OFFICIAL CELL AND MOLEC BIO EXAM 1
1/186
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
187 Terms
An ionic bond between two atoms is formed as a result of the
transfer of electrons from one atom to another.
What is the major force/bond that generates the organized structure of lipid bilayers
is the hydrophobic effect, which drives the nonpolar tails of lipids to avoid water, leading to the formation of a bilayer.
The complex macromolecules of the cell are built from simpler molecular monomer subunits (e.g amino acids, nucleotides) that are linked together through what type of chemical reaction?
condensation
The covalent bonds that form monomers into polymers can be broken down by the addition of __________ in a process called __________.
water; hydrolysis
DNA is synthesized by covalently linking nucleotides in a long chain. The DNA strand will become part of a stable helix of two complementary strands. What is the principal force that holds the two strands together?
Hydrogen bonding between bases.
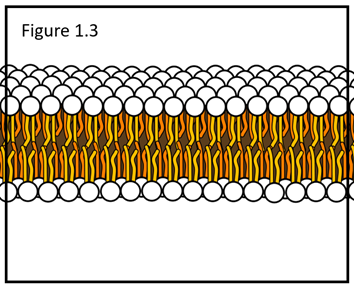
The cell membrane is a lipid bilayer like the one shown below (Figure 1.3) and is primarily composed of which type of molecule?
phospholipids
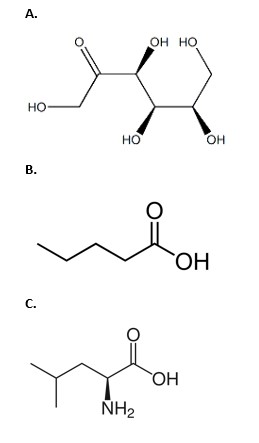
Which of the molecules below is an amino acid?
A molecule that contains an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a distinctive side chain (R group). Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. (aka c)
A covalent bond between two atoms is formed as a result of the:
sharing of electron pairs.
Water molecules are ______________ and form a network of __________________ that give water distinct properties.
polar, hydrogen bonds
Oxidation is the process by which oxygen atoms are added to a target molecule. Generally, the atom that is oxidized will experience which of the following with respect to the electrons in its outer shell?
a net loss
When there is an excess of nutrients available in the human body, insulin is released to stimulate the synthesis of glycogen from glucose. This is a specific example of a/an __________ process, a general process in which larger molecules are made from smaller molecules.
anabolic
At first glance, it may seem that living systems are able to defy the second law of thermodynamics. However, on closer examination, it becomes clear that although cells create organization from raw materials in the environment, they also contribute to disorder in the environment by releasing
heat
NADH and NADPH are activated carrier molecules that function in completely different metabolic reactions. Both carry energy in the form of __________ .
high energy electrons
The potential energy stored in high-energy bonds is commonly harnessed when the bonds are split by the addition of __________ in a process called __________.
water; hydrolysis
ΔG° indicates the change in the standard free energy as a reactant is converted to product. Given what you know about these values, which reaction below is the most favorable?
A reaction with a negative ΔG° value.
The second law of thermodynamics states that the disorder in any system is always ______________.
increasing
The best way to know if an organic molecule has been reduced is to see if there was an increase in the number of __________ bonds.
