Exam 1
1/43
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What are the 3 Main Factors that make something a disorder?
Deviation from normal
Distress or impairment
Persistence over time
What is meant by “Scientist-practicioner”?
Mental health professionals whose clinical work is influenced by research (and vice versa)
What are the basic components of psychoanalysis?
emphasized the role of unconscious drives
releasing emotional tension (catharsis) from early trauma through talk therapy
Free association, dream analysis
What Is the structure of the mind?
Id - (pleasure principle; illogical, emotional, irrational)
Ego - (rational; mediates between superego and id)
Superego - (moral principle)

What are the major themes of humanism?
people are basically good
humans strive toward self-actualization (desire to become the most one can be)
What is meant by a multidimensional, integrative approach to understanding psychopathology?
psych disorders are the products of multiple interacting factors
its not nature or nurture, its both
Nature - genes
Nurture = everything else
What is meant by polygenetic?
that more than one gene contributes to most traits
What are the 2 primary models for conceptualizing how genes and environment interact?
Diasthesis-Stress Model
person has a genetic vulnerability
stress “turns on” the genes
Gene-Environment Correlation Model
person has a genetic vulnerability
that person also has an inherited tendency to create the kind of stressful experience needed to turn on the genes (and ultimately develop a disorder)
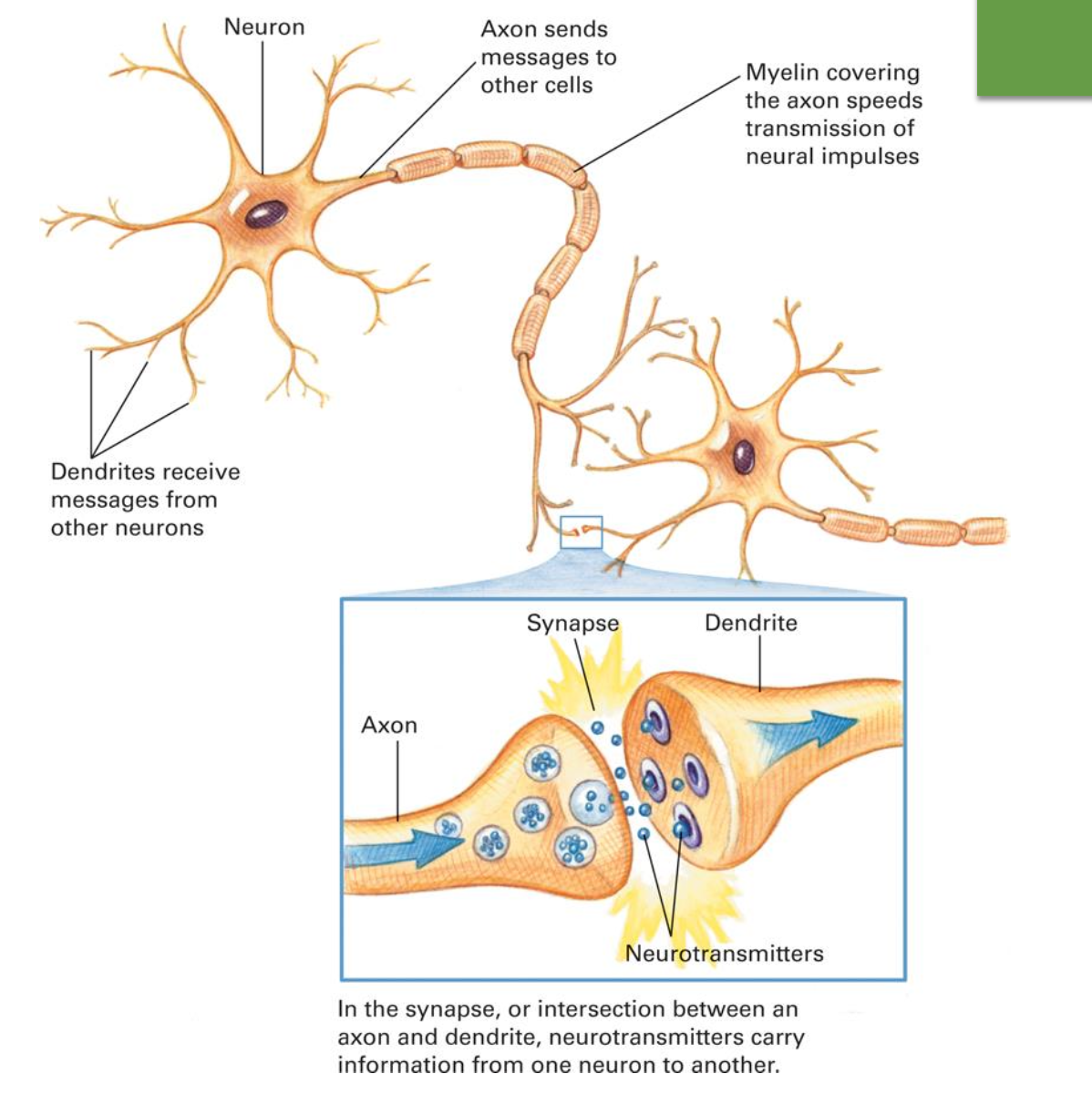
Describe the structure of a neuron including the function of each part.
