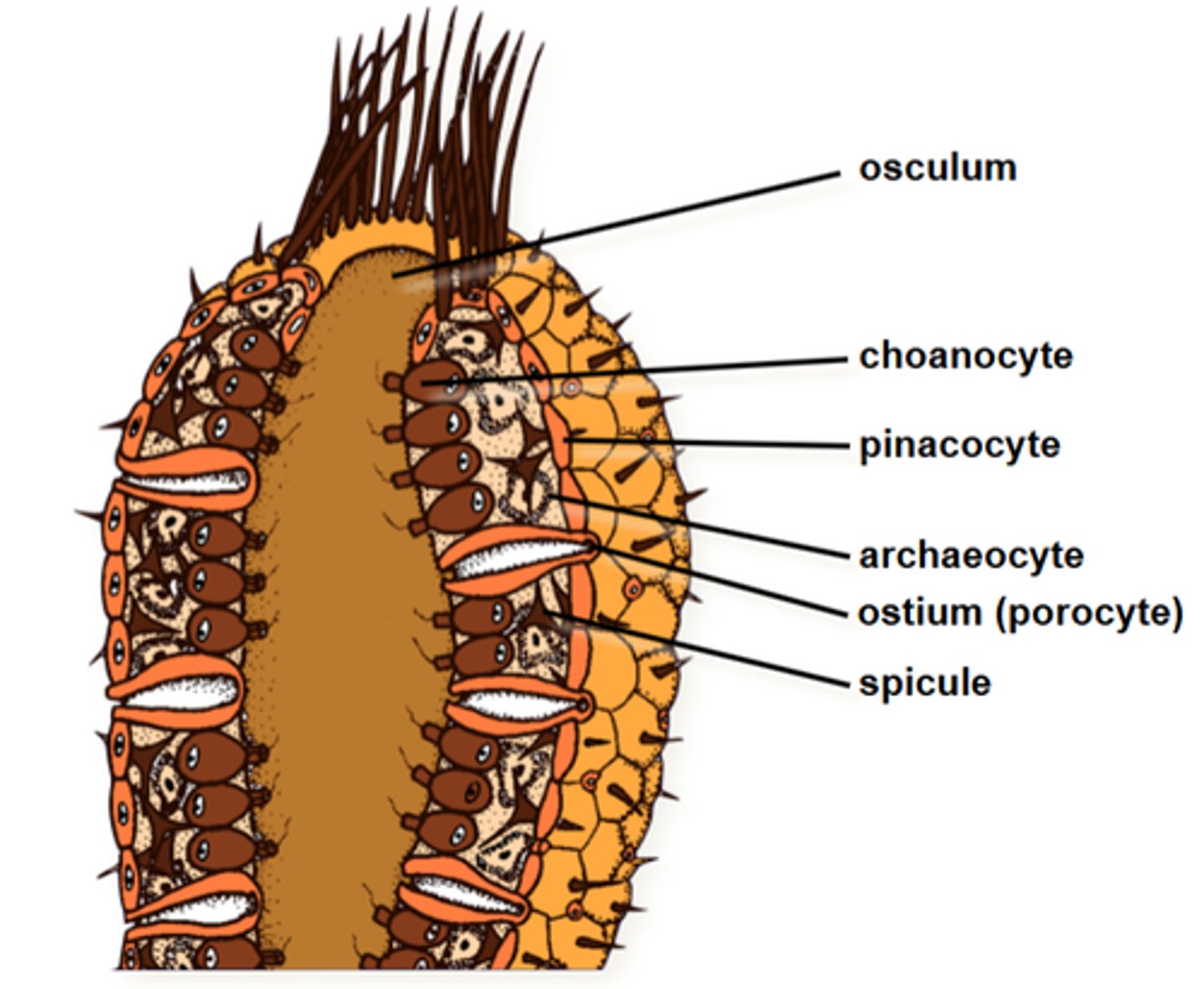
Phylum Porifera myocytes
muscle cells arranged in circular bands around pores, regulate water flow through contraction
Phylum Porifera Describe Archaeocytes
(amoebocytes) ameboid cells that move in the mesohyl. they can specialize into sclerocytes, spongocytes, collencytes, and lophocytes
Phylum Porifera Describe Pinacocytes
flat cells that cover the outside of sponges
analagous to epithelial cells, closest thing a sponge has to true tissues
Phylum Porifera
What do each of these specialized Archaeocytes make:
Sclerocytes –
Spongocytes –
Collencytes –
Lophocytes –
Sclerocytes - make spicules
Spongocytes - make spongin
Collencytes - make collagen
Lophocytes - make collagen
Phylum Porifera: Sponges are made of...
