Bio Hon Final Exam Study Set (UNDER CONSTRUCTION)
1/308
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
309 Terms
abiotic
Non-living
biotic
Living
ecosystem
..., A biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment.
producer
..., An autotrophic organism that makes its own food and serves as a source of food for other organisms in a food chain.
photoautotrophs
..., An organism that makes energy from sunlight
chemoautotrophs
An organism that derives energy from inorganic compounds, such as hydrogen sulfide.
photosynthesis (equation)
..., 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy -> C6H12O6 + 6CO2
chemosynthesis (decription)
...using energy from inorganic compounds, such as hydrogen sulfid
consumer
..., An organism that obtains energy from other organisms
cellular respiration equation
..., C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy (reverse of photosynthesis reaction)
heterotroph
..., An organism that cannot make its own food, and thus must ingest other organisms or their byproducts
herbivore
..., A consumer that only eats plants
carnivore
..., A consumer that eats only animals.
omnivore
..., A consumer that eats both plants and animals.
decomposer
..., An organism that breaks down wastes and dead organisms.
keystone species
..., a species whose impact on its community or ecosystem are much larger and more influential than would be expected from mere abundance
primary consumer
..., An organism that eats producers
secondary consumer
..., An organism that eats primary consumers
tertiary consumer
..., An organism that eats secondary consumers
numbers pyramid
..., represents the number of individual organisms at each trophic level
biomass pyramid
..., Diagram representing the biomass in each trophic level of an ecosystem
energy pyramid
..., A diagram that shows the amount of energy that moves from one feeding level to another in a food web
Rule of 10
