FON- Ch 15 Elimination and Gastric Intubation
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Urinary Elimination
removes excess fluid and metabolic waste (urine) to maintain electrolyte balance
- Micturition/ Voiding/ Urination
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
infection of one or more organs of the urinary tract
(kidneys, ureter, bladder, urethra)
Characteristics of Urine
- Volume: 30mL/hr
- Color: pale straw to amber
- Clarity: transparent (clear)
- Odor: faintly aromatic
- Residual Urine: less than 50mL
Commode
chair with an opening in the seat under which a receptacle is places
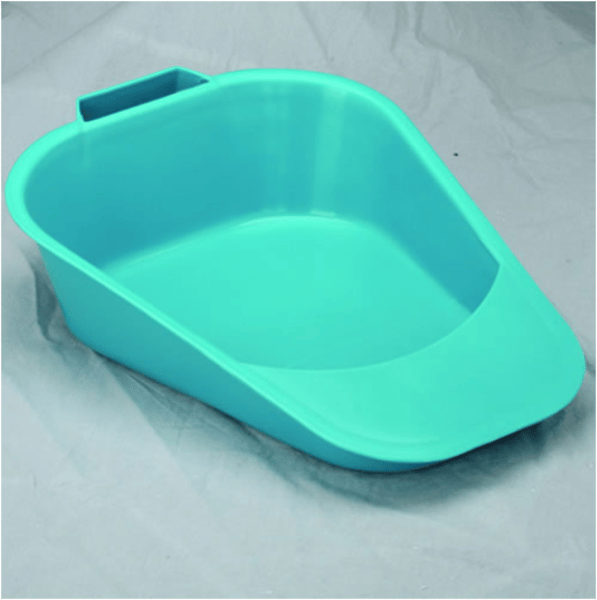
Bedpan
vessel for receiving the urinary and fecal discharges of a patient unable to leave his or her bed
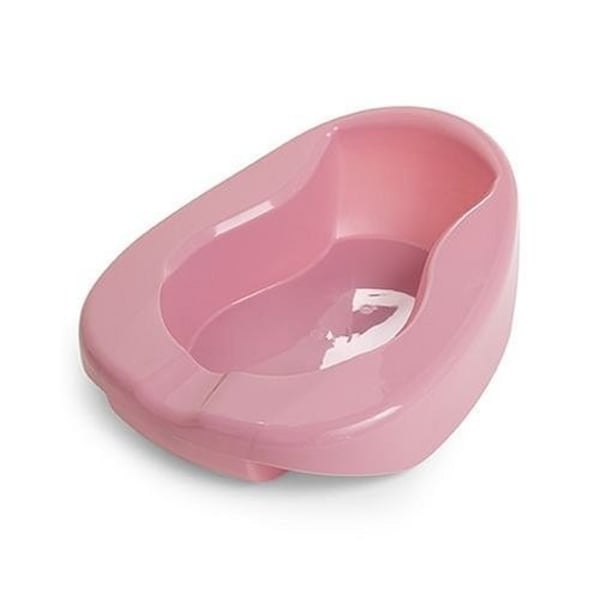

Fracture Bedpan
A curved, smooth upper end and a tapered lower end used for patients unable to lift their hips.

Urinals
Used to collect urine; male and female urinals differ in shape
Urinary Catheters
soft plastic or rubber tubing
- maintain urine flow
- divert urine flow
- facilitate healing postoperatively
- introduce new medications by irrigation
- dilate/prevent narrowing of the urinary tract
Catheritization
inserting a catheter tubing into the urinary bladder/ureter/kidneys
Urinary Catheter
Urinary meatus and the urethra into the urinary bladder
French (Fr) System
catheter size 14-Fr (thicker diameter) to 24-Fr (thinner diameter)
Indwelling Catheter
- stay inside the body for a while, urine drains into a bag
- Coudé catheter
- Foley catheter
- Malecot, De Pezzer, and Mushroom catheters
- Ureteral catheter
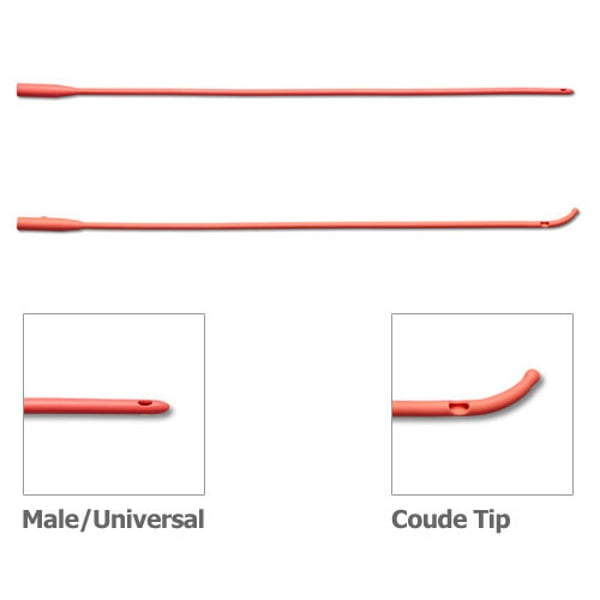
Coudé Catheter
- tapered tip aids in insertion for those with enlarged prostate glands (swollen)

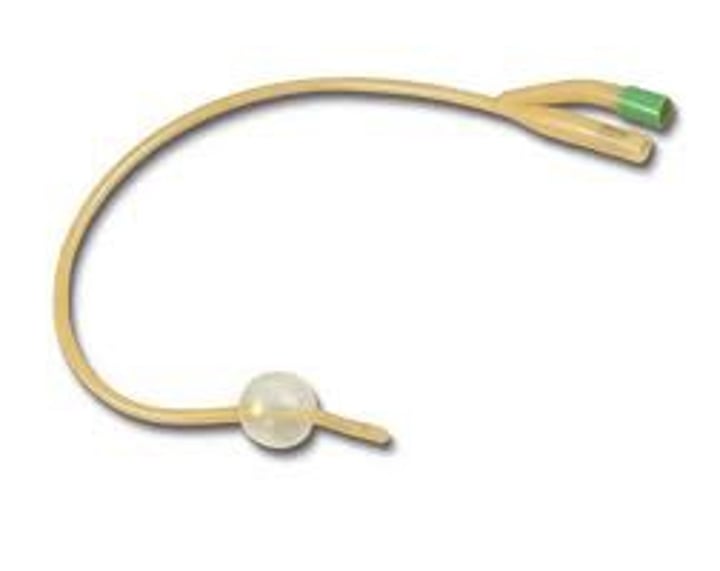
Foley Catheter
balloon near the tip (inflated after insertion) holds the catheter in place for continuous drainage
Malecot/ de Pezzer/ Mushroom Catheters
- used to drain urine from the renal pelvis of the kidney
- inserted by physician
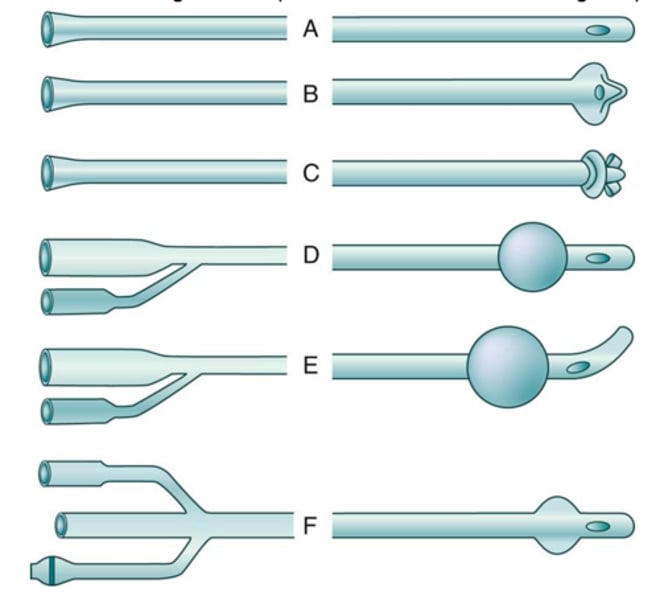
Robinson Catheter
multiple openings to facilitate intermittent drainage
Whistle-tip Catheter
slanted, larger orifice tip
- for pt with blood in the urine
Ureteral Catheter
Long and slender to pass into the ureter
Suprapubic Catheter (cystotomy/ vesicostomy)
catheter inserted into the bladder through the abdominal wall above symphysis pubis
- divert urine flow from the urethra to treat injury to the bony pelvis, urinary tract, surrounding organs/strictures/ obstructions
Simple Urethral Catheter
a straight catheter designed for in and out procedures (no balloon)
Condom (Texas) Catheter
external male catheter
