Study Guide for Quiz #2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
1
New cards
Scientific Revolution
New way to determine “truth” from nature
Emphasis on human reason
Use of experimentation & inductive reasoning
Isaac Newton:
Emphasis on human reason
Use of experimentation & inductive reasoning
Isaac Newton:
2
New cards
Isaac Newton
Best known for laws of motion
But alchemy as part of synthetic worldview in private writings
Most alchemical work ignored and hidden until the 20th century
But alchemy as part of synthetic worldview in private writings
Most alchemical work ignored and hidden until the 20th century
3
New cards
The Enlightenment
Emphasized human reason
Used a “Secular” approach: NOT irreligious; nearly all Enlightenment thinkers believed in God. God created the world, but human reason is capable of discovering its’ truths
Rejected Calvinist pre-destination
Used a “Secular” approach: NOT irreligious; nearly all Enlightenment thinkers believed in God. God created the world, but human reason is capable of discovering its’ truths
Rejected Calvinist pre-destination
4
New cards
Deism
Deists were radical Enlightenment thinkers
Questioned the authority of the Bible: Reason would lead to God; not revelation
Believed in laws of nature
Deists in America: Thomas Jefferson, Benjamin Franklin, Thomas Paine, James Madison, etc.
Questioned the authority of the Bible: Reason would lead to God; not revelation
Believed in laws of nature
Deists in America: Thomas Jefferson, Benjamin Franklin, Thomas Paine, James Madison, etc.
5
New cards
The Great Awakening
Evangelical religious movement in the 1730s and 1740s
Emphasis on human sin & depravity: Emotional & dramatic conversion experience, The “New Birth”, and complete surrender to God
Religious revivals; tent meetings; often outside
Challenged the authority of established clergy: Anti-intellectualism, Interracial
Emphasis on human sin & depravity: Emotional & dramatic conversion experience, The “New Birth”, and complete surrender to God
Religious revivals; tent meetings; often outside
Challenged the authority of established clergy: Anti-intellectualism, Interracial
6
New cards
Jonathan Edwards
Congregational minister in Massachusetts
Appealed to young people
Most famous sermon: “Sinners in the Hand of an Angry God”
Defends Trinity against Enlightenment thinkers
Appealed to young people
Most famous sermon: “Sinners in the Hand of an Angry God”
Defends Trinity against Enlightenment thinkers
7
New cards
George Whitefield
English preacher who traveled through North America in 1739-40
Mass celebrity
Thousands gathered to hear him speak: Intense, emotional style and believed in immediate conversions
Mass celebrity
Thousands gathered to hear him speak: Intense, emotional style and believed in immediate conversions
8
New cards
Old Light vs. New Light
Old Lights: Orthodox Protestants opposed the emotional “enthusiasm” of the Great Awakening
Emphasized importance of reason & the Bible
Influenced by Enlightenment ideas of rationality
New Lights: George Whitefield and Jonathan Edwards emphasized immediate conversion and strong emotions
Emphasized importance of reason & the Bible
Influenced by Enlightenment ideas of rationality
New Lights: George Whitefield and Jonathan Edwards emphasized immediate conversion and strong emotions
9
New cards
Benjamin Franklin
Born in Boston; moved to Philadelphia at 17
Worked as a printer; eventually became very successful
Inventor & scientist
Politician: Ambassador in Paris
Master of self-presentation & self-invention
Worked as a printer; eventually became very successful
Inventor & scientist
Politician: Ambassador in Paris
Master of self-presentation & self-invention
10
New cards
William Penn
Founder of Pennsylvania (1682)
Member of the “Society of Friends” or Quakers
“Holy Experiment”