- choanocytes
- mesohyl (gelatinous extracellular matrix in the center)
- archaeocytes (amoebocytes)
- pinococytes
- myocytes
Study this picture
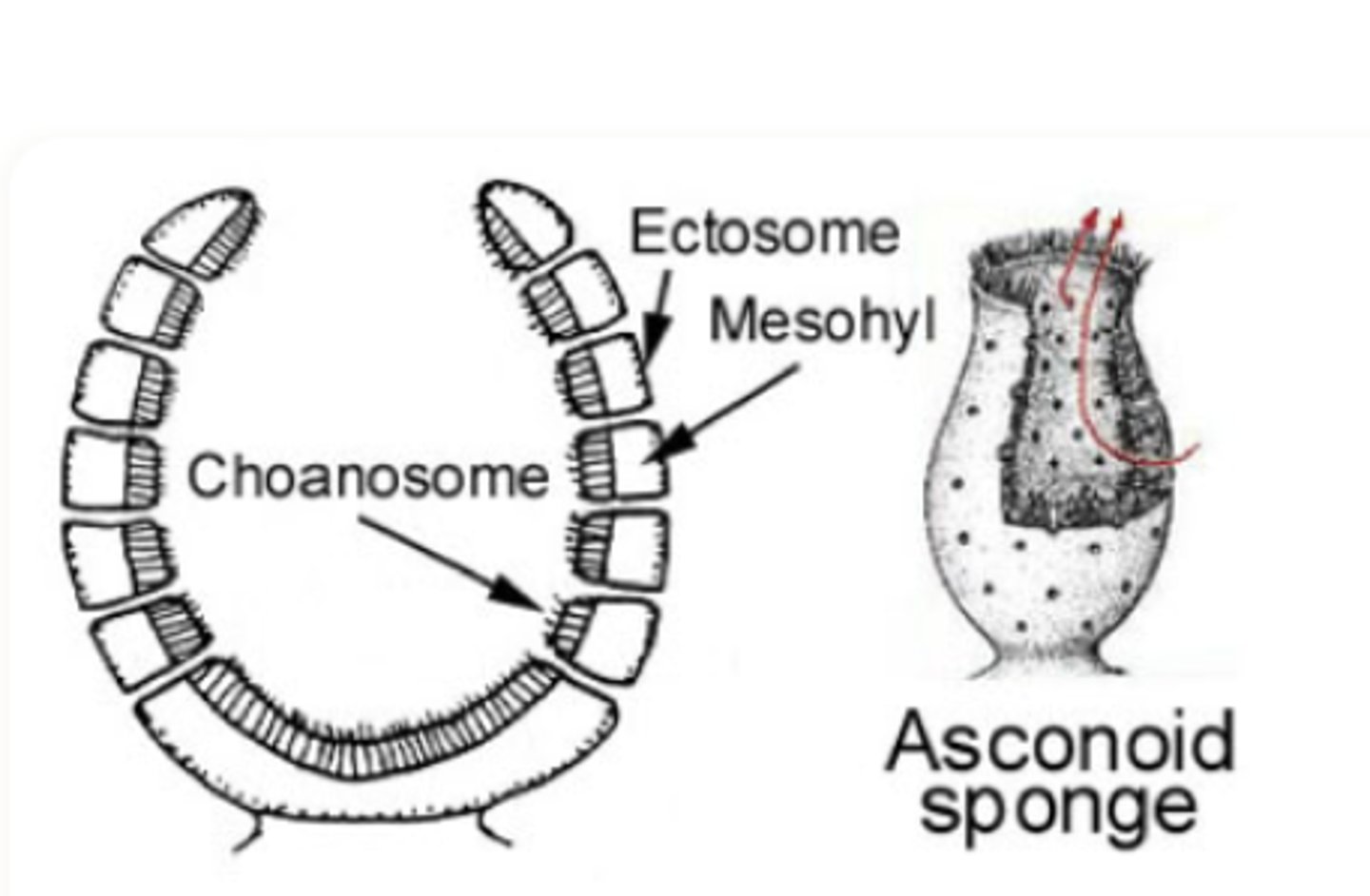
Phylum Porifera What are the three types of sponge body forms?
