Chapter 21 (Alpha Carbon Chemistry)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
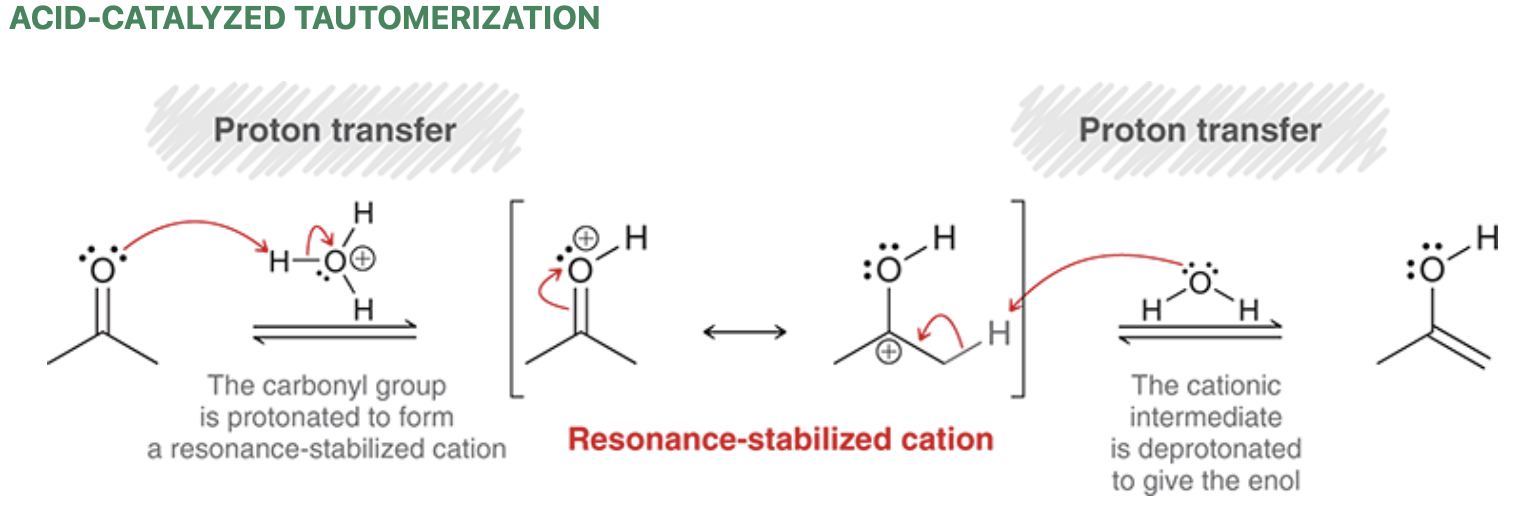
Acid-catalyzed (ketone) tautomerization mechanism
Tautomers are rapidly interconverting constitutional isomers that differ double bond placement and proton placement
Tautomerization refers to the formation of a tautomer.
In the case of a ketone, the tautomer that is formed is an enol
In acidic conditions, the ketone and enol are present at equilibrium
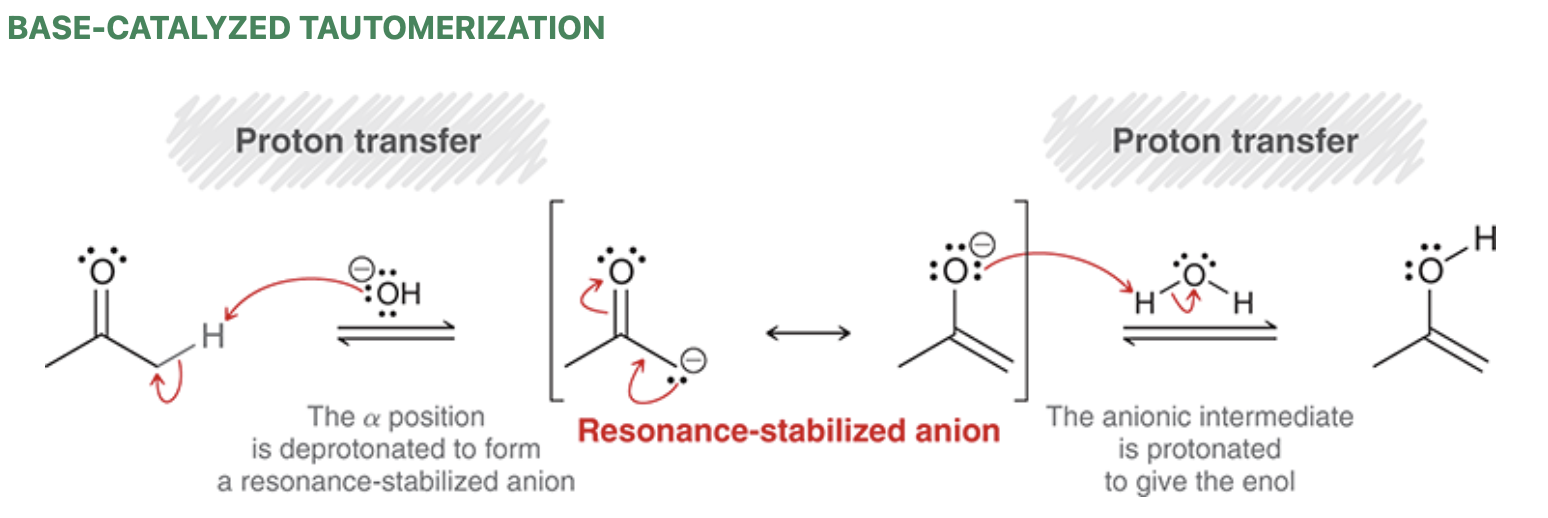
Base-catalyzed (ketone) tautomerization mechanism
In basic conditions, the ketone and enol are present in equilibrium
Enolate formation mechanism
An enolate is the resonance-stabilized intermediate that forms from treating ketone with a strong base
From from deprotonation at the alpha position
When the ketone treated with strong base, enol and enolate both present but enolate is predominant and more reactive

