Module 1 (DAANCE) (questions and verified answers)frequently most tested questions | already passed!!
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
142 Terms
What is the role of the Nervous System?
To provide overall control of body function
What are the three subdivisions in the Nervous System?
Central (CNS), Peripheral (PNS), and Autonomic (ANS)
What is a nerve action potential?
The nerve's threshold of stimulus
What is a synapse?
A junction between two neurons
How do local anesthetics exert their effects?
By interfering with the passage of Na+ ions through the ion channels and preventing depolarization with slowing or stopping of movement of the nerve impulse.
How are most of the intravenous, inhalation and local anesthetic drugs used in OMS utilized in the body?
Alteration of nerve conduction by modification of the actions of neurotransmitter substances and/or alteration of the movement of ions through membrane channels
What is the central nervous system and what does it consist of?
Overall control center of the body. Consists of the brain and spinal cord
What are the major components of the brain?
Cerebral Cortex, Core of the Brain, Cerebellum and the Brainstem
The cerebral cortex is responsible for?
Thought, learning, memory, consciousness, feeling of sensations such as pain or heat, and the initiation of muscle movement
What is the purpose of the core of the brain?
It serves as a relay station between sensory inputs from the periphery of the body to the cerebral cortex.
What is the purpose of the cerebellum?
Coordinating center for both sensory receptors, such as those for vision and hearing as well as coordination of movement
What does the brainstem consist of?
Midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
What is the purpose of the brainstem?
Contains the important control centers for autonomic nervous system functions.
What is the reticular formation responsible for?
Maintenance of consciousness or arousal
The medulla contains?
Important centers for the control of blood pressure, heart rate, respiration and digestion
The peripheral nervous system consists of?
The nerves that carry impulses away from the central nervous system to the various parts of the body and those that carry impulses from the periphery back to the CNS.
What are the two components to the peripheral nervous system?
Cranial nerves and Spinal nerves
What are cranial nerves?
Any of the 12 pairs of nerves connected with the brain; they are part of the peripheral nervous system
The trigeminal nerve, also known as ___________, supplies what?
Fifth cranial nerve, supplies sensation to the teeth and jaws.
Of the 12 cranial nerves, which nerve is the OMS surgeon primarily concerned with?
Trigeminal nerve
What are muscles of mastication?
Muscles responsible for jaw movement during chewing.
What does the facial nerve supply? And some examples
Motor fibers to the muscles of facial expression, smile, frown, etc.
Trigeminal is latin meaning?
Three pairs
What are the three paired divisions in the trigeminal nerve?
Ophthalmic, Maxillary, Mandibular
What is Ophthalmic division?
Upper division/First division that goes to the eye and forehead.
What is the maxillary division?
Also known as Second division, serves the maxilla.
What is the mandibular division?
Also known as, Third division, serves the mandible.
What does the autonomic nervous system regulate?
Internal organs and involuntary movements such as heart rate and digestion
What are the two subdivisions of the autonomic nervous system?
The sympathetic and Parasympathetic
Sympathetic nervous system does what?
Prepares the body for dealing with emergencies/tends to speed up processes
Parasympathetic nervous system does what?
Maintains the resting or vegetative state and tends to slow processes
The sympathetic nervous system exerts its effects through the action of a chemical substance called?
Norepinephrine
The effects of the sympathetic nervous system are often termed?
Adrenergic
The parasympathetic nervous system exerts its effects through the action of a chemical substance called?
Acetylcholine
The actions of the parasympathetic nervous system are called?
Cholinergic
What does the baroreceptor do?
Regulates blood pressure by responding to increased pressure by decreasing sympathetic output and increasing parasympathetic output to decrease heart rate and blood pressure and vice versa
Many drugs, such as barbiturates and Propofol, depress the vital centers, resulting in what?
Hypotension and respiratory depression
The anesthetic drug, Ketamine, stimulates the vital centers and causes what?
An increase in blood pressure and pulse
How much blood can the heart pump per minute?
5 quarts
The heart is made up of a specialized type of muscle called?
Myocardium
Why is the myocardium unique?
It has the ability to contract on its own, without stimulation by nerves
The two upper chambers of the heart are called?