Asconoid
Syconoid
Leuconoid
Phylum Porifera Asconoid
Smallest sponge with the simplest body plan
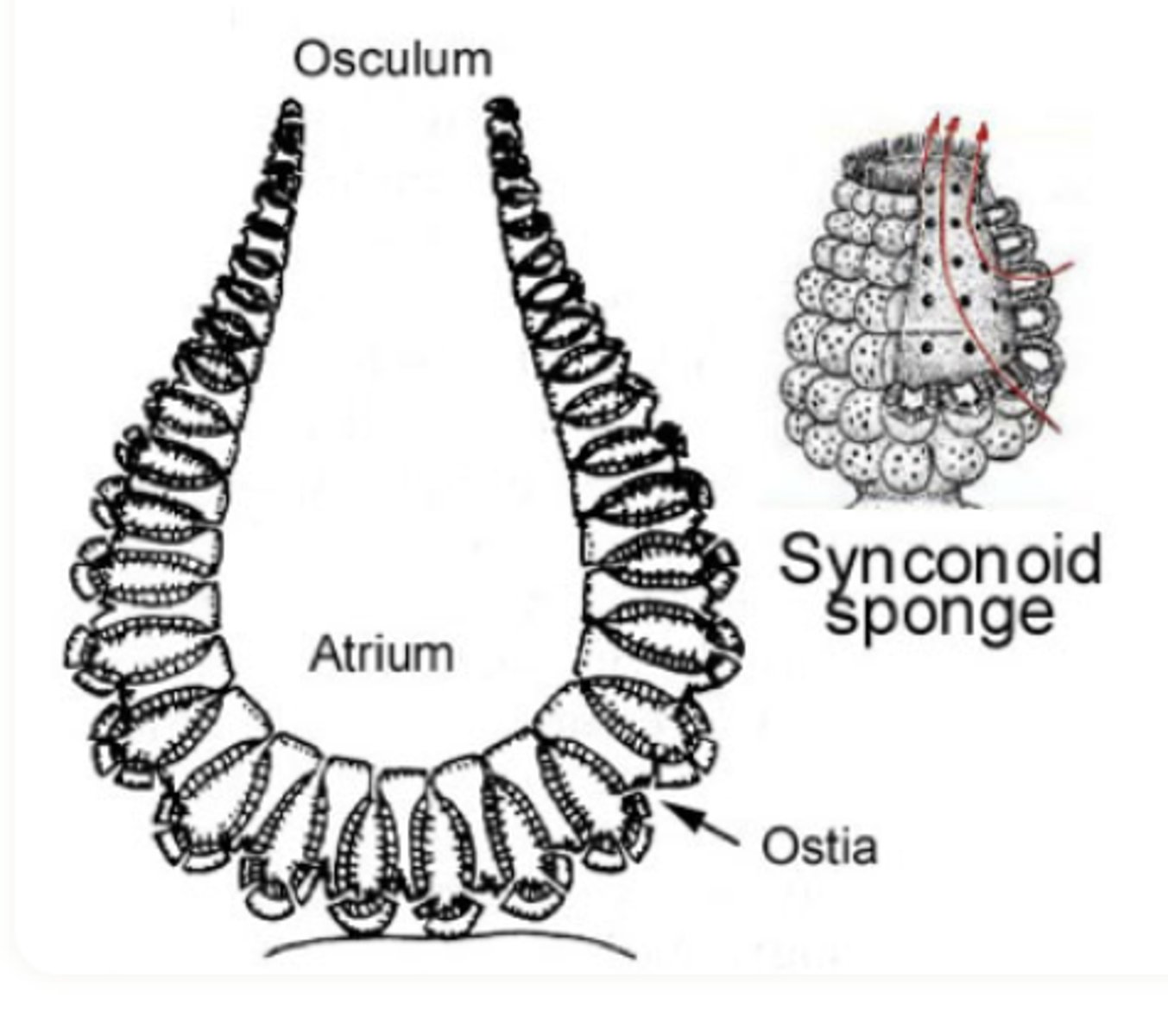
Phylum Porifera Syconoid
most efficient. has a lot of water
Phylum Porifera Leuconoid
most complex body form in sponges (best at filtering)
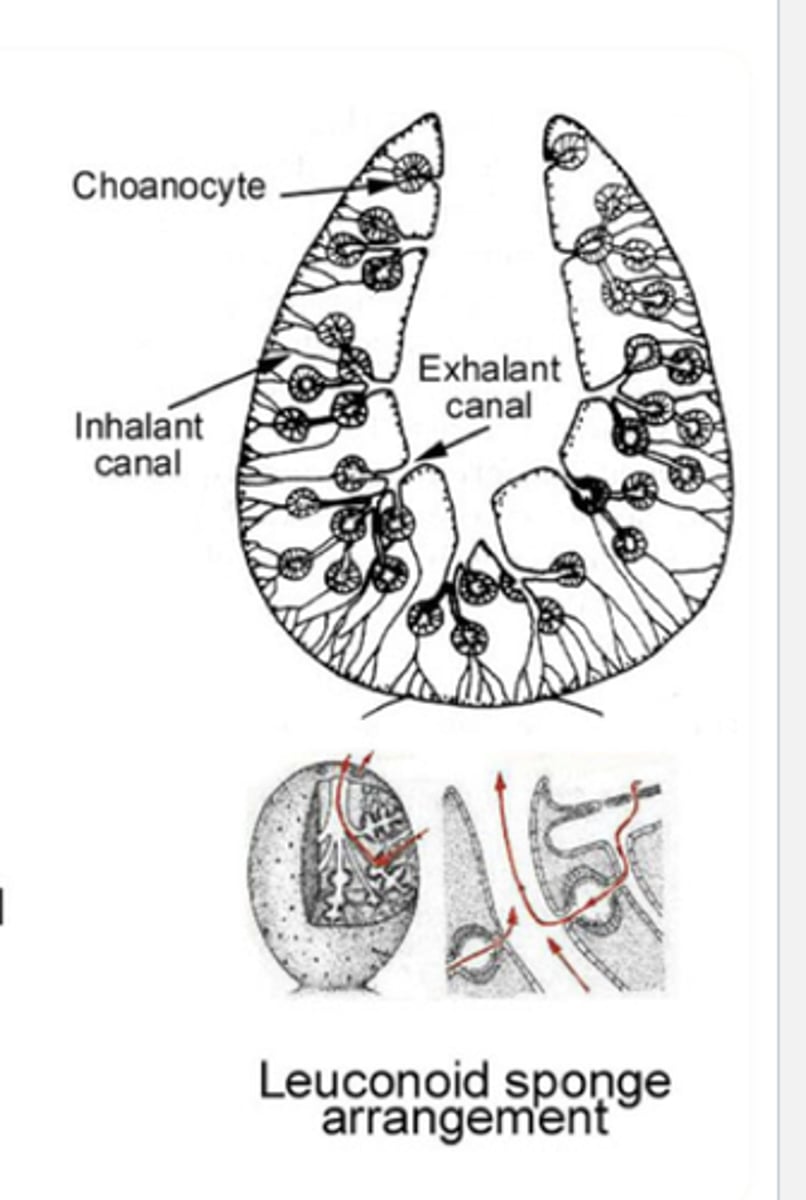
Phylum Porifera
Describe reproduction of sponges
Asexual
- create external or internal buds where buds detach and grow
- produce gemmules (internal buds) through somatic embryogenesis (process that creates embryos from vegetative cells without fertilization) Gemmules grow into sponges under more favorable conditions.
Sexual
- most sponges are monoecious (cross or self fertilize)
- produces parenchymula (free swimming larvae)
