Mr. Sinn unit #4 Political Geography
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
4.1 State
A geographic area organized into one political unit. A recognized government. Ex: The United States of America
4.1 Nation
A group of people who share a common history/cultural characteristics with a history of self-determination. Ex: Americans

4.1 nation-state
A sovereign state that is made up of subjects who are relatively homogenous. Ex: European Countries
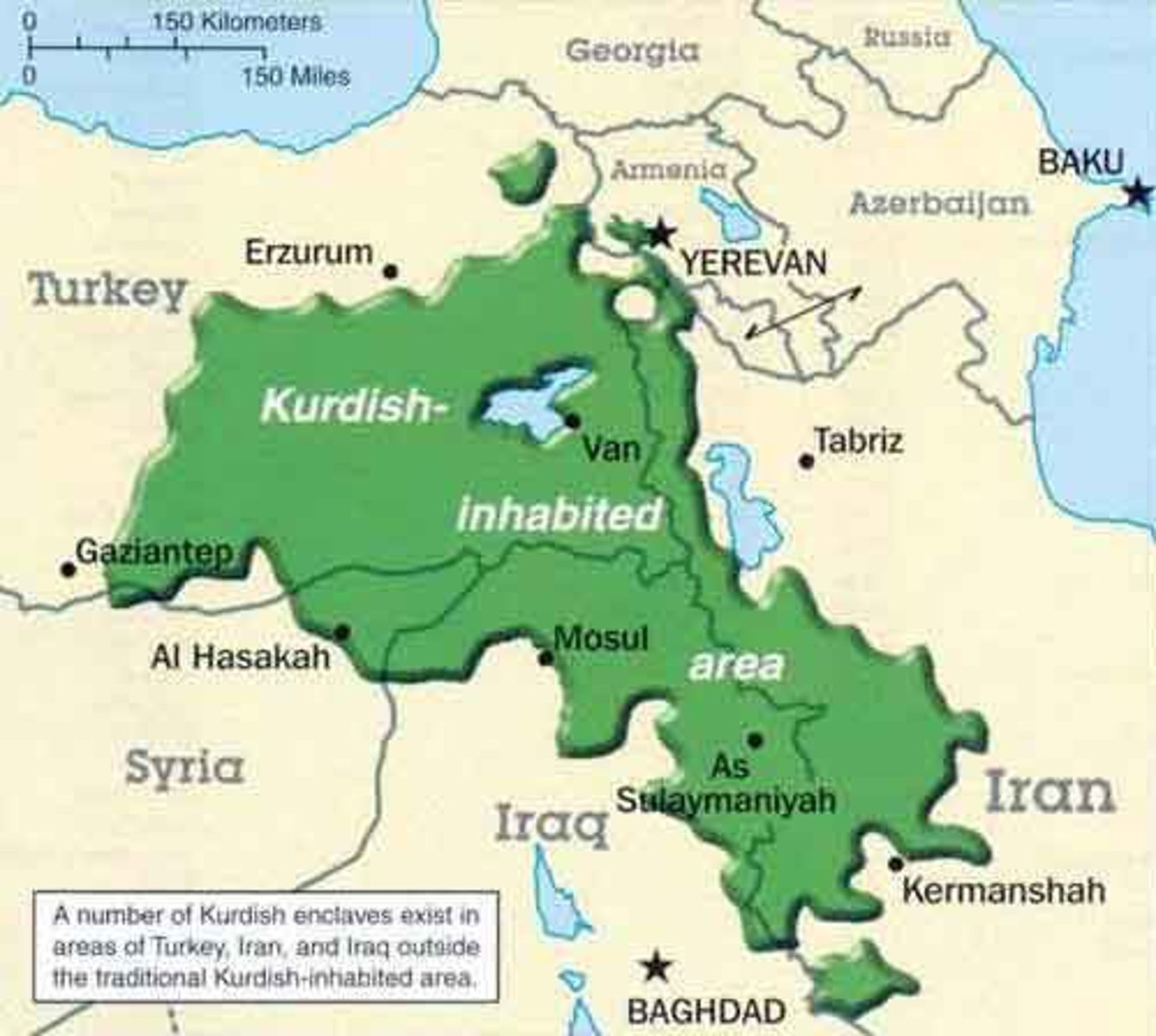
4.1 stateless nation
A nation with a history of self-determination but does not have a recognized state. Ex: The Kurds
