Bearings
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
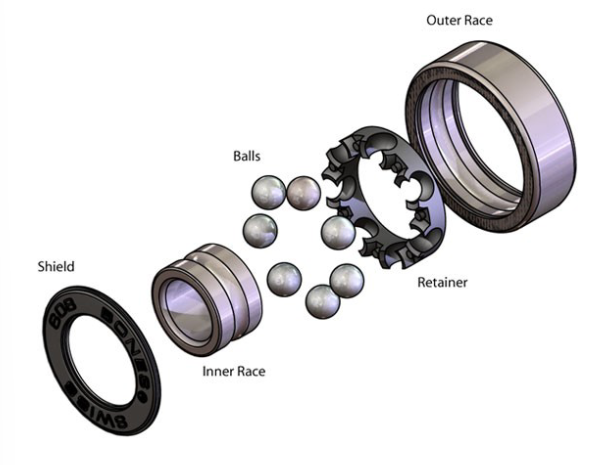
Bearing exploded view & parts
shielf
inner race
balls
retainer
outer race
Bearing image
What are bearings?
a machine element that constrains relative motion to only the desired motion
experience loads in two basic directions: axial load and radial load
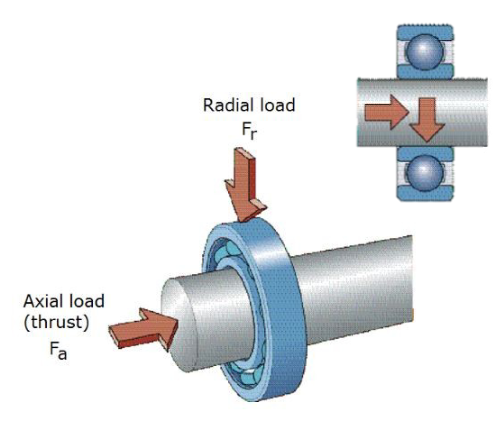
Axial load vs radial load
axial load - thrust (back and forth)
radial load - load pushing inwards towards the centre of the circle
Why are bearings used?
reduce friction between moving parts
provides free linear movement of the moving part or free rotation around a fixed axis
or it may prevent a motion by controlling the vectors of normal forces that bear on the moving parts

Bearing types
ball
cylindrical roller
needle roller
tapered roller
symmetrical roller
unsymmetrical rolelr
Examples of bearing applications
rolling track in airport security
sliding doors (like closet doors)
drill
fidget spinner
pillow block bearings - used to rotate a shaft
Ball bearings
most common
load: can handle both radial and thrust loads, usualyl found in applications where load is relatively small
load transmitted from outer race → ball → inner race
since ball is a sphere, only contacts inner and outer race at small point which helps it spin very smoothly
however, also means not much is holding hte load; if bearing is overloaded, ball can deform, ruining bearing
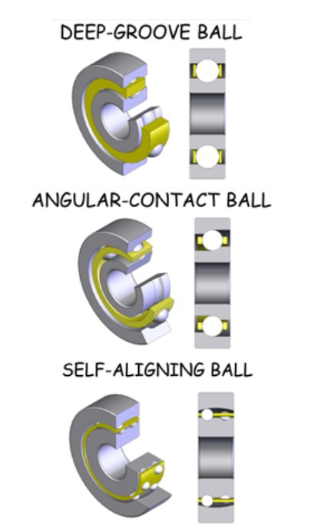
Types of ball bearings
deep groove ball
angular contact ball
self-aligning ball
Roller bearings
used in applications like conveyer belt rollers
load: can hold heavy radial load, but not much thrust (axial) load
allows contact between inner and outer race in a line, which spreads load over larger area
much stronger than ball bearing
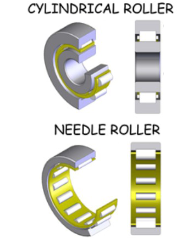
variation of this type is a needle bearing, which uses cylinders w/ small diameter which allows it to fit into small places
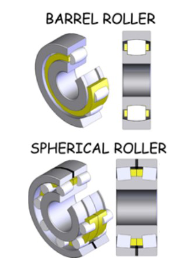
Types of roller bearings
barrel roller
spherical roller
cylindrical roller
needle roller

Tapered roller bearigns
roller bearing with a conical shape
load: can support large radial and large thrust (axial) loads
used in car hubs, where they are usually mounted in pairs facing opposite directions so they can handle thrust in both directions
Ball thrust bearings
used for low speed applications
load: cannot handle much radial load
barstools and lazy susan turntables use these
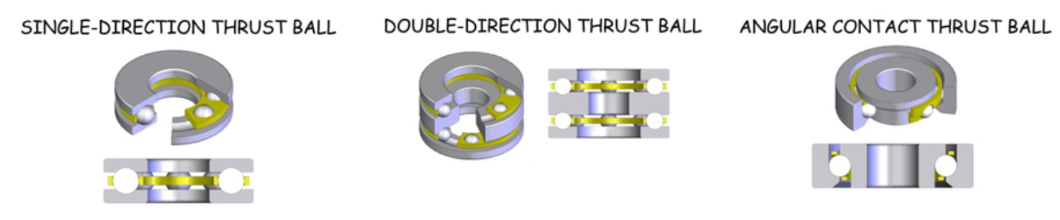
Types of ball thrust bearings
single direction thrust ball
double direction thrust ball
angular contact thrust ball

Linear bearings
rollers provide low friction for heavy loads in a linear motion
Sleeve bearings
a type of linear bearing
made to slide over rods/shafts to provide an extremely low friction motion
excellent for shock absorption
minimize energy usage, noise, wear
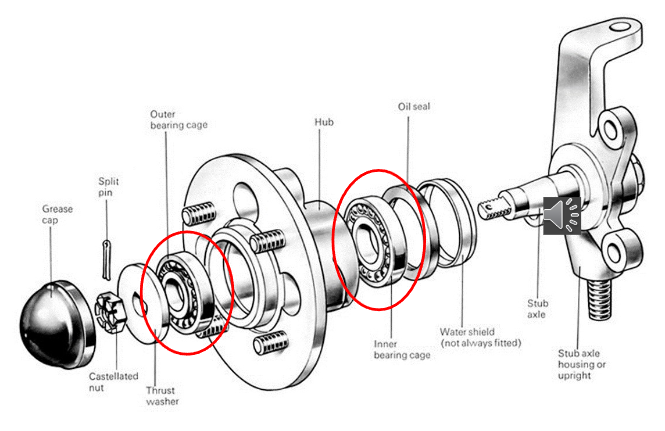
Example of bearings in a car
wheel bearing hub