Chapter 11 Nerves
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Homeostasis
relative stability in the body --> balance / nervous system purpose is to regulate body structure and maintain homeostasis
Nervous System
made up of brain, spinal cord, nerves and various sensory structures / sensory input, integration, motor output
Sensory Input
moves signals from sense organs to brain
Integration
interpretation of signals in the form of an appropriate response / CNS
Motor Output
conduct signals to body effectors (muscles and glands)
Central Nervous System (CNS)
consists of brain and spinal cord / responsible for integrating and processing incoming signals from nerves
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
made up of all the nerves and sensory receptors that send information to and from the nervous system
2 Main Types of Cells
Glial Cells = responsible for nourishing, protecting, and maintaining neurons
Neurons (nerve cells) = basic structural and functional units of the nervous system
Purpose of Neurons
1. respond to chemical and physical stimuli
2. conduct electrical impulses
3. release chemicals that regulate various body functions
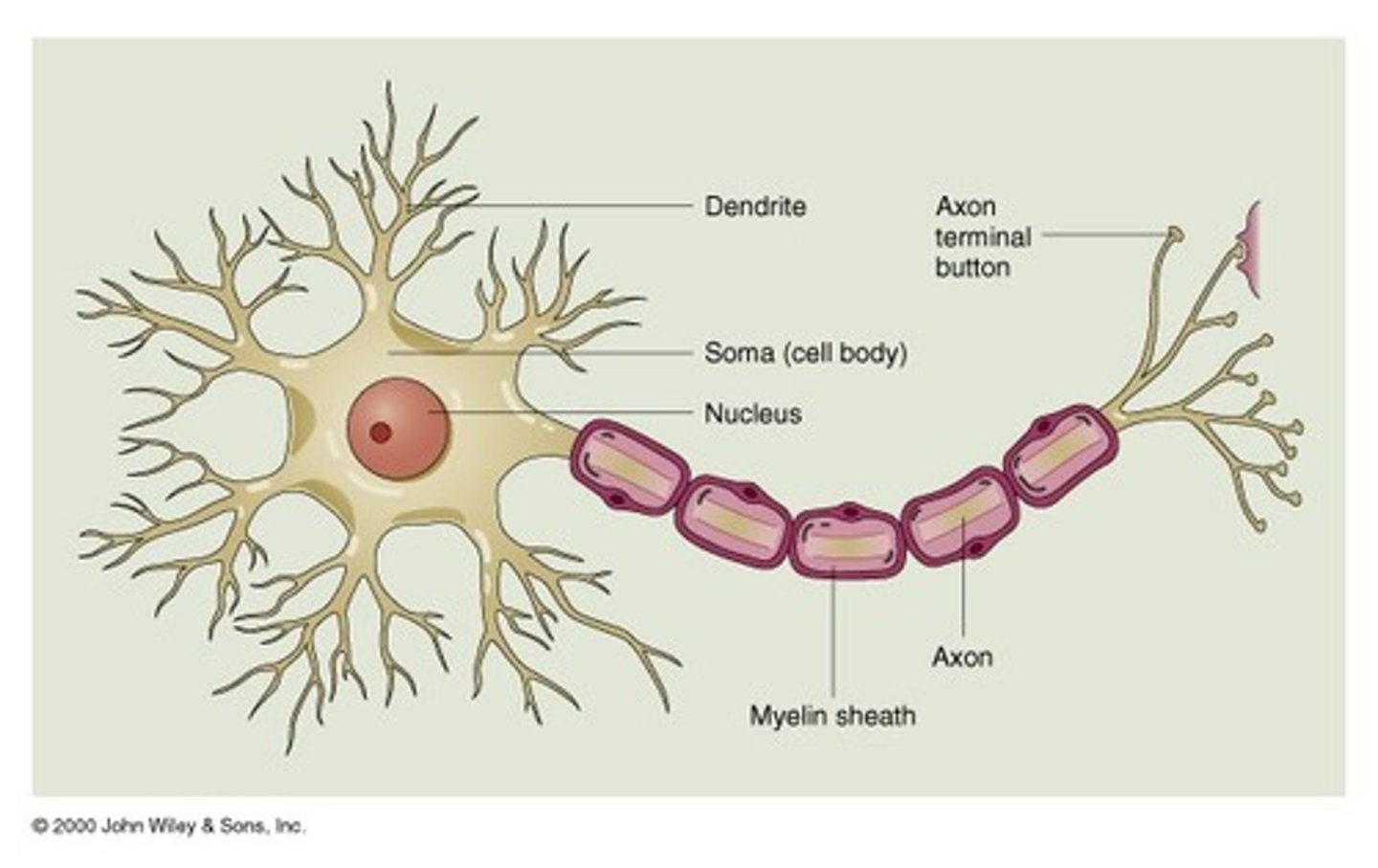
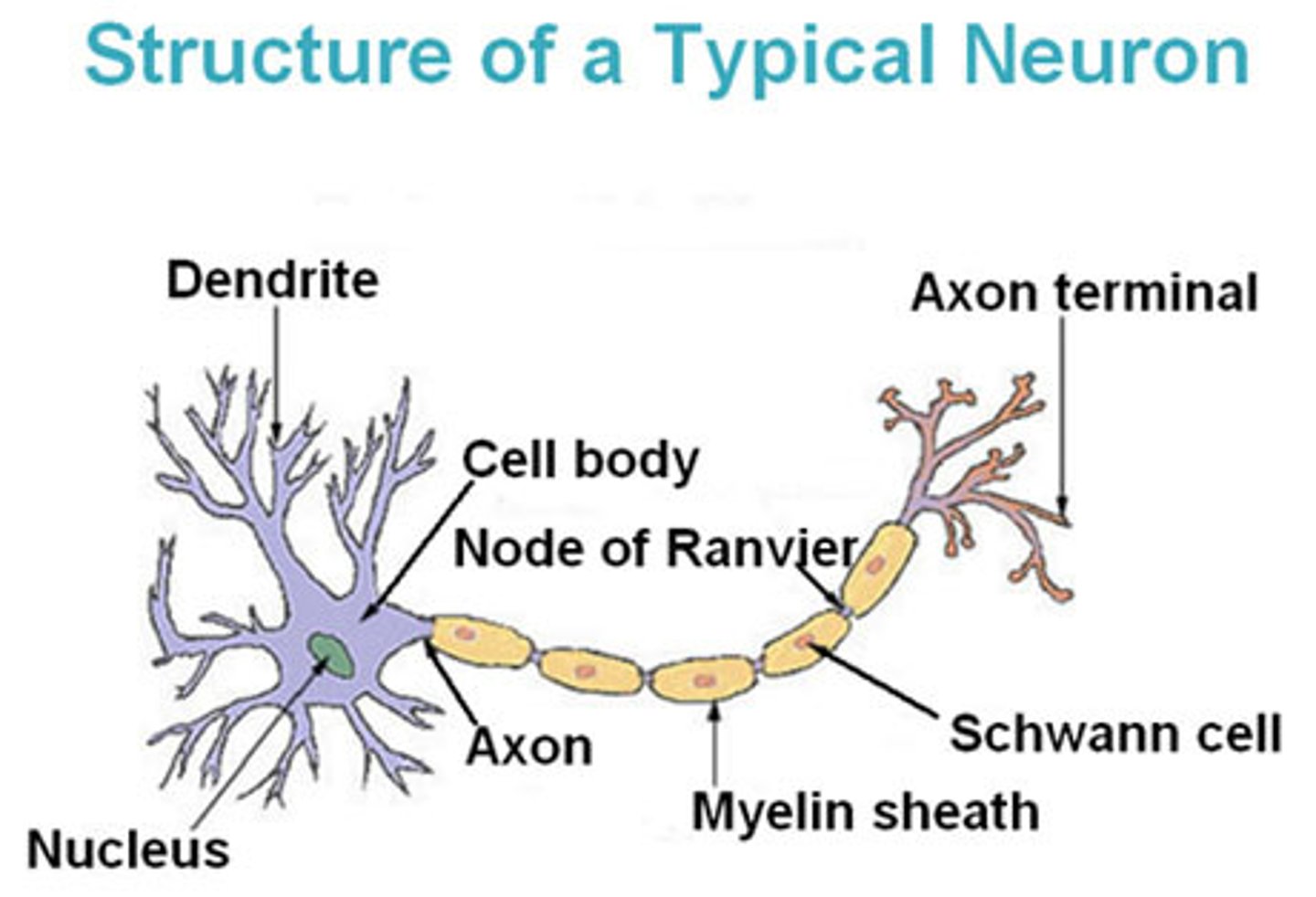
Each Neuron Consists Of
Cell Body = cell's life support center
Dendrites = receives messages from other cells
Axon = passes messages away from cell body to other neurons (membrane prevents oppositely charged ions to become attracted / stores potential energy)
Myelin Sheath = covers axon and some neurons to help speed up impulses