- used for incontinent men to minimize skin irritation from urine
- limits infection of indwelling
- remove daily for cleansing and inspecting
Intermittent Self Catheterization
(short term/ straight catheters)
- used for the pt who experiences spinal cord injures or other neurological disorders that interfere with urinary elimination
- drain urine in the bladder and removed after drainage is complete
Documentation After Catheter Insertion
- type of procedure
- time and date
- characteristics of urine
- patient response
- patient teaching done
- assessment data of the urinary meatus
Self-Catheterization
for pt with spinal cord injury or neurological disorders
- promotes independence
Routine Catheter Care - Indwelling Catheter
- aseptic technique
- perineal hygiene every 8hrs
- cleans with mild soap and water first 2 inches of the catheter
- clean urinary meatus down the catheter
- Don't use powders or lotions
Routine Catheter Care - Condom Catheter
- secure catheter to the penile shaft (snug/secure)
- do NOT tape: limits blood supply to the penis (necrosis)
Assessing During Routine Catheter Care
assess urethral meatus and surrounding tissue for:
- inflammation
- swelling
- discharge
- Note: amount, color, odor, consistency of discharge
Removal of Indwelling Catheter
- after surgery: 8-24hrs
- maintain fluid intake: 1.5-2 L/day
- check for signs of UTI: 2-3 days later
- mild burning with first void
- assess for urinary retention
- most void adequately within 8 hrs after removal
Incontinence
inability to control urine or bowel elimination
- pressure in bladder great or sphincters too weak
- pt exercises to strengthen muscles around sphincters
Stress Incontinence
small leakage of urine when one laughs, coughs or lifts heavy objects
Urge Incontinence
constant leakage when bladder contains urine
Bladder Training
achievement of voluntary control over voiding
- muscles of the perineum
-clamp- unclamp routine to improve bladder tone
Kegal Exercises
- exercises pelvic floor: stop urine flow during voiding
- hold tension doe 10 secs and relax for 10 secs
-
Crede's Method
gentle manual pressure over lower abdomen to express urine from the bladder at regular intervals
Habit Training
voiding schedule
- regular intervals (1.5-2 hrs)
Defecation
elimination of bowel wastes
- expelling feces ( indigested food, dead bacteria, fat, bile pigment, living cells, intestinal mucosa, water)
Characteristics of normal Stool (Feces)
- Amount: moderate
- Color: brown (affected by dietary changes)
- Odor: affected by foods
- Consistency: normal soft/formed
- Frequency: 1-3 days
Normal Elimination Depends on:
- balanced diet (high fiber)
- fluid intake 2000- 3000 mL
- activity promoting muscle tone and peristalsis