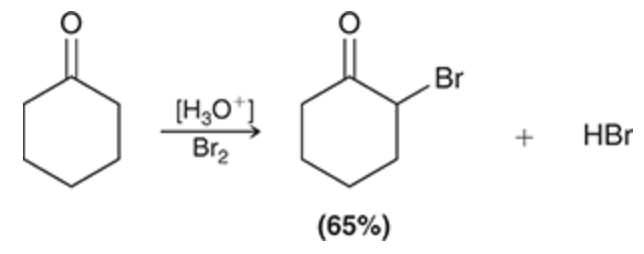
[H3O+], Br2
(Ketone/aldehyde substrate)
Alpha halogenation
Halogenation occurs at the alpha position
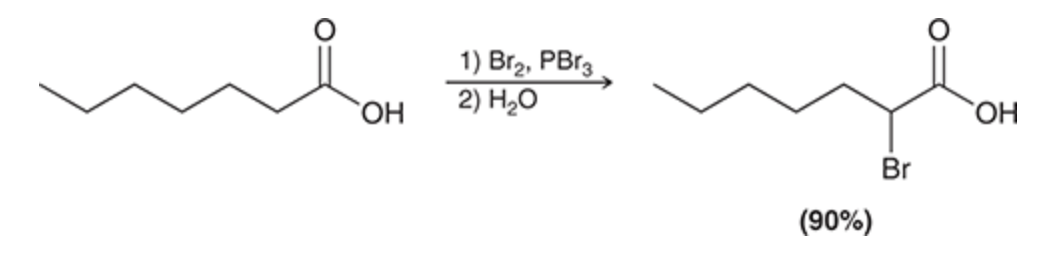
Br2, PBr3
H20
(CA substrate)
Alpha halogenation of the CA
Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky (HVZ) reaction
Br added to alpha position of CA carbonyl
NaOH, Br2
(Cyclic ketone substrate)
Base-catalyzed alpha halogenation
Bromination occurs until all alpha protons are removed and replaced with Br, I, or Cl

NaOH, Br2
H3O+
(Methyl ketone substrate)
Formation of a carboxylic acid + CHBr3 (bromoform)


