10) intro to electrical stim 2
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
pulse characteristics
waveforms
stimulation paramaters
pulse/phase charge
pulse =
isolated electrical event
pulse duration
time to complete one pulse
phase =
unidirectional flow of a pulse
phase duration =
time to complete one phase
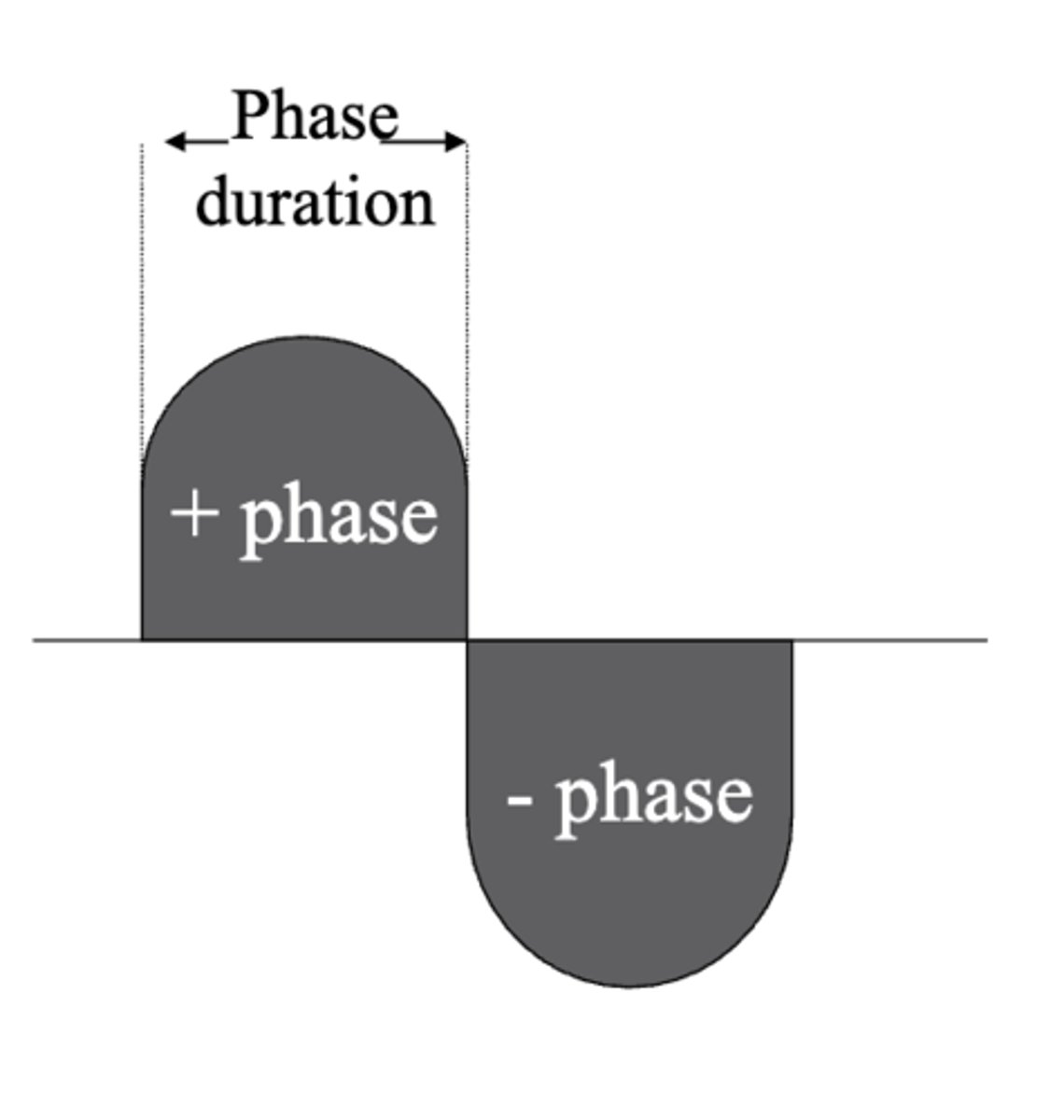
1 or 2 phases make up a
pulse
pulse/phase charge =
area under the curve
2 phases =
one pulse
with an AC current being used on skin, what net charge occurs
net 0 charge
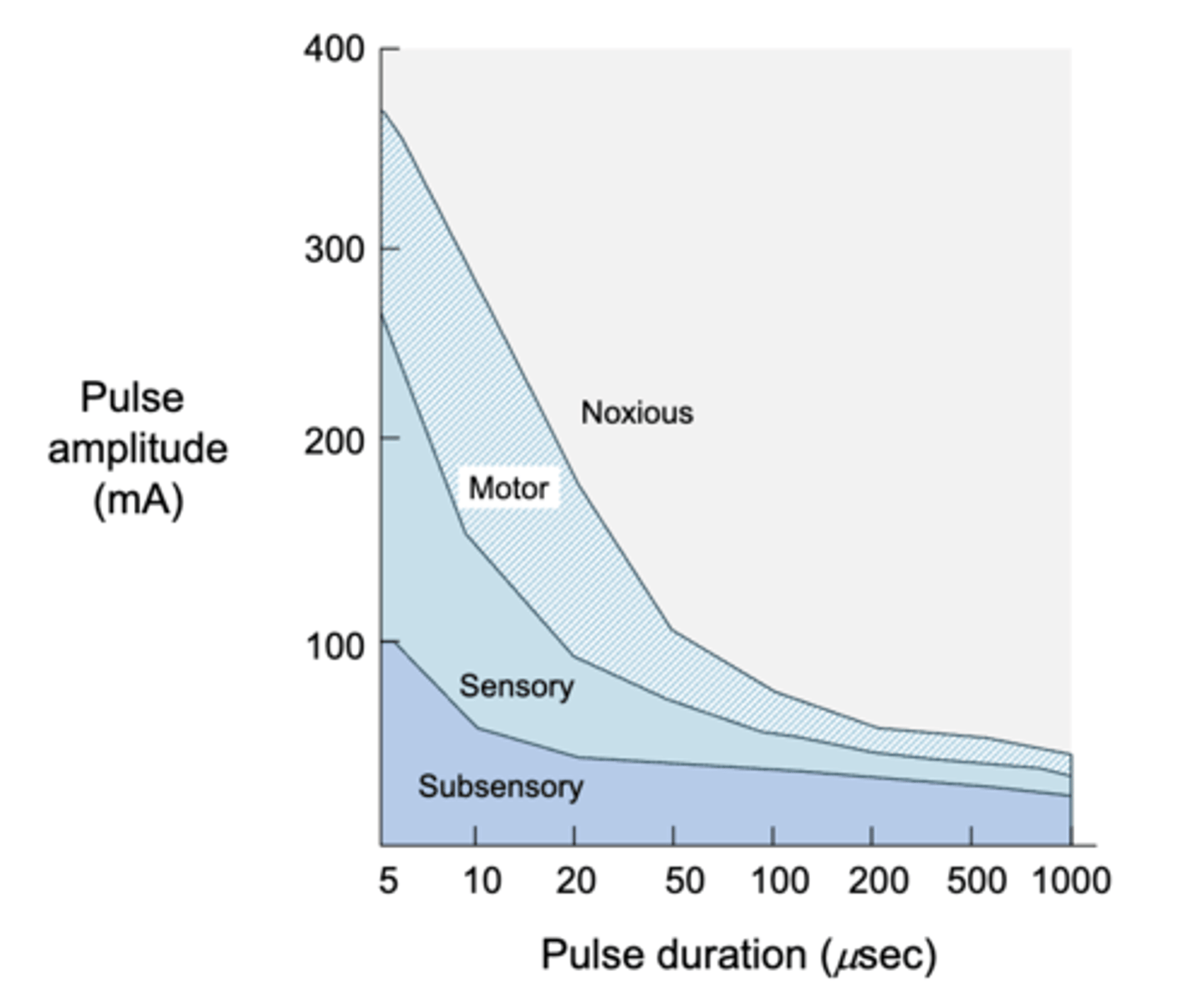
strength-duration curve
shows the relationship between pulse duration and pulse amplitude
factors that effect peripheral nerve action
type of nerve/size of nerve
location
nerve fibers vary in
diameter and internal resistance
the largest diameter/lowest internal resistance are the
most easily excitable
- alpha will be recruited first
motor points
point where the motor nerve is most accessible
- usually muscle belly
motor points is where the ________ motor response is found at the _______ pulse charge
- greatest
- lowest
pulse/phase charge involves which pulse characteristics
amplitude and phase/pulse duration
Which fibers would require the lowest pulse charge to be recruited?
