BIOL-109: Chapter 13- Sex Machine
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Terms and "check yourself" questions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
sexual dimorphism
one species being different in appearance, sounds, and smells
secondary sex characteristics
traits that become recognizable during puberty
endocrine system
hormones secreted from glands have an effect at 1 or more location in the body
hypothalamus
sends signals to the pituitary gland
pituitary gland
releases luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
testis
houses tube-like structures (seminiferous tubules) where sperm is made
scrotum
pouch of skin holding testes - contracts and expands to adjust distance from body
seminiferous tubules
inside testes, site of sperm production
epididymis
beside testes, sperm matured and stored here before ejaculation
seminal vesicles
produce alkaline (basic) fluid neutralizing acidity of vagina
bulbourethral glands
provides mucus-rich alkaline fluid lubricating inside of urethra which causes sperm to pass through easier
prostate gland
wraps around urethra and allows for muscle contractions that push semen forward and blocks urine flow during ejaculation
ductus/vas deferens
muscle lined tubes carrying sperm from epididymis to abdominal cavity
ejaculatory ducts
vas deferens and seminal vesicle duct that empties into urethra
penis
forms circle around urethra
urethra
tube running from bladder through penis
follicle
tiny ovarian sac nourishing oocyte
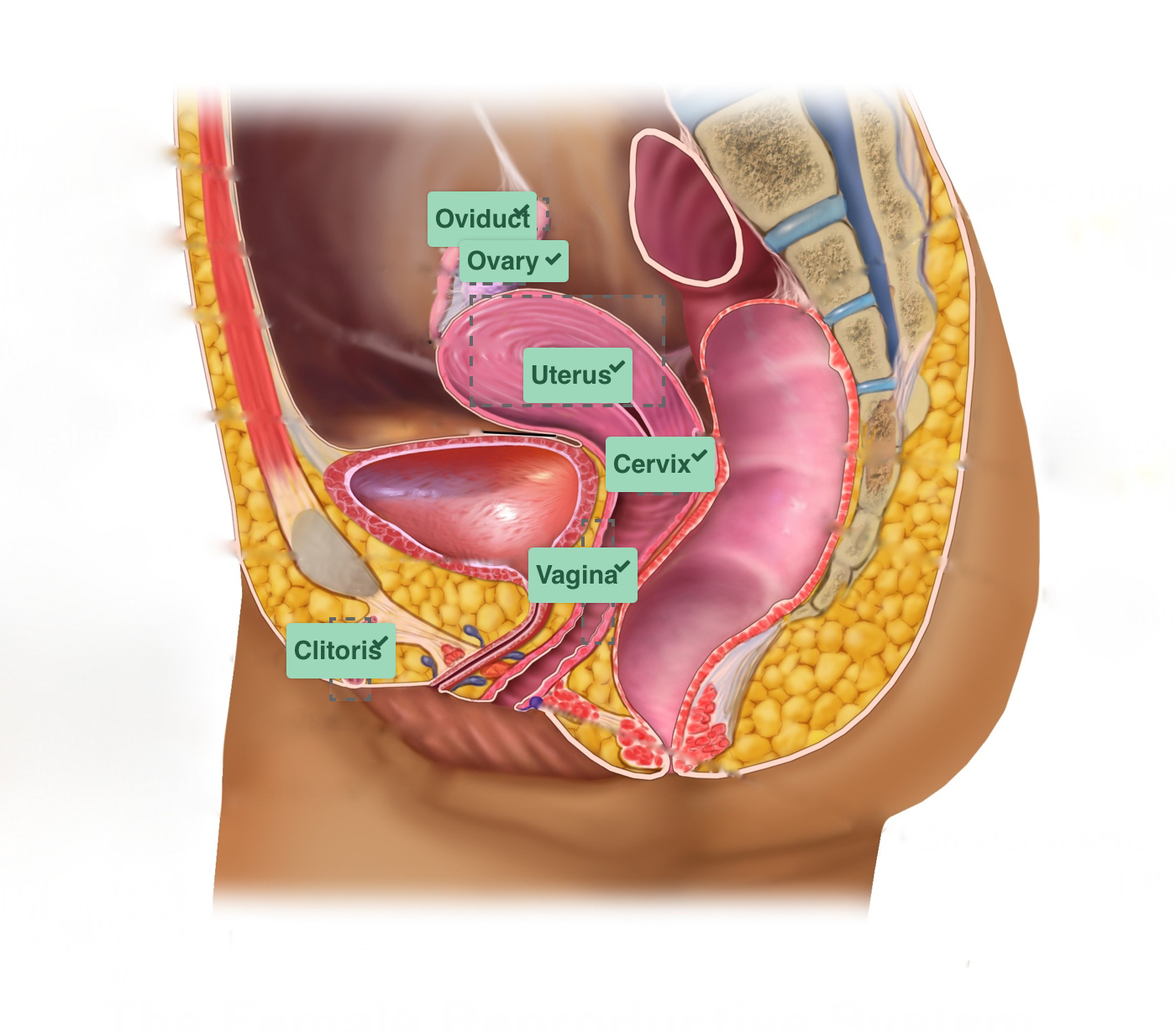
labia minora
inner lips
labia majora
outer lips
ovary
site of egg production, fertilized egg is in corpus luteum, produces estrogen, progesterone, testosterone
corpus luteum
site of egg maturation, produces progesterone to maintain pregnancy (possible or occuring)
uterus
where fertilized egg implants and develops, sheds thick blood lining monthly
vagina
opening to female reproductive tract, sperm entry, unfertilized egg, discharge, and baby exit
cervix
opening between vagina and uterus, closed to open based on sperm or baby passage
oviducts (fallopian tubes)
transport mature eggs to uterus, sperm and egg fertilize if here at same time
clitoris
sensitive organ similar to head of penis
ovulation
rupture of mature follicle
luteal phase
empty follicle collapses and is known as corpus luteum
follicular phase
begins first day of menstruation
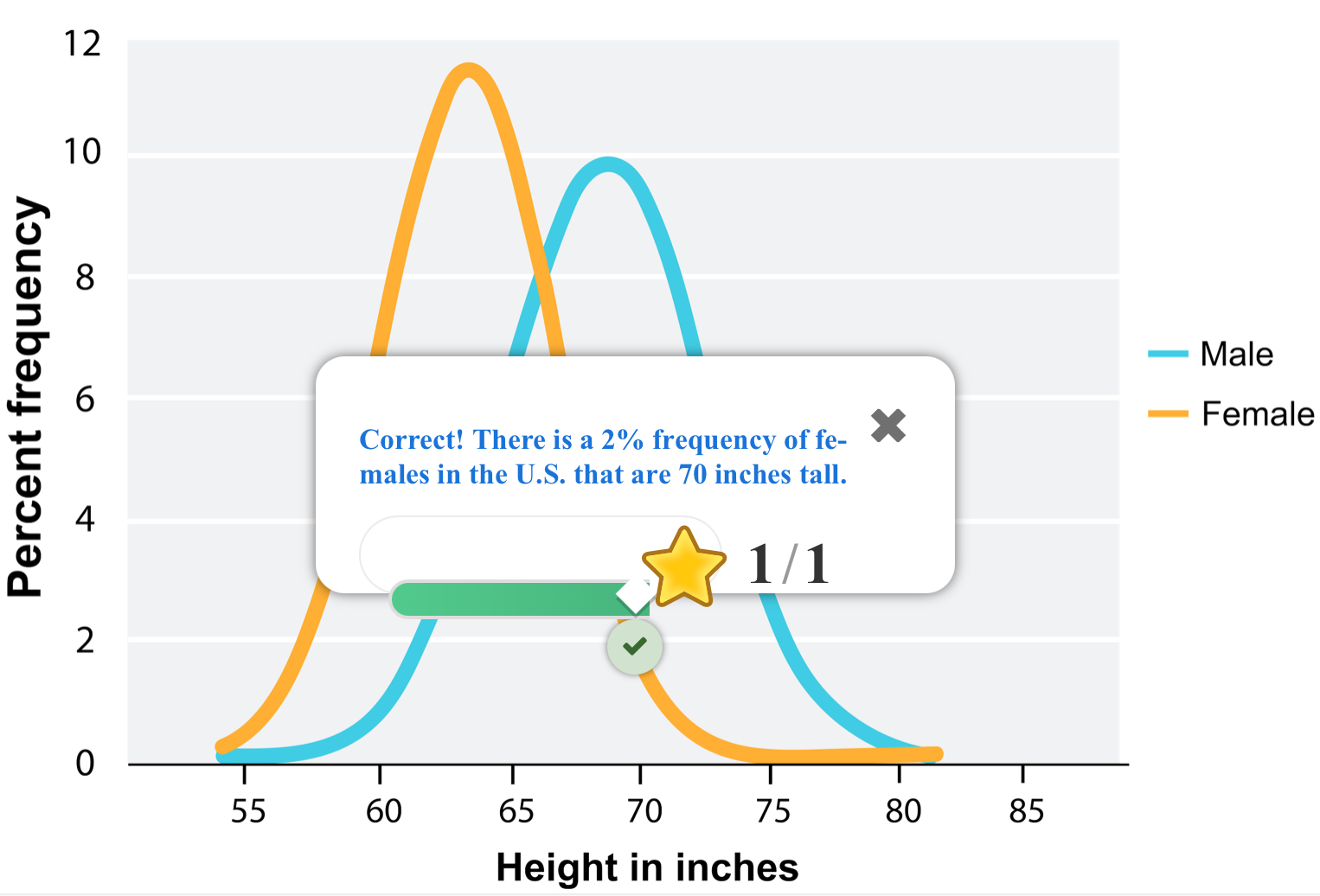