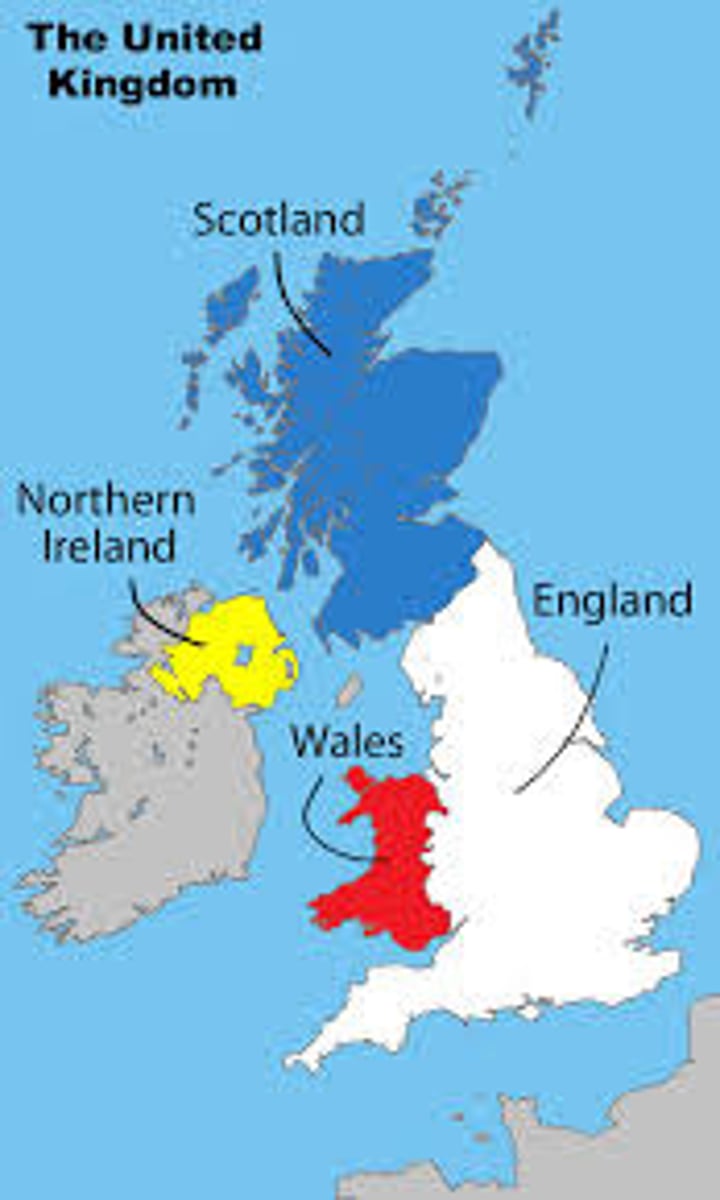
4.1 multinational state
A state that contains two or more nations who have agreed to coexist as one state. Ex: The United Kingdom
4.1 multistate nation
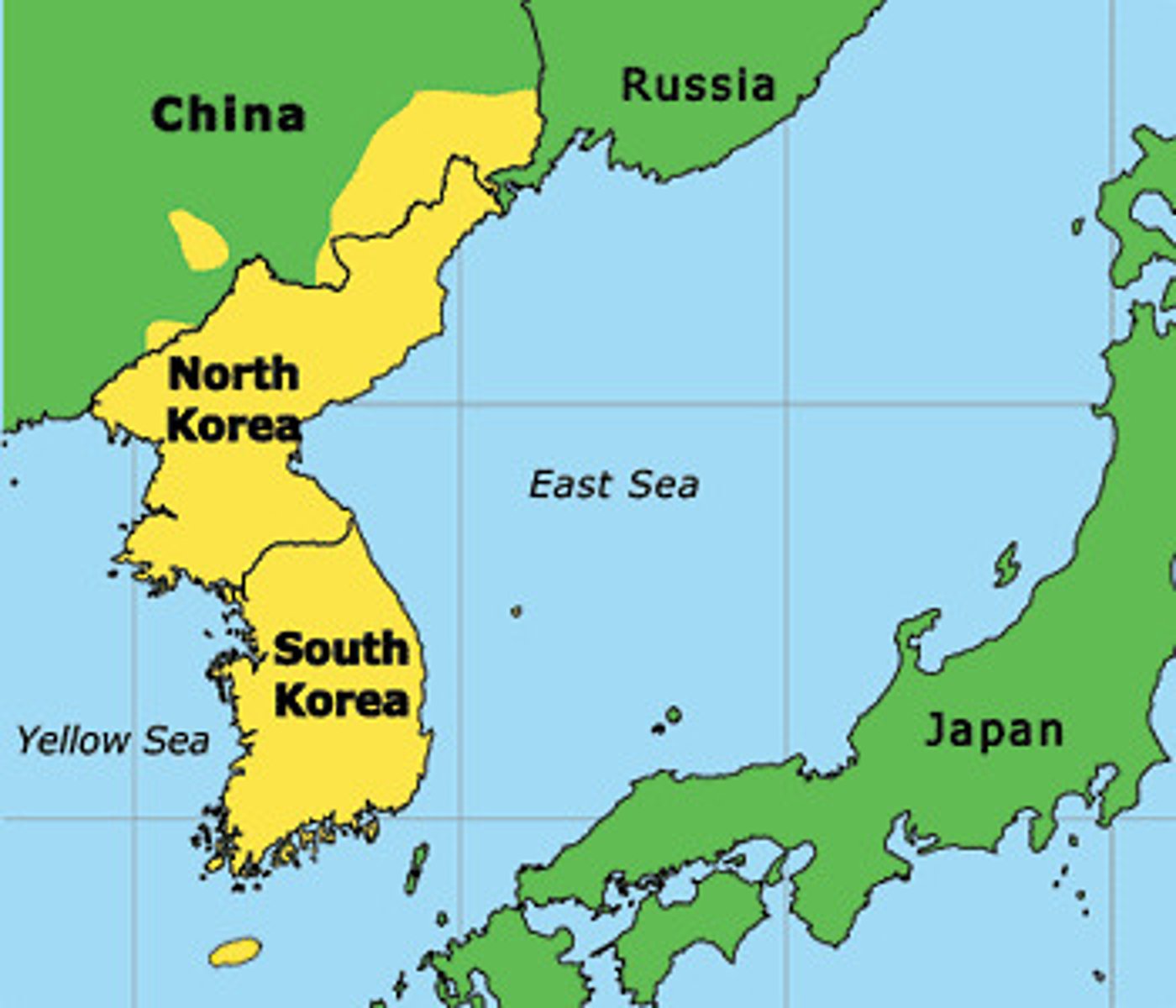
a nation that stretches across borders and across states. Ex: North and South Korea
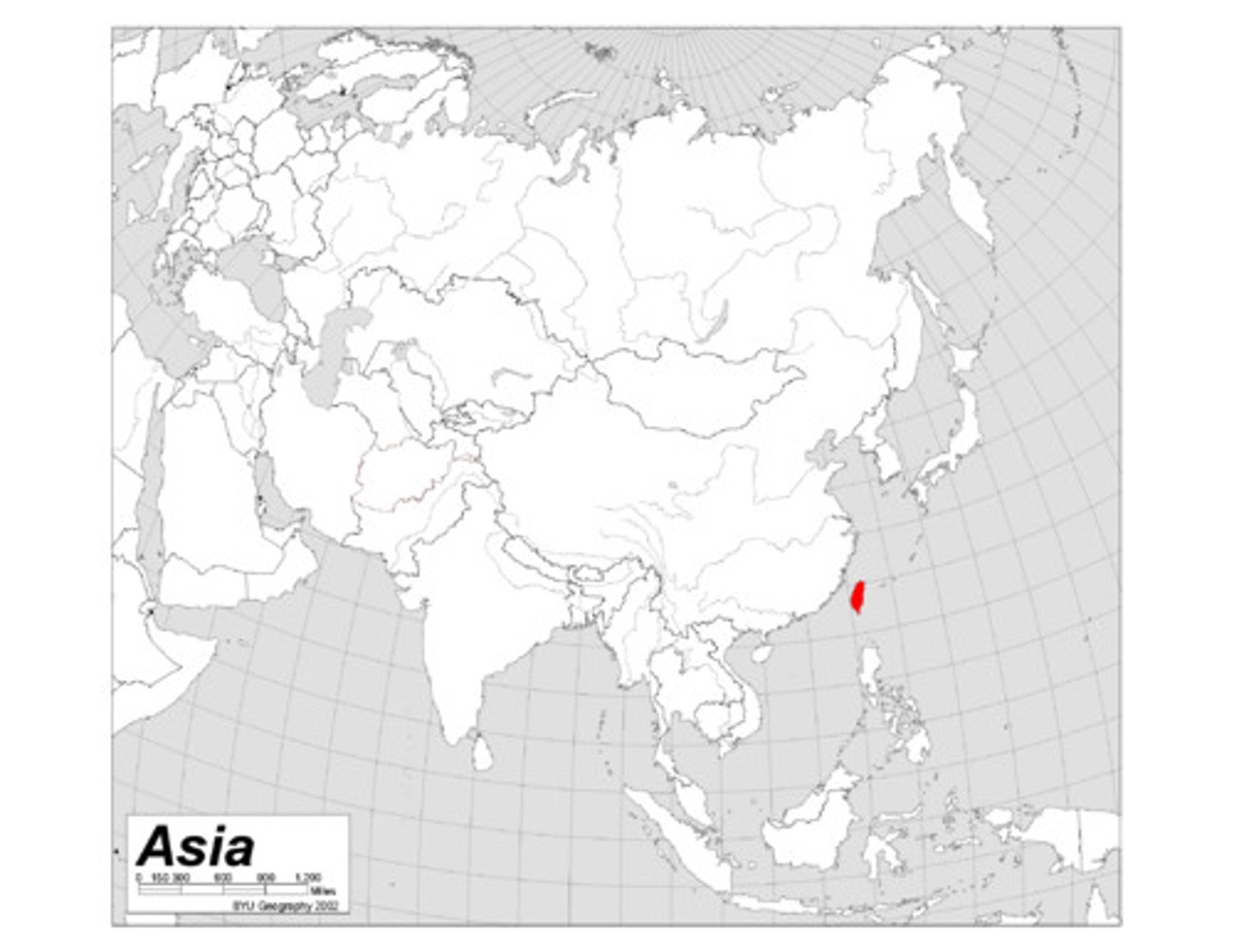
4.1 Autonomous regions
The territory of a country that has autonomy or a degree of sovereignty, often geographically distinct from the rest of the country. Ex: Taiwan
4.2 semi autonomous regions