Atria (atrium is singular)
The left atrium receives blood from? Is it oxygen-rich or poor?
Lungs via the pulmonary vein and is oxygen-rich
The right atrium receives blood from? Is it oxygen-rich or poor?
Peripheral circulation and is oxygen-poor
The two lower chambers of the heart are called?
Ventricles
Where do the ventricles receive blood from?
Atria
The right side of the heart is filled with what blood? The left side?
Right side is deoxygenated blood. The left side is filled with oxygenated blood.
The right atrium receives (oxygen rich or poor) blood via?
Superior and inferior vena cava bring oxygen poor blood from the body to the right atrium
Arteries are?
Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart
What are veins?
Blood vessels that transport blood back to the heart
What is the normal sequence for the flow of blood through the heart and lungs?
Right atrium, right ventricle, pulmonary artery, lungs, pulmonary veins, left atrium, left ventricle, aorta
The numerous vessels that pierce the myocardium?
Coronary arteries and veins
What is ischemia?
When reduced oxygen supply damages the heart cells but does not actually cause necrosis
What are arteriole?
Any of the small arterial branches located at the end of an artery (furthest from the heart)
What are capillaries? What is their purpose?
Any of the minute vessels that connect the arterioles and venules, forming a network in nearly all parts of the body. This is were the exchange of oxygen and other material takes place between the blood and the cells of the body.
What is the main difference between veins and arteries?
Arteries have much thicker walls to handle the pressure of the blood flow in them.
What are venules?
Smallest veins
What is diastolic?
Ventricular relaxation
What is systolic?
Contraction of ventricles
What is normal blood pressure?
120/80
What is cardiac output? How do you figure cardiac output?
The total amount of blood pumped out of the left ventricle in one minute
Stroke volume x heart rate
What is stroke volume?
The amount of blood pumped from a ventricle in each beat
What is bradycardia and tachycardia?
Bradycardia is a heart rate below 60 beats per minute.
Tachycardia is a rapid heart rate over 100 beats per minute.
The heart's normal rate and rhythm are controlled by?
The cardiac conduction system
What is automaticity?
The ability of the heart to start and maintain rhythmic activity without the use of the nervous system
What is termed the heart's pacemaker?
Sinoatrial node (SA Node)
After the atrioventricular (AV) node is stimulated, it transmits the electrical impulse throughout a special band of cardiac muscle fibers called?
The bundle of His
The bundle of His branches into the right and left bundle branches in the ventricles and does what?
Carries the impulse that stimulates the ventricles to contract
What is the purpose of the conducting system?
To assure that the ventricles contract as a unit by spreading the impulse rapidly to all the ventricular muscle fibers almost simultaneously.
What is the Purkinje fiber system?
Specialized cardiac muscle fibers that rapidly transmit impulses in the heart and coordinate contraction of the heart; Networks of this form the AV and SA nodes
What is the cardioacceleratory center?
A group of neurons in the brain stem involved in the acceleration of the heart action.
What is the cardioinhibitory center?
A group of neurons in the brain stem that has an inhibitory influence on the heart action via the vagus nerve
What are sinus rhythms?
Rhythms that originate in the SA node
What takes over if the SA node fails?
Ectopic pacemakers
What is the term to describe the lack of oxygen?
Hypoxia
What are the elements of a normal sinus rhythm on a cardiac monitor tracing?
P wave, QRS complex and the T wave.