Axon - fiber that extends from the cell body of a neuron and transmits electrochemical impulses from that neuron to the dendrites of a receiving neuron
Neurotransmitter - brain chemical that carries information from the axon of a sending neuron to the dendrites of a receiving neuron
Dendrites - receive messages from other neurons
Myelin - covering the axon speeds transmission of neural impulses
Synapse - intersection between axon and dendrite
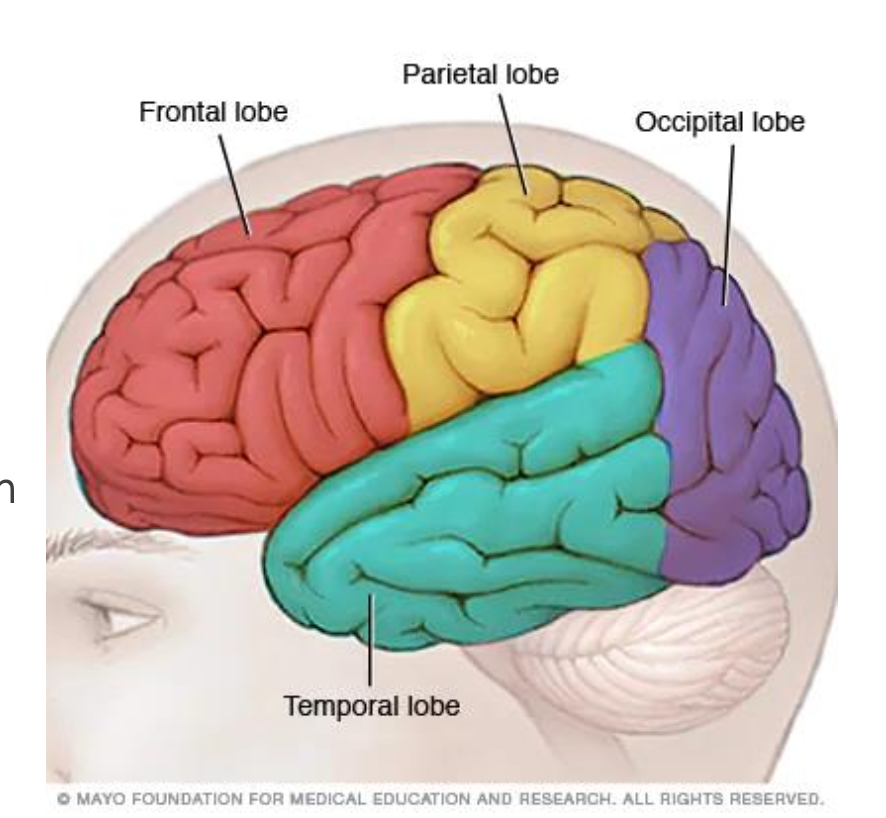
Describe the 4 lobes of the cerebral cortex and their unique responsibilities.
