Cell structure & levels of organisation
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is the level of organisation?
Organelles → cells → tissues → organs → organ systems
Organelles are…
Specialised sub-cellular structures found within living cells
Cells are…
The basic structural unit of a living organism
Tissues are…
A group of cells with similar structures that work together to perform the same function
Organs are…
A group of tissues that work together to perform specific functions
Organ systems are…
A group of organs with similar functions that work together to perform body functions
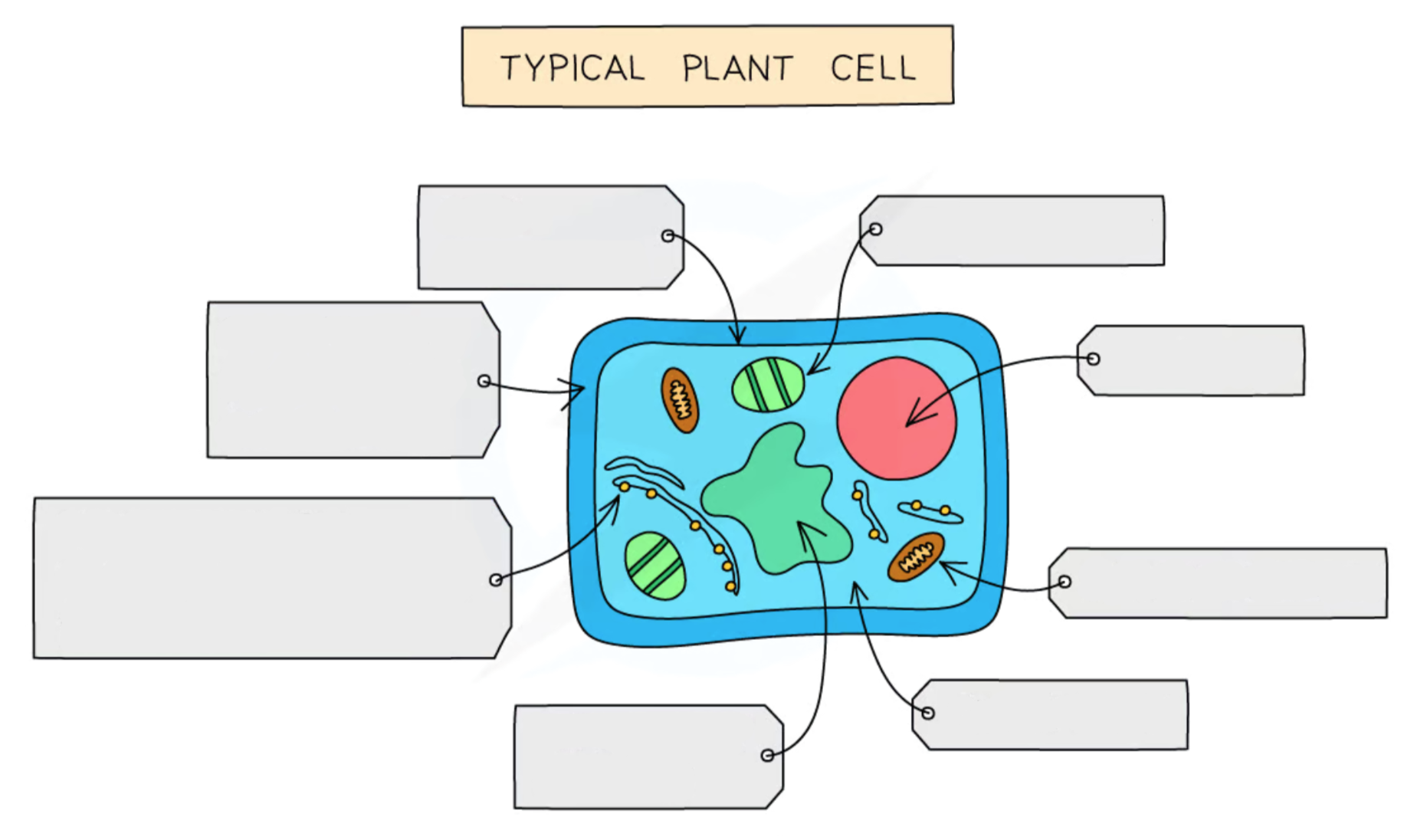
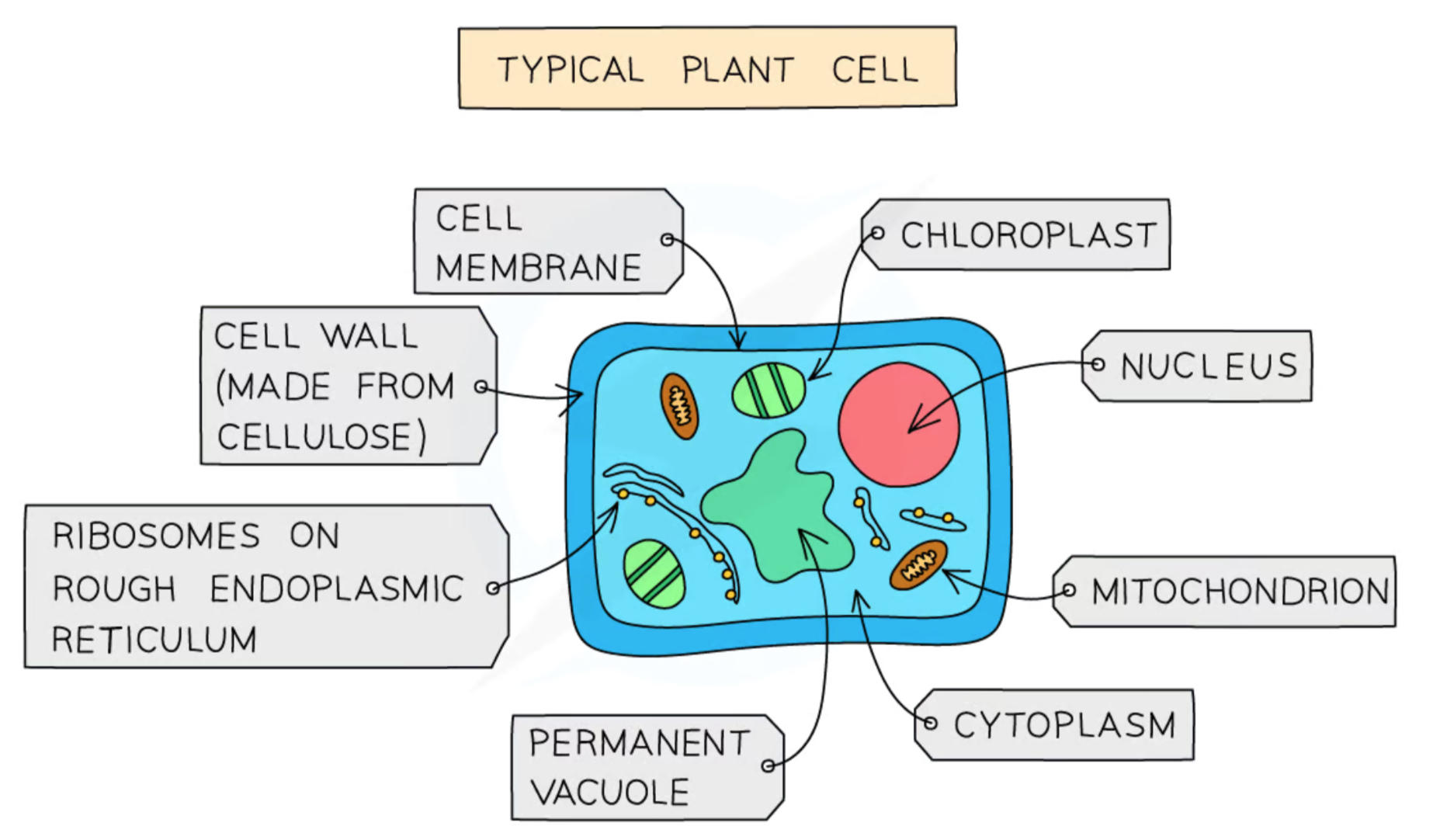