C-H
The energy used by the cell to generate specific biological molecules and highly ordered structures is stored in the form of:
chemical bonds
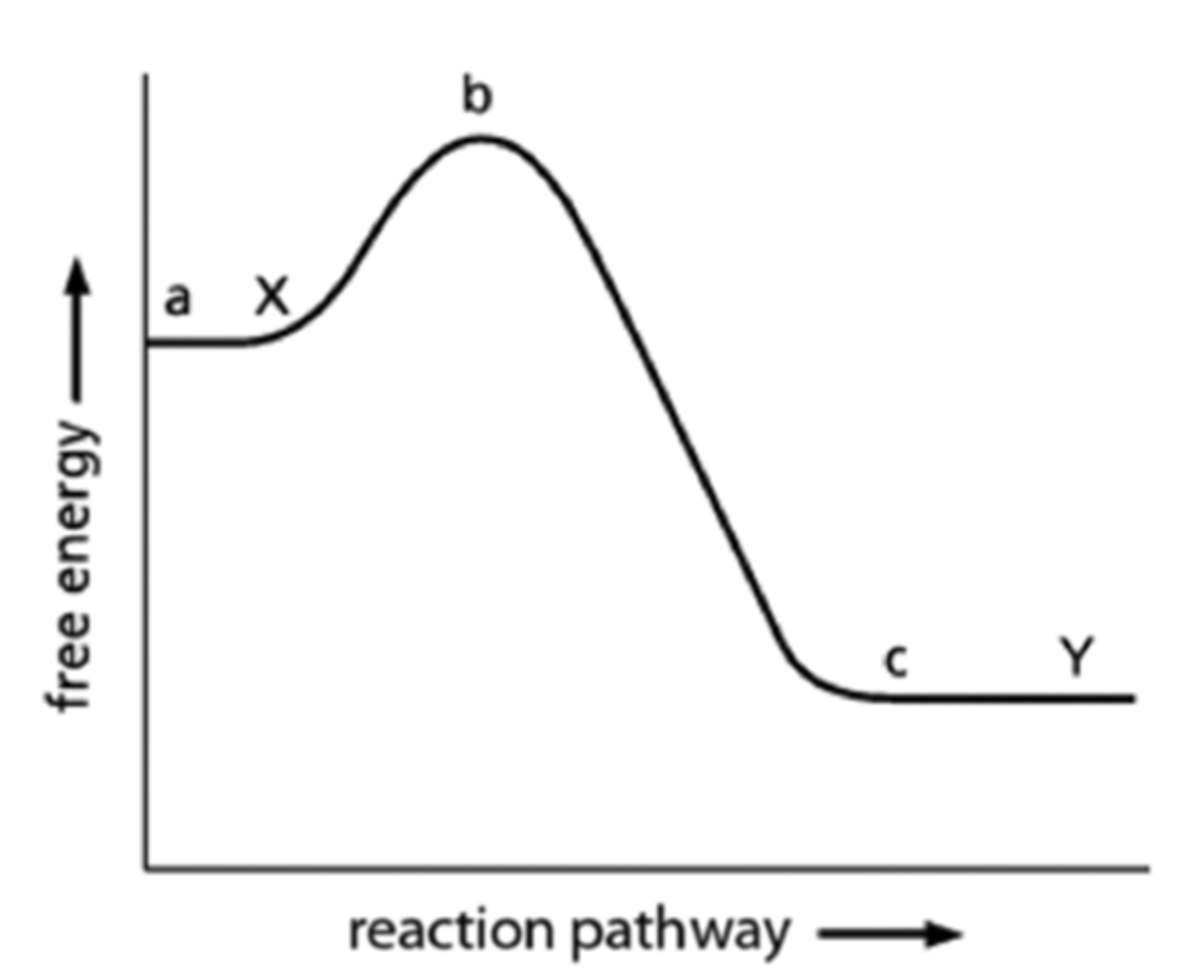
For the energy diagram for the reaction X→Y shown below. Which equation below provides the correct calculation for the amount of free-energy change when X is converted to Y?
c-a
NADH is an activated carrier that is primarily is associated with ____________ processes and is most abundant in the form NAD+ which can receive electrons and drive the oxidation of organic molecules.
catabolic
Enzymes facilitate chemical reactions by:
lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to proceed.
Polypeptides are synthesized from amino acid building blocks. The condensation reaction between the growing polypeptide chain and the next amino acid to be added involves the loss of:
a water molecule (H2O).