Cultivated goodwill among the Lenni Lenape (Delaware)
Member of the “Society of Friends” or Quakers
“Holy Experiment”
Cultivated goodwill among the Lenni Lenape (Delaware)
11
New cards
Quaker
Religious minority that believed in Pacifism
Wore Plain Clothes
Practiced religious tolerance and led the diverse populating of Pennsylvania with many different sects of European society
Wore Plain Clothes
Practiced religious tolerance and led the diverse populating of Pennsylvania with many different sects of European society
12
New cards
Seven Years' War
AKA French and Indian War: Conflict between the French and English throughout the Atlantic World
In North America, English settlers were trying to claim more Native land and defeat the French
Native nations often forced to choose sides, and support either the French or English
In North America, English settlers were trying to claim more Native land and defeat the French
Native nations often forced to choose sides, and support either the French or English
13
New cards
General Edward Braddock
British general sent to defeat French at Fort Duquesne after Washington's defeat
Had 2,200 troops and lost the battle in part because of arrogance
Died during the retreat
Had 2,200 troops and lost the battle in part because of arrogance
Died during the retreat
14
New cards
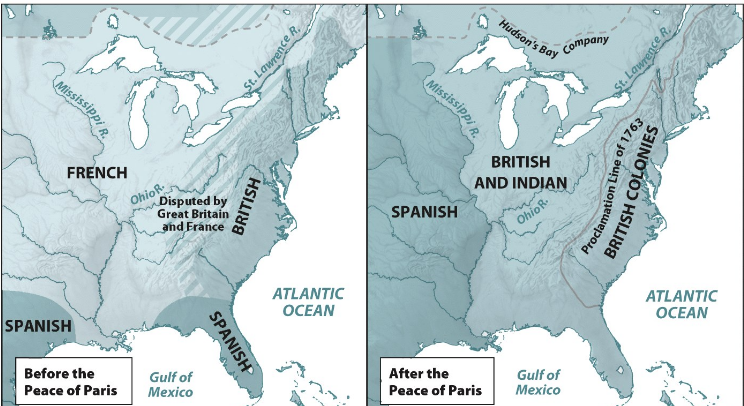
Line of Proclamation
1763: “Line of Proclamation”
British announce that colonists should not settle past the Appalachian Mountains.
intended to stabilize British relations with Indians
British announce that colonists should not settle past the Appalachian Mountains.
intended to stabilize British relations with Indians
15
New cards
Neolin
Lenni Lenape (Delaware) prophet
Vision in 1760: Indians should join together against all Whites
Urged his followers to stop trading with Europeans
Preaching contained elements of Native and Christian traditions (ex: depiction of heaven/hell)
Vision in 1760: Indians should join together against all Whites
Urged his followers to stop trading with Europeans
Preaching contained elements of Native and Christian traditions (ex: depiction of heaven/hell)
16
New cards
Pontiac's War
Pontiac was a native leader who fights at Detroit
native people succeed to capture all forts except detroit, niagara, and pitt
One of the reasons for the creation of the Line of Proclamation
native people succeed to capture all forts except detroit, niagara, and pitt
One of the reasons for the creation of the Line of Proclamation
17
New cards
Paxton Boys
Scots-Irish colonists on the Pennsylvania frontier
Attacked Native people indiscriminately
Massacred a Native village at Conestoga
Rising tensions & racial animosity as English people take Native land
Attacked Native people indiscriminately
Massacred a Native village at Conestoga
Rising tensions & racial animosity as English people take Native land
18
New cards
The Stamp Act
Britain greatly indebted after Seven Years War
English Parliament decided to tax colonists, because they paid far less in taxes than people in Britain
Stamp Act: Taxed goods produced in the colonies, paid in currency, and paid the salaries of customs officials
19
New cards
Townshend Acts
Tax on imports from Britain
Difference between tariffs and taxes
Paid salaries of royal officials
Customs officials got 1/3 of smuggled goods
Smugglers tried without a jury
Difference between tariffs and taxes
Paid salaries of royal officials
Customs officials got 1/3 of smuggled goods
Smugglers tried without a jury
20
New cards
Boston Massacre
crowd gathers at customs house and taunt soldiers
colonists pelt soldiers with snowballs and stones
british soldiers start firing and 5 people die
Media produced is used as propaganda for the Revolution
colonists pelt soldiers with snowballs and stones
british soldiers start firing and 5 people die