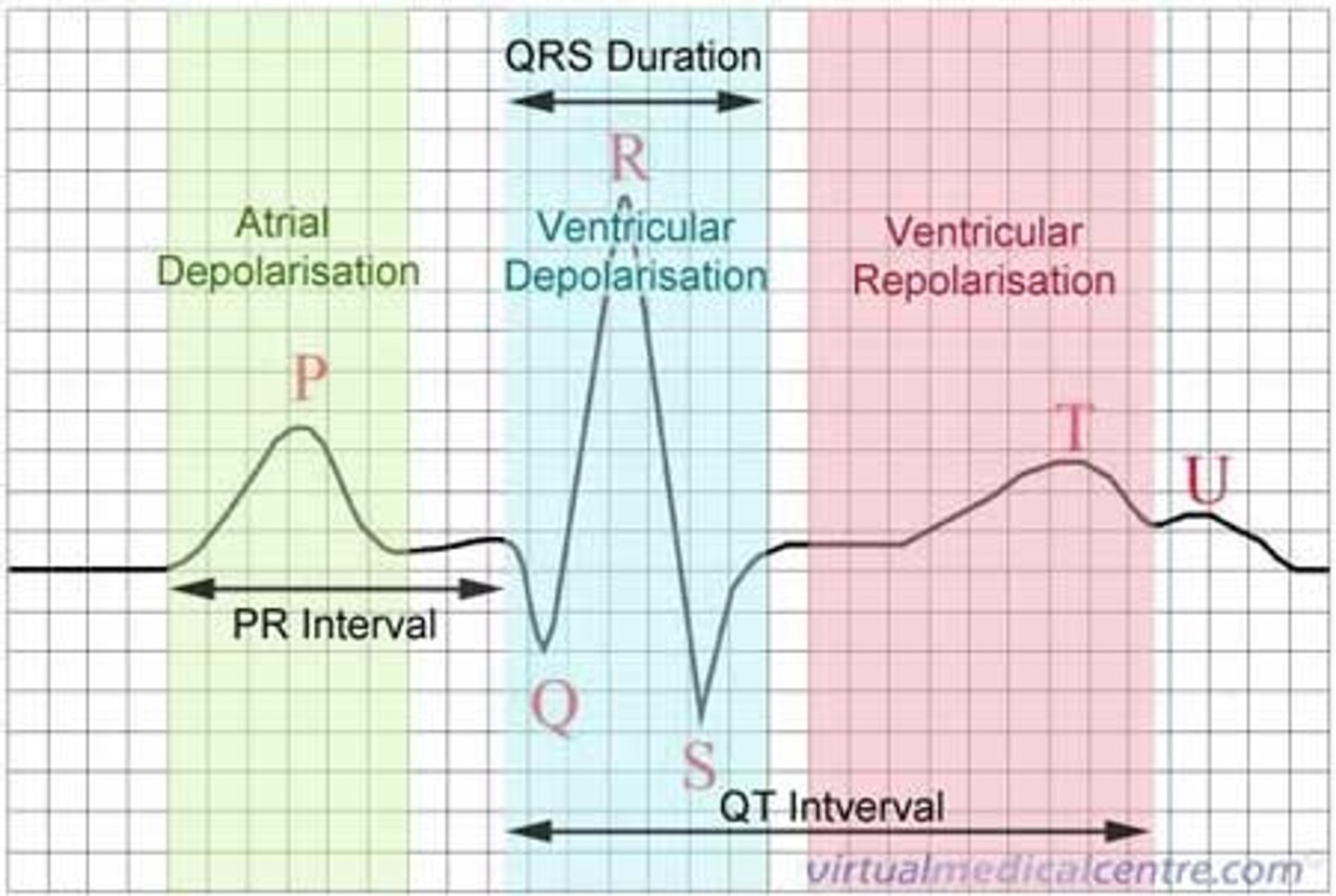
What is depolarization?
A reversal of the states electrical charge of the conducting fiber
What is repolarization?
A return of the initial state of electrical charge
The P wave is a reflection of which polarization and produces what?
Depolarization and produces the muscular contraction of the atria
The QRS complex is a reflection of?
The activity producing ventricular contraction
The T wave on a cardiac monitor tracing is evidence of what change in polarization?
Repolarization of the ventricles
In a normal cardiac monitor, the number of P waves is equal to the number of what?
QRS complexes
The number of QRS complexes per minute represents what?
The heart rate
After leaving the heart, the aorta branches into several large arteries that supply the head and neck. What is the sequence on the right side?
