Lecture 15: Pseudomonas and Burkholderia
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What are the characteristics of Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
Gram _
Motility?
Respiratory pattern?
Oxidase _
Catalase _
Gram - rods
Motile
Obligate aerobe
Oxidase +
Catalase +
T/F: P. aeruginosa has an inherent resistant to antimicrobials
True, (ESKAPE)
P. aeruginosa is a notorious opportunist, it is able to escape being killedby drugs/cleaners by hiding itself in what?
Biofilm
How does Biofilm facilitate the survival of P. aeruginosa in and outside the host?
Inside Host
Prevents phagocytosis
Protection from antimicrobials
Facilitates colonization and long-term persistence
Outside Host
Survival under environmental stressors and low nutrition
What is the key virulence factor of P. aeruginosa?
Biofilm
Biofilm is just one way that P. aeruginosa can be resistant to antibiotics, what are the other 2?
Intrinsic resistance
Acquired Resistance
Biofilm
P. aeruginosa is a common cause of what disease in…
Companion animals
Horses
Sheep
Cattle
Mink
Poultry
Reptiles
Skin infections (Otitis externa/pyoderma)
Corneal ulcer
Fleece rot
Mastitis
Hemorrhagic pneumoniae
Embryo mortality and omphalitis (bacterial infection of the umbilical stump)
Necrotic stomatitis
Mouth rot/canker mouth
What predisposes sheep to disease by P. aeruginosa?
P. aeruginosa causes fleece rot in sheep
Prevent it by shearing them before rainy season
What type of environment do P. aeruginosa prefer?
Aqueous
T/F: Some strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa produce pigment
True

Which bacteria produces an aromatic compound that smells grape-like or fruity?
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
What are the 2 species of Burkholderia do we discuss?
Burkholderia mallei
Burkholderia pseudomallei
What bacteria causes Glanders in Equidae? Describe the infection
Burkholderia mallei
Serial development of nodules in the upper respiratory tract, lungs, and skin.

What is the concern regarding Burkholderia mallei for equestrians?
Burkholderia mallei is a zoonotic disease
What are the characteristics of Burkholderia mallei?
Gram _
Shape?
Motility?
Intracellular/Extracellular?
Unique features
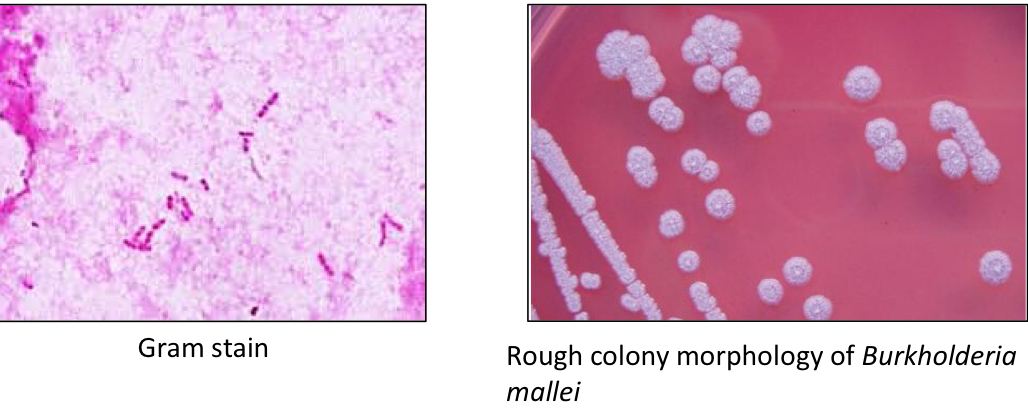
Gram -
Rods
Non-motile
Facultative intracellular
Bipolar (More stain at either end of the rod)
Glanders (Burkholderia mallei) is primarily a disease of the _________ _____ and ______
Respiratory system and Skin
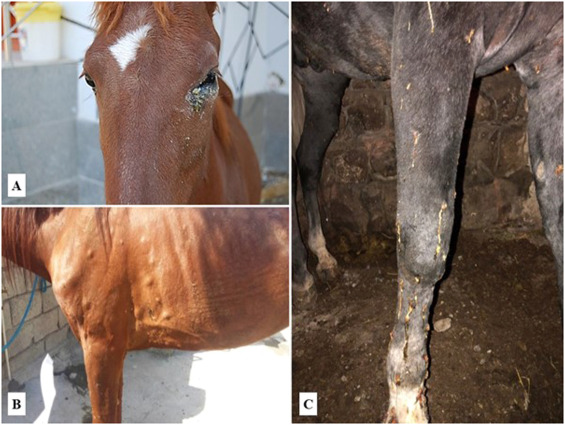
What is the incubation period of Burkholderia mallei (Glanders)?
3 days → 2 weeks
An important characteristic of Burkholderia mallei (Glanders) is that it causes acute __________, what does this mean for the C.S?
Burkholderia mallei causes acute septicemia
The C.S presents quickly due to the bacterias’s swiftness in entering the blood stream
Burkholderia mallei (Glanders) can present as a cutaneous or pulmonary infection, describe the difference in presentation of each
Pulmonary
Pyogranulomas with caseous centers
Fatal in donkeys
Chronic/Subclinical in horses
Cutaneous
aka “Farcy“
Nodules/Subcutaneous abscesses along the lymphatic vessels
Discharge yellow honey-like pus