Frontal - thinking and reasoning abilities, memory
Parietal - touch recognition
Occipital - integrates visual input
Temporal - recognition of sights and sounds, long-term memory storage
Describe the function of the HPA Axis.
integration of the endocrine and nervous system function
body’s stress response system
involves the hypothalamus, pituitary, and adrenal glands
What is the difference between clinical assessment and diagnosis?
Clinical assessment - the systematic evaluation and measurement of psychological, biological, and social factors in an individual with a possible psychological disorder
Diagnosis - the process of determining that those factors meet all criteria for a specific psychological disorder
What is the purpose of the clinical interview? What are its components?
Purpose: to understand this patients experience, factors that contributed to onset/maintenance, and identify what else you need to know in order to establish a diagnosis
helps to identify what other assessment tools may be needed
help make recommendations and plan for treatment
Components:
presenting problem
medical and social history
prior treatments
health behaviors
structure/semistructured/unstructured
What are some situations in which a professional may want to gather information from someone other than the patient?
patient may not be good at explaining history and may have a bad memory
family are the one that encouraged the patient to get help
get insight to see if they are doing well medically
Identify general ethical issues relevant to assessment/diagnosis?
patients age
patients privacy
right to refuse care
disclosure of sensitive/reportable info
dual relationships
personal bias
Distinguish between reliability, validity, and standardization.
Reliability - consistency in measurement, test-retest reliability
Validity - what an assessment measures and how well it does so
Standardization - ensures consistency in the use of a tool/technique, provides population benchmarks (norms) for comparison
Recognize/distinguish different types of psychological testing and the purpose of neurological testing.
Personality testing: MMPI
Intelligence testing - gives overall IQ and verbal and performance domains (blocks, pictures, designs) : WAIS, WISC
Projective testing - used to assess unconscious processes and is rooted in psychoanalytic tradition. Scoring/interpretation tends to be more subjective. : Rorschach Inkblot Test
Objective testing - more objective scoring and test stimuli is less ambiguous (what you see is what you get)
Neurological testing - assess broad range of skills and abilities, goal is to understand brain behavior relations, test range of skills including concentration, processing speed, mental flexibility, memory, and visual-spatial abilities
Describe the meaning of comorbidity.
two or more disorders for the same person
What is the difference between anxiety and fear?
Anxiety - worry about possible future danger/threat eg. “What if the plane goes down” when there is no indication of a problem
Fear - present-oriented mood state eg. [as engine is sputtering] “The plane is going down
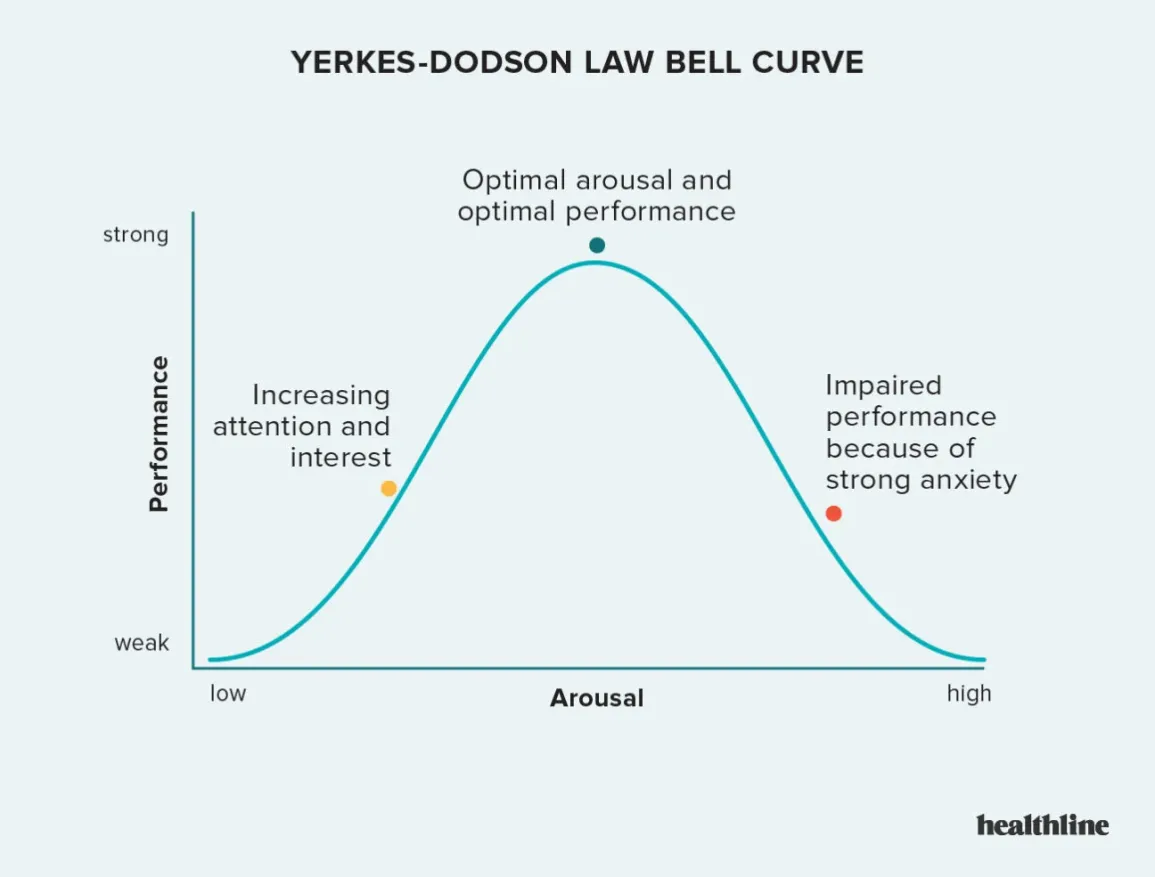