The first large artery is the brachiocephalic artery. It branches into the common carotid artery that goes up into the neck and into the right subclavian artery that goes up into the arm
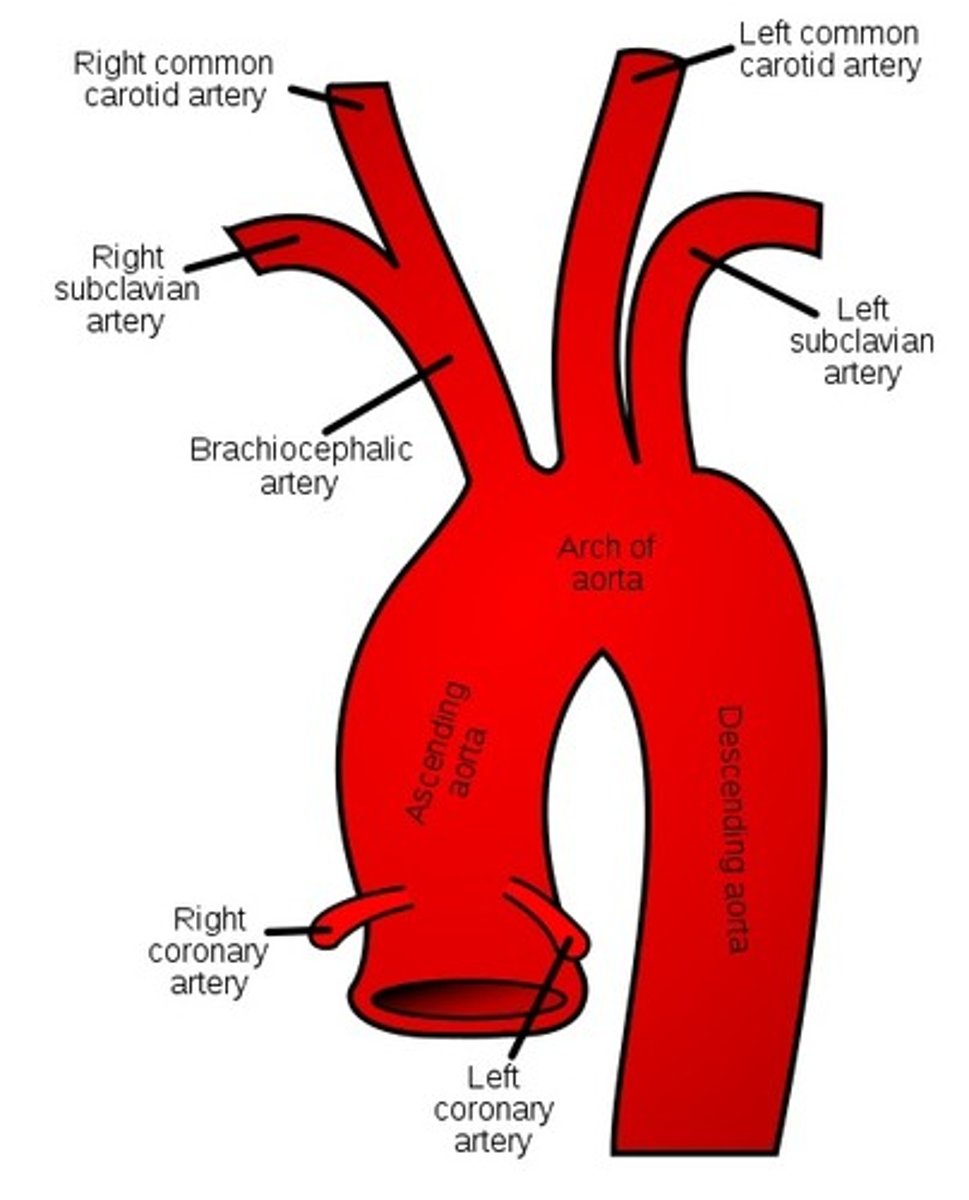
After leaving the heart, the aorta branches into several large arteries that supply the head and neck. What is the sequence on the left side?
The left common carotid artery branches off the aorta directly and goes into the neck.