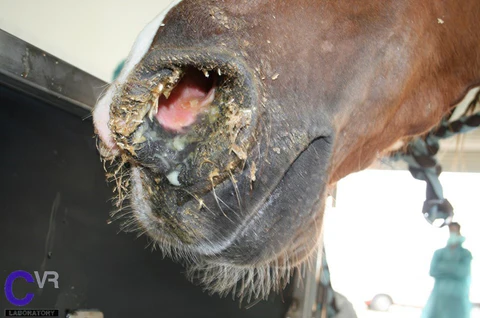
What are the general C.S of a Burkholderia mallei (Glanders) infection in horses?
Fever, mucopurulent/blood-tinged nasal discharge, respiratory distress (See image)
Lymphadenitis of the head/neck region
Similar to Equine strangles (SEE)
Nodules/ulcers in the upper airway, nasal septum, and skin
T/F: Local or generalized lymphadenopathy (swollen lymph nodes) is typically in all types of glanders
True
T/F: Human glanders is fatal in 95% of cases if left untreated after septicemia
True
What is Burkholderia pseudomallei commonly known as?
Meliodiosis (Pseudoglanders)
What are the characteristics of Burkholderia pseudomallei? What is the main difference between Burkholderia pseudomallei and Burkholderia mallei?
Gram _
Shape?
Motility?
Intracellular/Extracellular?
Gram -
Rods
Motile
Facultative intracellular
Bipolar
Burkholderia pseudomallei is Motile and Burkholderia mallei is non-motile
Burkholderia pseudomallei, unlike B mallei, is a __________ (soil bacterium)
Saprophyte, it is an endosymbiote of Amoebae (just need to know it’s a saprophyte)
What is the gross presentation of meliodiosis (pseudoglanders) caused by Burkholderia pseudomallei?
Sepsis, pneumonia, and visceral abscesses (abscesses on organs)
What is Whitmore’s Disease?
Human Meliodiosis (pseudoglanders)
Asymptomatic to acute spesis
Often fatal
Burkholderia pseudomallei grows at __°C
42°C (107°F), this is likely why the bacteria is only found in hotter/moist climates (Asia and Australia)
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a Gram-negative, _____ (resp. pattern) rod
Aerobic
Pseudomonas infections are commonly nosocomial, they occur as the result of __________ of medical devices and solutions
Contamination
T/F: Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a facultative anaerobe
False, it is an obligate aerobe
T/F: P. aeruginosa is a commensal of dog’s skin
False, P. aueruginosa is a transient bacteria, meaning they are temporarily present on or in the body and do not permanently colonize
List 2 mechanisms that contribute to Pseudomonas resistance to antibiotics
Intrinsic resistance
Efflux Pump (pumps out antibiotics)
Acquired resistance
Gene mutation, horizontal gene transfer
Biofilm
List two characteristics that aid in the diagnosis of Pseudomonas
Fruity odor
Non-lactose fermenter on MacConkey
Pigment
Oxidase +
List 3 disease conditions in livestock/ and or large animals caused by pseudomonas
Ocular infections in horses
Fleece rot in sheep
Mastitis in Cattle
P. aeruginosa causes __________ in mink?
Hemorrhagic pneumoniae
T/F: Burkolderia mallei is a host-adapted pathogen
True, it is specific to Equidae
T/F: B. mallei and B. pseudomallei are categorized as foreign animal diseases in Canada
True
Gram staining of an ear swab of a dog shows a moderate number of Gram-negative rods. Which organism will you highly suspect?
Pseudomonas aeruginoas