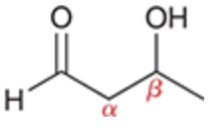
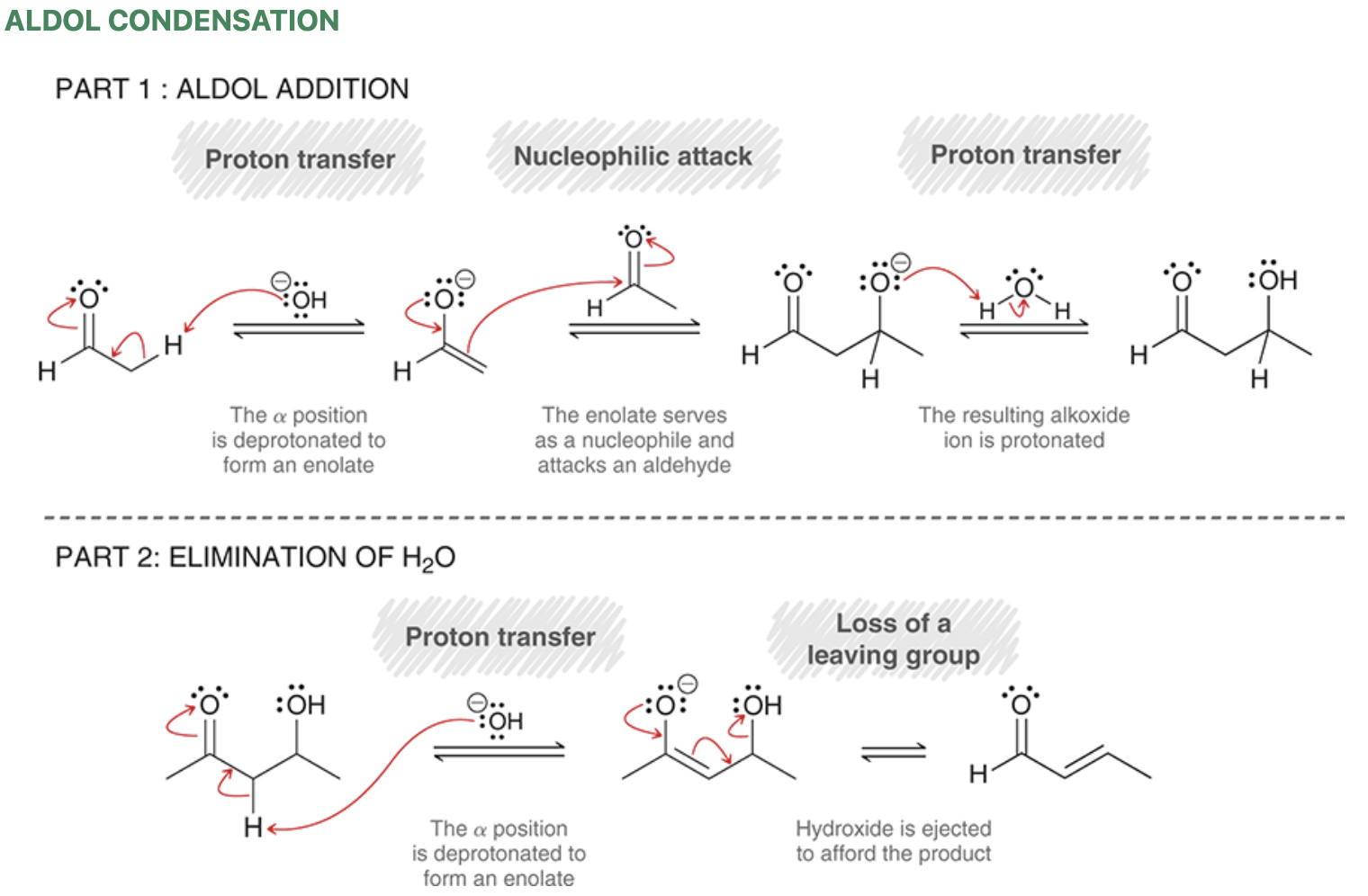
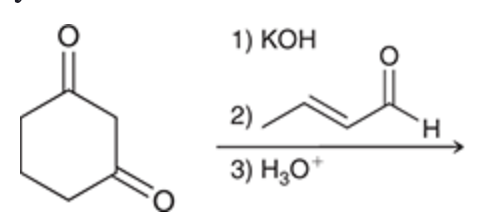
Aldol formation
Enolate and aldehyde present at equilibrium
Note: hydroxyl located beta relative to carbonyl
Product of aldol reaction is always a beta-hydroxy aldehyde or beta-hydroxy ketone