Phylum Porifera Which sponges develops blastula
Calcarea and a few Demospongiae
Phylum Porifera Describe blastula
made only by certain sponges, free swimming larvae from fertilized eggs that becomes inverted (leaving flagellated cells outside) to swim away to find a new place to grow
advantages of asexual reproduction
- No dilution of gene pool, offspring are all you (if you have good genes)
- clones favored in stable environments
- all of your population is reproductive
- offspring are often robust (strong/healthy) vs. individual gametes
disadvantage of asexual reproduction
• Offspring often do not disperse long distances
• Everyone is the same (Not favored in environments that change)
• Muller’s ratchet
– You accumulate negative mutations over time (easier to make mistakes then correct answer)
– Can lead to a less fit population
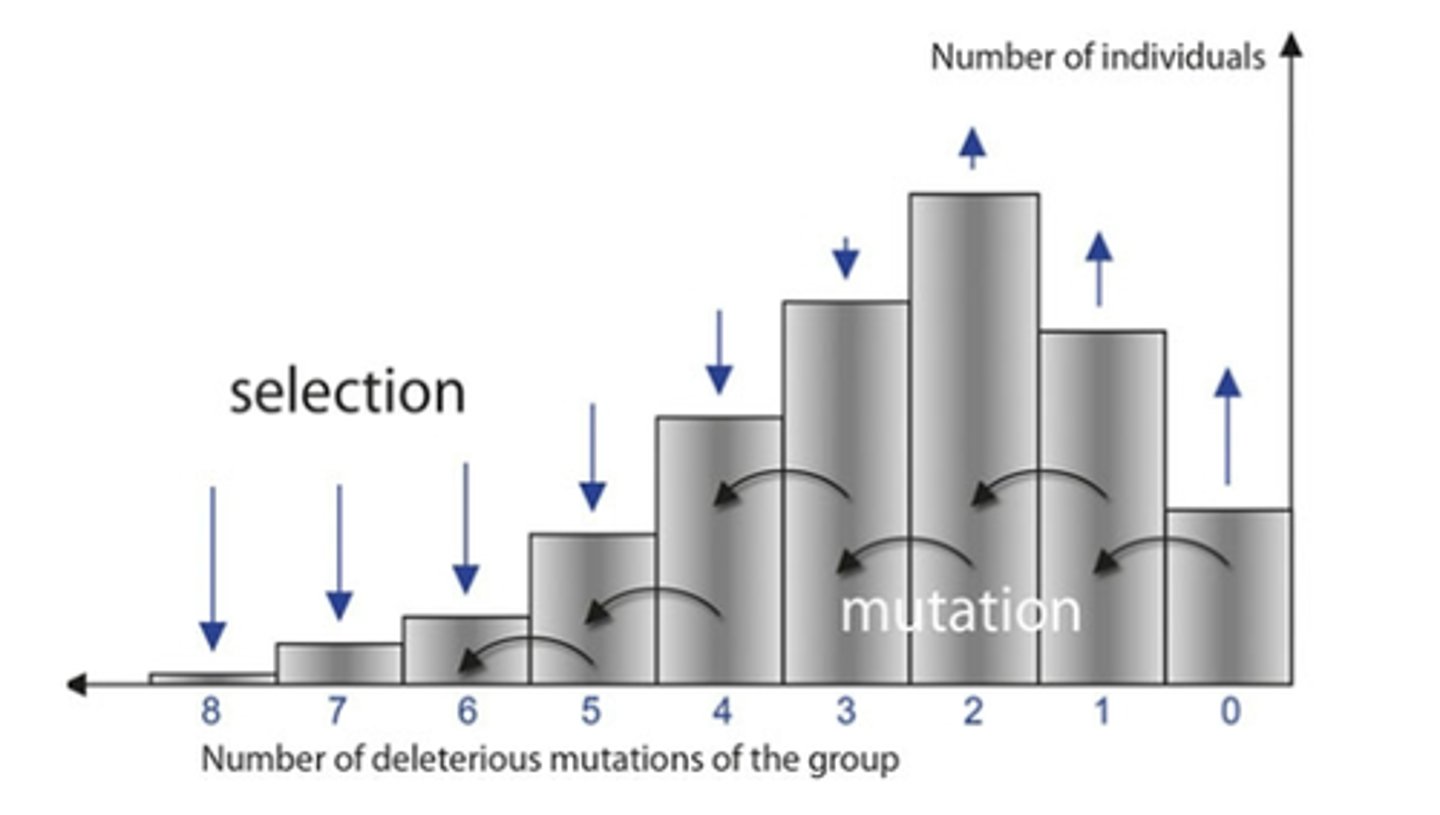
Advantages of sexual reproduction
- BIG ADVANTAGE: genetic variation for selection to act upon
- good at dispersing (and packaged well)
Disadvantages of sexual reproduction
- some population not reproductive
- fragile offspring
- diluted gene pool (good if bad genes, but bad if wasted good genes)
- most reproductive effort is wasted (finding partner/most gametes or offspring do not survive to reproduce)
Phylum Porifera
Taxonomy of sponges:
Class ____________________ - small calcareous sponges
Class ____________________ - siliceous
Class ____________________ - 95% of the species