..., only about 10 percent of the energy available within one trophic level is transferred to organisms at the next trophic level
intraspecific competition
..., Competition among members of the same species
interspecific competition
..., Competition between members of different species
niche
..., An organism's particular role in an ecosystem, or how it makes its living.
commensalism
..., +/0
mutualism
..., +/+
parasitism
..., +/-
Limiting factors
..., Anything that limits (restricts) the size of a population
J-curve
..., a growth curve that depicts exponential growth
S-curve
..., a curve that depicts logistic growth; shape of an "S"
carrying capacity
..., Largest number of individuals of a population that a environment can support
Immigration
..., Migration in to a location
Emigration
..., Migration out of a location
Formula for population growth
..., (Births + Immigration) - (Deaths + Emigration)
r-selection
..., High rate. Common in unstable environments, the ability to reproduce quickly
k-selection
..., High care. "slow and few" less offspring and it takes longer
invasive species
..., species that enter new ecosystems and multiply, harming native species and their habitats
primary succession
..., Succession that occurs in an area in which no trace of a previous community is present.
secondary succession
..., Succession following a disturbance that destroys a community without destroying the soil
pioneer species
..., First species to populate an area during succession
chlorophyll
Absorbs light energy.
Pigment that gives a plant its green color. Found in the chloroplast

oxygen
product of photosynthesis
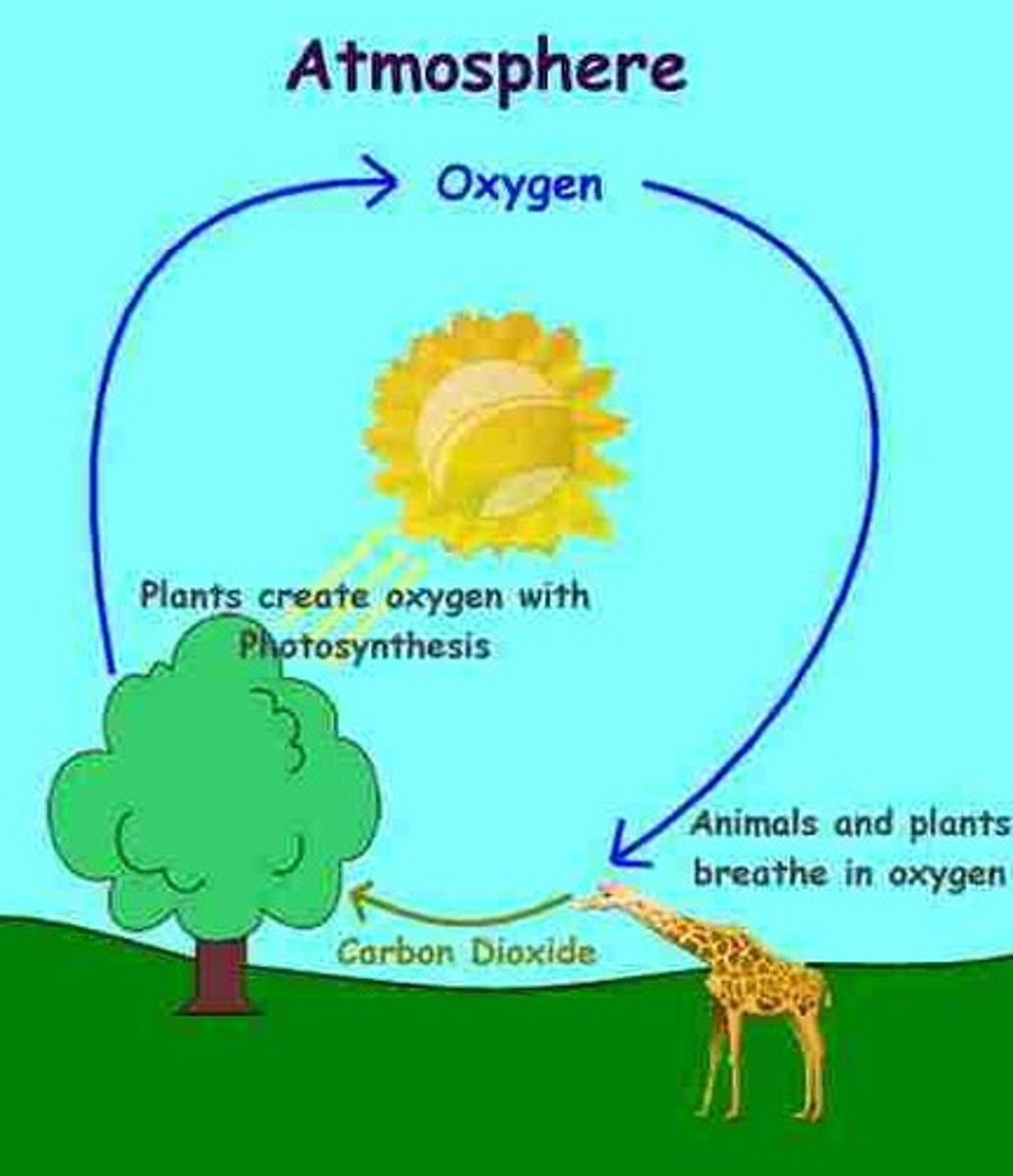
carbon dioxide
Gas taken in and used during photosynthesis.
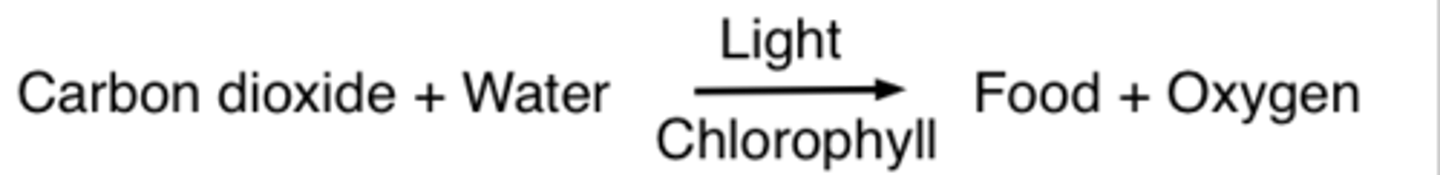
Photosynthesis word equation
carbon dioxide + water --> glucose and oxygen
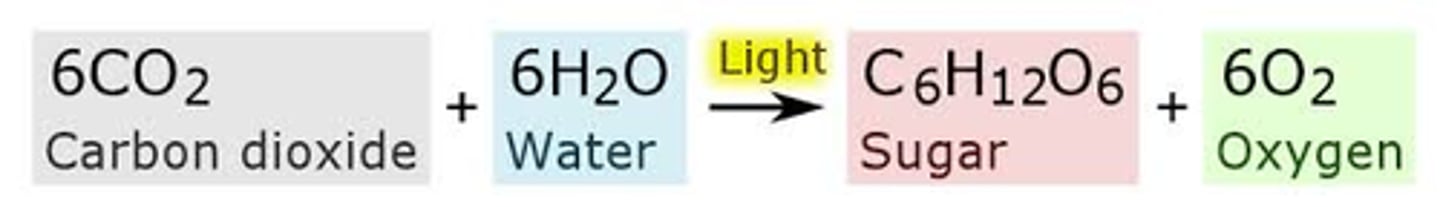
Photosynthesis symbol equation
CO2+H2O --> C6H12O6 + O2
Autotrophs
Organisms that produce their own food.