Describe the relationship between physiological arousal and performance.
Up until a point arousal increases performance, too much arousal hinders performance
Prevalence rates for anxiety disorders and general demographic trends
younger people experience more anxiety compared to older people
women experience more anxiety than men
non hispanic whites experience more anxiety compared to other races
Clinical Descriptions
Specific phobia - fear of specific objects or situations, object/situation consistency triggers fear and is avoided or endured with difficulty ex. needles
Social anxiety disorder - fear of negative evaluation in social situations, consistently trigger fear and avoided or endured with difficulty
Panic disorder - recurrent, unexpected panick attacks, persistent worry over having subsequent attacks, significant maladaptive change in behavior. Often paired with Agoraphobia - fear of avoiding places or situations
Generalized anxiety disorder - excessive worry that Is difficult to control, occurring most days for over 6 months, presence of 3+ of the following: restlessness, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, irritability, muscle tension, and sleep disturbance
Biological and psychological contributions to anxiety disorders.
Biological contributions
genetics - more likely if anxiety is in family history
deficits in GABA, norepinephrine, and serotonin
limbic system
Psychological contributions
early history of uncontrollable and unpredictable environmental stressors
conditioning
cognitive appraisals play a role ex. catastrophic thinking (thinking the worst of things)
General prevalence rates for PTSD amongst trauma survivors.
20% of trauma survivors develop PTSD
What is the criteria and causes for PTSD
Criteria
exposure to potentially traumatic life events
re-experiencing symptoms (flashbacks or intrusive thoughts or images)
avoidance symptoms
negative impact on cognitions and mood
Causes
intensity of the trauma and one’s reaction to it (true alarm, fear for one’s own safety)
biological vulnerability
uncontrollability and unpredictability
learn alarms through direct conditioning and observational learning
What is the difference between obsessions and compulsions in OCD?
Obsessions - intrusive and nonsensical thoughts, images, or urges ex. contamination
Compulsions - thoughts or actions to neutralize anxious thoughts ex. hand washing to the point of hands getting raw
Describe the OCD cycle and causes of OCD?
Cycle
Obsessions → Anxiety/Distress → Compulsions → Temporary Relief → Repeat
Causes
parallels other anxiety disorders
early life experiences
learning that some thoughts are dangerous/unacceptable
thought-action fusion - the thought is similar to the actions thinking something will make it more likely to happen
Distinguish between situations where anxiety and fear are normal vs abnormal reactions.
Job Interview - Normal Anxiety
Seeing a Bear Outside House - Normal Fear
Driving on the highway thinking you are going to get hit - Abnormal Anxiety
Seeing a friendly dog - Abnormal Fear
What is the Role of Mental Status Exams and what are some circumstances in which they may be appropriate to administer?