Two or three α helices can sometimes wrap around each other to form coiled-coils. The stable wrapping of one helix around another is typically driven by __________ interactions.
hydrophobic
The quaternary structure of a protein refers to:
its combination of separate polypeptide components
GTP binding proteins switch off when:
GTP is hydrolyzed to GDP
Motor proteins use the energy in ATP to transport organelles, rearrange elements of the cytoskeleton during cell migration, and move chromosomes during cell division. Which of the following mechanisms is sufficient to ensure the unidirectional movement of a motor protein along its substrate?
A conformational change is coupled to ATP hydrolysis
The primary structure of a protein refers to:
the linear sequence of amino acids.
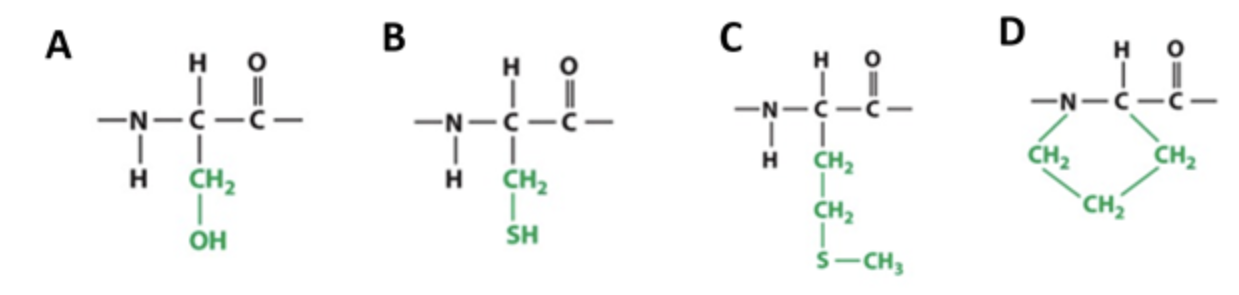
Which of the amino acids depicted below can form a disulfide bond:
Cysteine (B)
TRUE/FALSE Allosteric regulators are often products of other chemical reactions in the same biochemical pathway.
True
TRUE/FALSE Allosteric regulators block the active sites of enzymes and prevent substrate binding, inhibiting enzyme activity.
False
Motor proteins use the energy in ATP to transport organelles, rearrange elements of the cytoskeleton during cell migration, and move chromosomes during cell division. Which of the following mechanisms is sufficient to ensure the unidirectional movement of a motor protein along its substrate?
A conformational change is coupled to ATP hydrolysis
Molecular chaperones can work by creating an “isolation chamber.” What is the purpose of this chamber?
This protects unfolded proteins from interacting with other proteins in the cytosol, until protein folding is completed.
The quaternary structure of a protein refers to:
its combination of separate polypeptide components
Polypeptides are synthesized from amino acid building blocks. The condensation reaction between the growing polypeptide chain and the next amino acid to be added involves the loss of:
a water molecule.
Two or three α helices can sometimes wrap around each other to form coiled-coils. The stable wrapping of one helix around another is typically driven by __________ interactions.
hydrophobic
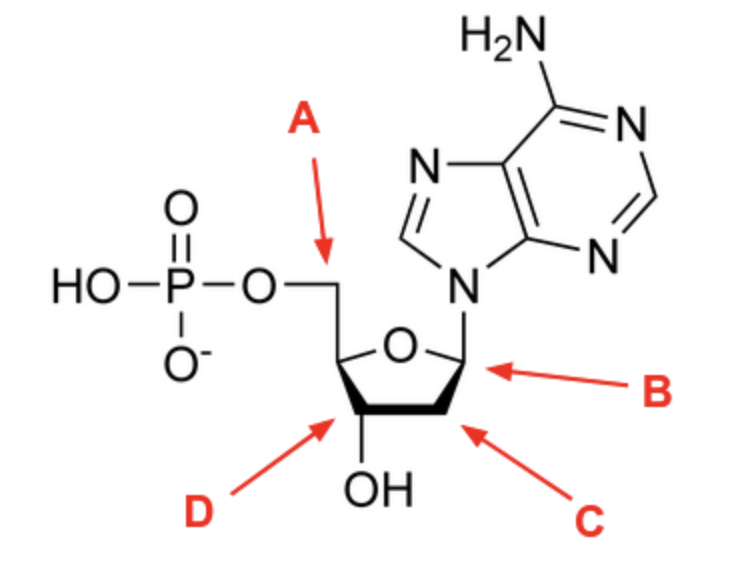
Identify the 5’ carbon on the nucleotide below:
A
Because hydrogen bonds hold the two strands of a DNA molecule together, the strands can be separated without breaking any covalent bonds. Every unique DNA molecule “melts” at a different temperature. In this context, Tm (melting temperature) is the point at which two strands separate, or become denatured.
