Working Capital Management and Inventory Management
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover essential vocabulary terms and definitions regarding Working Capital Management and Inventory Management.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Current Assets
Cash, marketable securities, receivables, and inventories that a company owns.
Current Liabilities
Obligations such as bills payable, bank overdrafts, and outstanding expenses that a company must pay.
Gross Working Capital
Total current assets of a company.
Net Working Capital
Current Assets - Current Liabilities.
Liquidity
How quickly and easily an asset can be converted into cash without significantly affecting its market price. It is a measure of how readily an asset can be bought or sold in the market
Hedging Approach
A financing strategy where long-term funds are used to finance fixed current assets while short-term funds finance temporary working capital.
-More Risky, expects you to fully use the short term funds, not ideal in emergency
-Low Cost
Take the lowest number in table, that’s perm. capital, temporary adds up to the total
Conservative Approach
A financing method suggesting long-term funds only, to cover all current asset needs, using short-term funds only for emergencies.
Trade-off Approach
Financing strategy that balances between hedging and conservative approaches based on average fund requirements.
The average of Total Min fund required, and max fund required.
Find the middle of min and max, and temporary adds it up.
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
The optimal order quantity a company should purchase to minimize total inventory costs. A firm should place neither too large nor too small orders.
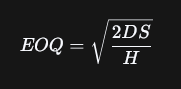
Carrying Cost
The cost associated with storing unsold goods, including storage and capital costs.
Ordering Cost
Fixed costs related to placing and receiving inventory orders.
Cash Management
The process of managing a company's cash flow to ensure sufficient cash for operations.
Motive for Cash Management
Transaction Motive: The need to hold cash to meet day-to-day operating expenses. Ex - Salaries, bills, suppliers
Precautionary Motive: To handle unexpected emergencies. Ex - Sudden expenses, repairs, a fire.
Speculative Motive: To take advantage of profitable opportunities (discounts, investments)
Functions of Cash Management
Cash Planning & Budgeting
Forecasting cash inflows and outflows to avoid shortages.
Managing Cash Flows
Accelerating collections (e.g., early payment discounts).
Delaying payments (without harming supplier relations).
Optimal Cash Balance Maintenance
Ensuring enough liquidity without excessive idle cash.
Short-Term Investments
Investing surplus cash in liquid securities (T-bills, money market funds).
Bank Relationship Management
Negotiating favorable terms (lower fees, overdraft facilities).
Risk Management
Protecting against fraud, currency fluctuations, and interest rate risks.
Fluctuations in working capital
Change in sales
Policy changes
Changes in Technology
Compensating Cash Balance
A minimum cash balance maintained to compensate banks for services.
Inventory Management
The supervision of non-capitalized assets, or inventory, to ensure the right amount of stock is maintained.
Factors Influencing Working Capital Requirement
Nature of Business
Production Cycle
Business Cycle (upward and downward phase)
Credit Policy
Availability of raw material
Dividend policy
Depreciation policy
Operating efficiency
Estimating Working Capital Requirement (Numerical)
Working Capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities.
Need for working capital
Conversion of cash to inventory
inventory to receivables
receivables to cash
and Repeat
Inventory ABC System
A - largest investment and number of items are least.
B - least investment and number of items are highest.
C - in the middle
Reorder point
Lead Time x average daily usage of inventory + safety Stock (extra inventories when actual time or usage is unexpected)
Reorder level
Maximum consumption x Maximum reorder period
Max level of stock
Reorder level + reorder quantity – (Minimum usage * minimum reorder period)
Min level of stock
Reorder level – (Normal usage * average reorder period)
Objectives of Cash Management
Meeting Payments Schedule
Importance of sufficient cash
• Prevents insolvency
• Prompt payment helps in maintaining good relations with trade
creditors and suppliers of raw material.
• Cash discount can be availed if payment is made within due date
• Strong credit rating
• Meet unanticipated cash need during emergencies
Minimising funds committed to cash balances
– Ideal cash is non-earning asset
– Important to determine the factors affecting cash balance