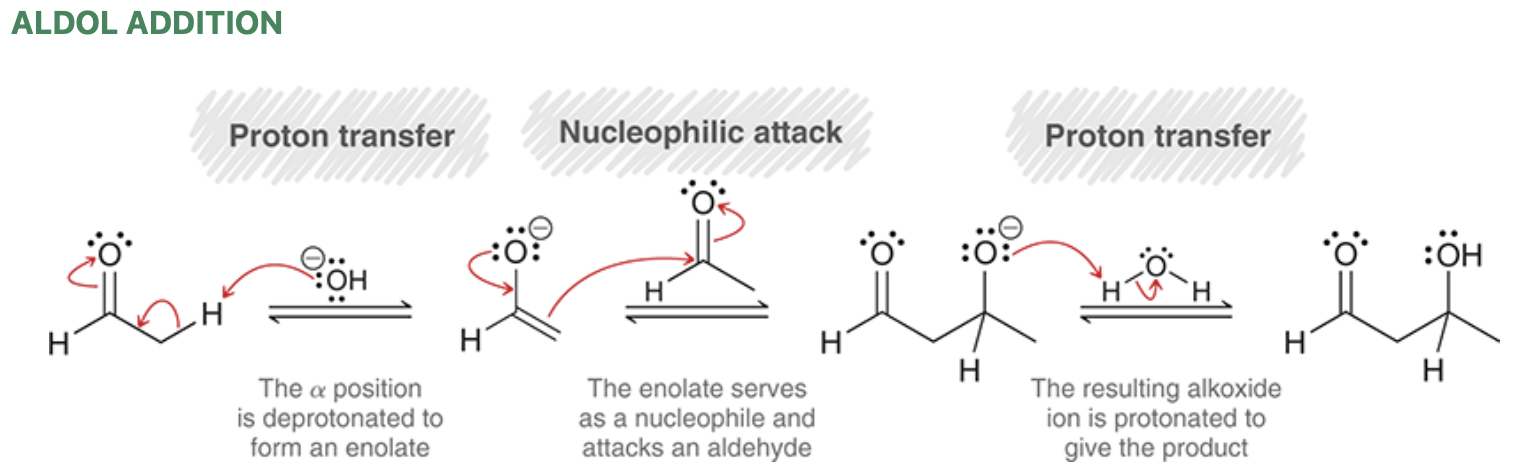
Aldol addition mechanism
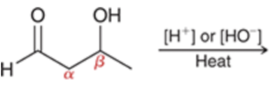
Aldol condensation
Condensation = reaction where addition is accompanied by the loss of a small molecule (water, CO2, or N2)
Form alpha,beta-unsaturated ketone/aldehydes