Assuming the sequencing represent double-stranded DNA molecules, which molecule will melt at the lowest temperature?
A) GGCGCACC
B) TATTGTCT
C) GACTCCTG
D) CTAACTG
B. More A-T bonds
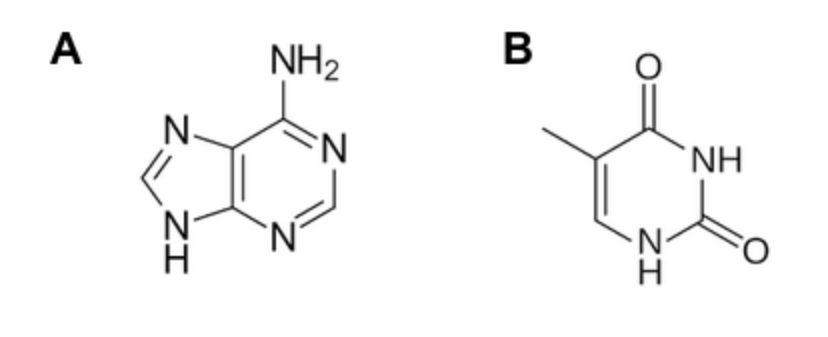
Which of the bases shown below is a purine?
A
You have isolated DNA from the squirrel that inhabits your backyard. When you measure the nucleotide content you observe that it is 29% Adenine and 21% Guanine. What do you expect the percentage of the other nucleotides to be?
Thymine - 29%, Cytosine - 21%
The human genome comprises 23 pairs of chromosomes found in nearly every cell in the body. How many telomeres are there in each cell?
92- 4 telomeres on the ends of each chromosome
Stepwise condensation of linear DNA into condensed chromatin happens in five different packing processes. Which of the processes listed has a direct requirement for histone H1?
formation of the chromatin fiber
Which of the following structural characteristics is not normally observed in a double-stranded DNA molecule?
parrallel strands
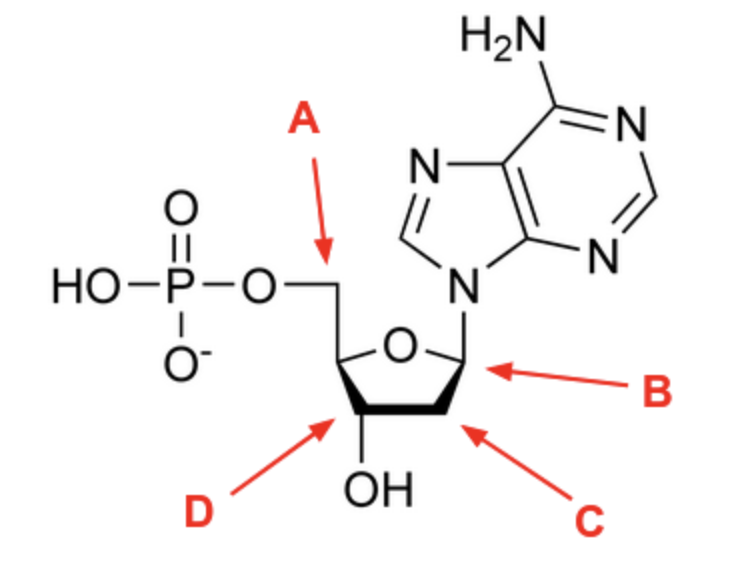
Identify the 3’ carbon on the nucleotide below:
D
Which of the following is the true statement about the DNA double helix:
In a DNA double helix, the two DNA strands are complementary
Which of the following aspects of DNA would you expect differ between different eukaryotic species:
ratio of A + T to G + C
Which of the following elements is not one of the six major constituents of biological materials?