The territory of a country that has a small amount of autonomy often is not geographically distinct from the rest of the country. Ex: Native Americans

4.2 Self-determination
Nations have the right to govern themselves to preserve cultural characteris

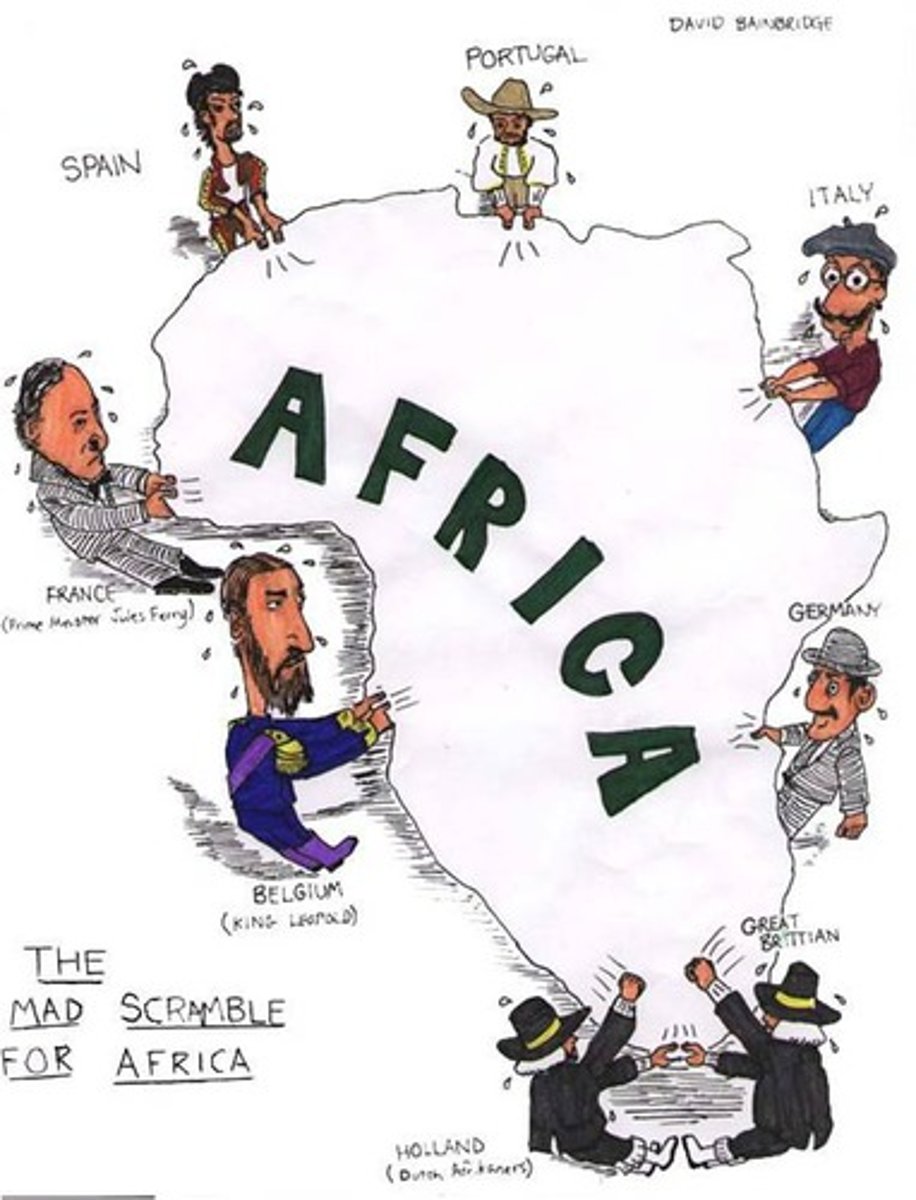
4.2 Colonialism
An attempt by one country to establish settlements and to impose its political, economic, and cultural principles in another territory. Ex: Europe's scramble for Africa. Sates were divided on longitude and latitude which broke up nations and cultures to only benefit Europe. .