Role - to see how the patient is doing through
appearance and behavior (cleanliness, eye contact)
thought content and processes (how are they speaking)
mood and affect (how pt states they feel)
intellectual functioning
sensorium (orientation, place, time)
Circumstances
Self-referral for anxiety or by neurologist for neurological testing
pre-surgical assessment
admitted for suicide attempt
What Classification systems are used to diagnose psychopathology and distinguish the 3 approaches to classification.
Systems
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM)
International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10)
3 Approaches
Classical (or pure) categorical approach - strict categories
dimensional approach - classification along dimensions
prototypical approach - combines classical and dimensional views
Difference between classical and operant conditioning.
Classical
people learn associations between neutral stimuli (unconditioned stimuli) and stimuli that already have meaning (conditioned stimuli) ex. Pavlovs dogs
conditioning explains the acquisition of some fears
Operant
reinforcement/punishment
voluntary behavior is controlled by consequences)
Describe early types of biological treatments.
Insulin shock therapy - give patients higher and higher doses of insulin to result in convulsions. Some got better, some didn’t
Electroconvulsive therapy - delivering electrical currents to the brain to “reset” things, sort of a last result
Frontal lobotomy - sever connections in the brain by inserting tool through eye to brain
Tranquilizers - sedate patients
Identify prevailing beliefs about the causes of and treatments for abnormal behavior in the Middle Ages.
Supernatural
the devil and witches were responsible for irrational behavior
treatments for demonic possession included exorcisms, torture, and religious services
moon and stars
Historical
Hippocrats and Galen - Humoral Theory - 4 humors must be in balance. Treated with bloodletting or changing environmental conditions
Hysteria “the wandering uterus” - psychological symptoms were a result of the uterus moving around in the body. Treatment was to get married
Syphilis and biological link with madness. Treatment was to give small amounts of malaria
Describe the role of serotonin and dopamine.