You are given a description of a person, including the fact that they are 70 inches tall. Given the average heights in the U.S. shown in figure 1, can you assume this person is male?
no
Point to where on the graph in figure 1 you could look to see what proportion of females in the US. are 70 inches tall.
Drag and drop the structure names to their correct locations in the diagram
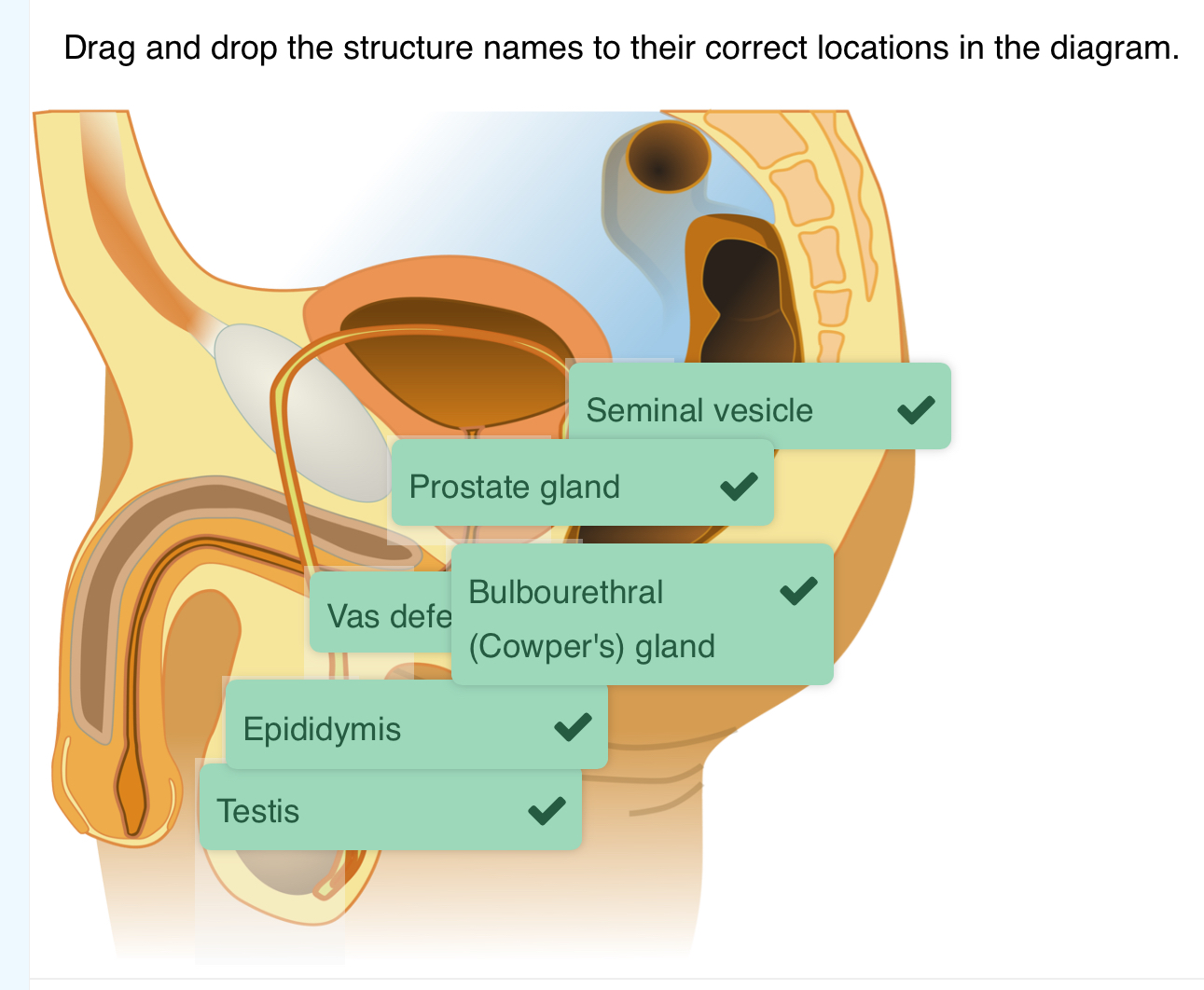
this structure holds the testes and contracts or expands to adjust the distance the testes are from the body to regulate their temperature
scrotum
sperm mature here and are stores here prior to ejaculation
epididymis
these structures are within the testes and are the actual sites of sperm production
seminiferous tubules
this structure runs from the bladder through the penis and is where urine and semen exit the body
urethra
This structure carry sperm from the epididymis of each testis
vas deferens
this structure provide a mucus0rich alkaline fluid that lubricates the inside of the urethra to allow for easier passage of sperm and neutralizes the urethra
bulbourethral glands
this structure helps propel semen and blocks urine flow from the bladder during ejaculation
prostate gland
this structure produces an alkaline (basic) fluid that can neutralize the acidity of the vagina. This contains fructose and other nutrients to provide energy for the sperm
seminal vesicles
Fill in the blanks.
__ is released from the hypothalamus
— and — are released from the —
— causes increased production of — from the —
GRH
LH, FSH, pituitary
LH, testosterone, testes
Drag and Drop
During the ___ phase, one follicle begins to mature and produces ___. At first the ___ provides a ___ feedback for ___ production in the brain, resulting in low ___ production by the pituitary, but when ___ levels become high enough, it switches to a ___ feedback. There is then a peak in circulating ___ levels.
follicular, estrogen, estrogen, negative, GRH, LH and FSH, estrogen, positive, LH and FSH
Which structure (s) produces progesterone to maintain a pregnancy?
The placenta and the corpus luteum
After 5-7 days the ___ begins to grow again. During this time an oocyte begins to mature within a group of cells called a ___, which secretes the hormone estrogen. Early in this phase the ___ is regulated through a ___ feedback loop in which the estrogen in the bloodstream represses LH and FSH secretion. However, once the follicle has reached sufficient size, the feedback shifts to a ___ feedback and there is a surge in LH, FSH, and estrogen that triggers ___.