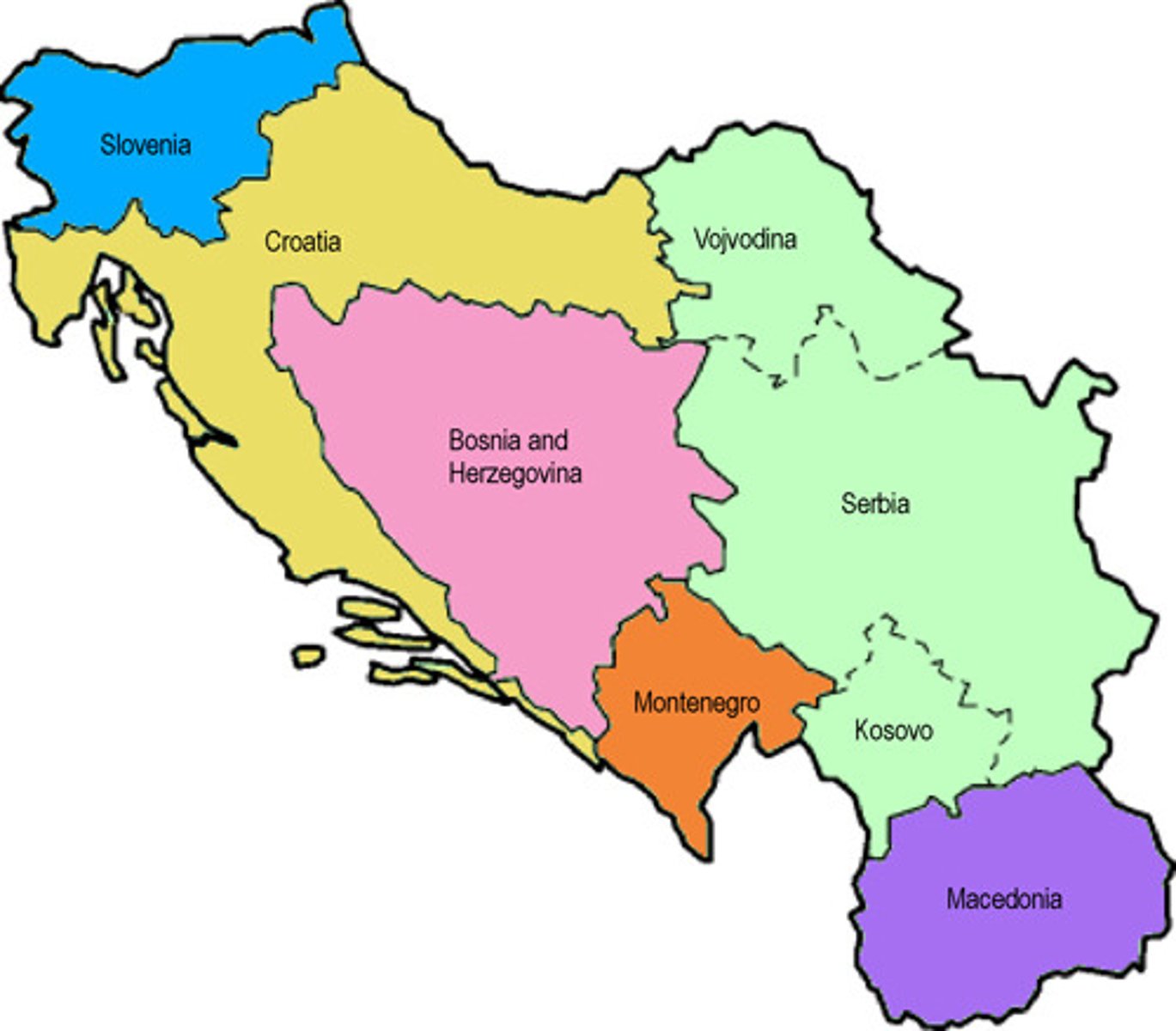
4.2 Devolution
The transfer of power from a central government to a lower level of government. Ex: Yugoslavia
4.3 Neocolonialism
The use of political, economic, or cultural pressures to control or influence other countries. Ex: China using Africa. China issuing a lot of money to help build infrastructure in Africa.
4.3 Territoriality
The attempt by an individual or group to affect, influence, or control people phenomenon or relationships by delimiting asserting control over a geographic area. communicate over a space
4.3 Shatterbelt Regions
A region caught between stronger external cultural/political forces. ex: the cold war. All of Western Europe was in between the conflicts of the Cold War

4.3 Chokepoints
strategic narrow passageways on land or sea that may be easily closed off by force or even the threat of force. How the world trades.
