Evolution: Scientists & Theories
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
SBI3U (Secours) - hyperdocs #2 and #3 + homework
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Until the ___th century, most people believed earth was only a few __________ years old
19, thousand
Immutable
means unchangeable, it used to be believed that all species were immutable
Georges Louis Leclerc
suggested that similar organisms all probably have a common ancestor
Erasmus Darwin
Charles Darwin’s grandfather, proposed that all life could have a single source
Jean Lamarck
used fossil records to suggest that organisms had become more complex
believed that species did not become extinct, instead they adapted into new ones
suggested that acquired traits from a parent’s lifetime could be passed on to their offspring (evolution through use and disuse)
this idea was flawed but revolutionary for the time, introducing the idea that the mechanism for evolution is adaptation to environment

Paleontology
The study of fossils to describe prehistoric life
Early paleontologists (Cuvier and Anning)
Fossils are more complex closer to the surface, and resemble living organisms
Catastrophism
Cuvier’s theory: the pattern of fossils could be accounted for by a series of global catastrophes that wiped out most species on Earth
Charles Lyell
uniformitarianism theory
his work was published in a famous book, Principles of Geology
concluded that the earth was much older than previously thought
Uniformitarianism
Developped by Lyell, the theory that geological processes occur very slowly and gradually.
Assumes natural laws and processes have not changed over time.
Thomas Malthus
economist perspective
argued that the growth of a population will always outrun its ability to feed itself
Stephen Jay Gould
his book, Ontogeny and Phylogeny, explored the subject of recapitulation, which suggested that an embryo’s stages of development reflected those of their ancestors
contributed to the theory of punctuated equilibrium: the idea that species typically remain relatively stable without much change until experiencing rapid bursts of change (explains lack of fossils)
Charles Darwin
the theory of evolution by natural selection
emphasized that the appearance of variations was a random process
provided definitive proof for his theory, changing the notion that species were immutable
Darwin spent ___ ______ on a journey around the world aboard the ________
5 years, HMS Beagle
Darwin collected evidence for his theory for how long?
20 years
Darwin’s theory was eventually published in the now-famous book called?
On the origin of Species by means of Natural Selection
Alfred Russell Wallace
developed the same theory as Darwin and shared his ideas with him