Heterotrophs
Organisms that consume other organisms for food.
Law of Conservation of Matter
Matter cannot be created or destroyed.
Law of Conservation of Energy
Energy cannot be created or destroyed.
Photosynthesis Equation
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Byproduct of photosynthesis released into the atmosphere.
oxygen
Gas absorbed by plants during photosynthesis.
carbon dioxide
2nd Law of Thermodynamics
Energy cannot be changed from one form to another without a loss of usable energy (typically heat)
auto-
self
troph
feeder
hetero-
other
Producers
An organism that makes organic food molecules from carbon dioxide , water and other inorganic raw materials
Consumers
An organism that obtains its food by eating plants or animals
Aerobic
Requiring molecular oxygen
Fermentation
The anaerobic harvest of food by some cells
Two types of fermentation and their products
Alcoholic fermentation makes Ethanol and CO2
Lactic acid fermentation makes Lactic Acid
Anaerobic
Lacking or not requiring molecular oxygen
Evolution
Any net directional or cumulative change in the characteristics of organisms in a population over many generations - i.e. descent with modification.
Natural Selection
Process by which individuals that are better suited to their environment survive and reproduce most successfully; also called survival of the fittest
Adaptive Trait
A heritable trait that enhances an individuals fitness; an evolutionary adaptation.
Mutations
A change in the nucleotide sequence of an organism's DNA, ultimately creating genetic diversity. Mutations also can occur in the DNA or RNA of a virus.
Artificial Selection
Humans modifying other species over many generations by selecting and breeding individuals that possess desired traits
Species
A group of organisms of common ancestry able to reproduce fertile offspring only among themselves, usually geographically distinct.