Class Calcarea - small calcareous sponges
Class Hexactinellida - siliceous
Class Demospongiae - 95% of the species

Synctial cellular structure
many nuclei in a single cell (two ways)
- Fusion of many cells
- Cellular replication without cytokinesis
Phylum Porifera
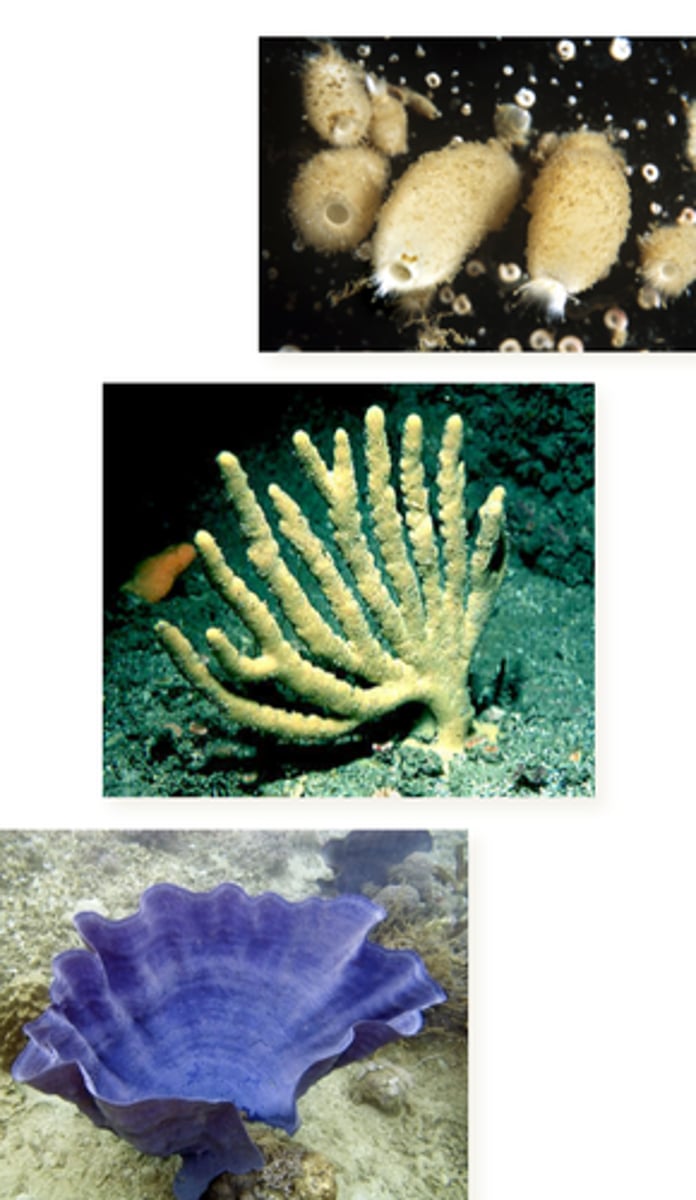
Describe Calcarea (Calcispongidae) sponges
- spicules
- sponge shape
- sponge body form type
• Calcium carbonate spicules
• Any of the three sponge forms
• Typically small and vase shaped
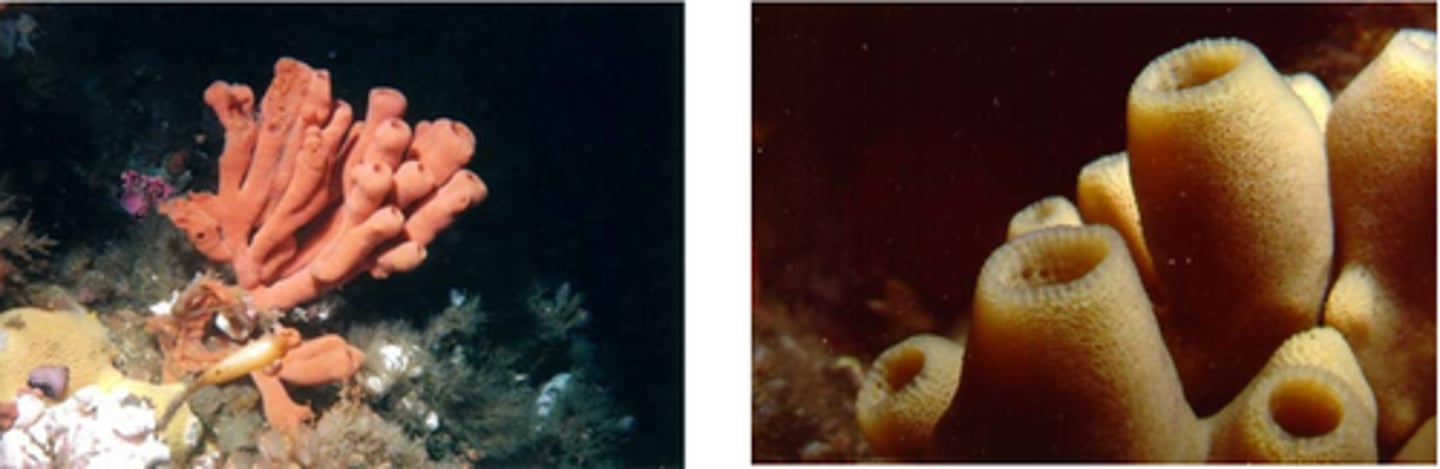

Phylum Porifera
Describe hexactinellida sponges
Glass sponges
• Mostly deep sea
• Vase or funnel shaped
bodies
• Synctial cellular structure
Phylum Porifera
Describe Desmospongiae sponges
- sponge shape
- spicule
- which species?