Aldol condensation mechanism
E1CB mechanism — elimination that involves the formation of an anion.
Trans configuration will be major
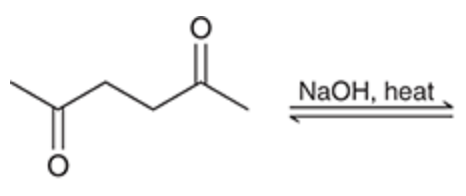
Intramolecular aldol reaction

Intramolecular aldol reaction mechanism

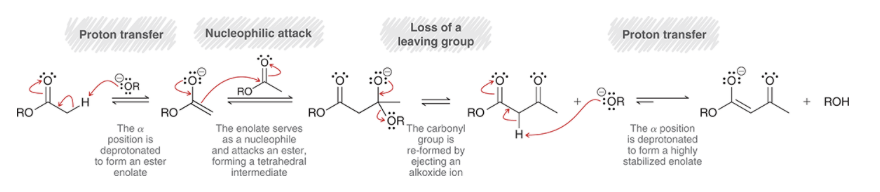
Claisen condensation reaction
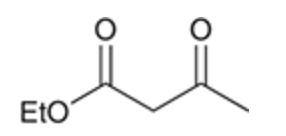
Claisen condensation mechanism

Intramolecular Claisen condensation
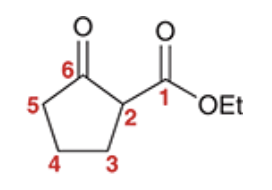
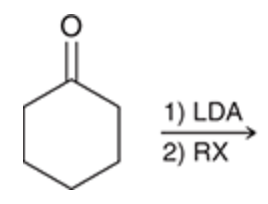
Alkylation at the alpha position
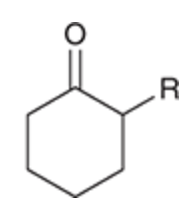
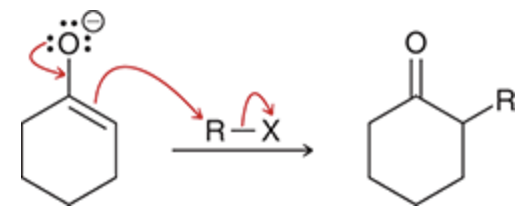
Alkylation mechanism

Kinetic vs. thermodynamic product formation in alkylation at the alpha position

Acetoacetic ester synthesis
Results in an alkylation product while preventing polyalkylation
Hydronium results in reduction of the ester to a carboxylic acid
Heat results in cleavage to loose the carboxylic acid group
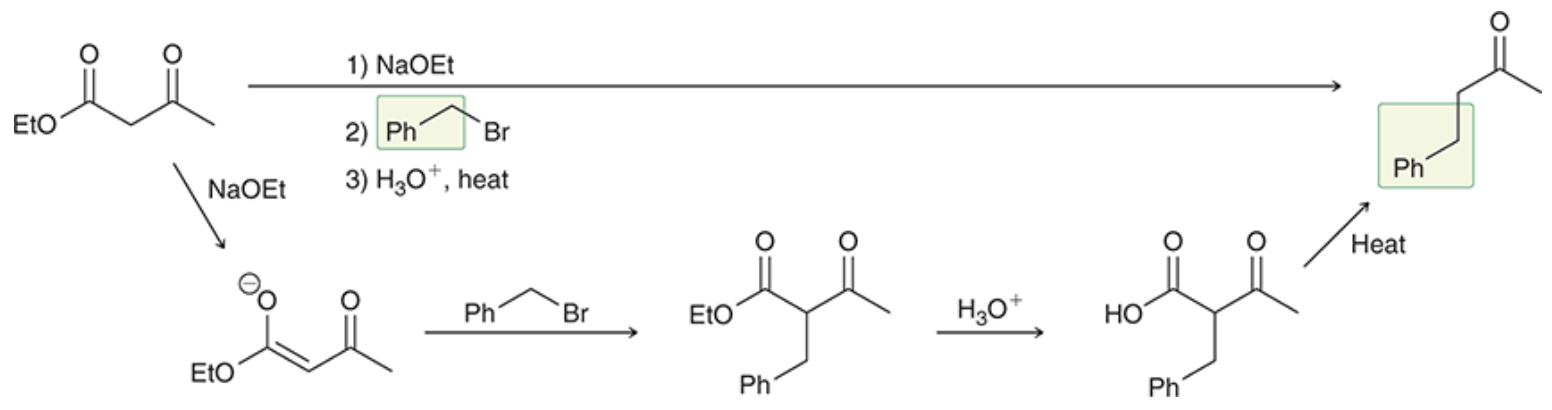