Speciation
Divergent process in which natural selection has caused populations of one species to diverge to form new species,
Extinction
A term that describes a species that no longer has any known living individuals.
Mass Extinction Events
the elimination of a large proportion of the world's species in a very short time period due to some extreme and rapid change or catastrophic event
4 Things That Must Happen for Natural Selection to Occur (AKA VIDA)
V - individuals in a pop. vary in some traits
I - the trait is inherited
D - More offspring are born than can survive and those with the trait have a better chance of surviving and reproducing.
A - The frequency of an adaptive trait will increase in the population over time
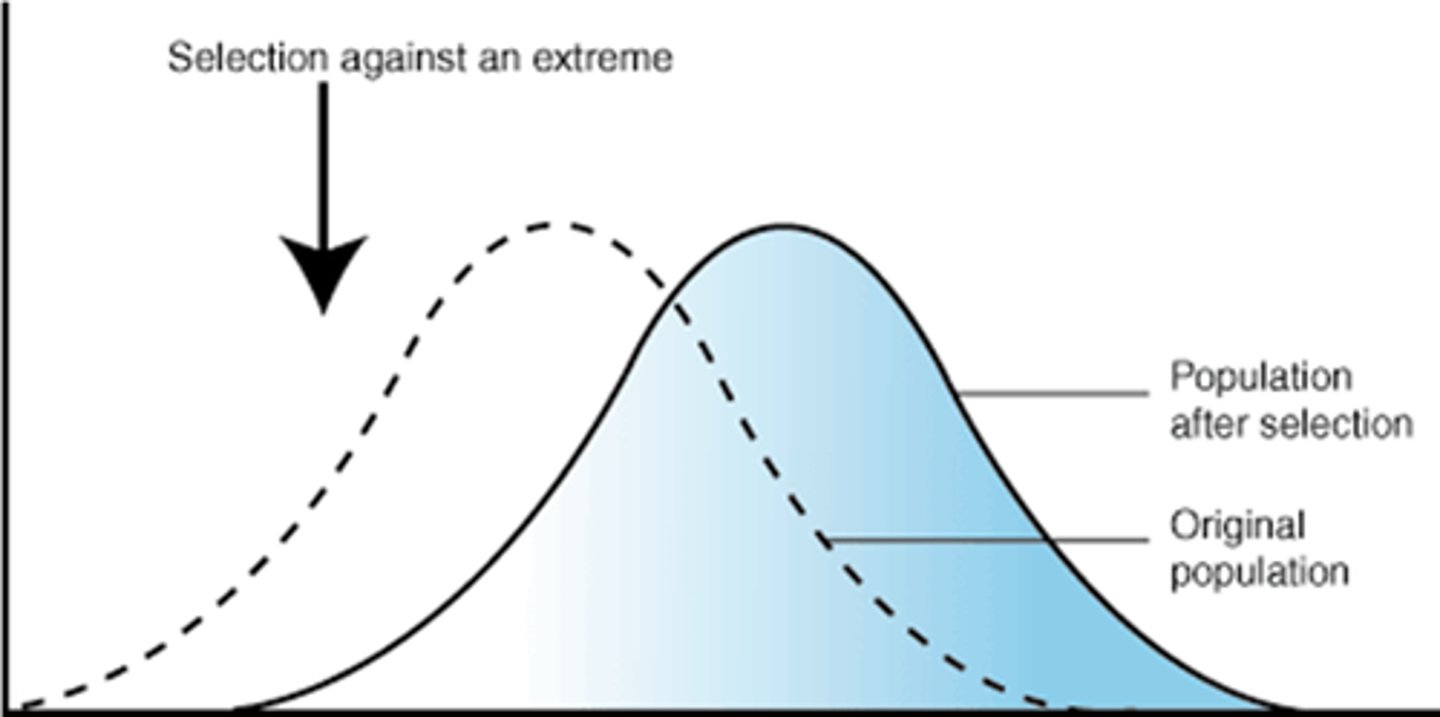
Directional Selection
An extreme phenotype is favored over others, leading to shift in allele frequency toward one extreme or the other
