AP Psych Scientific Method: Research Methods & Data Practice
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
hypothesis
must be testable/falsifiable, an offered explanation for a phenomenon
experimental design
two groups (experimental & control), independent variable, dependent variable, random sampling, random assignment
experimental group
gets experimental manipulation, independent variable
control group
is left alone, NO experimental manipulation, dependent variable
Bobo Doll Study
occurred in 1961 (Bandura, Ross, & A. Ross), investigated relationship between observed aggression & imitated aggressive behavior in children by demonstrating said aggression on an inflatable clown named Bobo.
experimental group: children observing adults modelling aggressive behavior
control group: children not observing any behavior at all
single-blind study
one group of participants does not know a certain detail of the experiment they are in (ex: which group they are in)
double-blind study
both groups of participants do not know a certain detail of the experiment they are in
placebo effect
expected outcome based on prior knowledge or experience, like a manifestation
placebo control
occurs in order to ensure the only cause of the difference between the exp. & control groups is the experimental manipulation, a PILL with no actual effect
independent variable
manipulated/controlled by the experimenter, only difference, cause
dependent variable
measurement of the effect of the independent variable, effect
sample
a portion of people taken from a population as a representation of said population
population
a diverse, large group of people
random sample
a subset of a population in which every member of said population has an equal chance of being selected, ensures equivalence between characteristics, better generalization
random assignment
participants have an equal chance of being assigned to either group (exp. & control)
matching
grouping participants with a similar level of a certain trait
reverse causation
when one believes X causes Y, but in reality, Y causes X
conceptual definition
defining a concept in terms of other concepts
operational definition
explanation of how a variable or concept is used or assessed in a study
internal validity
the assurance that the only difference between the two groups (exp. & control) is only caused by the independent variable/experimental manipulation
external validity
the extent of how the results of a study can be applied to real life situations and/or generalized to populations
reliability
the assurance that the data is correct, if many trials were conducted, the results would stay the same
observation
examination
pros: abundance of info
cons: can’t apply to larger populations due to limitation of small samples, can’t generalize
survey research
lists of questions to be answered by research participants
pros: very convenient in collecting data from large samples, not time costly, can be done in 3 days (paper, online, orally/in person), easier to conduct generalization
cons: limited & subjective, less in-depth data, inaccurate answers
archival research
uses existing records in order to estimate possibilities/chances
pros: easy, collectible data to answer research questions, less time & money costly,
cons: no control over data at all, reliant on the past, no interactions w/ participants, data has to be modified in order to answer questions
Hogan Twins
girls conjoined at the head and are able to share sensory experiences despite being each their own person
clinical/case study
extreme focus/concentration on individuals under a particular, unique situation (ex: rare genetic disorder)
pro & con (at the same time): easy to conduct generalization for people who are rare, but cannot do the same for a more common population
generalization
the act of applying information to a population in order to gain a better understanding of said population
naturalistic observation
gathering data through observation of behavior in a setting that’s natural
pros: validity
cons: difficulty preparing & controlling (subjects), no control of behavior to be examined, costly in terms of time & money, need to be lucky
structured observation
examines living beings participating in certain activities (opposite of naturalistic observation)
observer bias
when observers are prone to projecting their ideals upon the end results of their data, expecting an outcome that caters to them
Jenkins Survey
asked how participants would treat certain people regarding their ethnicities in order to research about the backlash of the 9/11 attack on arab-americans
result: participants indirectly held some sort of prejudice against arab-americans
longitudinal research
repeatedly obtaining info over a long duration of time (ex: decades or even life-long)
pros: no worries over sociocultural aspects
cons: very time and money costly, uncertain results due to how much time is needed to come to a conclusion, consent & participation needed from all parties, if no commitment then discontinuation
cross-sectional research
compares multiple segments of a population simultaneously
pros: not too time costly