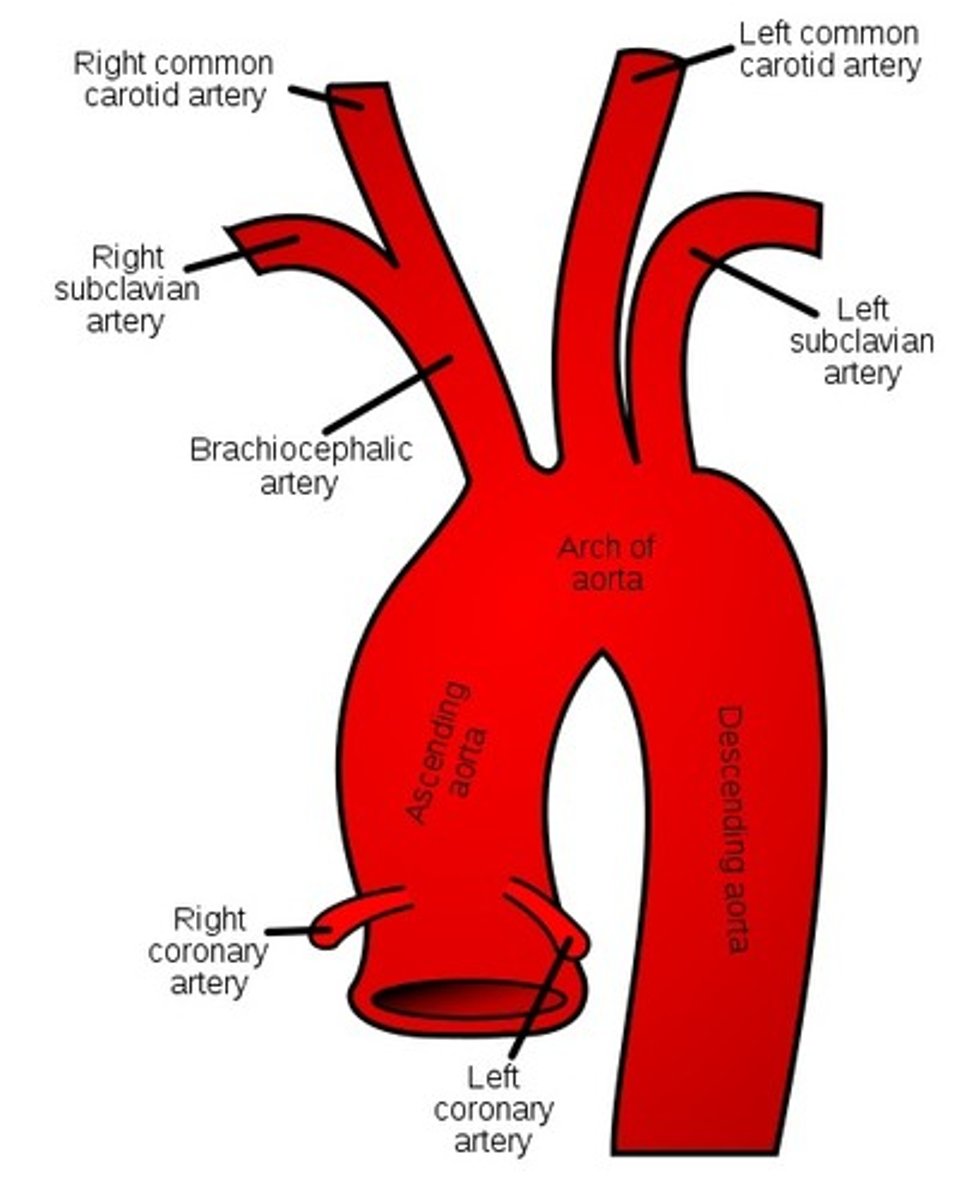
Just below the angle of the mandible, common carotid artery divides into the internal carotid artery and the external carotid artery, which has 8 branches. What are the 3 most important branches to OMS?
Lingual
Facial
Maxillary
What does the lingual artery supply?
Tongue and floor of mouth
What does the facial artery supply?
Face, tonsil palate, and submandibular gland
What does the maxillary artery supply?
Maxilla, sinuses, teeth, and a portion of the nose
What does the inferior alveolar artery supply?
Mandible and teeth
What is the pterygoid plexus?
A network of veins corresponding to the second and third parts of the maxillary artery
Why do veins of the head and neck play an important role in treating odontogenic infections right away?