A mature ___ is released from the ovary and is swept into one of the ___ where the oocyte may be fertilized. If it is not fertilized, the ___ degrades, causing a drop in ___. The uterine lining begins to shed, signifying the onset of menstruation (back to day 1).
uterine lining, follicle, estrogen, negative, positive, ovulation
oocyte, oviducts, corpus luteum, progesterone
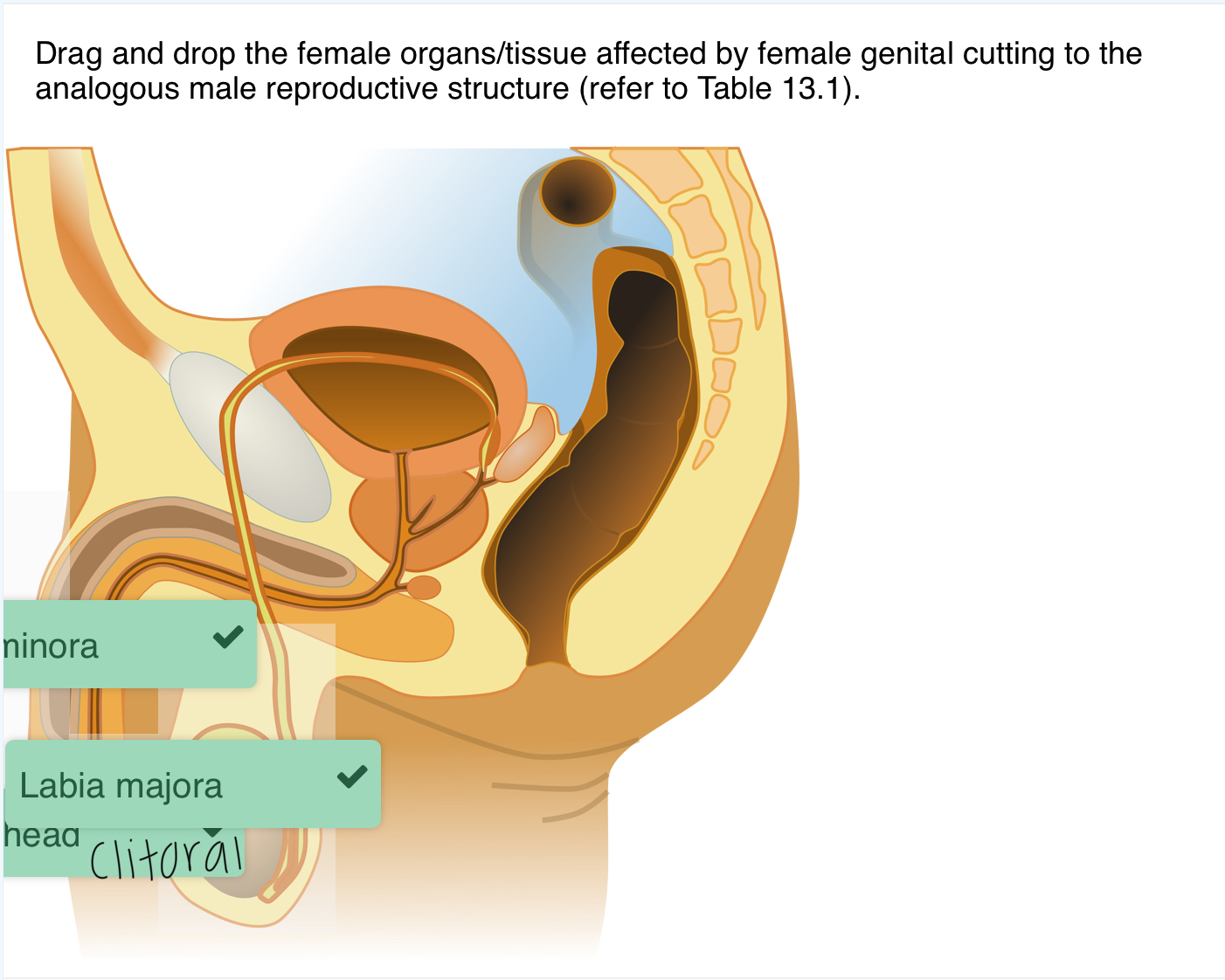
Drag and drop the female organs/tissue affected by female genital cutting to the analogous male reproductive structure