cons: limited by sociocultural aspects (meaning those who grew up in different times will be different socially & culturally)
correlational
relationship between two or more variables, said variables are affected equally & simultaneously
pros: excels in evaluating relationships between variables
cons: cannot discern causality/cause & effect between variables
does not equal causation b/c variables vary & do not necessarily establish causality
in order to establish causality, rule out any other variables (usually through a controlled study)
correlation coefficient
r, represents strength and direction of the relationship between the variables
closer to 1: stronger relation, more eligible for predictions
closer to 0: weaker relation, less eligible for predictions
positive: variables move in the same direction
negative: variables move in opposite directions
confounding/third variable
outlier, unexpected factor
illusory correlations
correlations that are imaginary & false, but thought to be true
confirmation bias
ignoring evidence that would tell one’s gut feeling is false
causation
when one thing causes another thing to happen
equals correlation due to an already existing relationship between variables based on cause & effect
controlled study
two equivalent groups of people although w/ differing experiences are compared, results are compared as well
epidemiological/observational studies
subjects observed over time, no ethical limits as long as the researchers aren’t forcing harm upon said subjects (subjects are doing it themselves or life is doing it to them)
measures of central tendency
single values that attempt to present descriptions of data sets by identification of central positions within said data sets
3 measures of central tendency
mean, median, mode
mean
arithmetic average
how to get: add all values in a data set & then divide by the # of values
pros: can be used with discrete data (occurs at certain points/intervals, countable & non-continuous) or continuous data (any value within a range, appear at any place across the continuum/continuous sequence), best for normal/symmetrical distribution b/c it includes all values
cons: susceptible to influence of outliers of which are abnormally large or small (skewed values)
median
middle score of a data set
how to get: arrange values from smallest to greatest and, if odd, take the middle mark. if even, take the two middle marks & divide by two
pros: best retains normal distribution (perfectly normal values, all measures identical) & strong resistance to influence of skewed values/outliers
cons: not so great in certain conditions when it comes to categorical data
mode
frequency of a value/score in a data set
how to get: identify the value that happens the most in a data set
cons: not unique, conflict occurs when two or more values share the highest frequency
measure of spread/dispersion
a method in order to describe variability in a sample and/or population
large spread: large differences, little representation
small spread: small differences, a lot of representation
has a strong relationship w/ measures of central tendency, provides idea of how well the measures of central tendency represent a data set
range
difference between lowest and highest scores of a data set
how to get/formula: maximum value minus minimum value
pros: sets boundaries of scores, instantly identifies when a value has broken a critical threshold when measuring targeted variable, useful in detecting errors when entering data
cons: has limitations
standard deviation
measure of spread/dispersion of scores in a data set
two of them: sample & population standard deviation
sample standard deviation
requirements: having only a sample, wanting to make a generalized statement towards a population of which the said sample is from
population standard deviation
requirements: having the entire population, having a sample of larger population, exclusive interest of said population, no desire for generalization
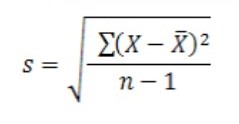
formula for sample standard deviation (tip to remember, s = sample)
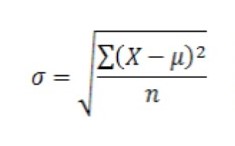
formula for population standard deviation
null hypothesis
“devil’s advocate” position, suggests that whatever is attempting to be proven did NOT happen, that there is ZERO effect(s) (hence the definition of null as ZERO), UNACCEPTABLE, only find evidence to fight against it
high p-value = fail to reject null & can’t accept alternative
low p-value = reject null & accept alternative
alternative hypothesis
states the opposite of one’s hypothesis, that there is DIFFERENCE
p-value
chance of finding a difference within your study between variables
low p-value = high difference, rejects null hypothesis, accepts alternative hypothesis
high p-value = low difference, fail to reject null hypothesis, not accepting of alternative hypothesis
failing to reject = not necessarily accept, but still consider as possibility
one-tailed hypothesis
has a CLEAR direction, predicts direction of the effect (ex: positive or negative)
pros = researcher bias acceptable ONLY when biological activity/presence is measured
cons = reflects researcher bias
two-tailed prediction
direction is AMBIGUOUS/UNSAID, does not make decision over direction of the effect