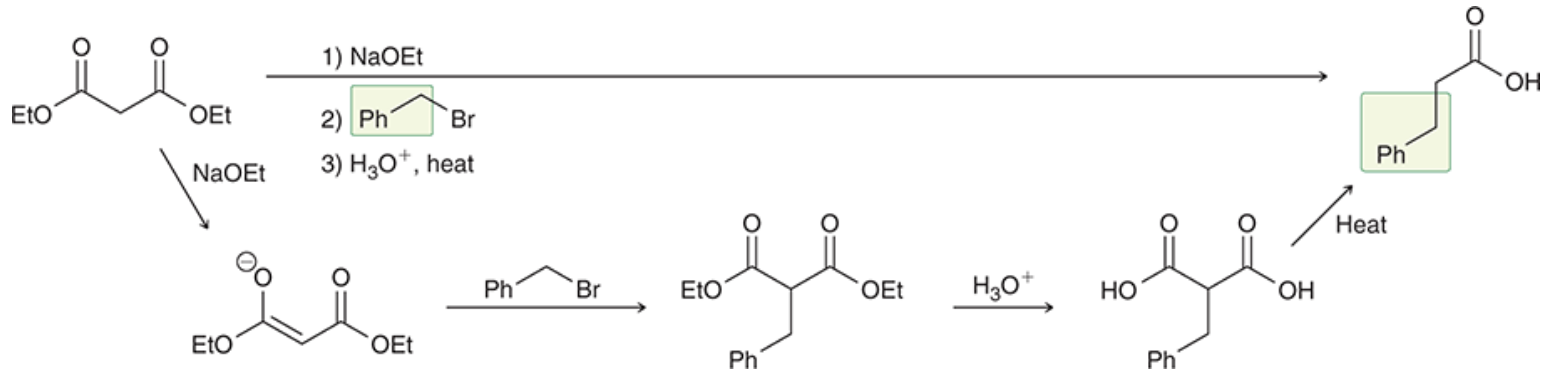
Malonic ester synthesis
Alkylation product that conserves a carboxylic acid group

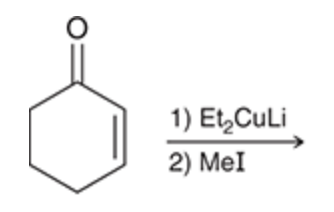
Beta alkylation
Occurs with the treatment of an alpha,beta unsaturated ketone with lithium dialkyl cuprate

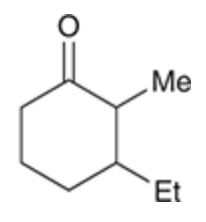
Alkylation at alpha and beta positions
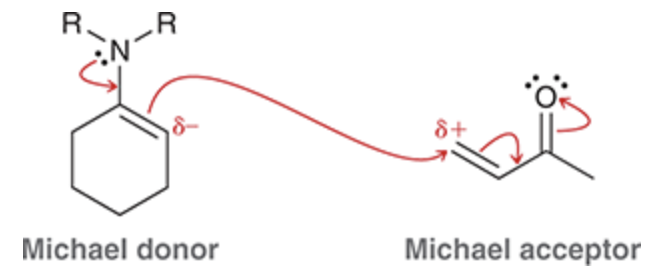
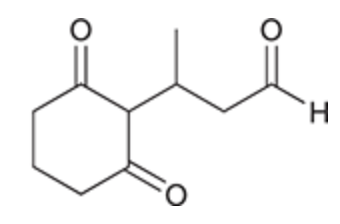
Michael reaction
Michael donor — the highly stabilized enolate
Michael acceptor — alpha, beta unsaturated ketone
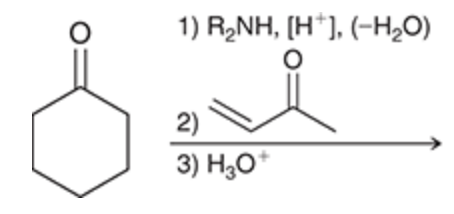
Stork enamine synthesis
Used when need to accomplish addition at the alpha position but do not have a highly stabilized enolate
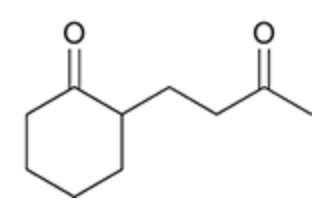
Stork enamine synthesis mechanism
Notice: beta position attacked