Example of Directional Selection
Darwin's finches and beak depth
-at the time of drought only large and hard seeds available
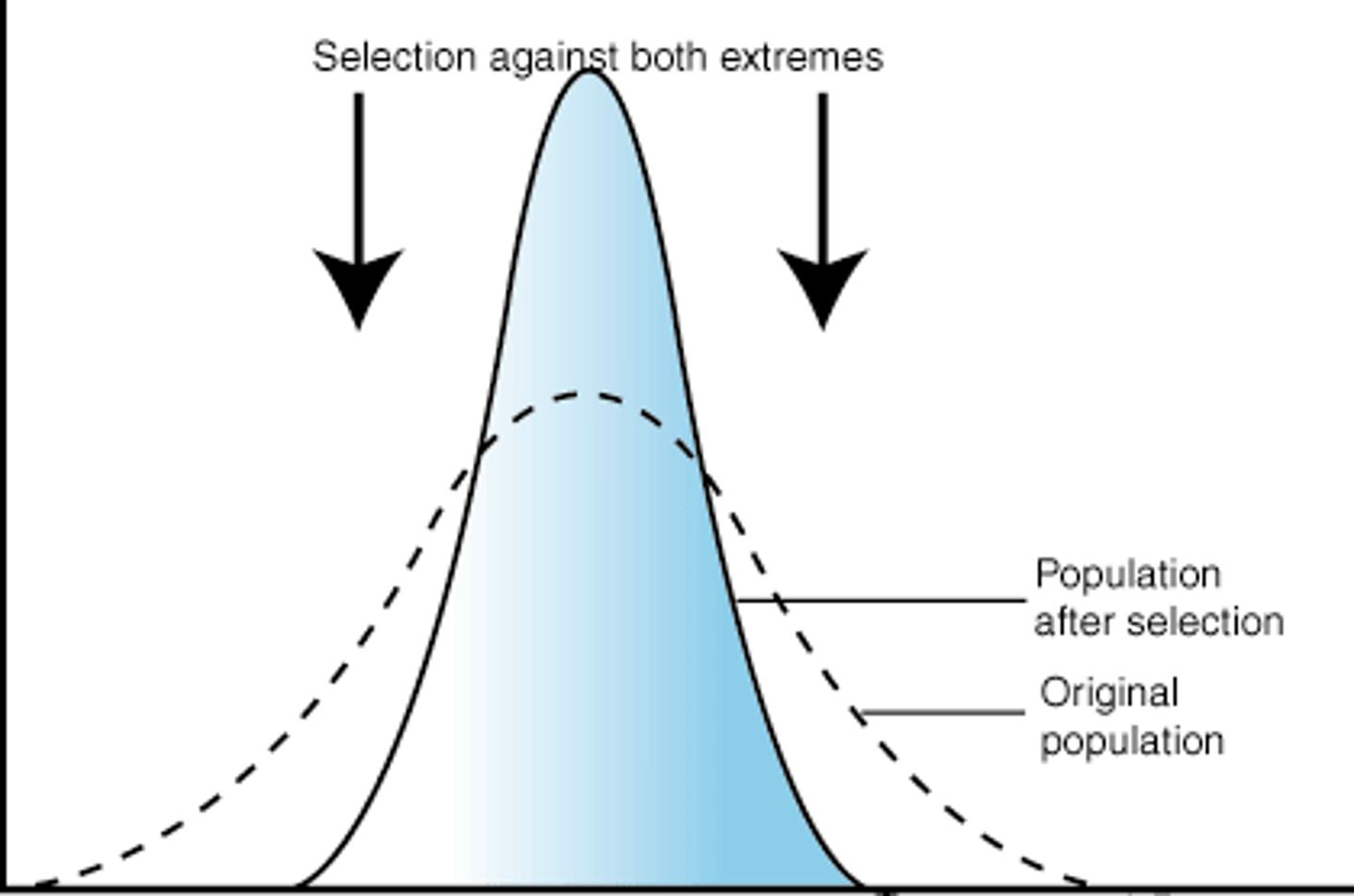
Stabilizing Selection
Acting against the extreme phenotypes and favoring the average.
Example of Stabilizing Selection
Birth Weight
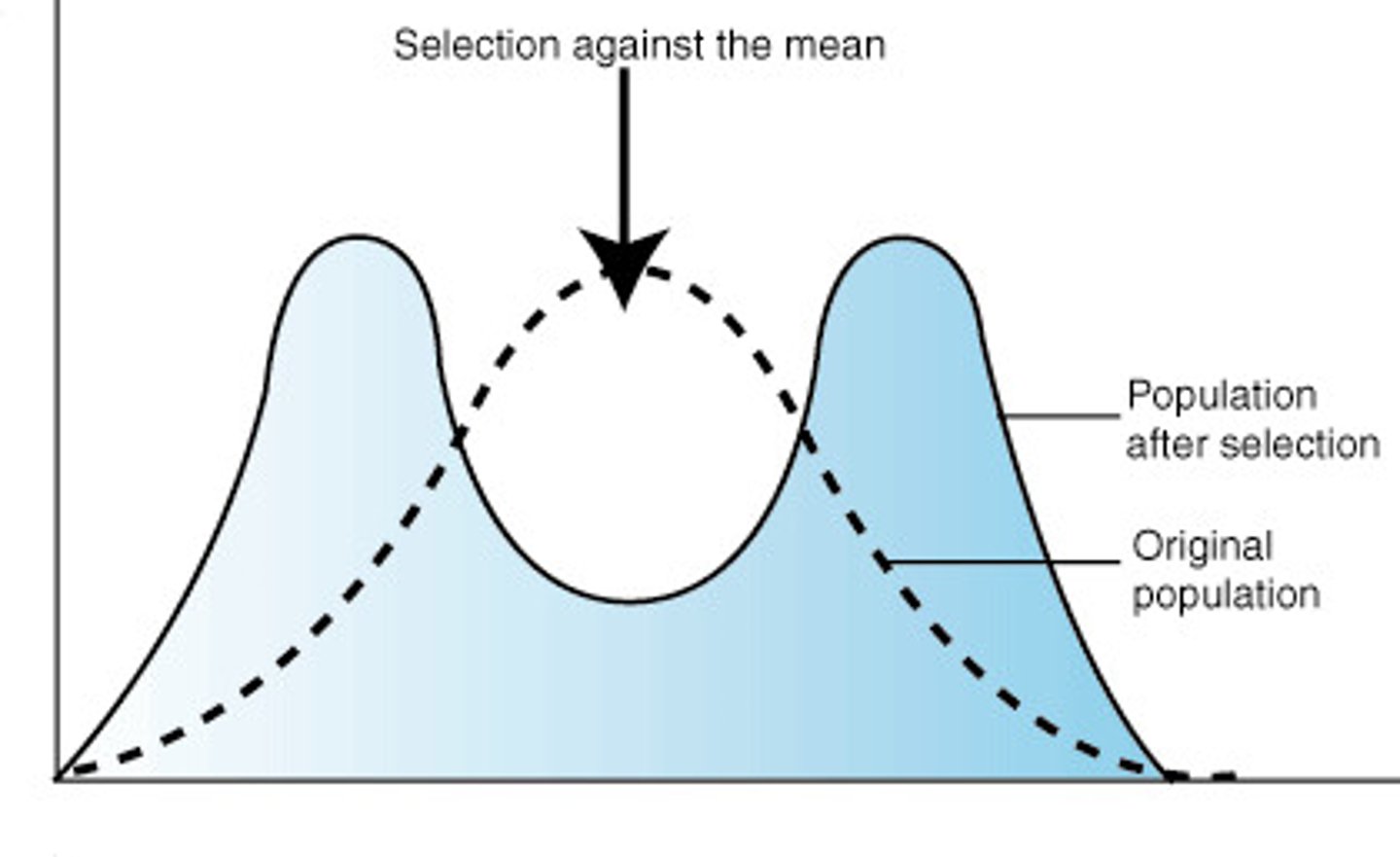
Disruptive Selection
Extreme phenotypes favored over intermediates, leading to selection against average phenotypes.
Disruptive Selection looks like:
Stabilizing Selection looks like:
Directional Selection looks like:
What is microevolution?
Evolution occurring within populations by changing phenotypic and/or allele frequencies.
What are the three types of selection in evolution?
Disruptive, Stabilizing, and Directional selection.
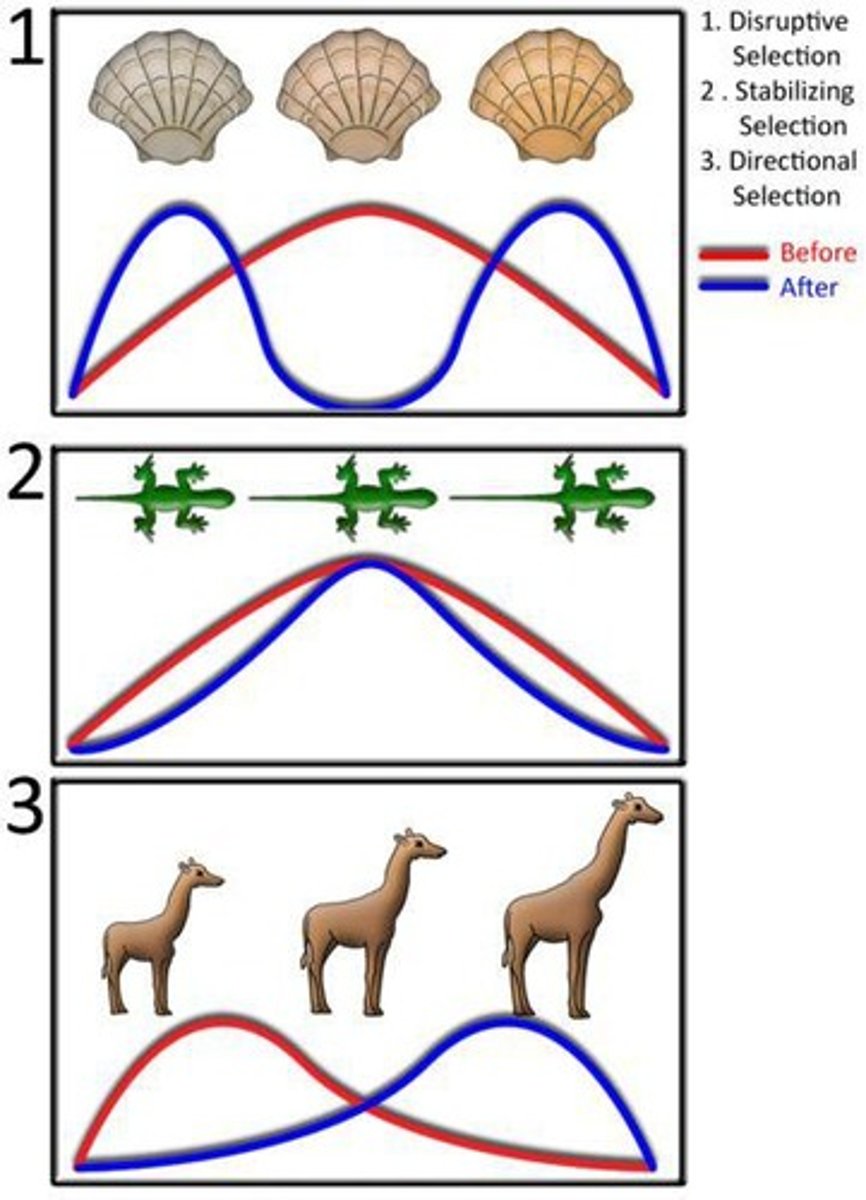
Provide an example of disruptive selection in cichlid fish.