sensory
frequency
the number of pulses each second
carrier frequency modulation
Used only for Burst-Modulated AC currents
- Russian waveforms
- Interferential waveforms
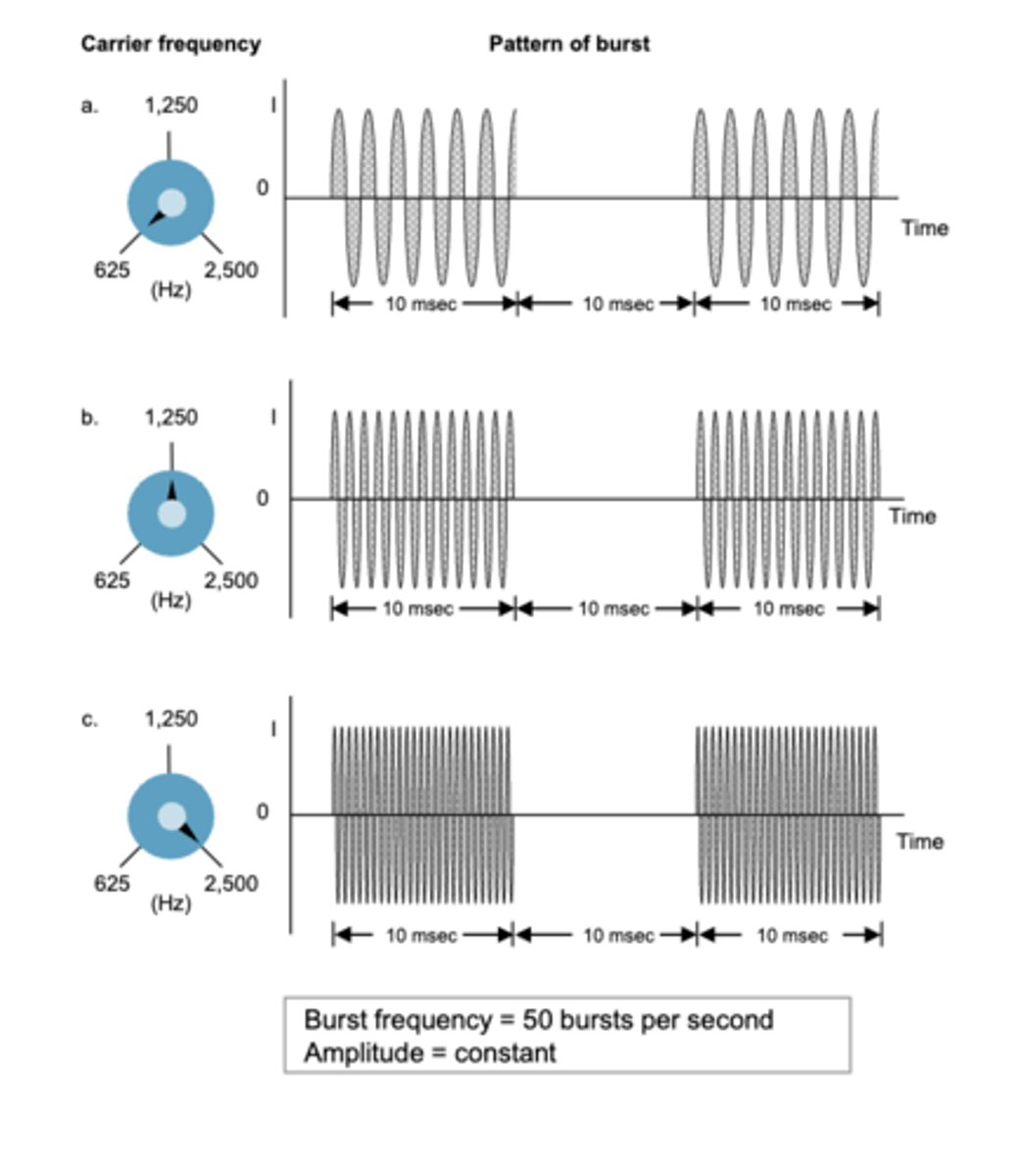
burst frequency =
number of bursts per second (bps)
ramp up
time across successive pulses to reach peak amplitude
(usually in seconds)
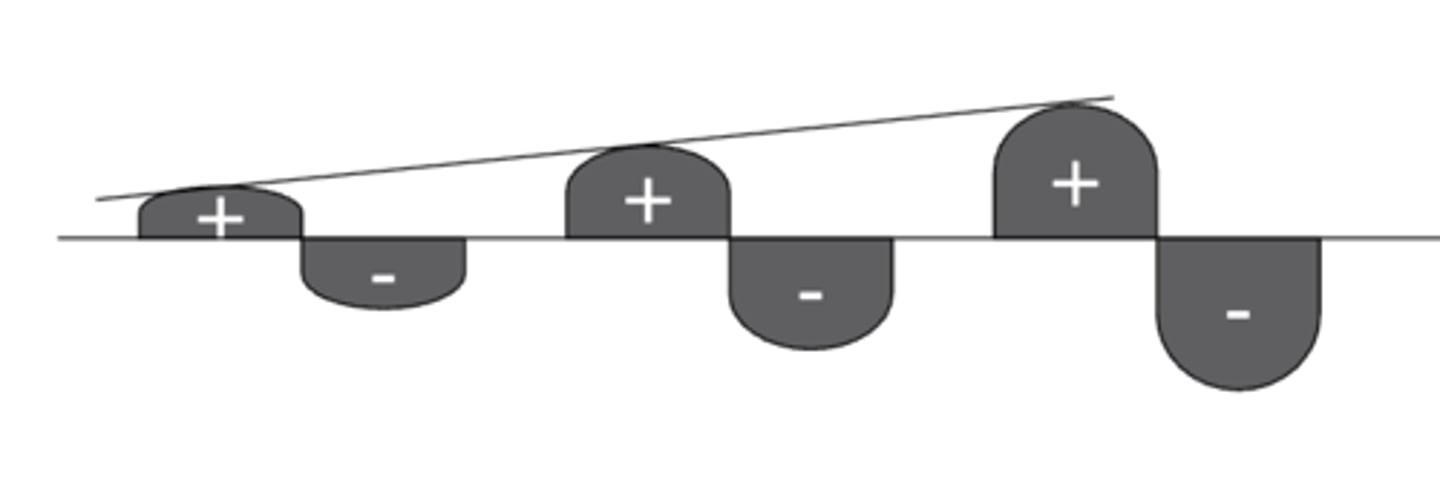
ramp down
returning to baseline
duty cycle =
on time/(on time+off time) x 100
on/off times for pain/edema management
often continuous
higher intensity estim may require on/off time (1:1)
on/off times for strengthening
need on/off times to mitigate fatigue (1 min on:50 sec off)
functional electrical stimulation on/off times
on/off controlled by a trigger
modes with two channels working
continuous
synchronous
reciprocal
primary parameters
pulse duration - usually less than or equal to 400 milisec
amplitude - up to 100 mA
frequency - up to 100 pps
pulse duration and amplitude together are the most important in
how strong the electrical stimulus is and what effects it can create (pulse charge!!)
types of electrodes
single use
reusable
carbon
metal
electrode size
-Relative to muscle size
-Current Density
electrode placement
at least 2 electrodes are needed
- monopolar
- bipolar
- quadripolar
contraindications
cardiac problems - pacemaker
electronic devices
carotid sinus
pregnant
broken/damaged skin
DVT (local)
seizures
cancer (local)
Precautions
open skin lesions
skin conditions
open epiphysis
reduced sensation
allergies
metal implants
cog/communication impairments
mental status