Label this diagram of a plant cell
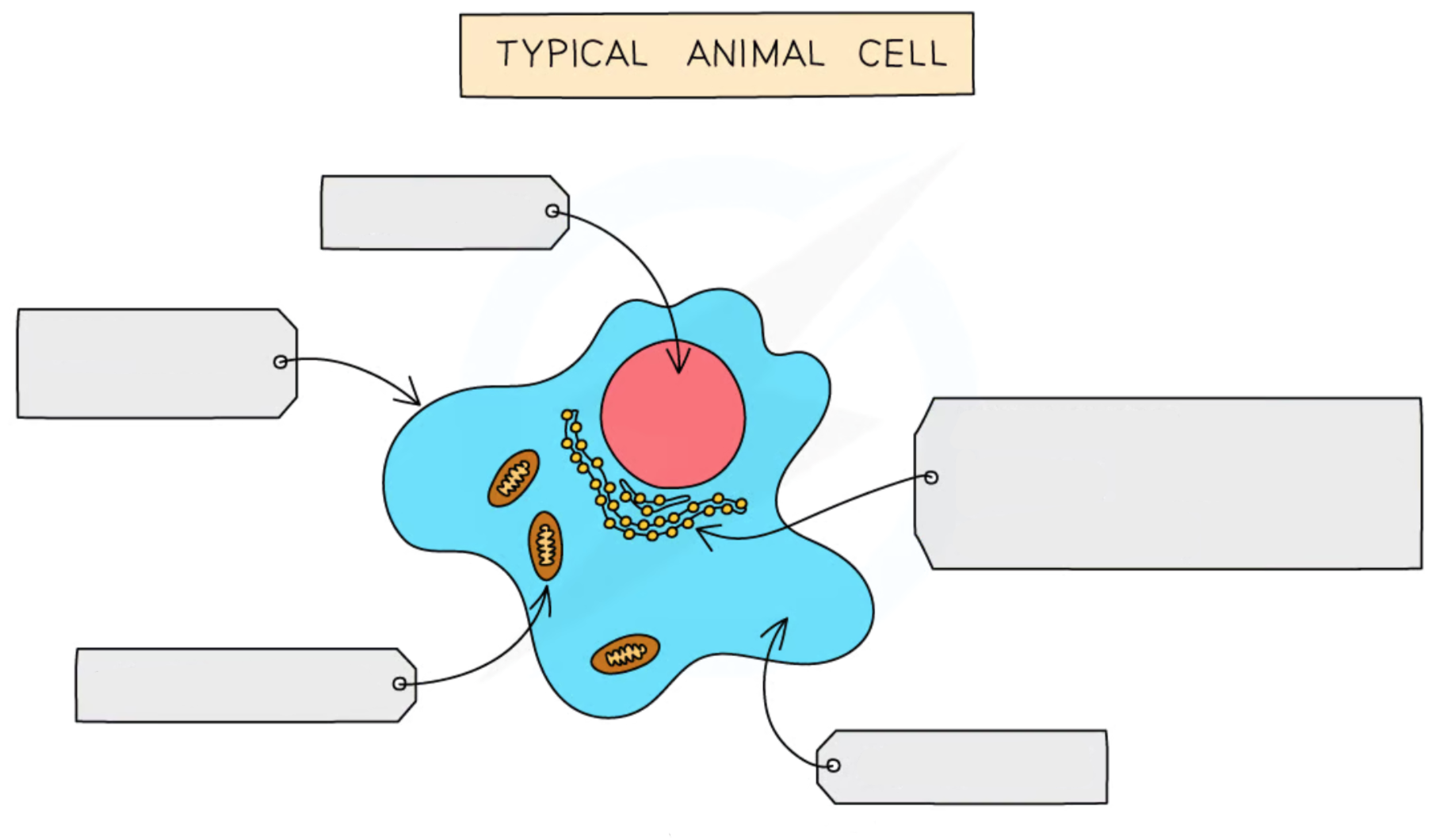
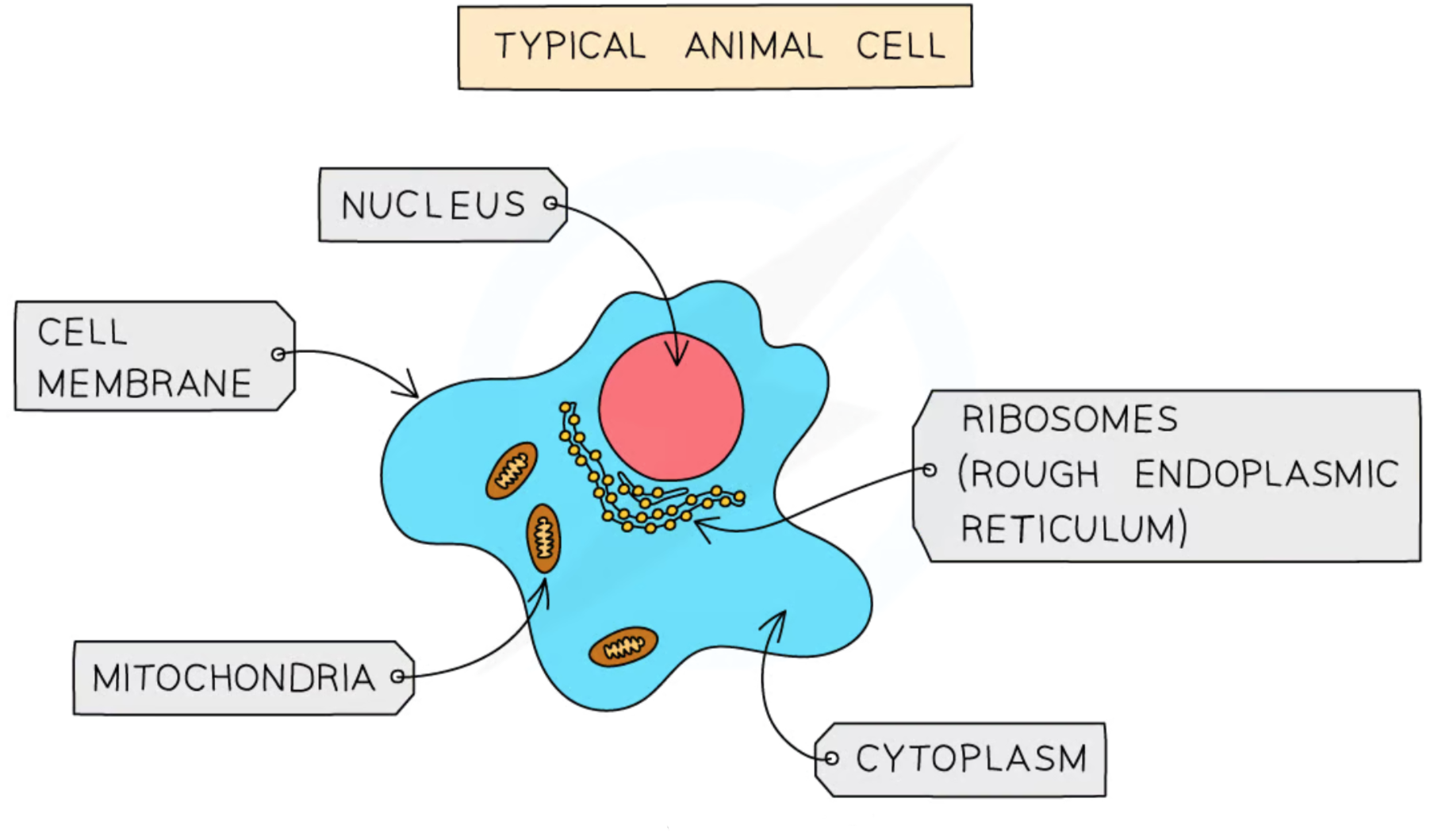
Label this diagram of an animal cell
What organelles are found in both plant & animal cells?