Intermediate males obtained fewer matings than males at either extreme of the color range.
Give an example of stabilizing selection.
Birth mass, where average-sized babies are favored because small babies are less likely to survive and large babies are harder to deliver.
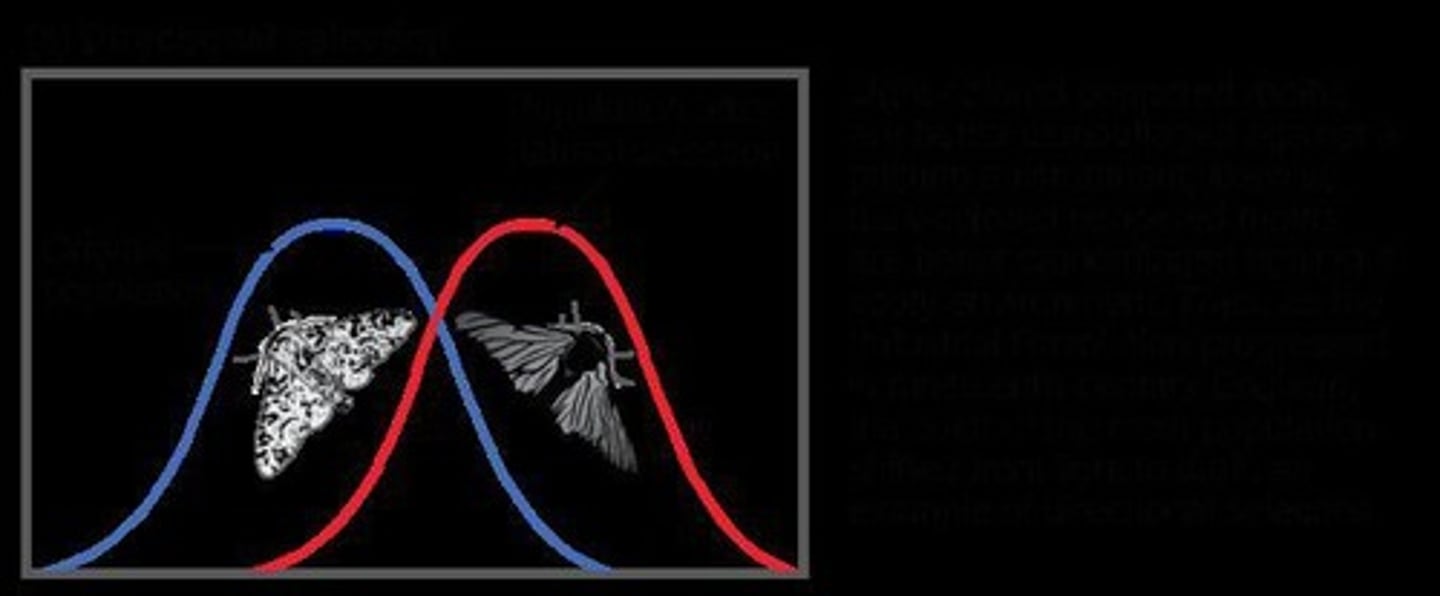
Describe the example of directional selection involving peppered moths.
During the Industrial Revolution, black moths were better camouflaged against soot-covered trees, leading to an increase in black moths and a decrease in white moths.
What is coevolution?
A process where two or more species reciprocally affect each other's evolution.
What is an example of coevolution?
Plants and their pollinators, which have exclusive relationships that influence each other's evolution.
What is speciation?