Terminal Branches = form junctions with other neurons
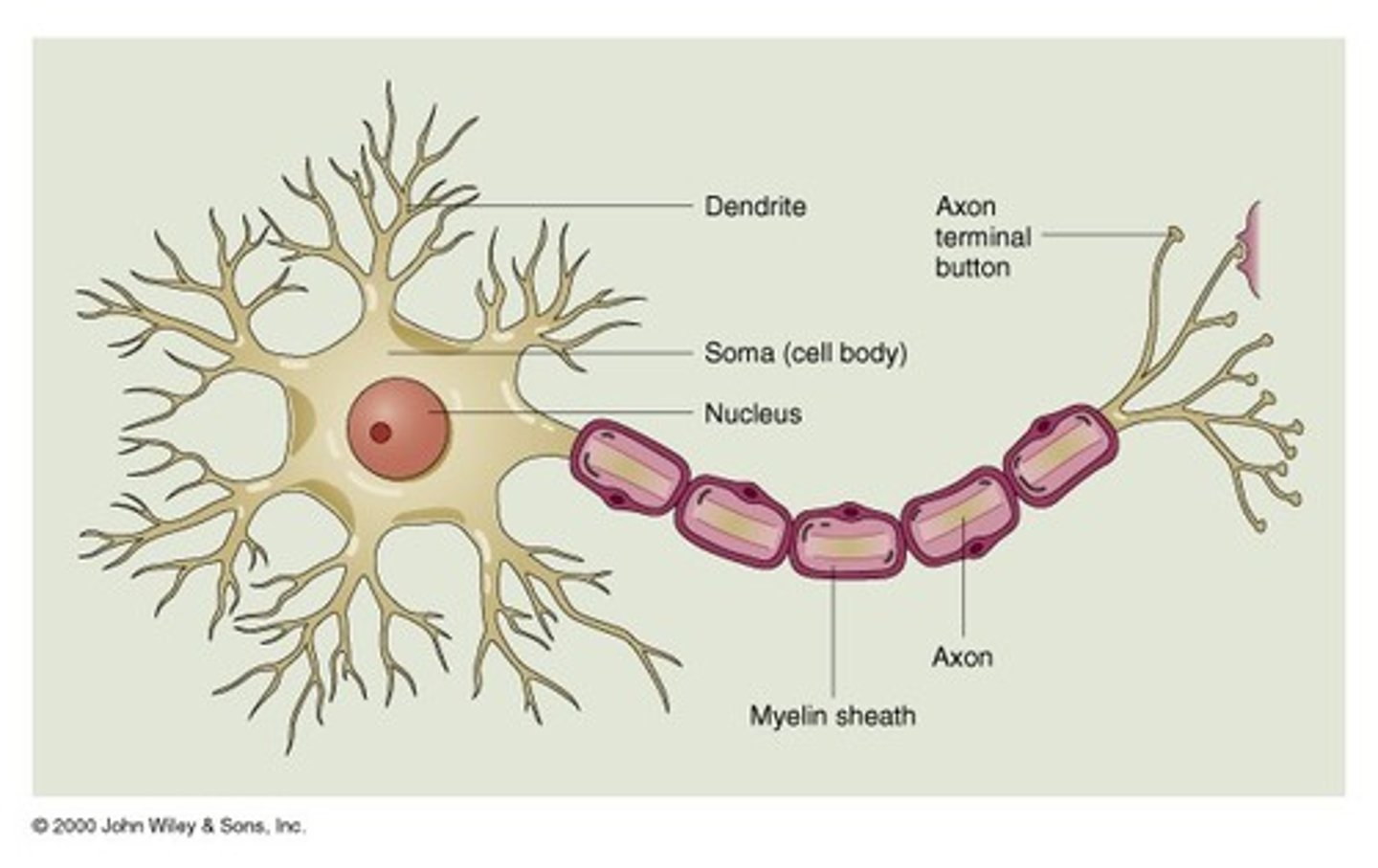
Synapse
gap between 2 neurons that do not physically connect
Types of Neurons
Sensory = gather information from senses and turn it into electrochemical impulses that get carried to spinal cord and brain / blood pressure, taste buds, photo and pain receptors
Motor Effectors = move information from brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands (effectors)
Interneuron = found in CNS and acts as a link between sensory and motor neurons
Direction of Nerve Flow
sensory (afferent) --> interneuron (in CNS)
--> motor (efferent)
Reflex Arc
connection of neurons that models the basic organization of the nervous system / moves directly through the brain and spinal cord without the conscious mind being involved
Reflex Flow