Silicon
Which of the following monomer building blocks is necessary to assemble selectively permeable boundaries (cell membranes) around and inside cells?
fatty acids
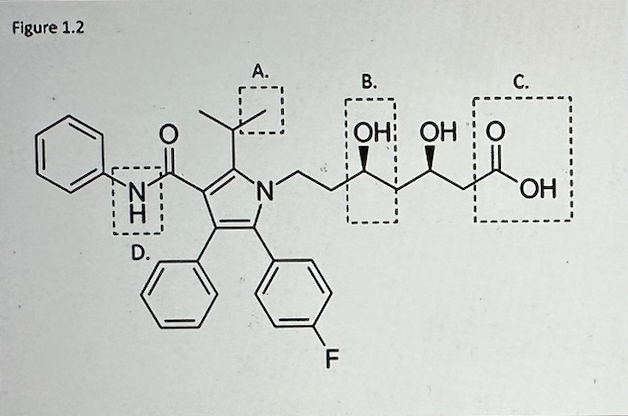
Which of the functional groups highlighted in the molecule below (Figure 1.2) is nonpolar?
A
The energy used by the cell to generate specific biological molecules and highly ordered structures is stored in the form of
chemical bonds
NADH and NADPH are activated carrier molecules that function in completely different metabolic reactions. Both carry two additional _______ and one additional _______.
• This combination can also be referred to as a hydride ion.
electrons; protons
Molecular chaperones can work by creating an isolation chamber." What is the purpose of this chamber?
This protects unfolded proteins from interacting with other proteins in the cytosol, until protein folding is completed.
The quaternary structure of a protein refers to:
its combination of separate polypeptide components
TRUE/FALSE Disulfide bonds are more common for extracellular proteins, compared to intracellular proteins
true
Motor proteins use the energy in ATP to transport organelles, rearrange elements of the cytoskeleton during cell migration, and move chromosomes during cell division. Which of the following mechanisms is sufficient to ensure the unidirectional movement of a motor protein along its substrate?
A conformational change is coupled to ATP hydrolysis
Polypeptides are synthesized from amino acid building blocks. The condensation reaction between the growing polypeptide chain and the next amino acid to be added involves the loss of:
a water molecule.
Fredrick Griffith provided important insights into biochemical basis of heredity when he observed that a harmless strain of Streptococcus pneumonia could be transformed into a virulent strain when it was combined with:
Heat killed virulent Streptococcus pneumonia
The N-terminal tail of histone H3 can be extensively modified, and depending on the number, location, and combination of these modifications, these changes may promote the formation of heterochromatin. What is the result of heterochromatin formation?
gene silencing
Hershey and Chase used radiolabeled macromolecules in phage viruses to identify the material that contained heritable information that was transferred to their bacterial hosts. What radioactive atom was used to track proteins during this experiment?
35S
Gregor Mendel
revealed that heredity is the result of discrete units of inheritance
Nettie Maria Stevens
An American geneticist who discovered sex chromosomes in mealworms which would later be termed “X” and “Y” chromosomes (1905)
Wilhelm Ludvig Johannsen
Danish scientist who coined the term gene to refer to the unit or particle of inheritance. (1903)
Archibald Garrod
identifies alkaptonuria as a heritable genetic disease that follows Mendel’s laws.