The veins of the head and neck do not have valves. Infections can spread through the venous system and propagate backward all the way into the cranial cavity.
What is a hematoma?
Clotted or partially clotted blood outside the blood vessel and confined to an anatomic space.
What is the anterior surface of the elbow between the arm and the forearm called?
Antecubital fossa
Which artery is of concern when looking for intravenous access in the antecubital fossa? And what does it branch in to?
Brachial artery branches into radial and ulnar arteries
Intra-arterial injection produces what color blood?
Bright red pulsatile blood
Which veins are available for venipuncture in the antecubital fossa?
Cephalic veins, basilic vein, median cubital vein
What is phlebitis?
Inflammation of a vein
Where are cephalic veins located?
Outer aspect of the forearm
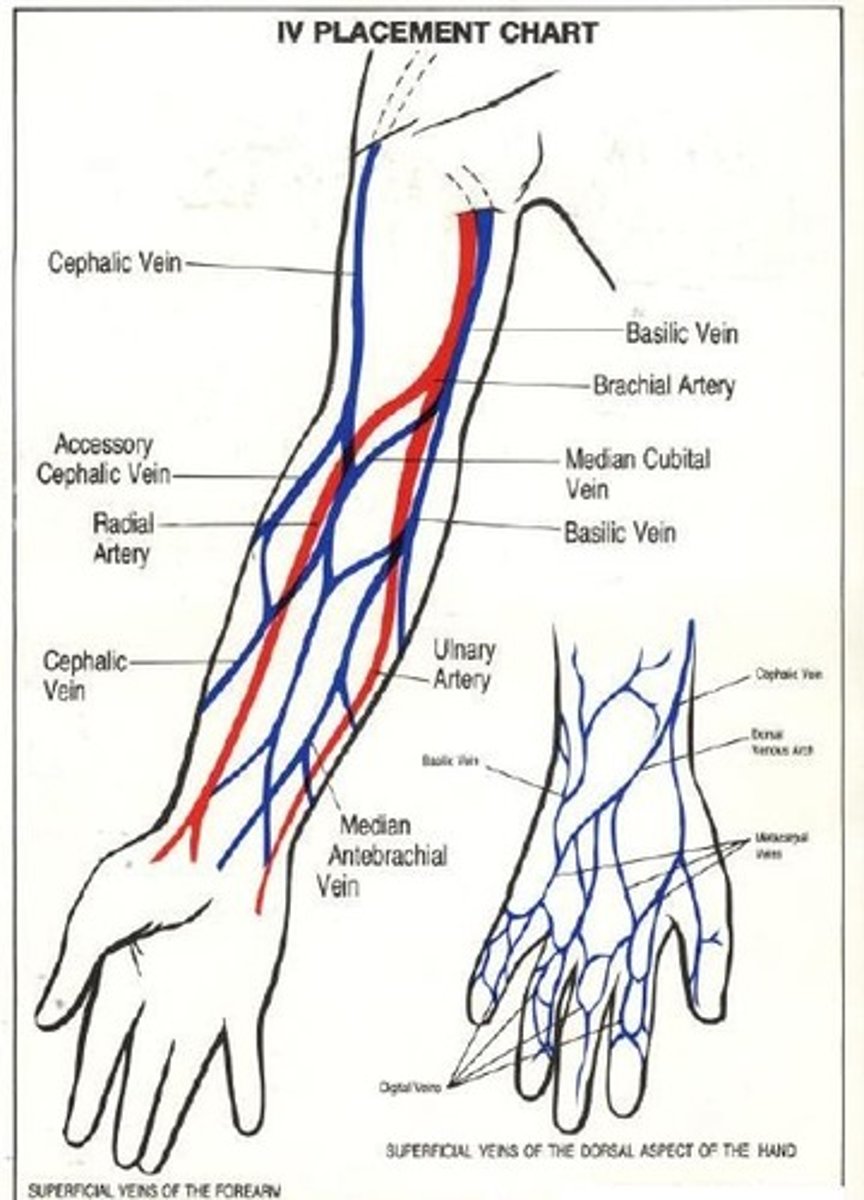
Where is the median cubital vein located?
Bridge between the Cephalic and basilic vein