Media produced is used as propaganda for the Revolution

21
New cards
Boston Tea Party
Tea Act, 1773: Parliament reduces the cost of tea, but includes a small tax
Nov. 1773: First ships with British tea arrive in Boston harbor
Dec 16, 1773: 50-60 men dressed as Indians dumped 45 tons of tea into Boston Harbor
Nov. 1773: First ships with British tea arrive in Boston harbor
Dec 16, 1773: 50-60 men dressed as Indians dumped 45 tons of tea into Boston Harbor
22
New cards
Coercive Acts
AKA “The Intolerable Acts”
Closed the port of Boston until tea (with tax) was paid for
Curbed Massachusetts self-government
Protected British officials and soldiers
Colonists forced to provide supplies to British soldiers
Closed the port of Boston until tea (with tax) was paid for
Curbed Massachusetts self-government
Protected British officials and soldiers
Colonists forced to provide supplies to British soldiers
23
New cards
First Continental Congress
In response to the Coercive Acts
Petitioned King George III to remove the Acts
Representatives of 12 colonies
Sought to avoid war
Petitioned King George III to remove the Acts
Representatives of 12 colonies
Sought to avoid war
24
New cards
Committees of Observation & Safety
created to “…to observe the conduct of all persons”
To ensure boycotts
Shadow government
Spy network; peer pressure to conform
To ensure boycotts
Shadow government
Spy network; peer pressure to conform
25
New cards
Lexington & Concord
British soldiers sent to concord, burned supplies but couldn't find any arms
colonists had 4,000 militia and british had 700 even though the artwork depicts the british are a large, invading body
colonists attacked as the soldiers marked back (78 died, 220 wounded for british and about 90 for colonists)
colonists had 4,000 militia and british had 700 even though the artwork depicts the british are a large, invading body
colonists attacked as the soldiers marked back (78 died, 220 wounded for british and about 90 for colonists)

26
New cards
2nd Continental Congress
May 1775 in Philadelphia
George Washington named Commander-in-Chief of the Continental Army
BUT no call for Independence
“Olive Branch Petition”: Sought to reconcile with King George III
George Washington named Commander-in-Chief of the Continental Army
BUT no call for Independence
“Olive Branch Petition”: Sought to reconcile with King George III
27
New cards
Thomas Paine
Common Sense published in January 1776.
Sold 120,000 copies in 3 months; eventually sold 500,000 (colonial population was 2.5 million)
Ridiculed the idea of hereditary monarchy
Insulted the Crown
Encouraged Independence
Sold 120,000 copies in 3 months; eventually sold 500,000 (colonial population was 2.5 million)
Ridiculed the idea of hereditary monarchy
Insulted the Crown
Encouraged Independence
28
New cards
Declaration of Independence vs. Constitution
Declaration:
drew on other documents, VA Constitution, English Declaration of Rights, George Mason’s VA Declaration of Rights
Key points: Inalienable rights; Gov’t by consent of the people; right to Revolution
Published 1776
Constitution:
3/5 Compromise: Gave slave states more representatives in Congress.
Slave Trade: Could not be outlawed for 20 years (until 1808)
Fugitive Slave Clause: even free states must return runaway slaves to slave owners.
Written in 1787
Sets up how the American government is going to run
drew on other documents, VA Constitution, English Declaration of Rights, George Mason’s VA Declaration of Rights
Key points: Inalienable rights; Gov’t by consent of the people; right to Revolution
Published 1776
Constitution:
3/5 Compromise: Gave slave states more representatives in Congress.
Slave Trade: Could not be outlawed for 20 years (until 1808)
Fugitive Slave Clause: even free states must return runaway slaves to slave owners.