Alkaptonuria - “black urine” - inborn error of metabolism
Ernest Everett Just
An American embryologist who was the first to conceptualize epigenetics: the environment contributes to how the information in DNA becomes physical characteristics of an organism
Thomas Hunt Morgan
An American geneticist who discovered that certain mutations were inherited together (linked)
Frederick Griffith
a British bacteriologist whose focus was the epidemiology and pathology of bacterial pneumonia.
Avery, McCarty, and McLeod
R-strain could be transformed with
DNA extracts from dead S - strain
Alfred Hershey and Marsha Chase
labeled bacteriophages with
radioactive elements
Erwin Chargaff
Nucleotides occur in predictable
ratios in living things
James Watson
- Francis Crick
Rosalind Franklin
- Maurice Wilkins
Discovery of the structure of DNA
Linus Pauling
Major contributions to quantum physics, biophysics, and peace advocate.
What are the 6 elemental constituents of life
CHONPS: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, & sulfur
What is the content % of Carbon in the cell and its relative electronegativity?
10% and ~2.2
What is the content % of Hydrogen in the cell and its relative electronegativity?
~63% and ~3.4 (high electronegativity)
What is the content % of Oxygen in the cell and its relative electronegativity?
~24% and ~2.5
What is the content % of Nitrogen in the cell and its relative electronegativity?
1.4% and ~3.0 (high electronegativity)
What is the content % of Phosphorus in the cell and its relative electronegativity?
0.2% and ~2.2
What is the content % of Sulfur in the cell and its relative electronegativity?
~0.01% and ~2.6
Properties of polar covalent bonds
Occur when atoms with different electronegativities share electrons unevenly, resulting in a molecule with partial positive and negative charges.
Properties of nonpolar covalent bonds
Occur when atoms with similar electronegativities share electrons evenly, resulting in a molecule with no partial charges.
What are the four main noncovalent bonds/interactions that shape macromolecules?
Hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, van der Waals forces, hydrophobic interactions.
How to hydrogen bonds arise?
They arise when a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen or nitrogen, experiences an attraction to another electronegative atom.
How to ionic bonds arise?
They arise when one atom donates an electron to another atom, resulting in the formation of positively and negatively charged ions that attract each other.
How to Van der Waals attractions arise?
They arise from transient dipoles that occur when electron distributions around atoms fluctuate, leading to weak attractions between nearby molecules or atoms. Together they are strong
How to hydrophobic interactions arise?
They arise when nonpolar molecules aggregate in aqueous environments to minimize their exposure to water, driven by the tendency of water to exclude nonpolar substances.
Hydrogen bond relative strength:
Stronger than Van der Waals interactions but weaker than ionic and covalent bonds.
Ionic bond relative strength:
Stronger than hydrogen bonds but weaker than covalent bonds.
Van der Waals attraction relative strength:
Weaker than hydrogen bonds and ionic bonds, but can be significant in large molecules.
Hydrophobic interaction relative strength:
Weaker than hydrogen bonds but can influence molecular structure significantly.
What are the four main categories of carbon-based molecules that make up the cell?
Sugars, Fatty acids, Amino acids, Nucleotides.
What macromolecule has the subunit of sugars?
Glycogen and Starch
What macromolecule has the subunit of fatty acids?
Membrane lipids and fats
What is it called when a molecule is partly hydrophobic and partly hydrophilic?
Amphipathic
What macromolecule has the subunit of amino acids?
Proteins
What macromolecule has the subunit of nucleotides?
DNA and RNA
Complex molecues are built through the ________ of simple subunits and broken down through ________.
condensation and hydrolysis
How are complex macromolecules built through the condensation of simple subunits and broken down through hydrolysis?
by joining simple subunits together and releasing water molecules as a byproduct.
What bond type links subunits in glycogen and starch?
glycosidic bonds
What bond type links subunits in membrane lipids and fat?
ester bonds
What bond type links subunits in proteins?
peptide bonds
What bond type links subunits in DNA and RNA?
phosphodiester bonds