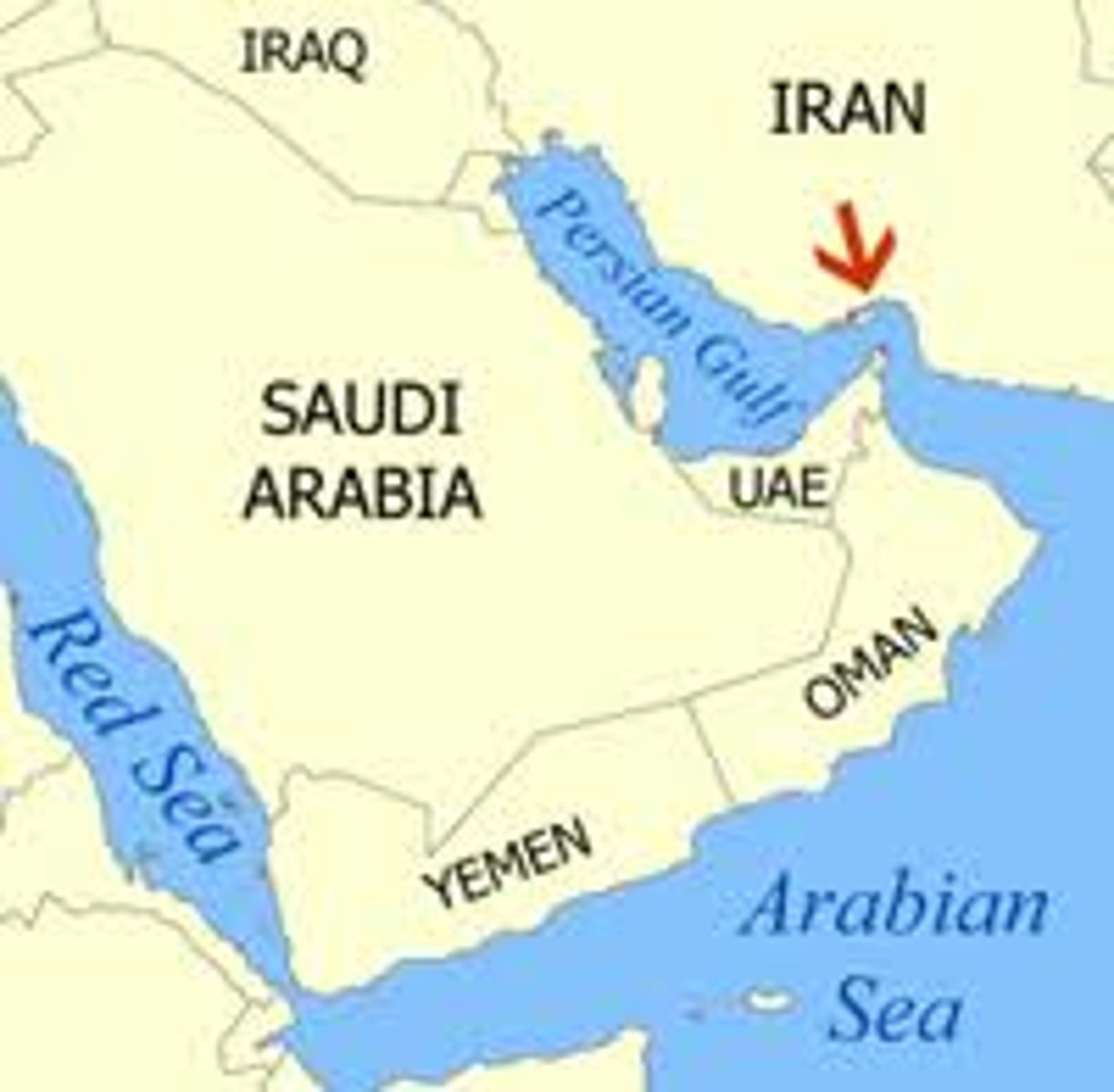
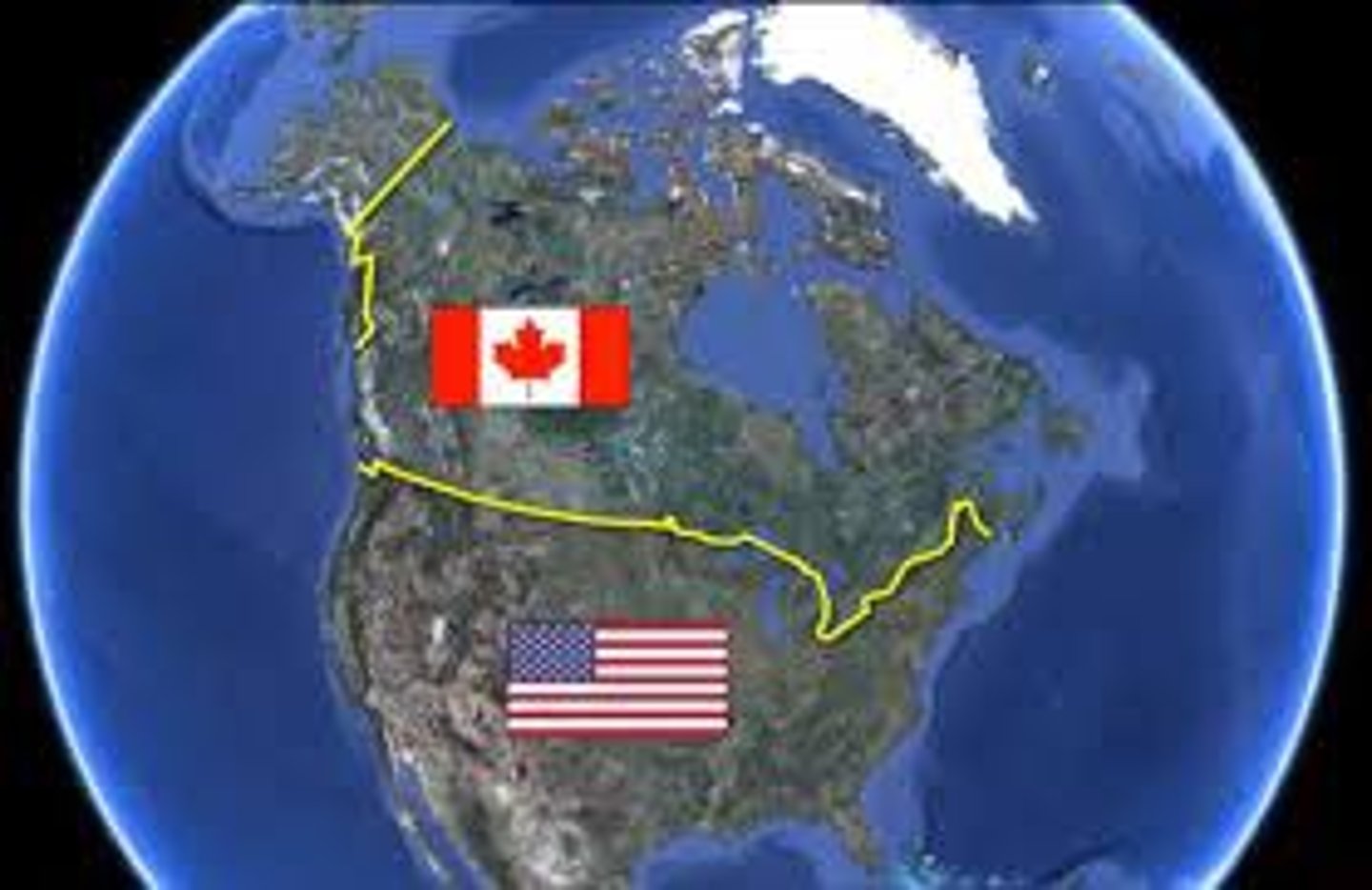
4.4 geometric boundary
A boundary that is a straight line, and is not connected to cultural differences or the physical terrain. Ex: The U.S. and Canadian border.
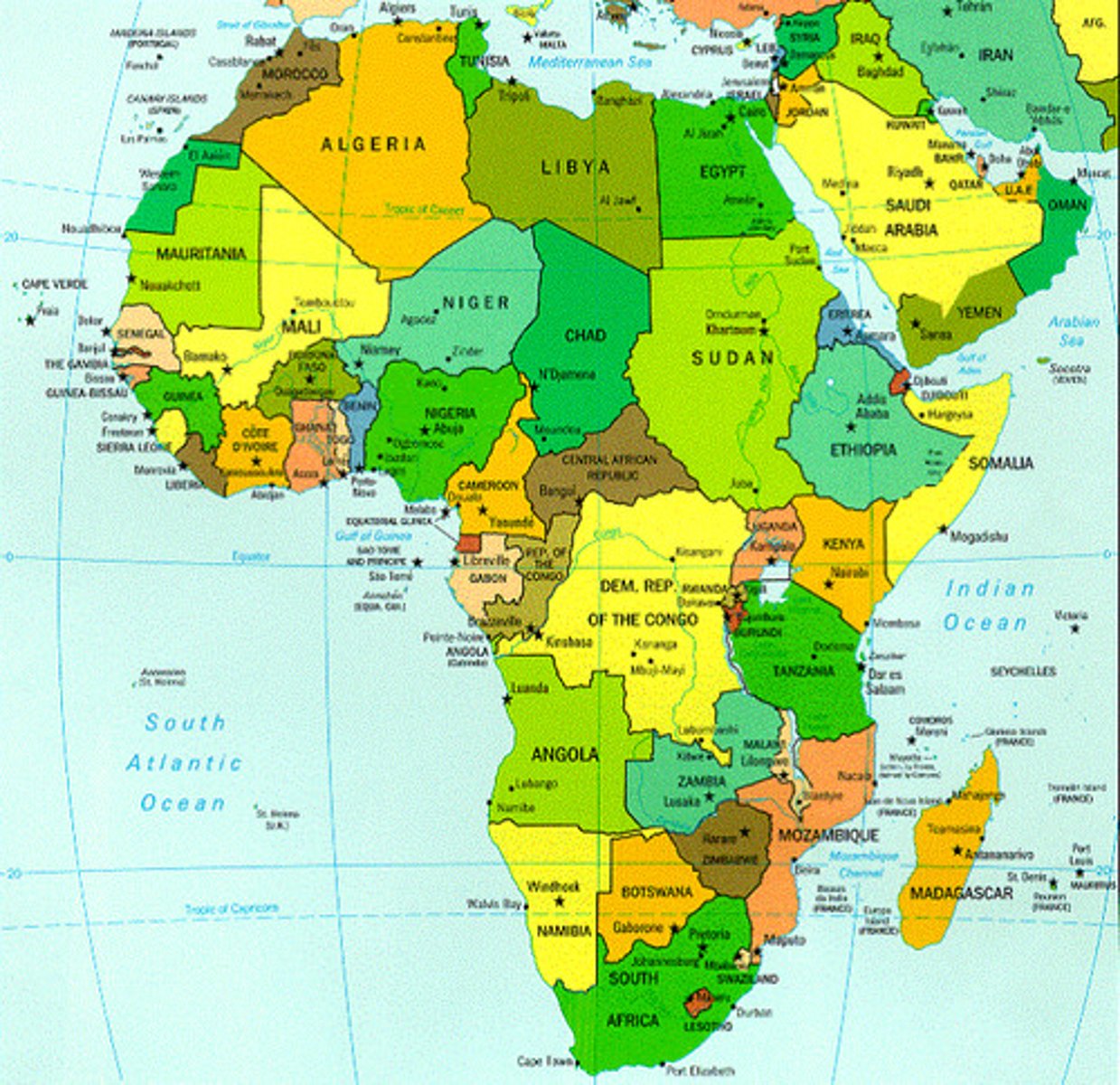
4.4 superimposed boundary
a boundary line placed over and ignoring an existing cultural pattern Ex: Africa
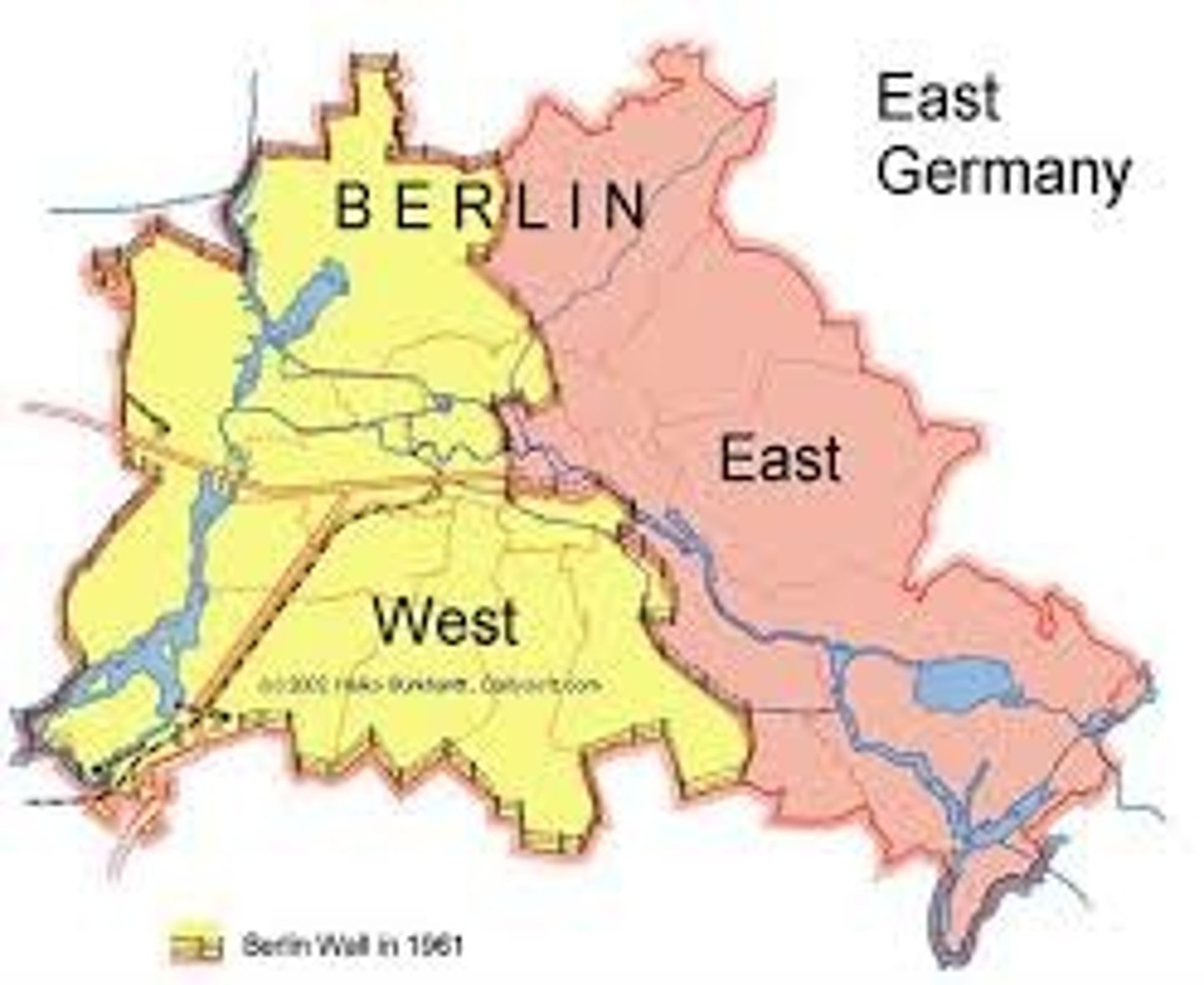
4.4 relic boundary
a former boundary line that is still discernible and marked by some cultural landscape features. Ex: The Berlin Wall
4.4 subsequent boundary (society)
a boundary that developed with the evolution of the cultural landscape and is adjusted as the cultural landscape changes. Ex: Yugoslavia because the states were created based on the ethnic groups that resided in that area.
4.4 antecedent boundary
A boundary that has existed before the development of the cultural landscape. (Very similar to Relic boundary so don't get it confused lmao). Ex: The Himalayan Mountains
4.4 consequent boundary (physical)
Boundaries divide different ethnic groups by physical features on the landscape. Ex: the boundary between India and current-day Pakistan was created to separate the main religions in the region, Hindu and Islam.
Locational Boundary Dispute
Conflict over the location or place of a boundary. Ex a river dispute

Operational Boundary Dispute
The dispute comes from issues that occur on the boundary. Ex: the U.S. and Mexico Border
Allocational Boundary Dispute
A boundary dispute that involves conflicting claims to the natural resources of a border region.