Written in 1787
Sets up how the American government is going to run
29
New cards
Dunmore's Proclamation
Lord Dunmore, Royal Governor of Virginia
1775: Dunmore calls on slaves to join the British forces; promised them freedom
Hundreds of enslaved people joined the British
1775: Dunmore calls on slaves to join the British forces; promised them freedom
Hundreds of enslaved people joined the British
30
New cards
Harry Washington
Enslaved by George Washington
Escaped in 1776; joined the British forces in the American Revolution to fight for his freedom
Served in Dunmore’s all-black regiment, “the black Pioneers”
After the war, he was resettled in Nova Scotia, and then in Sierra Leone, Africa
Escaped in 1776; joined the British forces in the American Revolution to fight for his freedom
Served in Dunmore’s all-black regiment, “the black Pioneers”
After the war, he was resettled in Nova Scotia, and then in Sierra Leone, Africa
31
New cards
Treaty of Paris
Depicted in a painting by Benjamin West
Demanded unconditional independence and boundaries would be Florida, Canada
mortality estimates: 25,000 casualties
Demanded unconditional independence and boundaries would be Florida, Canada
mortality estimates: 25,000 casualties

32
New cards
Ratification Debates
Federalists:
Did not trust the people
Focus: Economic Growth
Wanted a strong Army
Strong central gov’t
Hated French Rev.
No direct accountability to voters
Style: high fashion
Anti-Federalists:
Did not trust the Gov’t
Focus: Public Interest
Feared a strong army
Independent farmer
Supported French Rev. (anti-monarchist)
Voters keep tabs on reps
Style: street clothes, no wigs, “common citizen”
Did not trust the people
Focus: Economic Growth
Wanted a strong Army
Strong central gov’t
Hated French Rev.
No direct accountability to voters
Style: high fashion
Anti-Federalists:
Did not trust the Gov’t
Focus: Public Interest
Feared a strong army
Independent farmer
Supported French Rev. (anti-monarchist)
Voters keep tabs on reps
Style: street clothes, no wigs, “common citizen”
33
New cards
Bill of Rights
States suggested over 200 amendments. Madison chose 12; 10 were ratified
These became the first 10 Amendments to the Constitution. They are a list of demands from states that national gov. must protect/abide by
Bill of Rights guaranteed: freedom of speech, freedom of religion, due process, no cruel and unusual punishments
These became the first 10 Amendments to the Constitution. They are a list of demands from states that national gov. must protect/abide by
Bill of Rights guaranteed: freedom of speech, freedom of religion, due process, no cruel and unusual punishments
34
New cards
French Support of Revolutionary War
Resented British victory in the French & Indian War
Wanted to prevent the British from gaining too much power
Declaration of Independence was well-received in France as an embodiment of the Enlightenment spirit
American lobbying: Benjamin Franklin arrives in France: 1776, Thomas Jefferson is also an American diplomat
Wanted to prevent the British from gaining too much power
Declaration of Independence was well-received in France as an embodiment of the Enlightenment spirit
American lobbying: Benjamin Franklin arrives in France: 1776, Thomas Jefferson is also an American diplomat
35
New cards
Origins of French Revolution
Enlightenment ideals embodied in the American Revolution: liberty, freedom, etc.
Financial Crisis: American Revolution, Seven Years War
Famine among the common people
Nobility still living luxuriously
Financial Crisis: American Revolution, Seven Years War
Famine among the common people
Nobility still living luxuriously
36
New cards
Haitian Caste System
Grand blancs: White colonial elites; planters and merchants who owned many slaves.
Petit blancs: Poor whites; arrived in Saint-Domingue looking for work & fortune
Free People of Color: about 2/3 were mixed race. Many owned slaves of their own.
Slaves: Majority of the population; most worked on sugar plantations.
Petit blancs: Poor whites; arrived in Saint-Domingue looking for work & fortune
Free People of Color: about 2/3 were mixed race. Many owned slaves of their own.
Slaves: Majority of the population; most worked on sugar plantations.
37
New cards
Vincent Oge
Wealthy mixed-race slave owner from Saint-Domingue
1789: Presented a petition to the National Assembly in Paris in favor of voting rights for free people of color.