Serotonin - influences information processing, behavior, mood, and thoughts
dysregulated serotonin may contribute to depression
low serotonin linked to impulsivity
Dopamine - gives you feeling of pleasure, satisfaction, and motivation (rewarding sensation)
link between excessive dopamine and schizophrenia
link between reduced dopamine and Parkinson’s disease
implicated in depression and ADHD
Role of the Limbic System.
helps to regulate our emotional experiences and expressions and ability to learn and control our impulses
also involved in basic drives
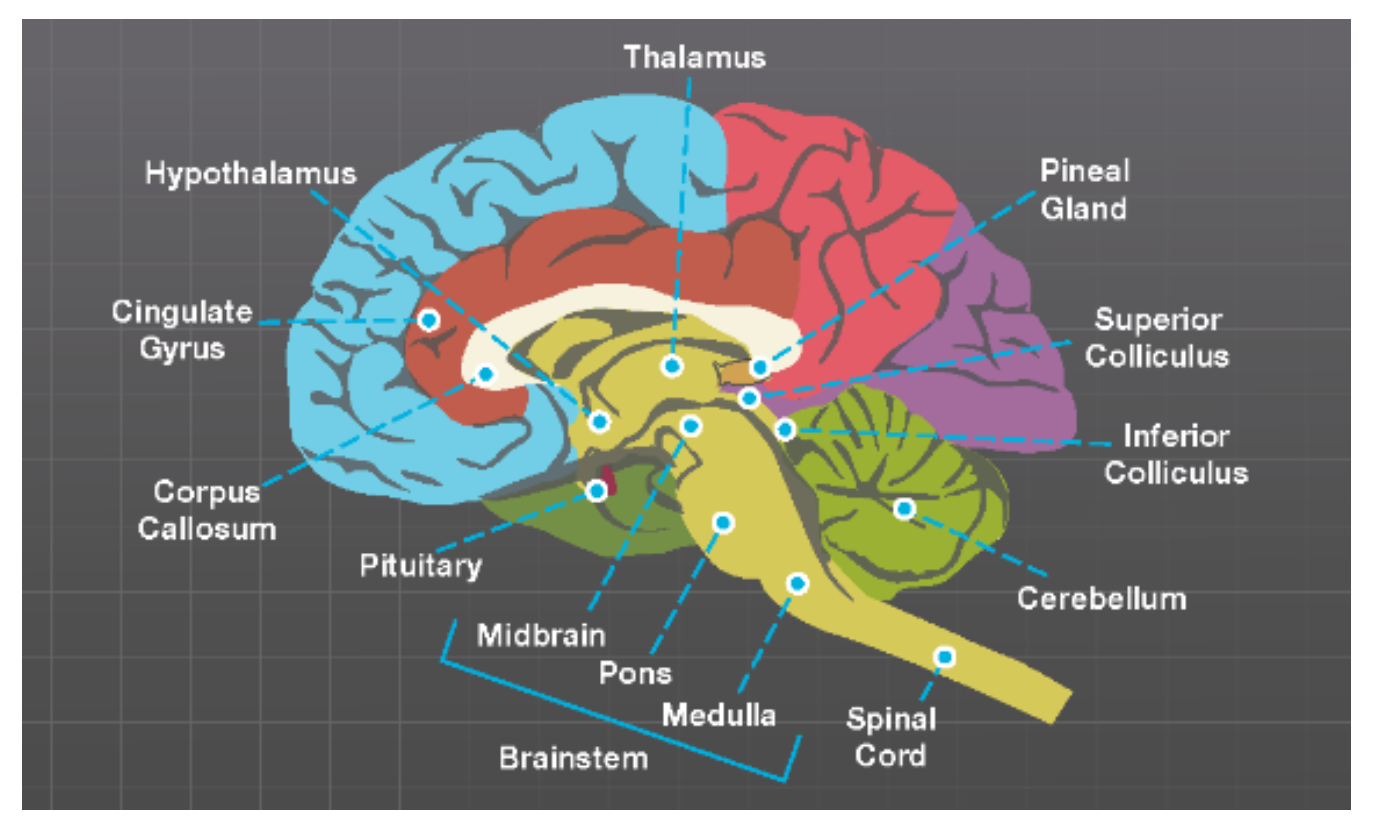
Distinguish between the responsibilities of the brainstem vs the forebrain and recognize structures within both.
Brainstem - vital function of life ex. breathing
hindbrain
midbrain - arousal, temp regulation, coordination
thalamus and hypothalamus
Forebrain - sensory processing, behavior response to stress and fear
limbic system
basal ganglia - motor control
cerebral cortex (largest part of the brain)
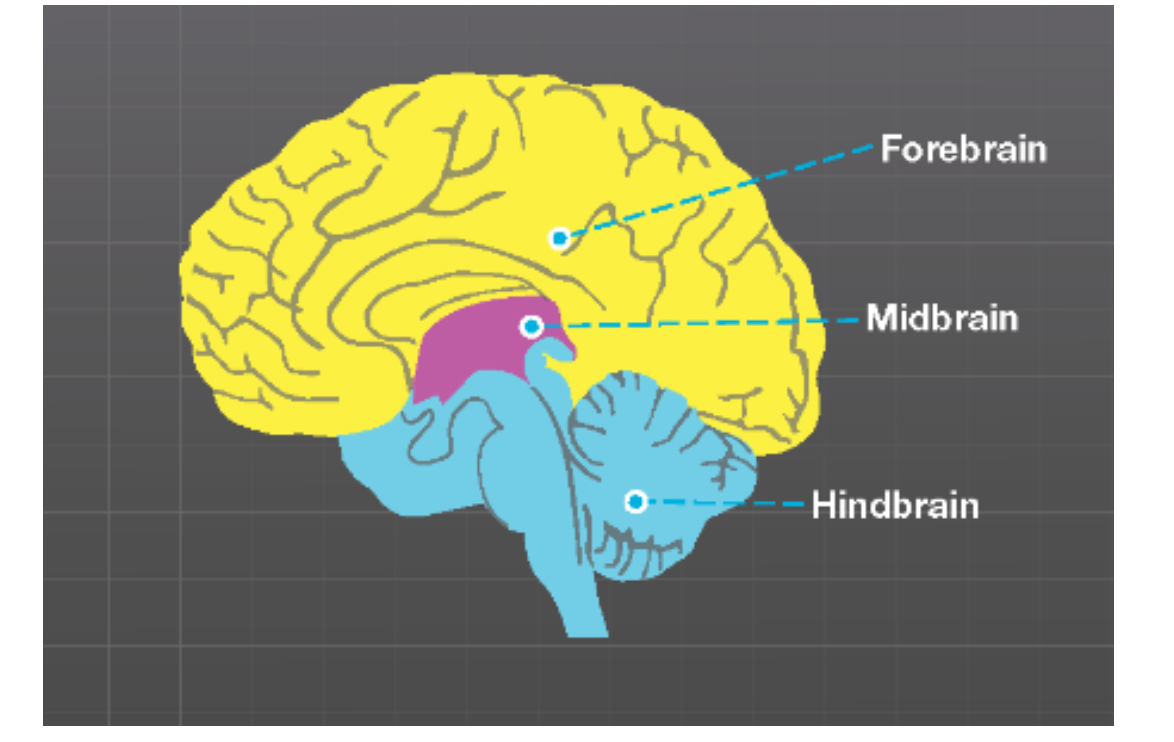
Recognize the branches of the nervous system and their responsibilities.
Central Nervous System - take in sensory info, process info, and send out motor signals
Brain and Spinal Cord
Peripheral Nervous System
somatic - controls voluntary muscles and movements
autonomic branches - involuntary processes, regulates cardiovascular system and body temp, sympathetic and parasympathetic
endocrine system - regulates all hormones ex. adrenal and thyroid glands
Function and components of emotion and describe how emotions relate to psychopathology.
Some emotions can affect us both mentally and physically
Components of emotion
cognition
physiology
behavior
Ways in which the sociocultural context can influence psychopathology
Taijin kyofusho - fear of being disrespectful to others
Dhat - anxiety related to semen loss
Susto - belief that you have been victim of black magic
Hippocampus and Amygdala Roles
Hippocampus - main job is to help with memory, helping move short term memory to long term
Amygdala - feeling of fear and perception of threat, memory is involved, tendency toward aggression
Recognize evidence-based treatments for anxiety & related disorders including the components and assumptions of cognitive-behavioral therapy and the role of exposure.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