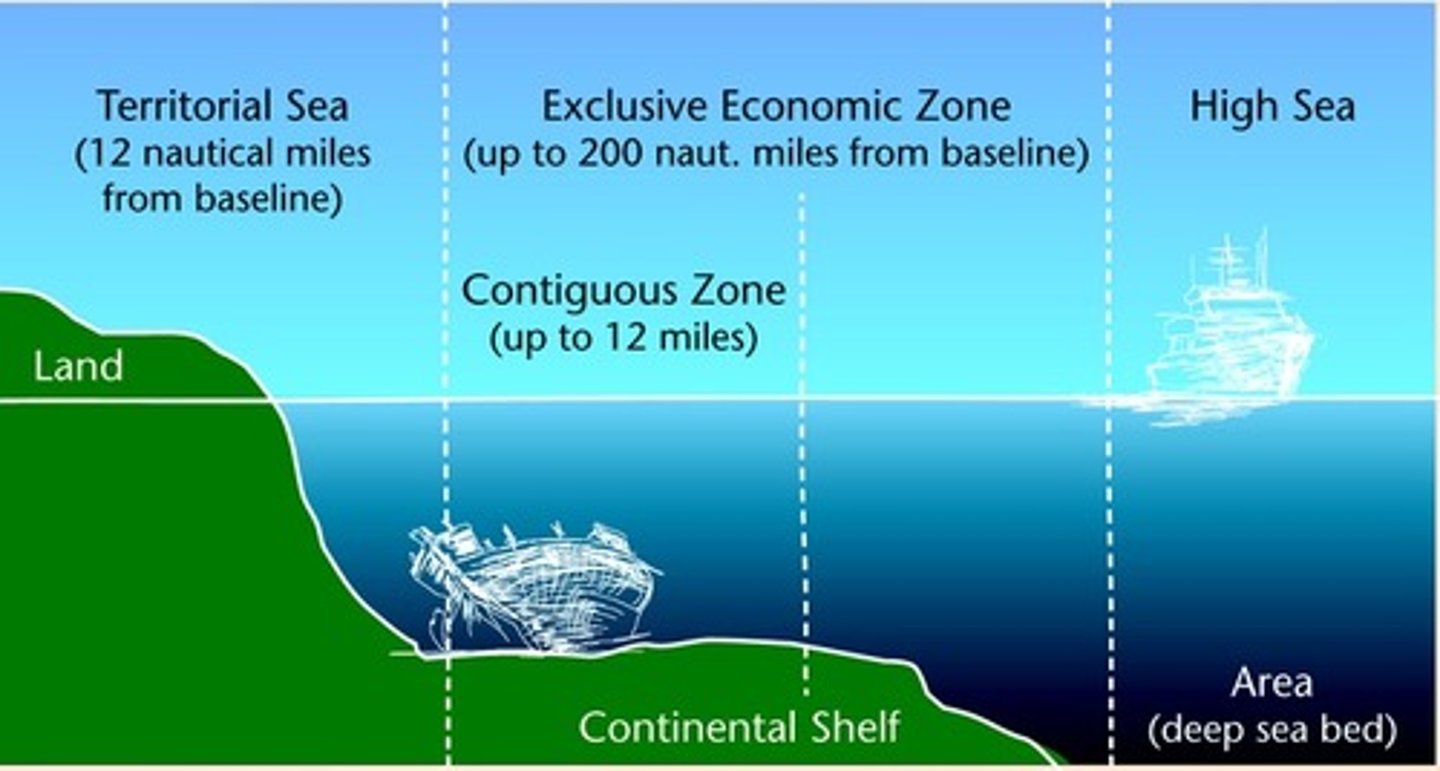
UNCLOS (United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea)
meant to resolve allocational boundary disputes. has multiple zones and international waters.
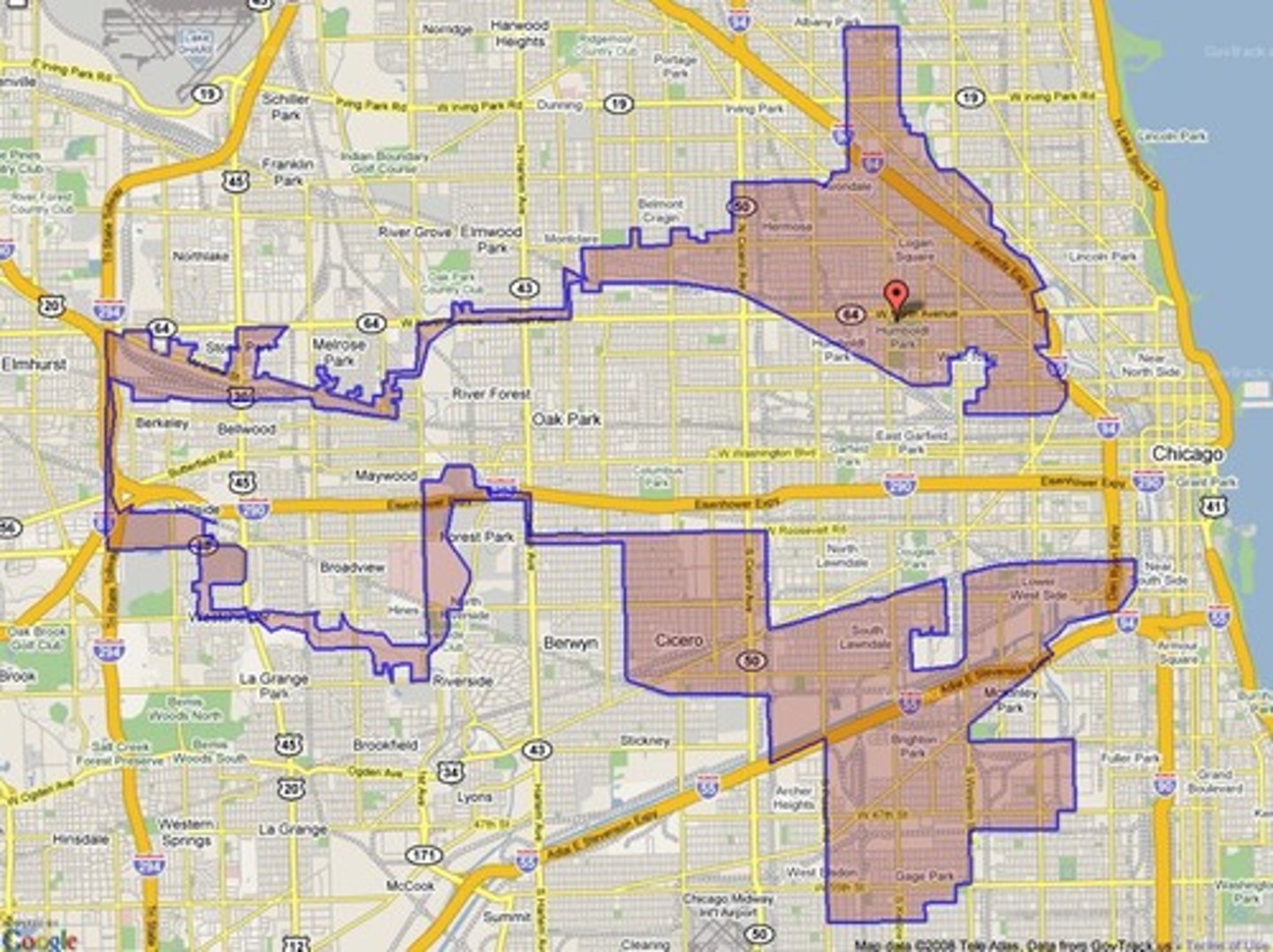
4.6 Gerrymandering
Redistricting voting districts in a manner that favors one political party over another. This is illegal. politicians. politicians are picking their voters basically. two techniques include cracking and packing.