• Siliceous, but not six rayed
• All leuconoid, all shapes
• Very diverse, most species (Contains all freshwater sponges)

Describe Phylum Placozoa
- what is unique about them
- how do they eat
- how do they reproduce
• ONE species – monotypic (having only one member) family and genus
• Scavengers (Glide over food, secrete digestive enzymes, absorb the products)
• Reproduce asexually by budding and fission (not sure if they're sexual since they produce eggs in captivity)
Describe Phylum Placozoa greek name
plakos (tablet) and zoon (animal)
what is the only species in Phylum Placozoa
Trichoplax adhaerens
Phylum Porifera
siliceous spicules (hexactinellida)
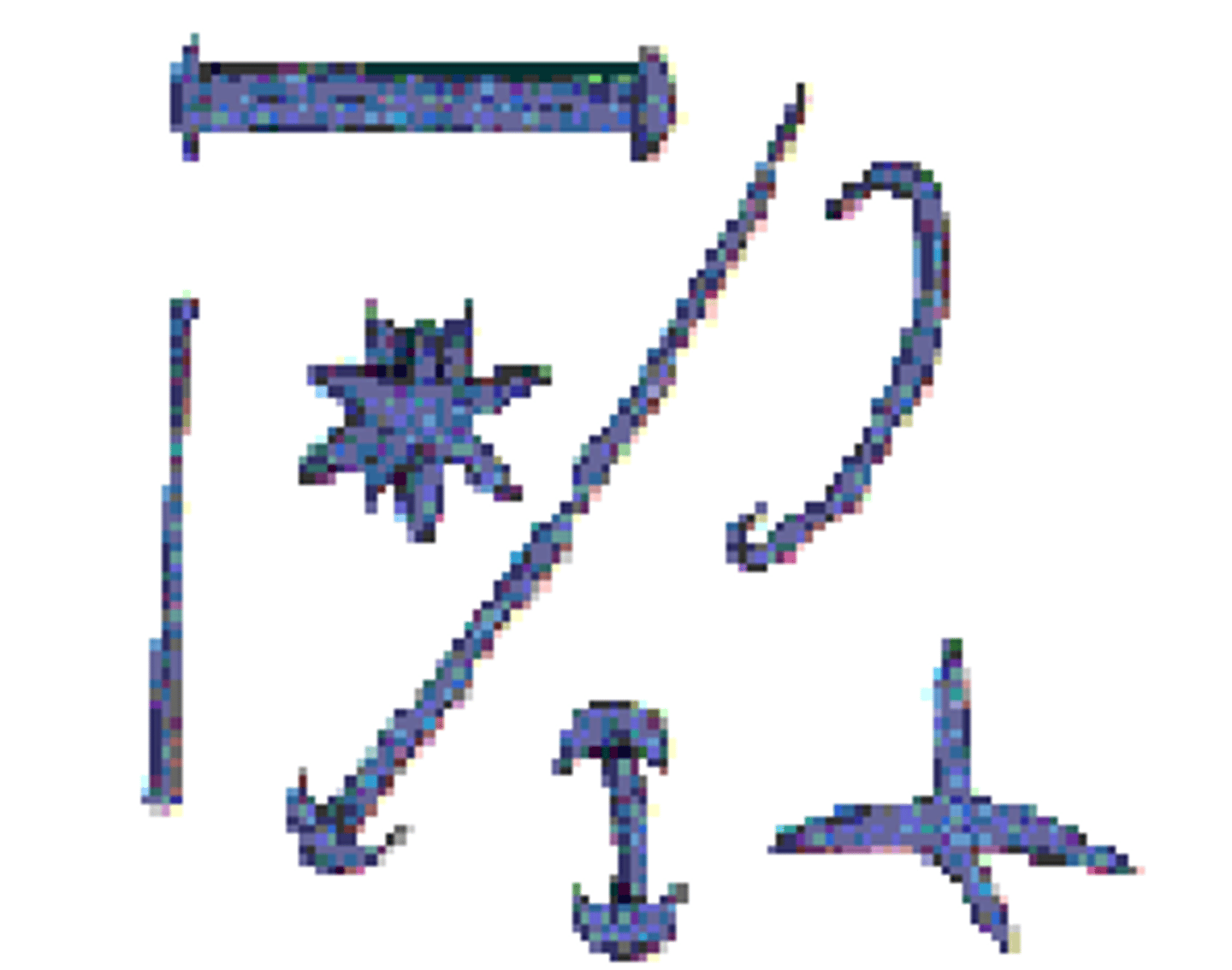
Phylum Porifera
siliceous spicules (demospongiae)
not six rayed
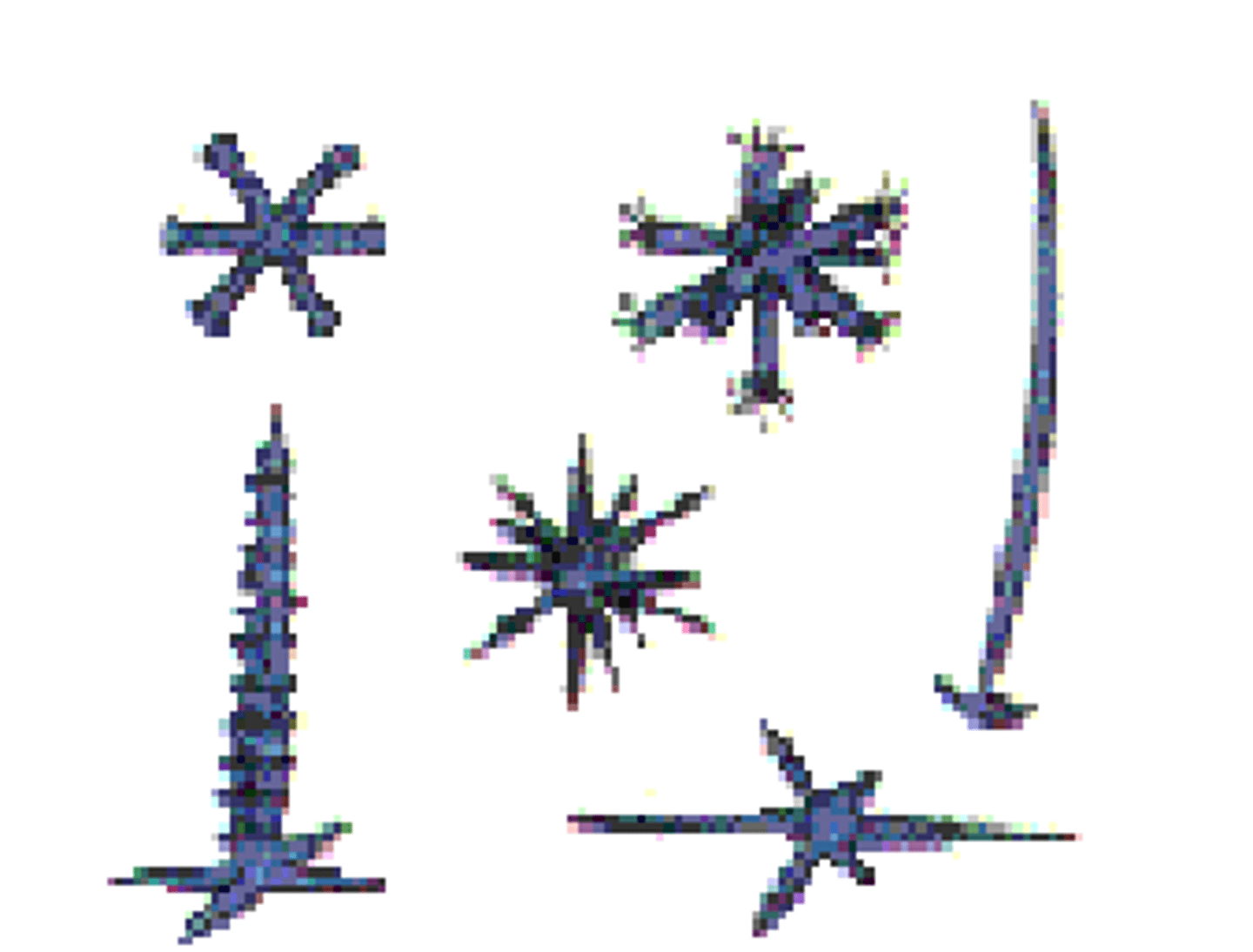

Phylum Porifera
calcareous spicules