the mechanism of evolution described by Darwin is called _______ ________
natural selection
Natural Selection
the process in which the characteristics of a population change over generations, when individuals with heritable traits survive and reproduce, passing on their traits to their offspring
For natural selection to occur, there must be ______ within a species
diversity
Fitness
an organism's ability to survive and reproduce successfully
Survival of the Fittest
organisms that have favourable traits will adapt to their environment and will survive, giving them a better chance of reproducing and passing that favourable trait
Darwin’s 6 proofs
Fossil Records
Biogeography
Homologous Structures (comparative anatomy)
Analogous Structures (comparative anatomy)
Embryology (comparative anatomy)
Malthus’ theory
Another source of proof that came after Darwin and remains ongoing is the __________ __ ____
evolution of DNA
Fossil Records
showed that species didn’t stay the same over time, fossils from before were slightly different than those of today
✩ supports Darwin’s idea that life progressed from simple to complex

Transitional Fossil
possess a mix of features from both the ancestral and descendant groups
Biogeography
study of geographic ditsribution of organisms (based on both living and fossils)
✩ observed endemic species, such as birds on different islands in the Galapagos Islands who adapted to their unique environments and food sources
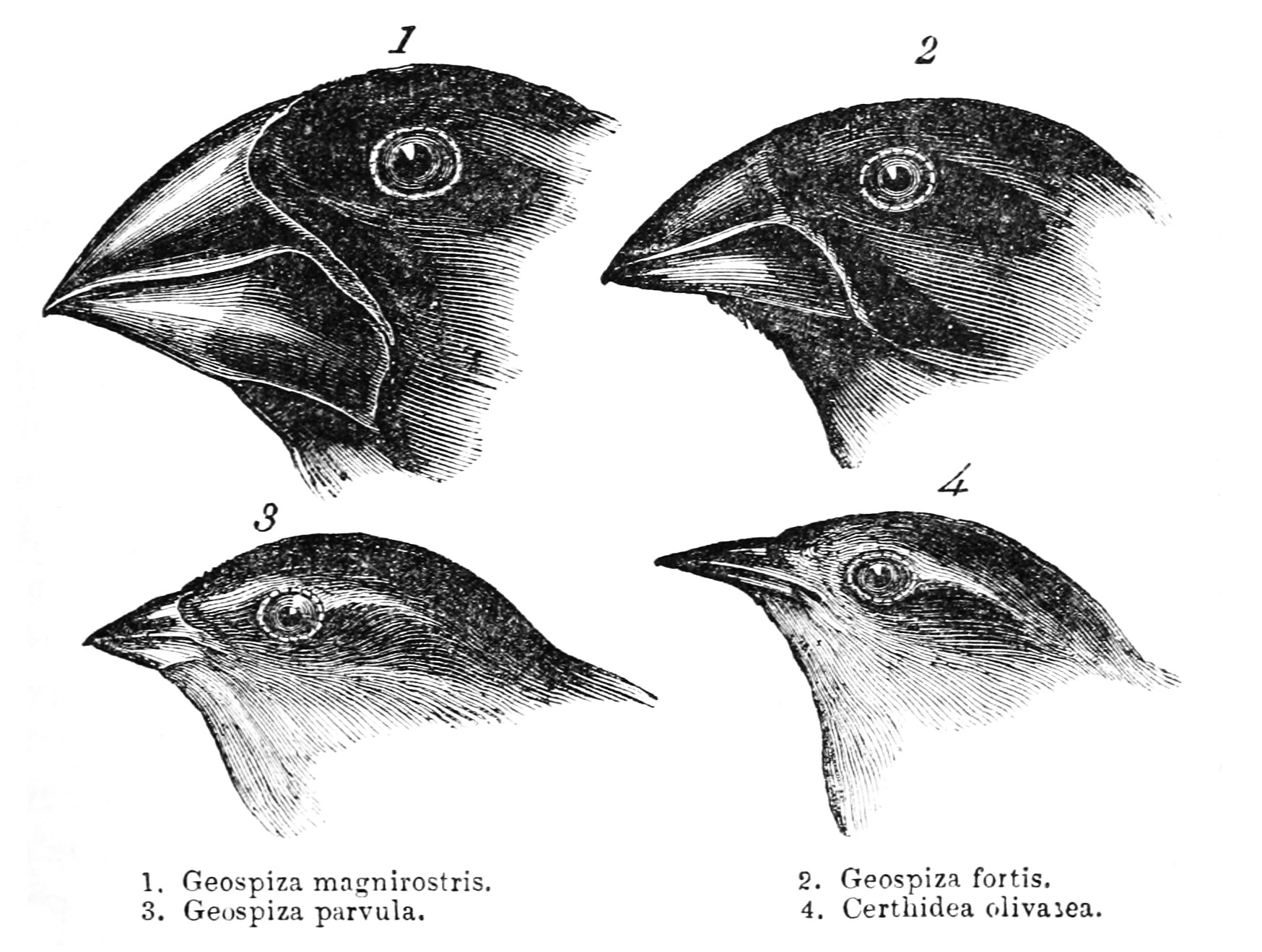
Endemic Species
species that live in a limited area
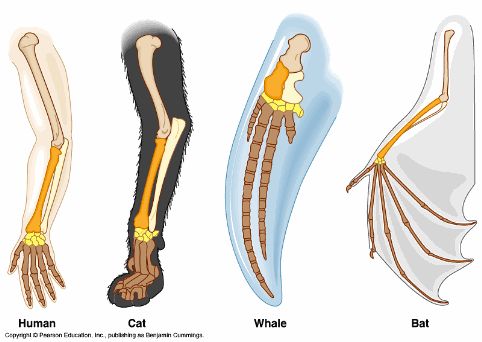
Homologous Structures
A structure with a common evolutionary origin that may serve different functions in modern species
✩ despite having current differences in their functions, similar bone structures/anatomy provided evidence for common ancestry
Vestigial Structures
a type of homologous structure that have lost their original function
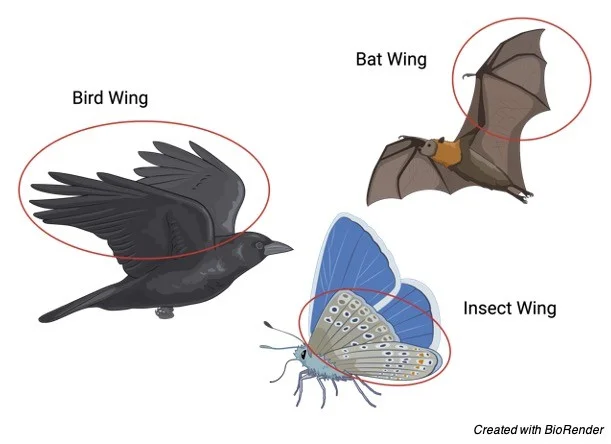
Analogous Structures
A structure that perferms the same function as another but is NOT similar in origin NOR anatomic structure
✩ demonstrates that similar environmental pressures can lead to similar traits developping independently of lineage
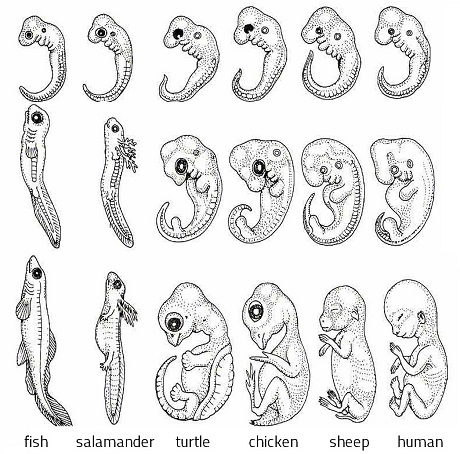
Embryology
branch of biology that studies the formation and development of embryos and fetuses
✩ suggests shared ancestry because embryos of different organisms share basic structures
“The attempt to Malthus”
the theory that human population growth will inevitably overwhelm food production
✩ inspired Darwin with the idea that competition within an animal population leads to evolution and keeps numbers stable
Evolution of DNA
the changes that have occured in the structure and function of DNA over time, resulting in diversity and complexity of life