4.7 Unitary Government
A way of organizing a nation so that all power resides in the central government. Pro: quickly implement decisions and laws, Con: difficult to understand the regional concerns. Ex: The United Kingdom. Their central government is in London

4.7 Federal Government
A form of government in which powers are divided between a central government and several local/regional governments. Pro: Can create a national government identity while also focusing on regional activities and concerns, Con: see disputes between regional governments and central governments. Ex: The United States

4.7 Confederation Government
the regional authorities hold the most power and the central government does really exist. Pro: regional governments have all power to adapt their laws to fit that particular region, Con: struggle to keep a national identity. Ex: The confederate states of America (1861-1865).
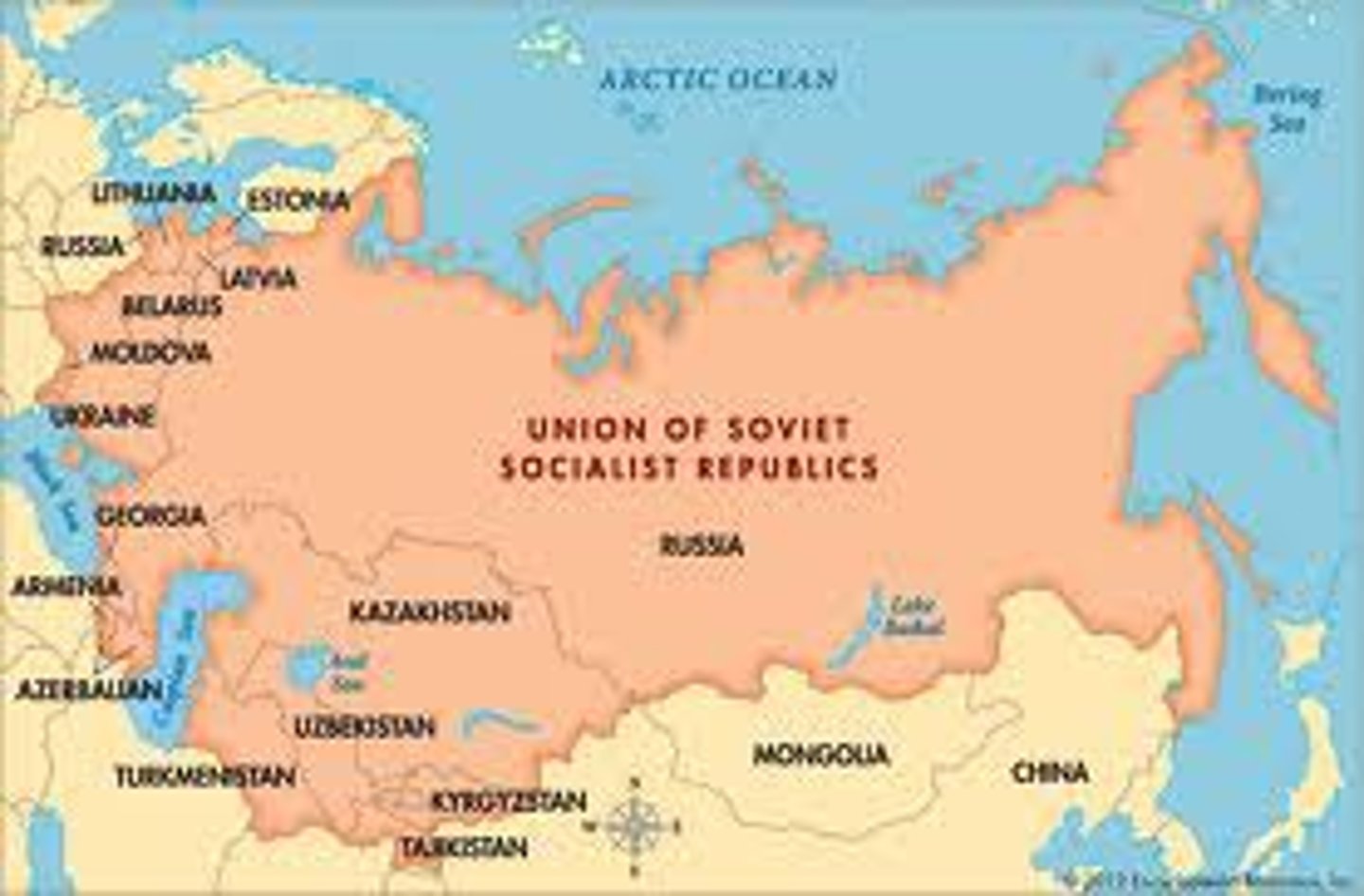
4.8 Devolution
Transferring responsibility for policies from the federal government to state and local governments.power shifting downwards. Ex: The Soviet Unions Falling into 16 independent states
4.8 Factors of Devolution
Economic: regional opportunity
Social: Ethnic groups wanting representation
Political: Multinational states wanting semi-autonomous regions. seeing the government shift power down to these groups. Ex: Brexit
Environmental: physical boundaries
4.8 Irredentism
A policy of advocating for coups or separatist movements into another country based on advocating for the restoration of a former territory, or moral claim to the land. Ex: Somalia's invasion of Ethiopia during the Ogaden War of 1977-78.
4.9 Supranational Organization
an organization that is formed when states willingly relinquish some degree of sovereignty in order to gain the benefits of belonging to a larger political-economic entity. a political factor that challenges sovereignty. Communication of multiple states. Ex: The U.N., NATO, E.U., international trade deals, etc. Britain leaving the European Union for more sovereignty.

4.9 Economic factors that challenge sovereignty
International trade deals, tariffs or sanctions,

4.9 Cultural factors that challenge sovereignty
countries risk losing their own cultural identity to a globalized world. Banning parts of the internet or blocking social media in effort to slow down the diffusion of information.
4.9 Technology
The knowledge that people use to make a way of life in their surroundings. social media and the internet are a diffusion of information and fake news spreading intentionally creating issues in other states such as election meddling.

4.10 Ethnonationalism
A form of nationalism where the nation is defined in terms of ethnicity.
4.10 centripetal factors
Political: developed states develop more patriotism. Ex: the U.S. on 9/11 united people
Economy: High GDP, low unemployment, accessibility, stability
cultural: homogenous; unified from a shared culture/history
geography: compact and sense of community.
4.10 Centrifugal Factors
political: abused citizens, money not disbursed wisely, and rebellion/uprising occurs
Economy: lack of opportunity, high unemployment
Cultural: many national groups and a state's history of self-determination or if prejudice or racism is occurring
Geography: states that re more spread out or fragmented can create isolated groups or cultures