The formation of a new species, where a group can successfully interbreed in nature, producing fertile offspring.
What are the two forms of speciation?
Allopatric and Sympatric speciation.
What is allopatric speciation?
Speciation that occurs when groups are physically separated by geography, leading to reproductive isolation.
What are isolating mechanisms in sympatric speciation?
Behavioral, Temporal, and Polyploidy isolation.
What is an example of behavioral isolation?
Bird song, where differences in behavior prevent breeding.
What is genetic drift?
A change in allele frequencies that occurs in small populations due to chance occurrences.
What is the genetic bottleneck effect?
A reduction in alleles due to a disaster, leading to a loss of genetic diversity.
What is the founder effect?
When a few individuals colonize a new area, leading to reduced genetic variation.
What are polygenic traits?
Traits that are controlled by two or more genes, such as height, skin color, and eye color.
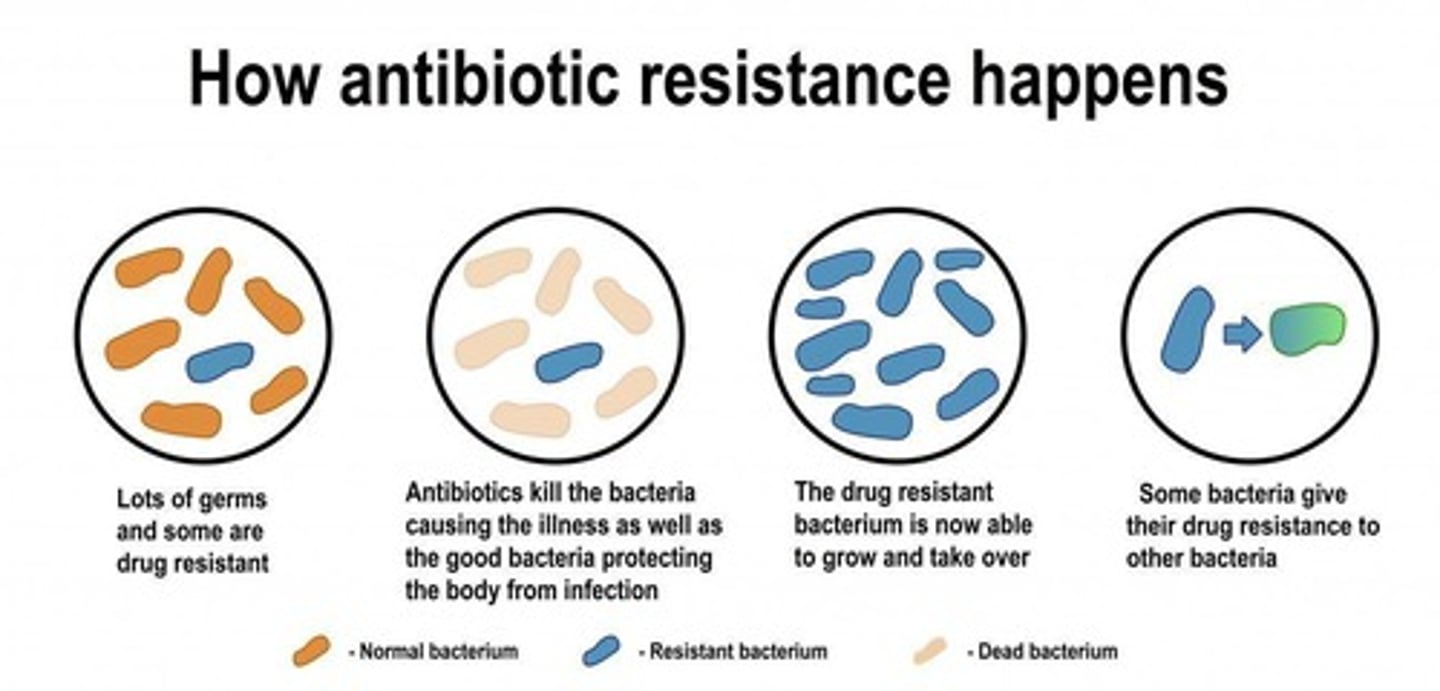
What is antibiotic resistance?
The ability of bacteria to survive and reproduce despite the presence of antibiotics.
How does stabilizing selection affect birth weight in humans?
Low and high birth weights result in higher infant mortality, favoring average birth weights.