- routine time for defecation
Hemorrhoids
swollen, inflamed veins in the anus and lower rectum
- straining during bowel movements
- increased pressure during pregnancy/ heaving lifting
- internal (rectum) or external (anus)
- discomfort and pain as hard stool pass through the irritated rectum
Goal for Patients with Hemorrhoids
- decrease pain
- prevent elimination problems
- prevent damage to swollen tissue
Flatulence
presence of air or gas (flatus) in the intestinal tract
- consuming gas producing liquids and foods
- swallows excessive amounts of air or constipation
-decreased peristalsis, abdominal surgery, narcotic medication, decreased physical activity
- ambulate to relieve discomfort
Enema
- a solution into the colon via the anus
- promotes defecation
- volume and type: lubricate, break ip decal mass, stretch the rectal wall, initiate defecation reflex
Reasons for Enemas
1. Cleanse the colon before a diagnostic procedure or abdominal surgery
2. Management of constipation or fecal impaction
3. Administration of medication
Cleansing Enema
- stimulates peristalsis (large volumes of fluid tp distend the bowel)
- empty colon completely
- Used before surgery or GI diagnostic procedure
- Place in Left Sims
- encourage pt to retain fluid for at least 5 minutes
- 750-1000 mL
- mild cramping
Tap Water Enema
- primary purpose is to cleanse the bowel of stool
Water and Soap Solution Enema (cleansing enema)
- step to purge air from tubing
- open the clamp and fill the tubing with solution, then reclamp
Oil Retention Enema
- used when fecal impaction is suspected (lubricates rectum and colon, softens feces)
- enema should be retained for 30 min
Documentation After Enema
- Type and volume of enema
- Characteristics of the result (stool):
color, presence of mucus, presence of blood, amount
- how patient tolerated the procedure
Fecal Impaction
collection of feces in the rectum
Rectal Suppository
oval/cone-shaped mass that melts at body temperature and is inserted into the rectum
Colostomy
creation of an artificial opening into the colon
- pt with cancer of the colon, intestinal obstructions, intestinal trauma, inflammatory disease of the colon
- permanent or temporary
Ileostomy
opening in the ileum (small intestine)
- entire colon removed or bypassed
- pt inflammatory bowel conditions and cancer of large intestine
Urostomy
diversion of urine away from a diseased or defective bladder
- pt cognitive anomaly, bladder removed because of disease, trauma, or obstruction
Intake & Output
- maintain homeostasis
- normal daily lost must be met by the normal daily intake
- 2500mL
Medicated Enema
to bring down an extremely high potassium level
Return-Flow Enema
expel flatus