at the core of the problem is 1) faulty ways of thinking and 2) unhelpful behaviors
we can practice more adaptive ways of thinking and behaving
people can learn to be their own therapist
Recognize faulty cognitions
all or none thinking
emotional reasoning
over generalizing
Treatments
real life - being exposed to a fear in real life
imagined - vividly imagining a fear
virtual reality - using vr to be exposed to a fear
interceptive - bringing sensations into play in an effort to disconfirm the idea that physical sensations will lead to harmful events
Clinical Descriptions of Somatic Symptom Disorder and Functional Neurological Symptom Disorder
Somatic Symptom Disorder
at least one bodily symptom that is distressing and/or significantly impairing
excessively thinking about, worrying about, and/or spending time devoted to these symptoms
symptoms typically last 6+ months
Functional Neurological Symptom Disorder
at least one symptom affecting a persons sensation, perception, or voluntary movement without identified cause (tingling, blindness, partial paralysis)
typically comes on suddenly
causes significantly distress or impairment
Causal Factors and Components of treatment for somatic symptom disorder and functional neurological symptom disorder.
Factors for Somatic Symptom Disorder
familial history of illness
stressful life events
sensitivity to physical sensations
experience suggesting that there are benefits to illness (treated nice)
Treatment for Somatic Symptom Disorder
support for CBT
reduce tendency to visit numerous medical specialists
assign “gatekeeper” physician
reduce supportive consequences of talk about physical symptoms
Treatment for Functional Neurological Symptom Disorder
similar to Somatic Symptom Disorder
if onset after a trauma, may need to process trauma or treat post traumatic symptoms
remove sources of secondary gain
reduce supportive consequences of talk about physical symptoms
Clinical Description of Factitious Disorder
purposely faking physical symptoms
may actually indicate physical symptoms or just pretend to have them
no obvious external gains
different from malingering (faking symptoms for a benefit such as money or attention)