General Assembly 1790: “all proprietors…ought to be active citizens”
Incited a rebellion in Saint-Domingue in 1790
Executed in 1791
1789: Presented a petition to the National Assembly in Paris in favor of voting rights for free people of color.
General Assembly 1790: “all proprietors…ought to be active citizens”
Incited a rebellion in Saint-Domingue in 1790
Executed in 1791
38
New cards
Touissant L'ouverture
Becomes the leader of Saint-Domingue
Tried to reconcile with whites
Slavery abolished, but ex-slaves should return to their plantations
Wanted to remain in the French Empire
Wants Haiti to be a Catholic nation
Tried to reconcile with whites
Slavery abolished, but ex-slaves should return to their plantations
Wanted to remain in the French Empire
Wants Haiti to be a Catholic nation
39
New cards
Napoleon's Campaign
1802: Napoleon sends Leclerc to take control of Saint-Domingue
Regains Louisiana territory from Spain
Arrests Touissaint L’ouverture
Reinstates slavery
Leclerc begins a reign of terror that is continued by his successor, Rochambeau
Regains Louisiana territory from Spain
Arrests Touissaint L’ouverture
Reinstates slavery
Leclerc begins a reign of terror that is continued by his successor, Rochambeau
40
New cards
Effects of the Haitian Revolution
Widespread fear of slave revolt: Increased slave controls & paranoia
Stimulated slave economy in the U.S.
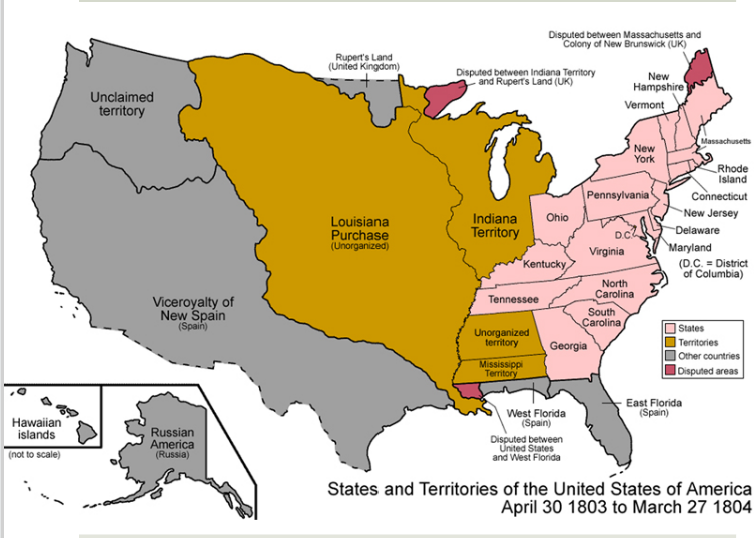
Louisiana Purchase: Without Saint-Domingue, Napoleon had no need for the Louisiana Territory. Sold to the United States for $15 million. Land would be used to extend & strengthen slavery.
Inspired abolitionists in the United States
Stimulated slave economy in the U.S.
Louisiana Purchase: Without Saint-Domingue, Napoleon had no need for the Louisiana Territory. Sold to the United States for $15 million. Land would be used to extend & strengthen slavery.
Inspired abolitionists in the United States
41
New cards
Gabriel's Rebellion
Gabriel: Literate enslaved man living near Richmond, Virginia
Planned a revolt inspired by the American and Haitian Revolutions
Inverts Patrick Henry's phrase “Liberty or Death” into "Death or Liberty"
Planned a revolt inspired by the American and Haitian Revolutions
Inverts Patrick Henry's phrase “Liberty or Death” into "Death or Liberty"
42
New cards
3/5th Compromise
3/5 Compromise: Gave slave states more representatives in Congress.
Slave Trade: Could not be outlawed for 20 years (until 1808)
Fugitive Slave Clause: even free states must return runaway slaves to slave owners.
Slave Trade: Could not be outlawed for 20 years (until 1808)
Fugitive Slave Clause: even free states must return runaway slaves to slave owners.