Nucleus
Cytoplasm
Cell membrane
Mitochondria
Ribosomes
What organelles are found in just plant cells?
Cell wall
Vacuole
Chloroplasts
Nucleus
Contains genetic material
Like the ‘control center’ for the cell
Cytoplasm
Jelly like substance where organelles are found
Most chemical reactions occur here
Contains enzymes to catalyze these reactions
Cell membrane
Contains receptor molecules which identify & selectively control what enters & leaves the cell
Mitochondria
The site of aerobic respiration which provides energy for the cell
Ribosomes
The site of protein synthesis
Found on the rough endoplasmic reticulum
Chloroplasts
The site of photosynthesis which provides food for plants
Contains chlorophyll pigment which collects light needed for photosynthesis & also makes it green
Vacuole
A large sac filled with cell sap that pushes other organelles to the side of the cell to make the cell rigid
Plants have a large & permanent vacuole
Cell wall
A rigid outer-coating around the cell that provides strength & support
Made of cellulose in plants
What are specialised cells?
Cell that have developed specific characteristics in order to perform a particular function
(e.g. sperm cells, nerve cells, muscle cells, phloem cells, xylem cells, root hair cells)
What is cell differentiation?
The process in which cells become specialised by gaining new sub-cellular structures to be suited for its role
Cells can either differentiate once early on or throughout their whole lives
Stem cells are…
Undifferentiated cells which can undergo division to produce many similar cells
Some of these cells will differentiate to become specialised
Stem cells are important for…
Development, growth & repair
What are the 3 types of stem cell?
Embryonic stem cells
Adult stem cells
Meristems in plants
Embryonic stem cells
- Form when an egg & sperm fuse together & to produce a zygote
- Can differentiate into any type of cell in the body
- Scientists clone them & can direct what they differentiate into
- Can potentially be used to replace insulin-producing cells in those suffering from diabetes, new neural cells for diseases such as Alzheimer’s or nerve cells for those paralysed with spinal cord injuries
Adult stem cells
- Form in specific parts of the body including bone marrow, hair follicles, the brain, fat tissue, intestines, breasts & testes
- Can only differentiate into cells that grow in the region where they were formed (e.g. formed in bone marrow → blood cells)
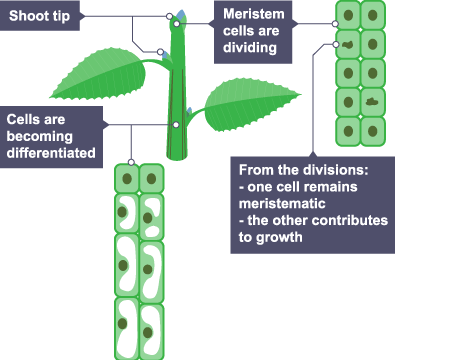
Meristems in plants
- Found in the tips of roots & shoots
- Can differentiate into any type of plant cell throughout their life
- Can be used to make clones of the plant which is useful if the parent plant has desirable features, for scientific research or to save a rare plant from extinction
Advantages of stem cells in medicine
- Can be used to replace damaged cells
- Can grow organs for transplants
- Bone marrow transplants for adult stem cells can be used to treat blood cell cancers
- No rejection if it is made from the patients own cells
- Can be used to test drugs as an alternative to animal testing
Disadvantages of stem cells in medicine
- Destroys unused embryos which causes ethical issues
- No guarantee on the success rate or if there will be any long term effects
- Mutations could occur in cultured stem cells
- Difficult to find suitable stem cell donors