stimulus --> pain receptor --> sensory neuron --> interneuron --> spinal cord
--> motor neuron --> effector (muscle) --> response
Ions
inside of an inactive axon has a negative charge and the outside of the nerve cell has a positive charge / difference in charge is due to the concentrations of + and - charged particles / movement causes an electrical current
Resting Potential
voltage is -70mV / positively charged sodium (Na+) ions are constantly being transported out of the cell making the outside of the cell positively charged
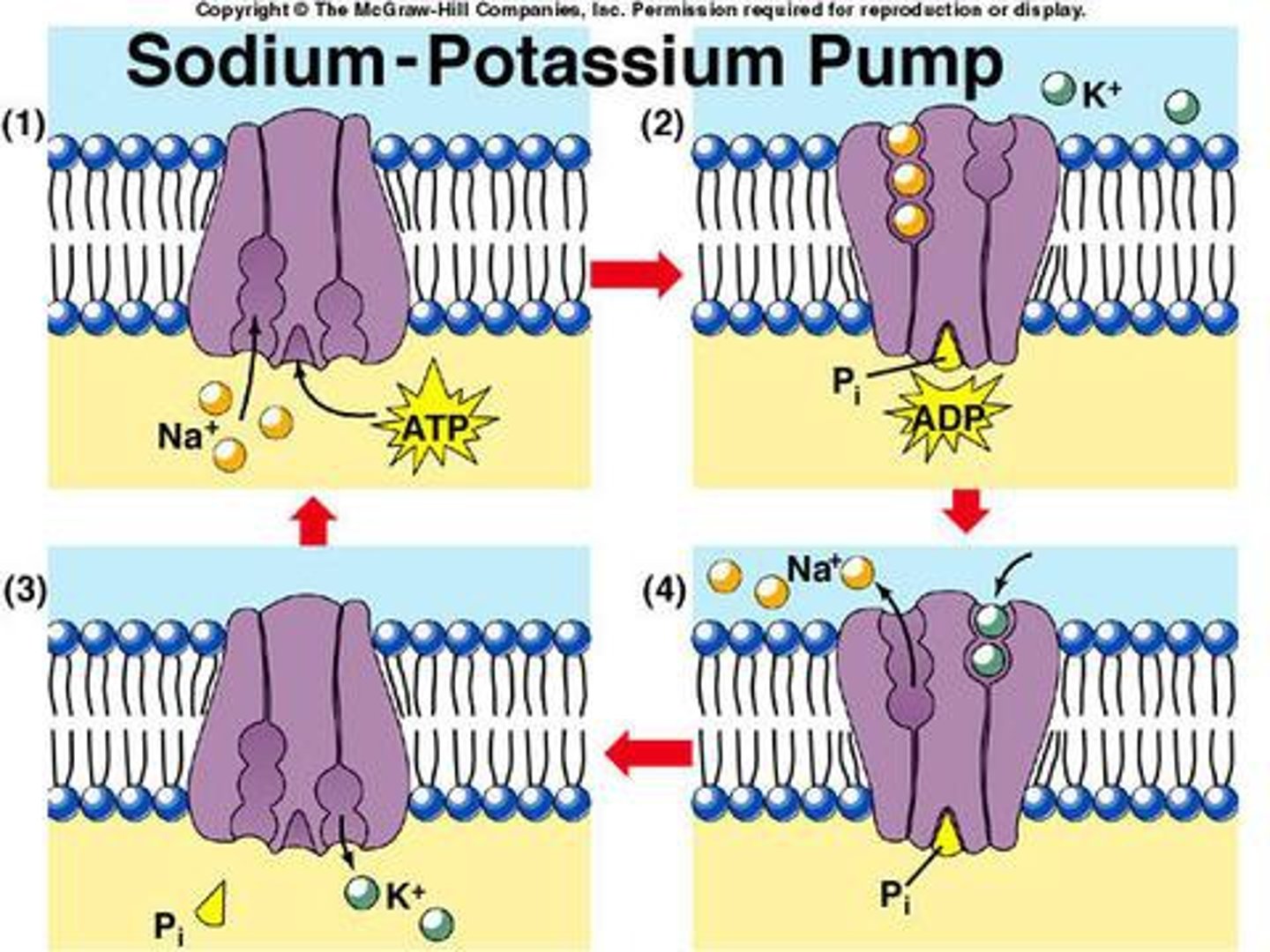
Sodium-Potassium Pump
Na+ is constantly transported out of the cell by active transport / 3 NA+ out and 2 K+ (potassium) in / requires ATP energy
Action Potential
neuron becomes excited due to a stimulus / explosion of electrical activity created by the movement of ions / occurs in depolarization and repolarization
Depolarization
stimulus will cause Na+ ions to leak into cell creating a more positive cell
Threshold Potential
-55mV / voltage regulated channels open and all the sodium ions that are built up outside of the cell flood in / up until +45mV has been reached
Repolarization
the change to +45mV causes sodium channels to close and causes potassium (K+) channels to open and they rush out of the cell
Hyper-Polarization
ions are on wrong sides of membrane (K+ on outside and Na+ on inside) so the sodium-potassium pump works to re-regulate the concentration
"All Or None" Principle
there is no big or small action potential, they are all the same size / the neuron either does not reach threshold potential or a full action potential is fired
Nerve Impulse
electrical signal that travels from dendrites, past the cell body, and along the axon toward the axon terminal / some axons are encased in myelin sheath
Myelin Sheath
fatty and insulating layer around nerve axons
Shwann Cells
type of glial cell / actual cell on axon
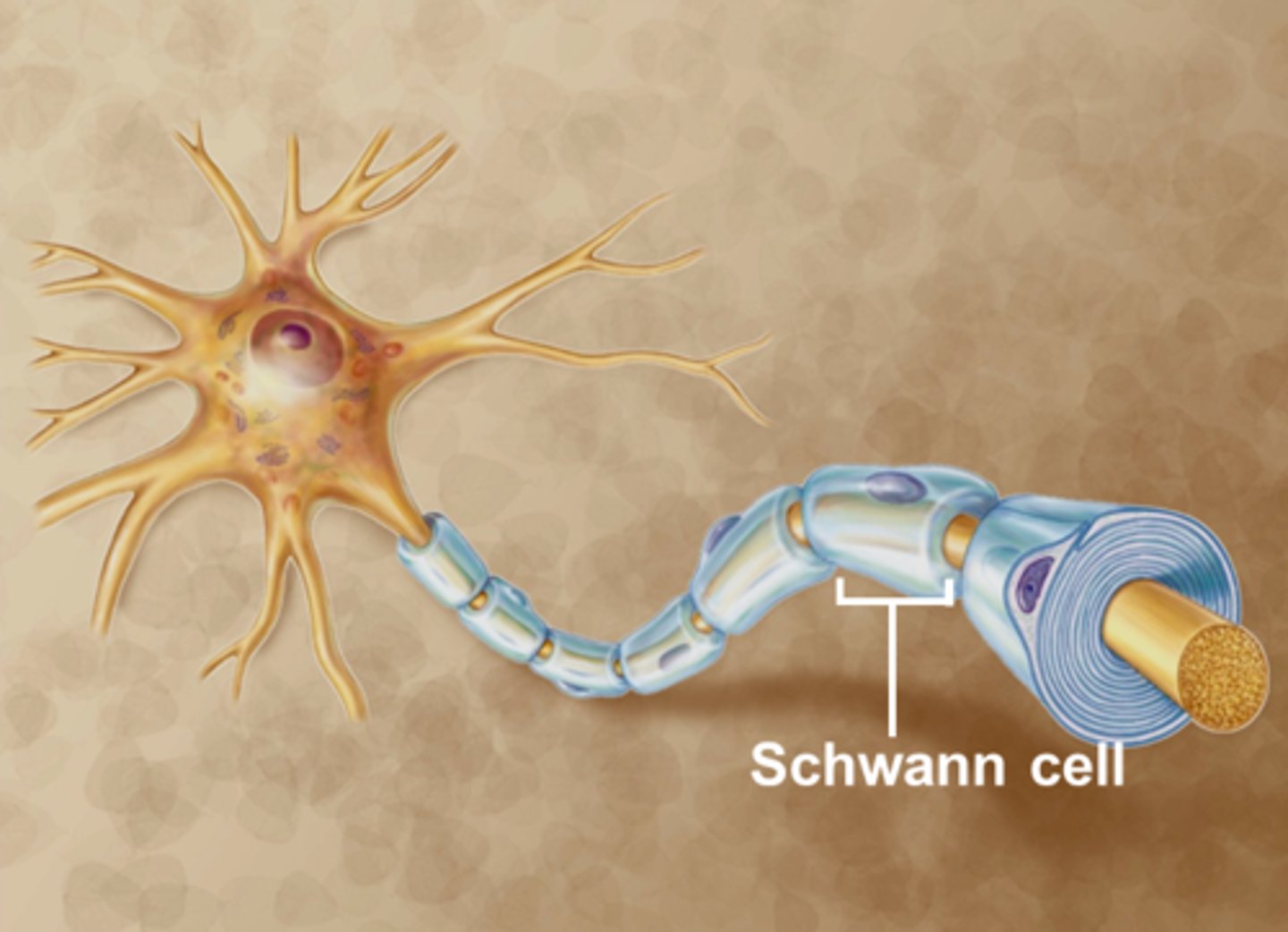
Nodes of Ranvier
points along the axon where signals are transmitted / spaces in between each schwann cell / speed up signal transmission as action potentials jump from one node to the next
Saltatory Conduction
nerve impulse conduction in myelinated nerve fibres because they jump from node to node
White Matter & Grey Matter
CNS myelinated fibres are found in white matter / unmyelinated fibres are found in grey matter / most PNS neurons are myelinated